Selected Answers and Solutions
|
|
|
- Phebe Randall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 value for the w idth of the box w ould be negative or zero. 3. height =.9 in., length «. in., w idth ~. in., m axim um volum e ~. in 3 5. radius =.55 in., height = 3.9 in. m inim um surface area = 5.9 in 7. (6.67,.83), Sam ple answ er: A m inim um tim e o f.83 hours w ill be obtained if the racer takes a path that w ill have him her at the sidew alk 3.33 m iles before the pier. 9. m = ; Sam ple answ er: The slope of the tangent line is. The tangent line is a horizontal line. 9. vertex: ( - 8, - ) ; focus: ( 8, 3); directrix: = ; axis o f sm m etr: x = 8. Sam ple answ er: The focus is feet above the ground. CHAPTER 7 Conic Sections and Parametric Equations (3) a. - 8x + l = + = 8x Page Chapter 7 Get Read. x = ; (, - ) ; (, - 3 ) 3. x = - ; (, - 8 ) ; ( -, - ) 5. x = ; (, - ) ; (, - 6 ) 7.x = 5; (, 55); (5,53.75) vertical asm ptote at x = 5 7. vertical asm ptotes at x = 5 and x = ; horizontal asm ptote at = 9. vertical asm ptote at x =. Pages 8-3 Lesson 7-. vertex: (3, 7); focus: (3, ); directrix: = ; axis of sm m etr: x = 3 + l + 5 = 8x l + 5 = 8x - 5 ( + 5 ) = 8 (x - 3) b. The equation in standard form has as the squared term, w hich m eans that the parabola opens horizontall. Because p = 8, p = 5 and the graph opens to the right. The equation is in the form ( fc) = p(x h), so h = 3 and fc = 5. Since the stern is located at the vertex o f the parabola form ed, it is at the p oint (;, fc) or (3, 5). The sw im m er is at the focus, located at (h + p, fc), w hich is (3 + 5, 5) or (8, 5). The distance the sw im m er is from the stem o f the boat represents the length of rope needed to attach the sw im m er to the stern. U sing the distance form ula, the distance betw een these tw o points is ( 8-3 ) + ( ( 5)) or 5. Therefore, the length o f rope attaching the sw im m er to the stern o f the boat 3. vertex: (, ); focus: (3, ); directrix: x = 7; axis of sm m etr: = - ( - ) = (x+ ) is 5 feet. 5. x = 8( + 7); vertex: (, 7); focus: (, 5); directrix: = 9; axis o f sm m etr: x = 5. vertex: ( 8,3 ); focus: ( 8,5 ); directrix: = ; axis of sm m etr: x 7. x = ( + ); vertex: (, ); focus: (, 7); directrix: = 5; axis o f sm m etr: x = 7. vertex: (, 5); focus: (7, 5); directrix: x = 5; axis o f sm m etr: = 5 9. = (x - 3); vertex: (3, ); focus: (8, ); directrix: x = ; axis o f sm m etr: = R9 ; Selected Answers
2 . ( ) = (x ); vertex: (, ); focus: (.5, ); directrix: x =.5; axis of sm m etr: =. ( + 9 ) = (x + 6) 3. (x + 6) = 8( + 9); vertex: ( 6, 9); focus: ( 6,.5); directrix: = 3.5; axis of sm m etr: x = in. 7. ( + l ) = (x + ) 9. (x + 3 ) = 8( - ) i i 8 v ) i (x + 3) _ ) T f 8 + x = 6 J - o n o Y, k f 6- o * w ( + l ) = (x + ) 3. ( - ) = 3(x - 7) s r - - x >< CJ C CJ 33. (x - l ) = ( - 6) 35. (x - 8) = 6( + 7) * L S * ix ' T ( x - ) = ( 6) 37. (x - l ) = ( - 5) 39. (x + ) = - ( - ) 8: i, - 8 r-)z = (-- 5 ) - t t For Homework Help, go to H o tm a th.co m k -k x + = - -- )- A K = 8x 5 (! 7. = x + The graph opens verticall. D eterm ine the vertex and focus..5(x - 6) = - 9 (x - 6 ) = ( - 9) Because p =, p =. The vertex is (6,9 ) and the focus is (6,8 ). We need to determ ine d, the distance betw een the focus and the point of tangenc, C. This is one leg of the isosceles triangle. d = j{x - x l ) + ( - l ) = ( - 6 ) + (5-8 ) = 5 U se J to find A, the end point o f the other leg o f the isosceles triangle. Since p is negative, the parabola opens dow n and A w ill be above the focus. A = (6, 8 + 5) or (6, 3 ) Points A and C b o th lie on the line tangent to the parabola. To find an equation for this line, first use tw o points to find the slope m. Then use a p oint on the line and the slope to w rite an equation for the line. - i = m ( x - * i ) 5 = (x ) 5 = x + Point-slope formula (x t) = (,5 ) and m = - Simplif. = x + 5 Solve for. 5. opens dow nw ard 53. opens upw ard 55. (x 3 ) = ( 5) 57. ( l ) = 6(x + 5) 59a. Sam ple answ er: x = 8.7( + ) 65. (, 8) 67. (, - ) 69a. 7a. ( ) = 8(x + 3) or ( - 59b. about 3.35 m 63. ( + 5 ) = 8(x + 3) -6 "(5,3 h 5, 7) 6 8 (--, - ) 3 ) : 69b..53 ft 8(x + 3) R9
3 Sam ple answ er: To prove that the endpoints o f the latus rectum and W and the point o f intersection o f the axis and directrix D are the vertices of a right isosceles triangle A D W, w e need to show that ZDW is a right angle and that D = WD. Since F = FW, FD = FD, and Z F D = ZWFD, A F D = A FW D b SA S. Thus, D = WD. To prove that ZDW is a right angle, w e can first p rove that Z D F and ZFDW are b oth 5 angles. Since F = FD and ZFD is a right angle, A F D is an isosceles right triangle. Therefore, ZDF is 5. This also m eans that ZFDW is 5. Likew ise, ZDW is a right angle. Thus, ADW is an isosceles right triangle. 73. Sam ple answ er: x = ( ) 75. Sam ple answ er: = x 77a. i. unit; ii. units; iii. units 77c. A s the focus is m oved farther aw a from the vertex, the parabolas becom e wider. 77d. Sam ple answ er: (x + l ) = ( + 7) 77e. Sam ple answ er: The parabolas all have a vertex of (,- ) and open dow nw ard. T he first equation produces the narrow est parabola and the second equation p roduces the w idest parabola. (79) The w idth of the sector is 3 units, so =.5. A = x and the area o f the sector is. square units. Substitute the values into the equation and solve for x. - = x(.5). = x. = x Therefore, the vertex o f the parabola is (, ), and tw o other points on the parabola are (.,.5 ) and (.,.5). Set up and solve a sstem o f equations using as the independent variable. a + b + c = x a( ) + b{ ) + c = a(.5) + b(.5) + c =. a(.5) + b(.5) + c =..5 a +.5b =..5a -.5b =..5a =. c = 97. f i x ) = x 3 - x - x +. G 3. G Pages 38- Lesson x x = 9 A 9x + + 6x =.5 ^ +.5b =.. +.5b =..5b = b = The equation of the parabola is -j - 8. Q uadrants and ; the vertex is (, 5) and p =. Since the vertex is to the left of the -axis, and the parabola opens to the left, no points w ill be to the right o f the -axis, or in Q uadrants and. 5 : x or L = x m ax at (7,8.5 ) = 8.5, m in at (, ) = cot 6 = 7-, csc 6>= 6 6 R9 Selected Answers 7 (x 3) ( + 3) l a ( x - ) ( ) 36 5 (* + <>), ( - 3), «( * - ), ( - s ), a. 8.8 in. i' 3 b. J ^ + ^ = l 5.( } + = ; ellipse 3 ' 7 ( x - 7 ) ( + ) 7. ( + 9) = (x 6); parabola 9. n ellipse x x = x + x =
4 {x + x + 36) + 7( ) + 3 = (x + 6 ) + 7( + 6 ) = (x + 6) ( + 6) + = 7 The related conic is an ellipse becau se a ==b and the graph is of the form + ( 7 ^ =. a b 33. (x - 3) + = 35. (x + ) + ( + 3) = 36 53b. ** > * > 5 f f N JU 53c. 5 das 55. ( 7,- ), ( 3, - 5 ) 57. ( -,3 ), ( 6, - 5 ) 59. ^ ^ = i - H 3, ) - ^ K A S - t i r i r " n, * v - 6. (x - 6.5) + ( -.5 ) = (x - l ) + ( + 7) = 6; center: (, 7), radius: 65. (x + l ) + ( ) = 6; center: (, ), radius: Sam ple answ er: N o; if a = p and b = p + r, then c = r. f a = p + r and b = p, then c = fr and the foci are (, ± r ). 37. P F i + PF = a J(x - ) + ( - c) + ^(x - ) + ( - ( - c ) ) = a jx + ( - c) + Jx + ( + c) = a jx + ( - c) = a - Jx + ( + c) x + c + c = a - a ^ x + ( + c) + ajx ^J7-~tf = a + c ajx + ( + c) = a + c x + + c + c a(x + + c + c) = a + ac + c! ax + a + flc + ac = a + ac + c ^ <P~ + ax = a ac (a c) + ax = fl(a c) b + ax = ab - + ^ = a b 3 9. i i ^ + ( - 3) =. ^ + ^ = ) a. The length o f the m ajor axis is or The value o f a is or The distance 87 from the focus (the sun) to the vertex is or Therefore, the value o f c, the focus to the center, is or 7.. n an ellipse, c = a b. The value o f b is «c = ~ T he valu e o f b, the length o f the m inor axis, is about or about 7.35 m illion mi. c 7 b. The eccentricit e is equal to. e = ^ ^ :.3 5. center: (, 6); foci: (+ 5 3, 6); vertices: (±, 6 ) 7. center: (, ); foci: (, ± 7 ); vertices: (, ± 6 5 ) ( + ), (x ) 9. + = ' 6 53a. x + = 6, x The area o f the ellipse A = tt. Substitute into the area form ula to obtain an equation w ith a and b. tt = -nab = ab Substitute a = b + 5 into the equation and solve for b. = (b + 5 )b = b + 5b = b + 5b = (b + 8)(b - 3) Since b cannot b e negative, b = 3 and a = or 8. Therefore, an equation for the ellipse is x v x v Yes; sam ple answ er: f (x, ) is a point on the ellipse, then ( x, ) m u st also b e on the ellipse. x (- = a b ( - x ), ( - ) + - b = a h = b Thus, ( x, ) is also a p oint on the ellipse and the ellipse is sm m etric w ith respect to the origin. 73. Sam ple answ er: W hen a is m u ch greater than c, j is close to. Since e = the valu e o f e is close to zero and the foci are near the center o f the ellipse. So, the ellipse is nearl circular. 75. vertex: - j; focus: 7^; directrix: = av,'s o f sm m etr: M R eal Babies and 3 M First Babies 79. sin (» + f ) - cos ( + f j 7 ' = sin cos ^ + cos sin ~ cos cos ^ + sin sin = i sin + cos cos + j sin For Homework Help, go to H o tm a th.c o m $ connecte^ticgrav^iil^orj R 9 3
5 = j sin 8 + j sin 9 = sin 6 8. J>L 83. ^ 6 85.[ - 7, 5 ] 6 3 tu rn in g p o in ts;,, and tu rn in g p o in ts;,5, and Pages real zeros and real zeros and i 93. B 95. C Lesson x z + 3z - x + 6 = 8. j - -, k " 8 - (- l va '- -7, ^ s U M )* s J» i Ss L - 5 x x - 8 = 87 (8.89, ) t- ( - l ) 5 ( + 8) 6 s 8x a. 3 Y(. 9). m n t, 3)r <7 ik if. _ -(o, 9.3: 8-8 (x n 3. 5, < (* ) 9 = _ =. 33b. 9 ft h p erb o la 9. ellip se 5. h p erb o la 53. circle p arabo la ) a. T h e co m m o n d ifferen ce is 8 k ilo m eters and the ab so lu te v alu e o f the d ifferen ce o f the d istan ces from an p o in t on a h p erbo la to the fo ci is a, so a = 8, a = 9, an d a = 8. T h e tw o airp o rts are the fo ci o f the h p erb o la and are 7 k ilo m eters ap art, so c = 7, c = 36, and c = 96. c = a + bz, so b = 96 8 S) 3x 5) 5 7 or 5. A irp o rt B is d ue sou th o f airp ort A, so the tran sv erse axis is v ertical and n-term goes w ith the -term. T h e eq u atio n for the h p erbo la is t. 8 it a ( - ) ( - ) -^ JU -- t >f J (x + 7) 5 ( + 3) 7? - ( 9. [x + ) ( - C (x + 3) = 33 rfp T 9. 3 )- - 6 ( + ) 9 the x -term. T h e eq u atio n fo r the h p erbo la is v -K (x - 3) 7 x-co o rd in ates o f the v ertice s are d ifferent, so the tran sv erse axis is h o rizo n tal and the a -term go es w ith o 5. (, 3). T h erefore, h = and k = 3. T h e con ju g ate axis is o f le n g th, so b =, b = 6, and b = 36. The S - 5 8, Me,c )? 5, 8, ) i ( - 3 )-,r (x + l ) = 9 (3? T h e v e rtice s are u n its ap art, so a =, a =, and a =. T h e cen ter is the m id p o in t o f the v ertices, or b. ^ = B - ' 5 =. C ( 36)- Airpo r t be: f e, - - -* T h e p lan e is on the top b ran ch b e cau se it is clo ser to airp o rt A. x irport bj (, - 3 B) (x -5 ) _ 9 R9! Selected Answers (- ) 7 C. B ecau se th e h ig h w a is the tran sv erse axis and the p lan e is k ilo m eters from the highw a, x =. S u b stitu te fo r x in the equ ation.
6
7 7. in tersectin g lin es 3x ± (3x) - ()(3x - ) = x and = x 9. p o in t at (, ) 5. b () = c -3x ± 96-3x G raph the conic. [ -, ] scl: b [ -, ] scl: 55b. A x - Bx - C + Dx + E + F = A '(x') + B 'x'' C '(') + D 'x' + E'' + F'; b su b tractin g o u t the x, x,, and F term s, the rem ain in g statem en t is true. A x - C = A '(x') C'('); A m u st eq u al A and B m u st equ al B' in o rd er fo r the statem en t to b e tru e. 55c. A x + Bx - C - Dx + E + F = A '(x') + B'x'' - C ( r) + D 'x ' + E'' - F'; b su btractin g ou t the x,, and F term s, the rem ain in g statem en t is true. A x + Bx + C = A ix ) + B'x'' - C '('); A m u st equal A', B m u st eq u al B', and C m u st eq u al C' in ord er for the statem en t to b e true. T h erefo re, B A C = (S ') (A'C); A (x cos 9 + sin 9) + B (x cos 9 - sin 9)( cos 9 x sin 9). 33. i 8(x') - 6 (-) = "s. ( v (57) For e ach eq u atio n, solv e fo r u sin g the qu ad ratic form u la. T h e n g rap h u sin g a g rap h in g calculator. ) 9 x - x = 5 - x() - (9 x ) = x ± J(x) (5)(9x ) x + 8-6x 39. Sx + bx - = - J [ - 6.6,.6 ] scl: b [ -, ] scl: Y AK x - x - - x - - = - ( x l) - (x x - ) = x + ± ( x l) ( )(x x ) x + +?x 6x , 7.5 8] scl: b [ - 5, 5] scl:. [ -.5 8,.5 8 ] scl: b [ -, 8] scl: [ -, ] scl: b [ -, ] scl: T h e g rap h s in te rsect at fo u r p o in ts: (.9,.), (.5,.5), (.9, -. ), (.9,.8). Equation Graph M inim um Angle of Rotation x - 5 x - 3 = parabola 36 6x = 5 x= 9 x + x - - x - fi = - ellipse 55a. A x + Bx - C + Dx + E + F = is eq u iv alen t to A'(x') + B'x'' + C '(') + D'x' + E'' - F' = b ro tatin g the A C con ic sectio n th ro u gh 9 su ch th at co t 9 = -. F is u n affected b th is ro tatio n, so F = F'. hperbola 8 59b. S am p le answ er: A p arab o la h as lin e o f s m m etr and the m in im u m an g le o f ro tatio n is a co m p lete circle. A n [ -, ] scl: b [ -, ] scl: R96 S e le c te d A n s w e r s ellip se and a h p erb o la h av e lin es o f s m m etr and the m in im u m an g le o f ro tatio n is a h a lf circle. 59c. 3
8 3. x = - f - r <r> _ i-t6 = [ (* + ( K ) = M + ( 63. 7^ -! CvJ 6. L et x = x' cos 9 + ' sin 9 and = x' sin 9 - ' cos 9. r = x + = (x ' cos 9 + ' sin 9) + ( x' sin 9 + ' cos 9) = ( x ^ c o s 9 - x''cos 9 sin 9 - ( ^ s in 9 + (x^ sin 9 - x''cos 9 sin 9 - ( ^ c o s 9 = [(xr) - ( ^cos 9 - [(x - ( ^ sin 9 = [ (* + ( ^ K c o s 9 - s in 9) t= ) ^ t = a ~ t = - cos 9 (x = x' cos 9 ' sin 9) 7. sin 9 ( = x' sin 9 - ' co s 9) x cos 9 - sin 9 x cos 9 - sin 9 x co s 9 - sin 9 x cos 9 - sin 9 8 = x' c o s 9 ' sin 9 cos 9 = x' s in 9 - v ' sin 9 cos 9 = x' c o s 9 - x' s in 9 = x' (cos 9 - s in 9) = x' = - F -5-6 ^ } p t h =7 - t--= 8 3 sin 9 (x = x' cos 9 ' sin 9) cos 9 ( = x' sin 9 - ' cos 9) x sin 9 = x' cos 9 sin 9 ' s in 9 cos 9 = x' cos 9 sin 9 - ' c o s 9 x sin 9 cos 9 = ' sin 9 ' c o s 9 9. =. 5 x -.5x -.5. = 5x + > x sin 9 cos 9 = ' (sin 9 - c o s 9) cos 9 x sin 9 = ' 65. Sam ple answ er: T he d iscrim in an t is d efin ed as B C, or in this in stan ce, (B ') AA'C'. S in ce a con ic th at is rotated has n o B' term, the d iscrim in an t red u ces to AA'C'. T hu s, onl the A' and C term s d eterm in e the tp e o f conic. T herefore, AA'C' < w o u ld b e an ellip se o r a circle, AA'C' = w ou ld be a parabo la, and AA'C' > w ou ld b e a h p erbola. For a circle or an ellip se, A' and C n e e d to share the sam e sign. For a p arab o la, eith er A! or C h as to b e equ al to. Fo r a h p erb o la, A' and C' n eed to h av e o p p o site signs. - t - f A M i f -r- A 5. = ^ i - 6 -f - -f 6x 8x i S 7 = o r 69. i > s J M a. s - d = 5,.35s -.5 d = b. sav in g s accou n t: $5; A -i - (x 3) 6 Pages ( 8 A 9. 9 = i =: certificate o f d ep o sit: $ es, es; (x ) (x - )(x - )(x - 3) ( 7) = r 5 7. = - x + ^ fx -l- 3 J = t 79. D 8. A Lesson 7-5. f =^ i x T +T J x = 3 cos e = 3 s in 9 = K = For Homework Help, go to H o t m a t h.c o m dl r R97 = b
9 x = tv co s 8 7.x = a n d = ^ 9 - ^ 5- x + 9 =. =.38 - v -^ 8x.9 = v, t = '- - = 9 - x - -t= - - A f= = J C 5a. ab o u t 7. ft s 5 b. ab o u t secon d 5c. abo u t.8 seco n d s 53. S am p le answ er: x = + f, = + 3f 55. S am p le answ er: T h e h o rizo n tal d istan ce is m o d eled b the cosin e fu n ctio n, w h ich is at 9. T h is w o u ld im p l th at the p ro jectile h as n o h o rizo n tal m o v em en t. T h e co rresp o n d in g p aram e tric eq u atio n w o u ld b e x =. 57. S am p le answ er: P aram etric equ atio n s sh ow both 3. x = f and = -f+ t+ 9. x = 5t and = - 5 f + f ou t= 6 * [ (x ' >u ll wl* + t--= 'i 6x ^ t= 5 ' h o rizo n tal and v e rtical p o sitio n s o f an o b ject o v er tim e, w h ile rectan g u lar e q u atio n s c a n o n l sh o w o n e or th e other. - - ( k s ** - CJ (x - 3) = tan x n 3 + n ; n - n 3;.97 = C t= 6 ( - ). 33. es (35) Solve the first eq u atio n for t. x = log t L6 69. h o riz o n ta l as m p to te at = ; v ertical as m p to te at x = 6; D = (x x ~ 6, x R) x = t u J Su bstitu te into second equation. k > = t+ 3 = * + 3 n x = lo g t, x m u st b e >, so the d o m ain restrictio n is x > = * = * 8, x ==.x = f + a n d = 7 + 3f 3. x = t and = 6 + f, < f < 5. b 7. a 7. v ertical as m p totes at x = 5; o b liq u e as m p to te at = x + 3; x -in tercep ts and 8; -in tercep t ; D = (, 5) U ( 5, ) (9) a. The p o sitio n equ atio n s are x = tv cos 9 and = fw sin 9 ~ gt + h. T h e in itial v elo cit z> is.75 and 9 is 5. T h e su rface o f the w ater is at =, so the v alu e o f the in itial h e ig h t h is.3. B su bstitu tion, the p o sitio n eq u atio n s are x = t.75 cos 5 and = t.75 sin 5.9 f +.3. b. Find the v alu e o f t for w h ich = in the v ertical b. ellip se 77. E 79a. x x = 79c. (x ') + 9 ( ') = 79d. ~.75 p o sitio n equation. = t.75 sin f +.3 = ~ t -.9 f +.3. The p o sitiv e zero in the grap h o f the eq u atio n is ab o u t.37, so t =.37 second s. S u b stitu te th is for t in x = t.75 cos 5, the h o rizo n tal position equ ation. x =.37(.75) ^ :.6. This m ean s th at w h en the frog reach es th e su rface o f the w ater, h e is o n l ab o u t.6 m from w here h e ju m p ed. T herefo re, h e is ab o u t.5.6 or.3 m eters from th e oth er bank. C. T h e. m eter d istan ce is a h o rizo n tal d istance, so su b stitu te the v alu es into the h o rizo n tal p o sitio n e q u atio n and solv e for u. R98 Selected Answers Pages con ic section Chapter 7 Stud Guide and Review 3. d irectrix 5. foci 7. cen ter 9. p aram etric. vertex: ( 3, ), focus: ( 3, ) ; axis o f sm m etr: x = 3; d irectrix: = * (-3, - )
10 3. vertex: (, ), focus: (, ); axis of smmetr: x = ; directrix: = (, - f ix t r. 3. -,] scl: b [-, ] scl: [-, ] scl: b [-, ] scl: (x - l) = 6(i - 5) ( 5-6 6x ( + ) = - ( x + 3). (x - 3) = (i+ 7) l- -3, - ' s M 8 C - [-5, 5] scl: b [-5, 5] scl: 7. (x - f3x'' + 3 (^ + (3 - )x' + (a3 + )' = ; parabola 9. 9(') + (x') = 36; ellipse ~ ~- f = - 3 l. = 3, t=-ia t= f = J - " f = t-.= n 53. = i (x - 3) ( ( + 6 ) _ 6 5 ( x - 5 ), ( - ) ^ ' l (x - l ) + ( ) = 3; circle 9. (x - ) = ( + 5); parabola 8 x - 57a. x + = 9 57b. 5 seconds 59a. 3x + 3x + + 8x 83 = 59b. * k! ix Pages Chapter 7 Connect to AP Calculus units units3 5. Sample answer: The approximation will get closer to the actual volume of the solid because as the clinders decrease in height, the will better fill the volume of the solid units3 v s r» i s u.*» ectors Page 8 Chapter 8 Get Read.3 ; ( ± ) 3. 9; ( - i - 8 ) ft. no solution 3. B «39, C as 5, c a 3. For Homework Help, go to Hotm ath.com connected.mcgraw-hill.com R 9 9
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W
 A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
A L A BA M A L A W R E V IE W Volume 52 Fall 2000 Number 1 B E F O R E D I S A B I L I T Y C I V I L R I G HT S : C I V I L W A R P E N S I O N S A N D TH E P O L I T I C S O F D I S A B I L I T Y I N
C o r p o r a t e l i f e i n A n c i e n t I n d i a e x p r e s s e d i t s e l f
 C H A P T E R I G E N E S I S A N D GROWTH OF G U IL D S C o r p o r a t e l i f e i n A n c i e n t I n d i a e x p r e s s e d i t s e l f i n a v a r i e t y o f f o r m s - s o c i a l, r e l i g i
C H A P T E R I G E N E S I S A N D GROWTH OF G U IL D S C o r p o r a t e l i f e i n A n c i e n t I n d i a e x p r e s s e d i t s e l f i n a v a r i e t y o f f o r m s - s o c i a l, r e l i g i
S ca le M o d e l o f th e S o la r Sy ste m
 N a m e ' D a t e ' S ca le M o d e l o f th e S o la r Sy ste m 6.1 I n t r o d u c t i o n T h e S olar System is large, at least w hen com pared to distances we are fam iliar w ith on a day-to-day basis.
N a m e ' D a t e ' S ca le M o d e l o f th e S o la r Sy ste m 6.1 I n t r o d u c t i o n T h e S olar System is large, at least w hen com pared to distances we are fam iliar w ith on a day-to-day basis.
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(4, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -9), find M 3. A( 2,0)
3. A( 2,0) and B(6, -2), find M 4. A( 3, 7) and M(4,-3), find B. 5. M(4, -9) and B( -10, 11) find A 6. B(4, 8) and M(-2, 5), find A
 Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
Midpoint and Distance Formula Class Work M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -8), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M (3. 5, 3) (1.
OH BOY! Story. N a r r a t iv e a n d o bj e c t s th ea t e r Fo r a l l a g e s, fr o m th e a ge of 9
 OH BOY! O h Boy!, was or igin a lly cr eat ed in F r en ch an d was a m a jor s u cc ess on t h e Fr en ch st a ge f or young au di enc es. It h a s b een s een by ap pr ox i ma t ely 175,000 sp ect at
OH BOY! O h Boy!, was or igin a lly cr eat ed in F r en ch an d was a m a jor s u cc ess on t h e Fr en ch st a ge f or young au di enc es. It h a s b een s een by ap pr ox i ma t ely 175,000 sp ect at
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
Circles. Example 2: Write an equation for a circle if the enpoints of a diameter are at ( 4,5) and (6, 3).
 Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
c. What is the average rate of change of f on the interval [, ]? Answer: d. What is a local minimum value of f? Answer: 5 e. On what interval(s) is f
![c. What is the average rate of change of f on the interval [, ]? Answer: d. What is a local minimum value of f? Answer: 5 e. On what interval(s) is f c. What is the average rate of change of f on the interval [, ]? Answer: d. What is a local minimum value of f? Answer: 5 e. On what interval(s) is f](/thumbs/87/95703678.jpg) Essential Skills Chapter f ( x + h) f ( x ). Simplifying the difference quotient Section. h f ( x + h) f ( x ) Example: For f ( x) = 4x 4 x, find and simplify completely. h Answer: 4 8x 4 h. Finding the
Essential Skills Chapter f ( x + h) f ( x ). Simplifying the difference quotient Section. h f ( x + h) f ( x ) Example: For f ( x) = 4x 4 x, find and simplify completely. h Answer: 4 8x 4 h. Finding the
Form and content. Iowa Research Online. University of Iowa. Ann A Rahim Khan University of Iowa. Theses and Dissertations
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 1979 Form and content Ann A Rahim Khan University of Iowa Posted with permission of the author. This thesis is available at Iowa Research
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 1979 Form and content Ann A Rahim Khan University of Iowa Posted with permission of the author. This thesis is available at Iowa Research
The Ability C ongress held at the Shoreham Hotel Decem ber 29 to 31, was a reco rd breaker for winter C ongresses.
 The Ability C ongress held at the Shoreham Hotel Decem ber 29 to 31, was a reco rd breaker for winter C ongresses. Attended by m ore than 3 00 people, all seem ed delighted, with the lectu res and sem
The Ability C ongress held at the Shoreham Hotel Decem ber 29 to 31, was a reco rd breaker for winter C ongresses. Attended by m ore than 3 00 people, all seem ed delighted, with the lectu res and sem
Conic Sections. Geometry - Conics ~1~ NJCTL.org. Write the following equations in standard form.
 Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
Conic Sections Midpoint and Distance Formula M is the midpoint of A and B. Use the given information to find the missing point. 1. A(, 2) and B(3, -), find M 2. A(5, 7) and B( -2, -), find M 3. A( 2,0)
H STO RY OF TH E SA NT
 O RY OF E N G L R R VER ritten for the entennial of th e Foundin g of t lair oun t y on ay 8 82 Y EEL N E JEN K RP O N! R ENJ F ] jun E 3 1 92! Ph in t ed b y h e t l a i r R ep u b l i c a n O 4 1922
O RY OF E N G L R R VER ritten for the entennial of th e Foundin g of t lair oun t y on ay 8 82 Y EEL N E JEN K RP O N! R ENJ F ] jun E 3 1 92! Ph in t ed b y h e t l a i r R ep u b l i c a n O 4 1922
MA 162 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring Find the angle between the vectors v = 2i + 2j + k and w = 2i + 2j k. C.
 MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1
 Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Table of C on t en t s Global Campus 21 in N umbe r s R e g ional Capac it y D e v e lopme nt in E-L e ar ning Structure a n d C o m p o n en ts R ea
 G Blended L ea r ni ng P r o g r a m R eg i o na l C a p a c i t y D ev elo p m ent i n E -L ea r ni ng H R K C r o s s o r d e r u c a t i o n a n d v e l o p m e n t C o p e r a t i o n 3 0 6 0 7 0 5
G Blended L ea r ni ng P r o g r a m R eg i o na l C a p a c i t y D ev elo p m ent i n E -L ea r ni ng H R K C r o s s o r d e r u c a t i o n a n d v e l o p m e n t C o p e r a t i o n 3 0 6 0 7 0 5
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
l (D) 36 (C) 9 x + a sin at which the tangent is parallel to x-axis lie on
 Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
Dpp- to MATHEMATICS Dail Practice Problems Target IIT JEE 00 CLASS : XIII (VXYZ) DPP. NO.- to DPP- Q. If on a given base, a triangle be described such that the sum of the tangents of the base angles is
B ench mark Test 3. Special Segments in Triangles. Answers. Geometry B enchmark T ests. 1. What is AC if } DE is a midsegment of the triangle?
 a te enc LSSON h m a rk 00.00 T es ts More opy if needed ench mark Test Special Segments in Triangles 1. What is if } is a midsegment of the triangle? 11 1 nswers 1. 2. S ee grap h. a. b... 7.. 10 2. lac
a te enc LSSON h m a rk 00.00 T es ts More opy if needed ench mark Test Special Segments in Triangles 1. What is if } is a midsegment of the triangle? 11 1 nswers 1. 2. S ee grap h. a. b... 7.. 10 2. lac
I zm ir I nstiute of Technology CS Lecture Notes are based on the CS 101 notes at the University of I llinois at Urbana-Cham paign
 I zm ir I nstiute of Technology CS - 1 0 2 Lecture 1 Lecture Notes are based on the CS 101 notes at the University of I llinois at Urbana-Cham paign I zm ir I nstiute of Technology W hat w ill I learn
I zm ir I nstiute of Technology CS - 1 0 2 Lecture 1 Lecture Notes are based on the CS 101 notes at the University of I llinois at Urbana-Cham paign I zm ir I nstiute of Technology W hat w ill I learn
Bellman-F o r d s A lg o r i t h m The id ea: There is a shortest p ath f rom s to any other verte that d oes not contain a non-negative cy cle ( can
 W Bellman Ford Algorithm This is an algorithm that solves the single source shortest p ath p rob lem ( sssp ( f ind s the d istances and shortest p aths f rom a source to all other nod es f or the case
W Bellman Ford Algorithm This is an algorithm that solves the single source shortest p ath p rob lem ( sssp ( f ind s the d istances and shortest p aths f rom a source to all other nod es f or the case
LESSON 2: CIRCLES AND SECTORS
 LESSON : CIRCLES AND SECTORS G.C.1 1. B similar G.C.1. Similar figures have the same shape and proportional size differences. This is true of circles in which the radius is used to scale the figure larger
LESSON : CIRCLES AND SECTORS G.C.1 1. B similar G.C.1. Similar figures have the same shape and proportional size differences. This is true of circles in which the radius is used to scale the figure larger
CIRCLES: #1. What is an equation of the circle at the origin and radius 12?
 1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
1 Pre-AP Algebra II Chapter 10 Test Review Standards/Goals: E.3.a.: I can identify conic sections (parabola, circle, ellipse, hyperbola) from their equations in standard form. E.3.b.: I can graph circles
LU N C H IN C LU D E D
 Week 1 M o n d a y J a n u a ry 7 - C o lo u rs o f th e R a in b o w W e w ill b e k ic k in g o ff th e h o lid a y s w ith a d a y fu ll o f c o lo u r! J o in u s fo r a ra n g e o f a rt, s p o rt
Week 1 M o n d a y J a n u a ry 7 - C o lo u rs o f th e R a in b o w W e w ill b e k ic k in g o ff th e h o lid a y s w ith a d a y fu ll o f c o lo u r! J o in u s fo r a ra n g e o f a rt, s p o rt
Chapter 7 Page 1 of 16. Lecture Guide. Math College Algebra Chapter 7. to accompany. College Algebra by Julie Miller
 Chapter 7 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 7 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
Chapter 7 Page 1 of 16 Lecture Guide Math 105 - College Algebra Chapter 7 to accompan College Algebra b Julie Miller Corresponding Lecture Videos can be found at Prepared b Stephen Toner & Nichole DuBal
The details of the derivation of the equations of conics are com-
 Part 6 Conic sections Introduction Consider the double cone shown in the diagram, joined at the verte. These cones are right circular cones in the sense that slicing the double cones with planes at right-angles
Part 6 Conic sections Introduction Consider the double cone shown in the diagram, joined at the verte. These cones are right circular cones in the sense that slicing the double cones with planes at right-angles
1 is equal to. 1 (B) a. (C) a (B) (D) 4. (C) P lies inside both C & E (D) P lies inside C but outside E. (B) 1 (D) 1
 Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
Single Correct Q. Two mutuall perpendicular tangents of the parabola = a meet the ais in P and P. If S is the focus of the parabola then l a (SP ) is equal to (SP ) l (B) a (C) a Q. ABCD and EFGC are squares
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9
 P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
Math 190 (Calculus II) Final Review
 Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
9.1 Circles and Parabolas. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
9.1 Circles and Parabolas Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane and a double-napped cone. Write equations of circles in
3) Find the distance for each set of ordered pairs (remember to provide EXACT answers): 5) x 2 + y 2 + 6x 6y + 9 = 0 A) Ellipse (x 1) 2
 Algebra Chapter Review 1) State the Midpoint Formula: State the Distance Formula: ID: 1 Name Date ) Find the midpoint for each set of ordered pairs: a) (1, ), (, ) b) (-, 0), (-, 3) Period c) (, ), (-,
Algebra Chapter Review 1) State the Midpoint Formula: State the Distance Formula: ID: 1 Name Date ) Find the midpoint for each set of ordered pairs: a) (1, ), (, ) b) (-, 0), (-, 3) Period c) (, ), (-,
Apply & Practice 3.5 Set 1: P #3-18 (mult. of 3); 19 #21 write explicit #27-33 (mult. of 3) point #39-40 eqn tang line from graph
 Ch 0 Homework Complete Solutions V Part : S. Stirling Calculus: Earl Transcendental Functions, 4e Larson WATCH for the product rule and the chain rule. If the order that our terms are in differ from the
Ch 0 Homework Complete Solutions V Part : S. Stirling Calculus: Earl Transcendental Functions, 4e Larson WATCH for the product rule and the chain rule. If the order that our terms are in differ from the
Precalculus Conic Sections Unit 6. Parabolas. Label the parts: Focus Vertex Axis of symmetry Focal Diameter Directrix
 PICTURE: Parabolas Name Hr Label the parts: Focus Vertex Axis of symmetry Focal Diameter Directrix Using what you know about transformations, label the purpose of each constant: y a x h 2 k It is common
PICTURE: Parabolas Name Hr Label the parts: Focus Vertex Axis of symmetry Focal Diameter Directrix Using what you know about transformations, label the purpose of each constant: y a x h 2 k It is common
The Distance Formula. The Midpoint Formula
 Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Math 120 Intermediate Algebra Sec 9.1: Distance Midpoint Formulas The Distance Formula The distance between two points P 1 = (x 1, y 1 ) P 2 = (x 1, y 1 ), denoted by d(p 1, P 2 ), is d(p 1, P 2 ) = (x
Math 101 chapter six practice exam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
Math 1 chapter si practice eam MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Which equation matches the given calculator-generated graph and description?
T h e C S E T I P r o j e c t
 T h e P r o j e c t T H E P R O J E C T T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S A r t i c l e P a g e C o m p r e h e n s i v e A s s es s m e n t o f t h e U F O / E T I P h e n o m e n o n M a y 1 9 9 1 1 E T
T h e P r o j e c t T H E P R O J E C T T A B L E O F C O N T E N T S A r t i c l e P a g e C o m p r e h e n s i v e A s s es s m e n t o f t h e U F O / E T I P h e n o m e n o n M a y 1 9 9 1 1 E T
V o l. 21, N o. 2 M ar., 2002 PRO GR ESS IN GEO GRA PH Y ,, 2030, (KZ9522J 12220) E2m ail: w igsnrr1ac1cn
 21 2 2002 3 PRO GR ESS IN GEO GRA PH Y V o l. 21, N o. 2 M ar., 2002 : 100726301 (2002) 022121209 30, (, 100101) : 30,, 2030 16, 3,, 2030,,, 2030, 13110 6 hm 2 2010 2030 420 kg 460 kg, 5 79610 8 kg7 36010
21 2 2002 3 PRO GR ESS IN GEO GRA PH Y V o l. 21, N o. 2 M ar., 2002 : 100726301 (2002) 022121209 30, (, 100101) : 30,, 2030 16, 3,, 2030,,, 2030, 13110 6 hm 2 2010 2030 420 kg 460 kg, 5 79610 8 kg7 36010
Few thoughts on PFA, from the calorim etric point of view
 1 Few thoughts on PFA, from the calorim etric point of view discussing pad siz e, M oliere radius, distance from the interaction point. H enri Videau 2 H ave you had anytim e a close view at show ers?
1 Few thoughts on PFA, from the calorim etric point of view discussing pad siz e, M oliere radius, distance from the interaction point. H enri Videau 2 H ave you had anytim e a close view at show ers?
+ 4 Ex: y = v = (1, 4) x = 1 Focus: (h, k + ) = (1, 6) L.R. = 8 units We can have parabolas that open sideways too (inverses) x = a (y k) 2 + h
 Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
CHAPTER 11 Vector-Valued Functions
 CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
CHAPTER Vector-Valued Functions Section. Vector-Valued Functions...................... 9 Section. Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions.... Section. Velocit and Acceleration.....................
What are S M U s? SMU = Software Maintenance Upgrade Software patch del iv ery u nit wh ich once ins tal l ed and activ ated prov ides a point-fix for
 SMU 101 2 0 0 7 C i s c o S y s t e m s, I n c. A l l r i g h t s r e s e r v e d. 1 What are S M U s? SMU = Software Maintenance Upgrade Software patch del iv ery u nit wh ich once ins tal l ed and activ
SMU 101 2 0 0 7 C i s c o S y s t e m s, I n c. A l l r i g h t s r e s e r v e d. 1 What are S M U s? SMU = Software Maintenance Upgrade Software patch del iv ery u nit wh ich once ins tal l ed and activ
1 x. II. CHAPTER 2: (A) Graphing Rational Functions: Show Asymptotes using dotted lines, Intercepts, Holes(Coordinates, if any.)
 FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
FINAL REVIEW-014: Before using this review guide be sure to study your test and quizzes from this year. The final will contain big ideas from the first half of the year (chapters 1-) but it will be focused
On the M in imum Spann ing Tree Determ ined by n Poin ts in the Un it Square
 Vol. 14 No. CH INESE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF M ATHEM ATICS June 1999 On the M in imum Spann ing Tree Determ ined by n Poin ts in the Un it Square Ye J ichang ( ) Xu Yinfeng ( ) Xu Chengxian ( ) (X iπan J
Vol. 14 No. CH INESE QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF M ATHEM ATICS June 1999 On the M in imum Spann ing Tree Determ ined by n Poin ts in the Un it Square Ye J ichang ( ) Xu Yinfeng ( ) Xu Chengxian ( ) (X iπan J
176 5 t h Fl oo r. 337 P o ly me r Ma te ri al s
 A g la di ou s F. L. 462 E l ec tr on ic D ev el op me nt A i ng er A.W.S. 371 C. A. M. A l ex an de r 236 A d mi ni st ra ti on R. H. (M rs ) A n dr ew s P. V. 326 O p ti ca l Tr an sm is si on A p ps
A g la di ou s F. L. 462 E l ec tr on ic D ev el op me nt A i ng er A.W.S. 371 C. A. M. A l ex an de r 236 A d mi ni st ra ti on R. H. (M rs ) A n dr ew s P. V. 326 O p ti ca l Tr an sm is si on A p ps
y mx 25m 25 4 circle. Then the perpendicular distance of tangent from the centre (0, 0) is the radius. Since tangent
 Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Semester 2 Final Review
 Name: Date: Per: Unit 6: Radical Functions [1-6] Simplify each real expression completely. 1. 27x 2 y 7 2. 80m n 5 3. 5x 2 8x 3 y 6 3. 2m 6 n 5 5. (6x 9 ) 1 3 6. 3x 1 2 8x 3 [7-10] Perform the operation
Name: Date: Per: Unit 6: Radical Functions [1-6] Simplify each real expression completely. 1. 27x 2 y 7 2. 80m n 5 3. 5x 2 8x 3 y 6 3. 2m 6 n 5 5. (6x 9 ) 1 3 6. 3x 1 2 8x 3 [7-10] Perform the operation
Review Exercises for Chapter 3. Review Exercises for Chapter r v 0 2. v ft sec. x 1 2 x dx f x x 99.4.
 Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Review Eercises for Chapter 6. r v 0 sin. Let f, 00, d 0.6. v 0 00 ftsec changes from 0 to dr 00 cos d 6 0 d 0 r dr 80 00 6 96 feet 80 cos 0 96 feet 8080 f f fd d f 99. 00 0.6 9.97 00 Using a calculator:
Class Diagrams. CSC 440/540: Software Engineering Slide #1
 Class Diagrams CSC 440/540: Software Engineering Slide # Topics. Design class diagrams (DCDs) 2. DCD development process 3. Associations and Attributes 4. Dependencies 5. Composition and Constraints 6.
Class Diagrams CSC 440/540: Software Engineering Slide # Topics. Design class diagrams (DCDs) 2. DCD development process 3. Associations and Attributes 4. Dependencies 5. Composition and Constraints 6.
FOR SALE T H S T E., P R I N C E AL BER T SK
 FOR SALE 1 50 1 1 5 T H S T E., P R I N C E AL BER T SK CHECK OUT THIS PROPERTY ON YOUTUBE: LIVINGSKY CONDOS TOUR W W W. LIV IN G S K YC O N D O S. C A Th e re is ou tstan d in g val ue in these 52 re
FOR SALE 1 50 1 1 5 T H S T E., P R I N C E AL BER T SK CHECK OUT THIS PROPERTY ON YOUTUBE: LIVINGSKY CONDOS TOUR W W W. LIV IN G S K YC O N D O S. C A Th e re is ou tstan d in g val ue in these 52 re
Summary, Review, and Test
 944 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analtic Geometr 45. Use the polar equation for planetar orbits, to find the polar equation of the orbit for Mercur and Earth. Mercur: e = 0.056 and a = 36.0 * 10 6 miles
944 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analtic Geometr 45. Use the polar equation for planetar orbits, to find the polar equation of the orbit for Mercur and Earth. Mercur: e = 0.056 and a = 36.0 * 10 6 miles
EKOLOGIE EN SYSTEMATIEK. T h is p a p e r n o t to be c i t e d w ith o u t p r i o r r e f e r e n c e to th e a u th o r. PRIMARY PRODUCTIVITY.
 EKOLOGIE EN SYSTEMATIEK Ç.I.P.S. MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE POLLUTION IN NORT H SEA. TECHNICAL REPORT 1971/O : B i o l. I T h is p a p e r n o t to be c i t e d w ith o u t p r i o r r e f e r e n c e to
EKOLOGIE EN SYSTEMATIEK Ç.I.P.S. MATHEMATICAL MODEL OF THE POLLUTION IN NORT H SEA. TECHNICAL REPORT 1971/O : B i o l. I T h is p a p e r n o t to be c i t e d w ith o u t p r i o r r e f e r e n c e to
w hole + ½ partial = 10u + (½ )(10u )
 MATH 10 MEASURE Self-Test ANSWERS (DETAILED answ ers start on NEXT PAGE.) 1. a. (½) (4u) + [(8u) (u) ] = (4 + 64)u (see diagram ) 1a. Perimeter = 4u + 8u + ½ (u) = (8 + 16)u (½) (u) b. 7.5 u [ 4 6 4 ½
MATH 10 MEASURE Self-Test ANSWERS (DETAILED answ ers start on NEXT PAGE.) 1. a. (½) (4u) + [(8u) (u) ] = (4 + 64)u (see diagram ) 1a. Perimeter = 4u + 8u + ½ (u) = (8 + 16)u (½) (u) b. 7.5 u [ 4 6 4 ½
(6, 4, 0) = (3, 2, 0). Find the equation of the sphere that has the line segment from P to Q as a diameter.
 Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
Solutions Review for Eam #1 Math 1260 1. Consider the points P = (2, 5, 1) and Q = (4, 1, 1). (a) Find the distance from P to Q. Solution. dist(p, Q) = (4 2) 2 + (1 + 5) 2 + (1 + 1) 2 = 4 + 36 + 4 = 44
SPU TTERIN G F R O M A LIQ U ID -PH A SE G A -IN EUTECTIC ALLOY KEVIN M A R K H U B B A R D YALE UNIVER SITY M A Y
 SPU TTERIN G F R O M A LIQ U ID -PH A SE G A -IN EUTECTIC ALLOY KEVIN M A R K H U B B A R D YALE UNIVER SITY M A Y 1 9 8 9 ABSTRACT S p u t t e r i n g f r o m a L i q u i d - P h a s e G a - I n E u t
SPU TTERIN G F R O M A LIQ U ID -PH A SE G A -IN EUTECTIC ALLOY KEVIN M A R K H U B B A R D YALE UNIVER SITY M A Y 1 9 8 9 ABSTRACT S p u t t e r i n g f r o m a L i q u i d - P h a s e G a - I n E u t
IIT JEE Maths Paper 2
 IIT JEE - 009 Maths Paper A. Question paper format: 1. The question paper consists of 4 sections.. Section I contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for
IIT JEE - 009 Maths Paper A. Question paper format: 1. The question paper consists of 4 sections.. Section I contains 4 multiple choice questions. Each question has 4 choices (A), (B), (C) and (D) for
Review Exercises for Chapter 2
 Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Review Eercises for Chapter 367 Review Eercises for Chapter. f 1 1 f f f lim lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 1 1 lim 1 1 lim lim 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4. 8. f f f f lim lim lim lim lim f 4, 1 4, if < if (a) Nonremovable
Conic section. Ans: c. Ans: a. Ans: c. Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ. 1. A circle
 Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
Episode:43 Faculty: Prof. A. NAGARAJ Conic section 1. A circle gx fy c 0 is said to be imaginary circle if a) g + f = c b) g + f > c c) g + f < c d) g = f. If (1,-3) is the centre of the circle x y ax
668 Chapter 11 Parametric Equatins and Polar Coordinates
 668 Chapter Parametric Equatins and Polar Coordinates 5. sin ( sin Á r and sin ( sin Á r Ê not symmetric about the x-axis; sin ( sin r Ê symmetric about the y-axis; therefore not symmetric about the origin
668 Chapter Parametric Equatins and Polar Coordinates 5. sin ( sin Á r and sin ( sin Á r Ê not symmetric about the x-axis; sin ( sin r Ê symmetric about the y-axis; therefore not symmetric about the origin
(IGBP) km 2,? PRO GR ESS IN GEO GRA PH Y. V o l. 20, N o. 4 D ec., 2001 : (2001) m m 3,
 20 4 2001 12 PRO GR ESS IN GEO GRA PH Y V o l. 20, N o. 4 D ec., 2001 : 100726301 (2001) 0420355209, (, 100101) :, 501 mm 502 mm, 765 10 8 m 3 638 10 8 m 3, 127 10 8 m 3,,, ;, : ; ; : P42616; P343 : A
20 4 2001 12 PRO GR ESS IN GEO GRA PH Y V o l. 20, N o. 4 D ec., 2001 : 100726301 (2001) 0420355209, (, 100101) :, 501 mm 502 mm, 765 10 8 m 3 638 10 8 m 3, 127 10 8 m 3,,, ;, : ; ; : P42616; P343 : A
For all questions, answer choice E. NOTA" means none of the above answers is correct.
 For all questions, answer choice " means none of the above answers is correct. 1. The sum of the integers 1 through n can be modeled by a quadratic polynomial. What is the product of the non-zero coefficients
For all questions, answer choice " means none of the above answers is correct. 1. The sum of the integers 1 through n can be modeled by a quadratic polynomial. What is the product of the non-zero coefficients
( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x 2 = - 8y.
 PROBLEMS 04 - PARABOLA Page 1 ( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x - 8. [ Ans: ( 0, - ), 8, ] ( ) If the line 3x 4 k 0 is
PROBLEMS 04 - PARABOLA Page 1 ( 1 ) Find the co-ordinates of the focus, length of the latus-rectum and equation of the directrix of the parabola x - 8. [ Ans: ( 0, - ), 8, ] ( ) If the line 3x 4 k 0 is
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review.
 Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
Pre-Calculus Final Exam Review Name: May June 2015 Use the following schedule to complete the final exam review. Homework will be checked in every day. Late work will NOT be accepted. Homework answers
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3 2, 5 2 C) - 5 2
 Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Lecture 17. Implicit differentiation. Making y the subject: If xy =1,y= x 1 & dy. changed to the subject of y. Note: Example 1.
 Implicit differentiation. Lecture 17 Making y the subject: If xy 1,y x 1 & dy dx x 2. But xy y 2 1 is harder to be changed to the subject of y. Note: d dx (f(y)) f (y) dy dx Example 1. Find dy dx given
Implicit differentiation. Lecture 17 Making y the subject: If xy 1,y x 1 & dy dx x 2. But xy y 2 1 is harder to be changed to the subject of y. Note: d dx (f(y)) f (y) dy dx Example 1. Find dy dx given
Algebra 2 End of Term Final REVIEW
 Algebra End of Term Final REVIEW DO NOT WRITE IN TEST BOOKLET. 1. Graph. a. c. x x x x. Express as a single logarithm. Simplif, if possible. a. 5 c. 3 3. The volume V of a clinder varies jointl with the
Algebra End of Term Final REVIEW DO NOT WRITE IN TEST BOOKLET. 1. Graph. a. c. x x x x. Express as a single logarithm. Simplif, if possible. a. 5 c. 3 3. The volume V of a clinder varies jointl with the
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, April 5, 2017 Problem Set 8
 Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, April 5, 2017 Problem Set 8 1. Determine the coordinates of the vertices and foci for each of the following ellipses. (a) + 9y 2 = 36 We want equation to be of the
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, April 5, 2017 Problem Set 8 1. Determine the coordinates of the vertices and foci for each of the following ellipses. (a) + 9y 2 = 36 We want equation to be of the
CK- 12 Algebra II with Trigonometry Concepts 1
 10.1 Parabolas with Verte at the Origin Answers 1. up. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, -0.5), directri: = 0.5 5.focus: (0.065, 0), directri: = -0.065 6.focus: (-1.5, 0), directri: = 1.5 7.focus: (0, ), directri:
10.1 Parabolas with Verte at the Origin Answers 1. up. left 3. down 4.focus: (0, -0.5), directri: = 0.5 5.focus: (0.065, 0), directri: = -0.065 6.focus: (-1.5, 0), directri: = 1.5 7.focus: (0, ), directri:
Math 4399 Mathematics Instructional Design. Homework4. Please record all answers on the answer sheet for Homework 4.
 Math 4399 Mathematics Instructional Design Homework4 Please record all answers on the answer sheet for Homework 4. DIRECTIONS Read each question carefull. For a multiple-choice question, determine the
Math 4399 Mathematics Instructional Design Homework4 Please record all answers on the answer sheet for Homework 4. DIRECTIONS Read each question carefull. For a multiple-choice question, determine the
Th e E u r o p e a n M ig r a t io n N e t w o r k ( E M N )
 Th e E u r o p e a n M ig r a t io n N e t w o r k ( E M N ) H E.R E T h em at ic W o r k sh o p an d Fin al C o n fer en ce 1 0-1 2 Ju n e, R agu sa, It aly D avid R eisen zein IO M V ien n a Foto: Monika
Th e E u r o p e a n M ig r a t io n N e t w o r k ( E M N ) H E.R E T h em at ic W o r k sh o p an d Fin al C o n fer en ce 1 0-1 2 Ju n e, R agu sa, It aly D avid R eisen zein IO M V ien n a Foto: Monika
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 2012, Brooks/Cole
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 2012, Brooks/Cole
Parabola. The fixed point is called the focus and it is denoted by S. A (0, 0), S (a, 0) and P (x 1, y 1 ) PM=NZ=NA+AZ= x 1 + a
 : Conic: The locus of a point moving on a plane such that its distance from a fixed point and a fixed straight line in the plane are in a constant ratio é, is called a conic. The fixed point is called
: Conic: The locus of a point moving on a plane such that its distance from a fixed point and a fixed straight line in the plane are in a constant ratio é, is called a conic. The fixed point is called
2015 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 205 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 205 Solutions 205 University of Waterloo 205 CTMC Solutions Page 2 Individual Problems.
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 205 Canadian Team Mathematics Contest April 205 Solutions 205 University of Waterloo 205 CTMC Solutions Page 2 Individual Problems.
Lesson 9.1 Using the Distance Formula
 Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
STEEL PIPE NIPPLE BLACK AND GALVANIZED
 Price Sheet Effective August 09, 2018 Supersedes CWN-218 A Member of The Phoenix Forge Group CapProducts LTD. Phone: 519-482-5000 Fax: 519-482-7728 Toll Free: 800-265-5586 www.capproducts.com www.capitolcamco.com
Price Sheet Effective August 09, 2018 Supersedes CWN-218 A Member of The Phoenix Forge Group CapProducts LTD. Phone: 519-482-5000 Fax: 519-482-7728 Toll Free: 800-265-5586 www.capproducts.com www.capitolcamco.com
Math 180 Chapter 10 Lecture Notes. Professor Miguel Ornelas
 Math 180 Chapter 10 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 10.1 Section 10.1 Parabolas Definition of a Parabola A parabola is the set of all points in a plane
Math 180 Chapter 10 Lecture Notes Professor Miguel Ornelas 1 M. Ornelas Math 180 Lecture Notes Section 10.1 Section 10.1 Parabolas Definition of a Parabola A parabola is the set of all points in a plane
Foundations of Calculus. November 18, 2014
 Foundations of Calculus November 18, 2014 Contents 1 Conic Sections 3 11 A review of the coordinate system 3 12 Conic Sections 4 121 Circle 4 122 Parabola 5 123 Ellipse 5 124 Hyperbola 6 2 Review of Functions
Foundations of Calculus November 18, 2014 Contents 1 Conic Sections 3 11 A review of the coordinate system 3 12 Conic Sections 4 121 Circle 4 122 Parabola 5 123 Ellipse 5 124 Hyperbola 6 2 Review of Functions
EXAM II CALCULUS BC SECTION I PART A Time-55 minutes Number of questions-28 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION
 6 EXAM II CALCULUS BC SECTION I PART A Time-55 minutes Number of questions-8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USE ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION irections: Solve each of the following problems, using the available
6 EXAM II CALCULUS BC SECTION I PART A Time-55 minutes Number of questions-8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USE ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION irections: Solve each of the following problems, using the available
Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane
 3110 General Mathematics 1 31 10 General Mathematics For the students from Pharmaceutical Faculty 1/004 Instructor: Dr Wattana Toutip (ดร.ว ฒนา เถาว ท พย ) Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane Overview:
3110 General Mathematics 1 31 10 General Mathematics For the students from Pharmaceutical Faculty 1/004 Instructor: Dr Wattana Toutip (ดร.ว ฒนา เถาว ท พย ) Chapter 1 Analytic geometry in the plane Overview:
Coordinate goemetry in the (x, y) plane
 Coordinate goemetr in the (x, ) plane In this chapter ou will learn how to solve problems involving parametric equations.. You can define the coordinates of a point on a curve using parametric equations.
Coordinate goemetr in the (x, ) plane In this chapter ou will learn how to solve problems involving parametric equations.. You can define the coordinates of a point on a curve using parametric equations.
Definition 1.1 Let a and b be numbers, a smaller than b. Then the set of all numbers between a and b :
 1 Week 1 Definition 1.1 Let a and b be numbers, a smaller than b. Then the set of all numbers between a and b : a and b included is denoted [a, b] a included, b excluded is denoted [a, b) a excluded, b
1 Week 1 Definition 1.1 Let a and b be numbers, a smaller than b. Then the set of all numbers between a and b : a and b included is denoted [a, b] a included, b excluded is denoted [a, b) a excluded, b
Day 4: Motion Along a Curve Vectors
 Day 4: Motion Along a Curve Vectors I give my stuents the following list of terms an formulas to know. Parametric Equations, Vectors, an Calculus Terms an Formulas to Know: If a smooth curve C is given
Day 4: Motion Along a Curve Vectors I give my stuents the following list of terms an formulas to know. Parametric Equations, Vectors, an Calculus Terms an Formulas to Know: If a smooth curve C is given
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 10-1 Introduction to Conic Sections
 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 10-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Graphing Parabolas and Hperbolas on a Calculator A is a single curve, whereas a has two congruent branches. Identif and describe each
Find this vocabular word in Lesson 10-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Graphing Parabolas and Hperbolas on a Calculator A is a single curve, whereas a has two congruent branches. Identif and describe each
Section 8.2: Integration by Parts When you finish your homework, you should be able to
 Section 8.2: Integration by Parts When you finish your homework, you should be able to π Use the integration by parts technique to find indefinite integral and evaluate definite integrals π Use the tabular
Section 8.2: Integration by Parts When you finish your homework, you should be able to π Use the integration by parts technique to find indefinite integral and evaluate definite integrals π Use the tabular
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
CHAPTER 3 Applications of Differentiation
 CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
CHAPTER Applications of Differentiation Section. Etrema on an Interval.............. Section. Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. 7 Section. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and the First Derivative
Chapter Summary. How does Chapter 10 fit into the BIGGER PICTURE of algebra?
 Page of 5 0 Chapter Summar WHAT did ou learn? Find the distance between two points. (0.) Find the midpoint of the line segment connecting two points. (0.) Use distance and midpoint formulas in real-life
Page of 5 0 Chapter Summar WHAT did ou learn? Find the distance between two points. (0.) Find the midpoint of the line segment connecting two points. (0.) Use distance and midpoint formulas in real-life
Directions: This is a final exam review which covers all of the topics of the course. Please use this as a guide to assist you in your studies.
 MATH 1113 Precalculus FINAL EXAM REVIEW irections: This is a final exam review which covers all of the topics of the course. Please use this as a guide to assist you in your studies. Question: 1 QI: 758
MATH 1113 Precalculus FINAL EXAM REVIEW irections: This is a final exam review which covers all of the topics of the course. Please use this as a guide to assist you in your studies. Question: 1 QI: 758
Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed.
 Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed. Part A: (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) Do the following problems. Write the answer in the space provided. Only the answers
Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed. Part A: (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) Do the following problems. Write the answer in the space provided. Only the answers
Grain Reserves, Volatility and the WTO
 Grain Reserves, Volatility and the WTO Sophia Murphy Institute for Agriculture and Trade Policy www.iatp.org Is v o la tility a b a d th in g? De pe n d s o n w h e re yo u s it (pro d uc e r, tra d e
Grain Reserves, Volatility and the WTO Sophia Murphy Institute for Agriculture and Trade Policy www.iatp.org Is v o la tility a b a d th in g? De pe n d s o n w h e re yo u s it (pro d uc e r, tra d e
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola
 Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
Honors Precalculus Chapter 8 Summary Conic Sections- Parabola Definition: Focal length: y- axis P(x, y) Focal chord: focus Vertex x-axis directrix Focal width/ Latus Rectum: Derivation of equation of parabola:
Spontaneous reactions occur only between the reactants shown in red.
 Energy revision Solutions Question 1 The react io n b et w een so lut io n s of h yd roch lo ric acid an d so d ium h yd roxid e can b e rep resen t ed b y t h e f o llow in g eq uat io n. HCl(aq ) + NaOH(aq
Energy revision Solutions Question 1 The react io n b et w een so lut io n s of h yd roch lo ric acid an d so d ium h yd roxid e can b e rep resen t ed b y t h e f o llow in g eq uat io n. HCl(aq ) + NaOH(aq
Math 262 Exam 1 - Practice Problems. 1. Find the area between the given curves:
 Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
S U E K E AY S S H A R O N T IM B E R W IN D M A R T Z -PA U L L IN. Carlisle Franklin Springboro. Clearcreek TWP. Middletown. Turtlecreek TWP.
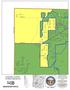 F R A N K L IN M A D IS O N S U E R O B E R T LE IC H T Y A LY C E C H A M B E R L A IN T W IN C R E E K M A R T Z -PA U L L IN C O R A O W E N M E A D O W L A R K W R E N N LA N T IS R E D R O B IN F
F R A N K L IN M A D IS O N S U E R O B E R T LE IC H T Y A LY C E C H A M B E R L A IN T W IN C R E E K M A R T Z -PA U L L IN C O R A O W E N M E A D O W L A R K W R E N N LA N T IS R E D R O B IN F
Straight Lines. Distance Formula. Gradients. positive direction. Equation of a Straight Line. Medians. hsn.uk.net
 Distance Formula Straight Lines Distance ( ) + ( ) between points (, ) and (, ) Gradients m between the points (, ) and (, ) where Positive gradients, negative gradients, zero gradients, undefined gradients
Distance Formula Straight Lines Distance ( ) + ( ) between points (, ) and (, ) Gradients m between the points (, ) and (, ) where Positive gradients, negative gradients, zero gradients, undefined gradients
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students. Francis Joseph H. Campeña, De La Salle University Manila
 KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila February 9, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
KEMATH1 Calculus for Chemistry and Biochemistry Students Francis Joseph H Campeña, De La Salle University Manila February 9, 2015 Contents 1 Conic Sections 2 11 A review of the coordinate system 2 12 Conic
Feasibility Analysis, Dynamics, and Control of Distillation Columns With Vapor Recompression.
 Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1981 Feasibility Analysis, Dynamics, and Control of Distillation Columns With Vapor Recompression.
Louisiana State University LSU Digital Commons LSU Historical Dissertations and Theses Graduate School 1981 Feasibility Analysis, Dynamics, and Control of Distillation Columns With Vapor Recompression.
Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse
 Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 2: Ellipse Oct 2017 1 / 24 Introduction Problem 2.1 Let A, F 1 and F 2 be three points that form a triangle F 2
Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 2: Ellipse Oct 2017 1 / 24 Introduction Problem 2.1 Let A, F 1 and F 2 be three points that form a triangle F 2
Name Please print your name as it appears on the class roster.
 Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
Berkele Cit College Practice Problems Math 1 Precalculus - Final Eam Preparation Name Please print our name as it appears on the class roster. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes
Chapter 9. Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry. 9.3 The Parabola. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.3 The Parabola Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Graph parabolas with vertices at the origin. Write equations of parabolas in
Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analytic Geometry 9.3 The Parabola Copyright 014, 010, 007 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Objectives: Graph parabolas with vertices at the origin. Write equations of parabolas in
How to use this Algebra II - Semester 2 Study Packet
 Excellence is not an act, but a habit. Aristotle Dear Algebra II Student, First of all, Congrats! for making it this far in your math career. Passing Algebra II is a huge mile-stone Give yourself a pat
Excellence is not an act, but a habit. Aristotle Dear Algebra II Student, First of all, Congrats! for making it this far in your math career. Passing Algebra II is a huge mile-stone Give yourself a pat
