Complex Social System, Elections. Introduction to Network Analysis 1
|
|
|
- Sheila Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Complex Social System, Elections Introduction to Network Analysis 1
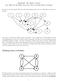
2 Complex Social System, Network I person A voted for B A is more central than B if more people voted for A In-degree centrality index = number of in-edges Introduction to Network Analysis 2
3 Complex Social System, Network II person A convinced B Central because it mediates information between groups - Betweeness centrality (between groups) Another example: friendship network, degree-based centrality Introduction to Network Analysis 3
4 Measures and Metrics Q: What are the most important nodes and edges? Degree centrality: Closeness centrality: Edge removal centrality: There are many different ways to quantify the importance Can you come up with your interesting new measure of importance? Is it important for different types of networks? Can you compute it efficiently? Introduction to Network Analysis 4
5 Eccentricity from U. Brandes Network Analysis Introduction to Network Analysis 5
6 Eigenvector Centrality degree centrality Repeating last step t times Rewrite this linear combination with eigenvectors of A d(i)=2 Eigenvector centrality is defined by values Introduction to Network Analysis 6
7 Eigenvector Centrality Introduction to Network Analysis 7
8 PageRank Markov Chain: probabilities of visiting the pages after k steps is P k x. Problem: dangling nodes (d + (i)=0) Solution: damping factor a (usually small) transition matrix regular random walk teleportation Note: P is still a Markov matrix with no 0s Introduction to Network Analysis 8
9 Eigenproblem-based Centralities: Computational Problems These problems are equivalent to solving eigenproblems, namely, P v = v. Gaussian elimination is very expensive. Iterative computation of P v is less expensive because P is usually sparse. Principal eigenvector of P is a PageRank. It can be solved by Power Method (iterative) and by Algebraic Multigrid. Parallel computation Sublinear computation Updating PageRank vector, evolving networks Further reading: Berkhin ``A Survey on PageRank computing Langville, Meyer ``Deeper Inside PageRank Introduction to Network Analysis 9
10 Hubs and Authorities Observation: In some networks a vertex may be important if it points to others with high centrality. Examples: X, Y, Z Cool Survey 9/11 contacts X sends an information to many leaders but they don t know X. X is influential. Scientific paper citations Raddicchi et al. Diffusion of scientific credits and the ranking of scientists Introduction to Network Analysis 10
11 Hubs and Authorities Authorities are nodes that contain useful information on a topic of interest. Hubs are nodes that point to best authorities. HITS Algorithm computes for each node i its authority and hub centralities x i and y i, respectively same leading (see eigenvector centrality) eigenvalue in both cases! All eigenvalues of AA T and A T A are the same (check and prove!). Multiplying both sides of the first equation by A T gives i.e., once we have a vector of authorities, the hub centrality can be calculated faster Note: Authority centrality of A = Eigenvector centrality of co-citation matrix AA T Current applications: Teoma.com and Ask.com Further reading: Kleinberg, Authoritative sources in a hyper-linked environment Introduction to Network Analysis 11
12 Closeness Centrality Problems: i-j path is infinity (for example different connected components) Solution: Harmonic Mean Distance Centrality In practice C spans relatively small range of values Geodesic distances are integers, often small because distance increases logarithmically with the size of the network Example: Internet Movie Database highest centrality = , lowest centrality = , ratio 3.6 for 500K actors Introduction to Network Analysis 12
13 Shortest Paths-based Centrality is a number of s-t shortest paths containing i is a number of all s-t shortest-paths Observation: In practice, communication or transport of goods in networks follow different kinds of paths that tend to be shortest. Question: How much work can be done by a node? Disadvantage? Stress Centrality for nodes Relation between stress centralities Betweenness Centrality for edges Interpretation: BC is a quantification of communication control which has a vertex over all pairs of nodes. Introduction to Network Analysis 13
Link Analysis. Leonid E. Zhukov
 Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Structural Analysis and Visualization
Link Analysis Ranking
 Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Link Analysis Ranking How do search engines decide how to rank your query results? Guess why Google ranks the query results the way it does How would you do it? Naïve ranking of query results Given query
Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks
 Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Network Analysis Degree Distribution: The case of Citation Networks Papers (in almost all fields) refer to works done earlier on same/related topics Citations A network can be defined as Each node is
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks
 Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
Node Centrality and Ranking on Networks Leonid E. Zhukov School of Data Analysis and Artificial Intelligence Department of Computer Science National Research University Higher School of Economics Social
DATA MINING LECTURE 13. Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS
 DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
DATA MINING LECTURE 3 Link Analysis Ranking PageRank -- Random walks HITS How to organize the web First try: Manually curated Web Directories How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu How to organize/navigate it? First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart
Finding central nodes in large networks
 Finding central nodes in large networks Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands Woudschoten Conference 2017 Complex networks Networks: Internet, WWW, social
Finding central nodes in large networks Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands Woudschoten Conference 2017 Complex networks Networks: Internet, WWW, social
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu 2/7/2012 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive Datasets 2 Web pages are not equally important www.joe-schmoe.com
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining. Prof. Matteo Matteucci
 Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Link Analysis Information Retrieval and Data Mining Prof. Matteo Matteucci Hyperlinks for Indexing and Ranking 2 Page A Hyperlink Page B Intuitions The anchor text might describe the target page B Anchor
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides
 Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Thanks to Jure Leskovec, Stanford and Panayiotis Tsaparas, Univ. of Ioannina for slides Web Search: How to Organize the Web? Ranking Nodes on Graphs Hubs and Authorities PageRank How to Solve PageRank
Online Social Networks and Media. Link Analysis and Web Search
 Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Online Social Networks and Media Link Analysis and Web Search How to Organize the Web First try: Human curated Web directories Yahoo, DMOZ, LookSmart How to organize the web Second try: Web Search Information
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence
 Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Web Structure Mining Nodes, Links and Influence 1 Outline 1. Importance of nodes 1. Centrality 2. Prestige 3. Page Rank 4. Hubs and Authority 5. Metrics comparison 2. Link analysis 3. Influence model 1.
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (2 of 4) 19 Computing spectral ranking with the push procedure
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 19-04/02/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (2 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 19-04/02/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (2 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
CS 277: Data Mining. Mining Web Link Structure. CS 277: Data Mining Lectures Analyzing Web Link Structure Padhraic Smyth, UC Irvine
 CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
CS 277: Data Mining Mining Web Link Structure Class Presentations In-class, Tuesday and Thursday next week 2-person teams: 6 minutes, up to 6 slides, 3 minutes/slides each person 1-person teams 4 minutes,
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank. Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018
 Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Lab 8: Measuring Graph Centrality - PageRank Monday, November 5 CompSci 531, Fall 2018 Outline Measuring Graph Centrality: Motivation Random Walks, Markov Chains, and Stationarity Distributions Google
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis. Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa
 Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Introduction to Search Engine Technology Introduction to Link Structure Analysis Ronny Lempel Yahoo Labs, Haifa Outline Anchor-text indexing Mathematical Background Motivation for link structure analysis
Link Analysis. Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze
 Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
Link Analysis Reference: Introduction to Information Retrieval by C. Manning, P. Raghavan, H. Schutze 1 The Web as a Directed Graph Page A Anchor hyperlink Page B Assumption 1: A hyperlink between pages
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68
 CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
CSI 445/660 Part 6 (Centrality Measures for Networks) 6 1 / 68 References 1 L. Freeman, Centrality in Social Networks: Conceptual Clarification, Social Networks, Vol. 1, 1978/1979, pp. 215 239. 2 S. Wasserman
A Note on Google s PageRank
 A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
A Note on Google s PageRank According to Google, google-search on a given topic results in a listing of most relevant web pages related to the topic. Google ranks the importance of webpages according to
Node and Link Analysis
 Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
Node and Link Analysis Leonid E. Zhukov School of Applied Mathematics and Information Science National Research University Higher School of Economics 10.02.2014 Leonid E. Zhukov (HSE) Lecture 5 10.02.2014
PageRank. Ryan Tibshirani /36-662: Data Mining. January Optional reading: ESL 14.10
 PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
PageRank Ryan Tibshirani 36-462/36-662: Data Mining January 24 2012 Optional reading: ESL 14.10 1 Information retrieval with the web Last time we learned about information retrieval. We learned how to
Pseudocode for calculating Eigenfactor TM Score and Article Influence TM Score using data from Thomson-Reuters Journal Citations Reports
 Pseudocode for calculating Eigenfactor TM Score and Article Influence TM Score using data from Thomson-Reuters Journal Citations Reports Jevin West and Carl T. Bergstrom November 25, 2008 1 Overview There
Pseudocode for calculating Eigenfactor TM Score and Article Influence TM Score using data from Thomson-Reuters Journal Citations Reports Jevin West and Carl T. Bergstrom November 25, 2008 1 Overview There
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes
 Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes Dario Fasino, University of Udine (Italy) Lecture notes for the second part of the course Nonnegative and spectral matrix
Applications to network analysis: Eigenvector centrality indices Lecture notes Dario Fasino, University of Udine (Italy) Lecture notes for the second part of the course Nonnegative and spectral matrix
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors
 MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
MultiRank and HAR for Ranking Multi-relational Data, Transition Probability Tensors, and Multi-Stochastic Tensors Michael K. Ng Centre for Mathematical Imaging and Vision and Department of Mathematics
How does Google rank webpages?
 Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Linear Algebra Spring 016 How does Google rank webpages? Dept. of Internet and Multimedia Eng. Konkuk University leehw@konkuk.ac.kr 1 Background on search engines Outline HITS algorithm (Jon Kleinberg)
Introduction to Data Mining
 Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Introduction to Data Mining Lecture #9: Link Analysis Seoul National University 1 In This Lecture Motivation for link analysis Pagerank: an important graph ranking algorithm Flow and random walk formulation
Data and Algorithms of the Web
 Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
Data and Algorithms of the Web Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank some slides from: Anand Rajaraman, Jeffrey D. Ullman InfoLab (Stanford University) Link Analysis Algorithms Page Rank Hubs and Authorities
ELEC6910Q Analytics and Systems for Social Media and Big Data Applications Lecture 3 Centrality, Similarity, and Strength Ties
 ELEC6910Q Analytics and Systems for Social Media and Big Data Applications Lecture 3 Centrality, Similarity, and Strength Ties Prof. James She james.she@ust.hk 1 Last lecture 2 Selected works from Tutorial
ELEC6910Q Analytics and Systems for Social Media and Big Data Applications Lecture 3 Centrality, Similarity, and Strength Ties Prof. James She james.she@ust.hk 1 Last lecture 2 Selected works from Tutorial
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation
 Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
Computing PageRank using Power Extrapolation Taher Haveliwala, Sepandar Kamvar, Dan Klein, Chris Manning, and Gene Golub Stanford University Abstract. We present a novel technique for speeding up the computation
Slides based on those in:
 Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
Spyros Kontogiannis & Christos Zaroliagis Slides based on those in: http://www.mmds.org High dim. data Graph data Infinite data Machine learning Apps Locality sensitive hashing PageRank, SimRank Filtering
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University.
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu What is the structure of the Web? How is it organized? 2/7/2011 Jure Leskovec, Stanford C246: Mining Massive
0.1 Naive formulation of PageRank
 PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
PageRank is a ranking system designed to find the best pages on the web. A webpage is considered good if it is endorsed (i.e. linked to) by other good webpages. The more webpages link to it, and the more
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
6.207/14.15: Networks Lecture 7: Search on Networks: Navigation and Web Search Daron Acemoglu and Asu Ozdaglar MIT September 30, 2009 1 Networks: Lecture 7 Outline Navigation (or decentralized search)
1998: enter Link Analysis
 1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
1998: enter Link Analysis uses hyperlink structure to focus the relevant set combine traditional IR score with popularity score Page and Brin 1998 Kleinberg Web Information Retrieval IR before the Web
CS54701 Information Retrieval. Link Analysis. Luo Si. Department of Computer Science Purdue University. Borrowed Slides from Prof.
 CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
CS54701 Information Retrieval Link Analysis Luo Si Department of Computer Science Purdue University Borrowed Slides from Prof. Rong Jin (MSU) Citation Analysis Web Structure Web is a graph Each web site
Google PageRank. Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano
 Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
Google PageRank Francesco Ricci Faculty of Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano fricci@unibz.it 1 Content p Linear Algebra p Matrices p Eigenvalues and eigenvectors p Markov chains p Google
How works. or How linear algebra powers the search engine. M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University
 How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
How works or How linear algebra powers the search engine M. Ram Murty, FRSC Queen s Research Chair Queen s University From: gomath.com/geometry/ellipse.php Metric mishap causes loss of Mars orbiter
Data Mining and Matrices
 Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Data Mining and Matrices 10 Graphs II Rainer Gemulla, Pauli Miettinen Jul 4, 2013 Link analysis The web as a directed graph Set of web pages with associated textual content Hyperlinks between webpages
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 2 Web pages are important if people visit them a lot. But we can t watch everybody using the Web. A good surrogate for visiting pages is to assume people follow links
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University 2 Web pages are important if people visit them a lot. But we can t watch everybody using the Web. A good surrogate for visiting pages is to assume people follow links
CS47300: Web Information Search and Management
 CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
CS473: Web Information Search and Management Using Graph Structure for Retrieval Prof. Chris Clifton 24 September 218 Material adapted from slides created by Dr. Rong Jin (formerly Michigan State, now
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper)
 PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
PageRank: The Math-y Version (Or, What To Do When You Can t Tear Up Little Pieces of Paper) In class, we saw this graph, with each node representing people who are following each other on Twitter: Our
Analysis of Google s PageRank
 Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills AN05 p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web page [Brin & Page 1998]
Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills AN05 p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web page [Brin & Page 1998]
The Push Algorithm for Spectral Ranking
 The Push Algorithm for Spectral Ranking Paolo Boldi Sebastiano Vigna March 8, 204 Abstract The push algorithm was proposed first by Jeh and Widom [6] in the context of personalized PageRank computations
The Push Algorithm for Spectral Ranking Paolo Boldi Sebastiano Vigna March 8, 204 Abstract The push algorithm was proposed first by Jeh and Widom [6] in the context of personalized PageRank computations
Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank
 Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills Cedya p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance
Mathematical Properties & Analysis of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca M. Wills Cedya p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance
Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute
 Rethinking Network Structure Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute Università della Svizzera Italiana, December 16, 2011 Measuring network structure Central nodes Community structure Strength
Rethinking Network Structure Kristina Lerman USC Information Sciences Institute Università della Svizzera Italiana, December 16, 2011 Measuring network structure Central nodes Community structure Strength
Math 2J Lecture 16-11/02/12
 Math 2J Lecture 16-11/02/12 William Holmes Markov Chain Recap The population of a town is 100000. Each person is either independent, democrat, or republican. In any given year, each person can choose to
Math 2J Lecture 16-11/02/12 William Holmes Markov Chain Recap The population of a town is 100000. Each person is either independent, democrat, or republican. In any given year, each person can choose to
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks
 ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
ECEN 689 Special Topics in Data Science for Communications Networks Nick Duffield Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Texas A&M University Lecture 8 Random Walks, Matrices and PageRank Graphs
LINK ANALYSIS. Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS
 LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
LINK ANALYSIS Dr. Gjergji Kasneci Introduction to Information Retrieval WS 2012-13 1 Outline Intro Basics of probability and information theory Retrieval models Retrieval evaluation Link analysis Models
Improving Diversity in Ranking using Absorbing Random Walks
 Improving Diversity in Ranking using Absorbing Random Walks Andrew B. Goldberg with Xiaojin Zhu, Jurgen Van Gael, and David Andrzejewski Department of Computer Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison
Improving Diversity in Ranking using Absorbing Random Walks Andrew B. Goldberg with Xiaojin Zhu, Jurgen Van Gael, and David Andrzejewski Department of Computer Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University.
 Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Slide source: Mining of Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Anand Rajaraman, Jeff Ullman Stanford University http://www.mmds.org #1: C4.5 Decision Tree - Classification (61 votes) #2: K-Means - Clustering
Link Analysis. Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016
 Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
Link Analysis Stony Brook University CSE545, Fall 2016 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 The Web, circa 1998 Match keywords, language (information retrieval) Explore directory The Web, circa 1998
IR: Information Retrieval
 / 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
/ 44 IR: Information Retrieval FIB, Master in Innovation and Research in Informatics Slides by Marta Arias, José Luis Balcázar, Ramon Ferrer-i-Cancho, Ricard Gavaldá Department of Computer Science, UPC
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu November 16, 2015 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
1 Searching the World Wide Web
 Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
Hubs and Authorities in a Hyperlinked Environment 1 Searching the World Wide Web Because diverse users each modify the link structure of the WWW within a relatively small scope by creating web-pages on
As it is not necessarily possible to satisfy this equation, we just ask for a solution to the more general equation
 Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Graphs and Networks Page 1 Lecture 2, Ranking 1 Tuesday, September 12, 2006 1:14 PM I. II. I. How search engines work: a. Crawl the web, creating a database b. Answer query somehow, e.g. grep. (ex. Funk
Extrapolation Methods for Accelerating PageRank Computations
 Extrapolation Methods for Accelerating PageRank Computations Sepandar D. Kamvar Stanford University sdkamvar@stanford.edu Taher H. Haveliwala Stanford University taherh@cs.stanford.edu Christopher D. Manning
Extrapolation Methods for Accelerating PageRank Computations Sepandar D. Kamvar Stanford University sdkamvar@stanford.edu Taher H. Haveliwala Stanford University taherh@cs.stanford.edu Christopher D. Manning
Local properties of PageRank and graph limits. Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands MIPT 2018
 Local properties of PageRank and graph limits Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands MIPT 2018 Centrality in networks Network as a graph G = (V, E) Centrality
Local properties of PageRank and graph limits Nelly Litvak University of Twente Eindhoven University of Technology, The Netherlands MIPT 2018 Centrality in networks Network as a graph G = (V, E) Centrality
Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search
 CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
CCST907 Hidden Order in Daily Life: A Mathematical Perspective Lecture 7 Mathematics behind Internet Search Dr. S. P. Yung (907A) Dr. Z. Hua (907B) Department of Mathematics, HKU Outline Google is the
Web Ranking. Classification (manual, automatic) Link Analysis (today s lesson)
 Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Link Analysis Web Ranking Documents on the web are first ranked according to their relevance vrs the query Additional ranking methods are needed to cope with huge amount of information Additional ranking
Information Retrieval and Search. Web Linkage Mining. Miłosz Kadziński
 Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
Web Linkage Analysis D24 D4 : Web Linkage Mining Miłosz Kadziński Institute of Computing Science Poznan University of Technology, Poland www.cs.put.poznan.pl/mkadzinski/wpi Web mining: Web Mining Discovery
Why matrices matter. Paul Van Dooren, UCL, CESAME
 Why matrices matter Paul Van Dooren, UCL, CESAME Where are matrices coming from? ma trix (mā'trĭks) n., pl., ma tri ces (mā'trĭ-sēz') Anatomy. The womb (uterus).... Geology. The solid matter in which a
Why matrices matter Paul Van Dooren, UCL, CESAME Where are matrices coming from? ma trix (mā'trĭks) n., pl., ma tri ces (mā'trĭ-sēz') Anatomy. The womb (uterus).... Geology. The solid matter in which a
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity. Due July 18, 2014
 Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Class President: A Network Approach to Popularity Due July 8, 24 Instructions. Due Fri, July 8 at :59 PM 2. Work in groups of up to 3 3. Type up the report, and submit as a pdf on D2L 4. Attach the code
Krylov Subspace Methods to Calculate PageRank
 Krylov Subspace Methods to Calculate PageRank B. Vadala-Roth REU Final Presentation August 1st, 2013 How does Google Rank Web Pages? The Web The Graph (A) Ranks of Web pages v = v 1... Dominant Eigenvector
Krylov Subspace Methods to Calculate PageRank B. Vadala-Roth REU Final Presentation August 1st, 2013 How does Google Rank Web Pages? The Web The Graph (A) Ranks of Web pages v = v 1... Dominant Eigenvector
Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4)
 Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Stat260/CS294: Spectral Graph Methods Lecture 18-03/31/2015 Lecture: Local Spectral Methods (1 of 4) Lecturer: Michael Mahoney Scribe: Michael Mahoney Warning: these notes are still very rough. They provide
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications
 Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
Data science with multilayer networks: Mathematical foundations and applications CDSE Days University at Buffalo, State University of New York Monday April 9, 2018 Dane Taylor Assistant Professor of Mathematics
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition
 Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2016 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2016 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y
 Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Page rank computation HPC course project a.y. 2015-16 Compute efficient and scalable Pagerank MPI, Multithreading, SSE 1 PageRank PageRank is a link analysis algorithm, named after Brin & Page [1], and
Calculating Web Page Authority Using the PageRank Algorithm
 Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jacob Miles Prystowsky and Levi Gill Math 45, Fall 2005 1 Introduction 1.1 Abstract In this document, we examine how the Google Internet search engine uses the PageRank algorithm to assign quantitatively
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University
 Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
Jeffrey D. Ullman Stanford University We ve had our first HC cases. Please, please, please, before you do anything that might violate the HC, talk to me or a TA to make sure it is legitimate. It is much
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Lecture 6: Numerical Linear Algebra: Applications in Machine Learning Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis April 27, 2017 Principal Component Analysis Principal
PageRank algorithm Hubs and Authorities. Data mining. Web Data Mining PageRank, Hubs and Authorities. University of Szeged.
 Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
Web Data Mining PageRank, University of Szeged Why ranking web pages is useful? We are starving for knowledge It earns Google a bunch of money. How? How does the Web looks like? Big strongly connected
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities
 6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
6.207/14.15: Networks Lectures 4, 5 & 6: Linear Dynamics, Markov Chains, Centralities 1 Outline Outline Dynamical systems. Linear and Non-linear. Convergence. Linear algebra and Lyapunov functions. Markov
Eigenvalues of Exponentiated Adjacency Matrices
 Eigenvalues of Exponentiated Adjacency Matrices Tracy Powell Lesley A Ward, Advisor Estelle Basor, Reader November 21, 25 Department of Mathematics 2 Chapter Problem A graph G is made up of vertices, or
Eigenvalues of Exponentiated Adjacency Matrices Tracy Powell Lesley A Ward, Advisor Estelle Basor, Reader November 21, 25 Department of Mathematics 2 Chapter Problem A graph G is made up of vertices, or
UpdatingtheStationary VectorofaMarkovChain. Amy Langville Carl Meyer
 UpdatingtheStationary VectorofaMarkovChain Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC NSMC 9/4/2003 Outline Updating and Pagerank Aggregation Partitioning
UpdatingtheStationary VectorofaMarkovChain Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC NSMC 9/4/2003 Outline Updating and Pagerank Aggregation Partitioning
Complex Networks CSYS/MATH 303, Spring, Prof. Peter Dodds
 Complex Networks CSYS/MATH 303, Spring, 2011 Prof. Peter Dodds Department of Mathematics & Statistics Center for Complex Systems Vermont Advanced Computing Center University of Vermont Licensed under the
Complex Networks CSYS/MATH 303, Spring, 2011 Prof. Peter Dodds Department of Mathematics & Statistics Center for Complex Systems Vermont Advanced Computing Center University of Vermont Licensed under the
Math 304 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks.
 Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Math 30 Handout: Linear algebra, graphs, and networks. December, 006. GRAPHS AND ADJACENCY MATRICES. Definition. A graph is a collection of vertices connected by edges. A directed graph is a graph all
Multimedia Databases - 68A6 Final Term - exercises
 Multimedia Databases - 8A Final Term - exercises Exercises for the preparation to the final term June, the 1th 00 quiz 1. approximation of cosine similarity An approximate computation of the cosine similarity
Multimedia Databases - 8A Final Term - exercises Exercises for the preparation to the final term June, the 1th 00 quiz 1. approximation of cosine similarity An approximate computation of the cosine similarity
arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Apr 2017
![arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Apr 2017 arxiv: v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Apr 2017](/thumbs/93/111385143.jpg) arxiv:1704.08027v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Apr 2017 Ranking in evolving complex networks CONTENTS Hao Liao, 1 Manuel Sebastian Mariani, 2, 1, a) Matúš Medo, 3, 2, 4, b) Yi-Cheng Zhang, 2 and Ming-Yang Zhou
arxiv:1704.08027v1 [physics.soc-ph] 26 Apr 2017 Ranking in evolving complex networks CONTENTS Hao Liao, 1 Manuel Sebastian Mariani, 2, 1, a) Matúš Medo, 3, 2, 4, b) Yi-Cheng Zhang, 2 and Ming-Yang Zhou
Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications
 Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and Applications p. 1/36 Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications Che-Rung Lee cherung@gmail.com National Tsing Hua University Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and
Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and Applications p. 1/36 Eigenvalue Problems Computation and Applications Che-Rung Lee cherung@gmail.com National Tsing Hua University Eigenvalue ProblemsComputation and
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES
 CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
CS6220: DATA MINING TECHNIQUES Mining Graph/Network Data Instructor: Yizhou Sun yzsun@ccs.neu.edu March 16, 2016 Methods to Learn Classification Clustering Frequent Pattern Mining Matrix Data Decision
Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Enviroment
 Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Enviroment Dimitris Sakavalas June 15, 2010 Outline Introduction Problem description Authorities and Broad-topic queries Algorithm outline Construction of a Focused
Authoritative Sources in a Hyperlinked Enviroment Dimitris Sakavalas June 15, 2010 Outline Introduction Problem description Authorities and Broad-topic queries Algorithm outline Construction of a Focused
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition
 Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2018 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Linear Algebra review Powers of a diagonalizable matrix Spectral decomposition Prof. Tesler Math 283 Fall 2018 Also see the separate version of this with Matlab and R commands. Prof. Tesler Diagonalizing
Analysis and Computation of Google s PageRank
 Analysis and Computation of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca S. Wills ANAW p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web
Analysis and Computation of Google s PageRank Ilse Ipsen North Carolina State University, USA Joint work with Rebecca S. Wills ANAW p.1 PageRank An objective measure of the citation importance of a web
Cutting Graphs, Personal PageRank and Spilling Paint
 Graphs and Networks Lecture 11 Cutting Graphs, Personal PageRank and Spilling Paint Daniel A. Spielman October 3, 2013 11.1 Disclaimer These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what
Graphs and Networks Lecture 11 Cutting Graphs, Personal PageRank and Spilling Paint Daniel A. Spielman October 3, 2013 11.1 Disclaimer These notes are not necessarily an accurate representation of what
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval
 Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
Lecture 12: Link Analysis for Web Retrieval Trevor Cohn COMP90042, 2015, Semester 1 What we ll learn in this lecture The web as a graph Page-rank method for deriving the importance of pages Hubs and authorities
2. The Power Method for Eigenvectors
 2. Power Method We now describe the power method for computing the dominant eigenpair. Its extension to the inverse power method is practical for finding any eigenvalue provided that a good initial approximation
2. Power Method We now describe the power method for computing the dominant eigenpair. Its extension to the inverse power method is practical for finding any eigenvalue provided that a good initial approximation
Wiki Definition. Reputation Systems I. Outline. Introduction to Reputations. Yury Lifshits. HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte
 Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
Reputation Systems I HITS, PageRank, SALSA, ebay, EigenTrust, VKontakte Yury Lifshits Wiki Definition Reputation is the opinion (more technically, a social evaluation) of the public toward a person, a
CS 3750 Advanced Machine Learning. Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya
 CS 375 Advanced Machine Learning Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya Outline SVD and LSI Kleinberg s Algorithm PageRank Algorithm Vector Space Model Vector space model represents
CS 375 Advanced Machine Learning Applications of SVD and PCA (LSA and Link analysis) Cem Akkaya Outline SVD and LSI Kleinberg s Algorithm PageRank Algorithm Vector Space Model Vector space model represents
Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms
 Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms dataminingbook.info Mohammed J. Zaki 1 Wagner Meira Jr. 2 1 Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA
Data Mining and Analysis: Fundamental Concepts and Algorithms dataminingbook.info Mohammed J. Zaki 1 Wagner Meira Jr. 2 1 Department of Computer Science Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY, USA
Hub, Authority and Relevance Scores in Multi-Relational Data for Query Search
 Hub, Authority and Relevance Scores in Multi-Relational Data for Query Search Xutao Li 1 Michael Ng 2 Yunming Ye 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Shenzhen Graduate School, Harbin Institute of Technology,
Hub, Authority and Relevance Scores in Multi-Relational Data for Query Search Xutao Li 1 Michael Ng 2 Yunming Ye 1 1 Department of Computer Science, Shenzhen Graduate School, Harbin Institute of Technology,
AXIOMS FOR CENTRALITY
 AXIOMS FOR CENTRALITY From a paper by Paolo Boldi, Sebastiano Vigna Università degli Studi di Milano! Internet Math., 10(3-4):222 262, 2014. Proc. 13th ICDMW. IEEE, 2013. Proc. 4th WebScience. ACM, 2012.!
AXIOMS FOR CENTRALITY From a paper by Paolo Boldi, Sebastiano Vigna Università degli Studi di Milano! Internet Math., 10(3-4):222 262, 2014. Proc. 13th ICDMW. IEEE, 2013. Proc. 4th WebScience. ACM, 2012.!
On the eigenvalues of specially low-rank perturbed matrices
 On the eigenvalues of specially low-rank perturbed matrices Yunkai Zhou April 12, 2011 Abstract We study the eigenvalues of a matrix A perturbed by a few special low-rank matrices. The perturbation is
On the eigenvalues of specially low-rank perturbed matrices Yunkai Zhou April 12, 2011 Abstract We study the eigenvalues of a matrix A perturbed by a few special low-rank matrices. The perturbation is
Bounds on the Ratio of Eigenvalues
 Bounds on the Ratio of Eigenvalues Tracy Powell Lesley A Ward, Advisor Estelle Basor, Reader December 0, 2005 Department of Mathematics Abstract In this paper, we find lower and upper bounds for the leading
Bounds on the Ratio of Eigenvalues Tracy Powell Lesley A Ward, Advisor Estelle Basor, Reader December 0, 2005 Department of Mathematics Abstract In this paper, we find lower and upper bounds for the leading
Uncertainty and Randomization
 Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Uncertainty and Randomization The PageRank Computation in Google Roberto Tempo IEIIT-CNR Politecnico di Torino tempo@polito.it 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 1993: Robustness of Linear Systems 16 Years
Updating PageRank. Amy Langville Carl Meyer
 Updating PageRank Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC SCCM 11/17/2003 Indexing Google Must index key terms on each page Robots crawl the web software
Updating PageRank Amy Langville Carl Meyer Department of Mathematics North Carolina State University Raleigh, NC SCCM 11/17/2003 Indexing Google Must index key terms on each page Robots crawl the web software
Ten good reasons to use the Eigenfactor TM metrics
 Ten good reasons to use the Eigenfactor TM metrics Massimo Franceschet Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Udine Via delle Scienze 206 33100 Udine, Italy massimo.franceschet@dimi.uniud.it
Ten good reasons to use the Eigenfactor TM metrics Massimo Franceschet Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Udine Via delle Scienze 206 33100 Udine, Italy massimo.franceschet@dimi.uniud.it
Math 307 Learning Goals. March 23, 2010
 Math 307 Learning Goals March 23, 2010 Course Description The course presents core concepts of linear algebra by focusing on applications in Science and Engineering. Examples of applications from recent
Math 307 Learning Goals March 23, 2010 Course Description The course presents core concepts of linear algebra by focusing on applications in Science and Engineering. Examples of applications from recent
