Name Class Date. Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of a Parabola
|
|
|
- Preston Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Class Date 1. Parabolas Essential Question: How is the distance formula connected with deriving equations for both vertical and horizontal parabolas? Eplore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation of a Parabola A parabola is defined as a set of points equidistant from a line (called the directri) and a point (called the focus). The focus will alwas lie on the ais of smmetr, and the directri will alwas be perpendicular to the ais of smmetr. This definition can be used to derive the equation for a horizontal parabola opening to the right with its verte at the origin using the distance formula. (The derivations of parabolas opening in other directions will be covered later.) (-p, ) (-p, 0) Directri d Resource Locker (, ) d (p, 0) Focus The coordinates for the focus are given b. B Write down the epression for the distance from a point (, ) to the coordinates of the focus: ( - ) d = + ( - ) The distance from a point to a line is measured b drawing a perpendicular line segment from the point to the line. Find the point where a horizontal line from (, ) intersects the directri (defined b the line = -p for a parabola with its verte on the origin). Write down the epression for the distance from a point, (, ) to the point from Step C: ( - ) d = + ( - ) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Setting the two distances the same and simplifing gives. ( - p) + = ( + p) To continue solving the problem, square both sides of the equation and epand the squared binomials. + p + p + = + p + p Collect terms. + p + p + = 0 Finall, simplif and arrange the equation into the standard form for a horizontal parabola (with verte at (0, 0)): = Module 1 53 Lesson
2 Reflect 1. Wh was the directri placed on the line = -p?. Discussion How can the result be generalized to arrive at the standard form for a horizontal parabola with a verte at (h, k) : ( - k) = p ( - h)? Eplain 1 Writing the Equation of a Parabola with Verte at (0, 0) The equation for a horizontal parabola with verte at (0, 0) is written in the standard form as = p. It has a vertical directri along the line = -p, a horizontal ais of smmetr along the line = 0, and a focus at the point (p, 0). The parabola opens toward the focus, whether it is on the right or left of the origin (p > 0 or p < 0). Vertical parabolas are similar, but with horizontal directrices and vertical aes of smmetr: Parabolas with Vertices at the Origin Vertical Horizontal Equation in standard form = p = p p > 0 Opens upward Opens rightward p < 0 Opens downward Opens leftward Focus (0, p) (p, 0) Directri = -p = -p Ais of Smmetr = 0 = 0 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module 1 5 Lesson
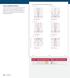
3 Eample 1 Find the equation of the parabola from the description of the focus and directri. Then make a sketch showing the parabola, the focus, and the directri. Focus (, 0), directri = A vertical directri means a horizontal parabola. Confirm that the verte is at (0, 0) : a. The -coordinate of the verte is the same as the focus: 0. b. The -coordinate is halfwa between the focus () and the directri (+): 0. c. The verte is at (0, 0) Use the equation for a horizontal parabola, = p, and replace p with the coordinate of the focus: = () Simplif: = -3 Plot the focus and directri and sketch the parabola. B Focus (0, -), directri = A [vertical/horizontal] directri means a [vertical/horizontal] parabola. Confirm that the verte is at (0, 0) : a. The -coordinate of the verte is the same as the focus: 0. b. The -coordinate is halfwa between the focus, and the directri, : c. The verte is at (0, 0). Use the equation for a vertical parabola,, and replace p with the -coordinate of the focus: = Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Simplif: = Plot the focus, the directri, and the parabola. Your Turn Find the equation of the parabola from the description of the focus and directri. Then make a sketch showing the parabola, the focus, and the directri. 3. Focus (, 0), directri = -. Focus ( 0, - 1_ ), directri = 1_ Module 1 55 Lesson
4 Eplain Writing the Equation of a Parabola with Verte at (h, k) The standard equation for a parabola with a verte (h, k) can be found b translating from (0, 0) to (h, k): substitute ( - h) for and ( - k) for. This also translates the focus and directri each b the same amount. Parabolas with Verte (h, k) Vertical Horizontal Equation in standard form ( - h) = p ( - k) ( - k) = p ( - h) p > 0 Opens upward Opens rightward p < 0 Opens downward Opens leftward Focus (h, k + p) (h + p, k) Directri = k - p = h - p Ais of Smmetr = h = k p is found halfwa from the directri to the focus: For vertical parabolas: p = For horizontal parabolas: p = ( value of focus) - ( value of directri) ( value of focus) - ( value of directri) The verte can be found from the focus b relating the coordinates of the focus to h, k, and p. Eample Find the equation of the parabola from the description of the focus and directri. Then make a sketch showing the parabola, the focus, and the directri. Focus (3, ), directri = 0 A horizontal directri means a vertical parabola. ( value of focus) - ( value of directri) p = = _ - 0 = 1 h = the -coordinate of the focus = 3 Solve for k: The -value of the focus is k + p, so k + p = k + 1 = k = 1 Write the equation: ( - 3) = ( - 1) Plot the focus, the directri, and the parabola Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module 1 56 Lesson
5 B Focus (-1, -1), directri = 5 A vertical directri means a parabola. - ( value of focus) - ( value of directri) p = = = k = the -coordinate of the focus = Solve for h: The -value of the focus is h + p, so h + p = h + (-3) = h = Write the equation: ( + 1) = ( - ) Your Turn Find the equation of the parabola from the description of the focus and directri. Then make a sketch showing the parabola, the focus, and the directri. 5. Focus (5, -1), directri = Focus (-, 0), directri = Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Eplain 3 Rewriting the Equation of a Parabola to Graph the Parabola A second-degree equation in two variables is an equation constructed b adding terms in two variables with powers no higher than. The general form looks like this: a + b + c + d + e = 0 Epanding the standard form of a parabola and grouping like terms results in a second-degree equation with either a = 0 or b = 0, depending on whether the parabola is vertical or horizontal. To graph an equation in this form requires the opposite conversion, accomplished b completing the square of the squared variable. Module 1 57 Lesson
6 Eample 3 Convert the equation to the standard form of a parabola and graph the parabola, the focus, and the directri = 0 Isolate the terms and complete the square on. Isolate the terms. - = - 1 Add _- ( ) to both sides. - + = - Factor the perfect square trinomial on the left side. ( - ) = - Factor out from the right side. ( - ) = ( - ) This is the standard form for a vertical parabola. Now find p, h, and k from the standard form ( - h) = p ( - k) in order to graph the parabola, focus, and directri. p =, so p = 1 h =, k = Verte = (h, k) = (, ) Focus = (h, k + p) = (, + 1) = (, 3) Directri: = k p = 1, or = B = 0 Isolate the terms. + = 1 Add ( ) _ to both sides. + + = Factor the perfect square trinomial. ( + ) Factor out on the right. ( + ) = = ( + ) Identif the features of the graph using the standard form of a horizontal parabola, ( - k) = p ( - h) : p =, so p = h =, k = Verte = (h, k) = (, ) Focus = (h + p, k) = (, ) Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Directri: = h - p, or = Module 1 5 Lesson
7 Your Turn Convert the equation to the standard form of a parabola and graph the parabola, the focus, and the directri = = Eplain Solving a Real-World Problem Parabolic shapes occur in a variet of applications in science and engineering that take advantage of the concentrating propert of reflections from the parabolic surface at the focus. Eample Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Parabolic microphones are so-named because the use a parabolic dish to bounce sound waves toward a microphone placed at the focus of the parabola in order to increase sensitivit. The dish shown has a cross section dictated b the equation = 3 where and are in inches. How far from the center of the dish should the microphone be placed? The cross section matches the standard form of a horizontal parabola with h = 0, k = 0, p =. Therefore the verte, which is the center of the dish, is at (0, 0) and the focus is at (, 0), inches awa. Module 1 59 Lesson
8 B A reflective telescope uses a parabolic mirror to focus light ras before creating an image with the eepiece. If the focal length (the distance from the bottom of the mirror s bowl to the focus) is 10 mm and the mirror has a 70 mm diameter (width), what is the depth of the bowl of the mirror?? 70 mm 10 mm parabolic mirror eepiece plane mirror prime focus The distance from the bottom of the mirror s bowl to the focus is p. The verte location is not specified (or needed), so use (0, 0) for simplicit. The equation for the mirror is a horizontal parabola (with the distance along the telescope and the position out from the center). ( - ) = p ( - ) = Since the diameter of the bowl of the mirror is 70 mm, the points at the rim of the mirror have -values of 35 mm and -35 mm. The -value of either point will be the same as the -value of the point directl above the bottom of the bowl, which equals the depth of the bowl. Since the points on the rim lie on the parabola, use the equation of the parabola to solve for the -value of either edge of the mirror. = mm The bowl is approimatel.19 mm deep. Your Turn 9. A football team needs one more field goal to win the game. The goalpost that the ball must clear is 10 feet (~3.3 d) off the ground. The path of the football after it is kicked for a 35-ard field goal is given b the equation - 11 = ( - 0), in ards. Does the team win? Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module Lesson
9 Elaborate 10. Eamine the graphs in this lesson and determine a relationship between the separation of the focus and the verte, and the shape of the parabola. Demonstrate this b finding the relationship between p for a vertical parabola with verte of (0, 0) and a, the coefficient of the quadratic parent function = a. 11. Essential Question Check-In How can ou use the distance formula to derive an equation relating and from the definition of a parabola based on focus and directri? Evaluate: Homework and Practice Find the equation of the parabola with verte at (0, 0) from the description of the focus and directri and plot the parabola, the focus, and the directri. Online Homework Hints and Help Etra Practice 1. Focus at (3, 0), directri: = -3. Focus at (0, -5), directri: = 5 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Focus at (-1, 0), directri: = 1. Focus at (0, ), directri: = Module Lesson
10 Find the equation of the parabola with the given information. 5. Verte: (-3, 6) ; Directri: = Verte: (6, 0) ; Focus: (6, 11) Find the equation of the parabola with verte at (h, k) from the description of the focus and directri and plot the parabola, the focus, and the directri. 7. Focus at (5, 3), directri: = 7. Focus at (-3, 3), directri: = Convert the equation to the standard form of a parabola and graph the parabola, the focus, and the directri = = Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan 11. Communications The equation for the cross section of a parabolic satellite television dish is = 50, measured in inches. How far is the focus from the verte of the cross section? 1 Module 1 59 Lesson
11 1. Engineering The equation for the cross section of a spotlight is + 5 = 1, measured in inches. The bulb is located at the focus. How far is the bulb from the verte of the cross section? When a ball is thrown into the air, the path that the ball travels is modeled b the parabola - 7 = ( - 0), measured in feet. What is the maimum height the ball reaches? How far does the ball travel before it hits the ground? 1. A cable for a suspension bridge is modeled b - 55 = 0.005, where is the horizontal distance, in feet, from the support tower and is the height, in feet, above the bridge. How far is the lowest point of the cable above the bridge? Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credits: J. Aa./ Shutterstock 15. Match each equation to its graph. + 1 = 1_ 16 ( - ) A B. - 1 = 1_ ( 16 + ) C. + 1 = - 1_ Module Lesson
12 Derive the equation of the parabolas with the given information. 16. An upward-opening parabola with a focus at (0, p) and a directri = -p. 17. A leftward-opening parabola with a focus at (-p, 0) and directri at = p. H.O.T. Focus on Higher Order Thinking 1. Multi-Step A tennis plaer hits a tennis ball just as it hits one end line of the court. The path of the ball is modeled b the equation - = ( - 39) where = 0 is at the end line. The tennis net is 3 feet high, and the total length of the court is 7 feet. a. How far is the net located from the plaer? b. Eplain wh the ball will go over the net. c. Will the ball land "in," that is, inside the court or on the opposite endline? Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module 1 59 Lesson
13 19. Critical Thinking The latus rectum of a parabola is the line segment perpendicular to the ais of smmetr through the focus, with endpoints on the parabola. Find the length of the latus rectum of a parabola. Justif our answer. Hint: Set the coordinate sstem such that the verte is at the origin and the parabola opens rightward with the focus at (p, 0). 0. Eplain the Error Lois is finding the focus and directri of the parabola - = - 1_ ( + ). Her work is shown. Eplain what Lois did wrong, and then find the correct answer. h = -, k = p = - 1_, so p = - 1_, or p = Focus = (h, k + p) = (-, 7.75) Directri: = k - p, or =.15 Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Module Lesson
14 Lesson Performance Task Parabolic microphones are used for field audio during sports events. The microphones are manufactured such that the equation of their cross section is = 1 3, in inches. The feedhorn part of the microphone is located at the focus. a. How far is the feedhorn from the edge of the parabolic surface of the microphone? b. What is the diameter of the microphone? Eplain our reasoning. c. If the diameter is increased b 5 inches, what is the new equation of the cross section of the microphone? Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Compan Image Credits: Scott Boehm/AP Images Module Lesson
4.2 Parabolas. Explore Deriving the Standard-Form Equation. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. (x - p) 2 + y 2 = (x + p) 2
 COMMON CORE. d Locker d LESSON Parabolas Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities;
COMMON CORE. d Locker d LESSON Parabolas Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: COMMON CORE A-CED.A. Create equations in two or more variables to represent relationships between quantities;
7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 7.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
5-4. Focus and Directrix of a Parabola. Key Concept Parabola VOCABULARY TEKS FOCUS ESSENTIAL UNDERSTANDING
 5- Focus and Directri of a Parabola TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY TEKS ()(B) Write the equation of a parabola using given attributes, including verte, focus, directri, ais of smmetr, and direction of opening.
5- Focus and Directri of a Parabola TEKS FOCUS VOCABULARY TEKS ()(B) Write the equation of a parabola using given attributes, including verte, focus, directri, ais of smmetr, and direction of opening.
6.3 Interpreting Vertex Form and Standard Form
 Name Class Date 6.3 Interpreting Verte Form and Standard Form Essential Question: How can ou change the verte form of a quadratic function to standard form? Resource Locker Eplore Identifing Quadratic
Name Class Date 6.3 Interpreting Verte Form and Standard Form Essential Question: How can ou change the verte form of a quadratic function to standard form? Resource Locker Eplore Identifing Quadratic
20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors
 Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Name Class Date 20.2 Connecting Intercepts and Linear Factors Essential Question: How are -intercepts of a quadratic function and its linear factors related? Resource Locker Eplore Connecting Factors and
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Find the -intercept of the graph of the linear equation. 1. = + 3. = 3 + 5 3. = 10 75. = ( 9) 5. 7( 10) = +. 5 + 15 = 0 Find the distance between the two points.
Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Find the -intercept of the graph of the linear equation. 1. = + 3. = 3 + 5 3. = 10 75. = ( 9) 5. 7( 10) = +. 5 + 15 = 0 Find the distance between the two points.
Quadratic Function. Parabola. Parent quadratic function. Vertex. Axis of Symmetry
 Name: Chapter 10: Quadratic Equations and Functions Section 10.1: Graph = a + c Quadratic Function Parabola Parent quadratic function Verte Ais of Smmetr Parent Function = - -1 0 1 1 Eample 1: Make a table,
Name: Chapter 10: Quadratic Equations and Functions Section 10.1: Graph = a + c Quadratic Function Parabola Parent quadratic function Verte Ais of Smmetr Parent Function = - -1 0 1 1 Eample 1: Make a table,
Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas
 TEKS 9.2 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas that open up or down. Now You will graph and write equations of parabolas that open
TEKS 9.2 a.5, 2A.5.B, 2A.5.C Graph and Write Equations of Parabolas Before You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas that open up or down. Now You will graph and write equations of parabolas that open
Analytic Geometry in Two and Three Dimensions
 CHAPTER 8 Analtic Geometr in Two and Three Dimensions 8.1 Conic Sections and Parabolas 8.2 Ellipses 8.3 Hperbolas 8.4 Translation and Rotation of Aes 8.5 Polar Equations of Conics 8.6 Three-Dimensional
CHAPTER 8 Analtic Geometr in Two and Three Dimensions 8.1 Conic Sections and Parabolas 8.2 Ellipses 8.3 Hperbolas 8.4 Translation and Rotation of Aes 8.5 Polar Equations of Conics 8.6 Three-Dimensional
7.1 Connecting Intercepts and Zeros
 Locker LESSON 7. Connecting Intercepts and Zeros Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7a Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maima, and minima. Also A-REI.,
Locker LESSON 7. Connecting Intercepts and Zeros Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.7a Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maima, and minima. Also A-REI.,
9.5 Solving Nonlinear Systems
 Name Class Date 9.5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? Eplore Determining the Possible Number of
Name Class Date 9.5 Solving Nonlinear Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? Eplore Determining the Possible Number of
Characteristics of Quadratic Functions
 . Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Essential Question What tpe of smmetr does the graph of f() = a( h) + k have and how can ou describe this smmetr? Parabolas and Smmetr Work with a partner. a. Complete
. Characteristics of Quadratic Functions Essential Question What tpe of smmetr does the graph of f() = a( h) + k have and how can ou describe this smmetr? Parabolas and Smmetr Work with a partner. a. Complete
10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 Name Class Date 10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of quadratic functions and cubic functions, and how can ou find them? Resource
Name Class Date 10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of quadratic functions and cubic functions, and how can ou find them? Resource
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 10-1 Introduction to Conic Sections
 Find this vocabular word in Lesson 10-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Graphing Parabolas and Hperbolas on a Calculator A is a single curve, whereas a has two congruent branches. Identif and describe each
Find this vocabular word in Lesson 10-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Graphing Parabolas and Hperbolas on a Calculator A is a single curve, whereas a has two congruent branches. Identif and describe each
Section 7.3: Parabolas, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition by Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons
 Section 7.: Parabolas, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition b Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license. 0, Carl Stitz.
Section 7.: Parabolas, from College Algebra: Corrected Edition b Carl Stitz, Ph.D. and Jeff Zeager, Ph.D. is available under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike.0 license. 0, Carl Stitz.
13.2 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
Name Class Date. Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > related to the graph of f () = b? A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the
10.2 Graphing Square Root Functions
 Name Class Date. Graphing Square Root Functions Essential Question: How can ou use transformations of a parent square root function to graph functions of the form g () = a (-h) + k or g () = b (-h) + k?
Name Class Date. Graphing Square Root Functions Essential Question: How can ou use transformations of a parent square root function to graph functions of the form g () = a (-h) + k or g () = b (-h) + k?
Using Intercept Form
 8.5 Using Intercept Form Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f () = a( p)( q)? Using Zeros to Write Functions Work with a partner. Each graph represents a function of
8.5 Using Intercept Form Essential Question What are some of the characteristics of the graph of f () = a( p)( q)? Using Zeros to Write Functions Work with a partner. Each graph represents a function of
10.2 Graphing Exponential Functions
 Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
Name Class Date 10. Graphing Eponential Functions Essential Question: How do ou graph an eponential function of the form f () = ab? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Graphs of Eponential Functions Eponential
11.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Fair Game Review. Chapter 8. Graph the linear equation. Big Ideas Math Algebra Record and Practice Journal
 Name Date Chapter Graph the linear equation. Fair Game Review. =. = +. =. =. = +. = + Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Algebra Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued) Evaluate the
Name Date Chapter Graph the linear equation. Fair Game Review. =. = +. =. =. = +. = + Copright Big Ideas Learning, LLC Big Ideas Math Algebra Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review (continued) Evaluate the
13.1 Exponential Growth Functions
 Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
Name Class Date 1.1 Eponential Growth Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b - h + k where b > 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f
Chapter 11 Quadratic Functions
 Chapter 11 Quadratic Functions Mathematical Overview The relationship among parabolas, quadratic functions, and quadratic equations is investigated through activities that eplore both the geometric and
Chapter 11 Quadratic Functions Mathematical Overview The relationship among parabolas, quadratic functions, and quadratic equations is investigated through activities that eplore both the geometric and
3.1 Graph Quadratic Functions
 3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
3. Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMA3b, MMA3c Goal p Use intervals of increase and decrease to understand average rates of change of quadratic functions. Your
5.2 Solving Linear-Quadratic Systems
 Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
Name Class Date 5. Solving Linear-Quadratic Sstems Essential Question: How can ou solve a sstem composed of a linear equation in two variables and a quadratic equation in two variables? Resource Locker
15.4 Equation of a Circle
 Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
Name Class Date 1.4 Equation of a Circle Essential Question: How can ou write the equation of a circle if ou know its radius and the coordinates of its center? Eplore G.1.E Show the equation of a circle
Summary, Review, and Test
 944 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analtic Geometr 45. Use the polar equation for planetar orbits, to find the polar equation of the orbit for Mercur and Earth. Mercur: e = 0.056 and a = 36.0 * 10 6 miles
944 Chapter 9 Conic Sections and Analtic Geometr 45. Use the polar equation for planetar orbits, to find the polar equation of the orbit for Mercur and Earth. Mercur: e = 0.056 and a = 36.0 * 10 6 miles
3. TRANSLATED PARABOLAS
 3. TRANSLATED PARABOLAS The Parabola with Verte V(h, k) and Aes Parallel to the ais Consider the concave up parabola with verte V(h, k) shown below. This parabola is obtained b translating the parabola
3. TRANSLATED PARABOLAS The Parabola with Verte V(h, k) and Aes Parallel to the ais Consider the concave up parabola with verte V(h, k) shown below. This parabola is obtained b translating the parabola
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 3.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Define each term in our own words.. quadratic function. vertical motion Problem
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Define each term in our own words.. quadratic function. vertical motion Problem
Name Class Date. Solving by Graphing and Algebraically
 Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
Name Class Date 16-4 Nonlinear Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou solve a sstem of equations when one equation is linear and the other is quadratic? To estimate the solution to a sstem
Writing Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form (general form) of a quadratic function (.1) parabola (.1) leading coefficient (.) second differences (.) vertical motion model (.3) zeros (.3) interval (.3) open interval
Chapter Summar Ke Terms standard form (general form) of a quadratic function (.1) parabola (.1) leading coefficient (.) second differences (.) vertical motion model (.3) zeros (.3) interval (.3) open interval
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing
Name Class Date 15. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a log b ( h) + k where b > and b 1 related to the graph of f () = log b? Resource Locker Eplore 1 Graphing
3.2. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Relations. LEARN ABOUT the Math. Reasoning from a table of values and a graph of a quadratic model
 3. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Relations YOU WILL NEED grid paper ruler graphing calculator GOAL Describe the ke features of the graphs of quadratic relations, and use the graphs to solve problems.
3. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Relations YOU WILL NEED grid paper ruler graphing calculator GOAL Describe the ke features of the graphs of quadratic relations, and use the graphs to solve problems.
REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY REVIEW EXAMPLES AND EXERCISES
 Etra Eample. Graph.. 6. 7. (, ) (, ) REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY quadratic function, p. 6 standard form of a quadratic function, p. 6 parabola, p. 6 verte, p. 6 ais of smmetr, p. 6 minimum, maimum value, p.
Etra Eample. Graph.. 6. 7. (, ) (, ) REVIEW KEY VOCABULARY quadratic function, p. 6 standard form of a quadratic function, p. 6 parabola, p. 6 verte, p. 6 ais of smmetr, p. 6 minimum, maimum value, p.
10.2 INTRODUCTION TO CONICS: PARABOLAS
 Section 0.2 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 733 0.2 INTRODUCTION TO CONICS: PARABOLAS What ou should learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane a double-napped cone. Write equations of parabolas
Section 0.2 Introduction to Conics: Parabolas 733 0.2 INTRODUCTION TO CONICS: PARABOLAS What ou should learn Recognize a conic as the intersection of a plane a double-napped cone. Write equations of parabolas
Name Class Date. Understanding How to Graph g(x) = a(x - h ) 2 + k
 Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
Name Class Date - Transforming Quadratic Functions Going Deeper Essential question: How can ou obtain the graph of g() = a( h ) + k from the graph of f () =? 1 F-BF..3 ENGAGE Understanding How to Graph
Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form
 TEKS 4. 2A.4.A, 2A.4.B, 2A.6.B, 2A.8.A Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Before You graphed linear functions. Now You will graph quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can model sports revenue, as in
TEKS 4. 2A.4.A, 2A.4.B, 2A.6.B, 2A.8.A Graph Quadratic Functions in Standard Form Before You graphed linear functions. Now You will graph quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can model sports revenue, as in
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Lesson 9.1 Using the Distance Formula
 Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
Lesson. Using the Distance Formula. Find the eact distance between each pair of points. a. (0, 0) and (, ) b. (0, 0) and (7, ) c. (, 8) and (, ) d. (, ) and (, 7) e. (, 7) and (8, ) f. (8, ) and (, 0)
= x. Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit Graphing Quadratic Functions. Math Background
 Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit 3.1 3. Graphing Quadratic Functions Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Algebra II Notes Quadratic Functions Unit 3.1 3. Graphing Quadratic Functions Math Background Previousl, ou Identified and graphed linear functions Applied transformations to parent functions Graphed quadratic
Math 3 Unit 7: Parabolas & Circles
 Math 3 Unit 7: Parabolas & Circles Unit Title Standards 7.1 Introduction to Circles G.GPE.1, F.IF.8.a, F.IF.8 7.2 Converting Circles to Descriptive Form G.GPE.1, A.CED.4, F.IF.8 7.3 Definition of a Parabola
Math 3 Unit 7: Parabolas & Circles Unit Title Standards 7.1 Introduction to Circles G.GPE.1, F.IF.8.a, F.IF.8 7.2 Converting Circles to Descriptive Form G.GPE.1, A.CED.4, F.IF.8 7.3 Definition of a Parabola
The telescopes at the W.M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii use hyperbolic mirrors.
 UNIT 15 Conic Sections The telescopes at the W.M. Keck Observator in Hawaii use hperbolic mirrors. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including
UNIT 15 Conic Sections The telescopes at the W.M. Keck Observator in Hawaii use hperbolic mirrors. Copright 009, K1 Inc. All rights reserved. This material ma not be reproduced in whole or in part, including
1. Without the use of your calculator, evaluate each of the following quadratic functions for the specified input values. (c) ( )
 Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW FLUENCY Algebra II 1. Without the use of our calculator, evaluate each of the following quadratic functions for the specified input values. (a) g( x) g g ( 5) ( 3)
Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW FLUENCY Algebra II 1. Without the use of our calculator, evaluate each of the following quadratic functions for the specified input values. (a) g( x) g g ( 5) ( 3)
LESSON #42 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART 2 COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope
 Name Class Date 5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope Essential question: How can ou relate rate of change and slope in linear relationships? Resource Locker Eplore Determining Rates of Change For
Name Class Date 5.3 Interpreting Rate of Change and Slope Essential question: How can ou relate rate of change and slope in linear relationships? Resource Locker Eplore Determining Rates of Change For
D: all real; R: y g (x) = 3 _ 2 x 2 5. g (x) = 5 x g (x) = - 4 x 2 7. g (x) = -4 x 2. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company.
 AVOID COMMON ERRORS Watch for students who do not graph points on both sides of the verte of the parabola. Remind these students that a parabola is U-shaped and smmetric, and the can use that smmetr to
AVOID COMMON ERRORS Watch for students who do not graph points on both sides of the verte of the parabola. Remind these students that a parabola is U-shaped and smmetric, and the can use that smmetr to
Path of the Horse s Jump y 3. transformation of the graph of the parent quadratic function, y 5 x 2.
 - Quadratic Functions and Transformations Content Standards F.BF. Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() k, k f(), f(k), and f( k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative)
- Quadratic Functions and Transformations Content Standards F.BF. Identif the effect on the graph of replacing f() b f() k, k f(), f(k), and f( k) for specific values of k (both positive and negative)
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions
 Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
+ 4 Ex: y = v = (1, 4) x = 1 Focus: (h, k + ) = (1, 6) L.R. = 8 units We can have parabolas that open sideways too (inverses) x = a (y k) 2 + h
 Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
Unit 7 Notes Parabolas: E: reflectors, microphones, (football game), (Davinci) satellites. Light placed where ras will reflect parallel. This point is the focus. Parabola set of all points in a plane that
10.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
COMMON CORE Locker LESSON 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Name Class Date 0. Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Essential Question: What functions are the inverses of
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 8 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the linear equation. 1. = 5. = + 3 3. 1 = + 3. = + Evaluate the epression when =. 5. + 8. + 3 7. 3 8. 5 + 8 9. 8 10. 5 + 3 11. + + 1. 3 + +
Name Date Chapter 8 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the linear equation. 1. = 5. = + 3 3. 1 = + 3. = + Evaluate the epression when =. 5. + 8. + 3 7. 3 8. 5 + 8 9. 8 10. 5 + 3 11. + + 1. 3 + +
TRANSFORMATIONS OF f(x) = x Example 1
 TRANSFORMATIONS OF f() = 2 2.1.1 2.1.2 Students investigate the general equation for a famil of quadratic functions, discovering was to shift and change the graphs. Additionall, the learn how to graph
TRANSFORMATIONS OF f() = 2 2.1.1 2.1.2 Students investigate the general equation for a famil of quadratic functions, discovering was to shift and change the graphs. Additionall, the learn how to graph
C H A P T E R 9 Topics in Analytic Geometry
 C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
C H A P T E R Topics in Analtic Geometr Section. Circles and Parabolas.................... 77 Section. Ellipses........................... 7 Section. Hperbolas......................... 7 Section. Rotation
Properties of the Graph of a Quadratic Function. has a vertex with an x-coordinate of 2 b } 2a
 0.2 Graph 5 a 2 b c Before You graphed simple quadratic functions. Now You will graph general quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can investigate a cable s height, as in Eample 4. Ke Vocabular minimum value
0.2 Graph 5 a 2 b c Before You graphed simple quadratic functions. Now You will graph general quadratic functions. Wh? So ou can investigate a cable s height, as in Eample 4. Ke Vocabular minimum value
15.2 Graphing Logarithmic
 _ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
_ - - - - - - Locker LESSON 5. Graphing Logarithmic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A.5.A Determine the effects on the ke attributes on the graphs of f () = b and f () = log b
Shape and Structure. Forms of Quadratic Functions. Lesson 2.1 Assignment
 Lesson.1 Assignment Name Date Shape and Structure Forms of Quadratic Functions 1. Analze the graph of the quadratic function. a. The standard form of a quadratic function is f() 5 a 1 b 1 c. What possible
Lesson.1 Assignment Name Date Shape and Structure Forms of Quadratic Functions 1. Analze the graph of the quadratic function. a. The standard form of a quadratic function is f() 5 a 1 b 1 c. What possible
In order to take a closer look at what I m talking about, grab a sheet of graph paper and graph: y = x 2 We ll come back to that graph in a minute.
 Module 7: Conics Lesson Notes Part : Parabolas Parabola- The parabola is the net conic section we ll eamine. We talked about parabolas a little bit in our section on quadratics. Here, we eamine them more
Module 7: Conics Lesson Notes Part : Parabolas Parabola- The parabola is the net conic section we ll eamine. We talked about parabolas a little bit in our section on quadratics. Here, we eamine them more
QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW
 Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW Linear and eponential functions are used throughout mathematics and science due to their simplicit and applicabilit. Quadratic functions comprise another ver important
Name: Date: QUADRATIC FUNCTION REVIEW Linear and eponential functions are used throughout mathematics and science due to their simplicit and applicabilit. Quadratic functions comprise another ver important
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 The Quadratic Function (Vertex Form): Translations. and axis of symmetry is at x a.
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 7 Verte form of Quadratic Relations The epression a p q defines a quadratic relation called the verte form with a horizontal translation of p units and vertical translation of
7.2 Properties of Graphs
 7. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Functions GOAL Identif the characteristics of graphs of quadratic functions, and use the graphs to solve problems. LEARN ABOUT the Math Nicolina plas on her school
7. Properties of Graphs of Quadratic Functions GOAL Identif the characteristics of graphs of quadratic functions, and use the graphs to solve problems. LEARN ABOUT the Math Nicolina plas on her school
TEST REVIEW QUADRATICS EQUATIONS Name: 2. Which of the following statements is true about the graph of the function?
 Chapter MATHEMATICS 00 TEST REVIEW QUADRATICS EQUATIONS Name:. Which equation does not represent a quadratic function?. Which of the following statements is true about the graph of the function? it has
Chapter MATHEMATICS 00 TEST REVIEW QUADRATICS EQUATIONS Name:. Which equation does not represent a quadratic function?. Which of the following statements is true about the graph of the function? it has
8.7 The Parabola. PF = PD The fixed point F is called the focus. The fixed line l is called the directrix.
 8.7 The Parabola The Hubble Space Telescope orbits the Earth at an altitude of approimatel 600 km. The telescope takes about ninet minutes to complete one orbit. Since it orbits above the Earth s atmosphere,
8.7 The Parabola The Hubble Space Telescope orbits the Earth at an altitude of approimatel 600 km. The telescope takes about ninet minutes to complete one orbit. Since it orbits above the Earth s atmosphere,
Domain, Range, and End Behavior
 Locker LESSON 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship
Locker LESSON 1.1 Domain, Range, and End Behavior Common Core Math Standards The student is epected to: F-IF.5 Relate the domain of a function to its graph and, where applicable, to the quantitative relationship
Unit 10 - Graphing Quadratic Functions
 Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
Unit - Graphing Quadratic Functions PREREQUISITE SKILLS: students should be able to add, subtract and multipl polnomials students should be able to factor polnomials students should be able to identif
13.2 Exponential Decay Functions
 Name Class Date 13. Eponential Deca Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b h + k where < b < 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f () = ( 1 and f ()
Name Class Date 13. Eponential Deca Functions Essential Question: How is the graph of g () = a b h + k where < b < 1 related to the graph of f () = b? Eplore 1 Graphing and Analzing f () = ( 1 and f ()
9-1. The Function with Equation y = ax 2. Vocabulary. Graphing y = x 2. Lesson
 Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
Chapter 9 Lesson 9-1 The Function with Equation = a BIG IDEA The graph of an quadratic function with equation = a, with a 0, is a parabola with verte at the origin. Vocabular parabola refl ection-smmetric
For questions 5-8, solve each inequality and graph the solution set. You must show work for full credit. (2 pts each)
 Alg Midterm Review Practice Level 1 C 1. Find the opposite and the reciprocal of 0. a. 0, 1 b. 0, 1 0 0 c. 0, 1 0 d. 0, 1 0 For questions -, insert , or = to make the sentence true. (1pt each) A. 5
Alg Midterm Review Practice Level 1 C 1. Find the opposite and the reciprocal of 0. a. 0, 1 b. 0, 1 0 0 c. 0, 1 0 d. 0, 1 0 For questions -, insert , or = to make the sentence true. (1pt each) A. 5
Reteaching (continued)
 Quadratic Functions and Transformations If a, the graph is a stretch or compression of the parent function b a factor of 0 a 0. 0 0 0 0 0 a a 7 The graph is a vertical The graph is a vertical compression
Quadratic Functions and Transformations If a, the graph is a stretch or compression of the parent function b a factor of 0 a 0. 0 0 0 0 0 a a 7 The graph is a vertical The graph is a vertical compression
Solve Quadratic Equations by Graphing
 0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
0.3 Solve Quadratic Equations b Graphing Before You solved quadratic equations b factoring. Now You will solve quadratic equations b graphing. Wh? So ou can solve a problem about sports, as in Eample 6.
x Radical Sign: Radicand: the number beneath the radical sign
 Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing.
Sllabus Objective: 9.4 The student will solve quadratic equations using graphic and algebraic techniques to include the quadratic formula, square roots, factoring, completing the square, and graphing.
11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions
 Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
Locker LESSON 11.1 Inverses of Simple Quadratic and Cubic Functions Teas Math Standards The student is epected to: A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as f (). Also A..A,
Mth 95 Module 4 Chapter 8 Spring Review - Solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula
 Mth 95 Module 4 Chapter 8 Spring 04 Review - Solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula Write the quadratic formula. The NUMBER of REAL and COMPLEX SOLUTIONS to a quadratic equation ( a b
Mth 95 Module 4 Chapter 8 Spring 04 Review - Solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula Write the quadratic formula. The NUMBER of REAL and COMPLEX SOLUTIONS to a quadratic equation ( a b
13.1 Understanding Piecewise-Defined Functions
 Name Class Date 13.1 Understanding Piecewise-Defined Functions Essential Question: How are piecewise-defined functions different from other functions? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Piecewise-Defined
Name Class Date 13.1 Understanding Piecewise-Defined Functions Essential Question: How are piecewise-defined functions different from other functions? Resource Locker Eplore Eploring Piecewise-Defined
Attributes and Transformations of Quadratic Functions VOCABULARY. Maximum value the greatest. Minimum value the least. Parabola the set of points in a
 - Attributes and Transformations of Quadratic Functions TEKS FCUS VCABULARY TEKS ()(B) Write the equation of a parabola using given attributes, including verte, focus, directri, ais of smmetr, and direction
- Attributes and Transformations of Quadratic Functions TEKS FCUS VCABULARY TEKS ()(B) Write the equation of a parabola using given attributes, including verte, focus, directri, ais of smmetr, and direction
Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses. You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses.
 TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
TEKS 9.4 a.5, A.5.B, A.5.C Before Now Graph and Write Equations of Ellipses You graphed and wrote equations of parabolas and circles. You will graph and write equations of ellipses. Wh? So ou can model
UNCORRECTED SAMPLE PAGES. 3Quadratics. Chapter 3. Objectives
 Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
Chapter 3 3Quadratics Objectives To recognise and sketch the graphs of quadratic polnomials. To find the ke features of the graph of a quadratic polnomial: ais intercepts, turning point and ais of smmetr.
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 1.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Give an eample of each term.. quadratic function 9 0. vertical motion equation s
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Lots and Projectiles Introduction to Quadratic Functions Vocabular Give an eample of each term.. quadratic function 9 0. vertical motion equation s
3.1. Shape and Structure Forms of Quadratic Functions ESSENTIAL IDEAS TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS FOR MATHEMATICS 169A
 Shape and Structure Forms of Quadratic Functions.1 LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS In this lesson, ou will: Match a quadratic function with its corresponding graph. Identif ke characteristics of quadratic functions
Shape and Structure Forms of Quadratic Functions.1 LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS In this lesson, ou will: Match a quadratic function with its corresponding graph. Identif ke characteristics of quadratic functions
Additional Factoring Examples:
 Honors Algebra -3 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing and Factoring Learning Targets 1. I can solve quadratic equations by graphing. I can solve quadratic equations by factoring 3. I can write a quadratic
Honors Algebra -3 Solving Quadratic Equations by Graphing and Factoring Learning Targets 1. I can solve quadratic equations by graphing. I can solve quadratic equations by factoring 3. I can write a quadratic
14.3 Constructing Exponential Functions
 Name Class Date 1.3 Constructing Eponential Functions Essential Question: What are discrete eponential functions and how do ou represent them? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Discrete Eponential Functions
Name Class Date 1.3 Constructing Eponential Functions Essential Question: What are discrete eponential functions and how do ou represent them? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Discrete Eponential Functions
Chapter 9 Notes Alg. 1H 9-A1 (Lesson 9-3) Solving Quadratic Equations by Finding the Square Root and Completing the Square
 Chapter Notes Alg. H -A (Lesson -) Solving Quadratic Equations b Finding the Square Root and Completing the Square p. *Calculator Find the Square Root: take the square root of. E: Solve b finding square
Chapter Notes Alg. H -A (Lesson -) Solving Quadratic Equations b Finding the Square Root and Completing the Square p. *Calculator Find the Square Root: take the square root of. E: Solve b finding square
3.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots
 COMMON CORE -8-16 1 1 10 8 6 0 y Locker LESSON.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Name Class Date.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: What is an imaginary
COMMON CORE -8-16 1 1 10 8 6 0 y Locker LESSON.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Name Class Date.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Taking Square Roots Essential Question: What is an imaginary
Finding Complex Solutions of Quadratic Equations
 COMMON CORE y - 0 y - - 0 - Locker LESSON 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Name Class Date 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Essential Question: How can you find the
COMMON CORE y - 0 y - - 0 - Locker LESSON 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Name Class Date 3.3 Finding Comple Solutions of Quadratic Equations Essential Question: How can you find the
Essential Question How can you use a quadratic function to model a real-life situation?
 3. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A A..E A..A A..B A..C Modeling with Quadratic Functions Essential Question How can ou use a quadratic function to model a real-life situation? Work with a partner.
3. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS A..A A..E A..A A..B A..C Modeling with Quadratic Functions Essential Question How can ou use a quadratic function to model a real-life situation? Work with a partner.
Answers. Chapter Warm Up. Sample answer: The graph of h is a translation. 3 units right of the parent linear function.
 Chapter. Start Thinking As the string V gets wider, the points on the string move closer to the -ais. This activit mimics a vertical shrink of a parabola... Warm Up.. Sample answer: The graph of f is a
Chapter. Start Thinking As the string V gets wider, the points on the string move closer to the -ais. This activit mimics a vertical shrink of a parabola... Warm Up.. Sample answer: The graph of f is a
7.3 Triangle Inequalities
 Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Eplore G.5.D Verify the Triangle
Name lass Date 7.3 Triangle Inequalities Essential Question: How can you use inequalities to describe the relationships among side lengths and angle measures in a triangle? Eplore G.5.D Verify the Triangle
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Keira Godwin. Time Allotment: 13 days. Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to:
 Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
Keira Godwin Time Allotment: 3 das Unit Objectives: Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to: o Simplif comple rational fractions. o Solve comple rational fractional equations. o Solve quadratic
20.3 Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations
 20.3 Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations Essential Question: How can you use the Zero Product Property to solve quadratic equations in factored form? Resource Locker Explore Understanding
20.3 Applying the Zero Product Property to Solve Equations Essential Question: How can you use the Zero Product Property to solve quadratic equations in factored form? Resource Locker Explore Understanding
The Coordinate Plane. Circles and Polygons on the Coordinate Plane. LESSON 13.1 Skills Practice. Problem Set
 LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
LESSON.1 Skills Practice Name Date The Coordinate Plane Circles and Polgons on the Coordinate Plane Problem Set Use the given information to show that each statement is true. Justif our answers b using
10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles
 Name Class Date 10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles Essential Question: How do ou write a coordinate proof? Resource Locker Eplore G..B...use the distance, slope,... formulas
Name Class Date 10.3 Coordinate Proof Using Distance with Segments and Triangles Essential Question: How do ou write a coordinate proof? Resource Locker Eplore G..B...use the distance, slope,... formulas
Write Quadratic Functions and Models
 4.0 A..B, A.6.B, A.6.C, A.8.A TEKS Write Quadratic Functions and Models Before You wrote linear functions and models. Now You will write quadratic functions and models. Wh? So ou can model the cross section
4.0 A..B, A.6.B, A.6.C, A.8.A TEKS Write Quadratic Functions and Models Before You wrote linear functions and models. Now You will write quadratic functions and models. Wh? So ou can model the cross section
Lesson Goals. Unit 4 Polynomial/Rational Functions Quadratic Functions (Chap 0.3) Family of Quadratic Functions. Parabolas
 Unit 4 Polnomial/Rational Functions Quadratic Functions (Chap 0.3) William (Bill) Finch Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Graph and analze the graphs of quadratic functions. Solve
Unit 4 Polnomial/Rational Functions Quadratic Functions (Chap 0.3) William (Bill) Finch Lesson Goals When ou have completed this lesson ou will: Graph and analze the graphs of quadratic functions. Solve
IAS 3.1 Conic Sections
 Year 13 Mathematics IAS 3.1 Conic Sections Robert Lakeland & Carl Nugent Contents Achievement Standard.................................................. The Straight Line.......................................................
Year 13 Mathematics IAS 3.1 Conic Sections Robert Lakeland & Carl Nugent Contents Achievement Standard.................................................. The Straight Line.......................................................
NAME DATE PERIOD. Study Guide and Intervention. Transformations of Quadratic Graphs
 NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Write Quadratic Equations in Verte Form A quadratic function is easier to graph when it is in verte form. You can write a quadratic function of the form = a
NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Write Quadratic Equations in Verte Form A quadratic function is easier to graph when it is in verte form. You can write a quadratic function of the form = a
MAT 1033C -- Martin-Gay Intermediate Algebra Chapter 8 (8.1, 8.2, 8.5, 8.6) Practice for the Exam
 MAT 33C -- Martin-Ga Intermediate Algebra Chapter 8 (8.1 8. 8. 8.6) Practice for the Eam Name Date Da/Time: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
MAT 33C -- Martin-Ga Intermediate Algebra Chapter 8 (8.1 8. 8. 8.6) Practice for the Eam Name Date Da/Time: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
Study Guide and Intervention
 6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
6- NAME DATE PERID Stud Guide and Intervention Graphing Quadratic Functions Graph Quadratic Functions Quadratic Function A function defined b an equation of the form f () a b c, where a 0 b Graph of a
2 variables. is the same value as the solution of. 1 variable. You can use similar reasoning to solve quadratic equations. Work with a partner.
 9. b Graphing Essential Question How can ou use a graph to solve a quadratic equation in one variable? Based on what ou learned about the -intercepts of a graph in Section., it follows that the -intercept
9. b Graphing Essential Question How can ou use a graph to solve a quadratic equation in one variable? Based on what ou learned about the -intercepts of a graph in Section., it follows that the -intercept
Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
Polnomial and Rational Functions Figure -mm film, once the standard for capturing photographic images, has been made largel obsolete b digital photograph. (credit film : modification of work b Horia Varlan;
