UNIT # 01 (PART I) BASIC MATHEMATICS USED IN PHYSICS, UNIT & DIMENSIONS AND VECTORS. 8. Resultant = R P Q, R P 2Q
|
|
|
- Penelope April Marshall
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J-Phsics UNI # 0 (PAR I) ASIC MAHMAICS USD IN PHYSICS, UNI & DIMNSIONS AND VCORS XRCIS I. nclosed area : A r so da dr r Here r 8 cm, dr da 5 cm/s () (8) (5) 80 cm /s. Slope d d 6 9 if angen is parallel o he ais hen d d ( ) (+) 0 or 0 or. p n F dp d n ()n+ () +n F 0 + n 0 n e e 4. e side of cube be hen d cm/s V dv d cm /s 5. Check A e forces be A and and < A hen A Resulan 4 5 N 9. Required uni ecor A i ˆ 6ˆj kˆ A 6 i 6ˆj k ˆ 7. For zero resulan, sum of an wo forces remaining force. R P Q, R P Q R P 0 P Q P 0 P Q.P 0 R P +Q + P.Q P + Q P Q RQ 4. a c RP and b c RQ bu RP RQ a b c RP RQ a b c 5. cos r W r r 0 N Saring poin 0 / S 0 unis node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65 R A A cos R 8 and A sin A 8 + A 64 (A ) (A+) 64 A 4 A 0N & 6N c c c 0. c ± ˆ ˆ 4 4 i j kˆ 4 ˆ ˆi ˆj ˆi ˆ j 6i ˆ 8ˆ j Use R A + + Acos or see opions 0. Displacemen m. Required angle
2 J-Phsics. A A A sin A cos an 60 A A A cos 60 A A A A 4. A. Acos Projecion of A A. on A cos A.ˆ 5. P Q R Q R P Q R + P RP cos cos Now P Q R 0 P R Q P + R + PRcos Q cos 6. Resulan cos + ( + ) + ( )cos cos g cc kg kg m m u 7. n u n u n u n M M (n ) 000g 00cm 0g0cm 0. n 0 N 0 Uni of force in new ssem So uni of force in new ssem 0.N O R As [F] M so uni of force (0g) (0 cm( 0.s) (0 kg) (0 m) 00(s) 0. (kg) (m) (s) 0. N 8. mus be dimensionless 9. ensionforce bu surface ensionforce / lengh 4. F M, A A 4. [a], [C] [] [b] [] 8. Projecion on plane 0 9. Veloci of one ball ˆ ˆ i j Veoci of second ball ˆ ˆ i j Angle beween heir pah :. cos 5. e e cos sin. In a clockwise ssem kˆ ˆj ˆi ˆi ˆj kˆ 4. r 0 4 î (6 8) ĵ ( ) + ˆk (4) i ˆ ˆj 4kˆ XRCIS II. A an insan + 5 u m 4m 5m ms - Differeniaing w.r.. ime Here d, d u u 8 + d m/s. + 4 d d bu d d 0 So d d node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65
3 J-Phsics. I MR R R 8 R cal 4. J cal4. kgm s 4. kg m s di R dr MR dr dr 8 M 5 4 / R (5R 4 ) () () () 4 kg m s 6. Angle beween a and b, cos a.b ab 4 4. nowen G kg kg km 6 0 kg m newon engh a, ime a raio of uni of lengh 9 7. n u n u n u M n u M and raio of uni of ime / M M 8 7. Q 0 R P Q R sin 0 sin 90 sin 50 P / Q R / P 9. [k] [] [ ] [M ] [ ] M P Q R k (consan) Force Area Modulus of elasici P : Q: R k : k : k : : 0.. P + b c / / a V (R+b) V c wae eloci 8. a b c a b c a.b b.c c.a a b c 0, b c a 0 a b b c c a 0 c a b 0 & a b c a b c node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65 P (R +b) V C a V AV m V n m c and n. A m A m [] M M [ ] laen hea 4. C, G M, h M M hc G 9. a b c a b c (a b b c c a) + + +(cos + cos + cos ) cos + cos + cos 0. â bˆ cos cos
4 J-Phsics â bˆ sin. a a, cos a z a z a cos 5 a 5 z 5 Now a a a 50 4a a 5 50 a 5 a 5 a 5. C A C A + + Acos If C < A + hen cos < 0. herefore > Area of riangle a b b c c a 6. F F F F4 4ˆi 5ˆj 5k ˆ 5ˆi 8ˆj 6k ˆ i ˆ 4ˆj 7k ˆ + i ˆ ˆj kˆ moion will be in z plane 8. r F ˆi ˆj kˆ 7 5 4ˆj kˆ 4i ˆ 8ˆj 6kˆ ˆ ˆ k i j ˆi ˆ j d 0 ( k)d 0 k. Here 45 so inclinaion of AC wih ais is 45. So uni ecor along AC ˆi ˆj cos 45 ˆi sin 45 ˆ j a b. 7a 5b 0. 7a 5b + 6 a b a 4b 7a b 0 and 7a + 8b 0 a b (i)...(ii) adding (i) and (ii) b + 46 a b 0 a b b So 7a 5b + 8b 0 a b abcos b cos cos (/) For riangle AC : A C CA 0 Now A C CA A C CA CA 0 CA CA 9. r a cos i ˆ a sin j ˆ eloci dr a sin i ˆ a cos j ˆ d r Acceleraion a cos ˆi a sin j ˆ r rue /False. If XRCIS III A A 0 hen A. wo ecors are alwas coplanar. 0. A A cos 8, A A sin 8 8 an 60, 0 8. Displacemen dr di ˆ dj ˆ bu + k 5 so d + kd 0 k k ˆ ˆ dr di dj ˆi ˆ j d Work done is zero if F.dr 0 4 Fill in he blanks W F.d 0ˆi ˆj 8kˆ..0i ˆ ˆj 7kˆ 6i ˆ 5ˆj kˆ 0i ˆ ˆj 8kˆ 4ˆi 7ˆj 0kˆ J. Required ecor baˆ 7 4 i ˆ 4ˆj 4 i ˆ 4ˆj 5 5i ˆ 0ˆ j 5 node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65
5 J-Phsics. a b ˆi ˆj ˆi ˆj kˆ kˆ 0 5. e unknown displacemen be s W N S hen i 5 cos 7 i sin 7 j s 6i s j ˆ 0 0 ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ a b ˆi ˆj k i ˆ 6. Area ˆ kˆ ˆj 7. According o quesion 8ˆ Ai ˆ Aj ˆ 8ˆ A ˆj ˆi 8 A 5 A 8. According o quesion u u 0 and u u u 0 & u u 4 u cos ab PV M R PV 4. V [R][PV] (M )( ) M [nerg] Comprehension O V m/s m/s. For shores disance d 0 50 sec W. min Comprehension. a, b a + b 0.. dr d r dr ai ˆ bj ˆ a 0, ai ˆ ˆ bj 9. k / k / s/m Comprehension 4 node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65 0. a b c P d a b c M M M a + b + c 0, a b + c 0, a c a 5 6, b, c Comprehension. [b] [V] a. P [a] [PV V ]. [PV] [R], [Pb] [PV] [R] a PV P R and V V ab PV V PV R V V 5. e uni of lengh, ime and mass be, and M respeciel. According o quesion 9.8 (7.) (448) M 00 M (7.) (448) M 0 M b soling aboe equaion m. soling aboe equaion s. soling aboe equaion M 544. M 544. kg
6 J-Phsics XRCIS IV(A). A 4, A 6 so A + 0 and A + 9 (i) 0 4 6m and 9 6 m (ii) lengh m (iii) an an an 6. (i) e he angle beween A and is, hen (ii) (iii) A cos A 90 Resulan erj A ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ i j k i j 0 0 i ˆ ˆj kˆ ˆi ˆj e j e j i j k i j k i j Projecion of resulan on ais Required ecor j A e j j i j k. (i) Componen of A along F HG i j k I KJ A. i ˆ ˆj. ˆj kˆ ˆj kˆ A. ˆ ĵ k Componen of (ii) (iii) A A A ˆ i ˆ ˆj ˆj kˆ 5 Area of he parallelogram A 6 i j k 0 0 i 6 j k b g 7 unis Uni ecor perpendicular o boh A & A n i 6 j k 6 i j k A Componen along he ecor i j (A cos ) (A.) (i 4j).(i j) (i j) ( ) 4 (i j) 7 (i j) Componen along he ecor i j (A cos ) (A.) (i 4j).(i j)(i j) ( ) ( 4) (i j) (i j) 6. e wo forces are A and hen A + P, A Q A P Q Resulan k A A cos, P Q P Q P Q P Q P Q cos P Q (P Q ) cos P Q ( cos ) ( cos ) P cos Q sin 7. A A A cos (0) (6) (0)(6) cos sin 60 6 / an 0 6 cos an 7 8. Resulan force in erical direcion 50 N N 00 N 50cos cos 0 node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65
7 J-Phsics N Resulan force in horizonal direcion 00sin0 50 sin N so resulan pull (5) (5 ) 7.9N 9. a, b b a. (i) displacemen () (4) (5) 50m Disance r p 6 i 4 ˆj (i) ˆ 7 88 k 4 ˆ 6 ˆi 7 ˆj i 4j 5. F 5Pj, F 4Pi, F 0P (6i 8j)P 5 (( i i) (j 4j)) F4 5P Pi 9Pj 5 F F F F F 5Pj 4Pi 6Pi 8Pj 4 Pi 9P j Pi 4Pj F P ( ) (4) 0P 4 5 an 4 an ( ) (ii) (7) (5) 74m. e c is c ˆ ˆ i c j hen according o quesion c c 5 7. Displacemen (0) (40) 50km 40 an 5 N o 0 w N 40 km 0km s c + c 5 and a.c 0 c + 4 c 0...(i)...(ii) 9. Speed m / s 4. from equaion (i) and (ii) c ± 4, c dr (6 6) i + ( ) j m/s d a (6i 4j) m/s K.. 0. From graph m J 5J (a 0) 50 m/s d d d d node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65 (i) F ma 6(6i 4j) (6i 44 j)n (ii) r F ( 6)i ( 4 )j 6i 44j [( 44 ) + (44 6 ) + 44 ] k ( ) k (iii) p m 6[(6 6)i ( )j] [6( )i 7 j] 7 a d a m/s d b0. (i) ˆi a b e kˆ 0 (ii) a b e b0 (iii) a a b e kˆ 0 0. Dimension of M Dimension of M b
8 J-Phsics Dimension of 0 Dimension of 0 M 0. (i) c (ii) Q m [ ] Dimension of c 0 ( ) 0 [ M ] [ M ][ M K ] [ K ] 0 0 Dimension of [ M ] [ M ] [ M K ] (iii) R PV M [M K mol ] n molk. Surface ension (S) XRCIS IV() work done nerg Area Area A S ( ). Dimension of joule M Value of joule in sar ssem (0 0 ) (0 8 ) (0 ) 0 0 sar joule 4. e i & OP i j i + d j 4. Dimensions of a M [a] M [] and [ ] [M ] 0 5. m [] k [d] [g] [M 0 0 ] [ ] k [M ] [ ], k + 0, K 0,, and K 6 so OP (i ˆ dj) ˆ i ˆ dkˆ (d is consan) which is independen of posiion. 5. Vecor PP ˆ ˆ 5 i 5k and P P 4ˆi kˆ P(,,0) 6. R a g b [] [ ] a [ ] b a + b, a b 0 a, b R g 7. [b] [] [ ] dimensions of [a] dimensions of RV a RV [M ] M k mol [k] [ ] [M 5 mol ] 8. Y () (a) (F) z [M ] [ ] [ ] [M ] z z, + + z, z z,, 4 Y F a 4 [M] z [] ++z z [] 8 M P(,, ) P(4,,5) e angle beween hese ecors be hen cos ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ As PM PP sin 5 i 5k 4i k so PM 5 7 m 5 herefore 6. an 7 m.5 s m/s an node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65
9 J-Phsics 7. Area of riangle (i j+k) A A ˆj k A 5m 4k ˆ ˆ j i ( i j + k ) ( i + j +k ) A i j c 4 k ˆ. ˆ ˆ A, Aˆi ˆj 4c 4 kˆ ˆi ˆj hus, A,, C i ˆ 6 ˆj 4k ˆ A 4, ˆi 96 ˆj 8 4 k ˆ ˆi 94ˆj 4k ˆ. a 5 cos i ˆ sin j ˆ 8. law of reflecion i r 4 4 i ˆ A ˆj ; A 0, 4 ˆ i 4 ˆ j ; C i ˆ ˆj 4 0, C d 5 cos i ˆ sin j ˆ herefore d 0 d 5 cos 5 sin (5sin ) 0 d 5 sin +5 5 cos 5 cos Similarl, / k M A k d A d 0 sin 4 M A d A 8 4 / (cos ) cos d cos 0 M oal M +M 4 k A sin + sin 5 sin ˆi cos ˆj hus, node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65 0. m k an. dm k sec d dm m k sec k an d dm m d d sin cos sin % error is minimum when sin has maimum alue hence dr.i ˆ.8j ˆ.8 ˆ k A 4s,.ˆi 7.ˆj 8.8kˆ or 45 ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ P F. 60 i 5 j 40k. i 7. j 8.8k 044W s 5 cos i sin ˆj and ˆ ˆ r i ˆj kˆ dr (i) ˆi j ˆ kˆ d (iii) a ˆj () a (iii) speed (i) a ˆi j ˆ kˆ ˆ ˆi j ˆ k a ˆ ˆ ˆ a j ˆ As a + a a N so a N a a ˆi j ˆ kˆ ; a
10 J-Phsics XRCIS V(A). he dimensions of orque and work are[m ]. As we know ha formula of eloci is [ ] Fi ll i n he blanks : XRCIS V() M /. h h M. [X] [ capaciance] [M Q ] and [Z] [Magneic inducion] [M Q ] herefore [Y] X M Q Z M Q M Q 4 4. Planck's consan (in erms of uni) Momenum (p) 4. Newon's formula (h) J-s [M ][] [M ] kg-ms [M][][ ][M ] dimensions of force dimensions of area dimensions of eloci gradien. lecrical conducii J I / A I / A I F / q F / I FA M a V A M A P a PV M M Si ngle Choi ce M 5. A A M his is onl possible if he alue of boh ecors A and A is zero. his occurs when he angle beween A and is. 7. Momen of ineria and momen of a force do no hae same dimensions. 8. Dimensions of inducance, i.e. henr are [M /Q ] 0. M F q MC C qq. F 4 0 r [M ] 0 [ 0 ] [M 4 A ] A [M 4 I ] [M 6 I ] [M ] V 7. 0 [M 4 I ] [] [M I ] [ ] 8. Dimension formula of olzman consan k [M ] [ ] M M [M ]; [M ] [M ] 9. (i) Dipole momen Charge engh [I] [ ] Dipole momen [I ] [ ] [ I ] q (ii) lecric flu (iii) lecric field F q 0 [I ] 4 [M I ] [M I ] [M ] lecric field [M I ] [I ] node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65
11 J-Phsics MCQ'S q q. F 4 r 4. 0 M A 0 0 M A 4 0 ] M A + 4 F i i 4 r [M ] 0 A 0 0 MA di ol sec e (Hener) Ampere R ime consan; [] ohm sec I weber Ampere (Hener) Joule I (Ampere) 7. Mach he Column GM em ( A ) F R ( ) GM e M s F Work Mere s Coulomb Vol Mere Z(Hener) M Mere (Kg) (Mere) (S) R Kineic energ 8. Mach is I wih is II and selec he correc answer using he codes gien below he liss : is I A ns. ( C ) [II-J 0] is II P. olzmann consan.[m ] Q. Coefficien of iscosi.[m ] R. Planck consan.[m K ] S. hermal conducii 4.[M K ] Codes : P Q R S (A) 4 () 4 (C) 4 (D) 4 (P) olzmann consan nerg M emperaure K (Q) Coefficien of iscosi () : M K F A V, M M (R) Plank consan (h) : (S) M h; [h] hermal conducii Q K A M M [K] K M K R M (Mere) (S) node6\ : \Daa\04\Koa\J-Adanced\SMP\Ph\Soluion\Uni & \0 asic Mahs.p65 ( C ) ( D ) QV nerg F q QV nerg (farad)(ol) M m kg q q (r, s) GMe Work done R Mass (Veloci) (r, s)
Kinematics in two dimensions
 Lecure 5 Phsics I 9.18.13 Kinemaics in wo dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teaching/phsicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo36.uml.edu/danlo13/phsics1fall.hml 95.141, Fall 13, Lecure 5
Lecure 5 Phsics I 9.18.13 Kinemaics in wo dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teaching/phsicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo36.uml.edu/danlo13/phsics1fall.hml 95.141, Fall 13, Lecure 5
Kinematics in two Dimensions
 Lecure 5 Chaper 4 Phsics I Kinemaics in wo Dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teachin/phsicsi PHYS.141 Lecure 5 Danlo Deparmen of Phsics and Applied Phsics Toda we are oin o discuss:
Lecure 5 Chaper 4 Phsics I Kinemaics in wo Dimensions Course websie: hp://facul.uml.edu/andri_danlo/teachin/phsicsi PHYS.141 Lecure 5 Danlo Deparmen of Phsics and Applied Phsics Toda we are oin o discuss:
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 1-3
 A.P. Physics B Uni 1 Tes Reiew Physics Basics, Moemen, and Vecors Chapers 1-3 * In sudying for your es, make sure o sudy his reiew shee along wih your quizzes and homework assignmens. Muliple Choice Reiew:
A.P. Physics B Uni 1 Tes Reiew Physics Basics, Moemen, and Vecors Chapers 1-3 * In sudying for your es, make sure o sudy his reiew shee along wih your quizzes and homework assignmens. Muliple Choice Reiew:
 Page 1 o 13 1. The brighes sar in he nigh sky is α Canis Majoris, also known as Sirius. I lies 8.8 ligh-years away. Express his disance in meers. ( ligh-year is he disance coered by ligh in one year. Ligh
Page 1 o 13 1. The brighes sar in he nigh sky is α Canis Majoris, also known as Sirius. I lies 8.8 ligh-years away. Express his disance in meers. ( ligh-year is he disance coered by ligh in one year. Ligh
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
Suggested Practice Problems (set #2) for the Physics Placement Test
 Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Kinematics. Position. Lectures 3 and 4 Motion in One Dimension. A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan
 Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Integration of the equation of motion with respect to time rather than displacement leads to the equations of impulse and momentum.
 Inegraion of he equaion of moion wih respec o ime raher han displacemen leads o he equaions of impulse and momenum. These equaions greal faciliae he soluion of man problems in which he applied forces ac
Inegraion of he equaion of moion wih respec o ime raher han displacemen leads o he equaions of impulse and momenum. These equaions greal faciliae he soluion of man problems in which he applied forces ac
 Work Power Energy. For conservaive orce ) Work done is independen o he pah ) Work done in a closed loop is zero ) Work done agains conservaive orce is sored is he orm o poenial energy 4) All he above.
Work Power Energy. For conservaive orce ) Work done is independen o he pah ) Work done in a closed loop is zero ) Work done agains conservaive orce is sored is he orm o poenial energy 4) All he above.
1. The graph below shows the variation with time t of the acceleration a of an object from t = 0 to t = T. a
 Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
Kinemaics Paper 1 1. The graph below shows he ariaion wih ime of he acceleraion a of an objec from = o = T. a T The shaded area under he graph represens change in A. displacemen. B. elociy. C. momenum.
Topic 1: Linear motion and forces
 TOPIC 1 Topic 1: Linear moion and forces 1.1 Moion under consan acceleraion Science undersanding 1. Linear moion wih consan elociy is described in erms of relaionships beween measureable scalar and ecor
TOPIC 1 Topic 1: Linear moion and forces 1.1 Moion under consan acceleraion Science undersanding 1. Linear moion wih consan elociy is described in erms of relaionships beween measureable scalar and ecor
Phys 221 Fall Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko Brooks/Cole
 Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
Physics Notes - Ch. 2 Motion in One Dimension
 Physics Noes - Ch. Moion in One Dimension I. The naure o physical quaniies: scalars and ecors A. Scalar quaniy ha describes only magniude (how much), NOT including direcion; e. mass, emperaure, ime, olume,
Physics Noes - Ch. Moion in One Dimension I. The naure o physical quaniies: scalars and ecors A. Scalar quaniy ha describes only magniude (how much), NOT including direcion; e. mass, emperaure, ime, olume,
AP Calculus BC Chapter 10 Part 1 AP Exam Problems
 AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 02 Motion, Forces, and Newton s Laws Textbook Sections
 PHYSICS 220 Lecure 02 Moion, Forces, and Newon s Laws Texbook Secions 2.2-2.4 Lecure 2 Purdue Universiy, Physics 220 1 Overview Las Lecure Unis Scienific Noaion Significan Figures Moion Displacemen: Δx
PHYSICS 220 Lecure 02 Moion, Forces, and Newon s Laws Texbook Secions 2.2-2.4 Lecure 2 Purdue Universiy, Physics 220 1 Overview Las Lecure Unis Scienific Noaion Significan Figures Moion Displacemen: Δx
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Test points. Provide the best answer to the following questions and problems. Watch your sig figs.
 Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Course II. Lesson 7 Applications to Physics. 7A Velocity and Acceleration of a Particle
 Course II Lesson 7 Applicaions o Physics 7A Velociy and Acceleraion of a Paricle Moion in a Sraigh Line : Velociy O Aerage elociy Moion in he -ais + Δ + Δ 0 0 Δ Δ Insananeous elociy d d Δ Δ Δ 0 lim [ m/s
Course II Lesson 7 Applicaions o Physics 7A Velociy and Acceleraion of a Paricle Moion in a Sraigh Line : Velociy O Aerage elociy Moion in he -ais + Δ + Δ 0 0 Δ Δ Insananeous elociy d d Δ Δ Δ 0 lim [ m/s
2.1: What is physics? Ch02: Motion along a straight line. 2.2: Motion. 2.3: Position, Displacement, Distance
 Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
We may write the basic equation of motion for the particle, as
 We ma wrie he basic equaion of moion for he paricle, as or F m dg F F linear impulse G dg G G G G change in linear F momenum dg The produc of force and ime is defined as he linear impulse of he force,
We ma wrie he basic equaion of moion for he paricle, as or F m dg F F linear impulse G dg G G G G change in linear F momenum dg The produc of force and ime is defined as he linear impulse of he force,
INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY
 INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY I claim ha ha if acceleraion is consan, hen he elociy is a linear funcion of ime and he posiion a quadraic funcion of ime. We wan o inesigae hose claims, and a he same ime, work
INSTANTANEOUS VELOCITY I claim ha ha if acceleraion is consan, hen he elociy is a linear funcion of ime and he posiion a quadraic funcion of ime. We wan o inesigae hose claims, and a he same ime, work
Kinematics Vocabulary. Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion. Position. Coordinate System in One Dimension. Kinema means movement 8.
 Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 3
 SOLUTIONS TO ONEPTS HPTER 3. a) Disance ravelled = 50 + 40 + 0 = 0 m b) F = F = D = 50 0 = 30 M His displacemen is D D = F DF 30 40 50m In ED an = DE/E = 30/40 = 3/4 = an (3/4) His displacemen from his
SOLUTIONS TO ONEPTS HPTER 3. a) Disance ravelled = 50 + 40 + 0 = 0 m b) F = F = D = 50 0 = 30 M His displacemen is D D = F DF 30 40 50m In ED an = DE/E = 30/40 = 3/4 = an (3/4) His displacemen from his
Physics 218 Exam 1. with Solutions Fall 2010, Sections Part 1 (15) Part 2 (20) Part 3 (20) Part 4 (20) Bonus (5)
 Physics 18 Exam 1 wih Soluions Fall 1, Secions 51-54 Fill ou he informaion below bu o no open he exam unil insruce o o so! Name Signaure Suen ID E-mail Secion # ules of he exam: 1. You have he full class
Physics 18 Exam 1 wih Soluions Fall 1, Secions 51-54 Fill ou he informaion below bu o no open he exam unil insruce o o so! Name Signaure Suen ID E-mail Secion # ules of he exam: 1. You have he full class
Physics 101 Fall 2006: Exam #1- PROBLEM #1
 Physics 101 Fall 2006: Exam #1- PROBLEM #1 1. Problem 1. (+20 ps) (a) (+10 ps) i. +5 ps graph for x of he rain vs. ime. The graph needs o be parabolic and concave upward. ii. +3 ps graph for x of he person
Physics 101 Fall 2006: Exam #1- PROBLEM #1 1. Problem 1. (+20 ps) (a) (+10 ps) i. +5 ps graph for x of he rain vs. ime. The graph needs o be parabolic and concave upward. ii. +3 ps graph for x of he person
Review Equations. Announcements 9/8/09. Table Tennis
 Announcemens 9/8/09 1. Course homepage ia: phsics.bu.edu Class web pages Phsics 105 (Colon J). (Class-wide email sen) Iclicker problem from las ime scores didn ge recorded. Clicker quizzes from lecures
Announcemens 9/8/09 1. Course homepage ia: phsics.bu.edu Class web pages Phsics 105 (Colon J). (Class-wide email sen) Iclicker problem from las ime scores didn ge recorded. Clicker quizzes from lecures
One-Dimensional Kinematics
 One-Dimensional Kinemaics One dimensional kinemaics refers o moion along a sraigh line. Een hough we lie in a 3-dimension world, moion can ofen be absraced o a single dimension. We can also describe moion
One-Dimensional Kinemaics One dimensional kinemaics refers o moion along a sraigh line. Een hough we lie in a 3-dimension world, moion can ofen be absraced o a single dimension. We can also describe moion
Lecture 4 Kinetics of a particle Part 3: Impulse and Momentum
 MEE Engineering Mechanics II Lecure 4 Lecure 4 Kineics of a paricle Par 3: Impulse and Momenum Linear impulse and momenum Saring from he equaion of moion for a paricle of mass m which is subjeced o an
MEE Engineering Mechanics II Lecure 4 Lecure 4 Kineics of a paricle Par 3: Impulse and Momenum Linear impulse and momenum Saring from he equaion of moion for a paricle of mass m which is subjeced o an
Parametrics and Vectors (BC Only)
 Paramerics and Vecors (BC Only) The following relaionships should be learned and memorized. The paricle s posiion vecor is r() x(), y(). The velociy vecor is v(),. The speed is he magniude of he velociy
Paramerics and Vecors (BC Only) The following relaionships should be learned and memorized. The paricle s posiion vecor is r() x(), y(). The velociy vecor is v(),. The speed is he magniude of he velociy
CLASS XI SET A PHYSICS. 1. If and Let. The correct order of % error in. (a) (b) x = y > z (c) x < z < y (d) x > z < y
 PHYSICS 1. If and Le. The correc order of % error in (a) (b) x = y > z x < z < y x > z < y. A hollow verical cylinder of radius r and heigh h has a smooh inernal surface. A small paricle is placed in conac
PHYSICS 1. If and Le. The correc order of % error in (a) (b) x = y > z x < z < y x > z < y. A hollow verical cylinder of radius r and heigh h has a smooh inernal surface. A small paricle is placed in conac
2002 November 14 Exam III Physics 191
 November 4 Exam III Physics 9 Physical onsans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s ircle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses: m = kg, m
November 4 Exam III Physics 9 Physical onsans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s ircle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses: m = kg, m
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 2
 SOLUTIONS TO CONCPTS CHAPTR 1. As shown in the figure, The angle between A and B = 11 = 9 A = and B = 4m Resultant R = A B ABcos = 5 m Let be the angle between R and A 4 sin9 = tan 1 = tan 1 (4/) = 5 4cos9
SOLUTIONS TO CONCPTS CHAPTR 1. As shown in the figure, The angle between A and B = 11 = 9 A = and B = 4m Resultant R = A B ABcos = 5 m Let be the angle between R and A 4 sin9 = tan 1 = tan 1 (4/) = 5 4cos9
2001 November 15 Exam III Physics 191
 1 November 15 Eam III Physics 191 Physical Consans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s 2 Circle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh 1 poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses:
1 November 15 Eam III Physics 191 Physical Consans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.8 m/s 2 Circle he leer of he single bes answer. quesion is worh 1 poin Each 3. Four differen objecs wih masses:
10.1 EXERCISES. y 2 t 2. y 1 t y t 3. y e
 66 CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES SLUTIN We use a graphing device o produce he graphs for he cases a,,.5,.,,.5,, and shown in Figure 7. Noice ha all of hese curves (ecep he case a ) have
66 CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES SLUTIN We use a graphing device o produce he graphs for he cases a,,.5,.,,.5,, and shown in Figure 7. Noice ha all of hese curves (ecep he case a ) have
Chapter 12: Velocity, acceleration, and forces
 To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
0 time. 2 Which graph represents the motion of a car that is travelling along a straight road with a uniformly increasing speed?
 1 1 The graph relaes o he moion of a falling body. y Which is a correc descripion of he graph? y is disance and air resisance is negligible y is disance and air resisance is no negligible y is speed and
1 1 The graph relaes o he moion of a falling body. y Which is a correc descripion of he graph? y is disance and air resisance is negligible y is disance and air resisance is no negligible y is speed and
Exam I. Name. Answer: a. W B > W A if the volume of the ice cubes is greater than the volume of the water.
 Name Exam I 1) A hole is punched in a full milk caron, 10 cm below he op. Wha is he iniial veloci of ouflow? a. 1.4 m/s b. 2.0 m/s c. 2.8 m/s d. 3.9 m/s e. 2.8 m/s Answer: a 2) In a wind unnel he pressure
Name Exam I 1) A hole is punched in a full milk caron, 10 cm below he op. Wha is he iniial veloci of ouflow? a. 1.4 m/s b. 2.0 m/s c. 2.8 m/s d. 3.9 m/s e. 2.8 m/s Answer: a 2) In a wind unnel he pressure
Maxwell s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
 Phsics 36: Waves Lecure 3 /9/8 Maxwell s quaions and lecromagneic Waves Four Laws of lecromagneism. Gauss Law qenc all da ρdv Inegral From From he vecor ideni da dv Therefore, we ma wrie Gauss Law as ρ
Phsics 36: Waves Lecure 3 /9/8 Maxwell s quaions and lecromagneic Waves Four Laws of lecromagneism. Gauss Law qenc all da ρdv Inegral From From he vecor ideni da dv Therefore, we ma wrie Gauss Law as ρ
where the coordinate X (t) describes the system motion. X has its origin at the system static equilibrium position (SEP).
 Appendix A: Conservaion of Mechanical Energy = Conservaion of Linear Momenum Consider he moion of a nd order mechanical sysem comprised of he fundamenal mechanical elemens: ineria or mass (M), siffness
Appendix A: Conservaion of Mechanical Energy = Conservaion of Linear Momenum Consider he moion of a nd order mechanical sysem comprised of he fundamenal mechanical elemens: ineria or mass (M), siffness
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Physics Equation List :Form 4 Introduction to Physics
 Physics Equaion Lis :Form 4 Inroducion o Physics Relaive Deviaion Relaive Deviaion Mean Deviaion 00% Mean Value Prefixes Unis for Area and Volume Prefixes Value Sandard form Symbol Tera 000 000 000 000
Physics Equaion Lis :Form 4 Inroducion o Physics Relaive Deviaion Relaive Deviaion Mean Deviaion 00% Mean Value Prefixes Unis for Area and Volume Prefixes Value Sandard form Symbol Tera 000 000 000 000
4.5 Constant Acceleration
 4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
4.5 Consan Acceleraion v() v() = v 0 + a a() a a() = a v 0 Area = a (a) (b) Figure 4.8 Consan acceleraion: (a) velociy, (b) acceleraion When he x -componen of he velociy is a linear funcion (Figure 4.8(a)),
!!"#"$%&#'()!"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./0)1-*23)
 "#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
"#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 9
 PHYSICS 149: Lecure 9 Chaper 3 3.2 Velociy and Acceleraion 3.3 Newon s Second Law of Moion 3.4 Applying Newon s Second Law 3.5 Relaive Velociy Lecure 9 Purdue Universiy, Physics 149 1 Velociy (m/s) The
PHYSICS 149: Lecure 9 Chaper 3 3.2 Velociy and Acceleraion 3.3 Newon s Second Law of Moion 3.4 Applying Newon s Second Law 3.5 Relaive Velociy Lecure 9 Purdue Universiy, Physics 149 1 Velociy (m/s) The
Solution: b All the terms must have the dimension of acceleration. We see that, indeed, each term has the units of acceleration
 PHYS 54 Tes Pracice Soluions Spring 8 Q: [4] Knowing ha in he ne epression a is acceleraion, v is speed, is posiion and is ime, from a dimensional v poin of view, he equaion a is a) incorrec b) correc
PHYS 54 Tes Pracice Soluions Spring 8 Q: [4] Knowing ha in he ne epression a is acceleraion, v is speed, is posiion and is ime, from a dimensional v poin of view, he equaion a is a) incorrec b) correc
Section 3.8, Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations
 Secion 3.8, Mechanical and Elecrical Vibraions Mechanical Unis in he U.S. Cusomary and Meric Sysems Disance Mass Time Force g (Earh) Uni U.S. Cusomary MKS Sysem CGS Sysem fee f slugs seconds sec pounds
Secion 3.8, Mechanical and Elecrical Vibraions Mechanical Unis in he U.S. Cusomary and Meric Sysems Disance Mass Time Force g (Earh) Uni U.S. Cusomary MKS Sysem CGS Sysem fee f slugs seconds sec pounds
a. Show that these lines intersect by finding the point of intersection. b. Find an equation for the plane containing these lines.
 Mah A Final Eam Problems for onsideraion. Show all work for credi. Be sure o show wha you know. Given poins A(,,, B(,,, (,, 4 and (,,, find he volume of he parallelepiped wih adjacen edges AB, A, and A.
Mah A Final Eam Problems for onsideraion. Show all work for credi. Be sure o show wha you know. Given poins A(,,, B(,,, (,, 4 and (,,, find he volume of he parallelepiped wih adjacen edges AB, A, and A.
MEI Mechanics 1 General motion. Section 1: Using calculus
 Soluions o Exercise MEI Mechanics General moion Secion : Using calculus. s 4 v a 6 4 4 When =, v 4 a 6 4 6. (i) When = 0, s = -, so he iniial displacemen = - m. s v 4 When = 0, v = so he iniial velociy
Soluions o Exercise MEI Mechanics General moion Secion : Using calculus. s 4 v a 6 4 4 When =, v 4 a 6 4 6. (i) When = 0, s = -, so he iniial displacemen = - m. s v 4 When = 0, v = so he iniial velociy
x y θ = 31.8 = 48.0 N. a 3.00 m/s
 4.5.IDENTIY: Vecor addiion. SET UP: Use a coordinae sse where he dog A. The forces are skeched in igure 4.5. EXECUTE: + -ais is in he direcion of, A he force applied b =+ 70 N, = 0 A B B A = cos60.0 =
4.5.IDENTIY: Vecor addiion. SET UP: Use a coordinae sse where he dog A. The forces are skeched in igure 4.5. EXECUTE: + -ais is in he direcion of, A he force applied b =+ 70 N, = 0 A B B A = cos60.0 =
Displacement ( x) x x x
 Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 4758
 OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary General Cerificae of Educaion Advanced General Cerificae of Educaion MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 4758 Differenial Equaions Thursday 5 JUNE 006 Afernoon
OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary General Cerificae of Educaion Advanced General Cerificae of Educaion MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 4758 Differenial Equaions Thursday 5 JUNE 006 Afernoon
Brock University Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agostino. Solutions for Tutorial 3: Chapter 2, Motion in One Dimension
 Brock Uniersiy Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agosino Soluions for Tuorial 3: Chaper 2, Moion in One Dimension The goals of his uorial are: undersand posiion-ime graphs, elociy-ime graphs, and heir
Brock Uniersiy Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agosino Soluions for Tuorial 3: Chaper 2, Moion in One Dimension The goals of his uorial are: undersand posiion-ime graphs, elociy-ime graphs, and heir
Q2.4 Average velocity equals instantaneous velocity when the speed is constant and motion is in a straight line.
 CHAPTER MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE Discussion Quesions Q. The speedomeer measures he magniude of he insananeous eloci, he speed. I does no measure eloci because i does no measure direcion. Q. Graph (d).
CHAPTER MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE Discussion Quesions Q. The speedomeer measures he magniude of he insananeous eloci, he speed. I does no measure eloci because i does no measure direcion. Q. Graph (d).
Practicing Problem Solving and Graphing
 Pracicing Problem Solving and Graphing Tes 1: Jan 30, 7pm, Ming Hsieh G20 The Bes Ways To Pracice for Tes Bes If need more, ry suggesed problems from each new opic: Suden Response Examples A pas opic ha
Pracicing Problem Solving and Graphing Tes 1: Jan 30, 7pm, Ming Hsieh G20 The Bes Ways To Pracice for Tes Bes If need more, ry suggesed problems from each new opic: Suden Response Examples A pas opic ha
Mechanics Acceleration The Kinematics Equations
 Mechanics Acceleraion The Kinemaics Equaions Lana Sheridan De Anza College Sep 27, 2018 Las ime kinemaic quaniies graphs of kinemaic quaniies Overview acceleraion he kinemaics equaions (consan acceleraion)
Mechanics Acceleraion The Kinemaics Equaions Lana Sheridan De Anza College Sep 27, 2018 Las ime kinemaic quaniies graphs of kinemaic quaniies Overview acceleraion he kinemaics equaions (consan acceleraion)
Physics 20 Lesson 5 Graphical Analysis Acceleration
 Physics 2 Lesson 5 Graphical Analysis Acceleraion I. Insananeous Velociy From our previous work wih consan speed and consan velociy, we know ha he slope of a posiion-ime graph is equal o he velociy of
Physics 2 Lesson 5 Graphical Analysis Acceleraion I. Insananeous Velociy From our previous work wih consan speed and consan velociy, we know ha he slope of a posiion-ime graph is equal o he velociy of
University Physics with Modern Physics 14th Edition Young TEST BANK
 Universi Phsics wih Modern Phsics 14h Ediion Young SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formaing errors) a: hps://esbankreal.com/download/universi-phsics-modern-phsics- 14h-ediion-oung-soluions-manual-/
Universi Phsics wih Modern Phsics 14h Ediion Young SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formaing errors) a: hps://esbankreal.com/download/universi-phsics-modern-phsics- 14h-ediion-oung-soluions-manual-/
v 1 a rad = v2 R = 4 2 R T 2 v 1 2 =v 0 2 2a x 1 x 0 1mi=5280 ft=1709m 1Calorie=4200 J = kx F f = m i m i t 1 2 =
 Name Secion Phsics 1210 Final Exam Ma 2011 v1.0 This es is closed-noe and closed-book. No wrien, prined, or recorded maerial is permied. Calculaors are permied bu compuers are no. No collaboraion, consulaion,
Name Secion Phsics 1210 Final Exam Ma 2011 v1.0 This es is closed-noe and closed-book. No wrien, prined, or recorded maerial is permied. Calculaors are permied bu compuers are no. No collaboraion, consulaion,
Applications of the Basic Equations Chapter 3. Paul A. Ullrich
 Applicaions of he Basic Equaions Chaper 3 Paul A. Ullrich paullrich@ucdavis.edu Par 1: Naural Coordinaes Naural Coordinaes Quesion: Why do we need anoher coordinae sysem? Our goal is o simplify he equaions
Applicaions of he Basic Equaions Chaper 3 Paul A. Ullrich paullrich@ucdavis.edu Par 1: Naural Coordinaes Naural Coordinaes Quesion: Why do we need anoher coordinae sysem? Our goal is o simplify he equaions
Check in: 1 If m = 2(x + 1) and n = find y when. b y = 2m n 2
 7 Parameric equaions This chaer will show ou how o skech curves using heir arameric equaions conver arameric equaions o Caresian equaions find oins of inersecion of curves and lines using arameric equaions
7 Parameric equaions This chaer will show ou how o skech curves using heir arameric equaions conver arameric equaions o Caresian equaions find oins of inersecion of curves and lines using arameric equaions
Today: Graphing. Note: I hope this joke will be funnier (or at least make you roll your eyes and say ugh ) after class. v (miles per hour ) Time
 +v Today: Graphing v (miles per hour ) 9 8 7 6 5 4 - - Time Noe: I hope his joke will be funnier (or a leas make you roll your eyes and say ugh ) afer class. Do yourself a favor! Prof Sarah s fail-safe
+v Today: Graphing v (miles per hour ) 9 8 7 6 5 4 - - Time Noe: I hope his joke will be funnier (or a leas make you roll your eyes and say ugh ) afer class. Do yourself a favor! Prof Sarah s fail-safe
A B C D September 25 Exam I Physics 105. Circle the letter of the single best answer. Each question is worth 1 point
 2012 Sepember 25 Eam I Physics 105 Circle he leer of he single bes answer. Each uesion is worh 1 poin Physical Consans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.80 m/s 2 3. (Mark wo leers!) The below graph
2012 Sepember 25 Eam I Physics 105 Circle he leer of he single bes answer. Each uesion is worh 1 poin Physical Consans: Earh s free-fall acceleraion = g = 9.80 m/s 2 3. (Mark wo leers!) The below graph
Linear Motion I Physics
 Linear Moion I Physics Objecives Describe he ifference beween isplacemen an isance Unersan he relaionship beween isance, velociy, an ime Describe he ifference beween velociy an spee Be able o inerpre a
Linear Moion I Physics Objecives Describe he ifference beween isplacemen an isance Unersan he relaionship beween isance, velociy, an ime Describe he ifference beween velociy an spee Be able o inerpre a
Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points]
![Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points] Name: Total Points: Multiple choice questions [120 points]](/thumbs/88/115221528.jpg) Name: Toal Poins: (Las) (Firs) Muliple choice quesions [1 poins] Answer all of he following quesions. Read each quesion carefully. Fill he correc bubble on your scanron shee. Each correc answer is worh
Name: Toal Poins: (Las) (Firs) Muliple choice quesions [1 poins] Answer all of he following quesions. Read each quesion carefully. Fill he correc bubble on your scanron shee. Each correc answer is worh
Welcome Back to Physics 215!
 Welcome Back o Physics 215! (General Physics I) Thurs. Jan 19 h, 2017 Lecure01-2 1 Las ime: Syllabus Unis and dimensional analysis Today: Displacemen, velociy, acceleraion graphs Nex ime: More acceleraion
Welcome Back o Physics 215! (General Physics I) Thurs. Jan 19 h, 2017 Lecure01-2 1 Las ime: Syllabus Unis and dimensional analysis Today: Displacemen, velociy, acceleraion graphs Nex ime: More acceleraion
A man pushes a 500 kg block along the x axis by a constant force. Find the power required to maintain a speed of 5.00 m/s.
 Coordinaor: Dr. F. hiari Wednesday, July 16, 2014 Page: 1 Q1. The uniform solid block in Figure 1 has mass 0.172 kg and edge lenghs a = 3.5 cm, b = 8.4 cm, and c = 1.4 cm. Calculae is roaional ineria abou
Coordinaor: Dr. F. hiari Wednesday, July 16, 2014 Page: 1 Q1. The uniform solid block in Figure 1 has mass 0.172 kg and edge lenghs a = 3.5 cm, b = 8.4 cm, and c = 1.4 cm. Calculae is roaional ineria abou
Two Dimensional Dynamics
 Physics 11: Lecure 6 Two Dimensional Dynamics Today s lecure will coer Chaper 4 Saring Wed Sep 15, W-F oice hours will be in 3 Loomis. Exam I M oice hours will coninue in 36 Loomis Physics 11: Lecure 6,
Physics 11: Lecure 6 Two Dimensional Dynamics Today s lecure will coer Chaper 4 Saring Wed Sep 15, W-F oice hours will be in 3 Loomis. Exam I M oice hours will coninue in 36 Loomis Physics 11: Lecure 6,
The study of the motion of a body along a general curve. û N the unit vector normal to the curve. Clearly, these unit vectors change with time, uˆ
 Secion. Curilinear Moion he sudy of he moion of a body along a general cure. We define û he uni ecor a he body, angenial o he cure û he uni ecor normal o he cure Clearly, hese uni ecors change wih ime,
Secion. Curilinear Moion he sudy of he moion of a body along a general cure. We define û he uni ecor a he body, angenial o he cure û he uni ecor normal o he cure Clearly, hese uni ecors change wih ime,
k 1 k 2 x (1) x 2 = k 1 x 1 = k 2 k 1 +k 2 x (2) x k series x (3) k 2 x 2 = k 1 k 2 = k 1+k 2 = 1 k k 2 k series
 Final Review A Puzzle... Consider wo massless springs wih spring consans k 1 and k and he same equilibrium lengh. 1. If hese springs ac on a mass m in parallel, hey would be equivalen o a single spring
Final Review A Puzzle... Consider wo massless springs wih spring consans k 1 and k and he same equilibrium lengh. 1. If hese springs ac on a mass m in parallel, hey would be equivalen o a single spring
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS NCERT
 Chaper Ten MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS MCQ I 10.1 A all cylinder is filled wih iscous oil. A round pebble is dropped from he op wih zero iniial elociy. From he plo shown in Fig. 10.1, indicae he one
Chaper Ten MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF FLUIDS MCQ I 10.1 A all cylinder is filled wih iscous oil. A round pebble is dropped from he op wih zero iniial elociy. From he plo shown in Fig. 10.1, indicae he one
Introduction to Physical Oceanography Homework 5 - Solutions
 Laure Zanna //5 Inroducion o Phsical Oceanograph Homework 5 - Soluions. Inerial oscillaions wih boom fricion non-selecive scale: The governing equaions for his problem are This ssem can be wrien as where
Laure Zanna //5 Inroducion o Phsical Oceanograph Homework 5 - Soluions. Inerial oscillaions wih boom fricion non-selecive scale: The governing equaions for his problem are This ssem can be wrien as where
Main Ideas in Class Today
 Main Ideas in Class Toda Inroducion o Falling Appl Consan a Equaions Graphing Free Fall Sole Free Fall Problems Pracice:.45,.47,.53,.59,.61,.63,.69, Muliple Choice.1 Freel Falling Objecs Refers o objecs
Main Ideas in Class Toda Inroducion o Falling Appl Consan a Equaions Graphing Free Fall Sole Free Fall Problems Pracice:.45,.47,.53,.59,.61,.63,.69, Muliple Choice.1 Freel Falling Objecs Refers o objecs
BEng (Hons) Telecommunications. Examinations for / Semester 2
 BEng (Hons) Telecommunicaions Cohor: BTEL/14/FT Examinaions for 2015-2016 / Semeser 2 MODULE: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY MODULE CODE: ASE2103 Duraion: 2 ½ Hours Insrucions o Candidaes: 1. Answer ALL 4 (FOUR)
BEng (Hons) Telecommunicaions Cohor: BTEL/14/FT Examinaions for 2015-2016 / Semeser 2 MODULE: ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY MODULE CODE: ASE2103 Duraion: 2 ½ Hours Insrucions o Candidaes: 1. Answer ALL 4 (FOUR)
Kinematics Motion in 1 Dimension and Graphs
 Kinemaics Moion in 1 Dimension and Graphs Lana Sheridan De Anza College Sep 27, 2017 Las ime moion in 1-dimension some kinemaic quaniies graphs Overview velociy and speed acceleraion more graphs Kinemaics
Kinemaics Moion in 1 Dimension and Graphs Lana Sheridan De Anza College Sep 27, 2017 Las ime moion in 1-dimension some kinemaic quaniies graphs Overview velociy and speed acceleraion more graphs Kinemaics
ME 425: Aerodynamics
 ME 45: Aerodnamics Dr. A.B.M. Toiqe Hasan Proessor Deparmen o Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh Uniersi o Engineering & Technolog BUET, Dhaka Lecre-7 Fndamenals so Aerodnamics oiqehasan.be.ac.bd oiqehasan@me.be.ac.bd
ME 45: Aerodnamics Dr. A.B.M. Toiqe Hasan Proessor Deparmen o Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh Uniersi o Engineering & Technolog BUET, Dhaka Lecre-7 Fndamenals so Aerodnamics oiqehasan.be.ac.bd oiqehasan@me.be.ac.bd
Version 053 Midterm 1 OConnor (05141) 1
 Version 053 Miderm 1 OConnor (05141) 1 This prin-ou should have 36 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions ma coninue on he ne column or pae find all choices before answerin. V1:1, V:1, V3:3, V4:1, V5:4. 001
Version 053 Miderm 1 OConnor (05141) 1 This prin-ou should have 36 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions ma coninue on he ne column or pae find all choices before answerin. V1:1, V:1, V3:3, V4:1, V5:4. 001
Equations of motion for constant acceleration
 Lecure 3 Chaper 2 Physics I 01.29.2014 Equaions of moion for consan acceleraion Course websie: hp://faculy.uml.edu/andriy_danylo/teaching/physicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo360.uml.edu/danylo2013/physics1spring.hml
Lecure 3 Chaper 2 Physics I 01.29.2014 Equaions of moion for consan acceleraion Course websie: hp://faculy.uml.edu/andriy_danylo/teaching/physicsi Lecure Capure: hp://echo360.uml.edu/danylo2013/physics1spring.hml
1. The 200-kg lunar lander is descending onto the moon s surface with a velocity of 6 m/s when its retro-engine is fired. If the engine produces a
 PROBLEMS. The -kg lunar lander is descending ono he moon s surface wih a eloci of 6 m/s when is rero-engine is fired. If he engine produces a hrus T for 4 s which aries wih he ime as shown and hen cus
PROBLEMS. The -kg lunar lander is descending ono he moon s surface wih a eloci of 6 m/s when is rero-engine is fired. If he engine produces a hrus T for 4 s which aries wih he ime as shown and hen cus
Answers to 1 Homework
 Answers o Homework. x + and y x 5 y To eliminae he parameer, solve for x. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge y x.. x and y, x y x To eliminae he parameer, solve for. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge x y, x. (Noe:
Answers o Homework. x + and y x 5 y To eliminae he parameer, solve for x. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge y x.. x and y, x y x To eliminae he parameer, solve for. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge x y, x. (Noe:
Chapter 15 Oscillatory Motion I
 Chaper 15 Oscillaory Moion I Level : AP Physics Insrucor : Kim Inroducion A very special kind of moion occurs when he force acing on a body is proporional o he displacemen of he body from some equilibrium
Chaper 15 Oscillaory Moion I Level : AP Physics Insrucor : Kim Inroducion A very special kind of moion occurs when he force acing on a body is proporional o he displacemen of he body from some equilibrium
t A. 3. Which vector has the largest component in the y-direction, as defined by the axes to the right?
 Ke Name Insrucor Phsics 1210 Exam 1 Sepember 26, 2013 Please wrie direcl on he exam and aach oher shees of work if necessar. Calculaors are allowed. No noes or books ma be used. Muliple-choice problems
Ke Name Insrucor Phsics 1210 Exam 1 Sepember 26, 2013 Please wrie direcl on he exam and aach oher shees of work if necessar. Calculaors are allowed. No noes or books ma be used. Muliple-choice problems
Kinetics of a Particle: Impulse and Momentum
 Kineics of a Paricle: Impulse and Momenum Linear momenum L mv d Fma ( mv) d dl d Newon s nd law: The resulan of all forces acing on a paricle is equal o is ime rae of change of linear momenum. F d L L
Kineics of a Paricle: Impulse and Momenum Linear momenum L mv d Fma ( mv) d dl d Newon s nd law: The resulan of all forces acing on a paricle is equal o is ime rae of change of linear momenum. F d L L
Variable acceleration, Mixed Exercise 11
 Variable acceleraion, Mixed Exercise 11 1 a v 1 P is a res when v 0. 0 1 b s 0 0 v d (1 ) 1 0 1 0 7. The disance ravelled by P is 7. m. 1 a v 6+ a d v 6 + When, a 6+ 0 The acceleraion of P when is 0 m
Variable acceleraion, Mixed Exercise 11 1 a v 1 P is a res when v 0. 0 1 b s 0 0 v d (1 ) 1 0 1 0 7. The disance ravelled by P is 7. m. 1 a v 6+ a d v 6 + When, a 6+ 0 The acceleraion of P when is 0 m
Week 1 Lecture 2 Problems 2, 5. What if something oscillates with no obvious spring? What is ω? (problem set problem)
 Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
x i v x t a dx dt t x
 Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
Physics 3A: Basic Physics I Shoup - Miderm Useful Equaions A y A sin A A A y an A y A A = A i + A y j + A z k A * B = A B cos(θ) A B = A B sin(θ) A * B = A B + A y B y + A z B z A B = (A y B z A z B y
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration
 rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
rev 06/2017 Posiion, Velociy, and Acceleraion Equipmen Qy Equipmen Par Number 1 Dynamic Track ME-9493 1 Car ME-9454 1 Fan Accessory ME-9491 1 Moion Sensor II CI-6742A 1 Track Barrier Purpose The purpose
3, so θ = arccos
 Mahemaics 210 Professor Alan H Sein Monday, Ocober 1, 2007 SOLUTIONS This problem se is worh 50 poins 1 Find he angle beween he vecors (2, 7, 3) and (5, 2, 4) Soluion: Le θ be he angle (2, 7, 3) (5, 2,
Mahemaics 210 Professor Alan H Sein Monday, Ocober 1, 2007 SOLUTIONS This problem se is worh 50 poins 1 Find he angle beween he vecors (2, 7, 3) and (5, 2, 4) Soluion: Le θ be he angle (2, 7, 3) (5, 2,
s in boxe wers ans Put
 Pu answers in boxes Main Ideas in Class Toda Inroducion o Falling Appl Old Equaions Graphing Free Fall Sole Free Fall Problems Pracice:.45,.47,.53,.59,.61,.63,.69, Muliple Choice.1 Freel Falling Objecs
Pu answers in boxes Main Ideas in Class Toda Inroducion o Falling Appl Old Equaions Graphing Free Fall Sole Free Fall Problems Pracice:.45,.47,.53,.59,.61,.63,.69, Muliple Choice.1 Freel Falling Objecs
Two Dimensional Dynamics
 Physics 11: Lecure 6 Two Dimensional Dynamics Today s lecure will coer Chaper 4 Exam I Physics 11: Lecure 6, Pg 1 Brie Reiew Thus Far Newon s Laws o moion: SF=ma Kinemaics: x = x + + ½ a Dynamics Today
Physics 11: Lecure 6 Two Dimensional Dynamics Today s lecure will coer Chaper 4 Exam I Physics 11: Lecure 6, Pg 1 Brie Reiew Thus Far Newon s Laws o moion: SF=ma Kinemaics: x = x + + ½ a Dynamics Today
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
AP Calculus BC - Parametric equations and vectors Chapter 9- AP Exam Problems solutions
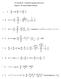 AP Calculus BC - Parameric equaions and vecors Chaper 9- AP Exam Problems soluions. A 5 and 5. B A, 4 + 8. C A, 4 + 4 8 ; he poin a is (,). y + ( x ) x + 4 4. e + e D A, slope.5 6 e e e 5. A d hus d d
AP Calculus BC - Parameric equaions and vecors Chaper 9- AP Exam Problems soluions. A 5 and 5. B A, 4 + 8. C A, 4 + 4 8 ; he poin a is (,). y + ( x ) x + 4 4. e + e D A, slope.5 6 e e e 5. A d hus d d
Experiment 123 Determination of the sound wave velocity with the method of Lissajous figures
 perimen 3 Deerminaion of he sound wave veloci wih he mehod of Lissajous figures The aim of he eercise To sud acousic wave propagaion in he air To deermine of he sound wave veloci in he air Mehodolog of
perimen 3 Deerminaion of he sound wave veloci wih he mehod of Lissajous figures The aim of he eercise To sud acousic wave propagaion in he air To deermine of he sound wave veloci in he air Mehodolog of
Method of Moment Area Equations
 Noe proided b JRR Page-1 Noe proided b JRR Page- Inrodcion ehod of omen rea qaions Perform deformaion analsis of flere-dominaed srcres eams Frames asic ssmpions (on.) No aial deformaion (aiall rigid members)
Noe proided b JRR Page-1 Noe proided b JRR Page- Inrodcion ehod of omen rea qaions Perform deformaion analsis of flere-dominaed srcres eams Frames asic ssmpions (on.) No aial deformaion (aiall rigid members)
Motion along a Straight Line
 chaper 2 Moion along a Sraigh Line verage speed and average velociy (Secion 2.2) 1. Velociy versus speed Cone in he ebook: fer Eample 2. Insananeous velociy and insananeous acceleraion (Secions 2.3, 2.4)
chaper 2 Moion along a Sraigh Line verage speed and average velociy (Secion 2.2) 1. Velociy versus speed Cone in he ebook: fer Eample 2. Insananeous velociy and insananeous acceleraion (Secions 2.3, 2.4)
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line
 Chaper Moion along a sraigh line Kinemaics & Dynamics Kinemaics: Descripion of Moion wihou regard o is cause. Dynamics: Sudy of principles ha relae moion o is cause. Basic physical ariables in kinemaics
Chaper Moion along a sraigh line Kinemaics & Dynamics Kinemaics: Descripion of Moion wihou regard o is cause. Dynamics: Sudy of principles ha relae moion o is cause. Basic physical ariables in kinemaics
