Chapter 7 Algebra: Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems
|
|
|
- Camilla Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 7 Algebra: Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems Check Points x y x ( x, y ) y ( ) 7 (,7) y ( ) 6 (,6) 1 y ( 1) 1 ( 1,) 0 y (0) 0 (0,) 1 y (1) 1 (1, ) y () (,) y () 1 (,1). a. Without the discount pass With the discount pass x y x ( x, y ) x y 10 x ( x, y ) 0 y (0) 0 (0,0) 0 y (0,10) y () (,) y 10 1 (,1) y () 8 (,8) y 10 1 (,1) 6 y (6) 1 (6,1) 6 y (6,16) 8 y (8) 16 (8,16) 8 y (8,18) 10 y (10) 0 (10,0) 10 y (10,0) 1 y (1) (1, ) 1 y 10 1 (1, ) Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 79
2 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems c. The graphs intersect at (10,0). This means that if the bridge is used ten times in a month, the total monthly cost is $0 with or without the discount pass.. a. f( x) x f (6) (6) 9 c. gx ( ) x 10 g( ) ( ) 10 6 hr () r 7r h( ) ( ) 7( ) 6. a. A car s required stopping distance at 0 miles an hour on dry pavement is about 190 feet. f( x) 0.087x 0.x66.6 f (0) 0.087(0) 0.(0) x f( x) x ( x, y ) or x,f(x) x g( x) x ( x, y) or x,f(x) f ( ) ( ) (, ) g( ) ( ) 7 (, 7) 1 f ( 1) ( 1) ( 1, ) 1 g( 1) ( 1) ( 1, ) 0 f (0) (0) 0 (0,0) 0 g(0) (0) (0, ) 1 f (1) (1) (1, ) 1 g(1) (1) 1 (1, 1) f () () (,) g() () 1 (,1) The graph of g is the graph of f shifted vertically down units. 80 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
3 Section 7.1 Graphing and Functions 7. a. y is a function of x.. y is a function of x. c. y is not a function of x. Two values of y correspond to an x-value. 8. a. The concentration is increasing from 0 to hours. The concentration is decreasing from to 1 hours.. c. The maximum concentration of 0.0 mg per 100 ml occurs after hours. d. None of the drug is left in the body. e. The graph defines y as a function of x because no vertical line intersects the graph in more than one point.. Concept and Vocabulary Check x-axis.. y-axis. origin. quadrants; four. x-coordinate; y-coordinate solution; satisfies 7. y; x; function 8. x; 6 9. more than once; function 7. Exercise Set Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 81
4 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems x y x Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
5 Section 7.1 Graphing and Functions. y x x x x y. x y x y x x 1. x y x x y x x y x x y x x y x x y x 1 1 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 8
6 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems. x y x gx ( ) x 1 a. g() () 1 1 g( ) ( ) h r r 1.. f(x) = x a. f(8) = 8 = f(1) = 1 =. f(x) = x 6 a. f(9) = 9 6 =. a. h 16 8 h hr () r f() = 6 =. f(x) = x a. f(7) = (7) = 1 = 19 f(0) = (0) = 0 = 6. f(x) = x a. f(7) = (7) = 8 = f(0) = (0) = 0 = g x x a. g 11 g 11 gx ( ) x a. g() () 9 1 g( ) ( ) 9 1 gx ( ) x a. g() () 16 1 a... h() () () 0 6 h( 1) ( 1) f x x x 1 a. f 1 (9) f f( x) x x a. f () () () () g( ) ( ) 9 7 f ( 1) ( 1) ( 1) 8 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
7 Section 7.1 Graphing and Functions x. f( x) x a. 6 f (6) f ( 6) x f x x f( x) x x a. f () 1 f ( ) 1 0. x f( x) x 1 7. x f x x x f( x) x x f x x Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 8
8 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems. x f( x) ( x 1) y is a function of x. 6. y is a function of x. 7. y is a function of x. 8. y is not a function of x. All values of y correspond to an x-value. 9. y is not a function of x. Two values of y correspond to an x-value. 60. y is not a function of x. Two values of y correspond to an x-value. 61. y is a function of x. 6. y is not a function of x. Two values of y correspond to an x-value.. x f x x g 1 1 f g f g f g f x f( x) ( x 1) Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
9 Section 7.1 Graphing and Functions a. G(10) 0.01(10) (10) In 1990, the wage gap was 69%. This is represented as (10, 69) on the graph. G (10) underestimates the actual data shown by the bar graph by % The coordinates of point A are (,7). When the football is yards from the quarterback, its height is 7 feet. 7. The coordinates of point B are (8,7). When the football is 8 yards from the quarterback, its height is 7 feet. 7. The coordinates of point C are approximately (6, 9.). 7. The coordinates of point D are approximately (, 9.). 7. The football s maximum height is 1 feet. It reaches this height when it is 1 yards from the quarterback. 76. The football s height is feet when it is caught by the receiver. The receiver is 0 yards from the quarterback when he catches the ball. 77. a. G(0) 0.01(0) (0) In 010, the wage gap was 81%. This is represented as (0,81) on the graph. 79. f (0) Twenty-year-old drivers have 0 accidents per 0 million miles driven. This is represented on the graph by point (0,0). 80. f (0) Fifty-year-old drivers have 00 accidents per 0 million miles driven. This is represented on the graph by point (0,00). 81. The graph reaches its lowest point at x. f () Drivers at age have 190 accidents per 0 million miles driven. This is the least number of accidents for any driver between ages 16 and Answers will vary. One possible answer is age 16 and age 7. f (16) f (7) Both 16-year-olds and 7-year-olds have approximately 6. accidents per 0 million miles driven. 89. makes sense G (0) underestimates the actual data shown by the bar graph by %. Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 87
10 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems 90. does not make sense; Explanations will vary. Sample explanation: The notation f( x ) does not mean multiplication of f by x. 91. makes sense 9. makes sense 9. f( 1) g( 1) 1 ( ) 9. f(1) g(1) ( ). Step 1. Plot the y-intercept of (0, 1) Step. Obtain a second point using the slope m. Rise m Run Starting from the y-intercept move up units and move units to the right. This puts the second point at (, 6). Step. Draw the line through the two points. f g( 1) f( ) 1 9. f g(1) f( ) 96. Check Points Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x (0) 6 x 6 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 (0) y 6 y 6 y ; resulting point (0, ) Find a checkpoint by substituting any value. (1) y 6 y 6 y y ; resulting point 1,. Solve for y. xy 0 y x0 y x 0 y x0 m and the y-intercept is (0, 0). Draw horizontal line that intersects the y-axis at.. a. 6 m 6 ( ) 1 ( ) 7 7 m 1 6. Draw vertical line that intersects the x-axis at. 88 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
11 Section 7. Linear Functions and Their Graphs 7. The two points shown on the line segment for Medicare are (007, 6) and (016, 909). 11 m For the period from 1970 through 010, the percentage of married men ages 0 to decreased by 0.8 per year. The rate of change 0.8% is per year. 8. a. The y-intercept is 8 and the slope is Change in y 8 16 m 0. Change in x The equation is Cx ( ) 0.x 8. Cx ( ) 0.x8 C(60) 0.(60) 8 7. The model projects that 7.% of the U.S. population will be college graduates in 00. Concept and Vocabulary Check x-intercept. y-intercept Exercise Set Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x y x 0 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 0 y y y ; resulting point (0, ). Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x y x 0 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 0 y y ; resulting point (0, ) y y 1. x x1. y mx b; slope; y-intercept. ; 6. 0, ; ; 7. horizontal 8. vertical. Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x (0) 1 x 1 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 (0) y 1 y 1 y ; resulting point (0, ) Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 89
12 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems. Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x (0) 10 x 10 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 (0) y 10 y 10 y ; resulting point (0, ) 7. Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x (0) 1 x 1 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 (0) y 1 0y 1 y 1 y ; resulting point (0, ). Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x 06 x 6 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 (0) y 6 y 6; resulting point (0, 6) 8. Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x (0) 6 x 6 x ; resulting point (, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 (0) y 6 0y 6 y 6 y ; resulting point (0, ) 6. Find the x-intercept by setting y = 0 x (0) 6 x 6; resulting point (6, 0) Find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 0y 6 y 6 y ; resulting point (0, ) m 1; line falls. 1 m ; line falls m ; line rises. 1 m ; line rises. ( 1) 1 m ; line falls Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
13 Section 7. Linear Functions and Their Graphs ( ) m 1 ; line falls. 6 m ; 0 Slope undefined. Line is vertical. ( ) 9 m ; 0 Slope undefined. Line is vertical m ; line falls. 0 m ; line rises m 0; line is horizontal. 7 0 m 0 ; line is horizontal. 1 ( ). y = x + Slope:, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using rise m 1 run. y = x + Slope:, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using rise m 1 run 1. y = x + Slope:, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using rise m 1 run. 1 y x Slope: 1, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using m 1 rise. run. y = x + 1 Slope:, y-intercept: 1 Plot point (0, 1) and second point using rise m 1 run Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 91
14 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems 6. 1 y x Slope: 1, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using m 1 rise. run 9. y x Slope:, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using rise m. run 7. f( x) x Slope:, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using rise m. run 0. y x Slope:, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using rise m. run 8. f( x) x Slope:, y-intercept: Plot point (0, ) and second point using m rise. run 1. f( x) x or f( x) x 0 Slope:, y-intercept: 0 Plot point (0, 0) and second point using rise m. run 9 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
15 Section 7. Linear Functions and Their Graphs. f( x) x or f( x) x 0 Slope:, y-intercept: 0 Plot point (0, 0) and second point using rise m. run c. 6. a. y = x y x or y x 0. a. x y 0 y = x or y = x + 0 Slope y-intercept = 0 c. Slope = y-intercept = 0 c. 7. a. x y y x. a. x + y = 0 y = x or y = x + 0 Slope = y-intercept = c. Slope = y-intercept = 0 c. 8. a. x + y = y = x +. a. y = x y xor y x 0 Slope = y-intercept = c. Slope = y-intercept = 0 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 9
16 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems 9. a. 7xy 1 y 7x1 7 y x7 7 Slope = y-intercept = 7 c.. y =. y = 0. a. xy 1 y x1 y x Slope y-intercept = c.. y =. x = 1. y = 6. x = 9 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
17 Section 7. Linear Functions and Their Graphs 7. x + 1 = 0 or x = 1. Ax ByC Ax C By A C x y B B The slope is A C and the y intercept is. B B 8. x + = 0 or x =. y 1 y 6 y y y m 0 a a a b 0 b b Since a and b are both positive, Therefore, the line falls. b0 b b m 0 a a a Since a and b are both positive, Therefore, the line falls. bc b c m a a 0 The slope is undefined. The line is vertical. ac c a m a a b b a is negative. b b is negative. a Since a and b are both positive, a is positive. b Therefore, the line rises y 1 y 1 y 6 6 y 61y 18 y 6 y 7. m1, m, m, m 8. b, b1, b, b 9. a. Change in y m 0. Change in x 6 0 For each year of aging, the percentage of Americans reporting a lot of stress decreases by 0.%. The rate of change is 0.% per year of aging.. Ax By C By Ax C A C y x B B A The slope is B and the y intercept is C B. 60. a. Change in y 6 16 m 0.16 Change in x For each minute of brisk walking, the percentage of patients with depression in remission increased by 0.16%. The rate of change is 0.16% per minute of brisk walking. Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc. 9
18 Chapter 7 Graphs, Functions, and Linear Systems 61. Px ( ) 0.7x Px ( ) 0.x 6. a. Find slope by using the endpoints of the line segment m The value of b is the y-intercept, or 60. W( x) mxb W( x) 16x60 W( x) 16x60 W( x) 16(0) In the year 00, the number of bachelor s degrees that will be awarded to women will be about 1,100, a. Find slope by using the endpoints of the line segment m The value of b is the y-intercept, or 70. M( x) mxb M( x) 8x70 M( x) 8x70 M( x) 8(0) In the year 00, the number of bachelor s degrees that will be awarded to men will be about 790, does not make sense; Explanations will vary. Sample explanation: Either point can be considered, x, y. x y or does not make sense; Explanations will vary. Sample explanation: Since college cost are going up, this function has a positive slope. 76. does not make sense; Explanations will vary. Sample explanation: The slope of lines whose equations are in this form can be determined in several ways. One such way is to rewrite the equation in slope-intercept form. 77. makes sense 78. false; Changes to make the statement true will vary. A sample change is: It is possible for m 79. false; Changes to make the statement true will vary. A sample change is: Vertical lines can not be expressed in slope-intercept forn. 80. true 81. false; Changes to make the statement true will vary. A sample change is: The line y x 7 is 7 equivalent to y x which has a y-intercept of First, find the slope using the points 0, and 100, m The slope, m, is 9 and the y-intercept, b, is. Instead of y mx b we will use F mc F mcb 9 F C 96 Copyright 01 Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs. Section 1.5 = = = 4. Check Point Exercises The slope of the line y = 3x+ 1 is 3.
 Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
Mini Lecture 2.1 Introduction to Functions
 Mini Lecture.1 Introduction to Functions 1. Find the domain and range of a relation.. Determine whether a relation is a function. 3. Evaluate a function. 1. Find the domain and range of the relation. a.
Mini Lecture.1 Introduction to Functions 1. Find the domain and range of a relation.. Determine whether a relation is a function. 3. Evaluate a function. 1. Find the domain and range of the relation. a.
Chapter 1 Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Exercises... The meaning of a [,,] by [,,] viewing rectangle is as follows: distance between x-axis minimum maximum tick x-value x-value marks [,,
Chapter Equations and Inequalities Section. Check Point Exercises... The meaning of a [,,] by [,,] viewing rectangle is as follows: distance between x-axis minimum maximum tick x-value x-value marks [,,
Chapter 3. Graphing Linear Equations and Functions
 Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
Chapter 3 Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3.1 Plot Points in a Coordinate Plane Coordinate Plane- Two intersecting at a angle. x-axis the axis y-axis the axis The coordinate plane is divided into.
Chapter 2. Polynomial and Rational Functions. 2.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Find the domains of rational functions. Use arrow notation.
Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions.6 Rational Functions and Their Graphs Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Find the domains of rational functions. Use arrow notation.
7. The set of all points for which the x and y coordinates are negative is quadrant III.
 SECTION - 67 CHAPTER Section -. To each point P in the plane there corresponds a single ordered pair of numbers (a, b) called the coordinates of the point. To each ordered pair of numbers (a, b) there
SECTION - 67 CHAPTER Section -. To each point P in the plane there corresponds a single ordered pair of numbers (a, b) called the coordinates of the point. To each ordered pair of numbers (a, b) there
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs. ( x x ) ( y y ) (1 7) ( 1 2) x x y y 100. ( 6) ( 3) x ( y 6) a. 101.
 Chapter Functions and Graphs... ( ) ( y y ) ( 7) ( ) y y y ( 6) ( ) 6 9 5 5 6y 6y 6y9 9 ( y ) y y Solution set:. 5. a. h, k 6, r ; ( ) [ y( 6)] ( ) ( y6) ( y6) b. ( ) ( y) [ ( )] ( y) So in the standard
Chapter Functions and Graphs... ( ) ( y y ) ( 7) ( ) y y y ( 6) ( ) 6 9 5 5 6y 6y 6y9 9 ( y ) y y Solution set:. 5. a. h, k 6, r ; ( ) [ y( 6)] ( ) ( y6) ( y6) b. ( ) ( y) [ ( )] ( y) So in the standard
Example: Plot the points (0, 0), (2, 1), ( 1, 3), , ( 1, 0), (3, 0) on the Cartesian plane: 5
 Graphing Equations: An Ordered Pair of numbers is two numbers (x, y) that is used to represent coordinate of points in the Cartesian plane. The first number is the x coordinate and the second number is
Graphing Equations: An Ordered Pair of numbers is two numbers (x, y) that is used to represent coordinate of points in the Cartesian plane. The first number is the x coordinate and the second number is
Math Placement Test Review Sheet Louisburg College _ Summer = c = d. 5
 1. Preform indicated operations with fractions and decimals: a. 7 14 15 = b. 2 = c. 5 + 1 = d. 5 20 4 5 18 12 18 27 = 2. What is the least common denominator of fractions: 8 21 and 9 14. The fraction 9
1. Preform indicated operations with fractions and decimals: a. 7 14 15 = b. 2 = c. 5 + 1 = d. 5 20 4 5 18 12 18 27 = 2. What is the least common denominator of fractions: 8 21 and 9 14. The fraction 9
Ch 3 Exam Review. Plot the ordered pairs on the rectangular coordinate system provided. 3) A(1, 3), B(-5, 3)
 Ch 3 Exam Review Note: These are only a sample of the type of problems that may appear on the exam. Keep in mind, anything covered in class can be covered on the exam. Solve the problem. 1) This bar graph
Ch 3 Exam Review Note: These are only a sample of the type of problems that may appear on the exam. Keep in mind, anything covered in class can be covered on the exam. Solve the problem. 1) This bar graph
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
Math 8 Honors Coordinate Geometry part 1 Unit Updated July 29, 2016
 Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Reviewing the basics The number line A number line is a visual representation of all real numbers. Each of the images below are examples of number lines. The top left one includes only positive whole numbers,
Rate of Change and slope. Objective: To find rates of change from tables. To find slope.
 Linear Functions Rate of Change and slope Objective: To find rates of change from tables. To find slope. Objectives I can find the rate of change using a table. I can find the slope of an equation using
Linear Functions Rate of Change and slope Objective: To find rates of change from tables. To find slope. Objectives I can find the rate of change using a table. I can find the slope of an equation using
Answer Explanations SAT Practice Test #1
 Answer Explanations SAT Practice Test #1 2015 The College Board. College Board, SAT, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. 5KSA09 Section 4: Math Test Calculator QUESTION 1.
Answer Explanations SAT Practice Test #1 2015 The College Board. College Board, SAT, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. 5KSA09 Section 4: Math Test Calculator QUESTION 1.
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Study Unit 2 : Linear functions Chapter 2 : Sections and 2.6
 1 Study Unit 2 : Linear functions Chapter 2 : Sections 2.1 2.4 and 2.6 1. Function Humans = relationships Function = mathematical form of a relationship Temperature and number of ice cream sold Independent
1 Study Unit 2 : Linear functions Chapter 2 : Sections 2.1 2.4 and 2.6 1. Function Humans = relationships Function = mathematical form of a relationship Temperature and number of ice cream sold Independent
Chapter 2 Integers and Introduction to Solving Equations
 Chapter Integers and Introduction to Solving Equations.1 Check Points 1. a. 500 b. 8.. a. 6> 7 because 6 is to the right of 7 on the number line. b. 8< 1 because 8 is to the left of 1 on the number line.
Chapter Integers and Introduction to Solving Equations.1 Check Points 1. a. 500 b. 8.. a. 6> 7 because 6 is to the right of 7 on the number line. b. 8< 1 because 8 is to the left of 1 on the number line.
ALGEBRA 2 MIDTERM REVIEW. Simplify and evaluate the expression for the given value of the variable:
 ALGEBRA 2 MIDTERM REVIEW Evaluating Expressions: 1.) -3 + 3(-2+ 5) 2 2.) ( -5 ) 2 3.) -5 2 Simplify and evaluate the expression for the given value of the variable: 4.) f(x) = x 2 + x 8; find f(-2) 5.)
ALGEBRA 2 MIDTERM REVIEW Evaluating Expressions: 1.) -3 + 3(-2+ 5) 2 2.) ( -5 ) 2 3.) -5 2 Simplify and evaluate the expression for the given value of the variable: 4.) f(x) = x 2 + x 8; find f(-2) 5.)
4. Smaller cylinder: r = 3 in., h = 5 in. 6. Let 3x the measure of the first angle. Let x the measure of the second angle.
 Chapter : Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable.6 Check Points. A, b A bh h h h The height of the sail is ft.. Use the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle. The radius is 0 ft.
Chapter : Linear Equations and Inequalities in One Variable.6 Check Points. A, b A bh h h h The height of the sail is ft.. Use the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle. The radius is 0 ft.
UMUC MATH-107 Final Exam Information
 UMUC MATH-07 Final Exam Information What should you know for the final exam? Here are some highlights of textbook material you should study in preparation for the final exam. Review this material from
UMUC MATH-07 Final Exam Information What should you know for the final exam? Here are some highlights of textbook material you should study in preparation for the final exam. Review this material from
MAC College Algebra
 MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
Summer Packet for Students Taking Introduction to Calculus in the Fall
 Summer Packet for Students Taking Introduction to Calculus in the Fall Algebra 2 Topics Needed for Introduction to Calculus Need to know: à Solve Equations Linear Quadratic Absolute Value Polynomial Rational
Summer Packet for Students Taking Introduction to Calculus in the Fall Algebra 2 Topics Needed for Introduction to Calculus Need to know: à Solve Equations Linear Quadratic Absolute Value Polynomial Rational
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide
 The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
The P/Q Mathematics Study Guide Copyright 007 by Lawrence Perez and Patrick Quigley All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Ch. Numerical Operations - Integers... - Fractions... - Proportion and Percent...
Math 1 packet for Coordinate Geometry part 1. Reviewing the basics. The coordinate plane
 Math 1 packet for Coordinate Geometry part 1 Reviewing the basics The coordinate plane The coordinate plane (also called the Cartesian plane named after French mathematician Rene Descartes, who formalized
Math 1 packet for Coordinate Geometry part 1 Reviewing the basics The coordinate plane The coordinate plane (also called the Cartesian plane named after French mathematician Rene Descartes, who formalized
Table of contents. Jakayla Robbins & Beth Kelly (UK) Precalculus Notes Fall / 53
 Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
Math 1010 Lesson 1-4 (Textbook 1.7 and 1.8) Different equations of Lines
 Math 00 Lesson -4 (Textbook.7 and.8) Different equations of Lines. slope intercept form = mx + b. standard form Ax + B = C m x x 3. point slope form ( ) Which one we use depends on what information is
Math 00 Lesson -4 (Textbook.7 and.8) Different equations of Lines. slope intercept form = mx + b. standard form Ax + B = C m x x 3. point slope form ( ) Which one we use depends on what information is
Sect 2.4 Linear Functions
 36 Sect 2.4 Linear Functions Objective 1: Graphing Linear Functions Definition A linear function is a function in the form y = f(x) = mx + b where m and b are real numbers. If m 0, then the domain and
36 Sect 2.4 Linear Functions Objective 1: Graphing Linear Functions Definition A linear function is a function in the form y = f(x) = mx + b where m and b are real numbers. If m 0, then the domain and
Chapter 9. Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry. 9.2 The Hyperbola. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9. The Hyperbola Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Locate a hyperbola s vertices and foci. Write equations of hyperbolas in standard
Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9. The Hyperbola Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Locate a hyperbola s vertices and foci. Write equations of hyperbolas in standard
Midterm Review Packet
 Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
Algebra 1 CHAPTER 1 Midterm Review Packet Name Date Match the following with the appropriate property. 1. x y y x A. Distributive Property. 6 u v 6u 1v B. Commutative Property of Multiplication. m n 5
Chapter P. Prerequisites. Slide P- 1. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
Chapter 2 Modeling with Linear Functions
 Chapter Modeling with Linear Functions Homework.1 1. a. b. c. In 199, t = 1. Notice on the scattergram, when t = 1, p is approximately 4.5. Therefore, 4.5% of deaths due to car accidents in 199 were due
Chapter Modeling with Linear Functions Homework.1 1. a. b. c. In 199, t = 1. Notice on the scattergram, when t = 1, p is approximately 4.5. Therefore, 4.5% of deaths due to car accidents in 199 were due
1.2. Functions and Their Properties. Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc.
 1.2 Functions and Their Properties Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. What you ll learn about Function Definition and Notation Domain and Range Continuity Increasing and Decreasing Functions Boundedness Local
1.2 Functions and Their Properties Copyright 2011 Pearson, Inc. What you ll learn about Function Definition and Notation Domain and Range Continuity Increasing and Decreasing Functions Boundedness Local
Math 1314 Test 2 Review Lessons 2 8
 Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Pre-Calc Chapter 1 Sample Test. D) slope: 3 4
 Pre-Calc Chapter 1 Sample Test 1. Use the graphs of f and g to evaluate the function. f( x) gx ( ) (f o g)(-0.5) 1 1 0 4. Plot the points and find the slope of the line passing through the pair of points.
Pre-Calc Chapter 1 Sample Test 1. Use the graphs of f and g to evaluate the function. f( x) gx ( ) (f o g)(-0.5) 1 1 0 4. Plot the points and find the slope of the line passing through the pair of points.
MATH 1710 College Algebra Final Exam Review
 MATH 1710 College Algebra Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) There were 480 people at a play.
MATH 1710 College Algebra Final Exam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) There were 480 people at a play.
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. Linear Equations & Graphs 1. A line has a y intercept of and a slope of. Find the equation of the line. A. B. C. D. Evaluate Functions 2. The graph of the function
Copyright 2015 Edmentum All rights reserved. Linear Equations & Graphs 1. A line has a y intercept of and a slope of. Find the equation of the line. A. B. C. D. Evaluate Functions 2. The graph of the function
Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3
 Section 3.1: Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3 Note: Make sure you already printed the graphing papers Plotting Points, Quadrant s signs, x-intercepts and y-intercepts Example 1: Plot the following
Section 3.1: Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3 Note: Make sure you already printed the graphing papers Plotting Points, Quadrant s signs, x-intercepts and y-intercepts Example 1: Plot the following
Unit 3 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
y2 + 4y - 5 c a + b 27 i C) ) (16, ) B) (16 3 3, )
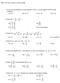 MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
MAT 107 Final, Version A, Spring 2008 1) If (4, 4) is the endpoint of a line segment, and (2, 1) is its midpoint, find the other endpoint. A) (0, 7) B) (-2, 0) C) (8, 10) D) (0, -2) 2) Solve for x: A)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. x )
 Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
SY14-15 Algebra Exit Exam - PRACTICE Version
 Student Name: Directions: Solve each problem. You have a total of 90 minutes. Choose the best answer and fill in your answer document accordingly. For questions requiring a written response, write your
Student Name: Directions: Solve each problem. You have a total of 90 minutes. Choose the best answer and fill in your answer document accordingly. For questions requiring a written response, write your
Example: f(x) = 2x² + 1 Solution: Math 2 VM Part 5 Quadratic Functions April 25, 2017
 Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 5 Quadratic Functions MATH 1 REVIEW THE CONCEPT OF FUNCTIONS The concept of a function is both a different way of thinking about equations and a different way of notating
Math 2 Variable Manipulation Part 5 Quadratic Functions MATH 1 REVIEW THE CONCEPT OF FUNCTIONS The concept of a function is both a different way of thinking about equations and a different way of notating
1-2 Analyzing Graphs of Functions and Relations
 Use the graph of each function to estimate the indicated function values. Then confirm the estimate algebraically. Round to the nearest hundredth, if necessary. 2. 6. a. h( 1) b. h(1.5) c. h(2) a. g( 2)
Use the graph of each function to estimate the indicated function values. Then confirm the estimate algebraically. Round to the nearest hundredth, if necessary. 2. 6. a. h( 1) b. h(1.5) c. h(2) a. g( 2)
Chapter 2 Functions and Their Graphs
 Chapter Functions and Their Graphs Section (, ) + ( ) ( ) + or or We must not allow the denominator to be + ; Domain: { } > > < Solution set: { < } or (, ) independent; dependent 6 range 7 [, ] We need
Chapter Functions and Their Graphs Section (, ) + ( ) ( ) + or or We must not allow the denominator to be + ; Domain: { } > > < Solution set: { < } or (, ) independent; dependent 6 range 7 [, ] We need
5. 2. The solution set is 7 6 i, 7 x. Since b = 20, add
 Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions Chapter Review Eercises... 5 8 6 8 The solution set is 8, 8. 5 5 5 5 5 5 The solution set is 5,5. Rationalize the denominator. 6 The solution set is. 8 8 9 6
Chapter : Quadratic Equations and Functions Chapter Review Eercises... 5 8 6 8 The solution set is 8, 8. 5 5 5 5 5 5 The solution set is 5,5. Rationalize the denominator. 6 The solution set is. 8 8 9 6
Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries. Lesson Goal: Mastery 70% or higher
 Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries For every lesson, you need to: Read through the LESSON REVIEW which is located below or on the last page of the lesson and 3-hole punch into your MATH BINDER. Read and work
Algebra 1 S1 Lesson Summaries For every lesson, you need to: Read through the LESSON REVIEW which is located below or on the last page of the lesson and 3-hole punch into your MATH BINDER. Read and work
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review
 Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
Section Properties of Rational Expressions
 88 Section. - Properties of Rational Expressions Recall that a rational number is any number that can be written as the ratio of two integers where the integer in the denominator cannot be. Rational Numbers:
88 Section. - Properties of Rational Expressions Recall that a rational number is any number that can be written as the ratio of two integers where the integer in the denominator cannot be. Rational Numbers:
Section 1.4 Circles. Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form.
 1 Section 1. Circles Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form. We begin by giving a definition of a circle: Definition: A Circle is the set of all points that are equidistant from
1 Section 1. Circles Objective #1: Writing the Equation of a Circle in Standard Form. We begin by giving a definition of a circle: Definition: A Circle is the set of all points that are equidistant from
1.4 CONCEPT QUESTIONS, page 49
 .4 CONCEPT QUESTIONS, page 49. The intersection must lie in the first quadrant because only the parts of the demand and supply curves in the first quadrant are of interest.. a. The breakeven point P0(
.4 CONCEPT QUESTIONS, page 49. The intersection must lie in the first quadrant because only the parts of the demand and supply curves in the first quadrant are of interest.. a. The breakeven point P0(
Math 0312 Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 and 2 Test Review
 Math 0312 Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 and 2 Test Review Name Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation for y. 1)
Math 0312 Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 and 2 Test Review Name Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation for y. 1)
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers
 Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Chapter 1-2 Add and Subtract Integers Absolute Value of a number is its distance from zero on the number line. 5 = 5 and 5 = 5 Adding Numbers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values and use the sign
Precalculus Notes: Unit P Prerequisite Skills
 Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
Syllabus Objective Note: Because this unit contains all prerequisite skills that were taught in courses prior to precalculus, there will not be any syllabus objectives listed. Teaching this unit within
Answer Explanations SAT Practice Test #1
 Answer Explanations SAT Practice Test #1 2015 The College Board. College Board, SAT, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. 5KSA09 QUESTION 43. Choice D is the best answer because
Answer Explanations SAT Practice Test #1 2015 The College Board. College Board, SAT, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. 5KSA09 QUESTION 43. Choice D is the best answer because
MAT College Algebra - Gateway 2: Linear Equations and. Name: Date: B
 Mathematics Department MAT 10 - College Algebra - Gateway : Linear Equations and Name: Date: 9919 B This exam covers material from Sections 1.1, 1.7,.1,.3, 3.1-3.3,.1, and.. The topics covered are function
Mathematics Department MAT 10 - College Algebra - Gateway : Linear Equations and Name: Date: 9919 B This exam covers material from Sections 1.1, 1.7,.1,.3, 3.1-3.3,.1, and.. The topics covered are function
Chapter 2 Differentiation. 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes. Calculus: A Complete Course, 8e Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2 Differentiation 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes 1) Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve y = 4x x 2 at the point (-1, 0). A) -1 2 C) 6 D) 2 1 E) -2 2) Find the equation of the tangent
Chapter 2 Differentiation 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes 1) Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve y = 4x x 2 at the point (-1, 0). A) -1 2 C) 6 D) 2 1 E) -2 2) Find the equation of the tangent
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
( ) ( ) SECTION 1.1, Page ( x 3) 5 = 4( x 5) = 7. x = = = x x+ 0.12(4000 x) = 432
 CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
CHAPTER Functions and Graphs SECTION., Page. x + x + x x x. x + x x x x x. ( x ) ( x ) x 6 x x x x x + x x 7. x + x + x + 6 8 x 8 6 x x. x x 6 x 6 x x x 8 x x 8 + x..x +..6.x. x 6 ( n + ) ( n ) n + n.
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal Asymptote Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Graphs
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal Asymptote Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Graphs
Algebra 2 Honors Unit 1 Review of Algebra 1
 Algebra Honors Unit Review of Algebra Day Combining Like Terms and Distributive Property Objectives: SWBAT evaluate and simplify expressions involving real numbers. SWBAT evaluate exponents SWBAT combine
Algebra Honors Unit Review of Algebra Day Combining Like Terms and Distributive Property Objectives: SWBAT evaluate and simplify expressions involving real numbers. SWBAT evaluate exponents SWBAT combine
CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Algebra I Name: Date: Period: # Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities Linear Equation/Inequalities equations/inequalities that will be represented using lines on the coordinate plane. Assignments
Algebra I Name: Date: Period: # Graphing Linear Equations and Inequalities Linear Equation/Inequalities equations/inequalities that will be represented using lines on the coordinate plane. Assignments
15. (,4)
 CHAPTER Algebra Toolbox CHAPTER Functions Graphs, and Models; Linear Functions Toolbox Exercises. {,,,,5,6,7,8} and { xx< 9, x N} Remember that x N means that x is a natural number.. (,7]. (,7 ] 5. (,)
CHAPTER Algebra Toolbox CHAPTER Functions Graphs, and Models; Linear Functions Toolbox Exercises. {,,,,5,6,7,8} and { xx< 9, x N} Remember that x N means that x is a natural number.. (,7]. (,7 ] 5. (,)
1.3 Linear Functions
 1.3 Linear Functions A function of the form f(x) = ax + b, where a and b are constants, is called a linear function. The graph of f(x) = ax + b or y = mx + b, is a line, with slope a (or m), and y intercept
1.3 Linear Functions A function of the form f(x) = ax + b, where a and b are constants, is called a linear function. The graph of f(x) = ax + b or y = mx + b, is a line, with slope a (or m), and y intercept
The Coordinate Plane; Graphs of Equations of Two Variables. A graph of an equation is the set of all points which are solutions to the equation.
 Hartfield College Algebra (Version 2015b - Thomas Hartfield) Unit TWO Page 1 of 30 Topic 9: The Coordinate Plane; Graphs of Equations of Two Variables A graph of an equation is the set of all points which
Hartfield College Algebra (Version 2015b - Thomas Hartfield) Unit TWO Page 1 of 30 Topic 9: The Coordinate Plane; Graphs of Equations of Two Variables A graph of an equation is the set of all points which
Systems of Linear Equations
 4 Systems of Linear Equations Copyright 2014, 2010, 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 4.1, Slide 1 1-1 4.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables R.1 Fractions Objectives 1. Decide whether an
4 Systems of Linear Equations Copyright 2014, 2010, 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 4.1, Slide 1 1-1 4.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables R.1 Fractions Objectives 1. Decide whether an
Final Jeopardy! Appendix Ch. 1 Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Ch. 4 Ch. 5
 Final Jeopardy! Appendix Ch. 1 Ch. Ch. 3 Ch. 4 Ch. 5 00 00 00 00 00 00 400 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 APPENDIX 00 Is the triangle
Final Jeopardy! Appendix Ch. 1 Ch. Ch. 3 Ch. 4 Ch. 5 00 00 00 00 00 00 400 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 APPENDIX 00 Is the triangle
SAMPLE FINAL EXAM QUESTIONS: ALGEBRA I
 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM QUESTIONS: ALGEBRA I The purpose of these sample questions is to clarify the course objectives, and also to illustrate the level at which objectives should be mastered. These sample questions
SAMPLE FINAL EXAM QUESTIONS: ALGEBRA I The purpose of these sample questions is to clarify the course objectives, and also to illustrate the level at which objectives should be mastered. These sample questions
6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation
 6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation FOCUS Relate the graph of a line to its equation in general form. We can write an equation in different forms. y 0 6 5 y 10 = 0 An equation for this
6.6 General Form of the Equation for a Linear Relation FOCUS Relate the graph of a line to its equation in general form. We can write an equation in different forms. y 0 6 5 y 10 = 0 An equation for this
Essential Academic Skills Subtest III: Mathematics (003)
 Essential Academic Skills Subtest III: Mathematics (003) NES, the NES logo, Pearson, the Pearson logo, and National Evaluation Series are trademarks in the U.S. and/or other countries of Pearson Education,
Essential Academic Skills Subtest III: Mathematics (003) NES, the NES logo, Pearson, the Pearson logo, and National Evaluation Series are trademarks in the U.S. and/or other countries of Pearson Education,
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Prep-Year Math Program Math Term 161 Recitation (R1, R2)
 Math 001 - Term 161 Recitation (R1, R) Question 1: How many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1? (a) 1 (b) Finite (c) 0 (d) Infinite (e) Question : A will contain how many elements
Math 001 - Term 161 Recitation (R1, R) Question 1: How many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1? (a) 1 (b) Finite (c) 0 (d) Infinite (e) Question : A will contain how many elements
Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review 3.1, 3.3, & 4.4. Name: Date: Period:
 Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review.1,., 4.1-4. & 4.4 Algebra I Name: Date: Period: Quest Topics Section.1 linear versus nonlinear rewrite linear equations in standard form: Ax By C find and use
Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review.1,., 4.1-4. & 4.4 Algebra I Name: Date: Period: Quest Topics Section.1 linear versus nonlinear rewrite linear equations in standard form: Ax By C find and use
Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
 Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 3 8 ( ) = + (a) f x 3x 4x x (b) ( ) g x 2 x + 3 = x 1 (a) f is a polynomial of degree 8. (b) g is
Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 3 8 ( ) = + (a) f x 3x 4x x (b) ( ) g x 2 x + 3 = x 1 (a) f is a polynomial of degree 8. (b) g is
6. 5x Division Property. CHAPTER 2 Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities. Toolbox Exercises. 1. 3x = 6 Division Property
 CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities Toolbox Exercises. x = 6 Division Property x 6 = x =. x 7= Addition Property x 7= x 7+ 7= + 7 x = 8.
CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities CHAPTER Linear Models, Equations, and Inequalities Toolbox Exercises. x = 6 Division Property x 6 = x =. x 7= Addition Property x 7= x 7+ 7= + 7 x = 8.
a) Graph the equation by the intercepts method. Clearly label the axes and the intercepts. b) Find the slope of the line.
 Math 71 Spring 2009 TEST 1 @ 120 points Name: Write in a neat and organized fashion. Write your complete solutions on SEPARATE PAPER. You should use a pencil. For an exercise to be complete there needs
Math 71 Spring 2009 TEST 1 @ 120 points Name: Write in a neat and organized fashion. Write your complete solutions on SEPARATE PAPER. You should use a pencil. For an exercise to be complete there needs
Exponential and quadratic functions problems [78 marks]
![Exponential and quadratic functions problems [78 marks] Exponential and quadratic functions problems [78 marks]](/thumbs/83/88526592.jpg) Exponential and quadratic functions problems [78 marks] Consider the functions f(x) = x + 1 and g(x) = 3 x 2. 1a. Write down x (i) the -intercept of the graph of ; y y = f(x) y = g(x) (ii) the -intercept
Exponential and quadratic functions problems [78 marks] Consider the functions f(x) = x + 1 and g(x) = 3 x 2. 1a. Write down x (i) the -intercept of the graph of ; y y = f(x) y = g(x) (ii) the -intercept
Section 10.1 Radical Expressions and Functions. f1-152 = = = 236 = 6. 2x 2-14x + 49 = 21x = ƒ x - 7 ƒ
 78 CHAPTER 0 Radicals, Radical Functions, and Rational Exponents Chapter 0 Summary Section 0. Radical Expressions and Functions If b a, then b is a square root of a. The principal square root of a, designated
78 CHAPTER 0 Radicals, Radical Functions, and Rational Exponents Chapter 0 Summary Section 0. Radical Expressions and Functions If b a, then b is a square root of a. The principal square root of a, designated
MA Lesson 21 Section The function values (or points on graph) are always rising.
 MA 1500 Lesson 1 Section. I Increasing, Decreasing, or Constant Functions A function is increasing if in an open interval, whenever x1 < x, then f ( x1 ) < f ( x). The function values (or points on graph)
MA 1500 Lesson 1 Section. I Increasing, Decreasing, or Constant Functions A function is increasing if in an open interval, whenever x1 < x, then f ( x1 ) < f ( x). The function values (or points on graph)
Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 1 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 2015 03 24 2 Table of Contents Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solve Systems by Elimination Choosing your Strategy Solving Systems of
1 Systems of Equations and Inequalities 2015 03 24 2 Table of Contents Solving Systems by Graphing Solving Systems by Substitution Solve Systems by Elimination Choosing your Strategy Solving Systems of
Sect The Slope-Intercept Form
 0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
ALGEBRA I SEMESTER EXAMS PRACTICE MATERIALS SEMESTER Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm. A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = cm 2. 6.
 1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
1. Use the diagram below. 9.3 cm A = (9.3 cm) (6.2 cm) = 57.66 cm 2 6.2 cm A rectangle s sides are measured to be 6.2 cm and 9.3 cm. What is the rectangle s area rounded to the correct number of significant
= = =
 . D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
. D - To evaluate the expression, we can regroup the numbers and the powers of ten, multiply, and adjust the decimal and exponent to put the answer in correct scientific notation format: 5 0 0 7 = 5 0
Algebra II. Simulation Test. Graphing Calculator Active. Chesterfield County Public Schools. Department of Mathematics
 lgebra II Simulation Test Graphing alculator ctive hesterfield ounty Public Schools epartment of Mathematics 011-1 REPORTING TEGORY: EXPRESSIONS N OPERTIONS (1 1) 1 Simplify the expression completely.
lgebra II Simulation Test Graphing alculator ctive hesterfield ounty Public Schools epartment of Mathematics 011-1 REPORTING TEGORY: EXPRESSIONS N OPERTIONS (1 1) 1 Simplify the expression completely.
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA TEST ONE PRACTICE SOLUTIONS SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS AND SIMPLIFY ANSWERS. PAGE 1 OF 8.
 SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS AND SIMPLIFY ANSWERS. PAGE 1 OF 8. 1. (a) Solve the inequality x 3 7. 7 x 3 7, 4 x 10 [ 4, 10] 7 + 3 x 3 + 3 7 + 3 or (b) Graph the solution to the inequality in (a), above. -6-4
SHOW ALL CALCULATIONS AND SIMPLIFY ANSWERS. PAGE 1 OF 8. 1. (a) Solve the inequality x 3 7. 7 x 3 7, 4 x 10 [ 4, 10] 7 + 3 x 3 + 3 7 + 3 or (b) Graph the solution to the inequality in (a), above. -6-4
Lecture 7: Sections 2.3 and 2.4 Rational and Exponential Functions. Recall that a power function has the form f(x) = x r where r is a real number.
 L7-1 Lecture 7: Sections 2.3 and 2.4 Rational and Exponential Functions Recall that a power function has the form f(x) = x r where r is a real number. f(x) = x 1/2 f(x) = x 1/3 ex. Sketch the graph of
L7-1 Lecture 7: Sections 2.3 and 2.4 Rational and Exponential Functions Recall that a power function has the form f(x) = x r where r is a real number. f(x) = x 1/2 f(x) = x 1/3 ex. Sketch the graph of
ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM
 First Round : March 7, 00 Second Round: April, 00 at The University of Alabama ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM Construction of this test directed by Congxiao Liu, Alabama A&M University and Alzaki Fadl
First Round : March 7, 00 Second Round: April, 00 at The University of Alabama ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM Construction of this test directed by Congxiao Liu, Alabama A&M University and Alzaki Fadl
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition ALGEBRA GRADE 8
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition ALGEBRA GRADE 8 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes You may use calculators. Mark
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition ALGEBRA GRADE 8 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes You may use calculators. Mark
Franklin Math Bowl 2010 Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6
 Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6 1. Carrie lives 10 miles from work. She leaves in the morning before traffic is heavy and averages 30 miles per hour. When she goes home at the end of the day, traffic
Group Problem Solving Test Grade 6 1. Carrie lives 10 miles from work. She leaves in the morning before traffic is heavy and averages 30 miles per hour. When she goes home at the end of the day, traffic
Review 1. 1 Relations and Functions. Review Problems
 Review 1 1 Relations and Functions Objectives Relations; represent a relation by coordinate pairs, mappings and equations; functions; evaluate a function; domain and range; operations of functions. Skills
Review 1 1 Relations and Functions Objectives Relations; represent a relation by coordinate pairs, mappings and equations; functions; evaluate a function; domain and range; operations of functions. Skills
Booker T. Washington Summer Math Packet 2015 Completed by Thursday, August 20, 2015 Each student will need to print the packet from our website.
 BTW Math Packet Advanced Math Name Booker T. Washington Summer Math Packet 2015 Completed by Thursday, August 20, 2015 Each student will need to print the packet from our website. Go to the BTW website
BTW Math Packet Advanced Math Name Booker T. Washington Summer Math Packet 2015 Completed by Thursday, August 20, 2015 Each student will need to print the packet from our website. Go to the BTW website
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards
 Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Algebra I Vocabulary Cards Table of Contents Expressions and Operations Natural Numbers Whole Numbers Integers Rational Numbers Irrational Numbers Real Numbers Absolute Value Order of Operations Expression
Study Island. Linear and Exponential Models
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. 1. A company is holding a dinner reception in a hotel ballroom. The graph represents the total cost of the ballroom rental and dinner. 3. In
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. 1. A company is holding a dinner reception in a hotel ballroom. The graph represents the total cost of the ballroom rental and dinner. 3. In
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION
 SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CCSS UG PROGRAMME MATHEMATICS (OPEN COURSE) (For students not having Mathematics as Core Course) MM5D03: MATHEMATICS FOR SOCIAL SCIENCES FIFTH SEMESTER STUDY NOTES Prepared
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION CCSS UG PROGRAMME MATHEMATICS (OPEN COURSE) (For students not having Mathematics as Core Course) MM5D03: MATHEMATICS FOR SOCIAL SCIENCES FIFTH SEMESTER STUDY NOTES Prepared
Brooklyn College Department of Mathematics. Precalculus. Preparatory Workbook. Spring Sandra Kingan
 Brooklyn College Department of Mathematics Precalculus Preparatory Workbook Spring 0 Sandra Kingan Supported by the CUNY Office of Academic Affairs through funding for the Gap Project CONTENTS. Review
Brooklyn College Department of Mathematics Precalculus Preparatory Workbook Spring 0 Sandra Kingan Supported by the CUNY Office of Academic Affairs through funding for the Gap Project CONTENTS. Review
Math 135 Intermediate Algebra. Homework 3 Solutions
 Math Intermediate Algebra Homework Solutions October 6, 007.: Problems,, 7-. On the coordinate plane, plot the following coordinates.. Next to each point, write its coordinates Clock-wise from upper left:
Math Intermediate Algebra Homework Solutions October 6, 007.: Problems,, 7-. On the coordinate plane, plot the following coordinates.. Next to each point, write its coordinates Clock-wise from upper left:
Chapter 2: Inequalities, Functions, and Linear Functions
 CHAPTER Chapter : Inequalities, Functions, and Linear Functions Exercise.. a. + ; ; > b. ; + ; c. + ; ; > d. 7 ; 8 ; 8 < e. 0. 0. 0.; 0. 0. 0.6; 0. < 0.6 f....0;. (0.).0;.0 >.0 Inequality Line Graph Inequality
CHAPTER Chapter : Inequalities, Functions, and Linear Functions Exercise.. a. + ; ; > b. ; + ; c. + ; ; > d. 7 ; 8 ; 8 < e. 0. 0. 0.; 0. 0. 0.6; 0. < 0.6 f....0;. (0.).0;.0 >.0 Inequality Line Graph Inequality
150. a. Clear fractions in the following equation and write in. b. For the equation you wrote in part (a), compute. The Quadratic Formula
 75 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations and Functions Preview Eercises Eercises 8 50 will help you prepare for the material covered in the net section. 8. a. Solve by factoring: 8 + - 0. b. The quadratic equation
75 CHAPTER Quadratic Equations and Functions Preview Eercises Eercises 8 50 will help you prepare for the material covered in the net section. 8. a. Solve by factoring: 8 + - 0. b. The quadratic equation
Foundations of High School Math
 Foundations of High School Math This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to
Foundations of High School Math This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to
3. Solve the following inequalities and express your answer in interval notation.
 Youngstown State University College Algebra Final Exam Review (Math 50). Find all Real solutions for the following: a) x 2 + 5x = 6 b) 9 x2 x 8 = 0 c) (x 2) 2 = 6 d) 4x = 8 x 2 e) x 2 + 4x = 5 f) 36x 3
Youngstown State University College Algebra Final Exam Review (Math 50). Find all Real solutions for the following: a) x 2 + 5x = 6 b) 9 x2 x 8 = 0 c) (x 2) 2 = 6 d) 4x = 8 x 2 e) x 2 + 4x = 5 f) 36x 3
Chapter 3A -- Rectangular Coordinate System
 Fry Texas A&M University! Fall 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 3A! Page61 Chapter 3A -- Rectangular Coordinate System A is any set of ordered pairs of real numbers. A relation can be finite: {(-3, 1), (-3,
Fry Texas A&M University! Fall 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 3A! Page61 Chapter 3A -- Rectangular Coordinate System A is any set of ordered pairs of real numbers. A relation can be finite: {(-3, 1), (-3,
