Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION
|
|
|
- Gary Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I FINAL EXAMINATION Problems Points Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no 5//6
2 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - Problem points Given is the electric circuit model, shown in Figure.. I C βi R R Vv 30V I β 5 R 6Ω R 3 R I R R 4Ω R 3 8Ω VC I C R 5 I 3 I R 4 R 4 7Ω R 5 5Ω V v + - Figure. The electric circuit model with positive reference directions for currents and voltages that ought to be calculated. Problem Statement For the electric circuit model of Figure., demonstrate an ability to: (a) use the Mesh Current Method analysis technique on a DC circuit that contains both, the voltage and current sources, (b) assign the active-convention coupled positive-reference-direction voltage and current to an ideal electrical energy source, (c) apply the determinant method for solving systems of linear algebraic equations, (d) calculate the power delivered by the energy sources V V and I C, (e) calculate the amount of electrical energy converted to heat in the circuit of Figure. during a time interval t4 minutes. Hint # For full credit: all equations, all answers to questions, all circuit models and other graphical representations are expected to be entered into the space designated for them; all shown numerical results must be preceded by the symbolic and numeric expressions whose evaluation produces these numerical results. Problem Solution For full credit, an explicit demonstration of understanding the following solution steps is expected.. Select and indicate in Figure. the positive reference directions for a feasible set of meshcurrents. 5//6
3 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - 3. Using the set of mesh currents selected in section., prepare the set of canonical form Mesh Current equations for the electrical circuit shown in Figure.. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (-). Using the Mesh Current Method, we only need to write two normal form equations, since Mesh Current I 3 is equal to the current βi R of the dependent current source. R I - R I - R 3 I 3 0 -R I + R I - R 3 I 3 V V (-) expressing I R in terms of the mesh currents which pass through R we obtain mesh current I3 expressed in terms of the rest of mesh currents as, I 3 βi R β(i - I).3 Eliminate from equations (-) the one mesh current whose expression in terms of the other two mesh currents is determined by the electric circuit model in Figure.. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (-). Substituting the known expressions for I 3 into the mesh current equations (-), and rearranging them we obtain, (R- β R3) I - (R - β R3)I 0 - (R+ β R3) I + (R+ β R3)I Vs (-).4 Calculate the numerical values of the coefficients (the self and mutual resistances of the meshes) in equations (-). Show your calculation in the space reserved for equations (-3). Self resistances of the two meshes for which the mesh current method equations (-) and (-)h been written are, R R + R + R Ω(-4) R R + R 4 + R Ω(-5) (-3) and the mutual resistances of those meshes are R R R 4 Ω(-6) R 3 R 3 R 3 8 Ω.(-7) R 3 R 3 R 5 5 Ω. 5//6
4 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm Calculate the values of determinants involved in the solution process of the system of equations (-). Show your calculation in the space reserved for equations (-4). R- β R3 -R + β R3 -R- β R3 R+ β R3 (R- β R3)(R+ βr3) + (- R +β R3)(R+ βr3) (8-5. 8). ( ) + ( )(4+5. 5) Ω 0 -R + β R3 V V R+ β R3 -V V (-R+β R3) 0. (4-5. 8) 30(- 86) -580VΩ (-4) R- β R3 0 -R- β R3 V V V V (R- β R3) 0(8-5. 8)30. (-6) -860VΩ.6 Calculate the values of mesh currents indicated in the electric circuit model of Figure.. Show your calculation in the space reserved for equations (-5). I A I A I 3 β(i - I) 5( ) 75A (-5).7 Applying the active convention for coupled positive reference directions of the current and voltage of a circuit element, show in Figure. the positive reference direction for the voltage V C of the current source I C ; then calculate the value of the voltage V C and the power P C delivered to the circuit by the current source I C. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (-6). V C (I 3 - I )R 3 + (I 3 - I )R 5 ( ). 8+(75-39) V P C I C V C I 3 V C kw (-6) 5//6
5 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm Based on the calculation result (-6), determine whether the current source I C delivers, or absorbs power in the circuit of Figure.. Check the correct answer on both lines below, yes no not applicable x current source I C delivers power to the circuit of Figure., x current source I C absorbs power from the circuit of Figure.. Since the active convention has been selected for the coupled positive reference directions of the current and voltage of the source I C, the positive sign of the numerical value of the power P C implies that the current source I C delivers power to the circuit of Figure.. 5//6
6 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - 6 Problem points Given is the electric circuit model shown in Figure.(a). R L a R 0 Ω Z T a v v + - C V oc L5mH C 5µF V T + - V ab (a) b v v 40cos30πt V (b) b Figure.(a) An electric circuit model. (b)phasor domain Thévenin's equivalent model for the circuit shown in Figure.(a). Problem Statement For the electric circuit model of Figure.(a): - prepare the Thévenin s equivalent circuit with respect to the pair of terminals a and b; - determine maximum real power that the circuit of Figure.(a) can deliver to a load connected to the pair of terminals a and b. Hint # For full credit, give answers to all questions, prepare all required circuit diagrams, write all equations for which the space is left, and show all symbolic and numerical expressions whose evaluation produces calculated numerical results. Problem Solution Explicit demonstration of understanding the following solution steps is expected.. For the circuit shown in Figure.(a), prepare the electrical model of the phasor domain Thévenin's equivalent circuit with respect to terminals a and b. Show the prepared model in the space reserved for Figure.(b). Determine the symbolic expressions (in terms of the circuit parameters R, L, C and V vm ), and determine the numerical values of the real and imaginary parts of the Thévenin's equivalent circuit voltage V T. Show the work and results in the space designated for equation (-). Electromotive force V T is equal to the voltage V oc between terminals a and b when they are left "open circuited". When there are no external elements connected between terminals a and b, no current flows through the inductor L and, therefore, no voltage drop appears across the impedance Z L, which makes the voltage V oc equal the voltage V c across the capacitor s impedance Z C, which voltage, in turn, is 5//6
7 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - 7 determined by the voltage divider formula, V V Z C V V jωc V T V ab V oc V C Z R +Z C R + jωc - j j j9.54 V V V +jωcr (- jωcr)v m +ω C R 0 o (-) ωcr 30π (ωcr) Determine the numerical values of the modulus V T, and argument φ VT, of the Thévenin's equivalent voltage V T ; show your calculation in the space reserved for equation (-). modv T V T V T V (-) argv T φ VT arctg rad 5.6 o Determine the symbolic expressions in terms of circuit parameters (R, L, and C), for the Thévenin's equivalent impedance Z T ; show your calculation in the space designated for equation (-3). With the voltage source deenergized, the impedance seen from the terminal pair a and b is that of Z L connected in series with the parallel connection of Z R and Z C. Z T Z L + R Z C Z R Z C Z R +Z C + Z L R R + R ωl(+ω C R ) ωcr +(ωcr) + j +(ωcr) jωc jωc + jωl R(- jωcr) +(ωcr) + jωl (-3).5 Determine the numerical values of the real and imaginary parts, R T and X T, of the Thévenin s equivalent impedance (Z T R T +jx T ); show your calculation in the space designated for equation 5//6
8 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - 8 (-4). ωcr 30π (ωcr).6.58 ωl 30π Ω Z T R ωl(+ω C R ) ωcr +(ωcr) + j +(ωcr) j 5(+.58) (-4) ( j0.)ω.6 Prepare the expression which shows the relation between the impedance Z T of the circuit in Figure.(b) and the impedance Z LD which would draw maximum real power from the circuit in Figure.(a) when connected between terminals a and b. Show your calculation in the space designated for equation (-5). Z LD is simply the complex conjugate of Z T. Z LD Z T * R T - jx T ( j0.)ω (-5).7 Determine the numerical value of the current I LD that would be delivered to the load impedance Z LD defined by equation (-5), when, connected to terminals a and b in the circuit of Fig.(a); Show your calculation in the space designated for equation (-6). Using the Thevenin's equivalent circuit of Figure.(b), the current through impedance Z L when connected to terminals a and b can be expressed as V I LD T ZT +Z LD V T V T R T +jx T +R T -jx o T R o A T 3.88 (-6).8 Determine the numerical value of the maximum real power that a load could draw when connected between terminals a and b of the circuit in Figure.(a). Show your calculation in the space designated for equation (-7). Using the derived current through Z L, the real power that could be delivered to Z L can be expressed as, I LD R T 3. maxp LD (-7) 0W 5//6
9 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm - 9 Problem 3 0 points Figure 3. shows the electrical model of a single capacitor RC-circuit. R I R II t0 - t0 + S i R R R N0 Figure 3. Electrical mode of a single capacitor RC-circuit. i C N C v C v R3 i R3 R 3 C 0mF V C (0- ) 0V I I 0A R I 50Ω R 50Ω R 50Ω R 3 50Ω Problem Statement Considering that switch S (which models a transistor) is closed at time t 0s, demonstrate an ability to: - determine the total quantity of the charge transfer to the capacitor, Q C, that will take place between times t0 and t, - determine voltage across resistor R 3, V R3 ( ), at the time when transient currents completely stop flowing in the circuit. Problem Solution Hint # For full credit, give answers to all questions, prepare all required circuit diagrams, write all equations for which the space is left, and show all symbolic and numerical expressions whose evaluation produces calculated numerical results. Explicit demonstration of understanding the following solution steps is expected. 3. Given the indicated positive reference directions for the voltages v C and v R3, show in the circuit model of Figure 3. the corresponding passive-convention positive-reference directions for currents through resistor R 3 and capacitor C. 3. To establish a base for clear thinking, write in the space designated for equation (3-) two KCL equations for the node N in Figure 3.: (a) one equation valid for the moment t0 -, and (b) the other one equation valid for the time t. Notice which of the currents values is equal to zero in both equations, and how that influences the strategy for solving the problem. Show your work in the space designated for equations (3-). KCL(0 - ): i R (0 - ) - i C (0 - ) - i R3 (0 - ) 0, where i R (0 - ) i C (0 - ) i R3 (0 - ) 0 (3-) KCL( ): i R ( ) - i C ( ) - i R3 ( ) 0, where i C ( ) 0 and i R ( ) i R3 ( ) 0 5//6
10 EECS:300, Electric Circuits I s6fs_elci7.fm Determine the common value of the currents i R ( ) and i R3 ( ) at the time when transient currents completely stops flowing in the circuit. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (3-). Since by definition, at t i C ( ) 0, the current i R3 ( ) is determined by the DC current divider formula, (3-) R I 50 i R3 ( ) I I 0 4A R I + R + R + R Determine the voltage v C ( ) across the capacitor C at the time when transient currents completely stop flowing in the circuit. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (3-3). v C ( ) i R3 ( )(R + R 3 ) 4(50+50) 400V (3-3) 3.5 Determine the charge Q C ( ) stored in the capacitor C at the time t. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (3-4). Q C ( ) C. v C ( ) C (3-4) 3.6 Determine the determine the total quantity of the charge transfer to the capacitor, Q C, between the times t0 -, and t. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (3-5). Q C Q C ( ) - Q C (0 - ) 4-0 4C (3-5) 3.7 Determine the energy W C stored in the capacitor C at the time when transient currents completely stopped flowing in the circuit. Show your work in the space reserved for equations (3-4). W C C. v C ( ) J (3-4) 3.8 Bonus Question: How much electrical energy has been converted to heat in the circuit of Figure 3. during the process which charged the capacitor C to the voltages v C ( ) and v C ( ) respectively. For full credit, mark your answers yes, no, or not applicable in all the given choices! yes no not applicable x W C x W C W C x. 5//6
Electric Circuits I Final Examination
 The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm - EECS:300 Electric Circuits I Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points.. 3. Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm
The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm - EECS:300 Electric Circuits I Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points.. 3. Total 34 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s8fs_elci7.fm
Electric Circuits I Final Examination
 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points. 4. 3. Total 38 Was the exam fair? yes no //3 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Problem 4 points
EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Electric Circuits I Final Examination Problems Points. 4. 3. Total 38 Was the exam fair? yes no //3 EECS:300 Electric Circuits I ffs_elci.fm - Problem 4 points
Electric Circuits I. Midterm #1 Examination
 EECS:2300, Electric Circuits I s8ms_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I Midterm # Examination Problems Points. 4 2. 6 3. 5 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS:2300, Electric Circuits I s8ms_elci7.fm - 2
EECS:2300, Electric Circuits I s8ms_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I Midterm # Examination Problems Points. 4 2. 6 3. 5 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS:2300, Electric Circuits I s8ms_elci7.fm - 2
Electric Circuits I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I Midterm # Problems Points. 3 2. 7 3. 5 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm
The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm - Electric Circuits I Midterm # Problems Points. 3 2. 7 3. 5 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo Section number s5ms_elci7.fm
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part I Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Mauro Forti October 27, 2018 Constitutive Relations in the Frequency Domain Consider a network with independent voltage and current sources at the same angular frequency
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Mauro Forti October 27, 2018 Constitutive Relations in the Frequency Domain Consider a network with independent voltage and current sources at the same angular frequency
Homework 2 SJTU233. Part A. Part B. Problem 2. Part A. Problem 1. Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω.
 Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors
 Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Chapter 10 AC Analysis Using Phasors 10.1 Introduction We would like to use our linear circuit theorems (Nodal analysis, Mesh analysis, Thevenin and Norton equivalent circuits, Superposition, etc.) to
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis In this unit, we consider circuits in which the sources are sinusoidal in nature. The review section of this unit covers most of section 9.1 9.9 of the text.
Electronics II. Final Examination
 The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 1 Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points 1. 11 2. 14 3. 15 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 2 Problem 1 11
The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 1 Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points 1. 11 2. 14 3. 15 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f17fs_elct27.fm 2 Problem 1 11
EE 40: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 2008: Midterm 2
 EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
EE 4: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Spring 8: Midterm Venkat Anantharam 3/9/8 Total Time Allotted : min Total Points:. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring two pages
= 32.0\cis{38.7} = j Ω. Zab = Homework 2 SJTU233. Part A. Part B. Problem 2. Part A. Problem 1
 Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
Homework 2 SJTU233 Problem 1 Find the impedance Zab in the circuit seen in the figure. Suppose that R = 5 Ω. Express Zab in polar form. Enter your answer using polar notation. Express argument in degrees.
EE221 - Practice for the Midterm Exam
 EE1 - Practice for the Midterm Exam 1. Consider this circuit and corresponding plot of the inductor current: Determine the values of L, R 1 and R : L = H, R 1 = Ω and R = Ω. Hint: Use the plot to determine
EE1 - Practice for the Midterm Exam 1. Consider this circuit and corresponding plot of the inductor current: Determine the values of L, R 1 and R : L = H, R 1 = Ω and R = Ω. Hint: Use the plot to determine
AC Circuit Analysis and Measurement Lab Assignment 8
 Electric Circuit Lab Assignments elcirc_lab87.fm - 1 AC Circuit Analysis and Measurement Lab Assignment 8 Introduction When analyzing an electric circuit that contains reactive components, inductors and
Electric Circuit Lab Assignments elcirc_lab87.fm - 1 AC Circuit Analysis and Measurement Lab Assignment 8 Introduction When analyzing an electric circuit that contains reactive components, inductors and
MAE140 Linear Circuits Fall 2016 Final, December 6th Instructions
 MAE40 Linear Circuits Fall 206 Final, December 6th Instructions. This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a handheld
MAE40 Linear Circuits Fall 206 Final, December 6th Instructions. This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a handheld
ECE 201 Fall 2009 Final Exam
 ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
ECE 01 Fall 009 Final Exam December 16, 009 Division 0101: Tan (11:30am) Division 001: Clark (7:30 am) Division 0301: Elliott (1:30 pm) Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO.. Write your Name,
Network Graphs and Tellegen s Theorem
 Networ Graphs and Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph Cut sets and Kirchhoff s current laws Loops and Kirchhoff s voltage laws Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph The analysis of a complex
Networ Graphs and Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph Cut sets and Kirchhoff s current laws Loops and Kirchhoff s voltage laws Tellegen s Theorem The concepts of a graph The analysis of a complex
To find the step response of an RC circuit
 To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis 9 Assessment Problems AP 9. [a] V = 70/ 40 V [b] 0 sin(000t +20 ) = 0 cos(000t 70 ).. I = 0/ 70 A [c] I =5/36.87 + 0/ 53.3 =4+j3+6 j8 =0 j5 =.8/ 26.57 A [d] sin(20,000πt
Electronics II. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I su3ms_elct7.fm Section Electronics II Midterm # Problems Points. 5. 6 3. 9 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su3ms_elct7.fm Problem
The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I su3ms_elct7.fm Section Electronics II Midterm # Problems Points. 5. 6 3. 9 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su3ms_elct7.fm Problem
Electronics II. Final Examination
 The University of Toledo f6fs_elct7.fm - Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points. 5. 0 3. 5 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f6fs_elct7.fm - Problem 5 points Given is
The University of Toledo f6fs_elct7.fm - Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points. 5. 0 3. 5 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f6fs_elct7.fm - Problem 5 points Given is
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Almost all electrical systems, whether signal or power, operate with alternating currents and voltages. We have seen that when any circuit is disturbed (switched on or
Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Almost all electrical systems, whether signal or power, operate with alternating currents and voltages. We have seen that when any circuit is disturbed (switched on or
Electronics II. Midterm II
 The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics II Midterm II Problems Points. 7. 7 3. 6 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Problem 7 points Equation (-)
The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics II Midterm II Problems Points. 7. 7 3. 6 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su7ms_elct7.fm - Problem 7 points Equation (-)
EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.
![EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain. EE313 Fall 2013 Exam #1 (100 pts) Thursday, September 26, 2013 Name. 1) [6 pts] Convert the following time-domain circuit to the RMS Phasor Domain.](/thumbs/95/123488230.jpg) Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
Name If you have any questions ask them. Remember to include all units on your answers (V, A, etc). Clearly indicate your answers. All angles must be in the range 0 to +180 or 0 to 180 degrees. 1) [6 pts]
Electric Circuits II Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits II Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin and Norton Equivalent
Electric Circuits II Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Table of Contents 1 2 3 4 5 Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin and Norton Equivalent
Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors
 Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors 1. Motivation 2. Sinusoid Features 3. Phasors 4. Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements 5. Impedance and Admittance 6. Kirchhoff s Laws in the Frequency Domain 7. Impedance
Chapter 10: Sinusoids and Phasors 1. Motivation 2. Sinusoid Features 3. Phasors 4. Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements 5. Impedance and Admittance 6. Kirchhoff s Laws in the Frequency Domain 7. Impedance
Sinusoids and Phasors
 CHAPTER 9 Sinusoids and Phasors We now begins the analysis of circuits in which the voltage or current sources are time-varying. In this chapter, we are particularly interested in sinusoidally time-varying
CHAPTER 9 Sinusoids and Phasors We now begins the analysis of circuits in which the voltage or current sources are time-varying. In this chapter, we are particularly interested in sinusoidally time-varying
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You may use the equation sheet provided but
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II
 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis (AC Analysis) Part II Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
EE221 Circuits II. Chapter 14 Frequency Response
 EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 1 Objectives : sinusoidal functions Impedance use phasors to determine the forced response of a circuit subjected to sinusoidal excitation Apply techniques
BFF1303: ELECTRICAL / ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING. Alternating Current Circuits : Basic Law
 BFF1303: ELECTRICAL / ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Alternating Current Circuits : Basic Law Ismail Mohd Khairuddin, Zulkifil Md Yusof Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering Universiti Malaysia Pahang Alternating
BFF1303: ELECTRICAL / ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Alternating Current Circuits : Basic Law Ismail Mohd Khairuddin, Zulkifil Md Yusof Faculty of Manufacturing Engineering Universiti Malaysia Pahang Alternating
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis. Phasors
 Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
Phasors: Impedance and Circuit Anlysis Lecture 6, 0/07/05 OUTLINE Phasor ReCap Capacitor/Inductor Example Arithmetic with Complex Numbers Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis with Complex Impedance Phasor
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, pm, Room TBA
 EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
4/27 Friday. I have all the old homework if you need to collect them.
 4/27 Friday Last HW: do not need to turn it. Solution will be posted on the web. I have all the old homework if you need to collect them. Final exam: 7-9pm, Monday, 4/30 at Lambert Fieldhouse F101 Calculator
4/27 Friday Last HW: do not need to turn it. Solution will be posted on the web. I have all the old homework if you need to collect them. Final exam: 7-9pm, Monday, 4/30 at Lambert Fieldhouse F101 Calculator
Electric Circuit Theory
 Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 11 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 11.1
Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 11 Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 11.1
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis
 Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis Chapter 5 Steady-State Sinusoidal Analysis 1. Identify the frequency, angular frequency, peak value, rms value, and phase of a sinusoidal signal. 2. Solve steady-state
Lecture #3. Review: Power
 Lecture #3 OUTLINE Power calculations Circuit elements Voltage and current sources Electrical resistance (Ohm s law) Kirchhoff s laws Reading Chapter 2 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Review: Power If an element is
Lecture #3 OUTLINE Power calculations Circuit elements Voltage and current sources Electrical resistance (Ohm s law) Kirchhoff s laws Reading Chapter 2 Lecture 3, Slide 1 Review: Power If an element is
EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3. Name:
 EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed Scientific calculators are allowed Complete
EECE 2510 Circuits and Signals, Biomedical Applications Final Exam Section 3 Instructions: Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed Scientific calculators are allowed Complete
Design Engineering MEng EXAMINATIONS 2016
 IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Design Engineering MEng EXAMINATIONS 2016 For Internal Students of the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant examination
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Design Engineering MEng EXAMINATIONS 2016 For Internal Students of the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine This paper is also taken for the relevant examination
AC analysis - many examples
 AC analysis - many examples The basic method for AC analysis:. epresent the AC sources as complex numbers: ( ). Convert resistors, capacitors, and inductors into their respective impedances: resistor Z
AC analysis - many examples The basic method for AC analysis:. epresent the AC sources as complex numbers: ( ). Convert resistors, capacitors, and inductors into their respective impedances: resistor Z
Two-Port Networks Admittance Parameters CHAPTER16 THE LEARNING GOALS FOR THIS CHAPTER ARE THAT STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 CHAPTER16 Two-Port Networks THE LEARNING GOALS FOR THIS CHAPTER ARE THAT STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Calculate the admittance, impedance, hybrid, and transmission parameter for two-port networks. Convert
CHAPTER16 Two-Port Networks THE LEARNING GOALS FOR THIS CHAPTER ARE THAT STUDENTS SHOULD BE ABLE TO: Calculate the admittance, impedance, hybrid, and transmission parameter for two-port networks. Convert
EE221 Circuits II. Chapter 14 Frequency Response
 EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
EE22 Circuits II Chapter 4 Frequency Response Frequency Response Chapter 4 4. Introduction 4.2 Transfer Function 4.3 Bode Plots 4.4 Series Resonance 4.5 Parallel Resonance 4.6 Passive Filters 4.7 Active
Consider a simple RC circuit. We might like to know how much power is being supplied by the source. We probably need to find the current.
 AC power Consider a simple RC circuit We might like to know how much power is being supplied by the source We probably need to find the current R 10! R 10! is VS Vmcosωt Vm 10 V f 60 Hz V m 10 V C 150
AC power Consider a simple RC circuit We might like to know how much power is being supplied by the source We probably need to find the current R 10! R 10! is VS Vmcosωt Vm 10 V f 60 Hz V m 10 V C 150
EIT Quick-Review Electrical Prof. Frank Merat
 CIRCUITS 4 The power supplied by the 0 volt source is (a) 2 watts (b) 0 watts (c) 2 watts (d) 6 watts (e) 6 watts 4Ω 2Ω 0V i i 2 2Ω 20V Call the clockwise loop currents i and i 2 as shown in the drawing
CIRCUITS 4 The power supplied by the 0 volt source is (a) 2 watts (b) 0 watts (c) 2 watts (d) 6 watts (e) 6 watts 4Ω 2Ω 0V i i 2 2Ω 20V Call the clockwise loop currents i and i 2 as shown in the drawing
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis
 Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
Chapter 10: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 10.5 10.6 10.9 Basic Approach Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Theorem Source Transformation Thevenin & Norton Equivalent Circuits
12. Introduction and Chapter Objectives
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Steady-State Sinusoidal Power 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter we will address the issue of power transmission via sinusoidal or AC) signals. This
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 1: Steady-State Sinusoidal Power 1. Introduction and Chapter Objectives In this chapter we will address the issue of power transmission via sinusoidal or AC) signals. This
Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004
 Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004 David E. Pellett Draft v.0.9 Notes Copyright 2004 David E. Pellett unless stated otherwise. References: Text for course: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, second edition,
Physics 116A Notes Fall 2004 David E. Pellett Draft v.0.9 Notes Copyright 2004 David E. Pellett unless stated otherwise. References: Text for course: Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering, second edition,
UNIT 4 DC EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT AND NETWORK THEOREMS
 UNIT 4 DC EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT AND NETWORK THEOREMS 1.0 Kirchoff s Law Kirchoff s Current Law (KCL) states at any junction in an electric circuit the total current flowing towards that junction is equal
UNIT 4 DC EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT AND NETWORK THEOREMS 1.0 Kirchoff s Law Kirchoff s Current Law (KCL) states at any junction in an electric circuit the total current flowing towards that junction is equal
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors)
 Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
Introduction to AC Circuits (Capacitors and Inductors) Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/
MAE140 - Linear Circuits - Winter 09 Midterm, February 5
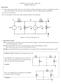 Instructions MAE40 - Linear ircuits - Winter 09 Midterm, February 5 (i) This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a
Instructions MAE40 - Linear ircuits - Winter 09 Midterm, February 5 (i) This exam is open book. You may use whatever written materials you choose, including your class notes and textbook. You may use a
REACTANCE. By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013
 REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
REACTANCE REACTANCE By: Enzo Paterno Date: 03/2013 5/2007 Enzo Paterno 1 RESISTANCE - R i R (t R A resistor for all practical purposes is unaffected by the frequency of the applied sinusoidal voltage or
Basics of Network Theory (Part-I)
 Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
Basics of Network Theory (PartI). A square waveform as shown in figure is applied across mh ideal inductor. The current through the inductor is a. wave of peak amplitude. V 0 0.5 t (m sec) [Gate 987: Marks]
ECE2262 Electric Circuit
 ECE2262 Electric Circuit Chapter 7: FIRST AND SECOND-ORDER RL AND RC CIRCUITS Response to First-Order RL and RC Circuits Response to Second-Order RL and RC Circuits 1 2 7.1. Introduction 3 4 In dc steady
ECE2262 Electric Circuit Chapter 7: FIRST AND SECOND-ORDER RL AND RC CIRCUITS Response to First-Order RL and RC Circuits Response to Second-Order RL and RC Circuits 1 2 7.1. Introduction 3 4 In dc steady
EE-201 Review Exam I. 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6) None of above
 EE-201, Review Probs Test 1 page-1 Spring 98 EE-201 Review Exam I Multiple Choice (5 points each, no partial credit.) 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6)
EE-201, Review Probs Test 1 page-1 Spring 98 EE-201 Review Exam I Multiple Choice (5 points each, no partial credit.) 1. The voltage Vx in the circuit below is: (1) 3V (2) 2V (3) -2V (4) 1V (5) -1V (6)
CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II. (AC Circuits)
 Will Moore MT & MT CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II (AC Circuits) Syllabus Complex impedance, power factor, frequency response of AC networks including Bode diagrams, second-order and resonant circuits, damping and
Will Moore MT & MT CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II (AC Circuits) Syllabus Complex impedance, power factor, frequency response of AC networks including Bode diagrams, second-order and resonant circuits, damping and
Chapter 9 Objectives
 Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
Chapter 9 Engr8 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 9 Objectives Understand the concept of a phasor; Be able to transform a circuit with a sinusoidal source into the frequency domain using phasor
Electric Circuits Fall 2015 Solution #5
 RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermeate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero cret.
RULES: Please try to work on your own. Discussion is permissible, but identical submissions are unacceptable! Please show all intermeate steps: a correct solution without an explanation will get zero cret.
Electric Circuit Theory
 Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 18 Two-Port Circuits Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 18.1 The Terminal Equations
Electric Circuit Theory Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Chapter 18 Two-Port Circuits Nam Ki Min nkmin@korea.ac.kr 010-9419-2320 Contents and Objectives 3 Chapter Contents 18.1 The Terminal Equations
AC Circuits Homework Set
 Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Problem 1. In an oscillating LC circuit in which C=4.0 μf, the maximum potential difference across the capacitor during the oscillations is 1.50 V and the maximum current through the inductor is 50.0 ma.
Electronics II. Midterm #2
 The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I su4ms_elct7.fm Section Electronics II Midterm # Problems Points. 8. 7 3. 5 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su4ms_elct7.fm Problem
The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I su4ms_elct7.fm Section Electronics II Midterm # Problems Points. 8. 7 3. 5 Total 0 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo su4ms_elct7.fm Problem
Possible
 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science ENGR 21. Introduction to Circuits and Instruments (4) ENGR 21 SPRING 24 FINAL EXAMINATION given 5/4/3 Possible 1. 1 2. 1 3. 1 4. 1 5. 1 6. 1 7.
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science ENGR 21. Introduction to Circuits and Instruments (4) ENGR 21 SPRING 24 FINAL EXAMINATION given 5/4/3 Possible 1. 1 2. 1 3. 1 4. 1 5. 1 6. 1 7.
Fall 2011 ME 2305 Network Analysis. Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis of RLC Circuits
 Fall 2011 ME 2305 Network Analysis Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis of RLC Circuits Engr. Humera Rafique Assistant Professor humera.rafique@szabist.edu.pk Faculty of Engineering (Mechatronics)
Fall 2011 ME 2305 Network Analysis Chapter 4 Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis of RLC Circuits Engr. Humera Rafique Assistant Professor humera.rafique@szabist.edu.pk Faculty of Engineering (Mechatronics)
Three Phase Circuits
 Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Amin Electronics and Electrical Communications Engineering Department (EECE) Cairo University elc.n102.eng@gmail.com http://scholar.cu.edu.eg/refky/ OUTLINE Previously on ELCN102 Three Phase Circuits Balanced
Chapter 5. Department of Mechanical Engineering
 Source Transformation By KVL: V s =ir s + v By KCL: i s =i + v/r p is=v s /R s R s =R p V s /R s =i + v/r s i s =i + v/r p Two circuits have the same terminal voltage and current Source Transformation
Source Transformation By KVL: V s =ir s + v By KCL: i s =i + v/r p is=v s /R s R s =R p V s /R s =i + v/r s i s =i + v/r p Two circuits have the same terminal voltage and current Source Transformation
Figure Circuit for Question 1. Figure Circuit for Question 2
 Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
Exercises 10.7 Exercises Multiple Choice 1. For the circuit of Figure 10.44 the time constant is A. 0.5 ms 71.43 µs 2, 000 s D. 0.2 ms 4 Ω 2 Ω 12 Ω 1 mh 12u 0 () t V Figure 10.44. Circuit for Question
Chapter 2. Engr228 Circuit Analysis. Dr Curtis Nelson
 Chapter 2 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 2 Objectives Understand symbols and behavior of the following circuit elements: Independent voltage and current sources; Dependent voltage and
Chapter 2 Engr228 Circuit Analysis Dr Curtis Nelson Chapter 2 Objectives Understand symbols and behavior of the following circuit elements: Independent voltage and current sources; Dependent voltage and
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 2018 Elad Alon and Miki Lustig Discussion 5A
 EECS 6B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 208 Elad Alon and Miki Lustig Discussion 5A Transfer Function When we write the transfer function of an arbitrary circuit, it always takes the
EECS 6B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 208 Elad Alon and Miki Lustig Discussion 5A Transfer Function When we write the transfer function of an arbitrary circuit, it always takes the
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department. EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 2 DC circuits and network theorems
 POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 2 DC circuits and network theorems Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of Experiment In this
POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY Electrical Engineering Department EE SOPHOMORE LABORATORY Experiment 2 DC circuits and network theorems Modified for Physics 18, Brooklyn College I. Overview of Experiment In this
Midterm Exam (closed book/notes) Tuesday, February 23, 2010
 University of California, Berkeley Spring 2010 EE 42/100 Prof. A. Niknejad Midterm Exam (closed book/notes) Tuesday, February 23, 2010 Guidelines: Closed book. You may use a calculator. Do not unstaple
University of California, Berkeley Spring 2010 EE 42/100 Prof. A. Niknejad Midterm Exam (closed book/notes) Tuesday, February 23, 2010 Guidelines: Closed book. You may use a calculator. Do not unstaple
Lecture 11 - AC Power
 - AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
- AC Power 11/17/2015 Reading: Chapter 11 1 Outline Instantaneous power Complex power Average (real) power Reactive power Apparent power Maximum power transfer Power factor correction 2 Power in AC Circuits
11. AC Circuit Power Analysis
 . AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
. AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
Electronics. Basics & Applications. group talk Daniel Biesinger
 Electronics Basics & Applications group talk 23.7.2010 by Daniel Biesinger 1 2 Contents Contents Basics Simple applications Equivalent circuit Impedance & Reactance More advanced applications - RC circuits
Electronics Basics & Applications group talk 23.7.2010 by Daniel Biesinger 1 2 Contents Contents Basics Simple applications Equivalent circuit Impedance & Reactance More advanced applications - RC circuits
Electronics II. Final Examination
 f3fs_elct7.fm - The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I Section Student Name Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points.. 3 3. 5 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no Analog Electronics f3fs_elct7.fm
f3fs_elct7.fm - The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronics I Section Student Name Electronics II Final Examination Problems Points.. 3 3. 5 Total 40 Was the exam fair? yes no Analog Electronics f3fs_elct7.fm
Schedule. ECEN 301 Discussion #20 Exam 2 Review 1. Lab Due date. Title Chapters HW Due date. Date Day Class No. 10 Nov Mon 20 Exam Review.
 Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
Schedule Date Day lass No. 0 Nov Mon 0 Exam Review Nov Tue Title hapters HW Due date Nov Wed Boolean Algebra 3. 3.3 ab Due date AB 7 Exam EXAM 3 Nov Thu 4 Nov Fri Recitation 5 Nov Sat 6 Nov Sun 7 Nov Mon
2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM In the circuit shown above, resistors 1 and 2 of resistance R 1 and R 2, respectively, and an inductor of inductance L are connected to a battery of emf e and
2005 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM In the circuit shown above, resistors 1 and 2 of resistance R 1 and R 2, respectively, and an inductor of inductance L are connected to a battery of emf e and
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: NETWORK ANALYSIS (10ES34) NOTE: FOR NUMERICAL PROBLEMS FOR ALL UNITS EXCEPT UNIT 5 REFER THE E-BOOK ENGINEERING CIRCUIT ANALYSIS, 7 th EDITION HAYT AND KIMMERLY. PAGE NUMBERS OF
SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS
 APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE CIRCUIT ANALYSIS
 SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1. Introduction A sinusoidal current has the following form: where I m is the amplitude value; ω=2 πf is the angular frequency; φ is the phase shift. i (t )=I m.sin
SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE CIRCUIT ANALYSIS 1. Introduction A sinusoidal current has the following form: where I m is the amplitude value; ω=2 πf is the angular frequency; φ is the phase shift. i (t )=I m.sin
2. The following diagram illustrates that voltage represents what physical dimension?
 BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
ECE Circuit Theory. Final Examination. December 5, 2008
 ECE 212 H1F Pg 1 of 12 ECE 212 - Circuit Theory Final Examination December 5, 2008 1. Policy: closed book, calculators allowed. Show all work. 2. Work in the provided space. 3. The exam has 3 problems
ECE 212 H1F Pg 1 of 12 ECE 212 - Circuit Theory Final Examination December 5, 2008 1. Policy: closed book, calculators allowed. Show all work. 2. Work in the provided space. 3. The exam has 3 problems
Basic RL and RC Circuits R-L TRANSIENTS: STORAGE CYCLE. Engineering Collage Electrical Engineering Dep. Dr. Ibrahim Aljubouri
 st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
st Class Basic RL and RC Circuits The RL circuit with D.C (steady state) The inductor is short time at Calculate the inductor current for circuits shown below. I L E R A I L E R R 3 R R 3 I L I L R 3 R
Review of DC Electric Circuit. DC Electric Circuits Examples (source:
 Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
Review of DC Electric Circuit DC Electric Circuits Examples (source: http://hyperphysics.phyastr.gsu.edu/hbase/electric/dcex.html) 1 Review - DC Electric Circuit Multisim Circuit Simulation DC Circuit
mywbut.com Lesson 16 Solution of Current in AC Parallel and Seriesparallel
 esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
esson 6 Solution of urrent in Parallel and Seriesparallel ircuits n the last lesson, the following points were described:. How to compute the total impedance/admittance in series/parallel circuits?. How
EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2013 Homework #8 solution
 EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2013 Homework #8 solution 5.110. The following table summarizes some of the basic attributes of a number of BJTs of different types, operating as amplifiers under various
EE 321 Analog Electronics, Fall 2013 Homework #8 solution 5.110. The following table summarizes some of the basic attributes of a number of BJTs of different types, operating as amplifiers under various
R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits
 P517/617 Lec4, P1 R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits Consider the following RLC series circuit What's R? Simplest way to solve for is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation. X L X C in 0
P517/617 Lec4, P1 R-L-C Circuits and Resonant Circuits Consider the following RLC series circuit What's R? Simplest way to solve for is to use voltage divider equation in complex notation. X L X C in 0
ENGR 2405 Chapter 8. Second Order Circuits
 ENGR 2405 Chapter 8 Second Order Circuits Overview The previous chapter introduced the concept of first order circuits. This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second
ENGR 2405 Chapter 8 Second Order Circuits Overview The previous chapter introduced the concept of first order circuits. This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second
ELEC 202 Electric Circuit Analysis II Lecture 10(a) Complex Arithmetic and Rectangular/Polar Forms
 Dr. Gregory J. Mazzaro Spring 2016 ELEC 202 Electric Circuit Analysis II Lecture 10(a) Complex Arithmetic and Rectangular/Polar Forms THE CITADEL, THE MILITARY COLLEGE OF SOUTH CAROLINA 171 Moultrie Street,
Dr. Gregory J. Mazzaro Spring 2016 ELEC 202 Electric Circuit Analysis II Lecture 10(a) Complex Arithmetic and Rectangular/Polar Forms THE CITADEL, THE MILITARY COLLEGE OF SOUTH CAROLINA 171 Moultrie Street,
Basic Electrical Circuits Analysis ECE 221
 Basic Electrical Circuits Analysis ECE 221 PhD. Khodr Saaifan http://trsys.faculty.jacobs-university.de k.saaifan@jacobs-university.de 1 2 Reference: Electric Circuits, 8th Edition James W. Nilsson, and
Basic Electrical Circuits Analysis ECE 221 PhD. Khodr Saaifan http://trsys.faculty.jacobs-university.de k.saaifan@jacobs-university.de 1 2 Reference: Electric Circuits, 8th Edition James W. Nilsson, and
D C Circuit Analysis and Network Theorems:
 UNIT-1 D C Circuit Analysis and Network Theorems: Circuit Concepts: Concepts of network, Active and passive elements, voltage and current sources, source transformation, unilateral and bilateral elements,
UNIT-1 D C Circuit Analysis and Network Theorems: Circuit Concepts: Concepts of network, Active and passive elements, voltage and current sources, source transformation, unilateral and bilateral elements,
I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers
 I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers A. Common-Emitter Amplifier: V i SUP i OUT R S V BIAS R L v OUT V Operating Point analysis: 0, R s 0, r o --->, r oc --->, R L ---> Find V BIAS such that I C
I. Frequency Response of Voltage Amplifiers A. Common-Emitter Amplifier: V i SUP i OUT R S V BIAS R L v OUT V Operating Point analysis: 0, R s 0, r o --->, r oc --->, R L ---> Find V BIAS such that I C
Thevenin Norton Equivalencies - GATE Study Material in PDF
 Thevenin Norton Equivalencies - GATE Study Material in PDF In these GATE 2018 Notes, we explain the Thevenin Norton Equivalencies. Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems are two equally valid methods of reducing
Thevenin Norton Equivalencies - GATE Study Material in PDF In these GATE 2018 Notes, we explain the Thevenin Norton Equivalencies. Thevenin s and Norton s Theorems are two equally valid methods of reducing
ECE Spring 2015 Final Exam
 ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
ECE 20100 Spring 2015 Final Exam May 7, 2015 Section (circle below) Jung (1:30) 0001 Qi (12:30) 0002 Peleato (9:30) 0004 Allen (10:30) 0005 Zhu (4:30) 0006 Name PUID Instructions 1. DO NOT START UNTIL
ECE 45 Average Power Review
 UC San Diego J. Connelly Complex Power ECE 45 Average Power Review When dealing with time-dependent voltage and currents, we have to consider a more general definition of power. We can calculate the instantaneous
UC San Diego J. Connelly Complex Power ECE 45 Average Power Review When dealing with time-dependent voltage and currents, we have to consider a more general definition of power. We can calculate the instantaneous
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9
 EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
EECE 2150 Circuits and Signals Final Exam Fall 2016 Dec 9 Name: Instructions: Write your name and section number on all pages Closed book, closed notes; Computers and cell phones are not allowed You can
Solved Problems. Electric Circuits & Components. 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown.
 Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
Solved Problems Electric Circuits & Components 1-1 Write the KVL equation for the circuit shown. 1-2 Write the KCL equation for the principal node shown. 1-2A In the DC circuit given in Fig. 1, find (i)
EIT Review 1. FE/EIT Review. Circuits. John A. Camara, Electrical Engineering Reference Manual, 6 th edition, Professional Publications, Inc, 2002.
 FE/EIT eview Circuits Instructor: uss Tatro eferences John A. Camara, Electrical Engineering eference Manual, 6 th edition, Professional Publications, Inc, 00. John A. Camara, Practice Problems for the
FE/EIT eview Circuits Instructor: uss Tatro eferences John A. Camara, Electrical Engineering eference Manual, 6 th edition, Professional Publications, Inc, 00. John A. Camara, Practice Problems for the
ELEC 2501 AB. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock midterm UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the midterm in 3 hour(s). Work on your own. Keep your notes and textbook closed. Attempt every question.
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock midterm UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the midterm in 3 hour(s). Work on your own. Keep your notes and textbook closed. Attempt every question.
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE
 EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 18 121025 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review RMS Values Complex Numbers Phasors Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis
EE292: Fundamentals of ECE Fall 2012 TTh 10:00-11:15 SEB 1242 Lecture 18 121025 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ee292/ 2 Outline Review RMS Values Complex Numbers Phasors Complex Impedance Circuit Analysis
