Lecture 17. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
|
|
|
- Osborn Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 17 PHYC 161 Fall 2016
2 Electric potential Potential is potential energy per unit charge. The potential of a with respect to b (V ab = V a V b ) equals the work done by the electric force when a unit charge moves from a to b.
3 Electric potential The potential due to a single point charge is: Like electric field, potential is independent of the test charge that we use to define it. For a collection of point charges:
4 Q23.8 The electric potential due to a point charge approaches zero as you move farther away from the charge. If the three point charges shown here lie at the vertices of an equilateral triangle, the electric potential at the center of the triangle is A. positive. B. negative. C. zero. D. either positive or negative. E. either positive, negative, or zero Pearson Education, Inc. Charge #1 +q y x Charge #2 q q Charge #3
5 Finding electric potential from the electric field If you move in the direction of the electric field, the electric potential decreases, but if you move opposite the field, the potential increases.
6 Electric potential and electric field Moving with the direction of the electric field means moving in the direction of decreasing V, and vice versa. To move a unit charge slowly against the electric force, we must apply an external force per unit charge equal and opposite to the electric force per unit charge. The electric force per unit charge is the electric field. The potential difference V a V b equals the work done per unit charge by this external force to move a unit charge from b to a: The unit of electric field can be expressed as 1 N/C = 1 V/m.
7 Oppositely charged parallel plates The potential at any height y between the two large oppositely charged parallel plates is V = Ey.
8 The electron volt When a particle with charge q moves from a point where the potential is V b to a point where it is V a, the change in the potential energy U is U a U b = q(v a V b ) If charge q equals the magnitude e of the electron charge, and the potential difference is 1 V, the change in energy is defined as one electron volt (ev): 1 ev = J
9 Electric potential and field of a charged conductor A solid conducting sphere of radius R has a total charge q. The electric field inside the sphere is zero everywhere.
10 Electric potential and field of a charged conductor The potential is the same at every point inside the sphere and is equal to its value at the surface.
11 Ionization and corona discharge At an electric-field magnitude of about V/m or greater, air molecules become ionized, and air becomes a conductor. For a charged conducting sphere, V surface = E surface R. Thus, if E m is the electric-field magnitude at which air becomes conductive (known as the dielectric strength of air), then the maximum potential V m to which a spherical conductor can be raised is V m = RE m.
12 Equipotential surfaces Contour lines on a topographic map are curves of constant elevation and hence of constant gravitational potential energy.
13 Equipotential surfaces and field lines An equipotential surface is a surface on which the electric potential is the same at every point. Field lines and equipotential surfaces are always mutually perpendicular. Shown are cross sections of equipotential surfaces (blue lines) and electric field lines (red lines) for a single positive charge.
14 Equipotential surfaces and field lines for a dipole
15 Field and potential of two equal positive charges
16 Equipotentials and conductors When all charges are at rest: the surface of a conductor is always an equipotential surface. the electric field just outside a conductor is always perpendicular to the surface.
17 Equipotentials and conductors If the electric field had a tangential component at the surface of a conductor, a net amount of work would be done on a test charge by moving it around a loop as shown here which is impossible because the electric force is conservative.
18 Potential gradient The components of the electric field can be found by taking partial derivatives of the electric potential: The electric field is the negative gradient of the potential:
19 Electric Field from the Potential Let s say that somehow we have determined the electric potential everywhere in space from a charge distribution. V b V a E dr b a dv b a b a E dr dv E dr ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ dv E i E j E k dxi dyj dzk PowerPoint Lectures for x y z University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young dvand Roger ExdxA. Freedman Eydy Ezdz Lectures by Jason Harlow
20 Electric Field from the Potential If we now hold y and z constant (so that dy and dz are zero) then, dv E dx E dy dv E x x y z E dx x dv dx y and z constant E dz V x Likewise then, for the other components of the electric field, PowerPoint Lectures for V V University Physics, 14th Edition Ey, Ez Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow y z
21 Potential gradient The components of the electric field can be found by taking partial derivatives of the electric potential: The electric field is the negative gradient of the potential:
Lecture 15. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 15 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Q23.11 A solid spherical conductor has a spherical cavity in its interior. The cavity is not centered on the center of the conductor. If there is a net positive charge on
Lecture 15 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Q23.11 A solid spherical conductor has a spherical cavity in its interior. The cavity is not centered on the center of the conductor. If there is a net positive charge on
Coulomb s Law Pearson Education Inc.
 Coulomb s Law Coulomb s Law: The magnitude of the electric force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance
Coulomb s Law Coulomb s Law: The magnitude of the electric force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance
Lecture 19. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 19 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 C Capacitors in Series Capacitors If you wanted in series: to replace these Have capacitors the same charge with just Potential one equivalent difference capacitor: across
Lecture 19 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 C Capacitors in Series Capacitors If you wanted in series: to replace these Have capacitors the same charge with just Potential one equivalent difference capacitor: across
Lecture 14. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 14 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Q22.3 Two point charges, +q (in red) and q (in blue), are arranged as shown. Through which closed surface(s) is/are the net electric flux equal to zero? A. surface A B. surface
Lecture 14 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Q22.3 Two point charges, +q (in red) and q (in blue), are arranged as shown. Through which closed surface(s) is/are the net electric flux equal to zero? A. surface A B. surface
Electric Potential. Chapter 23. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Reza Khanbabaie Goals for Chapter 23 Reminder about gravitational
Chapter 23 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Reza Khanbabaie Goals for Chapter 23 Reminder about gravitational
Chapter 23 Electric Potential. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential 23-1 Electrostatic Potential Energy and Potential Difference The electrostatic force is conservative potential energy can be defined. Change in electric potential energy
Chapter 23 Electric Potential 23-1 Electrostatic Potential Energy and Potential Difference The electrostatic force is conservative potential energy can be defined. Change in electric potential energy
PH 222-2A Spring 2015
 PH 222-2A Spring 215 Electric Potential Lectures 5-6 Chapter 24 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 24 Electric Potential In this chapter we will define the electric
PH 222-2A Spring 215 Electric Potential Lectures 5-6 Chapter 24 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 9 th edition) 1 Chapter 24 Electric Potential In this chapter we will define the electric
LESSON 2 PHYSICS NOTES
 LESSON 2 ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE SECTION I ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL ELECTRIC FIELD IS CONSERVATIVE In an electric field work done by the electric field in moving a unit positive charge from
LESSON 2 ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE SECTION I ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL ELECTRIC FIELD IS CONSERVATIVE In an electric field work done by the electric field in moving a unit positive charge from
Electric Force and Potential Energy
 Class 04 (Class 03: whiteboard exercises of Gauss' law.) Electric Force and Potential Energy For a charge q 0 in an electric field: The force picture F=q 0 E Can we similarly look for an energy picture?
Class 04 (Class 03: whiteboard exercises of Gauss' law.) Electric Force and Potential Energy For a charge q 0 in an electric field: The force picture F=q 0 E Can we similarly look for an energy picture?
Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field Sunday, January 31, Key concepts:
 Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy when dealing
Chapter 19 Electric Potential and Electric Field Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy when dealing
Chapter 23 Electric Potential. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential Units of Chapter 23 Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field Electric Potential Due to Point Charges Potential
Chapter 23 Electric Potential Units of Chapter 23 Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field Electric Potential Due to Point Charges Potential
Electric Potential. Capacitors (Chapters 28, 29)
 Electric Potential. Capacitors (Chapters 28, 29) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength
Electric Potential. Capacitors (Chapters 28, 29) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength
Chapter 19 Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Sunday, January 31, Key concepts:
 Chapter 19 Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy
Chapter 19 Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Sunday, January 31, 2010 10:37 PM Key concepts: electric potential electric potential energy the electron-volt (ev), a convenient unit of energy
Sharpen thinking about connections among electric field, electric potential difference, potential energy
 PHYS 2015 -- Week 6 Sharpen thinking about connections among electric field, electric potential difference, potential energy Apply the ideas to capacitance and the parallel plate capacitor For exclusive
PHYS 2015 -- Week 6 Sharpen thinking about connections among electric field, electric potential difference, potential energy Apply the ideas to capacitance and the parallel plate capacitor For exclusive
What will the electric field be like inside the cavity?
 What will the electric field be like inside the cavity? 1. There is no charge inside the gaussian surface so E = 0 2. There is no net flux through the surface but there is an E field 3. Gauss s law doesn
What will the electric field be like inside the cavity? 1. There is no charge inside the gaussian surface so E = 0 2. There is no net flux through the surface but there is an E field 3. Gauss s law doesn
COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 19 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND ELECTRIC FIELD
 COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 19 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND ELECTRIC FIELD Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Difference It takes work to move a charge against an electric field. Just as with gravity,
COLLEGE PHYSICS Chapter 19 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL AND ELECTRIC FIELD Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential Difference It takes work to move a charge against an electric field. Just as with gravity,
Electric Potential Practice Problems
 Electric Potential Practice Problems AP Physics Name Multiple Choice 1. A negative charge is placed on a conducting sphere. Which statement is true about the charge distribution (A) Concentrated at the
Electric Potential Practice Problems AP Physics Name Multiple Choice 1. A negative charge is placed on a conducting sphere. Which statement is true about the charge distribution (A) Concentrated at the
Electric Potential (Chapter 25)
 Electric Potential (Chapter 25) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength The potential
Electric Potential (Chapter 25) Electric potential energy, U Electric potential energy in a constant field Conservation of energy Electric potential, V Relation to the electric field strength The potential
Chapter 25. Electric Potential
 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
Lecture 4 Electric Potential and/ Potential Energy Ch. 25
 Lecture 4 Electric Potential and/ Potential Energy Ch. 5 Review from Lecture 3 Cartoon - There is an electric energy associated with the position of a charge. Opening Demo - Warm-up problems Physlet Topics
Lecture 4 Electric Potential and/ Potential Energy Ch. 5 Review from Lecture 3 Cartoon - There is an electric energy associated with the position of a charge. Opening Demo - Warm-up problems Physlet Topics
Chapter 17. Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential
 Chapter 17 Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential Consider gravity near the surface of the Earth The gravitational field is uniform. This means it always points in the same direction with
Chapter 17 Electric Potential Energy and the Electric Potential Consider gravity near the surface of the Earth The gravitational field is uniform. This means it always points in the same direction with
What You Already Know
 What You Already Know Coulomb s law Electric fields Gauss law Electric fields for several configurations Point Line Plane (nonconducting) Sheet (conducting) Ring (along axis) Disk (along axis) Sphere Cylinder
What You Already Know Coulomb s law Electric fields Gauss law Electric fields for several configurations Point Line Plane (nonconducting) Sheet (conducting) Ring (along axis) Disk (along axis) Sphere Cylinder
EX. Potential for uniformly charged thin ring
 EX. Potential for uniformly charged thin ring Q dq r R dφ 0 V ( Z ) =? z kdq Q Q V =, dq = Rdϕ = dϕ Q r 2πR 2π 2π k Q 0 = d ϕ 0 r 2π kq 0 2π = 0 d ϕ 2π r kq 0 = r kq 0 = 2 2 R + z EX. Potential for uniformly
EX. Potential for uniformly charged thin ring Q dq r R dφ 0 V ( Z ) =? z kdq Q Q V =, dq = Rdϕ = dϕ Q r 2πR 2π 2π k Q 0 = d ϕ 0 r 2π kq 0 2π = 0 d ϕ 2π r kq 0 = r kq 0 = 2 2 R + z EX. Potential for uniformly
Electric Potential. David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 212. Electricity is really just organized lightning. - George Carlin.
 Electricity is really just organized lightning. - George Carlin David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 212 Since the electric force is so similar to gravity, might it be conservative? Yes! If we move
Electricity is really just organized lightning. - George Carlin David J. Starling Penn State Hazleton PHYS 212 Since the electric force is so similar to gravity, might it be conservative? Yes! If we move
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 4 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 4 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy2140/
Electric Potential Lecture 5
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential Lecture 5 Dr. Armen Kocharian Electrical Potential Energy When a test charge is placed in an electric field, it experiences a force F = q o E The force is conservative ds
Chapter 23 Electric Potential Lecture 5 Dr. Armen Kocharian Electrical Potential Energy When a test charge is placed in an electric field, it experiences a force F = q o E The force is conservative ds
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 2 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/
General Physics (PHY 2140) Lecture 2 Electrostatics Electric flux and Gauss s law Electrical energy potential difference and electric potential potential energy of charged conductors http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~alan/
Chapter 25. Electric Potential
 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electric Potential Electromagnetism has been connected to the study of forces in previous chapters. In this chapter, electromagnetism will be linked to energy. By using an
Handout 3: Electric potential and electric potential energy. Electric potential
 Handout 3: Electric potential and electric potential energy Electric potential Consider a charge + fixed in space as in Figure. Electric potential V at any point in space is defined as the work done by
Handout 3: Electric potential and electric potential energy Electric potential Consider a charge + fixed in space as in Figure. Electric potential V at any point in space is defined as the work done by
4 Chapter. Electric Potential
 4 Chapter Electric Potential 4.1 Potential and Potential Energy... 4-3 4.2 Electric Potential in a Uniform Field... 4-7 4.3 Electric Potential due to Point Charges... 4-8 4.3.1 Potential Energy in a System
4 Chapter Electric Potential 4.1 Potential and Potential Energy... 4-3 4.2 Electric Potential in a Uniform Field... 4-7 4.3 Electric Potential due to Point Charges... 4-8 4.3.1 Potential Energy in a System
Ch 25 Electric Potential! Electric Energy, Electric Potential!
 Ch 25 Electric Potential Electric Energy, Electric Potential Energy concepts are going to be extremely important to us as we consider the behavior of charges in electric fields. How do energy concepts
Ch 25 Electric Potential Electric Energy, Electric Potential Energy concepts are going to be extremely important to us as we consider the behavior of charges in electric fields. How do energy concepts
E&M: Worksheet 6 Fields, Potential, and Energy
 Name Date Pd () (-) E&M: Worksheet 6 Fields, Potential, and Energy 1. Below are two parallel conducting plates, each carrying an equal quantity of excess charge of opposite type. The plates are separated
Name Date Pd () (-) E&M: Worksheet 6 Fields, Potential, and Energy 1. Below are two parallel conducting plates, each carrying an equal quantity of excess charge of opposite type. The plates are separated
Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics
 Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 24 Electric Potential Interactive Lecture Questions 24.2.1. Two electrons are separated by a distance R. If the
Halliday/Resnick/Walker Fundamentals of Physics Classroom Response System Questions Chapter 24 Electric Potential Interactive Lecture Questions 24.2.1. Two electrons are separated by a distance R. If the
Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law
 Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law Matter is made of particles which are or charged. The unit of charge is the ( ) Charges are, meaning that they cannot be It is thought that the total charge
Electrostatics Notes 1 Charges and Coulomb s Law Matter is made of particles which are or charged. The unit of charge is the ( ) Charges are, meaning that they cannot be It is thought that the total charge
r 4 r 2 q 2 r 3 V () r En dln (r) 1 q 1 Negative sign from integration of E field cancels the negative sign from the original equation.
 Question from last class Potential due to a Group of Point Charges rr V () r E dl r r 1 q 1 X rr N V () r E dl r n n N V(r) V n (r) 1 n1 4 o 1/30/2018 2 q 2 N r r N r r q n V () r En dln dr 2 n n r n r
Question from last class Potential due to a Group of Point Charges rr V () r E dl r r 1 q 1 X rr N V () r E dl r n n N V(r) V n (r) 1 n1 4 o 1/30/2018 2 q 2 N r r N r r q n V () r En dln dr 2 n n r n r
As we discussed in class, here are the key properties of the topographical map:
 Ch21P Page 1 1P22/1P92 Problems (2011) Chapter 21 Electric Potential Friday, January 14, 2011 10:03 AM In the previous chapter we learned about the use of the electric field concept to describe electric
Ch21P Page 1 1P22/1P92 Problems (2011) Chapter 21 Electric Potential Friday, January 14, 2011 10:03 AM In the previous chapter we learned about the use of the electric field concept to describe electric
charge of opposite signs attract / charges of the same sign repel
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 4.1 ELECTRICITY ELECTRIC FIELD ELECTRIC POTENTIAL QUESTIONS and PROBLEMS (with ANSWRES) ex41b ex41c electric force F E [N] charge of opposite signs attract / charges of the
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE MODULE 4.1 ELECTRICITY ELECTRIC FIELD ELECTRIC POTENTIAL QUESTIONS and PROBLEMS (with ANSWRES) ex41b ex41c electric force F E [N] charge of opposite signs attract / charges of the
Lecture 8 Multiple Choice Questions :
 Lecture 8 Multiple Choice Questions : 1. A point charge -3Q lies at the centre of a conducting shell of radius 2R. The net charge on the outer surface of the shell is -3Q Zero +1.5 Q d. +3Q 2. Two identical
Lecture 8 Multiple Choice Questions : 1. A point charge -3Q lies at the centre of a conducting shell of radius 2R. The net charge on the outer surface of the shell is -3Q Zero +1.5 Q d. +3Q 2. Two identical
Work and Energy. v f. v i. F(x ) F(x ) x f. Consider a block of mass m moving along the x-axis. Conservative force acting on block: F = F(x) Z xf
 Work and Energy Consider a block of mass m moving along the x-axis. Conservative force acting on block: F = F(x) Work done by F(x) on block: W if = Kinetic energy of block: K = 1 2 mv2 Potential energy
Work and Energy Consider a block of mass m moving along the x-axis. Conservative force acting on block: F = F(x) Work done by F(x) on block: W if = Kinetic energy of block: K = 1 2 mv2 Potential energy
Chapter 30. Inductance. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow
 Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 30 Looking forward at how a time-varying
Chapter 30 Inductance PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 30 Looking forward at how a time-varying
Chapter 13. Gravitation. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow
 Chapter 13 Gravitation PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Next one week Today: Ch 13 Wed: Review of Ch 8-11, focusing
Chapter 13 Gravitation PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Next one week Today: Ch 13 Wed: Review of Ch 8-11, focusing
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 6 th edition Giancoli 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for
Electromagnetic Waves
 Chapter 32 Electromagnetic Waves PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 32 To learn why a light
Chapter 32 Electromagnetic Waves PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 32 To learn why a light
Dielectrics. Chapter 24. PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman. Lectures by James Pazun
 Chapter 24 Capacitance and Dielectrics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Main Points 1. Equipotential ti regions (lines,
Chapter 24 Capacitance and Dielectrics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Main Points 1. Equipotential ti regions (lines,
Chapter 23 Electric Potential
 Chapter 23 Electric Potential 23-1 Electrostatic Potential Energy and Potential Difference The electrostatic force, here,f=qe is conservative potential energy can be defined. Change in electric potential
Chapter 23 Electric Potential 23-1 Electrostatic Potential Energy and Potential Difference The electrostatic force, here,f=qe is conservative potential energy can be defined. Change in electric potential
INTRODUCTION ELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL ENERGY. Introduction. Electrostatic potential energy. Electric potential. for a system of point charges
 Chapter 4 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Introduction Electrostatic potential energy Electric potential for a system of point charges for a continuous charge distribution Why determine electic potential? Determination
Chapter 4 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL Introduction Electrostatic potential energy Electric potential for a system of point charges for a continuous charge distribution Why determine electic potential? Determination
Electric Potential. 1/28/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1
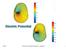 Electric Potential 1/28/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1 Notes! Correction set 1 Due Thursday evening at 10pm Name: Correction #1 RS Must answer all questions correctly to receive
Electric Potential 1/28/14 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 23 1 Notes! Correction set 1 Due Thursday evening at 10pm Name: Correction #1 RS Must answer all questions correctly to receive
Physics 1302, Exam 1 Review
 c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1302, Exam 1 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1302, Exam 1 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
Electric Potential II
 Electric Potential II Physics 2415 Lecture 7 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics Field lines and equipotentials Partial derivatives Potential along a line from two charges Electric breakdown of air Potential
Electric Potential II Physics 2415 Lecture 7 Michael Fowler, UVa Today s Topics Field lines and equipotentials Partial derivatives Potential along a line from two charges Electric breakdown of air Potential
+2Q -2Q. (a) 672 N m 2 /C (b) 321 N m 2 /C (c) 105 N m 2 /C (d) 132 N m 2 /C (e) 251 N m 2 /C
 1. The figure below shows 4 point charges located on a circle centered about the origin. The exact locations of the charges on the circle are not given. What can you say about the electric potential created
1. The figure below shows 4 point charges located on a circle centered about the origin. The exact locations of the charges on the circle are not given. What can you say about the electric potential created
Q1. A wave travelling along a string is described by
 Coordinator: Saleem Rao Wednesday, May 24, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. A wave travelling along a string is described by y( x, t) = 0.00327 sin(72.1x 2.72t) In which all numerical constants are in SI units. Find the
Coordinator: Saleem Rao Wednesday, May 24, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. A wave travelling along a string is described by y( x, t) = 0.00327 sin(72.1x 2.72t) In which all numerical constants are in SI units. Find the
Physics 1202: Lecture 3 Today s Agenda
 Physics 1202: Lecture 3 Today s Agenda Announcements: Lectures posted on: www.phys.uconn.edu/~rcote/ HW assignments, solutions etc. Homework #1: On Masterphysics: due this coming Friday Go to the syllabus
Physics 1202: Lecture 3 Today s Agenda Announcements: Lectures posted on: www.phys.uconn.edu/~rcote/ HW assignments, solutions etc. Homework #1: On Masterphysics: due this coming Friday Go to the syllabus
Capacitance and Dielectrics
 Chapter 24 Capacitance and Dielectrics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 24 To understand capacitors
Chapter 24 Capacitance and Dielectrics PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 24 To understand capacitors
Ch 7 Electric Potential
 Ch 7 Electric Potential Electric Energy, Electric Potential Energy concepts are going to be extremely important to us as we consider the behavior of charges in electric fields. How do energy concepts help
Ch 7 Electric Potential Electric Energy, Electric Potential Energy concepts are going to be extremely important to us as we consider the behavior of charges in electric fields. How do energy concepts help
y=1 1 J (a x ) dy dz dx dz 10 4 sin(2)e 2y dy dz sin(2)e 2y
 Chapter 5 Odd-Numbered 5.. Given the current density J = 4 [sin(x)e y a x + cos(x)e y a y ]ka/m : a) Find the total current crossing the plane y = in the a y direction in the region
Chapter 5 Odd-Numbered 5.. Given the current density J = 4 [sin(x)e y a x + cos(x)e y a y ]ka/m : a) Find the total current crossing the plane y = in the a y direction in the region
Chapter 16. Electric Energy and Capacitance
 Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Electric Potential Energy The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy function with this force Work
Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Electric Potential Energy The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy function with this force Work
Chapter 23 Electric Potential (Voltage)
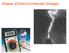 Chapter 23 Electric Potential (Voltage) Electric potential energy Recall how a conservative force is related to the potential energy associated with that force: The electric potential energy: Change in
Chapter 23 Electric Potential (Voltage) Electric potential energy Recall how a conservative force is related to the potential energy associated with that force: The electric potential energy: Change in
Be on time Switch off mobile phones. Put away laptops. Being present = Participating actively
 A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
A couple of house rules Be on time Switch off mobile phones Put away laptops Being present = Participating actively Het basisvak Toegepaste Natuurwetenschappen http://www.phys.tue.nl/nfcmr/natuur/collegenatuur.html
7. A capacitor has been charged by a D C source. What are the magnitude of conduction and displacement current, when it is fully charged?
 1. In which Orientation, a dipole placed in uniform electric field is in (a) stable (b) unstable equilibrium. 2. Two point charges having equal charges separated by 1 m in distance experience a force of
1. In which Orientation, a dipole placed in uniform electric field is in (a) stable (b) unstable equilibrium. 2. Two point charges having equal charges separated by 1 m in distance experience a force of
free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]
![free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m] free space (vacuum) permittivity [ F/m]](/thumbs/79/79624275.jpg) Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
Electrostatic Fields Electrostatic fields are static (time-invariant) electric fields produced by static (stationary) charge distributions. The mathematical definition of the electrostatic field is derived
4) A 3.0 pf capacitor consists of two parallel plates that have surface charge densities of 1.0
 Quantitative 3) Two parallel plates are separated by 1.0 mm. If the potential difference between them is 2.0 V, what is the magnitude of their surface charge densities? A) 18 nc/m2 4) A 3.0 pf capacitor
Quantitative 3) Two parallel plates are separated by 1.0 mm. If the potential difference between them is 2.0 V, what is the magnitude of their surface charge densities? A) 18 nc/m2 4) A 3.0 pf capacitor
Electrical Potential Energy. Chapter 25. Electric Potential Energy, final. Electric Potential Energy. Electric Potential.
 Chapter 25 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electrical Potential Energy! When a test charge, q 0 is placed in an electric field E, it experiences a force: F = q E 0! Is this force conservative? 1 2 Electric
Chapter 25 Chapter 25 Electric Potential Electrical Potential Energy! When a test charge, q 0 is placed in an electric field E, it experiences a force: F = q E 0! Is this force conservative? 1 2 Electric
Chapter 22 Electric Potential (Voltage)
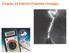 Chapter 22 Electric Potential (Voltage) Question 29.5 Work and Electric Potential I Which requires the most work, to move a positive charge from P to points 1, 2, 3 or 4? All points are the same distance
Chapter 22 Electric Potential (Voltage) Question 29.5 Work and Electric Potential I Which requires the most work, to move a positive charge from P to points 1, 2, 3 or 4? All points are the same distance
Electric Potential Energy Chapter 16
 Electric Potential Energy Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Sections: 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy
Electric Potential Energy Chapter 16 Electric Energy and Capacitance Sections: 1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9 The electrostatic force is a conservative force It is possible to define an electrical potential energy
Potentials and Fields
 Potentials and Fields Review: Definition of Potential Potential is defined as potential energy per unit charge. Since change in potential energy is work done, this means V E x dx and E x dv dx etc. The
Potentials and Fields Review: Definition of Potential Potential is defined as potential energy per unit charge. Since change in potential energy is work done, this means V E x dx and E x dv dx etc. The
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Chapter 10 Dynamics of Rotational Motion PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 10 Looking forward
Chapter 10 Dynamics of Rotational Motion PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 10 Looking forward
Slide 1 / Which of the following represents the electric field map due to a single positive charge? A B C
 Slide 1 / 21 1 Which of the following represents the electric field map due to a single positive charge? Slide 2 / 21 2 Which of the following represents the electric field map due to a single negative
Slide 1 / 21 1 Which of the following represents the electric field map due to a single positive charge? Slide 2 / 21 2 Which of the following represents the electric field map due to a single negative
Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 28 Looking forward
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 28 Looking forward
Chapter 20. Electric Potential Electric Potential Energy
 Chapter 20 Electric Potential Electric Potential Energy CONSERVTIVE FORCES conservative force gives back work that has been done against it Gravitational and electrostatic forces are conservative Friction
Chapter 20 Electric Potential Electric Potential Energy CONSERVTIVE FORCES conservative force gives back work that has been done against it Gravitational and electrostatic forces are conservative Friction
Ch 25 Electric Potential
 Ch 25 Electric Potential Electric Energy, Electric Potential Energy concepts are going to be extremely important to us as we consider the behavior of charges in electric fields. How do energy concepts
Ch 25 Electric Potential Electric Energy, Electric Potential Energy concepts are going to be extremely important to us as we consider the behavior of charges in electric fields. How do energy concepts
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 23: ELECTRIC POTENTIAL.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY If you release 2 charges, they move gain. Where did it come from? - Two charges have a stored energy between them, called - ENERGY CONSERVATION:
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY If you release 2 charges, they move gain. Where did it come from? - Two charges have a stored energy between them, called - ENERGY CONSERVATION:
LECTURE 19 EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES & ELECTRIC FIELD. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 19 EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES & ELECTRIC FIELD Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 19 2 Reading chapter 19-4. Equipotential surfaces 3 Clicker question: 1 Equipotential surfaces & electric field 4 Any
LECTURE 19 EQUIPOTENTIAL SURFACES & ELECTRIC FIELD Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 19 2 Reading chapter 19-4. Equipotential surfaces 3 Clicker question: 1 Equipotential surfaces & electric field 4 Any
Sources of Magnetic Field
 Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 28 To determine the
Chapter 28 Sources of Magnetic Field PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Thirteenth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Wayne Anderson Goals for Chapter 28 To determine the
PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I. Photo: J. M. Schwarz
 Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements In class today we will finish Chapter 17 on electric potential energy and electric potential and perhaps begin Chapter
Welcome back to PHY101: Major Concepts in Physics I Photo: J. M. Schwarz Announcements In class today we will finish Chapter 17 on electric potential energy and electric potential and perhaps begin Chapter
Review from yesterday. Please answer PROBLEM 3 in Knight on page 716 while we are waiting to start. It takes 3.0 μj to move a 15nC charge from A
 Review from yesterday Please answer PROBLEM 3 in Knight on page 716 while we are waiting to start. It takes 3.0 μj to move a 15nC charge from A to B 1 Review from yesterday Please answer PROBLEM 17 in
Review from yesterday Please answer PROBLEM 3 in Knight on page 716 while we are waiting to start. It takes 3.0 μj to move a 15nC charge from A to B 1 Review from yesterday Please answer PROBLEM 17 in
The Moon does not fall to Earth because
 The Moon does not fall to Earth because 1. It is in Earth s gravitational field. 2. The net force on it is zero. 3. It is beyond the main pull of Earth s gravity. 4. It is being pulled by the Sun and planets
The Moon does not fall to Earth because 1. It is in Earth s gravitational field. 2. The net force on it is zero. 3. It is beyond the main pull of Earth s gravity. 4. It is being pulled by the Sun and planets
05. Electric Potential I
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI PHY 204: Elementary Physics II Physics Course Materials 2015 05. Electric Potential I Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI PHY 204: Elementary Physics II Physics Course Materials 2015 05. Electric Potential I Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu Creative Commons
Reading: Electrostatics 3. Key concepts: Capacitance, energy storage, dielectrics, energy in the E-field.
 Reading: Electrostatics 3. Key concepts: Capacitance, energy storage, dielectrics, energy in the E-field. 1.! Questions about charging and discharging capacitors. When an uncharged capacitor is connected
Reading: Electrostatics 3. Key concepts: Capacitance, energy storage, dielectrics, energy in the E-field. 1.! Questions about charging and discharging capacitors. When an uncharged capacitor is connected
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
 1. A square loop of wire moves with a constant speed v from a field-free region into a region of uniform B field, as shown. Which of the five graphs correctly shows the induced current i in the loop as
1. A square loop of wire moves with a constant speed v from a field-free region into a region of uniform B field, as shown. Which of the five graphs correctly shows the induced current i in the loop as
Objects usually are charged up through the transfer of electrons from one object to the other.
 1 Part 1: Electric Force Review of Vectors Review your vectors! You should know how to convert from polar form to component form and vice versa add and subtract vectors multiply vectors by scalars Find
1 Part 1: Electric Force Review of Vectors Review your vectors! You should know how to convert from polar form to component form and vice versa add and subtract vectors multiply vectors by scalars Find
Roll Number SET NO. 42/1
 Roll Number SET NO. 4/1 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST TERM EXAMINATION PHYSICS CLASS: XII Sub. Code: 04 Time Allotted: Hrs 0.04.018 Max. Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There
Roll Number SET NO. 4/1 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST TERM EXAMINATION PHYSICS CLASS: XII Sub. Code: 04 Time Allotted: Hrs 0.04.018 Max. Marks: 70 General Instructions: 1. All questions are compulsory. There
Gauss Law. Challenge Problems
 Gauss Law Challenge Problems Problem 1: The grass seeds figure below shows the electric field of three charges with charges +1, +1, and -1, The Gaussian surface in the figure is a sphere containing two
Gauss Law Challenge Problems Problem 1: The grass seeds figure below shows the electric field of three charges with charges +1, +1, and -1, The Gaussian surface in the figure is a sphere containing two
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 17 Physics: Principles with Applications, 7 th edition Giancoli This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching
Phys 0175 Midterm Exam II Solutions Feb 25, m e te rs
 Phys 075 Midterm Eam II Solutions Feb 25, 2009. (6 pts) Locations F and G are just outside two uniformly charged large metal plates, which are 3 cm apart. Measured along the path indicated by the dotted
Phys 075 Midterm Eam II Solutions Feb 25, 2009. (6 pts) Locations F and G are just outside two uniformly charged large metal plates, which are 3 cm apart. Measured along the path indicated by the dotted
Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena
 Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena 1. History Electric Charge The ancient Greeks noticed that if you rubbed amber (petrified tree resin) on fur, then the amber would have a property that it could attract
Chapter 12 Electrostatic Phenomena 1. History Electric Charge The ancient Greeks noticed that if you rubbed amber (petrified tree resin) on fur, then the amber would have a property that it could attract
Exam One Solutions. Problem 1 (25 points): answers without work shown will not be given any credit.
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Exam One Solutions Problem 1 (25 points): answers without work shown will not be given any credit. Four point-like objects of
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Exam One Solutions Problem 1 (25 points): answers without work shown will not be given any credit. Four point-like objects of
Electricity and Magnetism. Electric Potential Energy and Voltage
 Electricity and Magnetism Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Work and Potential Energy Recall from Mechanics that E mech = K + U is a conserved quantity for particles that interact via conservative
Electricity and Magnetism Electric Potential Energy and Voltage Work and Potential Energy Recall from Mechanics that E mech = K + U is a conserved quantity for particles that interact via conservative
Electromagnetic Induction
 Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 29 Looking forward
Chapter 29 Electromagnetic Induction PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, 14th Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by Jason Harlow Learning Goals for Chapter 29 Looking forward
Fundamental Constants
 Fundamental Constants Atomic Mass Unit u 1.660 540 2 10 10 27 kg 931.434 32 28 MeV c 2 Avogadro s number N A 6.022 136 7 36 10 23 (g mol) 1 Bohr magneton μ B 9.274 015 4(31) 10-24 J/T Bohr radius a 0 0.529
Fundamental Constants Atomic Mass Unit u 1.660 540 2 10 10 27 kg 931.434 32 28 MeV c 2 Avogadro s number N A 6.022 136 7 36 10 23 (g mol) 1 Bohr magneton μ B 9.274 015 4(31) 10-24 J/T Bohr radius a 0 0.529
Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1
 Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1 Two Parallel Conducting Sheets Find the electric field to the left of the sheets, between the sheets and to the right of the sheets. 1/28/2018 2 Uniform
Conductors: External Electric Field 1/28/2018 1 Two Parallel Conducting Sheets Find the electric field to the left of the sheets, between the sheets and to the right of the sheets. 1/28/2018 2 Uniform
Electric Potential Energy & Voltage. Tesla Envy =jlzeqz4efqa&feature=related
 Electric Potential Energy & Voltage Tesla Envy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =jlzeqz4efqa&feature=related Ch 23 & 24: Electric Force and Field F qq k r 1 2rˆ 12 2 F qe kq Electric Field E due to q : E
Electric Potential Energy & Voltage Tesla Envy http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =jlzeqz4efqa&feature=related Ch 23 & 24: Electric Force and Field F qq k r 1 2rˆ 12 2 F qe kq Electric Field E due to q : E
Physics 4B Chapter 24: Electric Potential
 Physics 4B Chapter 24: Electric Potential There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will go in life; it
Physics 4B Chapter 24: Electric Potential There is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so. William Shakespeare It s not what happens to you that determines how far you will go in life; it
Physics 240 Fall 2003: Exam #1. Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor:
 Physics 4 Fall 3: Exam #1 Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor: Form #1 Instructions 1. Fill in your name above. This will be a 1.5
Physics 4 Fall 3: Exam #1 Please print your name: Please list your discussion section number: Please list your discussion instructor: Form #1 Instructions 1. Fill in your name above. This will be a 1.5
Essential University Physics
 Essential University Physics Richard Wolfson 22 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lecture prepared by Richard Wolfson Slide 22-1 In this lecture you ll learn The concept of electric potential difference Including
Essential University Physics Richard Wolfson 22 Electric Potential PowerPoint Lecture prepared by Richard Wolfson Slide 22-1 In this lecture you ll learn The concept of electric potential difference Including
Chapter 17 Electric Potential
 Chapter 17 Electric Potential Units of Chapter 17 Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field Equipotential Lines The Electron Volt, a Unit
Chapter 17 Electric Potential Units of Chapter 17 Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference Relation between Electric Potential and Electric Field Equipotential Lines The Electron Volt, a Unit
Chapter 24. QUIZ 6 January 26, Example: Three Point Charges. Example: Electrostatic Potential Energy 1/30/12 1
 QUIZ 6 January 26, 2012 An electron moves a distance of 1.5 m through a region where the electric field E is constant and parallel to the displacement. The electron s potential energy increases by 3.2
QUIZ 6 January 26, 2012 An electron moves a distance of 1.5 m through a region where the electric field E is constant and parallel to the displacement. The electron s potential energy increases by 3.2
Electric_Field_core_P1
 Electric_Field_core_P1 1. [1 mark] An electron enters the region between two charged parallel plates initially moving parallel to the plates. The electromagnetic force acting on the electron A. causes
Electric_Field_core_P1 1. [1 mark] An electron enters the region between two charged parallel plates initially moving parallel to the plates. The electromagnetic force acting on the electron A. causes
A Uniform Gravitational Field
 A Uniform Gravitational Field We could define a gravitational field in much the same way we have defined the electric field: E = F on q q, g = F on m m (note that m/s 2 = N/kg) The gravitational field
A Uniform Gravitational Field We could define a gravitational field in much the same way we have defined the electric field: E = F on q q, g = F on m m (note that m/s 2 = N/kg) The gravitational field
iclicker A metal ball of radius R has a charge q. Charge is changed q -> - 2q. How does it s capacitance changed?
 1 iclicker A metal ball of radius R has a charge q. Charge is changed q -> - 2q. How does it s capacitance changed? q A: C->2 C0 B: C-> C0 C: C-> C0/2 D: C->- C0 E: C->-2 C0 2 iclicker A metal ball of
1 iclicker A metal ball of radius R has a charge q. Charge is changed q -> - 2q. How does it s capacitance changed? q A: C->2 C0 B: C-> C0 C: C-> C0/2 D: C->- C0 E: C->-2 C0 2 iclicker A metal ball of
Exam 1 Solutions. The ratio of forces is 1.0, as can be seen from Coulomb s law or Newton s third law.
 Prof. Eugene Dunnam Prof. Paul Avery Feb. 6, 007 Exam 1 Solutions 1. A charge Q 1 and a charge Q = 1000Q 1 are located 5 cm apart. The ratio of the electrostatic force on Q 1 to that on Q is: (1) none
Prof. Eugene Dunnam Prof. Paul Avery Feb. 6, 007 Exam 1 Solutions 1. A charge Q 1 and a charge Q = 1000Q 1 are located 5 cm apart. The ratio of the electrostatic force on Q 1 to that on Q is: (1) none
