Numerical Simulations of the Jet in the Crab Nebula
|
|
|
- Abraham O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Numerical Simulations of the Jet in the Crab Nebula A. Mignone 1, A. Ferrari 1, E. Striani 2, M. Tavani 2 1 Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Torino 2 Iasf/iaps università di tor vergata (roma)
2 1. Observational Evidence 2. Numerical Models of Relativistic MHD jets 3. Results 4. Summary
3 X-ray observation (Chandra) show the emergence of a bipolar jets and extending to the SE and NEW of the pulsar; NE jet A region of diffuse emission (Anvil) may be associated with shocks and marks the base of the X-ray and optical jet; SE jet Knots of emission are seen along the jets; In the SE jet material flows with v/c 0.4 slowing down to 0.02 into the nebula;
4 SE jet morphology is S shaped and show remarkable time variability: evidence for some kind of flow instability (Current Driven?)
5 Jet forms downstream of the wind termination shock; Magnetic fields confine matter towards polar axis; tooth-paste effect: hoop stress of the azimuthal magnetic field carried by the wind (Lyubarsky 2002). Credit: S. Komissarov Models confirmed by 2D axisymmetric numerical simulations (Komissarov & Lyubarski 2003,2004, Del Zanna et al. 2004, Bogovalov et al. 2005)
6 For moderate/large = B 2 /(8 c 2 2 ) magnetic hoop stress suppresses high velocity outflows in the equatorial plane and divert them towards the polar axis partially driving the super-fast jet 1 1 Del Zanna et al, A&A (2004) 421,1063
7 Initial conditions from Del Zanna et al. (2004). Inside 0.2 < r < 1 (ly): freely expanding supernova ejecta (3 M sun, E = erg) Jet enters at the lower z boundary; Pulsar wind structure not considered: jet already formed as the result of the collimation process; Jet radius R j = cm Computational domain: x,y [-25,25] R j /c, z [0, 80] R j /c; ( ly).
8 Jet flow modeled by 5 parameters: 1. Sonic flow Mach number: M s = v j /c s 2. Bulk Lorentz factor: j = (1-v 2 j) -1/2 3. Jet/ambient dens. contrast: = j / e 4. Magnetization: = B 2 /(8 2 ); 5. Pitch angle: P = RB z /B
9 Parameters are constrained by 2D axisymmetric results 1.3 Ms 2 hot jet 2 4 =? Density contrast 10-6 Azimuthal field implies Pitch 0 (Bz = 0) This leaves and as free parameters. We consider hollow ( =10-6 ), hot (M s = 1.7) jets initially carrying purely axial current (B 0, B z = B R = 0). p(r) and B (R) set by radial momentum balance across the jet
10 We solve the equations for a relativistic perfectly conducting fluid describing energy/momentum and particle conservation (relativistic MHD equations) We use the PLUTO 1,2 code for astrophysical fluid dynamics (freely distributed Numerical resolution 320 x 320 x 768 zones ( 20 point on the jet)
11 We explore different values of Lorentz factor (= 2, 4) and magnetization (= 0.1, 1, 10) for a total of 6 different cases: Case Plasma A A A B B B
12 Case A A2 2 1 A B B2 4 1 B Sigma distribution
13 Case A A2 2 1 A B B2 4 1 B Pressure distribution
14 Case A A2 2 1 A B B2 4 1 B Sigma distribution
15 Case A A2 2 1 A B B2 4 1 B Sigma distribution
16 Jets have small propagation speed (0.02c 0.08c); Large over-pressurized turbulent cocoons; Collimated central spines moving at mildly relativistic speeds; Cocoon less magnetized than central spine; Large-scale deflections may be present.
17 3D models very different from 2D counterparts 1 : 3D 2D Strong toroidal configurations expected to become unstable to current driven modes. Most unstable mode m=1 (kink); Jet develops non-axisymmetric structures with large time-dependent deflections off the longitudinal axis; Deflection time-scale of the order of a few years; 1 Mignone et al. MNRAS (2010), 402, 7
18 Wiggling and deflection more pronounced at the terminal bow shock where magnetic field is amplified: Case A, t = 400 (R/c) Case C, t = 870 (R/c) =2, =1, t=140 yrs =4, =1, t=50 yrs
19 Jets are slow because of large density contrast ( j / e < 10-6 ); Faster jets reach the outer edge of the expanding nebula.
20 Deflection is quantified using the baricenter:
21 Case A2 and A3 (low-speed, moderately/highly magnetized) jets show the largest bending ( > 20 jet radii); Larger Lorentz factors (B2, B3) have a stabilizing effect; Weakly magnetized jets (A1, B1) are less affected by the growth of instability;
22 Flow direction is measured by computing the average angle of the mass flux vector with vertical direction:
23 Low-speed jets assume a large-scale curved structure; High-speed jets more parallel and build kicks in proximity of the jet head;
24 Magnetic field topology remains mainly toroidal or helical during the propagation; Azimuthal field has the effect of shielding the core preventing interaction with the surrounding. Magnetic field dissipates and becomes turbulent in the cocoon ( randomization)
25 3D models of azimuthally confined relativistic jets are very different from 2D axisymmetric models: Kink-unstable non-axisymmetric structures with large time-variability; Large ( 1 ) leads to considerable jet deflections; Pronounced asymmetric backflows; Jet wiggling progressively more pronounced towards the jet head Multiple strong shocks are formed by change of direction; Low-speed ( 2), moderately/highly magnetized jets ( 1-10) are promising candidates for explaining the morphology of the Crab jet. Future models will consider the jet-torus connection in 3D
26 Thank you
Morphologies of extragalactic jets
 MOMENTUM TRANSPORT IN TURBULENT HYDRO JETS AND EXTRAGALACTIC SOURCES MORPHOLOGY Attilio Ferrari University of Torino University of Chicago JETSET - CMSO with G. Bodo, S. Massaglia, A. Mignone, P. Rossi
MOMENTUM TRANSPORT IN TURBULENT HYDRO JETS AND EXTRAGALACTIC SOURCES MORPHOLOGY Attilio Ferrari University of Torino University of Chicago JETSET - CMSO with G. Bodo, S. Massaglia, A. Mignone, P. Rossi
Attilio Ferrari. CIFS, Università di Torino. 12th Agile Workshop, May 8, 2014
 Attilio Ferrari CIFS, Università di Torino 12th Agile Workshop, May 8, 2014 Plasma processes of astrophysical relevance Highly nonlinear (relativistic) physics Huge extension of physical parameters Scalability?
Attilio Ferrari CIFS, Università di Torino 12th Agile Workshop, May 8, 2014 Plasma processes of astrophysical relevance Highly nonlinear (relativistic) physics Huge extension of physical parameters Scalability?
Approximate Harten-Lax-Van Leer (HLL) Riemann Solvers for Relativistic hydrodynamics and MHD
 Approximate Harten-Lax-Van Leer (HLL) Riemann Solvers for Relativistic hydrodynamics and MHD Andrea Mignone Collaborators: G. Bodo, M. Ugliano Dipartimento di Fisica Generale, Universita di Torino (Italy)
Approximate Harten-Lax-Van Leer (HLL) Riemann Solvers for Relativistic hydrodynamics and MHD Andrea Mignone Collaborators: G. Bodo, M. Ugliano Dipartimento di Fisica Generale, Universita di Torino (Italy)
Instabilities of relativistic jets
 Instabilities of relativistic jets G. Bodo INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino, Italy A. Mignone, P. Rossi, G. Mamatsashvili, S. Massaglia, A. Ferrari show f Universality of relativistic jet phenomenon
Instabilities of relativistic jets G. Bodo INAF Osservatorio Astrofisico di Torino, Italy A. Mignone, P. Rossi, G. Mamatsashvili, S. Massaglia, A. Ferrari show f Universality of relativistic jet phenomenon
Pulsar Winds. John Kirk. Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg, Germany. < > p.1/18
 Pulsar Winds John Kirk Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg, Germany < > p.1/18 About 50 years after... The Crab Nebula Central star is source of particles and magnetic field (Piddington 1957)
Pulsar Winds John Kirk Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg, Germany < > p.1/18 About 50 years after... The Crab Nebula Central star is source of particles and magnetic field (Piddington 1957)
A Detailed Study of. the Pulsar Wind Nebula 3C 58
 A Detailed Study of Collaborators: D. J. Helfand S. S. Murray S. Ransom F. D. Seward B. M. Gaensler E. V. Gotthelf E. van der Swaluw the Pulsar Wind Nebula 3C 58 Pulsar Wind Nebulae Young NS powers a particle/magnetic
A Detailed Study of Collaborators: D. J. Helfand S. S. Murray S. Ransom F. D. Seward B. M. Gaensler E. V. Gotthelf E. van der Swaluw the Pulsar Wind Nebula 3C 58 Pulsar Wind Nebulae Young NS powers a particle/magnetic
Modelling the kinked jet of the Crab nebula
 MNRAS 436, 1102 1115 (2013) Advance Access publication 2013 October 4 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1632 Modelling the kinked jet of the Crab nebula A. Mignone, 1 E. Striani, 2,3,4 M. Tavani 2,3,4 and A. Ferrari
MNRAS 436, 1102 1115 (2013) Advance Access publication 2013 October 4 doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1632 Modelling the kinked jet of the Crab nebula A. Mignone, 1 E. Striani, 2,3,4 M. Tavani 2,3,4 and A. Ferrari
Magnetohydrodynamics of pulsar winds and plerions Yuri Lyubarsky
 Magnetohydrodynamics of pulsar winds and plerions Yuri Lyubarsky Ben-Gurion University, Israel Pulsar magneto sphere e Pulsar wind +, e, (ions?), electro-magnetic fields Pulsar wind nebula j j v B v v
Magnetohydrodynamics of pulsar winds and plerions Yuri Lyubarsky Ben-Gurion University, Israel Pulsar magneto sphere e Pulsar wind +, e, (ions?), electro-magnetic fields Pulsar wind nebula j j v B v v
Crab flares - explosive Reconnection Events in the Nebula
 Crab flares - explosive Reconnection Events in the Nebula Maxim Lyutikov (Purdue) in collaboration with Sergey Komissarov (Leeds) Lorenzo Sironi (Columbia) Oliver Porth (Frankfurt) - ApJ 2017; - JPP, 2017abc
Crab flares - explosive Reconnection Events in the Nebula Maxim Lyutikov (Purdue) in collaboration with Sergey Komissarov (Leeds) Lorenzo Sironi (Columbia) Oliver Porth (Frankfurt) - ApJ 2017; - JPP, 2017abc
Probing Pulsar Winds With X-rays!
 Probing Pulsar Winds With X-rays! Collaborators:! Bryan Gaensler! Steve Reynolds! David Helfand! Stephen Ng! Anne Lemiere! Okkie de Jager! Stephanie LaMassa! Jack Hughes! PWNe and Their SNRs! PWN Shock
Probing Pulsar Winds With X-rays! Collaborators:! Bryan Gaensler! Steve Reynolds! David Helfand! Stephen Ng! Anne Lemiere! Okkie de Jager! Stephanie LaMassa! Jack Hughes! PWNe and Their SNRs! PWN Shock
The origin of peculiar jet-torus structure in the Crab nebula
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, L93 L96 (2003) The origin of peculiar jet-torus structure in the Crab nebula S. S. Komissarov 1 and Y. E. Lyubarsky 2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Leeds,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 344, L93 L96 (2003) The origin of peculiar jet-torus structure in the Crab nebula S. S. Komissarov 1 and Y. E. Lyubarsky 2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics, University of Leeds,
Particle Transport in Young Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 Particle Transport in Young Pulsar Wind Nebulae Xiaping Tang and Roger A. Chevalier University of Virginia August 26, 2012, IAU symposium 291 Tang, Chevalier (UVA) PWN IAU 2012 1 / 12 Schematic view of
Particle Transport in Young Pulsar Wind Nebulae Xiaping Tang and Roger A. Chevalier University of Virginia August 26, 2012, IAU symposium 291 Tang, Chevalier (UVA) PWN IAU 2012 1 / 12 Schematic view of
Explosive reconnection of the double tearing mode in relativistic plasmas
 Explosive reconnection of the double tearing mode in relativistic plasmas Application to the Crab Jérôme Pétri 1 Hubert Baty 1 Makoto Takamoto 2, Seiji Zenitani 3 1 Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg,
Explosive reconnection of the double tearing mode in relativistic plasmas Application to the Crab Jérôme Pétri 1 Hubert Baty 1 Makoto Takamoto 2, Seiji Zenitani 3 1 Observatoire astronomique de Strasbourg,
Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics
 Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) The extreme Universe viewed in very high energy gamma-rays, Kashiwa 09/25/2012 OUTLINE
Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) The extreme Universe viewed in very high energy gamma-rays, Kashiwa 09/25/2012 OUTLINE
The origin of peculiar jet-torus structure in the Crab nebula
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (2003) The origin of peculiar jet-torus structure in the Crab nebula S.S.Komissarov 1, Y.E.Lyubarsky 2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics, the University of Leeds,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (2003) The origin of peculiar jet-torus structure in the Crab nebula S.S.Komissarov 1, Y.E.Lyubarsky 2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics, the University of Leeds,
Crab Pulsar. Chandra Image of the Crab Nebula. Crab is the most famous pulsar, which is studied in detail across the entire energy spectrum
 Crab Pulsar Chandra Image of the Crab Nebula Crab is the most famous pulsar, which is studied in detail across the entire energy spectrum Conventional view on the Crab Pulsar Related Emitting Zones Pulsar(Massaro+)
Crab Pulsar Chandra Image of the Crab Nebula Crab is the most famous pulsar, which is studied in detail across the entire energy spectrum Conventional view on the Crab Pulsar Related Emitting Zones Pulsar(Massaro+)
Magnetically-dominated relativistic jets.
 Magnetically-dominated relativistic jets. Serguei Komissarov University of Leeds UK N.Vlahakis, Y.Granot, A.Konigl, A.Spitkovsky, M.Barkov, J.McKinney, Y.Lyubarsky, M.Lyutikov, N.Bucciantini Plan 1. Astrophysical
Magnetically-dominated relativistic jets. Serguei Komissarov University of Leeds UK N.Vlahakis, Y.Granot, A.Konigl, A.Spitkovsky, M.Barkov, J.McKinney, Y.Lyubarsky, M.Lyutikov, N.Bucciantini Plan 1. Astrophysical
Politecnico di Torino. Porto Institutional Repository
 Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Proceeding] An Investigation of the Hydrodynamics of Hypersonic Jets in Astrophysical Conditions Original Citation: M. Belan; S. Massaglia; M. Mirzaei;
Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Proceeding] An Investigation of the Hydrodynamics of Hypersonic Jets in Astrophysical Conditions Original Citation: M. Belan; S. Massaglia; M. Mirzaei;
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Nov 2007
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Nov 2007 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 7 Nov 2007](/thumbs/87/96348326.jpg) Recent Progress in Studies of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Patrick Slane arxiv:0711.1002v1 [astro-ph] 7 Nov 2007 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. The synchrotron-emitting nebulae formed by
Recent Progress in Studies of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Patrick Slane arxiv:0711.1002v1 [astro-ph] 7 Nov 2007 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Abstract. The synchrotron-emitting nebulae formed by
Jin Matsumoto. Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
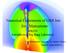 Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN) Schematic Picture of the GRB Jet Meszaros
Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN) Schematic Picture of the GRB Jet Meszaros
Pulsar Wind and pulsar wind nebulae
 Pulsar Wind and pulsar wind nebulae Takata Jumpei 1 Outline S1, Pulsar Wind (PW) and Pulsar Wind Nebula(PWN) around isolate pulsars. -PWN nebula around the Crab pulsar -Formation of PW and PWNe -Kennel
Pulsar Wind and pulsar wind nebulae Takata Jumpei 1 Outline S1, Pulsar Wind (PW) and Pulsar Wind Nebula(PWN) around isolate pulsars. -PWN nebula around the Crab pulsar -Formation of PW and PWNe -Kennel
Pulsar Wind Nebulae. Pennsylvania State University. General outlook Chandra results Polarization in radio and optical X-ray polarization
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae George Pavlov & Oleg Kargaltsev Pennsylvania State University General outlook Chandra results Polarization in radio and optical X-ray polarization Pulsar Wind Nebulae: extended objects
Pulsar Wind Nebulae George Pavlov & Oleg Kargaltsev Pennsylvania State University General outlook Chandra results Polarization in radio and optical X-ray polarization Pulsar Wind Nebulae: extended objects
Pulsar Wind INAF
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae @ INAF Niccolo Bucciantini INAF - Osservatorio di Arcetri INFN - Sezione di Firenze UniFi - Dipartimento di Fisica & Astronomia 1 Pulsar Wind Nebulae PWN PWNe are hot bubbles of relativistic
Pulsar Wind Nebulae @ INAF Niccolo Bucciantini INAF - Osservatorio di Arcetri INFN - Sezione di Firenze UniFi - Dipartimento di Fisica & Astronomia 1 Pulsar Wind Nebulae PWN PWNe are hot bubbles of relativistic
Modeling of Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 Modeling of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Elena Amato INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Collaborators: Jonathan Arons, Niccolo Bucciantini, Luca Del Zanna, Delia Volpi Pulsar Wind Nebulae Why are they interesting
Modeling of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Elena Amato INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri Collaborators: Jonathan Arons, Niccolo Bucciantini, Luca Del Zanna, Delia Volpi Pulsar Wind Nebulae Why are they interesting
Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy
 Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy Jonathan Arons UC Berkeley Cosmic Rays Acceleration in Supernova Remnants Pulsar Wind Nebulae Cosmic rays Cronin, 1999, RMP, 71, S165 J(E) = AE! p, p " 2.7,1GeV < E
Cosmic Pevatrons in the Galaxy Jonathan Arons UC Berkeley Cosmic Rays Acceleration in Supernova Remnants Pulsar Wind Nebulae Cosmic rays Cronin, 1999, RMP, 71, S165 J(E) = AE! p, p " 2.7,1GeV < E
Observational Constraints on Pulsar Wind Theories
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76, 494 c SAIt 2005 Memorie della Observational Constraints on Pulsar Wind Theories J.G. Kirk Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Postfach 10 39 80, 69029 Heidelberg, Germany e-mail:
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76, 494 c SAIt 2005 Memorie della Observational Constraints on Pulsar Wind Theories J.G. Kirk Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Postfach 10 39 80, 69029 Heidelberg, Germany e-mail:
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics
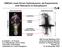 OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
Crazy Crab. M.Tavani. adapted from Gravitation by C.Misner, K.Thorne. J.A.Wheeler
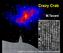 Crazy Crab M.Tavani 1 adapted from Gravitation by C.Misner, K.Thorne. J.A.Wheeler Crab inner Nebula (Chandra) 2 Crab inner Nebula (HST) Anvil Knot-1 Wisps 3 non-symmetric PULSAR wind (relativistic e+/e-,
Crazy Crab M.Tavani 1 adapted from Gravitation by C.Misner, K.Thorne. J.A.Wheeler Crab inner Nebula (Chandra) 2 Crab inner Nebula (HST) Anvil Knot-1 Wisps 3 non-symmetric PULSAR wind (relativistic e+/e-,
AGN jet launch scenarios
 AGN jet launch scenarios Rony Keppens Centre for mathematical Plasma Astrophysics Department of Mathematics, KU Leuven Rony Keppens (KU Leuven) Jet launch Nov. 2013, IAC winter school 1 / 48 Astrophysical
AGN jet launch scenarios Rony Keppens Centre for mathematical Plasma Astrophysics Department of Mathematics, KU Leuven Rony Keppens (KU Leuven) Jet launch Nov. 2013, IAC winter school 1 / 48 Astrophysical
PULSAR WIND NEBULAE AS COSMIC ACCELERATORS. Elena Amato INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri
 PULSAR WIND NEBULAE AS COSMIC ACCELERATORS Elena Amato INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri WHY PWNe ARE INTERESTING! PULSAR PHYSICS: THEY ENCLOSE MOST OF THE PULSAR SPIN- DOWN ENERGY ( L,, L PWN 0.1E
PULSAR WIND NEBULAE AS COSMIC ACCELERATORS Elena Amato INAF-Osservatorio Astrofisico di Arcetri WHY PWNe ARE INTERESTING! PULSAR PHYSICS: THEY ENCLOSE MOST OF THE PULSAR SPIN- DOWN ENERGY ( L,, L PWN 0.1E
The flaring Crab Nebula: Surprises & Challenges
 The flaring Crab Nebula: Surprises & Challenges M.Tavani (INAF & Univ. Rome-2) ESAC Workshop The Fast and the Furious Villafranca, Madrid, May 24, 2013 adapted from Gravitation by C.Misner, K.Thorne. J.A.Wheeler;image
The flaring Crab Nebula: Surprises & Challenges M.Tavani (INAF & Univ. Rome-2) ESAC Workshop The Fast and the Furious Villafranca, Madrid, May 24, 2013 adapted from Gravitation by C.Misner, K.Thorne. J.A.Wheeler;image
Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities
 Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities Mario Manuel Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics October 28 th, 2014 Ø Collimation and
Exploring Astrophysical Magnetohydrodynamics Using High-power Laser Facilities Mario Manuel Einstein Fellows Symposium Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics October 28 th, 2014 Ø Collimation and
Magnetic dissipation in pulsar winds
 Magnetic dissipation in pulsar winds Benoît Cerutti, CNRS & Univ. Grenoble Alpes, France. In collaboration with Sasha Philippov, UC Berkeley, USA. Cerutti & Philippov, A&A (2017) Third Purdue Workshop
Magnetic dissipation in pulsar winds Benoît Cerutti, CNRS & Univ. Grenoble Alpes, France. In collaboration with Sasha Philippov, UC Berkeley, USA. Cerutti & Philippov, A&A (2017) Third Purdue Workshop
Jin Matsumoto. Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
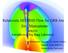 Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN), Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN), Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Simulations of relativistic reconnection in pulsar wind nebulae and pulsar winds
 Simulations of relativistic reconnection in pulsar wind nebulae and pulsar winds Benoît Cerutti Lyman Spitzer Jr. Fellow Princeton University, Dept. of Astrophysical Sciences Collaborators @ Colorado :
Simulations of relativistic reconnection in pulsar wind nebulae and pulsar winds Benoît Cerutti Lyman Spitzer Jr. Fellow Princeton University, Dept. of Astrophysical Sciences Collaborators @ Colorado :
Jet Stability: A computational survey
 Jet Stability Galway 2008-1 Jet Stability: A computational survey Rony Keppens Centre for Plasma-Astrophysics, K.U.Leuven (Belgium) & FOM-Institute for Plasma Physics Rijnhuizen & Astronomical Institute,
Jet Stability Galway 2008-1 Jet Stability: A computational survey Rony Keppens Centre for Plasma-Astrophysics, K.U.Leuven (Belgium) & FOM-Institute for Plasma Physics Rijnhuizen & Astronomical Institute,
High-Energy Neutrinos Produced by Interactions of Relativistic Protons in Shocked Pulsar Winds
 High-Energy Neutrinos Produced by Interactions of Relativistic Protons in Shocked Pulsar Winds S. Nagataki Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Oiwake-cho Kitashirakawa Sakyo-ku,
High-Energy Neutrinos Produced by Interactions of Relativistic Protons in Shocked Pulsar Winds S. Nagataki Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Oiwake-cho Kitashirakawa Sakyo-ku,
Jet Physics: implications for feedback. Robert Laing (ESO)
 Jet Physics: implications for feedback Robert Laing (ESO) Aims Quantify the physics of jets in low-power radio galaxies by fitting 3D models to very deep, high-resolution radio images. Geometry Velocity
Jet Physics: implications for feedback Robert Laing (ESO) Aims Quantify the physics of jets in low-power radio galaxies by fitting 3D models to very deep, high-resolution radio images. Geometry Velocity
Making Faranoff-Riley I radio sources
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 34512AA c ESO 2019 January 8, 2019 Making Faranoff-Riley I radio sources II. The effects of jet magnetization S. Massaglia 1, G. Bodo 2, P. Rossi 2, S. Capetti 2,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 34512AA c ESO 2019 January 8, 2019 Making Faranoff-Riley I radio sources II. The effects of jet magnetization S. Massaglia 1, G. Bodo 2, P. Rossi 2, S. Capetti 2,
Observations of wisps in magnetohydrodynamic simulations of the Crab Nebula
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 September 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Observations of wisps in magnetohydrodynamic simulations of the Crab Nebula N. F. Camus, 1 S. S. Komissarov,
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 2 September 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Observations of wisps in magnetohydrodynamic simulations of the Crab Nebula N. F. Camus, 1 S. S. Komissarov,
Stability of strong waves and its implications for pulsar wind shocks
 Stability of strong waves and its implications for pulsar wind shocks Iwona Mochol in collaboration with John Kirk Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg, Germany Madrid, 22/05/2013 Pulsar winds
Stability of strong waves and its implications for pulsar wind shocks Iwona Mochol in collaboration with John Kirk Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik Heidelberg, Germany Madrid, 22/05/2013 Pulsar winds
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling
 Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
The Crab Nebula: 3-dimensional Modeling
 The Crab Nebula: 3-dimensional Modeling Shinpei SHIBATA, Haruhiko TOMATSURI, Makiko SHIMANUKI, Kazuyuki SAITO, Yuji NAKAMURA, Department of Physics Yamagata University, Yamagata 990-8560, JAPAN, Koji MORI
The Crab Nebula: 3-dimensional Modeling Shinpei SHIBATA, Haruhiko TOMATSURI, Makiko SHIMANUKI, Kazuyuki SAITO, Yuji NAKAMURA, Department of Physics Yamagata University, Yamagata 990-8560, JAPAN, Koji MORI
Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae
 Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae Pulsars Characteristic parameters Pulsar wind nebulae Properties Evolution Exotic central compact objects - Magnetars The Crab Pulsar http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~pulsar/education/sounds/sounds.html
Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae Pulsars Characteristic parameters Pulsar wind nebulae Properties Evolution Exotic central compact objects - Magnetars The Crab Pulsar http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~pulsar/education/sounds/sounds.html
The Crab pulsar and its nebula: Surprises in gamma-rays
 The Crab pulsar and its nebula: Surprises in gamma-rays Based on Bühler & Blandford ROPP 2014 accept. arxiv 1309.7046 At 2 kpc 10''~0.1pc Rolf Bühler, DESY Zeuthen Physics Colloquium, Delaware, 7th May
The Crab pulsar and its nebula: Surprises in gamma-rays Based on Bühler & Blandford ROPP 2014 accept. arxiv 1309.7046 At 2 kpc 10''~0.1pc Rolf Bühler, DESY Zeuthen Physics Colloquium, Delaware, 7th May
Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets
 Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets Deciphering the Violent Universe, Playa del Carmen, December 11-15, 2017 Accretion disk coronae Star Formation
Particle Acceleration by Reconnection and VHE emission Around Black Holes and Relativistic Jets Deciphering the Violent Universe, Playa del Carmen, December 11-15, 2017 Accretion disk coronae Star Formation
Synergetic Growth of the Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in the Relativistic Jet. Jin Matsumoto RIKEN
 Synergetic Growth of the Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in the Relativistic Jet Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Morphological Dichotomy of the Jet 3C 31 Cygnus A FR I (Fanaroff-Riley Class I)
Synergetic Growth of the Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in the Relativistic Jet Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Morphological Dichotomy of the Jet 3C 31 Cygnus A FR I (Fanaroff-Riley Class I)
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 19 Apr 2004
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 0936 February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Axially symmetric relativistic MHD simulations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae in Supernova Remnants On the origin
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 0936 February 2, 2008 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) Axially symmetric relativistic MHD simulations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae in Supernova Remnants On the origin
Electrodynamics of Magnetized Rotators Anatoly Spitkovsky,, UC Berkeley
 Electrodynamics of Magnetized Rotators Anatoly Spitkovsky,, UC Berkeley Magnetized rotators are ubiquitous: pulsars, AGN, GRBs (?) Rotation very efficient at long-term energy storage Extraction of rotational
Electrodynamics of Magnetized Rotators Anatoly Spitkovsky,, UC Berkeley Magnetized rotators are ubiquitous: pulsars, AGN, GRBs (?) Rotation very efficient at long-term energy storage Extraction of rotational
NUMERICAL STUDY OF NON-THERMAL EMISSION FROM LAGRANGIAN PARTICLES IN AGN ENVIRONMENTS.
 13th AGILE Workshop, ASI, Rome May 25, 2015 NUMERICAL STUDY OF NON-THERMAL EMISSION FROM LAGRANGIAN PARTICLES IN AGN ENVIRONMENTS. Dr. Bhargav Vaidya Università degli Studi di Torino, Torino. Collaborators:
13th AGILE Workshop, ASI, Rome May 25, 2015 NUMERICAL STUDY OF NON-THERMAL EMISSION FROM LAGRANGIAN PARTICLES IN AGN ENVIRONMENTS. Dr. Bhargav Vaidya Università degli Studi di Torino, Torino. Collaborators:
Jin Matsumoto. Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
 Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Modeling the magnetized accretion and outflows in young stellar objects
 Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 40 47, (2018) Modeling the magnetized accretion and outflows in young stellar objects Ch. Fendt Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany (E-mail:
Contrib. Astron. Obs. Skalnaté Pleso 48, 40 47, (2018) Modeling the magnetized accretion and outflows in young stellar objects Ch. Fendt Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany (E-mail:
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales
 Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
Simulations of magnetic fields in core collapse on small and large scales Miguel Ángel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz CAMAP, Departament
Pulsar Wind Nebulae: A Multiwavelength Perspective
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae: Collaborators: J. D. Gelfand T. Temim D. Castro S. M. LaMassa B. M. Gaensler J. P. Hughes S. Park D. J. Helfand O. C. de Jager A. Lemiere S. P. Reynolds S. Funk Y. Uchiyama A Multiwavelength
Pulsar Wind Nebulae: Collaborators: J. D. Gelfand T. Temim D. Castro S. M. LaMassa B. M. Gaensler J. P. Hughes S. Park D. J. Helfand O. C. de Jager A. Lemiere S. P. Reynolds S. Funk Y. Uchiyama A Multiwavelength
Global Simulations of Black Hole Accretion. John F. Hawley Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia
 Global Simulations of Black Hole Accretion John F. Hawley Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia Collaborators and Acknowledgements Julian Krolik, Johns Hopkins University Scott Noble, JHU Jeremy
Global Simulations of Black Hole Accretion John F. Hawley Department of Astronomy, University of Virginia Collaborators and Acknowledgements Julian Krolik, Johns Hopkins University Scott Noble, JHU Jeremy
Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular
 Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular SLAC Accelerator seminar SLAC 15 June 2011 R. Buehler for the LAT collaboration and A. Tennant, E. Costa, D. Horns, C. Ferrigno, A.
Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular SLAC Accelerator seminar SLAC 15 June 2011 R. Buehler for the LAT collaboration and A. Tennant, E. Costa, D. Horns, C. Ferrigno, A.
Kelvin-Helmholtz instability: lessons learned and ways forward
 Kelvin-Helmholtz instability: lessons learned and ways forward A. Masson, K. Nykyri, C.P. Escoubet, H. Laakso SSW10, 14 November 2017, Aranjuez, Spain Outline 1. K-H instability: quick reminder 2. Lessons
Kelvin-Helmholtz instability: lessons learned and ways forward A. Masson, K. Nykyri, C.P. Escoubet, H. Laakso SSW10, 14 November 2017, Aranjuez, Spain Outline 1. K-H instability: quick reminder 2. Lessons
X-ray and multiwavelength observations of pulsarwind
 X-ray and multiwavelength observations of pulsarwind nebulae. Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) Collaborators: Martin Durant ( University of Toronto) George Pavlov (Penn State University)
X-ray and multiwavelength observations of pulsarwind nebulae. Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) Collaborators: Martin Durant ( University of Toronto) George Pavlov (Penn State University)
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 31 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 31 Jan 2011 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.he] 31 Jan 2011](/thumbs/93/111774931.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 November 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1011.1800v2 [astro-ph.he] 31 Jan 2011 On the origin of variable gamma-ray emission from the Crab Nebula
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 1 November 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1011.1800v2 [astro-ph.he] 31 Jan 2011 On the origin of variable gamma-ray emission from the Crab Nebula
Probing Pulsar Winds with Gamma Rays
 Probing Pulsar Winds with Gamma Rays Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) in coll. with Felix Aharonian&Sergey Bogovalov International School on Neutron Star Matter
Probing Pulsar Winds with Gamma Rays Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) in coll. with Felix Aharonian&Sergey Bogovalov International School on Neutron Star Matter
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 25 Aug 2003
 On the X-ray Image of The Crab Nebula: Comparison with Chandra Observations arxiv:astro-ph/0308422v1 25 Aug 2003 Shinpei SHIBATA 1, Haruhiko TOMATSURI 1, Makiko SHIMANUKI 1, Kazuyuki SAITO 1, Koji MORI
On the X-ray Image of The Crab Nebula: Comparison with Chandra Observations arxiv:astro-ph/0308422v1 25 Aug 2003 Shinpei SHIBATA 1, Haruhiko TOMATSURI 1, Makiko SHIMANUKI 1, Kazuyuki SAITO 1, Koji MORI
Observations of jet dissipation. Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford)
 Observations of jet dissipation Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford) Overview X-ray radio connections in radio galaxies and quasars: High-energy emission from non-thermal electrons. The interaction of radio galaxies
Observations of jet dissipation Robert Laing (ESO/Oxford) Overview X-ray radio connections in radio galaxies and quasars: High-energy emission from non-thermal electrons. The interaction of radio galaxies
Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes
 Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
Research Collection Other Conference Item Feedback from growth of supermassive black holes Author(s): Begelman, Mitchell C.; Ruszkowksi, Mateusz Publication Date: 2003 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-004585094
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse
 Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
Amplification of magnetic fields in core collapse Miguel Àngel Aloy Torás, Pablo Cerdá-Durán, Thomas Janka, Ewald Müller, Martin Obergaulinger, Tomasz Rembiasz Universitat de València; Max-Planck-Institut
How can jets survive MHD instabilities?
 How can jets survive MHD instabilities? Hubert Baty Observatoire Astronomique, 11 Rue de l université 67000 Strasbourg, France Rony Keppens FOM-Institute for Plasma Physics Rijnhuizen, Association Euratom/FOM,
How can jets survive MHD instabilities? Hubert Baty Observatoire Astronomique, 11 Rue de l université 67000 Strasbourg, France Rony Keppens FOM-Institute for Plasma Physics Rijnhuizen, Association Euratom/FOM,
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center. Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
The Black Hole in the Galactic Center Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) Why focus on the Galactic Center? The Best Evidence for a BH: M 3.6 10 6 M (M = mass of sun) It s s close! only ~ 10 55 Planck Lengths
Momentum transport from magnetic reconnection in laboratory an. plasmas. Fatima Ebrahimi
 Momentum transport from magnetic reconnection in laboratory and astrophysical plasmas Space Science Center - University of New Hampshire collaborators : V. Mirnov, S. Prager, D. Schnack, C. Sovinec Center
Momentum transport from magnetic reconnection in laboratory and astrophysical plasmas Space Science Center - University of New Hampshire collaborators : V. Mirnov, S. Prager, D. Schnack, C. Sovinec Center
X-ray Emission from O Stars. David Cohen Swarthmore College
 X-ray Emission from O Stars David Cohen Swarthmore College Young OB stars are very X-ray X bright L x up to ~10~ 34 ergs s -1 X-ray temperatures: few up to 10+ kev (10s to 100+ million K) K Orion; Chandra
X-ray Emission from O Stars David Cohen Swarthmore College Young OB stars are very X-ray X bright L x up to ~10~ 34 ergs s -1 X-ray temperatures: few up to 10+ kev (10s to 100+ million K) K Orion; Chandra
MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS
 Chapter 6 MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS 6.1 Introduction Magnetohydrodynamics is a branch of plasma physics dealing with dc or low frequency effects in fully ionized magnetized plasma. In this chapter we will study
Chapter 6 MAGNETOHYDRODYNAMICS 6.1 Introduction Magnetohydrodynamics is a branch of plasma physics dealing with dc or low frequency effects in fully ionized magnetized plasma. In this chapter we will study
Jin MATSUMOTO. Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets. National Astronomical Observatory of Japan
 Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin MATSUMOTO National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) Morphological
Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin MATSUMOTO National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) Morphological
Radiative MHD. in Massive Star Formation and Accretion Disks. Rolf Kuiper, Hubert Klahr, Mario Flock, Henrik Beuther, Thomas Henning
 Radiative MHD in Massive Star Formation and Accretion Disks, Hubert Klahr, Mario Flock, Henrik Beuther, Thomas Henning, Radiative MHD with Makemake and Pluto : We developed a fast 3D frequency-dependent
Radiative MHD in Massive Star Formation and Accretion Disks, Hubert Klahr, Mario Flock, Henrik Beuther, Thomas Henning, Radiative MHD with Makemake and Pluto : We developed a fast 3D frequency-dependent
X-ray polarimetry and new prospects in high-energy astrophysics
 X-ray polarimetry and new prospects in high-energy astrophysics Carmelo Sgrò INFN Pisa carmelo.sgro@pi.infn.it Frascati, March 31, 2016 A new exploration window: X-Ray polarimetry Spectroscopy, imaging
X-ray polarimetry and new prospects in high-energy astrophysics Carmelo Sgrò INFN Pisa carmelo.sgro@pi.infn.it Frascati, March 31, 2016 A new exploration window: X-Ray polarimetry Spectroscopy, imaging
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas
 The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
The Physics of Fluids and Plasmas An Introduction for Astrophysicists ARNAB RAI CHOUDHURI CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Preface Acknowledgements xiii xvii Introduction 1 1. 3 1.1 Fluids and plasmas in the
Polarization of the Crab Nebula with disordered magnetic components
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2007) Printed 7 February 2007 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Polarization of the Crab Nebula with disordered magnetic components Y. Nakamura, 1 S. Shibata, 2 1 Graduate
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2007) Printed 7 February 2007 (MN LaT E X style file v2.2) Polarization of the Crab Nebula with disordered magnetic components Y. Nakamura, 1 S. Shibata, 2 1 Graduate
Evolution of High Mass stars
 Evolution of High Mass stars Neutron Stars A supernova explosion of a M > 8 M Sun star blows away its outer layers. The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M Sun. Pressure becomes
Evolution of High Mass stars Neutron Stars A supernova explosion of a M > 8 M Sun star blows away its outer layers. The central core will collapse into a compact object of ~ a few M Sun. Pressure becomes
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 28 Nov 2005
 Relativistic MHD Simulations of Jets with Toroidal Magnetic Fields. arxiv:astro-ph/0511769v1 8 Nov 005 Andrea Mignone (mignone@to.astro.it), Silvano Massaglia and Gianluigi Bodo Dipartimento di Fisica
Relativistic MHD Simulations of Jets with Toroidal Magnetic Fields. arxiv:astro-ph/0511769v1 8 Nov 005 Andrea Mignone (mignone@to.astro.it), Silvano Massaglia and Gianluigi Bodo Dipartimento di Fisica
The ECHO code: from classical MHD to GRMHD in dynamical spacetimes
 The ECHO code: from classical MHD to GRMHD in dynamical spacetimes Luca Del Zanna Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Università di Firenze Main collaborators: N. Bucciantini, O. Zanotti, S. Landi 09/09/2011
The ECHO code: from classical MHD to GRMHD in dynamical spacetimes Luca Del Zanna Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Università di Firenze Main collaborators: N. Bucciantini, O. Zanotti, S. Landi 09/09/2011
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 2 Dec 2003
 3-D Simulations of MHD Jets - The Stability Problem Masanori Nakamura and David L. Meier arxiv:astro-ph/0312055v1 2 Dec 2003 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA
3-D Simulations of MHD Jets - The Stability Problem Masanori Nakamura and David L. Meier arxiv:astro-ph/0312055v1 2 Dec 2003 Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA
Magnetic Fields of Neutron Stars. Dipankar Bhattacharya IUCAA, Pune
 Magnetic Fields of Neutron Stars Dipankar Bhattacharya IUCAA, Pune Neutron Stars harbour the strongest known magnetic fields in the universe: 10 8-10 15 G Magnetic fields determine their interaction with
Magnetic Fields of Neutron Stars Dipankar Bhattacharya IUCAA, Pune Neutron Stars harbour the strongest known magnetic fields in the universe: 10 8-10 15 G Magnetic fields determine their interaction with
Experiments with a Supported Dipole
 Experiments with a Supported Dipole Reporting Measurements of the Interchange Instability Excited by Electron Pressure and Centrifugal Force Introduction Ben Levitt and Dmitry Maslovsky Collisionless Terrella
Experiments with a Supported Dipole Reporting Measurements of the Interchange Instability Excited by Electron Pressure and Centrifugal Force Introduction Ben Levitt and Dmitry Maslovsky Collisionless Terrella
Diffusive shock acceleration: a first order Fermi process. jan.-fév NPAC, rayons cosmiques E. Parizot (APC)
 1 Diffusive shock acceleration: a first order Fermi process 2 Shock waves Discontinuity in physical parameters shock front n 2, p 2, T 2 n 1, p 1, T 1 v 2 v 1 downstream medium (immaterial surface) upstream
1 Diffusive shock acceleration: a first order Fermi process 2 Shock waves Discontinuity in physical parameters shock front n 2, p 2, T 2 n 1, p 1, T 1 v 2 v 1 downstream medium (immaterial surface) upstream
JETS FROM YOUNG STARS: RADIATIVE MHD SIMULATIONS
 JETS FROM YOUNG STARS: RADIATIVE MHD SIMULATIONS O. TEŞILEANU 1,2, A. MIGNONE 1, S. MASSAGLIA 1 1 Dipartimento di Fisica Generale, Università degli Studi di Torino, via P. Giuria 1, 10125 Turin, Italy,
JETS FROM YOUNG STARS: RADIATIVE MHD SIMULATIONS O. TEŞILEANU 1,2, A. MIGNONE 1, S. MASSAGLIA 1 1 Dipartimento di Fisica Generale, Università degli Studi di Torino, via P. Giuria 1, 10125 Turin, Italy,
Turbulent Origins of the Sun s Hot Corona and the Solar Wind
 Turbulent Origins of the Sun s Hot Corona and the Solar Wind Steven R. Cranmer Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Turbulent Origins of the Sun s Hot Corona and the Solar Wind Outline: 1. Solar
Turbulent Origins of the Sun s Hot Corona and the Solar Wind Steven R. Cranmer Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Turbulent Origins of the Sun s Hot Corona and the Solar Wind Outline: 1. Solar
The Time Evolution of Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 The Time Evolution of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Okkie de Jager, S. Ferreira (NWU, South Africa) Science with the New Generation of High Energy Gamma-Ray Experiments (6th Workshop), Padova 8 10 October 2008 Contents
The Time Evolution of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Okkie de Jager, S. Ferreira (NWU, South Africa) Science with the New Generation of High Energy Gamma-Ray Experiments (6th Workshop), Padova 8 10 October 2008 Contents
Lecture 16: Winds, Jets and Outflows. HH 212 H 2 (Mc Caughrean & Zinnecker VLT)
 Lecture 16: Winds, Jets and Outflows HH 212 H 2 (Mc Caughrean & Zinnecker VLT) Losing Material from the Outer Disk Through Photoevaporation Formation & viscous spreading of disk Formation & viscous spreading
Lecture 16: Winds, Jets and Outflows HH 212 H 2 (Mc Caughrean & Zinnecker VLT) Losing Material from the Outer Disk Through Photoevaporation Formation & viscous spreading of disk Formation & viscous spreading
The Crab and other Animals Roger Blandford Yajie Yuan Rolf Buehler and Fermi Team Most of you!
 The Crab and other Animals Roger Blandford Yajie Yuan Rolf Buehler and Fermi Team Most of you! 13 v 2014 Purdue 1 Outline Observations of compact flares Crab Nebula - an introduction Crab Nebula particle
The Crab and other Animals Roger Blandford Yajie Yuan Rolf Buehler and Fermi Team Most of you! 13 v 2014 Purdue 1 Outline Observations of compact flares Crab Nebula - an introduction Crab Nebula particle
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 3 Mar 2006
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2008 February 5, 2008 Simulated synchrotron emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae arxiv:astro-ph/0603080v1 3 Mar 2006 L. Del Zanna 1, D. Volpi 1, E. Amato
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2008 February 5, 2008 Simulated synchrotron emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae arxiv:astro-ph/0603080v1 3 Mar 2006 L. Del Zanna 1, D. Volpi 1, E. Amato
Explosive X-point reconnection & Crab flares. Maxim Lyutikov (Purdue U.)
 Explosive X-point reconnection & Crab flares Maxim Lyutikov (Purdue U.) Spectra of Crab nebula & flares Tavani et al. 20 Beuhler et al., 2011 ] E 2.F [erg cm 2 s 1 9 11 Break at ~ 0 MeV Fermi CGRO COMPTEL
Explosive X-point reconnection & Crab flares Maxim Lyutikov (Purdue U.) Spectra of Crab nebula & flares Tavani et al. 20 Beuhler et al., 2011 ] E 2.F [erg cm 2 s 1 9 11 Break at ~ 0 MeV Fermi CGRO COMPTEL
Relativistic reconnection at the origin of the Crab gamma-ray flares
 Relativistic reconnection at the origin of the Crab gamma-ray flares Benoît Cerutti Center for Integrated Plasma Studies University of Colorado, Boulder, USA Collaborators: Gregory Werner (CIPS), Dmitri
Relativistic reconnection at the origin of the Crab gamma-ray flares Benoît Cerutti Center for Integrated Plasma Studies University of Colorado, Boulder, USA Collaborators: Gregory Werner (CIPS), Dmitri
MHD Flow Field and Momentum Transfer Process of Magneto-Plasma Sail
 J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) MHD Flow Field and Momentum Transfer Process of Magneto-Plasma Sail Hiroyuki NISHIDA, Ikkoh FUNAKI, Yoshifumi INATANI 1) and Kanya KUSANO 2) University of Tokyo,
J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) MHD Flow Field and Momentum Transfer Process of Magneto-Plasma Sail Hiroyuki NISHIDA, Ikkoh FUNAKI, Yoshifumi INATANI 1) and Kanya KUSANO 2) University of Tokyo,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 15 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 15 Jan 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 15 Jan 2011](/thumbs/88/115697806.jpg) Hydrodynamics of Hypersonic Jets: Experiments and Numerical Simulations arxiv:1101.2960v1 [astro-ph.im] 15 Jan 2011 Marco Belan, Sergio de Ponte Daniela Tordella Silvano Massaglia, Attilio Ferrari, Andrea
Hydrodynamics of Hypersonic Jets: Experiments and Numerical Simulations arxiv:1101.2960v1 [astro-ph.im] 15 Jan 2011 Marco Belan, Sergio de Ponte Daniela Tordella Silvano Massaglia, Attilio Ferrari, Andrea
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 2 Feb 2007
 Modeling Pulsar Wind Nebulae Bucciantini, N. Astronomy Department, University of California at Berkeley, 601 Camblell Hall, Berkeley, CA, 94706, USA, Email: nbucciantini@astro.berkeley.edu arxiv:astro-ph/0702084v1
Modeling Pulsar Wind Nebulae Bucciantini, N. Astronomy Department, University of California at Berkeley, 601 Camblell Hall, Berkeley, CA, 94706, USA, Email: nbucciantini@astro.berkeley.edu arxiv:astro-ph/0702084v1
Sound Waves Sound Waves:
 Sound Waves Sound Waves: 1 Sound Waves Sound Waves Linear Waves compression rarefaction 2 H H L L L Gravity Waves 3 Gravity Waves Gravity Waves 4 Gravity Waves Kayak Surfing on ocean gravity waves Oregon
Sound Waves Sound Waves: 1 Sound Waves Sound Waves Linear Waves compression rarefaction 2 H H L L L Gravity Waves 3 Gravity Waves Gravity Waves 4 Gravity Waves Kayak Surfing on ocean gravity waves Oregon
Cosmic Accelerators. 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves. Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford
 Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cosmic Accelerators 2. Pulsars, Black Holes and Shock Waves Roger Blandford KIPAC Stanford Particle Acceleration Unipolar Induction Stochastic Acceleration V ~ Ω Φ I ~ V / Z 0 Z 0 ~100Ω P ~ V I ~ V 2 /Z
Cooling Limits for the
 Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit
 Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
Prof. dr. A. Achterberg, Astronomical Dept., IMAPP, Radboud Universiteit Rough breakdown of MHD shocks Jump conditions: flux in = flux out mass flux: ρv n magnetic flux: B n Normal momentum flux: ρv n
Acceleration and Collimation of Relativistic Magnetized Jets
 Acceleration and Collimation of Relativistic Magnetized Jets Alexander (Sasha) Tchekhovskoy with Ramesh Narayan and Jonathan McKinney Harvard University Chandra X-ray Observatory Magnificent Galaxy Jets
Acceleration and Collimation of Relativistic Magnetized Jets Alexander (Sasha) Tchekhovskoy with Ramesh Narayan and Jonathan McKinney Harvard University Chandra X-ray Observatory Magnificent Galaxy Jets
Observations of. Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae I. Injection Spectrum I. Late-Phase Evolution II. PWNe and Magnetars PWNe and Their SNRs PWN Shock Reverse Shock Forward Shock Pulsar Wind Pulsar Termination Shock PWN
Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae I. Injection Spectrum I. Late-Phase Evolution II. PWNe and Magnetars PWNe and Their SNRs PWN Shock Reverse Shock Forward Shock Pulsar Wind Pulsar Termination Shock PWN
What We Can Learn from High-Resolution Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 What We Can Learn from High-Resolution Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Noel Klingler The George Washington University Oleg Kargaltsev The George Washington University George Pavlov Pennsylvania State
What We Can Learn from High-Resolution Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Noel Klingler The George Washington University Oleg Kargaltsev The George Washington University George Pavlov Pennsylvania State
Gravity Waves Gravity Waves
 Gravity Waves Gravity Waves 1 Gravity Waves Gravity Waves Kayak Surfing on ocean gravity waves Oregon Coast Waves: sea & ocean waves 3 Sound Waves Sound Waves: 4 Sound Waves Sound Waves Linear Waves compression
Gravity Waves Gravity Waves 1 Gravity Waves Gravity Waves Kayak Surfing on ocean gravity waves Oregon Coast Waves: sea & ocean waves 3 Sound Waves Sound Waves: 4 Sound Waves Sound Waves Linear Waves compression
