Electronic Circuits Laboratory EE462G Lab #2
|
|
|
- Anissa Richardson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electronic Circuits Laboratory EE46G Lab # Characterizing Nonlinear Elements, Curve Tracers, Transfer Characteristics, Curve Fit Programs Original slides prepared by Kevin D. Donohue (Spring 007) Modified by Zhi David Chen (Spring 016)
2 Instrumentation This lab requires: Tektronix s Curve Tracer 370B. For the data sheet you must save the displayed waveform to a floppy disk and paste (if BMP) or load and plot (if CSV) using excel or Matlab. Make special note of the curve dynamics. Make sure the scale allows the critical curve dynamics to be clearly seen over a useful range of interest. Poor parameter estimates result for mostly flat (or vertical) curve portions.
3 Instrumentation Example displays for diode with different collector settings 0,0 AC collector sweep Positive DC collector sweep 0,0
4 Instrumentation Example displays for FET drain characteristics with different gate-source voltage steps and horizontal and vertical scales. Offset 1.49 V Step. V Step Number 7 Offset 1.5 V Step.5 V Step Number 7
5 Acquisition Modes Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A
6 Acquisition Modes Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A
7 Screen Scaling Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A SPECS_EN,00.html
8 Screen Scaling Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A
9 Collector Supply Sweep Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A
10 Collector Supply Sweep Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A
11 Step Generator Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A
12 Step Generator Taken from Tektronix User Manual 370B Programmable Curve Tracer 070-A
13 Transfer Characteristics Transfer Characteristics A relation describing the amplitude input-output relationship of a device. A sufficient characterization in most engineering problems for instantaneous systems (present output does not depend on future or previous values). These systems are sometimes referred to as memoryless, and are typical of systems with no energy storage elements.
14 PN junction diode i D slope = 1 r d i D + v D open The band on the component usually denotes the cathode terminal Reverse bias v f Forward bias + v D r d i D + v f v D
15 Zener diode i Z (ma) Symbol i Z + v Z Reverse breakdown The band on the component usually denotes the cathode terminal + v Z i Z + r z v ZK v ZK open Reverse bias + v Z V f forward bias + v Z i Z r d + v Z (V ) v f
16 n-channel MOSFET + V GS _ A Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) is presented for charge flowing in an n- channel: I B Body or D D Substrate G D S n n p B + V DS _ G S D Drain G Gate S Source For many applications the body is connected to the source and thus most FETs are packaged that way.
17 FET Operation + V GS _ The current flow between the drain and the source can be controlled by applying a positive gate voltage: V GS n n p I D + V DS _ Three Regions of Operation: Cutoff region (V GS V tr ) Triode region (V GS V tr, V DS V GS - V tr ) Constant current region (CCR) (saturation) (V GS V tr, V GS - V tr V DS )
18 Cutoff Region In this region (V GS V tr ) the gate voltage is less than the threshold voltage and virtually no current flows through the reversed biased PN interface between the drain and body n p - - I D + V DS _ Typical values for V tr (or V to ) range from 1 to several volts. Cutoff region: I D =0 + V GS _ n
19 Triode Region + V GS _ In this region (V GS > V tr and V DS V GS - V tr ) the gate voltage exceeds the threshold voltage and pulls negative charges toward the gate. This results is an n-channel whose width controls the current flow I D between the drain and source. Triode Region: (V GS > V tr, V DS V GS - V tr ) V GS n n p I D W K p [ ] I = ( V V ) V V + V DS _ D L GS tr DS DS where: K p = µ ncox product of surface mobility of channel electrons µ n and gate capacitance per unit area C ox in units of amps per volts squared, W is the channel width, and L is channel length.
20 Constant Current Region (CCR) In this region (V GS > V tr and V GS - V tr V DS ) the drain-source voltage exceeds the excess gate voltage and pulls negative charges toward the drain and reduces the channel area at the drain. This limits the current making it more insensitive/independent to changes in V DS. I D CCR: V GS > V tr, V GS - V tr V DS + V GS _ n n p + V DS _ I D W = L K p ( VGS Vtr ) The material parameters can be combined into one constant: I D = K( VGS Vtr ) At the point of beginning of CCR (Saturation), for a given V GS, the following relation holds: I = D KV DS
21 NMOS Transfer Characteristics The relations between I D and V DS for the operational regions of the NMOS transistor can be used to generate its transfer characteristic. These can be conveniently coded in a Matlab function function ids = nmos(vds,vgs,kp,w,l,vto) % This function generates the drain-source current values "ids" for % and NMOS Transistor as a function of the drain-source voltage "vds". % ids = nmos(vds,vgs,kp,w,l,vto) % where "vds" is a vector of drain-source values % "vgs" is the gate voltage % "KP" is the device parameter % "W" is the channel width % "L" is the channel length % "vto" is the threshold voltage % and output "ids" is a vector of the same size of "vds" % containing the drain-source current values.
22 NMOS Transfer Characteristics ids = zeros(size(vds)); % Initialize output array with all zeros k = (W/L)*KP/; % Combine devices material parameters % For non-cutoff operation: if vgs >= vto % Find points in vds that are in the triode region ktri = find(vds<=(vgs-vto) & vds >= 0); % Points less than (gate threshold voltage) % If points are found in the triode region compute ids with proper formula if ~isempty(ktri) ids(ktri) = k*(*(vgs-vto).*vds(ktri)-vds(ktri).^); end % Find points in saturation region ksat = find(vds>(vgs-vto) & vds >= 0); % Points greater than the excess voltage % if points are found in the saturation regions compute ids with proper formula if ~isempty(ksat) ids(ksat) = k*((vgs-vto).^); end % If points of vds are outside these ranges, then the ids values remain zero end
23 NMOS Transfer Characteristics Plot the transfer characteristics of an NMOS transistor where KP = 50 µa/v, W= 160 µm, L= µm, V tr = V, and for VGS = [.5, 1,, 3, 4, 5, 6] volts vgs = [.5, 1,, 3, 4, 5, 6] vds =[0:.01:4]; for kc = 1:length(vgs) ids = nmos(vds,vgs(kc),50e-6,160e-6,e-6,); figure(1); plot(vds,ids*1000) hold on end ids = (50e-6/)*(160e-6/e-6)*vds.^; figure(1); plot(vds,ids*1000,'g:') hold off xlabel('vds in V') ylabel('id in ma') ID in ma Triode Region Boundary VGS = 6 VGS = 5 VGS = 4 VGS = 3 Saturation Region Boundary IDS=K(VDS) VGS =, 1, & VDS in V
24 Find K from Curve Trace Recall at the start of CCR the following holds: From graph: 0.4 = 0.7 = KV DS K = K3.4 One way to estimate K is to compute it for each equation and take the average. In this case it becomes K=.137 A/V, which for W=L=1, implies: K p = K* = 0.74 A/V I D = K.6 I D = KV DS
25 Find K from Curve Trace (LS) From graph: I D = 0.4 = 0.7 = 1.5 = KV DS K1.5 K3.4 K.6 K LS = A better approach uses a least-squares solution that gives the error in each equation equal weight. Find K to minimize mean square error for the measured data: M 1 E = M Take derivative with respect to K and set equal to 0 to obtain: K LS M ( VDSiI Di ) i= 1 = M ( VDSiVDSi ) i= 1 which for W=L=1, implies: K p = K LS * = 0.49 A/V i= 1 ( ) I Di KV DSi ( ) A =.146 ( ) V
26 Plot Diode TC Data was collected on the Tektronix s Curve Tracer 370B for a Diode and saved as a CSV file. Open file, process data and plot TC % Open CSV curve from Curve Tracer Output File fname = ['E11600E.CSV']; c = getcurves(fname); % Convert Cell Array to vector [id, vd] = interpcurves(c); % Plot it for observation figure(1) plot(vd,id*1000) title('diode Transfer Characteristic') xlabel('v_d in Volts') ylabel('i_d in milliamps') i d in milliamps Diode Transfer Characteristic Saturation from instrument range V d in Volts
27 Curve fit Parameter Estimation Given the TC curve for the diode in terms of its I-V values sampled and stored: a straight-forward iterative program can be written to vary parameters in the diode equation and compare its fit (error) to the measured data The parameters that result in the minimum error can then be used to described the device. The diode can be described with the Shockley equation: i D v D = I s exp 1 nvt where v D and i D is the voltage drop over and current through the diode, respectively, I s is the saturation current (typically on the order of ), n is the emission coefficient taking on values between 1 and, and V T is the thermal voltage (about equal to 0.06 at 300K).
28 Curve fit Parameter Estimation Matlab Example: Consider a parametric variation of the Shockley equation where the product of n and V T is taken as one parameter: α = n V T i D vd = I s exp 1 α Assume V T =.06, write a Matlab script to iterate with a range of values for n and I s while comparing the squared error between the measure i D values and those predicted with the equation. Find the n and I s that result in the minimum error. The I s range can be large so you may want to create range of values uniformly spaced on a log scale. This can be done with the Matlab command logspace: >> isvec = logspace(-18, -13,150); Type help logspace in Matlab for information on how this function works.
29 % Select parameters ranges and increments vt =.06; % Thermal voltage nt = [.5:.1:3]; % Trial values for emission coefficient n is = logspace(-1,-5,35); % Trial values of Is % Extract a curve from Curve Tracer Output c = getcurves(['e11600e.csv']); % Interpolate curve to a uniform set of points for x and y axes of TC [m, x] = interpcurves(c); % Trim data and Only use values less than.01 volt, if you look at a plot of the data % you will see it saturates close to 0 ma idlimit =.0175; dd = find(m < idlimit); % Find all points not affected by saturation cv = m(dd); % Trim data vector to just these points vds = x(dd); % Trim corresponding voltage axis
30 % Loop to compute squared error for every iteration of test value % parameter for n=1:length(nt) % Emission coefficient "n" loop for k=1:length(is) % Saturation current value loop ids = diodetc(vds,is(k),nt(n),vt); % generate Shockley equation values at measured % x-axis values (vds) and trial parameters (you need to % create this function as part of your prelab assignment). err(n,k) = mean(abs(ids - cv).^); % Compute MSE for this parameter combination plot(vds,ids,'g',vds,cv,'r') % Just to see a comparison of curves at % each iteration, plot it. This statement % and the next 4 can be commented out to % prevent plot and pause title(['compare curves is = ' numstr(is(k)) ' n = ' numstr(nt(n)) ]) xlabel('v_ds in Volts') ylabel('i_ds in Amps') pause(.3) end end
31 % Find point at which the minimum error occurred [mvtr, mkp] = find(min(min(err)) == err); ntmin = nt(mvtr(1)); % MSE index "n" disp([ 'Estimated n: ' numstr(ntmin) ]) ismin = is(mkp(1)); % MSE saturation current values disp([ 'Estimated Is ' numstr(ismin) ]) % Plot best fit ids = diodetc(vds,ismin,ntmin,vt); figure(1) plot(vds,ids,'g',vds,cv,'r') title('compare measured data (red) with MSE Shockley Eqn. fit (green)') xlabel('v_ds in Volts') ylabel('i_ds in Amps')
32 Best-fit-Curve with Diode Data Estimated n: Estimated Is.1063e compare measured data (red) with MSE Shockley Eqn. fit (green) i d s in Amps V d s in Volts
33 Plot MOSFET TC Data was collected on the Tektronix s Curve Tracer 370B for a NMOS FET and saved as a CSV file. Open file, process data and plot TC % Open CSV curve from Curve Tracer Output File fname = ['E11555E.CSV']; vstep = [1.496:.:.696]; % Need to provide the step sequence c = getcurves(fname,vstep); % Convert Cell Array to vector [ids, vds, vgs] = interpcurves(c); % Plot it for observation figure(1) plot(vds,ids*1000) title('fet Transfer Characteristic') xlabel('v_d_s in Volts') ylabel('i_d_s in milliamps') % Write the Vgs values on the plot near corresponding TC hold on % Step through vgs vector and write number on plot for k=1:length(vgs) text(mean(vds),1000*max(ids(k,:)),numstr(vgs(k),)) end hold off i ds in milliamps FET Transfer Characteristic v ds in Volts
34 Curve Fit Parameter Estimation Matlab Example: Consider a parametric variation of the model for the NMOS FET. Since the function NMOS already implements the NMOS FET I-V curves, use that to write a Matlab script to iterate with a range of values for V tr and K p for a given V gs while comparing the squared error between the measured i DS values and those predicted with the NMOS function. Find the V tr and K p that result in the minimum error for several values of V gs
35 % Extract a curve from Curve Tracer Output vgs = [1.496:.:.696]; % Gate voltages at which measurement was taken (you need to % get this information at the time the data is % collected. In this case the offset was 1.496, step % size was. volts, and 7 steps were generated. % Select row corresponding to the particular vgs value on which to perform % curve fit (should be between 1 and length of vgs) rwtest = 4; % Parameters to vary for curve fit. vto = [.5:.05:3]; % Range for threshold voltages kp = [.001:.005:.]; % Range of KP values % Fixed parameters (set W and L to one so they will have no effect) W= 1; L=1;
36 % read in data and sort in a cell array (rows don t have same number of points so we can t % use a regular matrix) c = getcurves(['e11555e.csv'], vgs); % Interpolation so curves and on a regular grid (x-axis) [m, vds, p] = interpcurves(c); cv = m(rwtest,:); % Get curve from family of curves on which to perform the fit. vgsv = p(rwtest); % Corresponding gate voltage % Loop to compute mean squared error for every iteration of test values % in parametric function for n=1:length(vto) % Loop through all threshold values for k=1:length(kp) % Loop through all KP values ids = nmos(vds,vgs(rwtest),kp(k),w,l,vto(n)); % Parametric curve err(n,k) = mean(abs(ids - cv).^); % mean square error with measured data end end
37 % Find point at which the minimum error occurred [mvtr, mkp] = find(min(min(err)) == err); kpmin = kp(mkp(1)); % Estimated kp values disp([ 'Estimated kp: ' numstr(kpmin) ]) vtrmin = vto(mvtr(1)); % Estimated threshold gate voltage disp([ 'Estimated threshold ' numstr(vtrmin) ]) % Plot best fit ids = nmos(vds,vgs(rwtest),kpmin,w,l,vtrmin); figure(1) plot(vds,ids,'g',vds,cv,'r') title(['compare MSE Curve to Data for Vgs = ' numstr(vgs(rwtest))]) xlabel('v_ds in Volts') ylabel('i_ds in Amps') figure() % Look at error surface imagesc(kp,vto,log10(err)) colormap(jet) ylabel('threshold Gate Voltage Values') xlabel('kp values') title('log of MSE Error surface') colorbar
38 Plot of Best-Fit with Error Surface Estimated kp: Estimated threshold 1.75 Volts i d s in Amps x 10-3 Compare MSE Curve to Data for Vgs =.096 Threshold Gate Voltage Values Log of MSE Error surface KP values V d s in Volts
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. 3. MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits 3. MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2 to
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005
 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Spring 2005 May 16, 2005 Final Exam (200 points) -OPEN BOOK- Problem NAME RECITATION TIME 1 2 3 4 5 Total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. The Devices. July 30, Devices.
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The July 30, 2002 1 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Devices July 30, 2002 Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification
 Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Chapter 13 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear Amplification Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 1/4/12 Chap 13-1 Chapter Goals Understanding of concepts related to: Transistors
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Digital Electronics Part II - Circuits
 Digital Electronics Part - Circuits Dr.. J. Wassell Gates from Transistors ntroduction Logic circuits are non-linear, consequently we will introduce a graphical technique for analysing such circuits The
Digital Electronics Part - Circuits Dr.. J. Wassell Gates from Transistors ntroduction Logic circuits are non-linear, consequently we will introduce a graphical technique for analysing such circuits The
The Devices. Jan M. Rabaey
 The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
The Devices Jan M. Rabaey Goal of this chapter Present intuitive understanding of device operation Introduction of basic device equations Introduction of models for manual analysis Introduction of models
MOS Transistor Theory
 CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
CHAPTER 3 MOS Transistor Theory Outline 2 1. Introduction 2. Ideal I-V Characteristics 3. Nonideal I-V Effects 4. C-V Characteristics 5. DC Transfer Characteristics 6. Switch-level RC Delay Models MOS
EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
EE105 - Fall 005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits ecture 7 MOS Transistor Announcements Homework 3, due today Homework 4 due next week ab this week Reading: Chapter 4 1 ecture Material ast lecture
Electronic Circuits 1. Transistor Devices. Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations. Prof. C.K. Tse: Transistor devices
 Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET:
 Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
Lecture 15: MOS Transistor models: Body effects, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the modes of operation of a MOS FET: oltage controlled resistor model I- curve (Square-Law Model)
EE105 Fall 2014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region
 EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
EE105 Fall 014 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Ming C. Wu wu@eecs.berkeley.edu 511 Sutardja Dai Hall (SDH) 1 NMOS Transistor Capacitances: Saturation Region Drain no longer connected to channel
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET )
 Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Device Models (PN Diode, MOSFET ) Instructor: Steven P. Levitan steve@ece.pitt.edu TA: Gayatri Mehta, José Martínez Book: Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective; Jan Rabaey Lab Notes: Handed
Lecture 28 Field-Effect Transistors
 Lecture 8 Field-Effect Transistors Field-Effect Transistors 1. Understand MOSFET operation.. Analyze basic FET amplifiers using the loadline technique. 3. Analyze bias circuits. 4. Use small-signal equialent
Lecture 8 Field-Effect Transistors Field-Effect Transistors 1. Understand MOSFET operation.. Analyze basic FET amplifiers using the loadline technique. 3. Analyze bias circuits. 4. Use small-signal equialent
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Lecture 5: CMOS Transistor Theory Slides courtesy of Deming Chen Slides based on the initial set from David Harris CMOS VLSI Design Outline q q q q q q q Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics
Fig. 1 CMOS Transistor Circuits (a) Inverter Out = NOT In, (b) NOR-gate C = NOT (A or B)
 1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
1 Introduction to Transistor-Level Logic Circuits 1 By Prawat Nagvajara At the transistor level of logic circuits, transistors operate as switches with the logic variables controlling the open or closed
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET
 ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
ECE 541/ME 541 Microelectronic Fabrication Techniques Lecture 04 Review of MOSFET Zheng Yang (ERF 3017, email: yangzhen@uic.edu) What is a Transistor? A Switch! An MOS Transistor V GS V T V GS S Ron D
Studio 3 Review MOSFET as current source Small V DS : Resistor (value controlled by V GS ) Large V DS : Current source (value controlled by V GS )
 Studio 3 Review MOSFET as current source Small V DS : Resistor (value controlled by V GS ) Large V DS : Current source (value controlled by V GS ) 1 Simulation Review: Circuit Fixed V GS, Sweep V DS I
Studio 3 Review MOSFET as current source Small V DS : Resistor (value controlled by V GS ) Large V DS : Current source (value controlled by V GS ) 1 Simulation Review: Circuit Fixed V GS, Sweep V DS I
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors. Context
 Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Model Extensions 300 Id 250 200 150 100 50 300 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 Vds Existing Model 250 200 Id 150 100 50 Slope is not 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 Actual Device Vds Model
Today s lecture. EE141- Spring 2003 Lecture 4. Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model
 - Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
- Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems
 Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Semiconductor Physics fall 2012 problems 1. An n-type sample of silicon has a uniform density N D = 10 16 atoms cm -3 of arsenic, and a p-type silicon sample has N A = 10 15 atoms cm -3 of boron. For each
Chapter7. FET Biasing
 Chapter7. J configurations Fixed biasing Self biasing & Common Gate Voltage divider MOS configurations Depletion-type Enhancement-type JFET: Fixed Biasing Example 7.1: As shown in the figure, it is the
Chapter7. J configurations Fixed biasing Self biasing & Common Gate Voltage divider MOS configurations Depletion-type Enhancement-type JFET: Fixed Biasing Example 7.1: As shown in the figure, it is the
At point G V = = = = = = RB B B. IN RB f
 Common Emitter At point G CE RC 0. 4 12 0. 4 116. I C RC 116. R 1k C 116. ma I IC 116. ma β 100 F 116µ A I R ( 116µ A)( 20kΩ) 2. 3 R + 2. 3 + 0. 7 30. IN R f Gain in Constant Current Region I I I C F
Common Emitter At point G CE RC 0. 4 12 0. 4 116. I C RC 116. R 1k C 116. ma I IC 116. ma β 100 F 116µ A I R ( 116µ A)( 20kΩ) 2. 3 R + 2. 3 + 0. 7 30. IN R f Gain in Constant Current Region I I I C F
Capacitors Diodes Transistors. PC200 Lectures. Terry Sturtevant. Wilfrid Laurier University. June 4, 2009
 Wilfrid Laurier University June 4, 2009 Capacitor an electronic device which consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulator Capacitor an electronic device which consists of two conductive
Wilfrid Laurier University June 4, 2009 Capacitor an electronic device which consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulator Capacitor an electronic device which consists of two conductive
Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors slamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices mpedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled
Chapter 6: Field-Effect Transistors slamic University of Gaza Dr. Talal Skaik FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices mpedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled
U1 is zero based because its noninverting terminal is connected to circuit common. Therefore, the circuit reference voltage is 0 V.
 When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to operate a zener-clamped op amp comparator circuit using dc and ac voltages. You will verify your results with an oscilloscope. U1 is zero based
When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to operate a zener-clamped op amp comparator circuit using dc and ac voltages. You will verify your results with an oscilloscope. U1 is zero based
ECE315 / ECE515 Lecture-2 Date:
 Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
Lecture-2 Date: 04.08.2016 NMOS I/V Characteristics Discussion on I/V Characteristics MOSFET Second Order Effect NMOS I-V Characteristics ECE315 / ECE515 Gradual Channel Approximation: Cut-off Linear/Triode
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 27. MOSFET Scaling and Velocity Saturation
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 27 MOSFET Scaling and Velocity Saturation Lecture Outline Industry push is always to pack more devices on a chip to increase functionality, which requires making
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 27 MOSFET Scaling and Velocity Saturation Lecture Outline Industry push is always to pack more devices on a chip to increase functionality, which requires making
Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor
 Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
Triode Working FET Fundamentals of the Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor The characteristics of energy bands as a function of applied voltage. Surface inversion. The expression for the
JFET Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14. JFET Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 15
 J Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14 V GS = 0 and V DS increases from 0 to a more positive voltage: Gate and Source terminals: at the same potential Drain: at positive potential => reverse biased
J Operating Characteristics: V GS = 0 V 14 V GS = 0 and V DS increases from 0 to a more positive voltage: Gate and Source terminals: at the same potential Drain: at positive potential => reverse biased
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 10 MOSFET part 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br ual-well Trench-Isolated
Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET
 ENE 311 Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices Impedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled devices. BJTs are current controlled devices.
ENE 311 Lecture 11: J-FET and MOSFET FETs vs. BJTs Similarities: Amplifiers Switching devices Impedance matching circuits Differences: FETs are voltage controlled devices. BJTs are current controlled devices.
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26. MOSFET Small Signal Modelling
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 26 MOSFET Small Signal Modelling Lecture Outline MOSFET small signal behavior will be considered in the same way as for the diode and BJT Capacitances will be considered
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
EE 330 Lecture 16. Devices in Semiconductor Processes. MOS Transistors
 EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
EE 330 Lecture 16 Devices in Semiconductor Processes MOS Transistors Review from Last Time Model Summary I D I V DS V S I B V BS = 0 0 VS VT W VDS ID = μcox VS VT VDS VS V VDS VS VT L T < W μc ( V V )
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies
 ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
ECE 497 JS Lecture - 12 Device Technologies Spring 2004 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jose@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 NMOS Transistor 2 ρ Source channel charge density
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI. Midterm Exam. Solutions
 P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
4.4 The MOSFET as an Amp and Switch
 10/31/004 section 4_4 The MSFET as an Amp and Switch blank 1/1 44 The MSFET as an Amp and Switch Reading Assignment: pp 70-80 Now we know how an enhancement MSFET works! Q: A: 1 H: The MSFET as an Amp
10/31/004 section 4_4 The MSFET as an Amp and Switch blank 1/1 44 The MSFET as an Amp and Switch Reading Assignment: pp 70-80 Now we know how an enhancement MSFET works! Q: A: 1 H: The MSFET as an Amp
Circuits. L2: MOS Models-2 (1 st Aug. 2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur. B. Mazhari, IITK. G-Number
 EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L: MOS Models- (1 st Aug. 013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 3 NMOS Models MOS MODEL Above Threshold Subthreshold ( GS > TN ) ( GS < TN ) Saturation ti Ti Triode ( DS >
Figure 1: MOSFET symbols.
 c Copyright 2008. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The MOSFET Device Symbols Whereas the JFET has a diode junction between
c Copyright 2008. W. Marshall Leach, Jr., Professor, Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The MOSFET Device Symbols Whereas the JFET has a diode junction between
! PN Junction. ! MOS Transistor Topology. ! Threshold. ! Operating Regions. " Resistive. " Saturation. " Subthreshold (next class)
 ESE370: ircuitlevel Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Lec 7: September 20, 2017 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1 Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold! Operating
ESE370: ircuitlevel Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Lec 7: September 20, 2017 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1 Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold! Operating
CHAPTER 3: TRANSISTOR MOSFET DR. PHAM NGUYEN THANH LOAN. Hà Nội, 9/24/2012
 1 CHAPTER 3: TRANSISTOR MOSFET DR. PHAM NGUYEN THANH LOAN Hà Nội, 9/24/2012 Chapter 3: MOSFET 2 Introduction Classifications JFET D-FET (Depletion MOS) MOSFET (Enhancement E-FET) DC biasing Small signal
1 CHAPTER 3: TRANSISTOR MOSFET DR. PHAM NGUYEN THANH LOAN Hà Nội, 9/24/2012 Chapter 3: MOSFET 2 Introduction Classifications JFET D-FET (Depletion MOS) MOSFET (Enhancement E-FET) DC biasing Small signal
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
1 Name: Student number: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Fall :00-11:00
 1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN
 ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN CMOS PROCESS CHARACTERIZATION VISHAL SAXENA VSAXENA@UIDAHO.EDU Vishal Saxena DESIGN PARAMETERS Analog circuit designers care about: Open-loop Gain: g m r o
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN CMOS PROCESS CHARACTERIZATION VISHAL SAXENA VSAXENA@UIDAHO.EDU Vishal Saxena DESIGN PARAMETERS Analog circuit designers care about: Open-loop Gain: g m r o
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23. The MOSFET Square Law Model
 ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
ELEC 3908, Physical Electronics, Lecture 23 The MOSFET Square Law Model Lecture Outline As with the diode and bipolar, have looked at basic structure of the MOSFET and now turn to derivation of a current
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation. Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation
 EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
EEC 118 Lecture #2: MOSFET Structure and Basic Operation Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Lab 1 this week, report due next week Bring
GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY School of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 NAME: GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY School of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 4430 First Exam Closed Book and Notes Fall 2002 September 27, 2002 General Instructions: 1. Write on one side of
NAME: GEORGIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY School of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 4430 First Exam Closed Book and Notes Fall 2002 September 27, 2002 General Instructions: 1. Write on one side of
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics. Lena Peterson
 Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Problem 9.20 Threshold bias for an n-channel MOSFET: In the text we used a criterion that the inversion of the MOSFET channel occurs when V s = ;2 F w
 Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 11 The nals for this course are set for Friday December 14, 6:30 8:30 pm and Friday Dec. 21, 10:30 am 12:30 pm. Please choose one of these times and inform
Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 11 The nals for this course are set for Friday December 14, 6:30 8:30 pm and Friday Dec. 21, 10:30 am 12:30 pm. Please choose one of these times and inform
EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY
 1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
1 EE 560 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY PART 1 TWO TERMINAL MOS STRUCTURE V G (GATE VOLTAGE) 2 GATE OXIDE SiO 2 SUBSTRATE p-type doped Si (N A = 10 15 to 10 16 cm -3 ) t ox V B (SUBSTRATE VOLTAGE) EQUILIBRIUM:
1. (50 points, BJT curves & equivalent) For the 2N3904 =(npn) and the 2N3906 =(pnp)
 HW 3 1. (50 points, BJT curves & equivalent) For the 2N3904 =(npn) and the 2N3906 =(pnp) a) Obtain in Spice the transistor curves given on the course web page except do in separate plots, one for the npn
HW 3 1. (50 points, BJT curves & equivalent) For the 2N3904 =(npn) and the 2N3906 =(pnp) a) Obtain in Spice the transistor curves given on the course web page except do in separate plots, one for the npn
The Devices: MOS Transistors
 The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
The Devices: MOS Transistors References: Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, R. F. Pierret, Addison-Wesley Digital Integrated Circuits: A Design Perspective, J. Rabaey et.al. Prentice Hall NMOS Transistor
Quantitative MOSFET. Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current.
 Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
Quantitative MOSFET Step 1. Connect the MOS capacitor results for the electron charge in the inversion layer Q N to the drain current. V DS _ n source polysilicon gate y = y * 0 x metal interconnect to
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Analog Electronics - I Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Analog Electronics - I Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Analog Electronics - I Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/90/101612294.jpg) . (a) S.E. Sem. [EXTC] Analog Electronics - Prelim Question Paper Solution Comparison between BJT and JFET BJT JFET ) BJT is a bipolar device, both majority JFET is an unipolar device, electron and minority
. (a) S.E. Sem. [EXTC] Analog Electronics - Prelim Question Paper Solution Comparison between BJT and JFET BJT JFET ) BJT is a bipolar device, both majority JFET is an unipolar device, electron and minority
MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations
 ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
ROMANIAN JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY Volume 10, Number 2, 2007, 189 197 MOSFET Model with Simple Extraction Procedures, Suitable for Sensitive Analog Simulations S. EFTIMIE 1, ALEX. RUSU
and V DS V GS V T (the saturation region) I DS = k 2 (V GS V T )2 (1+ V DS )
 ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes
 Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Final Examination EE 130 December 16, 1997 Time allotted: 180 minutes Problem 1: Semiconductor Fundamentals [30 points] A uniformly doped silicon sample of length 100µm and cross-sectional area 100µm 2
Class 05: Device Physics II
 Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Topics: 1. Introduction 2. NFET Model and Cross Section with Parasitics 3. NFET as a Capacitor 4. Capacitance vs. Voltage Curves 5. NFET as a Capacitor - Band Diagrams at V=0 6. NFET as a Capacitor - Accumulation
Practice 3: Semiconductors
 Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
Practice 3: Semiconductors Digital Electronic Circuits Semester A 2012 VLSI Fabrication Process VLSI Very Large Scale Integration The ability to fabricate many devices on a single substrate within a given
EE 230 Lecture 31. THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR
 EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
EE 23 Lecture 3 THE MOS TRANSISTOR Model Simplifcations THE Bipolar Junction TRANSISTOR Quiz 3 Determine I X. Assume W=u, L=2u, V T =V, uc OX = - 4 A/V 2, λ= And the number is? 3 8 5 2? 6 4 9 7 Quiz 3
Lecture #27. The Short Channel Effect (SCE)
 Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
Lecture #27 ANNOUNCEMENTS Design Project: Your BJT design should meet the performance specifications to within 10% at both 300K and 360K. ( β dc > 45, f T > 18 GHz, V A > 9 V and V punchthrough > 9 V )
EECS 141: FALL 05 MIDTERM 1
 University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences D. Markovic TuTh 11-1:3 Thursday, October 6, 6:3-8:pm EECS 141: FALL 5 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last SOLUTION
University of California College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences D. Markovic TuTh 11-1:3 Thursday, October 6, 6:3-8:pm EECS 141: FALL 5 MIDTERM 1 NAME Last SOLUTION
ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2015 April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
NAME: PUID: : ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 17, 2015 Mark Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam. You may use a calculator and the formula sheet at the end of this exam. Following the
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor
 Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. #05 Lecture No. #02 FETS and MOSFETS (contd.) In the previous lecture, we studied the working
Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. #05 Lecture No. #02 FETS and MOSFETS (contd.) In the previous lecture, we studied the working
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
EE 330 Lecture 17. MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow
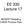 EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
EE 330 Lecture 17 MOSFET Modeling CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Lecture Limitations of Existing Models V DD V OUT V OUT V DD?? V IN V OUT V IN V IN V DD Switch-Level Models V DD Simple square-law
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7
 HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
HW 5 posted due in two weeks Lab this week Midterm graded Project to be launched in week 7 2 What do digital IC designers need to know? 5 EE4 EECS4 6 3 0< V GS - V T < V DS Pinch-off 7 For (V GS V T )
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 5: January 25, 2018 MOS Operating Regions, pt. 1 Lecture Outline! 3 Regions of operation for MOSFET " Subthreshold " Linear " Saturation!
Charge Storage in the MOS Structure. The Inverted MOS Capacitor (V GB > V Tn )
 The Inverted MO Capacitor (V > V Tn ) We consider the surface potential as Þxed (ÒpinnedÓ) at φ s,max = - φ p φ(x).5 V. V V ox Charge torage in the MO tructure Three regions of operation: Accumulation:
The Inverted MO Capacitor (V > V Tn ) We consider the surface potential as Þxed (ÒpinnedÓ) at φ s,max = - φ p φ(x).5 V. V V ox Charge torage in the MO tructure Three regions of operation: Accumulation:
The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET:
 6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
6.01 - Electronic Devices and Circuits Fall 003 The Gradual Channel Approximation for the MOSFET: We are modeling the terminal characteristics of a MOSFET and thus want i D (v DS, v GS, v BS ), i B (v
DC and Transient Responses (i.e. delay) (some comments on power too!)
 DC and Transient Responses (i.e. delay) (some comments on power too!) Michael Niemier (Some slides based on lecture notes by David Harris) 1 Lecture 02 - CMOS Transistor Theory & the Effects of Scaling
DC and Transient Responses (i.e. delay) (some comments on power too!) Michael Niemier (Some slides based on lecture notes by David Harris) 1 Lecture 02 - CMOS Transistor Theory & the Effects of Scaling
Digital Electronics Part II Electronics, Devices and Circuits
 Digital Electronics Part Electronics, Devices and Circuits Dr.. J. Wassell ntroduction n the coming lectures we will consider how logic gates can be built using electronic circuits First, basic concepts
Digital Electronics Part Electronics, Devices and Circuits Dr.. J. Wassell ntroduction n the coming lectures we will consider how logic gates can be built using electronic circuits First, basic concepts
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. Some Administrative Issues
 EE105 - Fall 006 Microelectronic evices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs Lecture 8: MOS Small Signal Model Some Administrative Issues REIEW Session Next Week Tu Sept 6 6:00-7:30pm; 060 alley
EE105 - Fall 006 Microelectronic evices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs Lecture 8: MOS Small Signal Model Some Administrative Issues REIEW Session Next Week Tu Sept 6 6:00-7:30pm; 060 alley
Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs
 EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
Lecture 310 Open-Loop Comparators (3/28/10) Page 310-1
 Lecture 310 Open-Loop Comparators (3/28/10) Page 310-1 LECTURE 310 OPEN-LOOP COMPARATORS LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Characterization of comparators Dominant pole, open-loop comparators Two-pole, open-loop
Lecture 310 Open-Loop Comparators (3/28/10) Page 310-1 LECTURE 310 OPEN-LOOP COMPARATORS LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Characterization of comparators Dominant pole, open-loop comparators Two-pole, open-loop
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues
 Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Nanoscale CMOS Design Issues Jaydeep P. Kulkarni Assistant Professor, ECE Department The University of Texas at Austin jaydeep@austin.utexas.edu Fall, 2017, VLSI-1 Class Transistor I-V Review Agenda Non-ideal
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.)
 Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
Lecture 9 MOSFET(II) MOSFET I V CHARACTERISTICS(contd.) Outline 1. The saturation region 2. Backgate characteristics Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 4, Section 4.4 6.012 Spring 2009 Lecture
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam
 Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Spring Semester 2012 Final Exam Note: Show your work, underline results, and always show units. Official exam time: 2.0 hours; an extension of at least 1.0 hour will be granted to anyone. Materials parameters
Review of Band Energy Diagrams MIS & MOS Capacitor MOS TRANSISTORS MOSFET Capacitances MOSFET Static Model
 Content- MOS Devices and Switching Circuits Review of Band Energy Diagrams MIS & MOS Capacitor MOS TRANSISTORS MOSFET Capacitances MOSFET Static Model A Cantoni 2009-2013 Digital Switching 1 Content- MOS
Content- MOS Devices and Switching Circuits Review of Band Energy Diagrams MIS & MOS Capacitor MOS TRANSISTORS MOSFET Capacitances MOSFET Static Model A Cantoni 2009-2013 Digital Switching 1 Content- MOS
ECE 546 Lecture 11 MOS Amplifiers
 ECE 546 Lecture MOS Amplifiers Spring 208 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 546 Jose Schutt Aine Amplifiers Definitions Used to increase
ECE 546 Lecture MOS Amplifiers Spring 208 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu ECE 546 Jose Schutt Aine Amplifiers Definitions Used to increase
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME
 ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
ELECTRONICS IA 2017 SCHEME CONTENTS 1 [ 5 marks ]...4 2...5 a. [ 2 marks ]...5 b. [ 2 marks ]...5 c. [ 5 marks ]...5 d. [ 2 marks ]...5 3...6 a. [ 3 marks ]...6 b. [ 3 marks ]...6 4 [ 7 marks ]...7 5...8
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015
 Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
Semiconductor Physics Problems 2015 Page and figure numbers refer to Semiconductor Devices Physics and Technology, 3rd edition, by SM Sze and M-K Lee 1. The purest semiconductor crystals it is possible
