Concentration Polarization in Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Effect of Membrane Splitting
|
|
|
- Emory Payne
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 763 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 4 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 4, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN ; ISSN The Italian Association of Chemical Engineering DOI:.333/CET4398 Concentration Polarization in Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Effect of Membrane Splitting Andrea P. Reverberi* a, Bruno Fabiano b, Cristiano Cerrato c, Vincenzo G. Dovì a a DCCI - Department of Chemistry and Industrial Chemistry, via Dodecaneso 3, 646 Genova,Italy b DICCA - Department of Civil, Chemical and Environmental Engineering Chemical Engineering Section, via Opera Pia 5, 645 Genova,Italy c DIMSET Department of Machinery, Energy Systems and Transports, via Montallegro, 645 Genova, Italy reverb@dichep.unige.it We propose a simulation study in order to evaluate the effects of concentration polarization damping by splitting a single spiral-wound membrane module in two units connected in series inside the same shell. The reverse osmosis process in each unit is described by the advection-diffusion equation in two dimensions which is solved by a finite difference technique. Several feed regimes and operating conditions are investigated and their influence on the permeate flow rate is assessed for a single and double cell assembly. Finally, optimal operating maps are traced for different configurations of feed flow rate and pressure.. Introduction Reverse osmosis represents a valid technique to separate dissolved salts from solvents and it has found many applications in water desalination (Nair and Kumar, 3) and in waste treatment (Tagliabue et al., 4). In the first case, when the permeate phase is the valuable product, reverse osmosis can be considered one of the most important physical process to obtain drinking water for arid countries (Eltawil et al., 9). In the second one, when the concentrate phase is the useful product, the process aims at obtaining concentrated solutions of polluting and/or radioactive cations and it is one of the most promising technique for radionuclides separation and confinement in nuclear plants (Abdel-Rahman et al., ). Many attempts have been done in order to minimize the effects of fouling and concentration polarization which represent the main causes of impairment in the process yield during time. The paper of Sablani et al. () is an excellent critical review for membrane separation processes and we refer the reader to the references quoted there. While fouling can be contrasted at a price of adopting upstream operation units in the reverse osmosis plant, concentration polarization is generally considered as a reversible process and its study requires adhoc techniques implying an accurate determination of the fluid dynamics and local concentration profiles inside the single cell (Madireddi et al., 999). The numerical methods are often based on discretization techniques to solve the Navier-Stokes equations in two or three dimensions with finite elements methods, as this approach allows to describe complex geometries of the cells with a good flexibility (Ma et al. 4). However, finite difference methods may be preferable to finite elements methods in cases of more complicated boundary conditions, or in the presence of discontinuities between initial and boundary conditions (Reverberi et al., 8). Ahmad and Lau (6) investigated the effects of different shapes of spacer filaments in a membrane channel. They proved that unsteady feed regimes and spacer geometries play a very important role to minimize polarization effects. They concluded that the presence of stagnant zones induced by spacers at the membrane surface is a critical phenomenon that triggers concentration polarization. Al-Bastaki and Abbas (999) proposed a feed regime based on square waves of pressure pulses and they obtained a moderate improvement in the permeate flow rate for sodium chloride solutions in the concentrate phase. Admittedly, this strategy seems to be valid in order to mitigate both concentration polarization and fouling Please cite this article as: Reverberi A.P., Fabiano B., Cerrato C., Dovì V.G., 4, Concentration polarization in reverse osmosis membranes: effect of membrane splitting, Chemical Engineering Transactions, 39, DOI:.333/CET4398
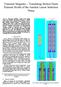
2 764 effects, but limited data have been collected to test the resistance of the membrane to mechanical stresses induced by the pressurization-depressurization cycles for longer times. The functionalization of the inner polymeric membrane structure with inorganic materials (Pascariu at al., 3) can be adopted in order to make the membrane capable of vibrating when subject to external variable magnetic fields. This effect breaks the concentration polarization layer with an increase in permeate yield. In spiral-wound reverse osmosis systems, the temperature of the concentrate phase may be used as a control parameter in order to improve the permeate flow rate (Goosen et al., ). It was shown that a small temperature increase of only C may rise the permeate flux by 6 % through a polimeric membrane when the solute is sodium chloride. The cause of this behaviour can be ascribed to a modification in the pore geometries of the membrane and to an increase of the solute diffusion coefficient, whose accurate determination often requires specific estimation techniques (Solisio et al., ). In particular, spurious experimental data in inverse problems may give biased diffusivity estimates (Reverberi et al., 3), owing to secondary effects often related to polymer hydration and interactions between polymer structure and diffusing species. In this paper, we propose a simulation study where the concentration profiles in a spiral-wound reverse osmosis unit are modelled in two dimensions. The unsteady advection-diffusion equation is solved by a finite difference discretization method. In particular, and this is the core of the work, the membrane inside the single module is splitted in two elements to exploit the mixing effects between membrane units. The paper is organized as follows. Firstly, we describe the model and we give some details about the numerical technique adopted to solve the advection-diffusion equation. Then, we present the results and we compare the process yield in case of membrane splitting with the one corresponding to the unsplitted membrane. In particular, the effects of inlet pressure and fluid speed are investigated according to different membrane geometries and technical solutions. Finally, we draw the conclusions and we trace the direction for future works.. The model The reverse osmosis cell is visualized in Figure -a, where a system of orthogonal coordinates is fixed at the centre of the cell inlet for symmetry reasons. In both snapshots (a) and (b), the membranes are represented by lines AB and CD. Figure : Scheme of membrane channels made of a single unit (a) or a double unit with elements U and U (b) The algorithmic scheme adopted in this work was already discussed elsewhere (Cerrato et al., 9); however it is worth recalling some essential points of it in the following, particularly as far as the boundary conditions are concerned. The dimensionless advection-diffusion equation describing the concentration profile in the membrane channel is: C DY T Y with C Y D X X C X C C U V X Y C=c/c, X=x/L, Y=y/h, T=tu /L, U=u/u, V=vL/u h ; D Y=D yl/u h ; D X=D x/u L () where x is the axial coordinate, y is the coordinate normal to the membrane, t is the time, L is the length of the channel, h is the half-height of the channel, u is the axial velocity and v is the velocity normal to the membrane. c is the reference concentration value corresponding to the salinity of the fresh solution ()
3 entering the first membrane element, c(x,y,t) is the concentration in the channel, u its velocity at the channel inlet, D X and D Y are the axial and radial diffusivities, respectively. The velocity profiles u and v can be determined by solving the Navier-Stokes equation in the space domain between the membranes. Here, instead, we adopt an alternative method assuming the validity of the semi-empirical velocity expressions proposed by Bhattacharyya et al. (99) in spiral-wound membranes. With such a choice, U and V are not treated as unknown variables of the problem, but they are a-priori known functions F and G of the space coordinates, namely: U( X,Y ) F X,Y,v V( X,Y ) G X,Y,v W dp,,,u dx,,u W where P is the total pressure, is the dynamic viscosity and v W is the fluid velocity normal to the membrane at the membrane surface, defined as wall permeation velocity. The dimensionless wall permeation velocity V w = v wl/u h is related to the membrane permeability A and to the pressure gap P at fixed X between two membrane sides according to: V W ( X, A( P ) L / u h (4) The transmembrane osmotic pressure in Eq(4) depends linearly on the difference between the transmembrane solute concentrations, that is: =K (C W -C P) (5) where K is the osmotic pressure constant, C w is the solute concentration at the wall and C p is the solute concentration in the permeate phase. Remembering that the rejection factor is defined as: R = -C p/c w (6) we can eliminate C p from the previous expression, obtaining: =K C WR (7) Figure -b represents a scheme of membrane splitting, namely it shows how a single module described in Figure -a can be divided into two elements U and U where the concentrate phase leaving the first unit at S =x /L enters the second one at the dimensionless coordinate S =x /L. We assume that the concentrate phase coming out of the first unit undergoes a perfect mixing in a narrow space gap between U and U, whence SS. This choice is motivated by the need of finding the upper limit of the permeate flux attainable by splitting the module in two units in series. The initial conditions for C(X,, whatever the unit considered, can be written as: C(X,)= At the channels inlet, we have different boundary conditions for U and U, that is: C(, T ) for unit U U ( S, T ) C( S, T ) dy C( S, T ) for unit U U ( S, T ) dy Analogous considerations must be applied to the velocity field. In fact, the inlet fluid velocity for unit U is the average fluid velocity at the exit of U, namely: U (, for unit U U ( S, U ( S, dy for unit U At the channels outlet, the assumption of null partial derivative may give unphysical results for U or U. Therefore, it can be assumed: C ( S, T ) X C (, T ) X for unit U for unit U 765 (3) (8) (9) ()
4 766 The previous conditions ensure the constancy of the first derivative at the exit without enforcing the more restrictive condition of null first derivative, which can be questionable for short membrane channels and even for lengthy channels near the membrane. On the axis, obvious symmetry considerations lead to: C ( X,, () Y At the membrane surface, the diffusive flux is equal to the convective mass transport through the membrane, that is: D Y C ( X,, VW CW CP () Y Replacing Eqs(4,6,7) in the previous equation, we can express the right hand side of Eq() as a function of the sole C w. So, Eq() can be used to update the solute concentration at the membrane surface. At this point, the problem and its boundary conditions have been completely outlined. Different algorithmic choices can be adopted to numerically solve Eq(); for the present simulations, we adopted a finitedifference scheme with asymmetric expansions of the terms containing the spatial derivatives at the boundaries. 3. Results and discussion All simulations presented in the following have been realized assuming the values of the geometric and physical constants reported in Table. Table : Values of constants adopted in the present simulation Parameter Value Channel length L [m]. Channel height h [m] 8-4 Inlet concentration c [kg m -3 ]. Rejection factor R.98 Diffusion coefficient D x [m s - ].6-9 Diffusion coefficient D y [m s - ].6-9 Dynamic viscosity [kg m - s - ] -3 Osmotic pressure constant K [Pa m 3 kg - ] Figure : Plot of membrane permeation velocity versus the axial coordinate of a single-unit membrane for two values of operating pressures and several inlet velocities For a single unit membrane, the effects of different feed flows on the permeation velocity are visualized in Figure for two operating pressure values. We remark that, at low pressure, the feed flow regime is nearly uninfluential as far as the polarization is concerned, as all curves for different values of u are nearly horizontal and very close to one another. An opposite situation occurs at higher pressures, where the
5 permeation velocity decreases markedly for growing values of the axial coordinate of the membrane with a very steep profile at the channel inlet. These aspects will be reconsidered in the case pertaining to the double-unit membrane. 767 Figure 3: Contour plot of curves at constant G versus the operating pressure and inlet velocity for a double-unit membrane splitted at one half of the total shell length (S =S =.5) We define Q i as the specific permeate flow rate, namely the permeate flow rate per membrane length in the direction normal to the plane x-y, obtainable by a configuration with i elements. The percent gain in terms of specific permeate flow, obtainable by a double-unit configuration with respect to a single-unit assembly, can be written as G = (Q -Q )/Q. For a double-unit membrane, the contour lines in Figure 3 are the curves at constant G and they are plotted versus the inlet velocity of the first unit U and the operating pressure of the cells. The inlet velocity ranges which the following figure refers to are chosen in a wide interval to have a wide picture of the effects for different operating regimes, typically chosen in commercial applications (u <. m/s) and in simulation and experimental tests, where u may even exceed. m/s (Lau et al., ). The aforementioned figure refers to a splitting point between membranes located at S =S =.5. Some interesting aspects should be pointed out, namely: i) For a wide range of pressure and concentrate flow rates, the gain obtained by a membrane splitting in two units spans over a satisfactory range, often exceeding % of the permeate volume obtainable by a single-unit module. ii) For the value of S here considered, at constant pressures sufficiently higher than the equilibrium value at which P= in Eq (4), the beneficial effects of a membrane splitting decrease for growing inlet concentrate velocity. This result is consistent with the trends of Figure pertaining to the single-unit membrane at high pressure, as the difference v w U,inlet -v w U,outlet decreases for growing values of u, thus mitigating the depolarizing role of U. On the opposite, when P, namely at very low pressures, we may have a reverse situation and the gain may increase for growing flow rates. However, this regime is technically meaningless as it corresponds to a minimal permeate flow rate close to its detection threshold. iii) When the membrane is splitted in two equal elements, that is for S =S =.5, we observe that the maximum values of G are obtained for those values of u typically used in commercial plants, namely u <. m/s. 4. Conclusions We have proposed a simulation study of a spiral-wound reverse osmosis cell in order to compare the yield of permeate phase in two different cases of single and double-unit membrane structure assembled in the same shell. We have assumed that the concentrate phase undergoes a perfect mixing before entering the second membrane element. This choice is motivated by the need of finding the upper limit of the aforementioned permeate yield. For some ranges of pressure and concentrate flow rates, the results are
6 768 promising and the percent gain in terms of specific permeate flow may be greater than % with respect to the values typical of an unsplitted membrane. As a general trend, the beneficial effects are particularly marked at low channel velocities and high pressures of the concentrate phase. These operating conditions correspond to critical regimes in terms of membrane polarization, as the polarizing effect of a highly concentrated boundary layer at the membrane surface is not damped by the convective effect of the fluid motion. We foresee that the future development of this study will be focused on experimental realizations of staggered membrane coils to assess the validity of such a technique in process optimisation. References Abdel-Rahman R.O., Ibrahium H.A., Yung-Tse Hung,, Liquid radioactive wastes treatment: A review, Water, 3(), Ahmad A.L., Lau K.K., 6, Impact of different spacer filaments geometries on D unsteady hydrodynamics and concentration polarization in spiral wound membrane channel, Journal of Membrane Science, 86(-), Al-Bastaki N.M., Abbas A., 999, Improving the permeate flux by unsteady operation of a RO desalination unit, Desalination, 3(-3), Bhattacharyya D., Back S.L., Kermode R.I., 99, Prediction of concentration polarization and flux behavior in reverse osmosis by numerical analysis, Journal of Membrane Science, 48(-3), 3-6. Cerrato C., Reverberi A.P., Dovì V.G., Bruzzone A.G., 9, A switching pressure approach in simulation and optimization of a reverse osmosis unit, Chemical Engineering Transactions, 8, , DOI:.333/CET9845 Eltawil M.A., Zhengming Z., Yuan L., 9, A review of renewable energy technologies integrated with desalination systems, Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 3(9), Goosen M.F.A., Sablani S.S., Al-Maskari S.S., Al-Belushi R.H., Wilf M.,, Effect of feed temperature on permeate flux and mass transfer coefficient in spiral-wound reverse osmosis systems, Desalination, 44(-3), Lau K.K., Abu Bakar M.Z., Ahmad A.L., Murugesan T.,, Effect of feed spacer mesh length ratio on unsteady hydrodynamics in D spiral wound membrane modules. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 49(), Ma S., Song L., Ong S.L., Ng W.J., 4, A -D streamline upwind Petrov/Galerkin finite element model for concentration polarization in spiral wound reverse osmosis modules, Journal of Membrane Science, 44(-), Madireddi K., Babcock R.B., Levine B., Kim J.H., Stenstrom M.K., 999, An unsteady-state model to predict concentration polarization in commercial spiral wound membranes, Journal of Membrane Science, 57(), Nair M., Kumar D., 3, Water desalination and challenges: The Middle-East perspective: a review, Desalination and Water Treatment, 5(-), 3-4. Pascariu V, Avadanei O., Gasner P., Stoica I., Reverberi A.P., Mitoseriu L., 3, Preparation and characterization of PbTiO3-epoxy resin compositionally graded thick films, Phase Transitions, 86(7), 75-75, DOI:.8/ Reverberi A.P., Bagnerini P., Maga L., Bruzzone A.G., 8, On the non-linear Maxwell-Cattaneo equation with non-constant diffusivity: shock and discontinuity waves. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 5(-), Reverberi A.P., Fabiano B., Dovì V.G., 3, Use of inverse modelling techniques for the estimation of heat transfer coefficients to fluids in cylindrical conduits, International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 4, 5-3, DOI:.6/j.icheatmasstransfer...5 Sablani S.S., Goosen M.F.A., Al-Belushi R., Wilf M.,, Concentration polarization in ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis: a critical review, Desalination, 4, Solisio C., Reverberi A.P., Del Borghi A., Dovì V.G.,, Inverse estimation of temperature profiles in landfills using heat recovery fluids measurements, Journal of Applied Mathematics, Volume, article number 7474, DOI:.55//7474 Tagliabue M., Reverberi A.P., Bagatin R., 4, Boron removal from water: needs, challenges and perspectives, Journal of Cleaner Production, DOI:.6/j.jclepro.3..4 (in press).
CFD STUDY OF MASS TRANSFER IN SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE
 GANIT J. Bangladesh Math. Soc. (ISSN 1606-3694) 31 (2011) 33-41 CFD STUDY OF MASS TRANSFER IN SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE Sharmina Hussain Department of Mathematics and Natural Science BRAC University,
GANIT J. Bangladesh Math. Soc. (ISSN 1606-3694) 31 (2011) 33-41 CFD STUDY OF MASS TRANSFER IN SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE Sharmina Hussain Department of Mathematics and Natural Science BRAC University,
A User-Defined Pervaporation Unit Operation in AspenPlus on the Basis of Experimental Results from Three Different Organophilic Membranes
 127 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
127 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
Numerical Study on Heat Transfer Enhancement in a Rectangular Duct with V-Shaped Ribs
 1285 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 70, 2018 Guest Editors: Timothy G. Walmsley, Petar S. Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-67-9;
1285 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 70, 2018 Guest Editors: Timothy G. Walmsley, Petar S. Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-67-9;
Reactor Design of Microwave Assisted Demetallization of Heavy Crude Oil
 511 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
511 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
PHEx: A Computational Tool for Plate Heat Exchangers Design Problems
 307 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
307 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
Separation Performance of Polymer Membranes for Organic Solvent Mixtures
 A publication of 1885 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 1885 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 2013 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A Numerical Study of the Effect of a Venetian Blind on the Convective Heat Transfer Rate from a Recessed Window with Transitional and Turbulent Flow
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 29, 2012 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-20-4; ISSN
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 29, 2012 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-20-4; ISSN
Optimization of the Coagulation Process to Remove Total Suspended Solids (TSS) from Produced Water
 115 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
115 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
Falling Film Evaporator: Drying of Ionic Liquids with Low Thermal Stress
 A publication of VOL. 29, 2012 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-20-4; ISSN
A publication of VOL. 29, 2012 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-20-4; ISSN
Indoor Testing of Solar Systems: A Solar Simulator for Multidisciplinary Research on Solar Technologies
 A publication of VOL. 39, 2014 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
A publication of VOL. 39, 2014 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
Estimate the extent of concentration polarization in crossflow filtration Select filtration unit operations to meet product requirements, consistent
 Membrane Separation Process Objectives Estimate the extent of concentration polarization in crossflow filtration Select filtration unit operations to meet product requirements, consistent with product
Membrane Separation Process Objectives Estimate the extent of concentration polarization in crossflow filtration Select filtration unit operations to meet product requirements, consistent with product
Effect of inter-filament distance on the improvement of Reverse Osmosis desalination process
 Effect of inter-filament distance on the improvement of Reverse Osmosis desalination process M. AMOKRANE a,b, D. SADAOUI a, M. DUDECK b a Laboratoire de Mécanique, Matériaux et Energétique (L2ME), Faculté
Effect of inter-filament distance on the improvement of Reverse Osmosis desalination process M. AMOKRANE a,b, D. SADAOUI a, M. DUDECK b a Laboratoire de Mécanique, Matériaux et Energétique (L2ME), Faculté
Condensation and Evaporation Characteristics of Flows Inside Three Dimensional Vipertex Enhanced Heat Transfer Tubes
 1777 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
1777 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 2017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
CENG 5210 Advanced Separation Processes. Reverse osmosis
 Reverse osmosis CENG 510 Advanced Separation Processes In osmosis, solvent transports from a dilute solute or salt solution to a concentrated solute or salt solution across a semipermeable membrane hich
Reverse osmosis CENG 510 Advanced Separation Processes In osmosis, solvent transports from a dilute solute or salt solution to a concentrated solute or salt solution across a semipermeable membrane hich
Mass transfer in the vicinity of a separation membrane the applicability of the stagnant film theory
 Journal of Membrane Science 202 (2002) 137 150 Mass transfer in the vicinity of a separation membrane the applicability of the stagnant film theory João M. Miranda, João B.L.M. Campos Centro de Estudos
Journal of Membrane Science 202 (2002) 137 150 Mass transfer in the vicinity of a separation membrane the applicability of the stagnant film theory João M. Miranda, João B.L.M. Campos Centro de Estudos
Membrane processes selective hydromechanical diffusion-based porous nonporous
 Membrane processes Separation of liquid or gaseous mixtures by mass transport through membrane (= permeation). Membrane is selective, i.e. it has different permeability for different components. Conditions
Membrane processes Separation of liquid or gaseous mixtures by mass transport through membrane (= permeation). Membrane is selective, i.e. it has different permeability for different components. Conditions
2.500 Desalination and Water Purification
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.500 Desalination and Water Purification Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 2.500 Desalination and Water Purification Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MASSACHUSETTS
CFD Investigation of Heat Transfer and Flow Patterns in Tube Side Laminar Flow and the Potential for Enhancement
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
The Modified Analogy of Heat and Momentum Transfers for Turbulent Flows in Channels of Plate Heat Exchangers
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING RANSACIONS VOL. 5, 0 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 0, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING RANSACIONS VOL. 5, 0 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 0, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN
CFD Modelling of the Fluid Flow Characteristics in an External-Loop Air-Lift Reactor
 A publication of 145 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 2, 21 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 21, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-958-2-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian Association
A publication of 145 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 2, 21 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 21, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-958-2-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian Association
Concentration polarization in a membrane placed under an impinging jet confined by a conical wall a numerical approach
 Journal of Membrane Science 182 (2001) 257 270 Concentration polarization in a membrane placed under an impinging jet confined by a conical wall a numerical approach João M. Miranda, João B.L.M. Campos
Journal of Membrane Science 182 (2001) 257 270 Concentration polarization in a membrane placed under an impinging jet confined by a conical wall a numerical approach João M. Miranda, João B.L.M. Campos
Compression and Expansion at the Right Pinch Temperature
 1939 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 56, 2017 Guest Editors: Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Wai Shin Ho, Jeng Shiun Lim Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-47-1;
1939 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 56, 2017 Guest Editors: Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Wai Shin Ho, Jeng Shiun Lim Copyright 2017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-47-1;
On the Applicability of RANS-Turbulence Models in CFD Simulations for the Description of Turbulent Free Jets During Biomass Combustion
 913 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
913 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
Separation through Dialysis
 Separation through Dialysis SOLVED WITH COMSOL MULTIPHYSICS 3.5a COPYRIGHT 2008. All right reserved. No part of this documentation may be photocopied or reproduced in any form without prior written consent
Separation through Dialysis SOLVED WITH COMSOL MULTIPHYSICS 3.5a COPYRIGHT 2008. All right reserved. No part of this documentation may be photocopied or reproduced in any form without prior written consent
Estimation of the Number of Distillation Sequences with Dividing Wall Column for Multi-component Separation
 343 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
343 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 61, 017 Guest Editors: Petar S Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Hon Loong Lam, Xia Liu, Jiří J Klemeš Copyright 017, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-51-8;
Fouling of reverse osmosis membranes using electrical impedance spectroscopy: Measurements and simulations
 Desalination 236 (2009) 187 193 Fouling of reverse osmosis membranes using electrical impedance spectroscopy: Measurements and simulations J.M. Kavanagh*, S. Hussain, T.C. Chilcott, H.G.L. Coster School
Desalination 236 (2009) 187 193 Fouling of reverse osmosis membranes using electrical impedance spectroscopy: Measurements and simulations J.M. Kavanagh*, S. Hussain, T.C. Chilcott, H.G.L. Coster School
Comparison of the Heat Transfer Efficiency of Nanofluids
 703 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 43, 2015 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-34-1; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
703 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 43, 2015 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-34-1; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Effect of the Type of Impellers on Mixing in an Electrochemical Reactor
 A publication of VOL. 35, 2013 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of VOL. 35, 2013 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
CFD Simulation of Mass Transfer Phenomena in Spacer Filled Channels for Reverse Electrodialysis Applications
 A publication of 1879 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of 1879 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 32, 213 Chief Editors: Sauro Pierucci, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 213, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-23-5; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Three-dimensional Modelling of Reactive Solutes Transport in Porous Media
 151 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 41, 214 Guest Editors: Simonetta Palmas, Michele Mascia, Annalisa Vacca Copyright 214, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-32-7; ISSN 2283-9216
151 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 41, 214 Guest Editors: Simonetta Palmas, Michele Mascia, Annalisa Vacca Copyright 214, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-32-7; ISSN 2283-9216
Helical Coil Flow: a Case Study
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Helical Coil Flow: a Case Study Marco Cozzini Renewable Energies and Environmental Technologies (REET) Research Unit, Fondazione Bruno Kessler
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2009 Milan Helical Coil Flow: a Case Study Marco Cozzini Renewable Energies and Environmental Technologies (REET) Research Unit, Fondazione Bruno Kessler
Feed. Figure 1. The above image depicts the construction of a typical spiral wound element.
 In a reverse osmosis (RO) process, pressure is applied to the saline side of a semi-permeable membrane to produce low salinity water. Upon application of the feed pressure, water molecules pass through
In a reverse osmosis (RO) process, pressure is applied to the saline side of a semi-permeable membrane to produce low salinity water. Upon application of the feed pressure, water molecules pass through
Lecture 10. Membrane Separation Materials and Modules
 ecture 10. Membrane Separation Materials and Modules Membrane Separation Types of Membrane Membrane Separation Operations - Microporous membrane - Dense membrane Membrane Materials Asymmetric Polymer Membrane
ecture 10. Membrane Separation Materials and Modules Membrane Separation Types of Membrane Membrane Separation Operations - Microporous membrane - Dense membrane Membrane Materials Asymmetric Polymer Membrane
Effects of solute permeability on permeation and solute rejection in membrane filtration
 Effects of solute permeability on permeation and solute rejection in membrane filtration Gustavo Lopes, Nelson Ibaseta, Pierrette Guichardon, Pierre Haldenwang To cite this version: Gustavo Lopes, Nelson
Effects of solute permeability on permeation and solute rejection in membrane filtration Gustavo Lopes, Nelson Ibaseta, Pierrette Guichardon, Pierre Haldenwang To cite this version: Gustavo Lopes, Nelson
CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE
 CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE In this chapter, the governing equations for the proposed numerical model with discretisation methods are presented. Spiral
CHAPTER 7 NUMERICAL MODELLING OF A SPIRAL HEAT EXCHANGER USING CFD TECHNIQUE In this chapter, the governing equations for the proposed numerical model with discretisation methods are presented. Spiral
Comparison of Conventional and Middle Vessel Batch Reactive Distillation Column: Application to Hydrolysis of Methyl Lactate to Lactic Acid
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
Biogas Clean-up and Upgrading by Adsorption on Commercial Molecular Sieves
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 29, 2012 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-20-4; ISSN
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 29, 2012 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-20-4; ISSN
A New Batch Extractive Distillation Operational Policy for Methanol Recovery
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 35, 2013 Guest Editors: Petar Varbanov, Jiří Klemeš, Panos Seferlis, Athanasios I. Papadopoulos, Spyros Voutetakis Copyright 2013, AIDIC Servizi
Validation 3. Laminar Flow Around a Circular Cylinder
 Validation 3. Laminar Flow Around a Circular Cylinder 3.1 Introduction Steady and unsteady laminar flow behind a circular cylinder, representing flow around bluff bodies, has been subjected to numerous
Validation 3. Laminar Flow Around a Circular Cylinder 3.1 Introduction Steady and unsteady laminar flow behind a circular cylinder, representing flow around bluff bodies, has been subjected to numerous
A mass transfer model for the prediction of permeate concentration during ultrafiltration of methyl violet dye solution
 Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 11, March 2005, pp. 205-211 A mass transfer model for the prediction of permeate concentration during ultrafiltration of methyl violet dye solution S Chatterjee
Indian Journal of Chemical Technology Vol. 11, March 2005, pp. 205-211 A mass transfer model for the prediction of permeate concentration during ultrafiltration of methyl violet dye solution S Chatterjee
Long-Term Performance of Borehole Heat Exchanger Fields with Groundwater Movement
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2 Paris Long-Term Performance of Borehole Heat Exchanger Fields with Groundwater Movement S. Lazzari *,1, A. Priarone 2 and E. Zanchini 1 1 Dipartimento
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2 Paris Long-Term Performance of Borehole Heat Exchanger Fields with Groundwater Movement S. Lazzari *,1, A. Priarone 2 and E. Zanchini 1 1 Dipartimento
Analysis of the Influence of Turbulence on the Heat Transfer Between Spherical Particles and Planar Surfaces
 13 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
13 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
Membrane Filtration 111 CAMBRIDGE. A Problem Solving Approach with MATLAB GREG FOLEY UNIVERSITY PRESS. Dublin City University
 Membrane Filtration A Problem Solving Approach with MATLAB GREG FOLEY Dublin City University 111 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Abbreviations page xv xviii 1 Introduction to membrane filtration
Membrane Filtration A Problem Solving Approach with MATLAB GREG FOLEY Dublin City University 111 CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Abbreviations page xv xviii 1 Introduction to membrane filtration
Simulation and Process Integration of Clean Acetone Plant
 469 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
469 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 39, 2014 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Peng Yen Liew, Jun Yow Yong Copyright 2014, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-30-3;
CFD Analysis for Thermal Behavior of Turbulent Channel Flow of Different Geometry of Bottom Plate
 International Journal Of Engineering Research And Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 13, Issue 9 (September 2017), PP.12-19 CFD Analysis for Thermal Behavior of Turbulent
International Journal Of Engineering Research And Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 13, Issue 9 (September 2017), PP.12-19 CFD Analysis for Thermal Behavior of Turbulent
1. Starting of a project and entering of basic initial data.
 PROGRAM VISIMIX TURBULENT SV. Example 1. Contents. 1. Starting of a project and entering of basic initial data. 1.1. Opening a Project. 1.2. Entering dimensions of the tank. 1.3. Entering baffles. 1.4.
PROGRAM VISIMIX TURBULENT SV. Example 1. Contents. 1. Starting of a project and entering of basic initial data. 1.1. Opening a Project. 1.2. Entering dimensions of the tank. 1.3. Entering baffles. 1.4.
Some physico-chemical data can be found at the web page (E-Tables):
 Reminiscences 1 Physical data have been supplied to Problem_#4. Some physico-chemical data can be found at the web page (E-Tables): http://uchi.vscht.cz/index.php/en/studium/navody-a-pomucky/e-tabulky
Reminiscences 1 Physical data have been supplied to Problem_#4. Some physico-chemical data can be found at the web page (E-Tables): http://uchi.vscht.cz/index.php/en/studium/navody-a-pomucky/e-tabulky
EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION
 EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION A. K. Kansal, P. Suryanarayana, N. K. Maheshwari Reactor Engineering Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
EFFECT OF DISTRIBUTION OF VOLUMETRIC HEAT GENERATION ON MODERATOR TEMPERATURE DISTRIBUTION A. K. Kansal, P. Suryanarayana, N. K. Maheshwari Reactor Engineering Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
Chemical Product and Process Modeling
 Chemical Product and Process Modeling Volume 4, Issue 4 2009 Article 5 CHEMPOR 2008 Determination of the Wall Shear Stress by Numerical Simulation: Membrane Process Applications Fanny Springer Rémy Ghidossi
Chemical Product and Process Modeling Volume 4, Issue 4 2009 Article 5 CHEMPOR 2008 Determination of the Wall Shear Stress by Numerical Simulation: Membrane Process Applications Fanny Springer Rémy Ghidossi
IV. Transport Phenomena. Lecture 23: Ion Concentration Polarization
 IV. Transport Phenomena Lecture 23: Ion Concentration Polarization MIT Student (and MZB) Ion concentration polarization in electrolytes refers to the additional voltage drop (or internal resistance ) across
IV. Transport Phenomena Lecture 23: Ion Concentration Polarization MIT Student (and MZB) Ion concentration polarization in electrolytes refers to the additional voltage drop (or internal resistance ) across
Research Article Performance of Single and Double Shaft Disk Separators
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Physical Separation in Science and Engineering Volume 8, Article ID 58617, 5 pages doi:1.1155/8/58617 Research Article Performance of Single and Double Shaft Disk Separators
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Physical Separation in Science and Engineering Volume 8, Article ID 58617, 5 pages doi:1.1155/8/58617 Research Article Performance of Single and Double Shaft Disk Separators
Beneficial Effect of Particle Adsorption in UF/MF Outside-In Hollow Fiber Filters. Yuriy Polyakov USPolyResearch, New Jersey Institute of Technology
 Beneficial Effect of Particle Adsorption in UF/MF Outside-In Hollow Fiber Filters Yuriy Polyakov USPolyResearch, New Jersey Institute of Technology NAMS 2005 BENEFICIAL EFFECT OF PARTICLE ADSORPTION Slide
Beneficial Effect of Particle Adsorption in UF/MF Outside-In Hollow Fiber Filters Yuriy Polyakov USPolyResearch, New Jersey Institute of Technology NAMS 2005 BENEFICIAL EFFECT OF PARTICLE ADSORPTION Slide
PRESSURE AND VELOCITY AMPLITUDES OF THE INCOMPRESSIBLE FLUID IN CONCENTRIC ANNULAR PASSAGE WITH OSCILLATORY BOUNDARY: TURBULENT FLOW
 Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 9, No. 2 (2014) 220-232 School of Engineering, Taylor s University PRESSURE AND VELOCITY AMPLITUDES OF THE INCOMPRESSIBLE FLUID IN CONCENTRIC ANNULAR
Journal of Engineering Science and Technology Vol. 9, No. 2 (2014) 220-232 School of Engineering, Taylor s University PRESSURE AND VELOCITY AMPLITUDES OF THE INCOMPRESSIBLE FLUID IN CONCENTRIC ANNULAR
Chapter 2 Mass Transfer Coefficient
 Chapter 2 Mass Transfer Coefficient 2.1 Introduction The analysis reported in the previous chapter allows to describe the concentration profile and the mass fluxes of components in a mixture by solving
Chapter 2 Mass Transfer Coefficient 2.1 Introduction The analysis reported in the previous chapter allows to describe the concentration profile and the mass fluxes of components in a mixture by solving
A Comparative Study of Carbon Capture for Different Power Plants
 1783 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 45, 2015 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Sharifah Rafidah Wan Alwi, Jun Yow Yong, Xia Liu Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi
1783 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 45, 2015 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Sharifah Rafidah Wan Alwi, Jun Yow Yong, Xia Liu Copyright 2015, AIDIC Servizi
Influence of Eccentricity and Angular Velocity on Force Effects on Rotor of Magnetorheological Damper
 EPJ Web of Conferences 18, 291 (218) EFM 217 https://doi.org/1.151/epjconf/21818291 Influence of Eccentricity and Angular Velocity on Force Effects on Rotor of Magnetorheological Damper Dominik Šedivý
EPJ Web of Conferences 18, 291 (218) EFM 217 https://doi.org/1.151/epjconf/21818291 Influence of Eccentricity and Angular Velocity on Force Effects on Rotor of Magnetorheological Damper Dominik Šedivý
THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE DIFFERENCE MODEL FOR TRANSPORT OF CONSERVATIVE POLLUTANTS
 Pergamon Ocean Engng, Vol. 25, No. 6, pp. 425 442, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0029 8018/98 $19.00 + 0.00 PII: S0029 8018(97)00008 5 THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE
Pergamon Ocean Engng, Vol. 25, No. 6, pp. 425 442, 1998 1998 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain 0029 8018/98 $19.00 + 0.00 PII: S0029 8018(97)00008 5 THREE-DIMENSIONAL FINITE
Design and CFD Modelling of a Low Pressure Turbine for Aeroengines
 697 A publication of VOL. 70, 2018 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Timothy G. Walmsley, Petar S. Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-67-9;
697 A publication of VOL. 70, 2018 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS Guest Editors: Timothy G. Walmsley, Petar S. Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-67-9;
Numerical Analysis of Flow Dynamics of Cyclone Separator Used for Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler
 991 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 46, 215 Guest Editors: Peiyu Ren, Yancang Li, Huiping Song Copyright 215, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-37-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
991 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 46, 215 Guest Editors: Peiyu Ren, Yancang Li, Huiping Song Copyright 215, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-9568-37-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS
 Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS Overview Introduction Important Concepts for Understanding water Movement through Vines Osmosis Water Potential Cell Expansion and the Acid Growth
Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS Overview Introduction Important Concepts for Understanding water Movement through Vines Osmosis Water Potential Cell Expansion and the Acid Growth
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH VOLUME 5, ISSUE 09, SEPTEMBER 2016 ISSN
 Numerical Analysis Of Heat Transfer And Fluid Flow Characteristics In Different V-Shaped Roughness Elements On The Absorber Plate Of Solar Air Heater Duct Jitesh Rana, Anshuman Silori, Rohan Ramola Abstract:
Numerical Analysis Of Heat Transfer And Fluid Flow Characteristics In Different V-Shaped Roughness Elements On The Absorber Plate Of Solar Air Heater Duct Jitesh Rana, Anshuman Silori, Rohan Ramola Abstract:
Dansk Mejeriteknisk Selskab Billund, June 14th Challenges in the Dairy Industry: Perspective on extreme performance membranes
 Dansk Mejeriteknisk Selskab Billund, June 14th 2018 Challenges in the Dairy Industry: Perspective on extreme performance membranes OLE LILLEVANG, TECHNOLOGY SPECIALIST GEA PRODUCT TECHNOLOGY CENTER FILTRATION
Dansk Mejeriteknisk Selskab Billund, June 14th 2018 Challenges in the Dairy Industry: Perspective on extreme performance membranes OLE LILLEVANG, TECHNOLOGY SPECIALIST GEA PRODUCT TECHNOLOGY CENTER FILTRATION
WATER-OIL SEPARATION PROCESS USING A CONCENTRIC TUBULAR CERAMIC MEMBRANE MODULE: A NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION
 WATER-OIL SEPARATION PROCESS USING A CONCENTRIC TUBULAR CERAMIC MEMBRANE MODULE: A NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION a Cunha, A. L. 1 ; b Farias Neto, S. R.; c Lima, A. G. B.; c Barbosa, E. S.; a Santos, J. P. L.;
WATER-OIL SEPARATION PROCESS USING A CONCENTRIC TUBULAR CERAMIC MEMBRANE MODULE: A NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION a Cunha, A. L. 1 ; b Farias Neto, S. R.; c Lima, A. G. B.; c Barbosa, E. S.; a Santos, J. P. L.;
Transient Magnetic Translating Motion Finite Element Model of the Annular Linear Induction Pump
 Transient Magnetic Translating Motion Finite Element Model of the Annular Linear Induction Pump Abstract The paper constitutes a study of the startup, steady state operation and dynamic behavior of a double
Transient Magnetic Translating Motion Finite Element Model of the Annular Linear Induction Pump Abstract The paper constitutes a study of the startup, steady state operation and dynamic behavior of a double
Competitive Adsorption of Methane and Carbon Dioxide on Different Activated Carbons
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL., Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 98-88-98--;
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL., Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 98-88-98--;
Hydraulic and Mass Transfer Performances of a Commercial Hybrid Packing: The RSP200X - Key Modelling Parameters for Gas Treatment Applications
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 69, 2018 Guest Editors: Elisabetta Brunazzi, Eva Sorensen Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-66-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 69, 2018 Guest Editors: Elisabetta Brunazzi, Eva Sorensen Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-66-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Experimental and Numerical Studies of Heat Transfer Characteristics for Impinging Jet on Dimple Surfaces
 1273 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 70, 2018 Guest Editors: Timothy G. Walmsley, Petar S. Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-67-9;
1273 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 70, 2018 Guest Editors: Timothy G. Walmsley, Petar S. Varbanov, Rongxin Su, Jiří J. Klemeš Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-67-9;
A Systematic Comparison of Stagewise/Interval-Based Superstructure Approaches for the Optimal Synthesis of Heat Exchange Networks
 793 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
793 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 52, 2016 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Peng-Yen Liew, Jun-Yow Yong, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš, Hon Loong Lam Copyright 2016, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l.,
Analysis of Heat Transfer in Pipe with Twisted Tape Inserts
 Proceedings of the 2 nd International Conference on Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, April 30 May 1, 2015 Paper No. 143 Analysis of Heat Transfer in Pipe with Twisted Tape Inserts
Proceedings of the 2 nd International Conference on Fluid Flow, Heat and Mass Transfer Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, April 30 May 1, 2015 Paper No. 143 Analysis of Heat Transfer in Pipe with Twisted Tape Inserts
CONCENTRATION POLARIZATION
 CONCENTRATION POLARIZATION Smart Membrane Products. More Water. Less Cost. www.waterplanet.com CONCENTRATION POLARIZATION: EARLY THEORIES Subir Bhattacharjee, Ph.D. Founder & CTO Water Planet, Inc. OVERVIEW
CONCENTRATION POLARIZATION Smart Membrane Products. More Water. Less Cost. www.waterplanet.com CONCENTRATION POLARIZATION: EARLY THEORIES Subir Bhattacharjee, Ph.D. Founder & CTO Water Planet, Inc. OVERVIEW
Chapter 3 Membrane Processes for Water Production
 Chapter 3 Membrane Processes for Water Production Application of Membrane Processes in Water Environment Fusion Tech Hydrology Molecular biology Surface Chem Nano particles Biofilm CFD Catalyst Space station
Chapter 3 Membrane Processes for Water Production Application of Membrane Processes in Water Environment Fusion Tech Hydrology Molecular biology Surface Chem Nano particles Biofilm CFD Catalyst Space station
Simulation of a 3D Flow-Focusing Capillary-Based Droplet Generator
 Simulation of a 3D Flow-Focusing Capillary-Based Droplet Generator D. Conchouso*, E. Rawashdeh, A. Arevalo, D. Castro, I. G. Foulds King Abdullah University of Science and Technology 4700 KAUST 23955,
Simulation of a 3D Flow-Focusing Capillary-Based Droplet Generator D. Conchouso*, E. Rawashdeh, A. Arevalo, D. Castro, I. G. Foulds King Abdullah University of Science and Technology 4700 KAUST 23955,
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS STUDY OF FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A SINGLE SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE
 BRAC University Journal, vol. V, no. 1, 008, pp. 1-8 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS STUDY OF FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A SINGLE SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE Sharmina Hussain Department of Mathematics and Natural
BRAC University Journal, vol. V, no. 1, 008, pp. 1-8 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS STUDY OF FLOW BEHAVIOUR IN A SINGLE SPACER FILLED MEMBRANE MODULE Sharmina Hussain Department of Mathematics and Natural
CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel
 CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel *1 Hüseyin Kaya, 2 Kamil Arslan 1 Bartın University, Mechanical Engineering Department, Bartın, Turkey
CFD Analysis of Forced Convection Flow and Heat Transfer in Semi-Circular Cross-Sectioned Micro-Channel *1 Hüseyin Kaya, 2 Kamil Arslan 1 Bartın University, Mechanical Engineering Department, Bartın, Turkey
MSWI Flue Gas Two-Stage Dry Treatment: Modeling and Simulation
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 26, 2012 Guest Editors: Valerio Cozzani, Eddy De Rademaeker Copyright 2012, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISBN 978-88-95608-17-4; ISSN 1974-9791 The Italian
Lecture 2 Flow classifications and continuity
 Lecture 2 Flow classifications and continuity Dr Tim Gough: t.gough@bradford.ac.uk General information 1 No tutorial week 3 3 rd October 2013 this Thursday. Attempt tutorial based on examples from today
Lecture 2 Flow classifications and continuity Dr Tim Gough: t.gough@bradford.ac.uk General information 1 No tutorial week 3 3 rd October 2013 this Thursday. Attempt tutorial based on examples from today
The effect of Entry Region on Thermal Field
 The effect of Entry Region on Thermal Field Flow Fractionation Nick Cox Supervised by Professor Bruce Finlayson University of Washington Department of Chemical Engineering June 6, 2007 Abstract Achieving
The effect of Entry Region on Thermal Field Flow Fractionation Nick Cox Supervised by Professor Bruce Finlayson University of Washington Department of Chemical Engineering June 6, 2007 Abstract Achieving
Author's Accepted Manuscript
 Author's Accepted Manuscript Visualization And Modelling Of The Polarization Layer In Crossflow Reverse Osmosis In A Slit-Type Channel R. Salcedo-Díaz, P. García-Algado, M. García- Rodríguez, J. Fernández-Sempere,
Author's Accepted Manuscript Visualization And Modelling Of The Polarization Layer In Crossflow Reverse Osmosis In A Slit-Type Channel R. Salcedo-Díaz, P. García-Algado, M. García- Rodríguez, J. Fernández-Sempere,
Mixing in Flow Devices:
 Mixing in Flow Devices: Spiral microchannels in two and three dimensions Prepared by Ha Dinh Mentor: Professor Emeritus Bruce A. Finlayson Department of Chemical Engineering University of Washington June
Mixing in Flow Devices: Spiral microchannels in two and three dimensions Prepared by Ha Dinh Mentor: Professor Emeritus Bruce A. Finlayson Department of Chemical Engineering University of Washington June
Investigating the effect of graphene oxide on scaling in thin-film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes
 Investigating the effect of graphene oxide on scaling in thin-film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes Ali Ansari, Bo Cao, Xinyi Yi, Yandi Hu, and Debora Rodrigues Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Investigating the effect of graphene oxide on scaling in thin-film composite polyamide reverse osmosis membranes Ali Ansari, Bo Cao, Xinyi Yi, Yandi Hu, and Debora Rodrigues Civil and Environmental Engineering,
Performance characteristics of turbo blower in a refuse collecting system according to operation conditions
 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 22 (2008) 1896~1901 Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology www.springerlink.com/content/1738-494x DOI 10.1007/s12206-008-0729-6 Performance characteristics
Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. Jayant Modak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
 Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. Jayant Modak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 26 Problem solving : Heterogeneous reactions Friends, in last few
Chemical Reaction Engineering Prof. Jayant Modak Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore Lecture No. # 26 Problem solving : Heterogeneous reactions Friends, in last few
Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions
 Chapter 1 Earth Science Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions Project Representative Yozo Hamano Authors Ataru Sakuraba Yusuke Oishi
Chapter 1 Earth Science Simulation Study on the Generation and Distortion Process of the Geomagnetic Field in Earth-like Conditions Project Representative Yozo Hamano Authors Ataru Sakuraba Yusuke Oishi
Table of Contents. Foreword... xiii. Preface... xv
 Table of Contents Foreword.... xiii Preface... xv Chapter 1. Fundamental Equations, Dimensionless Numbers... 1 1.1. Fundamental equations... 1 1.1.1. Local equations... 1 1.1.2. Integral conservation equations...
Table of Contents Foreword.... xiii Preface... xv Chapter 1. Fundamental Equations, Dimensionless Numbers... 1 1.1. Fundamental equations... 1 1.1.1. Local equations... 1 1.1.2. Integral conservation equations...
Computational fluid dynamics applied to membranes: State of the art and opportunities
 Chemical Engineering and Processing 45 (2006) 437 454 Computational fluid dynamics applied to membranes: State of the art and opportunities R. Ghidossi a, D. Veyret a, P. Moulin b, a Institut Universitaire
Chemical Engineering and Processing 45 (2006) 437 454 Computational fluid dynamics applied to membranes: State of the art and opportunities R. Ghidossi a, D. Veyret a, P. Moulin b, a Institut Universitaire
Dr. Christoph Johann Wyatt Technology Europe GmbH Copyright Wyatt Technology Europe GmbH All Rights reserved 1
 Dr. Christoph Johann Wyatt Technology Europe GmbH 2010 Copyright Wyatt Technology Europe GmbH All Rights reserved 1 Introduction Overview The Nature of Scattered Light: Intensity of scattered light Angular
Dr. Christoph Johann Wyatt Technology Europe GmbH 2010 Copyright Wyatt Technology Europe GmbH All Rights reserved 1 Introduction Overview The Nature of Scattered Light: Intensity of scattered light Angular
Numerical analysis of three-lobe journal bearing with CFD and FSI
 Numerical analysis of three-lobe journal bearing with CFD and FSI Pankaj Khachane 1, Dinesh Dhande 2 1PG Student at Department of Mechanical Engineering, AISSMSCOE Pune, Maharashtra, India 2Assistant Professor
Numerical analysis of three-lobe journal bearing with CFD and FSI Pankaj Khachane 1, Dinesh Dhande 2 1PG Student at Department of Mechanical Engineering, AISSMSCOE Pune, Maharashtra, India 2Assistant Professor
IV. Transport Phenomena Lecture 18: Forced Convection in Fuel Cells II
 IV. Transport Phenomena Lecture 18: Forced Convection in Fuel Cells II MIT Student (and MZB) As discussed in the previous lecture, we are interested in forcing fluid to flow in a fuel cell in order to
IV. Transport Phenomena Lecture 18: Forced Convection in Fuel Cells II MIT Student (and MZB) As discussed in the previous lecture, we are interested in forcing fluid to flow in a fuel cell in order to
Numerical Investigation of Convective Heat Transfer in Pin Fin Type Heat Sink used for Led Application by using CFD
 GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 8 July 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Numerical Investigation of Convective Heat Transfer in Pin Fin Type Heat Sink used for Led
GRD Journals- Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering Volume 1 Issue 8 July 2016 ISSN: 2455-5703 Numerical Investigation of Convective Heat Transfer in Pin Fin Type Heat Sink used for Led
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer
 CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
CENG 501 Examination Problem: Estimation of Viscosity with a Falling - Cylinder Viscometer You are assigned to design a fallingcylinder viscometer to measure the viscosity of Newtonian liquids. A schematic
Robust Model Predictive Control of Heat Exchangers
 A publication of CHEMICAL EGIEERIG RASACIOS VOL. 9, 01 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 01, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISB 978-88-95608-0-4; ISS 1974-9791 he
A publication of CHEMICAL EGIEERIG RASACIOS VOL. 9, 01 Guest Editors: Petar Sabev Varbanov, Hon Loong Lam, Jiří Jaromír Klemeš Copyright 01, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l., ISB 978-88-95608-0-4; ISS 1974-9791 he
Numerical Investigation of Thermal Performance in Cross Flow Around Square Array of Circular Cylinders
 Numerical Investigation of Thermal Performance in Cross Flow Around Square Array of Circular Cylinders A. Jugal M. Panchal, B. A M Lakdawala 2 A. M. Tech student, Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute
Numerical Investigation of Thermal Performance in Cross Flow Around Square Array of Circular Cylinders A. Jugal M. Panchal, B. A M Lakdawala 2 A. M. Tech student, Mechanical Engineering Department, Institute
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics. Eileen Nugent
 Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
Lecture 10 : Neuronal Dynamics Eileen Nugent Origin of the Cells Resting Membrane Potential: Nernst Equation, Donnan Equilbrium Action Potentials in the Nervous System Equivalent Electrical Circuits and
ULTRAFLITRATION OF WASTEWATER WITH PRETREATMENT: EVALUATION OF FLUX DECLINE MODELS
 ULTRAFLITRATION OF WASTEWATER WITH PRETREATMENT: EVALUATION OF FLUX DECLINE MODELS H. K. Shon, S. Vigneswaran,* J. Kandasamy and W.G. Shim 2 Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney, P.O.
ULTRAFLITRATION OF WASTEWATER WITH PRETREATMENT: EVALUATION OF FLUX DECLINE MODELS H. K. Shon, S. Vigneswaran,* J. Kandasamy and W.G. Shim 2 Faculty of Engineering, University of Technology, Sydney, P.O.
Laminar Forced Convection Heat Transfer from Two Heated Square Cylinders in a Bingham Plastic Fluid
 Laminar Forced Convection Heat Transfer from Two Heated Square Cylinders in a Bingham Plastic Fluid E. Tejaswini 1*, B. Sreenivasulu 2, B. Srinivas 3 1,2,3 Gayatri Vidya Parishad College of Engineering
Laminar Forced Convection Heat Transfer from Two Heated Square Cylinders in a Bingham Plastic Fluid E. Tejaswini 1*, B. Sreenivasulu 2, B. Srinivas 3 1,2,3 Gayatri Vidya Parishad College of Engineering
SELF-SUSTAINED OSCILLATIONS AND BIFURCATIONS OF MIXED CONVECTION IN A MULTIPLE VENTILATED ENCLOSURE
 Computational Thermal Sciences, 3 (1): 63 72 (2011) SELF-SUSTAINED OSCILLATIONS AND BIFURCATIONS OF MIXED CONVECTION IN A MULTIPLE VENTILATED ENCLOSURE M. Zhao, 1, M. Yang, 1 M. Lu, 1 & Y. W. Zhang 2 1
Computational Thermal Sciences, 3 (1): 63 72 (2011) SELF-SUSTAINED OSCILLATIONS AND BIFURCATIONS OF MIXED CONVECTION IN A MULTIPLE VENTILATED ENCLOSURE M. Zhao, 1, M. Yang, 1 M. Lu, 1 & Y. W. Zhang 2 1
Meysam ATASHAFROOZ, Seyyed Abdolreza GANDJALIKHAN NASSAB, and Amir Babak ANSARI
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 014, Vol. 18, No., pp. 479-49 479 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF ENTROPY GENERATION IN LAMINAR FORCED CONVECTION FLOW OVER INCLINED BACKWARD AND FORWARD FACING STEPS IN A DUCT UNDER BLEEDING
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 014, Vol. 18, No., pp. 479-49 479 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF ENTROPY GENERATION IN LAMINAR FORCED CONVECTION FLOW OVER INCLINED BACKWARD AND FORWARD FACING STEPS IN A DUCT UNDER BLEEDING
A Rate-Based Equation-Oriented Parallel Column Model: Application to Dividing Wall Columns
 A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 69, 2018 Guest Editors: Elisabetta Brunazzi, Eva Sorensen Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-66-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
A publication of CHEMICAL ENGINEERING TRANSACTIONS VOL. 69, 2018 Guest Editors: Elisabetta Brunazzi, Eva Sorensen Copyright 2018, AIDIC Servizi S.r.l. ISBN 978-88-95608-66-2; ISSN 2283-9216 The Italian
Heat Transfer of Condensation in Smooth Round Tube from Superheated Vapor
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Heat Transfer of Condensation in Smooth Round Tube from Superheated Vapor
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs International Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2016 Heat Transfer of Condensation in Smooth Round Tube from Superheated Vapor
Simulation analysis using CFD on vibration behaviors of circular cylinders subjected to free jets through narrow gaps in the vicinity of walls
 Fluid Structure Interaction V 85 Simulation analysis using CFD on vibration behaviors of circular cylinders subjected to free jets through narrow gaps in the vicinity of walls K. Fujita Osaka City University,
Fluid Structure Interaction V 85 Simulation analysis using CFD on vibration behaviors of circular cylinders subjected to free jets through narrow gaps in the vicinity of walls K. Fujita Osaka City University,
