U n 3 n Ba Kr (D) Br (C) Kr (B) Rb (E) 94 37
|
|
|
- Brandon Giles Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The critical angle for a transparent material in air is 30. The index of refraction of the material is most nearly (A) 0.33 (B) 0.50 (C) 1.0 (D) 1.5 (E) An object is placed as shown in the figure above. The center of curvature C and the focal point F of the reflecting surface are marked. As compared with the object, the image formed by the reflecting surface is (A) erect and larger (B) erect and the same size (C) erect and smaller (D) inverted and larger (E) inverted and smaller 38. When one uses a magnifying glass to read fine print, one uses a (A) converging lens to produce a virtual image of the print (B) converging lens to produce a real image of the print (C) mirror to produce a virtual image of the print (D) diverging lens to produce a real image of the print (E) diverging lens to produce a virtual image of the print Questions relate to photoelectric effect and the five graphs below 42. Which graph best shows the maximum kinetic energy K of the photoelectrons as a function of the frequency of incident light? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E 43. Which graph best shows the maximum kinetic energy K of the photoelectrons as a function of the intensity of incident light? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E U n 3 n Ba The additional product of the nuclear fission reaction shown above is (A) Kr (B) Br (C) Kr (D) Rb (E) Rb 45. The deuteron mass m d is related to the neutron mass m n and the proton mass m p by which of the following expressions? (A) m d = m n - m p (B) m d = m n + m p (C) m d =2(m n +m p ) (D) m d = m n + m p - (mass equivalent to deuteron binding energy) (E) m d = m n + m p + (mass equivalent to deuteron binding energy) 46. Electrons that have been accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 150 volts have a de Broglie wavelength of approximately 1 Angstrom (10 -l0 meter). In order to obtain electrons whose de Broglie wavelength is 0.5 Angstrom (5 x 10 -ll meter), what accelerating potential is required? (A) 37.5 V (B)75 V (C)300 V ( D)600 V (E)22,500 V 58. According to the Bohr model of the atom, electrons orbit the nucleus in definite orbits. According to the laws of classical physics, this model would be impossible because
2 (A) the positively charged nucleus attracts the electrons (B) Coulomb's law applies (C) accelerating electrons radiate energy (D) there is a centripetal force on the electrons (E) angular momentum is conserved 69. An illuminated object is placed 0.30 meter from a lens whose focal length is meter. The image is (A) inverted, real, and 0.30 meter from the lens on the opposite side from the object (B) upright, virtual, and 0.30 meter from the lens on the opposite side from the object (C) upright, real, and 0.10 meter from the lens on the same side as the object (D) upright, virtual, and 0.10 meter from the lens on the same side as the object (E) inverted, real, and 0.10 meter from the lens on the same side as the object 70. The energy level diagram above is for a hypothetical atom. A gas of these atoms initially in the ground state is irradiated with photons having a continuous range of energies between 7 and 10 electron volts. One would expect photons of which of the following energies to be emitted from the gas? (A) 1, 2, and 3 ev only (B) 4, 5, and 9 ev only (C) 1, 3, 5, and 10 ev only (D) 1, 5, 7, and 10 ev only (E) Since the original photons have a range of energies, one would expect a range of emitted photons with no particular energies Which of the following is true of a single-slit diffraction pattern? (A) It has equally spaced fringes of equal intensity. (B) It has a relatively strong central maximum. (C) It can be produced only if the slit width is less than one wavelength. (D) It can be produced only if the slit width is exactly one wavelength. (E) It can be produced only if the slit width is an integral number of wavelengths. 29. Which of the following CANNOT be accomplished by a single converging lens with spherical surfaces? (A) Converting a spherical wave front into a plane wave front (B) Converting a plane wave front into a spherical wave front (C) Forming a virtual image of a real object (D) Forming a real upright image of a real upright object (E) Forming a real inverted image of a real upright object 31. The image of the arrow is larger than the arrow itself in which of the following cases? (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and III only (D) II and III only (E) I, II and III
3 33. A postage stamp is placed 30 centimeters to the left of a converging lens of focal length 60 centimeters. Where is the image of the stamp located? (A) 60 cm to the left of the lens (B) 20 cm to the left of the lens (C) 20 cm to the right of the lens (D) 30 cm to the right of the lens (E) 60 cm to the right of the lens 34. The nuclear reaction X Y + Z occurs spontaneously. If M x, M Y, and M Z are the masses of the three particles. which of the following relationships is true'? (A) M x < M y - M z (B) M x < M y + M z (C) M x > M y + M z (D) M x - M y < M z (E) M x - M z < M y Which of the following graphs best represents the de Broglie wavelength λ of a particle as a function of the linear momentum p of the particle? 36. All of the following are properties of x-rays EXCEPT: (A) They penetrate light materials. (B) They ionize gases. (C) They are deflected by magnetic fields. (D) They discharge electrified bodies. (E) They are diffracted by crystals. 38. The half-life of Th is 24.1 days. If 4.0 x 10-5 kilogram of this isotope is present initially, what amount remains after 96.4 days? (A) 2.0 x 10-5 kg (B) 1.0 x 10-5 kg (C) 5.0 x lo-6 kg (D) 2.5 x l0-6 kg (E) 1.2 x 10-6 kg 2 1 H+ H H+ H + 4MeV 39. The equation above is an illustration of (A) artificially produced radioactive decay (C) nuclear disintegration (E) nuclear fusion (B) naturally occurring radioactive decay (D) nuclear fission 45. A proton collides with a nucleus of 14 7 N. If this collision produces a nucleus of 11 6 C and one other particle, that particle is (A) a proton (B) a neutron (C) a deuteron (D) an x particle (E) a β particle
4 46. The scattering of alpha particles by a thin gold foil was measured by Geiger and Marsden. The Rutherford model of the atom was proposed in order to explain why (A) more particles scattered through angles greater than 90 than through angles less than 90 (B) the fraction of particles scattered through large angles was too large to be explained by previous models of the atom (C) no particles passed through the foil undeflected (D) the most common scattering angle was about 90 (E) the most common scattering angle was about Light leaves a source at X and travels to Y along the path shown above. Which of the following statements is correct? (A) The index of refraction is the same for the two media. (B) Light travels faster in medium 2 than in medium 1. (C) Snell's law breaks down at the interface. (D) Light would arrive at Y in less time by taking a straight line path from X to Y than it does taking the path shown above. (E) Light leaving a source at Y and traveling to X would follow the same path shown above, but in reverse. 56. A nucleus of tritium contains 2 neutrons and I proton. If the nucleus undergoes beta decay, emitting an electron, the nucleus is transmuted into (A) the nucleus of an isotope of helium (B) the nucleus of an isotope of lithium (C) an alpha particle (D) a triton (E) a deuteron 64. Which of the following statements Is true of a beta Particle? (A) Its speed in a vacuum is 3 x 10 8 m/s. (B) It has a charge equal and opposite to that of an alpha particle. (C) It is more penetrating than a gamma ray of the same energy. (D) It has a mass of about 1,840 times that of a proton. (E) It can exhibit wave properties. Questions An electron and a positron, each of mass 9.1 x kilogram, are in the same general vicinity and have very small initial speeds. They then annihilate each other, producing two photons. 66. What is the approximate energy of each emerging photon? (A) 0.51 MeV (B) 2.0 MeV (C) 4.0 MeV (D) 6.6 MeV (E) It cannot be determined unless the frequency o the photon is known. 67. What is the angle between the paths of the emerging photons? (A) 0 (B) 30º (C) 45 (D) 90 (E)
5 26. Which three of the glass lenses above, when placed in air, will cause parallel rays of light to converge? (A) I, II, and III (B) I, III, and V (C) I, IV, and V (D) II, III, and IV (E) II, IV, and V Radio waves Infrared radiation Visible light Ultraviolet radiation Gamma radiation 29. For the five types of electromagnetic radiation listed above, which of the following correctly describes the way in which wavelength, frequency, and photon energy change as one goes from the top of the list to the bottom? Wavelength Frequency Photon Energy (A) Decreases Decreases Increases (B) Decreases Increases Increases (C) Increases Decreases Decreases (D) Increases Decreases Increases (E) Increases Increases Increases 30. Sound in air can best be described as which of the following types of waves? (A) Longitudinal (B) Transverse (C) Torsional (D) Electromagnetic (E) Polarized 31. An object is placed near a plane mirror, as shown above. Which of the labeled points is the position of the image? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E Questions deal with nuclear fission for which the following reaction is a good example U + n Ba+ Kr + neutrons + released energy The total number of free neutrons in the products of this reaction is (A) 2 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 5 (E) Which of the following statements is always true for neutron-induced fission reactions involving U? I. The end products always include Ba and Kr II. The rest mass of the end products is less than that of 92 U + 0n III. The total number of nucleons (protons plus neutrons) in the end products is less than that in 92 U + 0n. (A) II only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) I and III only (E) I, II, and III Questions 34-35
6 A hypothetical atom has four energy states as shown above. 34. Which of the following photon energies could NOT be found in the emission spectra of this atom after it has been excited to the n = 4 state? (A) 1 ev (B) 2 ev (C) 3 ev (D) 4 ev (E) 5 ev 35. Which of the following transitions will produce the photon with the longest wavelength? (A) n = 2 to n = 1 (B) n = 3 to n = 1 (C) n = 3 to n = 2 (D) n = 4 to n = 1 (E) n = 4 to n = Cobalt 60 is a radioactive source with a half-life of about 5 years. After how many years will the activity of a new sample of cobalt 60 be decreased to 1/8 its original value? (A) 2.5 years (B) 5 years (C) 10 years (D) 15 years (E) It depends on the original amount of cobalt Of the following phenomena, which provides the best evidence that light can have particle properties? (A) Interference of light in thin films (B) Electromagnetic radiation (C) Photoelectric effect (D) Electron diffraction (E) X-ray diffraction 38. Of the following phenomena, which provides the best evidence that particles can have wave properties? (A) The absorption of photons by electrons in an atom (B) The alpha-decay of radioactive nuclei (C) The interference pattern produced by neutrons incident on a crystal (D) The production of x-rays by electrons striking a metal target (E) The scattering of photons by electrons at rest 39. A muon. with a lifetime of 2 x 10-6 second in its frame of reference. is created in the upper atmosphere with a velocity of 0.998c toward the Earth. The lifetime of the muon, as measured by an observer on the Earth, is most nearly (A) 3 x 10-3 s (B) 3 x 10-3 (C) 3 x 10-4 s (D) 3 x 10-5 s (E) 3 x 10-6 s 53. In the photoelectric effect, the maximum speed of the electrons emitted by a metal surface when it is illuminated by light depends on which of the following? I. Intensity of the light II. Frequency of the light III. Nature of the photoelectric surface (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 54. Atoms of isotopes of the same element contain the same number of (A) protons but a different number of neutrons (B) electrons but a different number of protons (C) neutrons but a different number of protons (D) neutrons as electrons (E) protons as neutrons 60. Observations that indicate that visible light has a wavelength much shorter than a centimeter include which of the following? I. The colored pattern seen in a soap bubble
7 II. The colored pattern seen when light passes through a diffraction grating III. The bending of light when it passes from one medium to another medium (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 69. If the object distance for a converging thin lens is more than twice the focal length of the lens, the image is (A) virtual and erect (B) larger than the object (C) located inside the focal point (D) located at a distance between f and 2f from the lens (E) located at a distance more than by from the lens Quantum transitions that result in the characteristic sharp lines of the X-ray spectrum always involve (A) the inner electron shells (B) electron energy levels that have the same principal quantum number (C) emission of beta particles from the nucleus (D) neutrons within the nucleus (E) protons within the nucleus 11. Which of the following experiments provided evidence that electrons exhibit wave properties? I. Millikan oil-drop experiment II. Davisson-Germer electron-diffraction experiment III. J. J. Thomson's measurement of the charge-to-mass ratio of electrons (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and III only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 12. Quantities that are conserved in all nuclear reactions include which of the following? I. Electric charge II. Number of nuclei III. Number of protons (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and III only (D) II and III only (E) I, II, and III 26. A concave mirror with a radius of curvature of 1.0 m is used to collect light from a distant star. The distance between the mirror and the image of the star is most nearly (A) 0.25 m (B) 0.50 m (C) 0.75 m (D) 1.0 m (E) 2.0 m 27. When light passes from air into water, the frequency of the light remains the same. What happens to the speed and the wavelength of light as it crosses the boundary in going from air into water? Speed (A) Increases (B) Remains the same (C) Remains the same (D) Decreases (E) Decreases Wavelength Remains the same Decreases Remains the same Increases Decreases 28. A physics student places an object 6.0 cm from a converging lens of focal length 9.0 cm. What is the magnitude of the magnification of the image produced? (A) 0.6 (B) 1.5 (C) 2.0 (D) 3.0 (E) An object is placed at a distance of 1.5f from a converging lens of focal length f, as shown above. What type of image is formed and what is its size relative to the object? Type (A) Virtual (B) Virtual Size Larger Same size
8 (C) Virtual (D) Real (E) Real Smaller Larger Smaller 31. A light ray passes through substances 1, 2, and 3, as shown above. The indices of refraction for these three substances are n 1, n 2, and n 3, respectively. Ray segments in 1 and in 3 are parallel. From the directions of the ray, one can conclude that (A) n 3 must be the same as n 1 (B) n 2 must be less than n 1 (C) n 2 must be less than n 3 (D) n 1 must be equal to 1.00 (E) all three indices must be the same 32. At noon a radioactive sample decays at a rate of 4,000 counts per minute. At 12:30 PM. the decay rate has decreased to 2,000 counts per minute. The predicted decay rate at 1:30 PM. is (A) 0 counts per minute (B) 500 counts per minute (C) 667 counts per minute (D) 1,000 counts per minute (E) 1,333 counts per minute 33. A negative beta particle and a gamma ray are emitted during the radioactive decay of a nucleus of Pb. Which of the following is the resulting nucleus? (A) Hg (B) Tl (C) Bi (D) Bi (E) Po 34. If the momentum of an electron doubles, its de Broglie wavelength is multiplied by a factor of (A) 1/4 (B)1/2 (C) 1 (D) 2 (E) Quantum concepts are critical in explaining all of the following EXCEPT (A) Rutherford's scattering experiments (B) Bohr's theory of the hydrogen atom (C) Compton scattering (D) the blackbody spectrum (E) the photoelectric effect 36. The graph above shows the decay of a sample of carbon 14 that initially contained N o atoms. Which of the lettered points on the time axis could represent the half-life of carbon 14? (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D (E) E 37. If photons of light of frequency f have momentum p, photons of light of frequency 2f will have a momentum of (A) 2p (B) 2p (C) p (D) p 2 (E) ½ p
9 42. A beam of white light is incident on a triangular glass prism with an index of refraction of about 1.5 for visible light, producing a spectrum. Initially, the prism is in a glass aquarium filled with air, as shown above. If the aquarium is filled with water with an index of refraction of 1.3, which of the following is true? (A) No spectrum is produced. (B) A spectrum is produced, but the deviation of the beam is opposite to that in air. (C) The positions of red and violet are reversed in the spectrum. (D) The spectrum produced has greater separation between red and violet than that produced in air. (E) The spectrum produced has less separation between red and violet than that produced in air. 50. An object, slanted at an angle of 45, is placed in front of a vertical plane mirror, as shown above. Which of the following shows the apparent position and orientation of the object's image? 51. Plane sound waves of wavelength 0.12 m are incident on two narrow slits in a box with nonreflecting walls, as shown above. At a distance of 5.0 m from the center of the slits, a first-order maximum occurs at point P, which is 3.0 m from the central maximum. The distance between the slits is most nearly (A) 0.07 m (B) 0.09 m (C) 0.16 m (D) 0.20 m (E) 0.24 m 54. The disk-shaped head of a pin is 1.0 mm in diameter. Which of the following is the best estimate of the number of atoms in the layer of atoms on the top surface of the pinhead? (A) 10 4 (B) (C) (D) (E) In an experiment, light of a particular wavelength is incident on a metal surface, and electrons are emitted from the surface as a result. To produce more electrons per unit time but with less kinetic energy per electron, the experimenter should do which of the following? (A) Increase the intensity and decrease the wavelength of the light. (B) Increase the intensity and the wavelength of the light. (C) Decrease the intensity and the wavelength of the light. (D) Decrease the intensity and increase the wavelength of the light. (E) None of the above would produce the desired result. 69. Which of the following imposes a limit on the number of electrons in an energy state of an atom? (A) The Heisenberg uncertainty principle (B) The Pauli exclusion principle (C) The Bohr model of the hydrogen atom (D) The theory of relativity
10 (E) The law of conservation of energy The spherical mirror shown above has a center of curvature at point c. Which point is nearest to the focal point? a. a b. b c. c d. d e. e 26. An object is placed in front of a converging thin lens at a distance from the center of the lens equal to half the focal length. Compared to the object, the image is a. upright and larger b. upright and smaller c. inverted and larger d. inverted and smaller e. inverted and the same size 27. A radio station broadcasts on a carrier frequency of 100 MHz. The wavelength of this radio wave is most nearly a. 3.0 x 10-3 m b. 1.0 m c. 3.0 m d. 3.3 m e. 3.0 x 10 6 m 28. Which of the following is characteristic of both sound and light waves? a. They are longitudinal waves. b. They are transverse waves. c. They travel with the same velocity. d. They can be easily polarized. e. They give rise to interference effects. Questions relate to the photoelectric effect. For each question, choose an answer from the following graphs. 34. Which graph shows the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons versus the frequency of the light? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 35. Which graph shows the total photoelectric current versus the intensity of the light for a fixed frequency above the cutoff frequency? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 36. Which of the following statements about the number of protons Z and the number of neutrons N in stable nuclei is true? a. All stable nuclei have Z= N. b. Only heavy stable nuclei have Z = N. c. Heavy stable nuclei tend to have Z < N. d. All light stable nuclei have Z < N. e. All light stable nuclei have Z > N.
11 Questions A light ray R in medium I strikes a sphere of medium II with angle of incidence θ, as shown above. The figure shows five possible subsequent paths for the light ray. 50. Which path is possible if medium I is air and medium II is glass? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 51. Which path is possible if medium I is glass and medium II is air? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 53. A thin film with index of refraction n f separates two materials, each of which has an index of refraction less than n f. A monochromatic beam of light is incident normally on the film, as shown above. If the light has wavelength λ within the film, maximum constructive interference between the incident beam and the reflected beam occurs for which of the following film thicknesses? a. 3λ b. 2λ c. λ d. λ/2 e. λ/4 54. An object is placed on the axis of a converging thin lens of focal length 2 cm, at a distance of 8 cm from the lens. The distance between the image and the lens is most nearly a. 0.4 cm b. 0.8 cm c. 1.6 cm d. 2.0 cm e. 2.7 cm 55. A large lens is used to focus an image of an object onto a screen. If the left half of the lens is covered with a dark card, which of the following occurs? a. The left half of the image disappears. b. The right half of the image disappears. c. The image becomes blurred. d. The image becomes dimmer. e. No image is formed. 58. When 10 B is bombarded by neutrons, a neutron can be absorbed and an alpha particle ( 4 He) emitted. If the 10 B target is stationary, the kinetic energy of the reaction products is equal to the a. kinetic energy of the incident neutron b. total energy of the incident neutron c. energy equivalent of the mass decrease in the reaction d. energy equivalent of the mass decrease in the reaction, minus the kinetic energy of the incident neutron e. energy equivalent of the mass decrease in the reaction, plus the kinetic energy of the incident neutron
12 The nuclide 82 Pb emits an electron and becomes nuclide X. Which of the following gives the mass number and atomic number of nuclide X? Mass Atomic Number Number a b c d e A 50,000 W radio station transmits waves of wavelength 4 m. Which of the following is the best estimate of the number of photons it emits per second? a b c d e
SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Modern Physics SECTION A Quantum Physics and Atom Models 1. Light of a single frequency falls on a photoelectric material but no electrons are emitted. Electrons may
2. Determine the excess charge on the outer surface of the outer sphere (a distance c from the center of the system).
 Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges will yield
Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges will yield
MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION. Dr. Flera Rizatdinova
 MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the
MIDTERM 3 REVIEW SESSION Dr. Flera Rizatdinova Summary of Chapter 23 Index of refraction: Angle of reflection equals angle of incidence Plane mirror: image is virtual, upright, and the same size as the
1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated. with: Millikan A B. Thomson. Townsend. Plank Compton
 1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated with: A B C D E Millikan Thomson Townsend Plank Compton 1 2 The electron charge was measured the first time in: A B C D E Cathode ray experiment Photoelectric
1 The Cathode Rays experiment is associated with: A B C D E Millikan Thomson Townsend Plank Compton 1 2 The electron charge was measured the first time in: A B C D E Cathode ray experiment Photoelectric
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface
 Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
Physics 3204 UNIT 3 Test Matter Energy Interface 2005 2006 Time: 60 minutes Total Value: 33 Marks Formulae and Constants v = f λ E = hf h f = E k + W 0 E = m c 2 p = h λ 1 A= A T 0 2 t 1 2 E k = ½ mv 2
A) n L < 1.0 B) n L > 1.1 C) n L > 1.3 D) n L < 1.1 E) n L < 1.3
 1. A beam of light passes from air into water. Which is necessarily true? A) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength increases. B) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases. C) The
1. A beam of light passes from air into water. Which is necessarily true? A) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength increases. B) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases. C) The
SECTION A Waves and Sound
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Waves and Optics SECTION A Waves and Sound 1. Which of the following statements about the speed of waves on a string are true? I. The speed depends on the tension in
Quantum and Atomic Physics - Multiple Choice
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
PSI AP Physics 2 Name 1. The Cathode Ray Tube experiment is associated with: (A) J. J. Thomson (B) J. S. Townsend (C) M. Plank (D) A. H. Compton 2. The electron charge was measured the first time in: (A)
PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete
 PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete Written by Jeremy Robinson, Head Instructor Find Out More +Private Instruction +Review Sessions WWW.GRADEPEAK.COM Need Help? Online Private Instruction Anytime, Anywhere
PHYS 4 CONCEPT PACKET Complete Written by Jeremy Robinson, Head Instructor Find Out More +Private Instruction +Review Sessions WWW.GRADEPEAK.COM Need Help? Online Private Instruction Anytime, Anywhere
Cumulative Review 1 Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 Cumulative Review 1 Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. At what distance from the mirror is the image located? a. 0.10 m b. 0.20 m c. 0.30 m d. 0.40 m 2. At what distance
Cumulative Review 1 Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. At what distance from the mirror is the image located? a. 0.10 m b. 0.20 m c. 0.30 m d. 0.40 m 2. At what distance
Physics 126 Practice Exam #4 Professor Siegel
 Physics 126 Practice Exam #4 Professor Siegel Name: Lab Day: 1. Light is usually thought of as wave-like in nature and electrons as particle-like. In which one of the following instances does light behave
Physics 126 Practice Exam #4 Professor Siegel Name: Lab Day: 1. Light is usually thought of as wave-like in nature and electrons as particle-like. In which one of the following instances does light behave
Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: AP REVIEW 3 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. For a mass hanging from a spring, the maximum displacement the
Name: Class: Date: AP REVIEW 3 Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. For a mass hanging from a spring, the maximum displacement the
The Final Exam (Exam 4) will be on FRIDAY MAY 11 From 3 5 PM in LR1 VAN
 1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29:006 SPRING 2012 PRACTICE EXAM 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29:006 SPRING 2012 PRACTICE EXAM 4 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
= : K A
 Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Atoms and Nuclei. State two limitations of JJ Thomson s model of atom. 2. Write the SI unit for activity of a radioactive substance. 3. What observations led JJ Thomson to conclusion that all atoms have
Exam 2 Development of Quantum Mechanics
 PHYS420 (Spring 2002) Riq Parra Exam #2 (Friday, April 12 th, 2002) Exam 2 Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner
PHYS420 (Spring 2002) Riq Parra Exam #2 (Friday, April 12 th, 2002) Exam 2 Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner
Exam 2 Development of Quantum Mechanics
 PHYS40 (Spring 00) Riq Parra Exam # (Friday, April 1 th, 00) Exam Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner of each problem
PHYS40 (Spring 00) Riq Parra Exam # (Friday, April 1 th, 00) Exam Development of Quantum Mechanics Do NOT write your name on this exam. Write your class ID number on the top right hand corner of each problem
Slide 1 / 57. Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems
 Slide 1 / 57 Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems Slide 2 / 57 Multiple Choice Slide 3 / 57 1 The atomic nucleus consists of: A B C D E Electrons Protons Protons and electrons Protons
Slide 1 / 57 Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems Slide 2 / 57 Multiple Choice Slide 3 / 57 1 The atomic nucleus consists of: A B C D E Electrons Protons Protons and electrons Protons
Topic 7 &13 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics
 Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
Name: Date:. Isotopes provide evidence for the existence of A. protons. B. electrons. C. nuclei. Topic 7 &3 Review Atomic, Nuclear, and Quantum Physics D. neutrons.. The atomic line spectra of elements
THE NATURE OF THE ATOM. alpha particle source
 chapter THE NATURE OF THE ATOM www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom 1. Which model of atomic structure
chapter THE NATURE OF THE ATOM www.tutor-homework.com (for tutoring, homework help, or help with online classes) Section 30.1 Rutherford Scattering and the Nuclear Atom 1. Which model of atomic structure
A) m B) m C) m D) m E) m. 5. Which one of the following circuits has the largest resistance?
 Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges would yield
Use the following to answer question 1. Two point charges, A and B, lie along a line separated by a distance L. The point x is the midpoint of their separation. 1. Which combination of charges would yield
Multiple Choice Questions
 Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems PSI AP Physics B 1. The atomic nucleus consists of: (A) Electrons (B) Protons (C)Protons and electrons (D) Protons and neutrons (E) Neutrons and electrons
Nuclear Physics & Nuclear Reactions Practice Problems PSI AP Physics B 1. The atomic nucleus consists of: (A) Electrons (B) Protons (C)Protons and electrons (D) Protons and neutrons (E) Neutrons and electrons
Planck s Quantum Hypothesis Blackbody Radiation
 Planck s Quantum Hypothesis Blackbody Radiation The spectrum of blackbody radiation has been measured(next slide); it is found that the frequency of peak intensity increases linearly with temperature.
Planck s Quantum Hypothesis Blackbody Radiation The spectrum of blackbody radiation has been measured(next slide); it is found that the frequency of peak intensity increases linearly with temperature.
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Planck s Quantum Hypothesis; Blackbody Radiation Photon Theory of Light and the Photoelectric Effect Energy, Mass, and Momentum of a Photon Compton
WAVES AND PARTICLES. (c)
 WAVES AND PARTICLES 1. An electron and a proton are accelerated through the same potential difference. The ration of their De Broglie wave length will be -- (a) (b) (c) (d) 1 2. What potential must be
WAVES AND PARTICLES 1. An electron and a proton are accelerated through the same potential difference. The ration of their De Broglie wave length will be -- (a) (b) (c) (d) 1 2. What potential must be
Mock Examination Physics 2 nd Book Time 3 Hrs MM : 70
 Mock Examination Physics 2 nd Book Time 3 Hrs MM : 70 SECTION A 1. How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, If the incident violet light is replaced with red light? 2. What is principle
Mock Examination Physics 2 nd Book Time 3 Hrs MM : 70 SECTION A 1. How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, If the incident violet light is replaced with red light? 2. What is principle
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
NJCTL.org 2015 AP Physics 2 Nuclear Physics
 AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
AP Physics 2 Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
Bannerman High School Physics Department. Making Accurate Statements. Higher Physics. Quanta and Waves
 Bannerman High School Physics Department Making Accurate Statements Higher Physics Quanta and Waves Mandatory Key Area: Particle Physics 1. Use your knowledge of physics to estimate the ratio of the smallest
Bannerman High School Physics Department Making Accurate Statements Higher Physics Quanta and Waves Mandatory Key Area: Particle Physics 1. Use your knowledge of physics to estimate the ratio of the smallest
The wavefunction ψ for an electron confined to move within a box of linear size L = m, is a standing wave as shown.
 1. This question is about quantum aspects of the electron. The wavefunction ψ for an electron confined to move within a box of linear size L = 1.0 10 10 m, is a standing wave as shown. State what is meant
1. This question is about quantum aspects of the electron. The wavefunction ψ for an electron confined to move within a box of linear size L = 1.0 10 10 m, is a standing wave as shown. State what is meant
CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 94 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 94 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 7 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
T7-1 [255 marks] The graph shows the relationship between binding energy per nucleon and nucleon number. In which region are nuclei most stable?
![T7-1 [255 marks] The graph shows the relationship between binding energy per nucleon and nucleon number. In which region are nuclei most stable? T7-1 [255 marks] The graph shows the relationship between binding energy per nucleon and nucleon number. In which region are nuclei most stable?](/thumbs/77/75398334.jpg) T7-1 [255 marks] 1. In the Geiger Marsden experiment alpha particles were directed at a thin gold foil. Which of the following shows how the majority of the alpha particles behaved after reaching the foil?
T7-1 [255 marks] 1. In the Geiger Marsden experiment alpha particles were directed at a thin gold foil. Which of the following shows how the majority of the alpha particles behaved after reaching the foil?
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero?
 1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
Rb, which had been compressed to a density of 1013
 Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Modern Physics Study Questions for the Spring 2018 Departmental Exam December 3, 2017 1. An electron is initially at rest in a uniform electric field E in the negative y direction and a uniform magnetic
Absorber Alpha emission Alpha particle Atom. Atomic line spectra Atomic mass unit Atomic number Atomic structure. Background radiation
 Material that prevent radioactive emission from passing through it Release of alpha particle from unstable nucleus(a 2+ helium ion or a helium nucleus) The nucleus of a helium atom (two protons and two
Material that prevent radioactive emission from passing through it Release of alpha particle from unstable nucleus(a 2+ helium ion or a helium nucleus) The nucleus of a helium atom (two protons and two
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI
 UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
UNIT VIII ATOMS AND NUCLEI Weightage Marks : 06 Alpha-particles scattering experiment, Rutherford s model of atom, Bohr Model, energy levels, Hydrogen spectrum. Composition and size of Nucleus, atomic
1. What is the minimum energy required to excite a mercury atom initially in the ground state? ev ev ev
 Page 1 of 10 modern bank Name 25-MAY-05 1. What is the minimum energy required to excite a mercury atom initially in the ground state? 1. 4.64 ev 3. 10.20 ev 2. 5.74 ev 4. 10.38 ev 2. The diagram represents
Page 1 of 10 modern bank Name 25-MAY-05 1. What is the minimum energy required to excite a mercury atom initially in the ground state? 1. 4.64 ev 3. 10.20 ev 2. 5.74 ev 4. 10.38 ev 2. The diagram represents
1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of
 1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of 1 1 (A) 2 (B) 2 (C) 1 (D) 2 (E) 2 2. A railroad flatcar of mass 2,000 kilograms rolls
1. If the mass of a simple pendulum is doubled but its length remains constant, its period is multiplied by a factor of 1 1 (A) 2 (B) 2 (C) 1 (D) 2 (E) 2 2. A railroad flatcar of mass 2,000 kilograms rolls
Unit 6 Modern Physics
 Unit 6 Modern Physics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 6 Hwk. Pts.: / 46 Unit 6 Lab Pts.: / 16 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Essential Fundamentals of Modern Physics 1. A photon s energy
Unit 6 Modern Physics Early Booklet E.C.: + 1 Unit 6 Hwk. Pts.: / 46 Unit 6 Lab Pts.: / 16 Late, Incomplete, No Work, No Units Fees? Y / N Essential Fundamentals of Modern Physics 1. A photon s energy
FALL 2004 Final Exam, Part A
 Physics 152 FALL 2004 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 23 pts. possible Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use a calculator and both sides of 2 sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
Physics 152 FALL 2004 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: 23 pts. possible Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use a calculator and both sides of 2 sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
Physics 6C. Final Practice Solutions. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 6C Final Practice Solutions Use the following information for problems 1 and. A beam of white light with frequency between 4.00 x 10 14 Hz and 7.90 x 10 14 Hz is incident on a sodium surface, which
Physics 6C Final Practice Solutions Use the following information for problems 1 and. A beam of white light with frequency between 4.00 x 10 14 Hz and 7.90 x 10 14 Hz is incident on a sodium surface, which
Chapter 22 Quantum Mechanics & Atomic Structure 22.1 Photon Theory of Light and The Photoelectric Effect Homework # 170
 22.1 Photon Theory of Light and The Photoelectric Effect Homework # 170 See Homework #95 in "Chapter 12-Electrostatics" for the table of "Useful nformation" on atomic particles. 01. What is the energy
22.1 Photon Theory of Light and The Photoelectric Effect Homework # 170 See Homework #95 in "Chapter 12-Electrostatics" for the table of "Useful nformation" on atomic particles. 01. What is the energy
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Discovery and Properties of the electron
 Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions
 Slide 1 / 33 Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions The Nucleus Slide 2 / 33 Proton: The charge on a proton is +1.6x10-19 C. The mass of a proton is 1.6726x10-27 kg. Neutron: The neutron is neutral. The
Slide 1 / 33 Nuclear Physics and Nuclear Reactions The Nucleus Slide 2 / 33 Proton: The charge on a proton is +1.6x10-19 C. The mass of a proton is 1.6726x10-27 kg. Neutron: The neutron is neutral. The
ATOMIC WORLD P.1. ejected photoelectrons. current amplifier. photomultiplier tube (PMT)
 ATOMIC WORLD P. HKAL PAPER I 0 8 The metal Caesium has a work function of.08 ev. Given: Planck constant h = 6.63 0 34 J s, charge of an electron e =.60 0 9 C (a) (i) Calculate the longest wavelength of
ATOMIC WORLD P. HKAL PAPER I 0 8 The metal Caesium has a work function of.08 ev. Given: Planck constant h = 6.63 0 34 J s, charge of an electron e =.60 0 9 C (a) (i) Calculate the longest wavelength of
Energy levels and atomic structures lectures chapter one
 Structure of Atom An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are
Structure of Atom An atom is the smallest constituent unit of ordinary matter that has the properties of a element. Every solid, liquid, gas, and plasma is composed of neutral or ionized atoms. Atoms are
Bi β + Po Bismuth-214 is radioactive. It has a half-life of 20 minutes. (a) The nuclide notation for bismuth-214 is Bi.
 1 Bismuth-214 is radioactive. It has a half-life of 20 minutes. (a) The nuclide notation for bismuth-214 is Bi. State the composition of the nucleus of bismuth-214. [2] (b) Bismuth-214 decays by β-decay
1 Bismuth-214 is radioactive. It has a half-life of 20 minutes. (a) The nuclide notation for bismuth-214 is Bi. State the composition of the nucleus of bismuth-214. [2] (b) Bismuth-214 decays by β-decay
Modern Physics CHAPTER THE DUAL NATURE OF LIGHT. Two Models of Light
 CHAPTER 5 Modern Physics THE DUAL NATURE OF LIGHT Two Models of Light In the mid 1800s, scientists were convinced that the age-old question, What is light? had been answered conclusively. Light, they said,
CHAPTER 5 Modern Physics THE DUAL NATURE OF LIGHT Two Models of Light In the mid 1800s, scientists were convinced that the age-old question, What is light? had been answered conclusively. Light, they said,
Exam 4--PHYS 151--Spring 2017
 Name: Exam 4--PHYS 151--Spring 2017 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Electromagnetic radiation is caused by a. electricity b. radioactive
Name: Exam 4--PHYS 151--Spring 2017 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Electromagnetic radiation is caused by a. electricity b. radioactive
1. This question is about the Rutherford model of the atom.
 1. This question is about the Rutherford model of the atom. (a) Most alpha particles used to bombard a thin gold foil pass through the foil without a significant change in direction. A few alpha particles
1. This question is about the Rutherford model of the atom. (a) Most alpha particles used to bombard a thin gold foil pass through the foil without a significant change in direction. A few alpha particles
Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, Your Name: Questions
 Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, 1993 Your Name: Questions 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18.
Physics 107 Final Exam December 13, 1993 Your Name: Questions 1. 11. 21. 31. 41. 2. 12. 22. 32. 42. 3. 13. 23. 33. 43. 4. 14. 24. 34. 44. 5. 15. 25. 35. 45. 6. 16. 26. 36. 46. 7. 17. 27. 37. 47. 8. 18.
2. The figure shows the path of a portion of a ray of light as it passes through three different materials. Note: The figure is drawn to scale.
 1. The bending of light as it moves from one medium to another with differing indices of refraction is due to a change in what property of the light? A) amplitude B) period C) frequency D) speed E) color
1. The bending of light as it moves from one medium to another with differing indices of refraction is due to a change in what property of the light? A) amplitude B) period C) frequency D) speed E) color
YOUR NAME Sample Final Physics 1404 (Dr. Huang)), Correct answers are underlined.
 YOUR NAME Sample Final Physics 1404 (Dr. Huang)), Correct answers are underlined. Useful constants: e=1.6 10-19 C, m e =9.1 10-31 kg, m p =1.67 10-27 kg, ε 0 =8.85 10-12 C 2 /N m 2, c=3 10 8 m/s k e =8.99
YOUR NAME Sample Final Physics 1404 (Dr. Huang)), Correct answers are underlined. Useful constants: e=1.6 10-19 C, m e =9.1 10-31 kg, m p =1.67 10-27 kg, ε 0 =8.85 10-12 C 2 /N m 2, c=3 10 8 m/s k e =8.99
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation
 The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS
 CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
CHARGED PARTICLE INTERACTIONS Background Charged Particles Heavy charged particles Charged particles with Mass > m e α, proton, deuteron, heavy ion (e.g., C +, Fe + ), fission fragment, muon, etc. α is
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY
 PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
PHYSICS A2 UNIT 2 SECTION 1: RADIOACTIVITY & NUCLEAR ENERGY THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS / NUCLEAR RADIUS & DENSITY / PROPERTIES OF NUCLEAR RADIATION / INTENSITY & BACKGROUND RADIATION / EXPONENTIAL LAW OF DECAY
General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18
 95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter)
 Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
Al-Mustansiriyah University College of Science Physics Department Fourth Grade Nuclear Physics Dr. Ali A. Ridha Chapter Four (Interaction of Radiation with Matter) Different types of radiation interact
CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 76 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 76 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 12 TEST REVIEW 1. An alpha particle is accelerated through a potential difference of 10 kv.
Chapter 22 - Nuclear Chemistry
 Chapter - Nuclear Chemistry - The Nucleus I. Introduction A. Nucleons. Neutrons and protons B. Nuclides. Atoms identified by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 8 a. radium-8 or 88 Ra II.
Chapter - Nuclear Chemistry - The Nucleus I. Introduction A. Nucleons. Neutrons and protons B. Nuclides. Atoms identified by the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus 8 a. radium-8 or 88 Ra II.
D) g. 2. In which pair do the particles have approximately the same mass?
 1. A student constructs a model for comparing the masses of subatomic particles. The student selects a small, metal sphere with a mass of gram to represent an electron. A sphere with which mass would be
1. A student constructs a model for comparing the masses of subatomic particles. The student selects a small, metal sphere with a mass of gram to represent an electron. A sphere with which mass would be
PHYSICS. Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter
 PHYSICS Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter (The first 15 minutes of the examination are for reading the paper only. Candidates must NOT start writing during this time). -------------------------------------------------------------------
PHYSICS Paper 1 (THEORY) Three hours and a quarter (The first 15 minutes of the examination are for reading the paper only. Candidates must NOT start writing during this time). -------------------------------------------------------------------
10. A Kelvin thermometer and a Fahrenheit thermometer both give the same reading for a certain sample. The corresponding Celsius temperature is: A)
 Physics 223 practice final exam, Form X!! Fall 2017 Name Write your answers (one per question) on a Scantron form (882E) using a pencil. Write your name above. Return this exam with your scantron upon
Physics 223 practice final exam, Form X!! Fall 2017 Name Write your answers (one per question) on a Scantron form (882E) using a pencil. Write your name above. Return this exam with your scantron upon
PSI AP Physics How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge?
 PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
PSI AP Physics 2 Name Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently named
3 Radioactivity - Spontaneous Nuclear Processes
 3 Radioactivity - Spontaneous Nuclear Processes Becquerel was the first to detect radioactivity. In 1896 he was carrying out experiments with fluorescent salts (which contained uranium) and found that
3 Radioactivity - Spontaneous Nuclear Processes Becquerel was the first to detect radioactivity. In 1896 he was carrying out experiments with fluorescent salts (which contained uranium) and found that
Modern Physics, Waves, Electricity
 Name: Date: 1. Metal sphere has a charge of +12 elementary charges and identical sphere has a charge of +16 elementary charges. fter the two spheres are brought into contact, the charge on sphere is 4.
Name: Date: 1. Metal sphere has a charge of +12 elementary charges and identical sphere has a charge of +16 elementary charges. fter the two spheres are brought into contact, the charge on sphere is 4.
At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type of radiation.
 RADIOACTIVITY - SPONTANEOUS NUCLEAR PROCESSES OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: 1. For~, p and 7 decays a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type
RADIOACTIVITY - SPONTANEOUS NUCLEAR PROCESSES OBJECTIVES At the conclusion of this lesson the trainee will be able to: 1. For~, p and 7 decays a) Write a typical equation for the production of each type
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
Chapter Modern Physics
 121 Chapter Modern Physics 1. Diameter of a plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is 3 mm. If speed of light in material of lens is 2 10 8 m/s, the focal length of the lens is [2013] 15
121 Chapter Modern Physics 1. Diameter of a plano-convex lens is 6 cm and thickness at the centre is 3 mm. If speed of light in material of lens is 2 10 8 m/s, the focal length of the lens is [2013] 15
5.At what speed is a particle traveling if its kinetic energy is three times its rest energy? A) 0.879c B) 0.918c C) 0.943c D) 0.
 1.Two identical light waves, A and B, are emitted from different sources and meet at a point P. The distance from the source of A to the point P is L A ; and the source of B is a distance L B from P. Which
1.Two identical light waves, A and B, are emitted from different sources and meet at a point P. The distance from the source of A to the point P is L A ; and the source of B is a distance L B from P. Which
Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions. 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge?
 Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently
Quantum Physics and Atomic Models Chapter Questions 1. How was it determined that cathode rays possessed a negative charge? 2. J. J. Thomson found that cathode rays were really particles, which were subsequently
Higher Physics. Particles and Waves
 Perth Academy Physics Department Higher Physics Particles and Waves Particles and Waves Homework Standard Model 1 Electric Fields and Potential Difference 2 Radioactivity 3 Fusion & Fission 4 The Photoelectric
Perth Academy Physics Department Higher Physics Particles and Waves Particles and Waves Homework Standard Model 1 Electric Fields and Potential Difference 2 Radioactivity 3 Fusion & Fission 4 The Photoelectric
Final Exam, Part A. December 12, Score:
 Physics 152 December 12, 2005 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use a calculator and both sides of TWO sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
Physics 152 December 12, 2005 Final Exam, Part A Roster No.: Score: Exam time limit: 2 hours. You may use a calculator and both sides of TWO sheets of notes, handwritten only. Closed book; no collaboration.
Nuclear Physics Questions. 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of?
 Nuclear Physics Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
Nuclear Physics Questions 1. What particles make up the nucleus? What is the general term for them? What are those particles composed of? 2. What is the definition of the atomic number? What is its symbol?
5 Atomic Physics. 1 of the isotope remains. 1 minute, 4. Atomic Physics. 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom
 5 Atomic Physics 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom 1. In a fission reactor, which particle causes a Uranium-235 nucleus to split? A. alpha-particle B. gamma ray C. neutron D. proton 2. A radioactive
5 Atomic Physics 1. Radioactivity 2. The nuclear atom 1. In a fission reactor, which particle causes a Uranium-235 nucleus to split? A. alpha-particle B. gamma ray C. neutron D. proton 2. A radioactive
filled with water of refractive index 4/3. The water between them forms a thin equi-concave lens. Find the focal length of the combination of glass an
 LIKELY PROBLEMS IN PHYSICS FOR II PUC 1. A ray of light is incident at an angle of 30 0 on one side of a glass slab of thickness 0.05 m. The lateral shift of the ray on passing through the slab is 0.01
LIKELY PROBLEMS IN PHYSICS FOR II PUC 1. A ray of light is incident at an angle of 30 0 on one side of a glass slab of thickness 0.05 m. The lateral shift of the ray on passing through the slab is 0.01
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016
 Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
Physics 11 Exam 3 Spring 2016 Name: Circle the BEST Answer 1 Electromagnetic waves consist of A) compressions and rarefactions of electromagnetic pulses. B) oscillating electric and magnetic fields. C)
A graph of intensity of light incident on photo paper.
 1. What is the best model of light to explain the shape of the wave fronts beyond the opening? a) Light is a wave and every point on a wave front of light can be treated as a point source. b) Rays of light
1. What is the best model of light to explain the shape of the wave fronts beyond the opening? a) Light is a wave and every point on a wave front of light can be treated as a point source. b) Rays of light
Unified School District of De Pere Physics Benchmarks
 Content Standards: A. Students will understand that among the science disciplines, there are unifying themes: systems, order, organization, and interactions; evidence, models, and explanations; constancy,
Content Standards: A. Students will understand that among the science disciplines, there are unifying themes: systems, order, organization, and interactions; evidence, models, and explanations; constancy,
Radioactivity. (b) Fig shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1
 112 (a) What is meant by radioactive decay? Radioactivity [2] (b) Fig. 12.1 shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1 Put a tick alongside any of the
112 (a) What is meant by radioactive decay? Radioactivity [2] (b) Fig. 12.1 shows two samples of the same radioactive substance. The substance emits β-particles. Fig. 12.1 Put a tick alongside any of the
 CHAPTER 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. A protonis a positively charged particle having mass 1.6726 x 10(-27) kg and charge 1.6 x 10(-19) coulomb.
CHAPTER 19 THE ATOMIC NUCLEUS NUCLEAR STRUCTURE The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. A protonis a positively charged particle having mass 1.6726 x 10(-27) kg and charge 1.6 x 10(-19) coulomb.
UGC ACADEMY LEADING INSTITUE FOR CSIR-JRF/NET, GATE & JAM PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEST SERIES # 4. Atomic, Solid State & Nuclear + Particle
 UGC ACADEMY LEADING INSTITUE FOR CSIR-JRF/NET, GATE & JAM BOOKLET CODE PH PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEST SERIES # 4 Atomic, Solid State & Nuclear + Particle SUBJECT CODE 05 Timing: 3: H M.M: 200 Instructions 1.
UGC ACADEMY LEADING INSTITUE FOR CSIR-JRF/NET, GATE & JAM BOOKLET CODE PH PHYSICAL SCIENCE TEST SERIES # 4 Atomic, Solid State & Nuclear + Particle SUBJECT CODE 05 Timing: 3: H M.M: 200 Instructions 1.
Preview. Atomic Physics Section 1. Section 1 Quantization of Energy. Section 2 Models of the Atom. Section 3 Quantum Mechanics
 Atomic Physics Section 1 Preview Section 1 Quantization of Energy Section 2 Models of the Atom Section 3 Quantum Mechanics Atomic Physics Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 8A describe the photoelectric
Atomic Physics Section 1 Preview Section 1 Quantization of Energy Section 2 Models of the Atom Section 3 Quantum Mechanics Atomic Physics Section 1 TEKS The student is expected to: 8A describe the photoelectric
Atomic Theory. Contribution to Modern Atomic Theory
 Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
Alief High School Chemistry STAAR Review Reporting Category 2: Atomic Structure and Nuclear Chemistry C.6.A Understand the experimental design and conclusions used in the development of modern atomic theory,
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS. Atoms. 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model. 6. Hydrogen spectrum
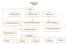 CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
Unit 1 Atomic Structure
 Unit 1 Atomic Structure 3-1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the
Unit 1 Atomic Structure 3-1 The Atom: From Philosophical Idea to Scientific Theory I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
Chapter 37 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Units of Chapter 37 37-7 Wave Nature of Matter 37-8 Electron Microscopes 37-9 Early Models of the Atom 37-10 Atomic Spectra: Key to the Structure
AISSCE 2016 EXPECTED (SURE SHORT) QUESTIONS WEIGHTAGE-WISE 2016
 CLASS: XII AISSCE 2016 Subject: Physics EXPECTED (SURE SHORT) QUESTIONS WEIGHTAGE-WISE 2016 Q3 Section A ( 1 Mark ) A force F is acting between two charges placed some distances apart in vacuum. If a brass
CLASS: XII AISSCE 2016 Subject: Physics EXPECTED (SURE SHORT) QUESTIONS WEIGHTAGE-WISE 2016 Q3 Section A ( 1 Mark ) A force F is acting between two charges placed some distances apart in vacuum. If a brass
Nuclear Chemistry Notes
 Nuclear Chemistry Notes Definitions Nucleons: Subatomic particles in the nucleus : protons and neutrons Radionuclides: Radioactive nuclei. Unstable nuclei that spontaneously emit particles and electromagnetic
Nuclear Chemistry Notes Definitions Nucleons: Subatomic particles in the nucleus : protons and neutrons Radionuclides: Radioactive nuclei. Unstable nuclei that spontaneously emit particles and electromagnetic
Unit 1 Atomic Structure
 Unit 1 Atomic Structure Defining the Atom I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike 3. Individual
Unit 1 Atomic Structure Defining the Atom I. Atomic Theory A. Modern Atomic Theory 1. All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms 2. Atoms of the same element are chemically alike 3. Individual
Dept. of Physics, MIT Manipal 1
 Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
Chapter 1: Optics 1. In the phenomenon of interference, there is A Annihilation of light energy B Addition of energy C Redistribution energy D Creation of energy 2. Interference fringes are obtained using
PHYSICS 2002 Practice Final - 1
 PHYSICS 2002 Practice Final - 1 Instructions: a. Print your name and student number below, then sign your name as it appears on your LSU I.D. card. b. Print and bubble in your name (LAST NAME FIRST), student
PHYSICS 2002 Practice Final - 1 Instructions: a. Print your name and student number below, then sign your name as it appears on your LSU I.D. card. b. Print and bubble in your name (LAST NAME FIRST), student
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Chapter 4 Atomic and nuclear physics INTRODUCTION: The technologies used in nuclear medicine for diagnostic imaging have evolved over the last century, starting with Röntgen s discovery of X rays and Becquerel
Chapter 4 Atomic and nuclear physics INTRODUCTION: The technologies used in nuclear medicine for diagnostic imaging have evolved over the last century, starting with Röntgen s discovery of X rays and Becquerel
Chapter 44. Nuclear Structure
 Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
Chapter 44 Nuclear Structure Milestones in the Development of Nuclear Physics 1896: the birth of nuclear physics Becquerel discovered radioactivity in uranium compounds Rutherford showed the radiation
Selected "Phacts" for the Physics Regents Exam You Should Know
 Selected "Phacts" for the Physics Regents Exam You Should Know I. Mechanics Study Hard! 1. Mass and inertia are the same thing. (Mass actually measures inertia in kilograms Much as monetary resources measures
Selected "Phacts" for the Physics Regents Exam You Should Know I. Mechanics Study Hard! 1. Mass and inertia are the same thing. (Mass actually measures inertia in kilograms Much as monetary resources measures
Physics 30 Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Worksheet 1: Velocity of EMR 1) Why did Galileo's attempt to measure speed of light fail? 2) How did Huygens measure distance and time when he used Roemer's data to compute the speed of light? 3) If in
Worksheet 1: Velocity of EMR 1) Why did Galileo's attempt to measure speed of light fail? 2) How did Huygens measure distance and time when he used Roemer's data to compute the speed of light? 3) If in
Units and Definition
 RADIATION SOURCES Units and Definition Activity (Radioactivity) Definition Activity: Rate of decay (transformation or disintegration) is described by its activity Activity = number of atoms that decay
RADIATION SOURCES Units and Definition Activity (Radioactivity) Definition Activity: Rate of decay (transformation or disintegration) is described by its activity Activity = number of atoms that decay
Thursday, April 23, 15. Nuclear Physics
 Nuclear Physics Some Properties of Nuclei! All nuclei are composed of protons and neutrons! Exception is ordinary hydrogen with just a proton! The atomic number, Z, equals the number of protons in the
Nuclear Physics Some Properties of Nuclei! All nuclei are composed of protons and neutrons! Exception is ordinary hydrogen with just a proton! The atomic number, Z, equals the number of protons in the
THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION PHYSICS (Theory)
 CLASS:XII Marks : 70 General Instructions: THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2016-17 PHYSICS (Theory) Time : Hrs (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This
CLASS:XII Marks : 70 General Instructions: THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2016-17 PHYSICS (Theory) Time : Hrs (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) All questions are compulsory. This
Physics 1302, Exam 4 Review
 c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1302, Exam 4 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
c V Andersen, 2006 1 Physics 1302, Exam 4 Review The following is a list of things you should definitely know for the exam, however, the list is not exhaustive. You are responsible for all the material
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In the equation E = hf, the f stands for 1) A) the smaller wavelengths of visible light. B) wave
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) In the equation E = hf, the f stands for 1) A) the smaller wavelengths of visible light. B) wave
