Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation.
|
|
|
- Mercy Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ship Hydrodynamics, Ship Propeller Acoustics and Cavitation. Content Introduction The Cavitation Tunnel The Depressurized Towing Tank... 4 Cavitation and Cavitation Inception Design and testing of marine propellers Special topics Literature Introduction. Before a new built ship is transferred to the operator test trials will be run at high sea to find out whether or not the new ship complies with the specifications. For example: verify the contracted speed power by speed trials. One of the important issues is cavitation on the propulsion system: the ship propeller. Cavitation cannot always be prevented so you want to control it by design. The designer and shipbuilder have made predictions of the type and amount of cavitation. This is usually tested at model scale in a testing facility like MARIN( At the end of the day the type and intensity of cavitation has to be tested at high sea in order to find out whether or not reality is within the margin of the allowable predictions. Below some videos are shown of so-called high sea testing. The videos are recorded from a view through a window in the stern of the top of the propeller. Vortex cavitation is shown. Click on the link: Part of the rudder is shown. A view from aside can be seen by clicking on the link: Cavitation observation such as shown in these videos are conducted already for several decades. These observations are essential to find out about noise and dynamic pressures produced by the cavitating propeller and whether or not a particular type of cavitation creates erosion of the propeller. By the way, nowadays to make observations windows in the stern are no longer necessary. By means of a small hole in the hull the observations can be made. 1
2 First and for all a model of the propeller is tested on laboratory scale. This can be done in a so-called cavitation tunnel and/ or a depressurized towing tank. The Cavitation Tunnel. Let us take a closer look at cavitation. Cavitation can be categorized schematically into: - Sheet cavitation; - Bubble cavitation and - Vortex cavitation. Here a typical example of sheet cavitation is shown. The model propeller shown is specially designed for this type of cavitation. 2
3 This model propeller shows bubble cavitation. The above model propeller displays vortex cavitation. No examples of supercavitating are shown here. With supercavitating the sheet cavity on the propeller blade stretches in chord wise direction beyond the trailing edge of the propeller blade. 3
4 Research in testing facilities is aimed to design a propeller showing allowable cavitation on full scale. In order to conduct test in a meaningful way test has to be done under full scale conditions. This condition can only partially be fulfilled. I come to that later on. In the old days model test where don in the open air. Than the conditions to test cavitation are not correctly scaled. To this end a cavitation tunnel is used. In the above picture a cavitation tunnel is shown. This is a closed circuit in which the water flow and pressure can be varied. These type of facility has created a considerable insight in cavitation erosion. Through clicking on the link below some observations in a cavitation tunnel are show: In this video a cavitating hydrofoil and two cavitating model propellers are subsequently shown. Cavitation inception research is extensively reported in Kuiper(1981, 2012). The Depressurized Towing Tank. However, it is not just erosion. What has also to be tested are the vibrations induced on the ship s hull by the dynamic behaviour of cavitation. To this end a Depressurized Towing Tank has been developed in the Netherlands by MARIN. The tank is schematically shown below: 4
5 The ship model is displayed below the red structure. Model with a length of 12 meters can be tested. The width of the tank is 18 meters, the length is about 240 meters and the height is 8 meters. The pressure can be lowered by a factor of 40. To give you an idea about the size an outside picture is shown below. 5
6 In this testing facility a completely scaled model can be tested the cavitating propeller included. A video of the propeller can be observed by clicking on the link: The recording has been made from inside the ship model. However not all the hydrodynamical scale rules are complied with. This was one of the reasons to construct a testing facility as the Depressurized Towing Tank shown above. With such a facility there is compliance with two hydrodynamical parameters: the Froude number and the cavitation index. In this way predictions for prototype flow, i.e. full scale, have been improved. However, Reynolds number similarity is not obtained. Nevertheless, experienced testers are able to predict rather accurately on basis of the test results the performance of the ship in full scale. This is supported by a lot of data created with full scale testing and trials. 6
7 Cavitation and Cavitation Inception. Cavitation basically is a non-stationary process. Consequently inception of cavitation is a subject of great importance to propeller design. In Kuiper(1981) a broad overview is presented. Inception is strongly influenced by nuclei, e.g., tiny gas bubbles and/or particulate matter. In Noordzij and Cruijff a brief overview on nuclei and nuclei measurement is presented. As mentioned, nuclei can influence cavitation inception. This is important in a circulating water tunnel(bernd, 1973) as well as in experiments without moving water(noordzij 1976). In the latter experiments use have been made of additional seeding of tiny gas bubbles by means of electrolysis. The above results are promising. As indicated in the legenda, the stabilizing effect of additional bubbles is clearly demonstrated. Consequently you want to know the size and number of nuclei. Keller(1973) developed an 7
8 optical technique for determining the nuclei spectra. Like Bernd, Keller concluded the number and size of the nuclei in water are dependent on the history of the particular water and on its content of contaminating particles. Keller concluded cavitation inception to be strongly affected by the nuclei content. This is of particular interest when a critical level for inception of a nuclei spectrum under proto type circumstances could be indicated. Then the critical level for testing facilities can be calculated and set. Since knowing the critical proto type spectrum a critical level for model testing can be meaningfully hypothesised. What could such a hypothesis look like? The hypothesis is: to obtain equal cavitation inception susceptibility for both proto type(full scale) as well as laboratory flow the encounter frequency with nuclei has to be the same for both types of flow. (Nota bene: Kuiper mentioned encounter frequency in Cavitation in Ship Propulsion. Kuiper dealt basically with dynamics of the cavitation nucleus: a tiny gasbubble). This will result in an expression for the number density of the nuclei, be it particulate or tiny bubbles, as a function of the scaling parameter λ. Let the number density, i.e. the number of nuclei per m 3 say, to be n. A typical distance for the nuclei is: Λ = n 1/3. (1) Then, a so-called encounter frequency for the propeller and the nuclei can be defined as V Λ, (2) where V is a typical velocity for the propeller, ωd/2 say. Here ω is the angular frequency and D the diameter of the propeller. Now let us define the dimensionless frequency No = V ωλ. (3) Then the basic assumption is this number No to be a constant. So : ( V ωλ ) m = ( V ωλ ) fs, (4) where subscripts m, fs denote model and full scale respectively. Usually for model testing Froude number is a constant. With model scale D m = 1, where D is D fs λ typical length scale, the diameter of the propeller say. We rewrite (4) : ( VD ) ωdλ m = ( VD ) ωdλ fs. (5) Since we keep the Froude number to be constant we have: V m = (ωd) m = λ 1/2. Plugging V fs (ωd) fs (1), and the Froude scaling into (5) we obtain: n m = λ 3 n fs. (6) So this No number is telling us the nuclei density in laboratory testing need to be much larger than in prototype flow. Design and testing of marine propellers. Geopolitics plays a special role in the world of marine propellers. Navy surface vessels have been surveyed by submarines for more than 100 years. Nowadays(2016) submarines play an ever increasing role in see bound strategies of the superpowers. Detecting submarines is an ever interesting issue. Detecting submarines has been done sensors measuring the noise produced by the submarines. Noise created on-board by the diesel-electric powering system and noise created out-board by the flow around the submarine. One of the main sources of this flow 8
9 noise is created by the propeller. We will focus on the hydrodynamics of the propeller. A non-cavitating propeller creates noise generated by the turbulent flow around the propeller. This noise is amplified when the propeller starts to cavitate. In the fore going sections various typed of cavitation are shown. Every type has its particular acoustic fingerprint. Consequently propeller design is a major tool in reducing noise produced by the propeller (Noordzij, et al). As mentioned before, to optimize a propeller design testing on a certain model scale and CFD are important tools. To make meaningful predictions with help of model scale testing there are certain conditions for such a testing facility. Two testing facilities are mentioned in the fore going sections. In Noordzij and Van der Kooij some ideas have been discussed based on the far field acoustics of a cavitating propeller. Special topics. In The Economist section on Science and Technology(January 21 st 2017) a particular example of supercavitating is discussed. It is about a submerged weapon: a kind of torpedo. Super cavitation is taken advantage of in order. Due to supercavtation the torpedo has a very low hydrodynamic drag. Literature. Bernd, L. H., Gas Nuclei, Surface Films and Turbulent Dissolving as Related to Cavitation Inception, Proceedings, IUTAM Symposium Non-Steady Flow of Water at High Speeds Leningrad 1971, (ed. L.I. Sedov and G. Y. Stepanov), Moskow, Nauka, Keller, A. p., The Influence of the Cavitation Nuclei Spectrum on Cavitation Inception. Investigated with a scattered light counting method. Proceedings, IUTAM Symposium Non- Steady Flow of Water at High Speeds Leningrad 1971, (ed. L.I. Sedov and G. Y. Stepanov), Moskow, Nauka, Kuiper, G., Cavitation Inception On Ship Propeller Models, Veenman, Kuiper, G., Physics of Cavitation: Cavitation Inception. Cavitation in ship propulsion, Noordzij, L., Some Experiments on Cavitation Inception with Propellers in the NSMB- Depressurized Towing Tank, Journal of International Shipbuilding Progress, Vol. 23, Noordzij, L., Cruijff, H. J., Introductory nuclei spectra measurements in the NMSB- Depressurized Towing Tank, Journal of International Shipbuilding Progress, Vol. 25, Noordzij, L., Van Oossanen, P. and A. M. Stuurman, Radiated Noise of Cavitating Propellers, Proceedings, Symposium on Noise and Fluid Engineering, ASME Winter Annual Meeting, Atlanta, Georgia, Dec Noordzij, L., Van der Kooij, J., Hydro- Acoustics of a Cavitating Screw Propeller; Far-Field Approximations, Journal of Ship Research, Vol. 25, June 1981, pp The Economist, Science and Technology, Torpedo Junction, January 21 st
10 10
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN
 ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
Flow Induced Noise Generation By Partial Cavities
 Flow Induced Noise Generation By Partial Cavities Harish Ganesh, Juliana Wu and Steven L. Ceccio University of Michigan, Ann Arbor USA 2nd FLINOVIA Symposium Penn-State University, State College, PA Sponsor:
Flow Induced Noise Generation By Partial Cavities Harish Ganesh, Juliana Wu and Steven L. Ceccio University of Michigan, Ann Arbor USA 2nd FLINOVIA Symposium Penn-State University, State College, PA Sponsor:
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Facilities: CHL (Computational Hydrodynamics Laboratory) in ECJ 8.502
 Ocean Engineering Group (OEG)/EWRE (August 28, 2018) Spyros A. Kinnas Professor and Director of OTRC s UT Office (Offshore Technology Research Center) Kinnas Home Page @SpyrosKinnas on twitter Research
Ocean Engineering Group (OEG)/EWRE (August 28, 2018) Spyros A. Kinnas Professor and Director of OTRC s UT Office (Offshore Technology Research Center) Kinnas Home Page @SpyrosKinnas on twitter Research
Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of a Wake Equalizing Duct
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
HIGH PEFORMANCE FOIL SECTIONS WITH DELAYED CAVITATION INCEPTION
 Proceedings of the 3rd ASME/JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference July 8-22, 999, San Francisco, California, FEDSM99-7294 HIGH PEFORMANCE FOIL SECTIONS WITH DELAYED CAVITATION INCEPTION Hajime Yamaguchi
Proceedings of the 3rd ASME/JSME Joint Fluids Engineering Conference July 8-22, 999, San Francisco, California, FEDSM99-7294 HIGH PEFORMANCE FOIL SECTIONS WITH DELAYED CAVITATION INCEPTION Hajime Yamaguchi
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
 Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Model-Ship Correlation Method in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank By Kaname Taniguchi*, Member Summary The model-ship correlation method which is developed and used in the Mitsubishi Experimental Tank
Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 211 Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings Daniele
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 211 Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings Daniele
A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using CFD
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
CAVITATION NUCLEI POPULATION DYNAMICS IN A WATER TUNNEL
 FED-Vol. 153, Cavitation and Multiphase Flow ASME 1993 CAVITATION NUCLEI POPULATION DYNAMICS IN A WATER TUNNEL Zkenhuan Liu, Kotaro ~ato,? and Christopher E. Brennen California Institute of Technology
FED-Vol. 153, Cavitation and Multiphase Flow ASME 1993 CAVITATION NUCLEI POPULATION DYNAMICS IN A WATER TUNNEL Zkenhuan Liu, Kotaro ~ato,? and Christopher E. Brennen California Institute of Technology
EXCITATION OF A SUBMARINE HULL BY PROPELLER FORCES. Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia 2 Senior Visiting Research Fellow, University of New South Wales
 ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 27 EXCITATION OF A SUBMARINE HULL BY PROPELLER FORCES Sascha Merz 1, Nicole Kessissoglou 1 and Roger Kinns 2 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University
ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 27 EXCITATION OF A SUBMARINE HULL BY PROPELLER FORCES Sascha Merz 1, Nicole Kessissoglou 1 and Roger Kinns 2 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University
CAV2001:sessionA Shridhar Gopalan and Joseph Katz The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore MD
 CAV2001:sessionA6.004 1 Tip Leakage Cavitation, Associated Bubble ynamics, Noise, Flow Structure and Effect of Tip Gap Size Shridhar Gopalan and Joseph Katz The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore M Han
CAV2001:sessionA6.004 1 Tip Leakage Cavitation, Associated Bubble ynamics, Noise, Flow Structure and Effect of Tip Gap Size Shridhar Gopalan and Joseph Katz The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore M Han
Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships
 (August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
(August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
Yiran Su 1, Seungnam Kim 1, Weikang Du 1, Spyros A. Kinnas 2, Mikael Grekula 3, Jan Hallander 3, Da- Qing Li 3
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Prediction of the Propeller-induced Hull Pressure Fluctuation via a Potential-based Method: Study of the Rudder Effect
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Prediction of the Propeller-induced Hull Pressure Fluctuation via a Potential-based Method: Study of the Rudder Effect
Cavitation Control on Hydrofoils
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 181 Cavitation Control on Hydrofoils Mohammad Mortezazadeh, Ali Katal, Khodayar
Proceedings of the International Conference on Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow Prague, Czech Republic, August 11-12, 2014 Paper No. 181 Cavitation Control on Hydrofoils Mohammad Mortezazadeh, Ali Katal, Khodayar
THE RELATION BETWEEN THE NUCLEI POPULATION AND THE CAVITATION EVENT RATE FOR CAVITATION ON A SCHIEBE BODY
 THE RELATION BETWEEN THE NUCLEI POPULATION AND THE CAVITATION EVENT RATE FOR CAVITATION ON A SCHIEBE BODY FED-Val. 190, Cavitation and Gas-Liquid Flow in Fluid Machinery and Devices ASME 1994 Zhenhuan
THE RELATION BETWEEN THE NUCLEI POPULATION AND THE CAVITATION EVENT RATE FOR CAVITATION ON A SCHIEBE BODY FED-Val. 190, Cavitation and Gas-Liquid Flow in Fluid Machinery and Devices ASME 1994 Zhenhuan
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
Dynamic Analysis of Composite Propeller of Ship Using FEA
 ISSN 232 339, Vol. 2, No. 5, September 23, pp. 5 Dynamic Analysis of Composite Propeller of Ship Using FEA V.D.RAJESWARI.SWARNA, G.BALAKRISHNA 2 P.G Student, Mechanical Department, PVPSIT, Vijayawada,
ISSN 232 339, Vol. 2, No. 5, September 23, pp. 5 Dynamic Analysis of Composite Propeller of Ship Using FEA V.D.RAJESWARI.SWARNA, G.BALAKRISHNA 2 P.G Student, Mechanical Department, PVPSIT, Vijayawada,
Numerical Simulation of Underwater Propeller Noise
 Numerical Simulation of Underwater Propeller Noise Bagheri M.R, a*, Seif M.S, a and Mehdigholi H, a a) Sharif University of Technology, Center of Excellence in Hydrodynamic and Dynamic of Marine Vehicles,
Numerical Simulation of Underwater Propeller Noise Bagheri M.R, a*, Seif M.S, a and Mehdigholi H, a a) Sharif University of Technology, Center of Excellence in Hydrodynamic and Dynamic of Marine Vehicles,
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 4: 2017
 Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes.
 13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #2 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
13.012 Marine Hydrodynamics for Ocean Engineers Fall 2004 Quiz #2 Student name: This is a closed book examination. You are allowed 1 sheet of 8.5 x 11 paper with notes. For the problems in Section A, fill
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 5: A dimensional analysis of propeller thrust starting with the functional expression
 ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
Scaling of Tip Vortex Cavitation Inception for a Marine Open Propeller
 27 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Seoul, Korea, 5-10 October 2008 Scaling of Tip Vortex Cavitation Inception for a Marine Open Propeller C.-T. Hsiao and G. L. Chahine (DYNAFLOW, INC., USA) ABSTRACT
27 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Seoul, Korea, 5-10 October 2008 Scaling of Tip Vortex Cavitation Inception for a Marine Open Propeller C.-T. Hsiao and G. L. Chahine (DYNAFLOW, INC., USA) ABSTRACT
Cavitation Inception and Dynamics in Vortical Flows
 Cavitation Inception and Dynamics in Vortical Flows Steve L. Ceccio Mechanical Engineering Naval Architecture & Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, 48109 American Physical Society
Cavitation Inception and Dynamics in Vortical Flows Steve L. Ceccio Mechanical Engineering Naval Architecture & Marine Engineering University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, 48109 American Physical Society
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power
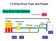 7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Hydro-Structure Analysis of Composite Marine Propeller under Pressure Hydrodynamic Loading
 American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers in Fully Wetted and Cavitating Flows
 Proceedings of the 7 th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV2009 Paper No. 60 August 17-22, 2009, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers
Proceedings of the 7 th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV2009 Paper No. 60 August 17-22, 2009, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers
Numerical study of the effects of trailing-edge bluntness on highly turbulent hydro-foil flows
 Numerical study of the effects of trailing-edge bluntness on highly turbulent hydro-foil flows T. Do L. Chen J. Tu B. Anderson 7 November 2005 Abstract Flow-induced noise from fully submerged lifting bodies
Numerical study of the effects of trailing-edge bluntness on highly turbulent hydro-foil flows T. Do L. Chen J. Tu B. Anderson 7 November 2005 Abstract Flow-induced noise from fully submerged lifting bodies
COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF PROPELLER SHEET CAVITATION AND PROPELLER-SHIP INTERACTION
 RINA conference MARINE CFD2008, 26-27 March 2008, Southampton, UK. COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF PROPELLER SHEET CAVITATION AND PROPELLER-SHIP INTERACTION J. Bosschers, G. Vaz, A.R. Starke, E. van Wijngaarden
RINA conference MARINE CFD2008, 26-27 March 2008, Southampton, UK. COMPUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF PROPELLER SHEET CAVITATION AND PROPELLER-SHIP INTERACTION J. Bosschers, G. Vaz, A.R. Starke, E. van Wijngaarden
Numerical modeling of rudder sheet cavitation including propeller/rudder interaction and the effects of a tunnel
 Numerical modeling of rudder sheet cavitation including propeller/rudder interaction and the effects of a tunnel Hanseong Lee Ocean Engineering Group The University of Texas at Austin, USA hslee@mail.utexas.edu
Numerical modeling of rudder sheet cavitation including propeller/rudder interaction and the effects of a tunnel Hanseong Lee Ocean Engineering Group The University of Texas at Austin, USA hslee@mail.utexas.edu
On the effect of elastic nonlinearity on aquatic propulsion caused by propagating flexural waves
 On the effect of elastic nonlinearity on aquatic propulsion caused by propagating flexural waves V.V. Krylov Department of Aeronautical and Automotive Engineering, Loughborough University, Loughborough,
On the effect of elastic nonlinearity on aquatic propulsion caused by propagating flexural waves V.V. Krylov Department of Aeronautical and Automotive Engineering, Loughborough University, Loughborough,
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method
 Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry To cite this article: L Crudu et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry To cite this article: L Crudu et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Testing and Extrapolation Methods Propulsion, Performance Propulsion Test
 7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder
 A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
A New Implementation of Vortex Lattice Method Applied to the Hydrodynamic Performance of the Propeller-Rudder Hassan Ghassemi, a,* and Farzam Allafchi, a a ) Department of Ocean Engineering, Amirkabir
Vibration Generations Mechanisms: Flow Induced
 Vibration Generations Mechanisms: Flow Induced Introduction That sound and vibration generation and flow are correlated is apparent from a range of phenomena that we can observe around us. A noteworthy
Vibration Generations Mechanisms: Flow Induced Introduction That sound and vibration generation and flow are correlated is apparent from a range of phenomena that we can observe around us. A noteworthy
 CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
CE 6303 MECHANICS OF FLUIDS L T P C QUESTION BANK 3 0 0 3 UNIT I FLUID PROPERTIES AND FLUID STATICS PART - A 1. Define fluid and fluid mechanics. 2. Define real and ideal fluids. 3. Define mass density
CAVITATION SCALE EFFECTS EMPIRICALLY FOUND RELATIONS AND THE CORRELATION OF CAVITATION NUMBER AND HYDRODYNAMIC COEFFICIENTS
 CAV00:lecture.00 CAVITATION SCALE EFFECTS EMPIRICALLY FOUND RELATIONS AND THE CORRELATION OF CAVITATION NUMBER AND HYDRODYNAMIC COEFFICIENTS Andreas P. Keller Institute of Hydraulic and Water Resources
CAV00:lecture.00 CAVITATION SCALE EFFECTS EMPIRICALLY FOUND RELATIONS AND THE CORRELATION OF CAVITATION NUMBER AND HYDRODYNAMIC COEFFICIENTS Andreas P. Keller Institute of Hydraulic and Water Resources
Teaching sessions week 40
 Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Study of the influence of the resonance changer on the longitudinal vibration of marine propulsion shafting system
 Study of the influence of the resonance changer on the longitudinal vibration of marine propulsion shafting system Zhengmin Li 1, Lin He 2, Hanguo Cui 3, Jiangyang He 4, Wei Xu 5 1, 2, 4, 5 Institute of
Study of the influence of the resonance changer on the longitudinal vibration of marine propulsion shafting system Zhengmin Li 1, Lin He 2, Hanguo Cui 3, Jiangyang He 4, Wei Xu 5 1, 2, 4, 5 Institute of
Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres
 Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres J. Artyszuk Maritime University of Szczecin, Poland Abstract A relatively small amount of data concerning the behaviour of propulsion coefficients,
Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres J. Artyszuk Maritime University of Szczecin, Poland Abstract A relatively small amount of data concerning the behaviour of propulsion coefficients,
Cavitations Analysis on Impeller Blades of Thai-made Irrigation Pump by Computational Fluid Dynamic technique
 Cavitations Analysis on Impeller Blades of Thai-made Irrigation Pump by Computational Fluid Dynamic technique Benya Kasantikul 1 and Santi Laksitanonta 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty
Cavitations Analysis on Impeller Blades of Thai-made Irrigation Pump by Computational Fluid Dynamic technique Benya Kasantikul 1 and Santi Laksitanonta 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty
On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PERFORMANCE OF KAPLAN TURBINE WITH DRAFT TUBE
 NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PERFORMANCE OF KAPLAN TURBINE WITH DRAFT TUBE Mohamed Adel and Nabil H. Mostafa ABSTRACT Mechanical Power Engineering Department, Engineering Faculty Zagazig University, Zagazig,
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF PERFORMANCE OF KAPLAN TURBINE WITH DRAFT TUBE Mohamed Adel and Nabil H. Mostafa ABSTRACT Mechanical Power Engineering Department, Engineering Faculty Zagazig University, Zagazig,
STUDY ON TIP LEAKAGE VORTEX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRESS TRANSPORT k-ω TURBULENCE MODEL
 THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 213, Vol. 17, No. 5, pp. 1551-1555 1551 STUDY ON TIP AKAGE VORX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRE TRANSPORT k-ω TURBUNCE MODEL Introduction by Desheng ZHANG *, Dazhi
THERMAL SCIENCE, Year 213, Vol. 17, No. 5, pp. 1551-1555 1551 STUDY ON TIP AKAGE VORX IN AN AXIAL FLOW PUMP BASED ON MODIFIED SHEAR STRE TRANSPORT k-ω TURBUNCE MODEL Introduction by Desheng ZHANG *, Dazhi
SURGE INSTABILITY ON A CAVITATING PROPELLER
 CAV2001:sessionB8.003 1 SURGE INSTABILITY ON A CAVITATING PROPELLER Mark E. Duttweiler 1 and Christopher E. Brennen California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125 Abstract This study details experiments
CAV2001:sessionB8.003 1 SURGE INSTABILITY ON A CAVITATING PROPELLER Mark E. Duttweiler 1 and Christopher E. Brennen California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125 Abstract This study details experiments
Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects
 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 19 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects So far, we have assumed a hydraulically smooth surface. In practice,
2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics, Spring 2005 Lecture 19 2.20 - Marine Hydrodynamics Lecture 19 Turbulent Boundary Layers: Roughness Effects So far, we have assumed a hydraulically smooth surface. In practice,
Studies on the Transition of the Flow Oscillations over an Axisymmetric Open Cavity Model
 Advances in Aerospace Science and Applications. ISSN 2277-3223 Volume 3, Number 2 (2013), pp. 83-90 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aasa.htm Studies on the Transition of the Flow
Advances in Aerospace Science and Applications. ISSN 2277-3223 Volume 3, Number 2 (2013), pp. 83-90 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/aasa.htm Studies on the Transition of the Flow
Two medium size cavitation tunnel hydro-acoustic benchmark experiment comparisons as part of a round robin test campaign
 Two medium size cavitation tunnel hydro-acoustic benchmark experiment comparisons as part of a round robin test campaign Giorgio Tani 1, Batuhan Aktas 2,*, Michele Viviani 1, Mehmet Atlar 2 1 Department
Two medium size cavitation tunnel hydro-acoustic benchmark experiment comparisons as part of a round robin test campaign Giorgio Tani 1, Batuhan Aktas 2,*, Michele Viviani 1, Mehmet Atlar 2 1 Department
Fluid Mechanics II 3 credit hour. External flows. Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1
 COURSE NUMBER: ME 323 Fluid Mechanics II 3 credit hour External flows Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 External flows The study of external
COURSE NUMBER: ME 323 Fluid Mechanics II 3 credit hour External flows Course teacher Dr. M. Mahbubur Razzaque Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering BUET 1 External flows The study of external
Full scale thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks
 070131-071 1 Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks Paulo Triunfante Martins 1, Victor Lobo 2, Member, IEEE Maneuvering and seakeeping are two very important naval architecture
070131-071 1 Estimating Maneuvering and Seakeeping Characteristics with Neural Networks Paulo Triunfante Martins 1, Victor Lobo 2, Member, IEEE Maneuvering and seakeeping are two very important naval architecture
Background and Motivation
 Background and Motivation Cavitation has been investigated in a variety of flows: Tip vortices, e.g., Arndt et al. (1991), Arndt and Maines (2000), Hsiao et al. (2003). Lifting and curved surfaces, e.g.,
Background and Motivation Cavitation has been investigated in a variety of flows: Tip vortices, e.g., Arndt et al. (1991), Arndt and Maines (2000), Hsiao et al. (2003). Lifting and curved surfaces, e.g.,
High Reynolds number experimentation in the US Navy s William B Morgan Large Cavitation Channel
 INSTITUTE OFPHYSICS PUBLISHING Meas. Sci. Technol. 16 (2005) 1701 1709 MEASUREMENTSCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY doi:10.1088/0957-0233/16/9/001 High Reynolds number experimentation in the US Navy s William B Morgan
INSTITUTE OFPHYSICS PUBLISHING Meas. Sci. Technol. 16 (2005) 1701 1709 MEASUREMENTSCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY doi:10.1088/0957-0233/16/9/001 High Reynolds number experimentation in the US Navy s William B Morgan
Motions and Resistance of a Ship in Regular Following Waves
 Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
Reprinted: 01-11-2000 Revised: 03-10-2007 Website: www.shipmotions.nl Report 440, September 1976, Delft University of Technology, Ship Hydromechanics Laboratory, Mekelweg 2, 2628 CD Delft, The Netherlands.
5 SIMILITUDE. 5.1 Use of Nondimensional Groups
 5 SIMIITDE 5. se of Nondimensional Groups For a consistent description of physical processes, we require that all terms in an equation must have the same units. On the basis of physical laws, some quantities
5 SIMIITDE 5. se of Nondimensional Groups For a consistent description of physical processes, we require that all terms in an equation must have the same units. On the basis of physical laws, some quantities
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Flow-Induced Noise of a Wall Mounted Airfoil
 Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Flow-Induced Noise of a Wall Mounted Airfoil Paul Croaker, Danielle Moreau, Manuj Awasthi, Mahmoud Karimi, Con Doolan, Nicole Kessissoglou School of Mechanical
Numerical and Experimental Investigation of the Flow-Induced Noise of a Wall Mounted Airfoil Paul Croaker, Danielle Moreau, Manuj Awasthi, Mahmoud Karimi, Con Doolan, Nicole Kessissoglou School of Mechanical
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve
 Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Self-Excited Vibration in Hydraulic Ball Check Valve L. Grinis, V. Haslavsky, U. Tzadka Abstract This paper describes an experimental, theoretical model and numerical study of concentrated vortex flow
Performance Assessment of the Waterjet Propulsion System through a Combined Analytical and Numerical Approach
 International Journal of Physics, 013, Vol. 1, No., -7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/1//1 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijp-1--1 Performance Assessment of the Waterjet
International Journal of Physics, 013, Vol. 1, No., -7 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ijp/1//1 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.1691/ijp-1--1 Performance Assessment of the Waterjet
Computation of the wavemaking resistance of a Harley surface effect ship
 Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
Proceedings of the Sixteenth Seventeenth (2007) (2007) International Offshore and and Polar Polar Engineering Conference Lisbon, Portugal, July 1-6, 2007 Copyright 2007 by The International Society of
PMarine Technology Society
 ddynamic Positioning Committee PMarine Technology Society DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 1999 DESIGN SESSION Thruster Noise Neal A. Brown NAB & Associates, Inc. & Offshore Model Basin INTRODUCTION
ddynamic Positioning Committee PMarine Technology Society DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 1999 DESIGN SESSION Thruster Noise Neal A. Brown NAB & Associates, Inc. & Offshore Model Basin INTRODUCTION
Comparative study of RANS and LES in simulating cavitating flows
 31st Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics California, USA, September 11-16, 2016 Comparative study of RANS and LES in simulating cavitating flows Aswin Gnanaskandan and Krishnan Mahesh (University of Minnesota,
31st Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics California, USA, September 11-16, 2016 Comparative study of RANS and LES in simulating cavitating flows Aswin Gnanaskandan and Krishnan Mahesh (University of Minnesota,
PRELIMINARY MODELLING OF A MARINE PROPULSION SYSTEM
 PRELIMINARY MODELLING OF A MARINE PROPULSION SYSTEM Andrew Youssef 1 Andrew Guzzomi 2, Jie Pan 3 and Paul Dylejko 4 1-3 School of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering UWA Australia, Perth WA 6009, Australia
PRELIMINARY MODELLING OF A MARINE PROPULSION SYSTEM Andrew Youssef 1 Andrew Guzzomi 2, Jie Pan 3 and Paul Dylejko 4 1-3 School of Mechanical and Chemical Engineering UWA Australia, Perth WA 6009, Australia
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012090 TITLE: Supercavitating Propellers DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited This paper is part
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012090 TITLE: Supercavitating Propellers DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited This paper is part
DSC HW 3: Assigned 6/25/11, Due 7/2/12 Page 1
 DSC HW 3: Assigned 6/25/11, Due 7/2/12 Page 1 Problem 1 (Motor-Fan): A motor and fan are to be connected as shown in Figure 1. The torque-speed characteristics of the motor and fan are plotted on the same
DSC HW 3: Assigned 6/25/11, Due 7/2/12 Page 1 Problem 1 (Motor-Fan): A motor and fan are to be connected as shown in Figure 1. The torque-speed characteristics of the motor and fan are plotted on the same
ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol. 24, No. 1 2017 ESTIMATION OF HULL S RESISTANCE AT PRELIMINARY PHASE OF DESIGNING Adam Charchalis Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering
Cavitation instabilities in hydraulic machines
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Cavitation instabilities in hydraulic machines To cite this article: Y Tsujimoto 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 012005 View
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering OPEN ACCESS Cavitation instabilities in hydraulic machines To cite this article: Y Tsujimoto 2013 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 52 012005 View
Experiment- To determine the coefficient of impact for vanes. Experiment To determine the coefficient of discharge of an orifice meter.
 SUBJECT: FLUID MECHANICS VIVA QUESTIONS (M.E 4 th SEM) Experiment- To determine the coefficient of impact for vanes. Q1. Explain impulse momentum principal. Ans1. Momentum equation is based on Newton s
SUBJECT: FLUID MECHANICS VIVA QUESTIONS (M.E 4 th SEM) Experiment- To determine the coefficient of impact for vanes. Q1. Explain impulse momentum principal. Ans1. Momentum equation is based on Newton s
Calculation of propeller s load noise using LES and BEM numerical acoustics coupling methods
 Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXIII 85 Calculation of propeller s load noise using LES and BEM numerical acoustics coupling methods Q. Yang 1, Y. Wang 1 & M. Zhang 2 1 College of
Boundary Elements and Other Mesh Reduction Methods XXXIII 85 Calculation of propeller s load noise using LES and BEM numerical acoustics coupling methods Q. Yang 1, Y. Wang 1 & M. Zhang 2 1 College of
Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods
 ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 27-33 10.2478/pomr-2014-0015 A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane Katarzyna Zelazny,
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 27-33 10.2478/pomr-2014-0015 A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane Katarzyna Zelazny,
Industries & Applications
 Industries & Applications Aerospace High Lift Devices Landing Gear ECS Jet and turbo noise Marine Propeller noise Cavitation Hull/propeller/rudder interaction Automotive Wing mirror Sunroof noise HVAC
Industries & Applications Aerospace High Lift Devices Landing Gear ECS Jet and turbo noise Marine Propeller noise Cavitation Hull/propeller/rudder interaction Automotive Wing mirror Sunroof noise HVAC
6. Laser Doppler Anemometry. Introduction to principles and applications
 6. Laser Doppler Anemometry Introduction to principles and applications Characteristics of LDA Invented by Yeh and Cummins in 1964 Velocity measurements in Fluid Dynamics (gas, liquid) Up to 3 velocity
6. Laser Doppler Anemometry Introduction to principles and applications Characteristics of LDA Invented by Yeh and Cummins in 1964 Velocity measurements in Fluid Dynamics (gas, liquid) Up to 3 velocity
APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS ON RUDDERS
 Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
CAVITATION EFFECTS ON FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION IN THE CASE OF A 2D HYDROFOIL
 Proceedings of ASME FEDSM2005 2005 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Conference Houston, TX, June 19-23, 2005 FEDSM2005-77477 CAVITATION EFFECTS ON FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION IN THE CASE OF A 2D
Proceedings of ASME FEDSM2005 2005 ASME Fluids Engineering Division Summer Conference Houston, TX, June 19-23, 2005 FEDSM2005-77477 CAVITATION EFFECTS ON FLUID STRUCTURE INTERACTION IN THE CASE OF A 2D
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Ice Testing Resistance Test in Level Ice
 TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 1 of 7 evision CONTENTS 1 PUPOSE OF POCEDUE CE ESSTANCE TESTS N LEVEL CE 3 PAAMETES 3.1 Ship model parameters 3. ce parameters to be measured 4
TTC ecommended ce Testing esistance Test in Level ce Page 1 of 7 evision CONTENTS 1 PUPOSE OF POCEDUE CE ESSTANCE TESTS N LEVEL CE 3 PAAMETES 3.1 Ship model parameters 3. ce parameters to be measured 4
Transactions on Engineering Sciences vol 9, 1996 WIT Press, ISSN
 The analysis of bubble cavitation inception in turbulent flow around a hydrofoil L. Wilczynski Ship Propeller Department, Institute of Fluid Flow Machinery of the Polish Academy ofsciences, Fiszera 14,
The analysis of bubble cavitation inception in turbulent flow around a hydrofoil L. Wilczynski Ship Propeller Department, Institute of Fluid Flow Machinery of the Polish Academy ofsciences, Fiszera 14,
CAV2001:sessionB9.001
 Figure 7b. DTMB 36-in. Water tunnel (1962) Figure 8. Circulating wa ter tank UT 2, VW S Berlin (1974) Figure 9. Depres surized tow ing tank of M ARIN in Ede-Wageningen (1972) 5 the depressurized towing
Figure 7b. DTMB 36-in. Water tunnel (1962) Figure 8. Circulating wa ter tank UT 2, VW S Berlin (1974) Figure 9. Depres surized tow ing tank of M ARIN in Ede-Wageningen (1972) 5 the depressurized towing
PROPELLER INDUCED STRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUST BEARING
 PROPELLER INDUCED TRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUT BEARING Jie Pan, Nabil Farag, Terry Lin and Ross Juniper* DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND MATERIAL ENGINEERING THE UNIVERITY OF WETERN AUTRALIA 35 TIRLING
PROPELLER INDUCED TRUCTURAL VIBRATION THROUGH THE THRUT BEARING Jie Pan, Nabil Farag, Terry Lin and Ross Juniper* DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL AND MATERIAL ENGINEERING THE UNIVERITY OF WETERN AUTRALIA 35 TIRLING
Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
Makoto Uchida. Yuuki Matsumoto
 ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
International Symposium of Cavitation and Multiphase Flow (ISCM 2014) Beijing, China October 2014
 International Symposium of Cavitation and Multiphase Flow (ISCM 2014) IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Volume 72 Beijing, China 18-21 October 2014 ISBN: 978-1-63439-883-1 ISSN:
International Symposium of Cavitation and Multiphase Flow (ISCM 2014) IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Volume 72 Beijing, China 18-21 October 2014 ISBN: 978-1-63439-883-1 ISSN:
Comparison of EFD and CFD investigations of velocity fields for selected body-propeller configurations
 Comparison of EFD and CFD investigations of velocity fields for selected body-propeller configurations P. HOFFMANN S. JAWORSKI A. KOZŁOWSKA * * Ship Design and Research Centre S.A., Ship Hydromechanics
Comparison of EFD and CFD investigations of velocity fields for selected body-propeller configurations P. HOFFMANN S. JAWORSKI A. KOZŁOWSKA * * Ship Design and Research Centre S.A., Ship Hydromechanics
Mt Introduction. 2. Governing gphysics. 3. Decomposition of resistance. 4. Similarity laws and scaling
 1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
1. Introduction 2. Governing gphysics 3. Decomposition of resistance 4. Similarity laws and scaling Mt 527 Importance of proper power-speed prediction Resistance, prop. efficiency, power Wake field Experimental,
Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid
 Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid mechanics has depended heavily on experimental results.
Chapter 7 DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS AND SIMILITUDE Because so few real flows can be solved exactly by analytical methods alone, the development of fluid mechanics has depended heavily on experimental results.
Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Effect of Operational Conditions on the Cavitation Inception Speed of Naval Propellers
 25 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics St. John s, Newfoundland and Labrador, CANADA 8-3 August 24 Effect of Operational Conditions on the Cavitation Inception Speed of Naval Propellers T.J.C. van Terwisga,2,
25 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics St. John s, Newfoundland and Labrador, CANADA 8-3 August 24 Effect of Operational Conditions on the Cavitation Inception Speed of Naval Propellers T.J.C. van Terwisga,2,
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION
 A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
DETERMINING OPTIMUM GEOMETRY FOR A BOW THRUSTER PROPELLER
 DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
Numerical Study on the Behavior of Air Layers Used for Drag Reduction
 28 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Pasadena, California, 12-17 September 2010 Numerical Study on the Behavior of Air Layers Used for Drag Reduction Jin-Keun Choi and Georges L. Chahine (DYNAFLOW, INC.,
28 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics Pasadena, California, 12-17 September 2010 Numerical Study on the Behavior of Air Layers Used for Drag Reduction Jin-Keun Choi and Georges L. Chahine (DYNAFLOW, INC.,
ONBOARD SHIP NOISE ANALYSIS
 Guidance Notes on Ship Noise Analysis GUIDANCE NOTES ON ONBOARD SHIP NOISE ANALYSIS FEBRUARY 2018 American Bureau of Shipping Incorporated by Act of Legislature of the State of New York 1862 2018 American
Guidance Notes on Ship Noise Analysis GUIDANCE NOTES ON ONBOARD SHIP NOISE ANALYSIS FEBRUARY 2018 American Bureau of Shipping Incorporated by Act of Legislature of the State of New York 1862 2018 American
ITTC Recommended Procedures Testing and Extrapolation Methods Resistance Resistance Test
 -0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
-0- Page 1 of 11 CONTENTS 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE. PARAMETERS.1 Data Reduction Equations. Definition of ariables 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE 3.1 Model and Installation 3.1.1 Model 3.1. Test condition 3.1.3
DUAL-MODE CONTRAPROPELLER WITH CURVE STACKING LINE FOR BLADE
 Anatolij-Branko R. Togunjac, Ph.D, Research and Design Institute for Fishing Fleet, GIPRORYBFLOT, M. Morskaya str.,18-20, St. Petersburg, 190000 Russia Leonid I. Vishnevsky, D.Sc,Krylov Shipbuilding Research
Anatolij-Branko R. Togunjac, Ph.D, Research and Design Institute for Fishing Fleet, GIPRORYBFLOT, M. Morskaya str.,18-20, St. Petersburg, 190000 Russia Leonid I. Vishnevsky, D.Sc,Krylov Shipbuilding Research
On the aeroacoustic tonal noise generation mechanism of a sharp-edged. plate
 On the aeroacoustic tonal noise generation mechanism of a sharp-edged plate Danielle J. Moreau, Laura A. Brooks and Con J. Doolan School of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Adelaide, South Australia,
On the aeroacoustic tonal noise generation mechanism of a sharp-edged plate Danielle J. Moreau, Laura A. Brooks and Con J. Doolan School of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Adelaide, South Australia,
6. Laser Doppler Anemometry. Introduction to principles and applications
 6. Laser Doppler Anemometry Introduction to principles and applications Characteristics of LDA Invented by Yeh and Cummins in 1964 Velocity measurements in Fluid Dynamics (gas, liquid) Up to 3 velocity
6. Laser Doppler Anemometry Introduction to principles and applications Characteristics of LDA Invented by Yeh and Cummins in 1964 Velocity measurements in Fluid Dynamics (gas, liquid) Up to 3 velocity
Nominal vs. Effective Wake Fields and Their Influence on Propeller Cavitation Performance
 Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Nominal vs. Effective Wake Fields and Their Influence on Propeller Cavitation Performance Pelle Bo Regener 1, * ID, Yasaman Mirsadraee 1,2 ID and Poul
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Nominal vs. Effective Wake Fields and Their Influence on Propeller Cavitation Performance Pelle Bo Regener 1, * ID, Yasaman Mirsadraee 1,2 ID and Poul
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 190 1987 006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA35) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & ivil Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University
1896 190 1987 006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA35) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & ivil Engineering Shanghai Jiao Tong University
