DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE. October 13-14, Thrusters. Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels
|
|
|
- Edwin Peters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Return to Session Directory DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 13-14, 2009 Thrusters Voith Schneider Propeller - An Efficient Propulsion System for DP Controlled Vessels Dirk Jürgens, Michael Palm Voith Turbo Schneider Propulsions Heidenheim, Germany
2 1. Introduction The Voith Schneider Propeller (VSP) offers a very fast and precise thrust control. The thrust is produced by rotating and additionally oscillating blades. The thrust is controlled by means of a kinematic gear and a control rod. The thrust follows the motion of the control rod immediately via an X/Y-logic. That means, the thrust can over zero steered in any direction very fast. The very fast and precise thrust control offers an efficient force for the DP-system of the ship. The faster the propulsion system can counteract a disturbance created by environmental forces the less energy is necessary to keep the vessel in the relevant watch circle. The paper will present the latest results of studies on the Voith Schneider Propeller in dynamic positioning applications. These investigations have been carried out by using experimental methods and computational fluid dynamics. Studies were conducted on the influence of the Voith Schneider Propeller on stern slamming conditions, the roll damping capabilities of the VSP and the impact of air ventilation. For the latter the results are compared to azimuth thrusters. The results show that the VSP has an alliviating impact on pressure loads due to stern slamming. The VSP influences positively the slamming behaviour of a vessel because of its vertical rotating axis. Furthermore the VSP is less prone to thrust losses due to ventilation effects compared to thruster- type propellers. Additionally the Voith Schneider Propeller can be used to reduce the roll motion of the vessel. The necessary logic, called Voith Roll Stabilization, can be combined with the DP system of the vessel and the steering system, including the auto pilot. 1. The technical and hydrodynamical principle of the VSP For a better understanding of the later presented hydrodynamical investigations, a short explanation of the technical principle of the VSP is required. A detailed description about the technology and theory can be found in [1] - [7]. The thrust of a VSP can be applied via a very fast X/Y-logic. Figure 1 shows the sectional drawing of a VSP and figure 2 the installation of two VSPs in a Offshore Support Vessel. Fig.1 Sectional drawing of a VSP Fig. 2 Two VSP installed in a Offshore Support Vessel DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 1
3 The thrust is created by vertically mounted blades in a rotor casing. While the rotor casing is rotating, the blades are oscillating. The blades oscillation is steered by the law of intersecting normals. Figure 3 shows the mechanical principle of the VSP and figure 4 the corresponding hydrodynamic thrust creation. A descriptive simulation program showing the technology of the VSP and the hydrodynamics can be downloaded at Fig. 3 Mechanical principle of the VSP Fig. 4 Hydrodynamic principle of the VSP Fig. 5 shows the forces acting at the propeller for selected blade positions as a function of the cycloid path for a stationary observer. Lift changes during revolution due to the nonstationary flow at the propeller blades. The forces acting across the desired direction of thrust cancel each other, whereas the forces acting in thrust direction are added over the propeller circumference. Fig. 5 Lift generation on a blade as a function of the cycloidal blade path DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 2
4 The thrust of the Voith Schneider Propeller can be adjusted in an ideal way by the X/Y-logic. Figure 7 explains this by some examples. The thrust can be steered extremely fast. From full ahead to full astern, a size VSP 36R5/300-2 (3800 kw input power) achieves this in 5 seconds. A different thrust value in longitudinal and transversal direction is just achieved by changing the amplitude and the phase angle of the oscillation blade of the VSP. This is done by moving the steering point via the kinematic that is shown in figure 1 and figure 3. Fig. 7.1: No thrust demand from the DP system Fig. 7.2: 39%Thrust demand (ahead) Fig. 7.3: 100%Thrust demand (ahead) Fig. 7.4: 100%Thrust demand (astern) DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 3
5 Fig. 7.5: 58%Thrust demand (astern); 41% thrust demand (port) Fig. 7.6: 57%Thrust demand (ahead); 27% thrust demand (starboard) The VSP offers a high efficiency for a steerable thruster. The reasons for that is the high aspect ratio of the blades; and that only the thrust producing blades are protruding outside the ship s hull. The free running curves of a VSP without propeller guard are shown in Fig. 8. The influence of the pitch is clearly visible and works similar to a normal controllable pitch screw propeller. The higher the pitch the higher is the maximum achievable efficiency. Fig. 8: Typical free running curves of a VSP DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 4
6 The definition of the coefficients for a VSP can be found in the following table. Voith is using a system that differs by constant factors from the coefficients known from the screw propeller theory. Voith definition Coefficients by analogy with screw propellers Conversion Advance ratio V λ = A πnd J VA = J = λπ nd Thrust coefficient k S = T ρ 2 DLu² T = 2 ρn D k T 3 L 2 π k T = k S 2 Torque coefficient Open-water efficiency ratio k D 2M = ρ D² Lu² 2 k η0 = k S D λ ρn M k Q = 2 4 D L 2 π k Q = k D 4 kt J η0 = - k 2π Q Peripheral velocity of VSP blades: u = πnd Table 1: Hydrodynamic coefficients for the VSP The forces in longitudinal and transversal direction of a VSP which can be achieved for different thrust and speed directions are plotted in fig. 9. Obviously the forward thrust is reduced with increasing speed but the steering forces are clearly growing with a higher speed. Fig. 9: Typical thrust plot for different speeds; VSP 36R6/300-2 (3800 kw Input Power) DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 5
7 2. Reduction of slamming induced pressures by the VSP A vessel under DP conditions can be faced the situation that waves are creating servere slamming. Figure 10 shows an OSV (LOA 90m), propelled by two VSPs, which was tested in the Ship Model Basin Vienna in maximum wave heights of 8 m. Fig. 10: Testing of stern slamming for a OSV under DP conditions Fig. 11 and 12 illustrate the positions of the sensors to measure the slamming pressure. The sensors were positioned near the VSPs and at the transom. The numbering of the sensors can be found in fig. 12. Fig. 11: Ship model and position of the pressure sensors DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 6
8 Fig. 12: Numbering of the pressure sensors The measurements have shown a very interesting effect. Even if the VSP does not produce any thrust, that means it works with zero pitch and a constant rpm, there is a clear reduction of the the slamming pressures. Fig. 13 explains this clearly. There the maximum slamming pressure in kpa is shown for the individual measuring points as defined in fig. 12. The measurements have been done for a still standing VSP (VSP off) and the running VSP with zero pitch (VSP on). In the second case, no thrust has been produced. Especially the pressure sensors positioned near the VSP (Nr. 5, 6 and 7) recorded a remarkable reduction. Fig. 13: Maximum slamming pressure at the measuring points defined in fig. 12, significant wave height Hs = 4.0m, draught of the vessel = 5.2 m Fig. 14 illustrates also the influence of the running VSPs. There the number of slams occurring in 30 minutes for the measuring points Nr. 4, 5,6 and 7 for a significant wave height of Hs = 4.0 m are shown. The measurements have been carried out for a working VSP with zero pitch and a still standing VSP. Besides the maximal amplitude also the frequency of occurance of slamming impacts is reduced by the presence of the Voith Schneider Propeller. DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 7
9 Fig. 14: Number of slams in 30 minutes at the measuring points defined in fig. 12, significant wave height Hs = 4.0m, draught of the vessel = 5.2 DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 8
10 3. Influence of ventilation on propeller thrust Large vertical ship motions induced by waves could expose the propulsion unit to the danger of ventilation. In this case entrapped air might reach the propeller plane or in extreme cases the propellers emerge at least partly from the water. This phenomenon has a significant influence on the propeller performance. Massive sudden breakdown of thrust and torque are the consequences while the strong fluctuation of the latter is believed to be responsible for potential mechanical failures of power transmission components. To study the influence of ventilation many investigations on thrusters [8-13] have been carried out. Fig. 14 shows that the phenomenon of ventilation on a thruster at zero advance speed even occurs if the thruster is fully submerged. Fig. 14: Thruster in ventilating conditions at zero advance speed (photo taken from [10]) DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 9
11 Dirk Jürgens/Michael Palm Thruster Session Voith Schneider Propeller Within an experimental and numerical study Voith tested the impact of ventilation on the thrust of their two propeller types, namely the Voith Schneider Propeller and the thruster-type Voith Radial Propeller. The diameter of the VSP was 200mm and the blade length was 150mm while the propeller diameter of the VRP was 210mm. Both propellers were adjusted to deliver the same thrust in full submerged conditions. The thrust and torque was measured for both propellers while emerging both units in discrete steps. Fig. 15 and 16 show the model test arrangement for both propeller variants. In Fig. 18 the relative thrust compared to the full submerged conditions are shown. The values are shown as a function of h/d (defined in Fig. 17). The Voith-Schneider-Propeller is less influenced by ventilation effects. The thrust for the VSP decreases more gradually with the emerging propeller while the thruster experiences a massive thrust reduction even before the propeller blades start to emerge. Fig. 15: VSP at h/d=0.5 Fig. 16: VRP at h/d=0.04 Fig. 17: Definition of the level of submergence h/d To gain more insight into the flow phenomena CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) calculations have been carried out as well. A RANSE-solver with the finite volume approach is used for this study. The phase front of the flow is captured with the volume-of-fluid method. Fig. 19 and 20 show the free surface and the pressure distribution for the VSP and the VRP variant. DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 10
12 VRP VSP 70 thrust [%] h/d Fig. 18: thrust losses as a function of propeller immersion at equal nominal thrust Fig. 19: CFD result for the VSP at h/d=0.5 Fig. 20: CFD result for the VRP at h/d=0.5 In Fig.21 and 22 the quantitive comparison between calculation and experiments are depicted. These first results show that the general behaviour in ventilating conditions of the different propulsion systems is quite well predicted. Since the CFD calculation have been conducted prior to the model tests, the comparison between CFD and model test was done at a smaller rpm than the one in Fig. 18, where the same thrust of both propulsion systems was adjusted. The studies are currently evaluated in detail to better understand the effect of ventilation on propeller performance. DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 11
13 thrust [%] VSP CFD VSP Exp h/d Fig. 21: Experimental and computational results for thrust reduction of the VSP at n=210rpm VRP CFD VRP Exp. 70 thrust [%] h/d Fig. 22: Experimental and computational results for thrust reduction of the VRP DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 12
14 4. Active Roll Damping with Voith-Schneider-Propellers Large roll amplitudes in high sea states could negatively affect the operability of duties and crews comfort and safety what on the other hand might lead to larger downtimes of the ship operations. To counteract the roll motions several active and passive systems with different degree of effect are widely used. The VSP characteristic allowing fast and stepless control of thrust in magnitude and direction has led to a further functionality besides propulsion and steering. With minor scope of electronic components the Voith-Schneider-Propeller can additionally be used as an active roll stabilizer. Fig. 23: Roll counteracting forces of the VSP Fig. 23 shows the basic principle of roll stabilisation with VSP. The moment that initiates the roll motion is partly equalized by the transversal thrust of the VSP. Since the thrust magnitude of the VSP is equal in all directions for zero advance speed a counteracting moment can be generated by applying.side forces. This principle holds for cruising speeds as well, as steering forces can be generated very fast due to the x/y-steering logic of the VSP. Fig. 9 gave an idea about the transversal forces for different ship speeds. To quantify the roll damping capability a test series with a 44m motor yacht have been carried out in a ship model basin. Fig. 24 shows the model test arrangement. The tests were conducted at zero advance speed at bow-quartering waves with a significant height of 1.5m and a peak period of 5 sec. In Fig. 25 the time response of the roll angle with and without active Voith Roll Stabilisation (VRS) is shown. In this case a roll reduction of 64.9% was achieved. Within the test programme also alternative systems for roll damping namely passive fins and active zero speed fins have been tested. In Fig. 26 the significant roll angles for the different variants can be seen. The VRS OFF mode means that the propellers are rotating at zero pitch. In this case the VSPs are acting as an passive roll damping systems and reduce the roll angle by a similar amount as the passive DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 13
15 fins do. In the VRS ON mode the Voith-Schneider-Propellers generate alternating side forces to counteract the roll motion with the effect already shown in Fig. 25. Currently the Voith-Roll-Stabilsation is implemented successfully on different offshore support vessels. Fig. 24: setup for roll damping test of a 44m yacht 12 9 Hs 1,5m VRS off Hs 1,5m VRS on, 100% 6 Rollangle [ ] time [s] Fig. 25: model tests results on a 40m motor yacht with bow quartering waves at a significant heigth of 1.5m DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 14
16 Fig. 26: roll angle for different roll damping systems on a 44m yacht 4. Conclusions The basic principle of the Voith-Schneider-Propeller providing a controllable pitch characteristic and very fast and precise steering capabilities makes the system an efficient option for ships that have high demands on dynamic positioning performance. Three physical phenomena that can have a large impact on dynamic positioning applications have been investigated with relation to the Voith-Schneider-Propeller. It was shown that the VSP has an alleviating impact on the pressure loads due to stern slamming. It is furthermore less prone to ventilation losses compared to azimuth thrusters. And finally the VSP provides besides propulsion and steering an effective functionality for roll damping. DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 15
17 REFERENCES [1] Jürgens, B.; Fork, W.: Faszination Voith-Schneider-Propeller, Geschichte und Technik [The Fascination of Voith-Schneider Propellers, History and Engineering], Hamburg [2] Bartels, J.-E.; Jürgens, D.: The Voith Schneider Propeller - Current Application and New Developments, Voith Publication; G 1849; Heidenheim [3] Bartels, J.-E.; Jürgens, D.: Voith-Schneider-Propeller-Gegenwärtige Anwendungen und neue Entwicklungen, Handbuch der Werften, Band XXVI, [4] Jürgens, D.; Grabert, R: New Hydrodynamic Aspects of Double-ended Ferries with Voith Schneider Propeller. 2nd International conference on Double Ended Ferries, Norway, Alesund, March [5] Jürgens, D.; Palm, M.; Singer, S.; Urban, K.: Numerical optimization of the Voith Schneider Propeller. ZAMMZ: Angew. Math. Mech. 87, No. 10, [6] Palm, M.: Matching the Reality of Ship Hydrodynamics through CFD. 2nd Symposium on Voith Schneider Technology, Heidenheim, 4-6 June [7] Jürgens, D.; Heinke, H.: Voith Schneider Propeller (VSP) - Investigations of the cavitation behaviour, First International Symposium on Marine Propulsion, SMP 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 2009 [8] Koushan, K.: Dynamics of propeller blade and duct loadings on ventilated thrusters in dynamic positioning mode, Dynamic Positioning Conference, Houston 2007 [9] Koushan, K.: Dynamics of ventilated propeller blade loading on thrusters due to forces sinusoidal heave motion, 26 th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics, Rome 2006 [10] Koushan, K.: Dynamics of propeller blade and duct loadings on ventilated ducted thrusters operating at zero speed, 2 nd Int. Conference on Technological Advances in Podded Propulsion, Brest 2006 [11] Koushan, K.: Dynamics of ventilated propeller blade loading on thrusters, World Maritime Technology Conference, London 2006 [12] Koushan, K: Dynamics of propeller blade und duct loadings on ventilated ducted thrusters due to forces periodic heave motions, Int. Conference on Violent Flows, Fukuoka 2007 [13] Califano, A:; Steen, S.: Analysis of different propeller ventilation mechnisms by means of RANS simulations, 1 st Int. Symposium on Marine Propulsors, Trondheim 2009 DP Conference Houston October 13-14, 2009 Page 16
Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions
 DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 2010 Thrusters Comparison of Thruster Axis Tilting versus Nozzle Tilting on the Propeller-Hull Interactions for a Drillship at DP-Conditions Michael Palm,
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller
 voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
voith.com Precise and safe maneuvering Voith Schneider Propeller 5 Voith Schneider Propeller. Voith Turbo offers tailor-made propulsion systems for a wide variety of applications for harbor assistance
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1
 Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Offshore Hydromechanics Module 1 Dr. ir. Pepijn de Jong 6. Real Flows part 2 Introduction Topics of Module 1 Problems of interest Chapter 1 Hydrostatics Chapter 2 Floating stability Chapter 2 Constant
Numerical Investigation of the Performance of Voith Schneider Propulsion
 American Journal of Marine Science, 214, Vol. 2, No. 3, 58-62 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/marine/2/3/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:12691/marine-2-3-3 Numerical Investigation of
American Journal of Marine Science, 214, Vol. 2, No. 3, 58-62 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/marine/2/3/3 Science and Education Publishing DOI:12691/marine-2-3-3 Numerical Investigation of
A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 27-33 10.2478/pomr-2014-0015 A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane Katarzyna Zelazny,
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(82) 2014 Vol 21; pp. 27-33 10.2478/pomr-2014-0015 A simplified method for calculating propeller thrust decrease for a ship sailing on a given shipping lane Katarzyna Zelazny,
Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Propeller Loads of Large Commercial Vessels at Crash Stop J.W. Hur, H. Lee, B.J. Chang 1 1 Hyundai Heavy Industries,
Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships
 (August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
(August 2006) (Rev.1 Jan 2007) (Corr.1 Oct 2007) Machinery Requirements for Polar Class Ships.1 Application * The contents of this Chapter apply to main propulsion, steering gear, emergency and essential
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page 1 of 9 CONTENTS Model Test Experiments... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Model Parameters... 3 2.2 Environmental Parameters... 3 2.3 Operation of Thrusters... 3 2.3.1 Thruster-Current
Page 1 of 9 CONTENTS Model Test Experiments... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Model Parameters... 3 2.2 Environmental Parameters... 3 2.3 Operation of Thrusters... 3 2.3.1 Thruster-Current
Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of a Wake Equalizing Duct
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 9 Number 2 June 2015 DOI: 10.12716/1001.09.02.11 Cavitation of a Propeller and Influence of
Full scale thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Full thruster performance and load determination based on numerical simulations Norbert Bulten 1, Rik
Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Numerical Analysis of Unsteady Open Water Characteristics of Surface Piercing Propeller Kohei Himei
Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 2011 Workshop: Propeller performance Potsdam Propeller Test Case (PPTC) Test Case Description Ulf Barkmann 1, Hans-Jürgen
Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Influence of Flow Transition on Open and Ducted Propeller Characteristics Anirban Bhattacharyya 1, Jan Clemens
Drag and Torque on Locked Screw Propeller
 http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 8 Number 3 September 24 DOI:.276/.8.3.6 Drag and Torque on Locked Screw Propeller T. Tabaczek
http://www.transnav.eu the International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 8 Number 3 September 24 DOI:.276/.8.3.6 Drag and Torque on Locked Screw Propeller T. Tabaczek
Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses
 (Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
(Feb 2005) (orr.1 Mar 2012) (orr.2 Nov 2012) Dimensions of propulsion shafts and their permissible torsional vibration stresses.1 Scope This UR applies to propulsion shafts such as intermediate and propeller
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines Testing and Extrapolation Methods Propulsion, Performance Propulsion Test
 7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
7.5- Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents... 2 1. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE... 2 2. PARAMETERS... 2 2.1 Data Reduction Equations... 2 2.2 Definition of Variables... 3 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3.1 Model and
Measurement of speed loss due to waves
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Measurement of speed loss due to waves Sverre Steen 1 and Zhenju Chuang 1 1 Department of Marine Technology,
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Measurement of speed loss due to waves Sverre Steen 1 and Zhenju Chuang 1 1 Department of Marine Technology,
IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS
 Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
Journal of KONES Powertrain and Transport, Vol., No. 015 IDENTIFICATION OF SHIP PROPELLER TORSIONAL VIBRATIONS Jan Rosłanowski Gdynia Maritime University, Faculty of Marine Engineering Morska Street 81-87,
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
7.5 02 Page 1 of 21 Table of Contents 1 PURPOSE... 2 2 ITTC DICTIONARY OF SHIP HYDRODYNAMICS PROPELLER SECTION... 2 COMMENTS OF THE PROPULSION COMMITTEE OF 22 nd ITTC Several of the symbols and definitions
DESIGN OF A HYBRID POWER/TORQUE THRUSTER CONTROLLER WITH LOSS ESTIMATION. Øyvind N. Smogeli, Asgeir J. Sørensen and Thor I. Fossen
 DESIGN OF A HYBRID POWER/TORQUE THRUSTER CONTROLLER WITH LOSS ESTIMATION Øyvind N. Smogeli, Asgeir J. Sørensen and Thor I. Fossen Department of Marine Technology Norwegian University of Science and Technology
DESIGN OF A HYBRID POWER/TORQUE THRUSTER CONTROLLER WITH LOSS ESTIMATION Øyvind N. Smogeli, Asgeir J. Sørensen and Thor I. Fossen Department of Marine Technology Norwegian University of Science and Technology
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results
 Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
Ship structure dynamic analysis - effects of made assumptions on computation results Lech Murawski Centrum Techniki Okrętowej S. A. (Ship Design and Research Centre) ABSTRACT The paper presents identification
VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD
 Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
Proceedings of COBEM 2007 Copyright 2007 by ABCM 19th International Congress of Mechanical Engineering November 5-9, 2007, Brasília, DF VIBRATION ANALYSIS IN SHIP STRUCTURES BY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Luiz
On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
 International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number 1 March 28 On an Advanced Shipboard Information and Decision-making System for Safe and Efficient Passage Planning
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN
 ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
ADVANCES IN FULL-SCALE WAKE-FIELD PREDICTIONS AND THE IMPLICATIONS FOR THE PROPELLER DESIGN Gert-Jan Zondervan*, Bram Starke Maritime Research Institute Netherlands PO Box 28, 67 AA Wageningen, The Netherlands
DP MAINTENANCE TRAINING
 DP MAINTENANCE TRAINING SINGAPORE Topics Day 2 Review Introduction to Serial Communications Serial Interface Cards Using the Workstation Diagnostics Screens Practical Applications Discussion of AMC Topics
DP MAINTENANCE TRAINING SINGAPORE Topics Day 2 Review Introduction to Serial Communications Serial Interface Cards Using the Workstation Diagnostics Screens Practical Applications Discussion of AMC Topics
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 4: 2017
 Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
Question 1a. Values of forward speed, propeller thrust and torque measured during a propeller open water performance test are presented in the table below. The model propeller was 0.21 meters in diameter
Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry To cite this article: L Crudu et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Prediction of induced vibrations for a passenger - car ferry To cite this article: L Crudu et al 2016 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method
 Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
Prediction of Propeller Performance Using Quasi-Continuous Method Hao Rui, a,* and Jaswar Koto, b a) Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia b) Ocean and
DETERMINING OPTIMUM GEOMETRY FOR A BOW THRUSTER PROPELLER
 DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
DEERMINING OPIMUM GEOMERY FOR A BOW HRUSER PROPELLER Y.H. OZDEMIR, S. BAYRAKAR,. YILMAZ, M.GUNER Yildiz echnical University, Dept. of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 34349 Besiktas, Istanbul,
Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres
 Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres J. Artyszuk Maritime University of Szczecin, Poland Abstract A relatively small amount of data concerning the behaviour of propulsion coefficients,
Wake fraction and thrust deduction during ship astern manoeuvres J. Artyszuk Maritime University of Szczecin, Poland Abstract A relatively small amount of data concerning the behaviour of propulsion coefficients,
Propeller-ice impacts measurements with a six-component blade load sensor
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Propeller-ice impacts measurements with a six-component blade load sensor Joris Brouwer 1, Gerco Hagesteijn
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Propeller-ice impacts measurements with a six-component blade load sensor Joris Brouwer 1, Gerco Hagesteijn
Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor Mohammed F. Islam 1, Ayhan Akinturk,
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 009 Performance Characteristics of Static and Dynamic Azimuthing Podded Propulsor Mohammed F. Islam 1, Ayhan Akinturk,
EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF A MARINE PROPELLER THRUST ESTIMATION SCHEME. Luca Pivano yvind N. Smogeli Thor Inge Fossen Tor Arne Johansen
 EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF A MARINE PROPELLER THRUST ESTIMATION SCHEME Luca Pivano yvind N. Smogeli Thor Inge Fossen Tor Arne Johansen Department of Engineering Cybernetics, Norwegian University of Science
EXPERIMENTAL VALIDATION OF A MARINE PROPELLER THRUST ESTIMATION SCHEME Luca Pivano yvind N. Smogeli Thor Inge Fossen Tor Arne Johansen Department of Engineering Cybernetics, Norwegian University of Science
Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on Pump Performance
 11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
11 th International Conference on Fast Sea Transportation FAST 2011, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, September 2011 Numerical Investigation of the Impact of SES-Waterjet Interactions and Flow Non-uniformity on
On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 On the advanced extrapolation method for a new type of podded propulsor via CFD simulations and model measurements Tomi
Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA
 Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
Research Article Prediction of Propeller Blade Stress Distribution Through FEA Kiam Beng Yeo, Wai Heng Choong and Wen Yen Hau ABSTRACT The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of marine propeller blade stress
A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using CFD
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 8 (2018) 36-42 doi 10.17265/2159-5879/2018.01.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Study on Effects of Blade Pitch on the Hydrodynamic Performances of a Propeller by Using
Numerical Analysis of Azimuth Propulsor Performance in Seaways: Influence of Oblique Inflow and Free Surface
 Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Numerical Analysis of Azimuth Propulsor Performance in Seaways: Influence of Oblique Inflow and Free Surface Nabila Berchiche, Vladimir I. Krasilnikov
Journal of Marine Science and Engineering Article Numerical Analysis of Azimuth Propulsor Performance in Seaways: Influence of Oblique Inflow and Free Surface Nabila Berchiche, Vladimir I. Krasilnikov
Deliverable D.6.1. Application of CFD tools to the development of a novel propulsion concept
 TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
TRIple Energy Saving by Use of CRP, CLT and PODded Propulsion Grant Agreement Number: 265809 Call identifier: FP7-SST-2010-RTD-1 Theme SST.2010.1.1-2.: Energy efficiency of ships WP 1 Deliverable D.6.1
Thrusters. Numerical Analysis of Flow Around a Thruster
 Thrusters Numerical Analysis of Flow Around a Thruster Norbert W. H. Bulten Wärtsilä Propulson, Netherlands October 17-18, 2006 Return to Session Directory Numerical Analysis of Flow around a Thruster
Thrusters Numerical Analysis of Flow Around a Thruster Norbert W. H. Bulten Wärtsilä Propulson, Netherlands October 17-18, 2006 Return to Session Directory Numerical Analysis of Flow around a Thruster
Hydro-Structure Analysis of Composite Marine Propeller under Pressure Hydrodynamic Loading
 American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, Vol. 3, No. 2, 41-46 Available online at http://pubs.sciepub.com/ajme/3/2/2 Science and Education Publishing DOI:10.12691/ajme-3-2-2 Hydro-Structure Analysis
ENGR 4011 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships Assignment 5: A dimensional analysis of propeller thrust starting with the functional expression
 ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
ENGR 40 Resistance & Propulsion of Ships ssignment 5: 07. -dimensional hydrofoil section is shown below. It has an incidence velocity V incidence at an angle of attack α E. For the case shown: sketch the
APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS ON RUDDERS
 Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
Proceedings of ASME 25 34th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE 25 May 3 - June 5, 25, St. John s, Newfoundland, Canada OMAE25-4796 APPLICATION OF ENERGY SAVING FINS
ROLL MOTION OF A RORO-SHIP IN IRREGULAR FOLLOWING WAVES
 38 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 9, o. 1, pp. 38-44 (2001) ROLL MOTIO OF A RORO-SHIP I IRREGULAR FOLLOWIG WAVES Jianbo Hua* and Wei-Hui Wang** Keywords: roll motion, parametric excitation,
38 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 9, o. 1, pp. 38-44 (2001) ROLL MOTIO OF A RORO-SHIP I IRREGULAR FOLLOWIG WAVES Jianbo Hua* and Wei-Hui Wang** Keywords: roll motion, parametric excitation,
Simulation of Plane Motion of Semiautonomous Underwater Vehicle
 Proceedings o the European Computing Conerence Simulation o Plane Motion o Semiautonomous Underwater Vehicle JERZY GARUS, JÓZEF MAŁECKI Faculty o Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Naval University
Proceedings o the European Computing Conerence Simulation o Plane Motion o Semiautonomous Underwater Vehicle JERZY GARUS, JÓZEF MAŁECKI Faculty o Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Naval University
MODELLING THE DYNAMICS OF SHIPS WITH DIFFERENT PROPULSION SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL PURPOSE
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 1(89) 2016 Vol. 23; pp. 31-36 10.1515/pomr-2016-0005 MODELLING THE DYNAMICS OF SHIPS WITH DIFFERENT PROPULSION SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL PURPOSE Witold Gierusz, Assoc. Prof. Gdynia Maritime
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 1(89) 2016 Vol. 23; pp. 31-36 10.1515/pomr-2016-0005 MODELLING THE DYNAMICS OF SHIPS WITH DIFFERENT PROPULSION SYSTEMS FOR CONTROL PURPOSE Witold Gierusz, Assoc. Prof. Gdynia Maritime
Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings
 Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 211 Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings Daniele
Second International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 11, Hamburg, Germany, June 211 Numerical and Experimental Characterization of a CP Propeller Unsteady Cavitation at Different Pitch Settings Daniele
Evaluation of Propeller Virtual Mass and Damping Coefficients by URANS- Method
 Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Evaluation of Propeller Virtual Mass and Damping Coefficients by URANS- Method Martio J. 1, Sánchez-Caja, A. 1,
Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 15, Austin, Texas, USA, June 2015 Evaluation of Propeller Virtual Mass and Damping Coefficients by URANS- Method Martio J. 1, Sánchez-Caja, A. 1,
ITTC Recommended Procedures and Guidelines
 Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Page of Table of Contents Waterjet Propulsion Test and Extrapolation... PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE.... PARAMETERS.... Nomenclature... 3. DESCRIPTION OF PROCEDURE... 3 3. Model and installation... 3 3.. Resistance
Teaching sessions week 40
 Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Teaching sessions week 40 Monday 28 September Lecture: Introduction to propulsion. Momentum theory of propeller action. Friday 2 October Lecture: Screw propeller Introduction of Marine Hydrodynamics 1
Performance Investigation of Ducted Aerodynamic Propulsors
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors Smp 9, Trondheim, Norway, June 29 Performance Investigation of Ducted Aerodynamic Propulsors Naipei P. Bi, Kevin R. Kimmel, David J. Haas Naval Surface
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors Smp 9, Trondheim, Norway, June 29 Performance Investigation of Ducted Aerodynamic Propulsors Naipei P. Bi, Kevin R. Kimmel, David J. Haas Naval Surface
The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory
 J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
J. Marine Sci. Appl. (2012) 11: 164-168 DOI: 10.1007/s11804-012-1118-1 The Calculations of Propeller Induced Velocity by RANS and Momentum Theory Qiuxin Gao *, Wei Jin and Dracos Vassalos Department of
Makoto Uchida. Yuuki Matsumoto
 ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
ADVANCED EDUCATION AND RESEARCH ON MARINE PROPULSION EXPERIMENTAL S TUDY ON PROPELLER AIR-DRAWINGS AND BEARING FORCES Makoto Uchida Professor, Dr. Faculty of Maritime Sciences, Kobe University 5-1-1 Fukae-Minami,
ZIG-ZAG MANEUVER SIMULATION BY CFD FOR A TANKER LIKE VESSEL
 V International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering MARINE 2013 B. Brinkmann and P. Wriggers (Eds) ZIG-ZAG MANEUVER SIMULATION BY CFD FOR A TANKER LIKE VESSEL G. DUBBIOSO, D. DURANTE,
V International Conference on Computational Methods in Marine Engineering MARINE 2013 B. Brinkmann and P. Wriggers (Eds) ZIG-ZAG MANEUVER SIMULATION BY CFD FOR A TANKER LIKE VESSEL G. DUBBIOSO, D. DURANTE,
Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 09, Trondheim, Norway, une 2009 Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results Scott Black and Susan Swithenbank Naval Surface Warfare
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 09, Trondheim, Norway, une 2009 Analysis of Crashback Forces Compared with Experimental Results Scott Black and Susan Swithenbank Naval Surface Warfare
Comparison of discharge measurements - Thermodynamic to US Clamp- On, stationary US and Needle Opening Curve
 IGHEM 2012 The 9 th International conference on hydraulic efficiency measurements Trondheim, Norway June 27 th - 30 th, 2012 XXXXXX Comparison of discharge measurements - Thermodynamic to US Clamp- On,
IGHEM 2012 The 9 th International conference on hydraulic efficiency measurements Trondheim, Norway June 27 th - 30 th, 2012 XXXXXX Comparison of discharge measurements - Thermodynamic to US Clamp- On,
SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE
 N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
N. Perez Síntesis Tecnológica. V.3 Nº 1 (26) 33-37 SCALE MODEL TESTS OF A FISHING VESSEL IN ROLL MOTION PARAMETRIC RESONANCE NELSON A. PEREZ M. Instituto de Ciencias Navales y Marítimas, M.Sc, nperez@uach.cl,
Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions
 Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions Islam M. F 1, Veitch B 1, Akinturk A 2, Bose N 3 and Liu P 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University of Newfoundland
Experiments with Podded Propulsors in Static Azimuthing Conditions Islam M. F 1, Veitch B 1, Akinturk A 2, Bose N 3 and Liu P 2 1 Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science, Memorial University of Newfoundland
Analysis of Unsteady Propeller Blade Forces by RANS
 First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 2009 Analysis of Unsteady Propeller Blade Forces by Vladimir Krasilnikov 1, Zhirong Zhang 2 and Fangwen Hong 2 1 Norwegian
First International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 09, Trondheim, Norway, June 2009 Analysis of Unsteady Propeller Blade Forces by Vladimir Krasilnikov 1, Zhirong Zhang 2 and Fangwen Hong 2 1 Norwegian
VALIDATION OF A TIME DOMAIN PANEL CODE FOR PREDICTING THE SEAKEEPING BEHAVIOUR OF A RIGID HULL INFLATABLE BOAT
 F(1ST2017 N\TES-FRNCE VLIDTION OF TIME DOMIN PNEL CODE FOR PREDICTING THE SEKEEPING BEHVIOUR OF RIGID HULL INFLTBLE BOT Callan Bird - Defence Science and Teclinology Group (DST), Melbourne, ustralia Frans
F(1ST2017 N\TES-FRNCE VLIDTION OF TIME DOMIN PNEL CODE FOR PREDICTING THE SEKEEPING BEHVIOUR OF RIGID HULL INFLTBLE BOT Callan Bird - Defence Science and Teclinology Group (DST), Melbourne, ustralia Frans
Experimental Validation of a Marine Propeller Thrust Estimation Scheme
 Modeling, Identification and Control, Vol. 8, No. 4, 7, pp. 5 Experimental Validation of a Marine Propeller Thrust Estimation Scheme Luca Pivano Øyvind N. Smogeli Tor Arne Johansen Thor Inge Fossen Department
Modeling, Identification and Control, Vol. 8, No. 4, 7, pp. 5 Experimental Validation of a Marine Propeller Thrust Estimation Scheme Luca Pivano Øyvind N. Smogeli Tor Arne Johansen Thor Inge Fossen Department
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
 PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
PLEASURE VESSEL VIBRATION AND NOISE FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1 Macchiavello, Sergio *, 2 Tonelli, Angelo 1 D Appolonia S.p.A., Italy, 2 Rina Services S.p.A., Italy KEYWORDS pleasure vessel, vibration analysis,
Transactions on the Built Environment vol 24, 1997 WIT Press, ISSN
 Comparison of model test with ship sea trial results for a given vessel series C.Behrendt & T.Kucharski Institute of Marine Plant Operation, Maritime University of Szczecin, 70-500 Szczecin, Poland Abstract
Comparison of model test with ship sea trial results for a given vessel series C.Behrendt & T.Kucharski Institute of Marine Plant Operation, Maritime University of Szczecin, 70-500 Szczecin, Poland Abstract
Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle
 POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
POLISH MARITIME RESEARCH 2(78) 2013 Vol 20; pp. 13-20 10.2478/pomr-2013-0012 Numerical calculations of the hydrodynamic performance of the contra-rotating propeller (CRP) for high speed vehicle Hassan
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation
 CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
CFD Analysis of a Propeller Flow and Cavitation S. Ramakrishna* GVP College of Engineering (A) Visakhapatnam V. Ramakrishna Scientist D N S T L Visakhapatnam A. Ramakrishna Professor A U C E (A) Visakhapatnam
ROLLER BEARING FAILURES IN REDUCTION GEAR CAUSED BY INADEQUATE DAMPING BY ELASTIC COUPLINGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIONS
 ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
ROLLER BEARIG FAILURES I REDUCTIO GEAR CAUSED BY IADEQUATE DAMPIG BY ELASTIC COUPLIGS FOR LOW ORDER EXCITATIOS ~by Herbert Roeser, Trans Marine Propulsion Systems, Inc. Seattle Flexible couplings provide
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM
 DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
DESIGN OPTIMIZATION STUDY ON A CONTAINERSHIP PROPULSION SYSTEM Brian Cuneo Thomas McKenney Morgan Parker ME 555 Final Report April 19, 2010 ABSTRACT This study develops an optimization algorithm to explore
Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further.
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 213 Flexible Elliptic Oscillating Duct. Taking the FOD one step further. Gerasimos Politis 1,Theodoros Ioannou
Ship Control in Manoeuvring Situations with Fuzzy Logic Controllers
 International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number March 28 Ship Control in Manoeuvring Situations with Fuzzy Logic Controllers L. Morawski Gnia Maritime University,
International Journal on Marine Navigation and Safety of Sea Transportation Volume 2 Number March 28 Ship Control in Manoeuvring Situations with Fuzzy Logic Controllers L. Morawski Gnia Maritime University,
Yiran Su 1, Seungnam Kim 1, Weikang Du 1, Spyros A. Kinnas 2, Mikael Grekula 3, Jan Hallander 3, Da- Qing Li 3
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Prediction of the Propeller-induced Hull Pressure Fluctuation via a Potential-based Method: Study of the Rudder Effect
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Prediction of the Propeller-induced Hull Pressure Fluctuation via a Potential-based Method: Study of the Rudder Effect
A STUDY INTO RESONANT PHENOMENA IN THE CATAMARAN FERRY PROPULSION SYSTEM
 Ante Šestan Nikola Vladimir Nenad Vulić Boris Ljubenkov ISSN 1333-1124 A STUDY INTO RESONANT PHENOMENA IN THE CATAMARAN FERRY PROPULSION SYSTEM Summary UDC 629.5.015.5 This paper describes the problem
Ante Šestan Nikola Vladimir Nenad Vulić Boris Ljubenkov ISSN 1333-1124 A STUDY INTO RESONANT PHENOMENA IN THE CATAMARAN FERRY PROPULSION SYSTEM Summary UDC 629.5.015.5 This paper describes the problem
Dessi, D., D Orazio, D.
 CORRELATION OF MODEL-SCALE AND FULL-SCALE DATA: SENSOR VALIDATION AND ELASTIC SCALING EVALUATION Dessi, D., D Orazio, D. INSEAN-CNR Rome - Italy 1 Project structure hydroelastic side This work was funded
CORRELATION OF MODEL-SCALE AND FULL-SCALE DATA: SENSOR VALIDATION AND ELASTIC SCALING EVALUATION Dessi, D., D Orazio, D. INSEAN-CNR Rome - Italy 1 Project structure hydroelastic side This work was funded
A numerical DP MODULE to help design and operation for projects including DP components
 DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE November 15-16, 25 Control Systems I A numerical DP MODULE to help design and operation for projects including DP components C. Le Cunff PRINCIPIA (La Ciotat, France) Return
DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE November 15-16, 25 Control Systems I A numerical DP MODULE to help design and operation for projects including DP components C. Le Cunff PRINCIPIA (La Ciotat, France) Return
Dynamics of Machinery
 Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Dynamics of Machinery Two Mark Questions & Answers Varun B Page 1 Force Analysis 1. Define inertia force. Inertia force is an imaginary force, which when acts upon a rigid body, brings it to an equilibrium
Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers in Fully Wetted and Cavitating Flows
 Proceedings of the 7 th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV2009 Paper No. 60 August 17-22, 2009, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers
Proceedings of the 7 th International Symposium on Cavitation CAV2009 Paper No. 60 August 17-22, 2009, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA Rate-Dependent Hydroelastic Response of Self-Adaptive Composite Propellers
Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos
 Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
Session 7 Stability of Damaged Ships Numerical Simulation of Progressive Flooding and Capsize Numerical Study of the Roll Decay of Intact and Damaged Ships by Q. Gao and D. Vassalos Qiuxin Gao and Dracos
Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods
 Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Third International Symposium on Marine Propulsors smp 13, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia, May 2013 Reliability assessment of ship powering performance extrapolations using Monte Carlo methods Iwan M.
Viscous investigation of a flapping foil propulsor
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Viscous investigation of a flapping foil propulsor To cite this article: Attapol Posri et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Viscous investigation of a flapping foil propulsor To cite this article: Attapol Posri et al 2018 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Maneuvering predictions in the early design phase using CFD generated PMM data
 9th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics othenburg, Sweden, 6-31 August 01 Maneuvering predictions in the early design phase using CFD generated PMM data Claus D. Simonsen, Janne F. Otzen, Christian Klimt,
9th Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics othenburg, Sweden, 6-31 August 01 Maneuvering predictions in the early design phase using CFD generated PMM data Claus D. Simonsen, Janne F. Otzen, Christian Klimt,
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Consideration of medium-speed four-stroke engines in ship vibration analyses I. Asmussen, A. Muller-Schmerl GermanischerLloyd, P.O. Box 111606, 20416Hamburg, Germany Abstract Vibration problems were recently
Consideration of medium-speed four-stroke engines in ship vibration analyses I. Asmussen, A. Muller-Schmerl GermanischerLloyd, P.O. Box 111606, 20416Hamburg, Germany Abstract Vibration problems were recently
Quantitative Assessment of Ship Behaviour in Critical Stern Quartering Seas
 Quantitative Assessment of Ship Behaviour in Critical Stern Quartering Seas Maria Acanfora* and Jerzy Matusiak Dept. of Applied Mechanics, School of Engineering, Aalto University of Espoo, Finland Abstract:
Quantitative Assessment of Ship Behaviour in Critical Stern Quartering Seas Maria Acanfora* and Jerzy Matusiak Dept. of Applied Mechanics, School of Engineering, Aalto University of Espoo, Finland Abstract:
AN EXPLORATORY STUDY ON THE WORKING PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY SAVING DEVICES (ESDS) PIV, CFD INVESTIGATIONS AND ESD DESIGN GUIDELINES
 Proceedings of the 3 st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE22 July -6, 22, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil OMAE22-8353 AN EXPLORATORY STUDY ON THE WORKING PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY
Proceedings of the 3 st International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE22 July -6, 22, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil OMAE22-8353 AN EXPLORATORY STUDY ON THE WORKING PRINCIPLES OF ENERGY
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power
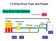 7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
7.2 Ship Drive Train and Power Ship Drive Train System EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw THP BHP SHP DHP Ship Drive Train and Power EHP Engine Reduction Gear Bearing Seals Strut Screw
Performance Analysis and Design of Vertical Axis Tidal Stream Turbine
 Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 2 (2012) 191-200 D DAVID PUBLISHING Performance Analysis and Design of Vertical Axis Tidal Stream Turbine Beom-Soo Hyun, Da-Hye Choi, Jun-Seon Han and Ji-Yuan
Journal of Shipping and Ocean Engineering 2 (2012) 191-200 D DAVID PUBLISHING Performance Analysis and Design of Vertical Axis Tidal Stream Turbine Beom-Soo Hyun, Da-Hye Choi, Jun-Seon Han and Ji-Yuan
Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods
 ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
ISSN (Print) : 2347-671 An ISO 3297: 27 Certified Organization Vol.4, Special Issue 12, September 215 Trajectory Tracking of a Near-Surface Torpedo using Numerical Methods Anties K. Martin, Anubhav C.A.,
Master Thesis. Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations
 Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
Master Thesis Investigation of inland ship resistance, propulsion and manoeuvring using literature study and potential flow calculations Author: Erik Rotteveel Supervisor: Frans Quadvlieg Graduation report
Keywords: Electric Machines, Rotating Machinery, Stator faults, Fault tolerant control, Field Weakening, Anisotropy, Dual rotor, 3D modeling
 Analysis of Electromagnetic Behavior of Permanent Magnetized Electrical Machines in Fault Modes M. U. Hassan 1, R. Nilssen 1, A. Røkke 2 1. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian University
Analysis of Electromagnetic Behavior of Permanent Magnetized Electrical Machines in Fault Modes M. U. Hassan 1, R. Nilssen 1, A. Røkke 2 1. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian University
Study on Extrapolation Method for Self-Propulsion Test with Pre-Swirl Device *
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Study on Extrapolation Method for Self-Propulsion Test with Pre-Swirl Device * Moon-Chan Kim 1, Yong-Jin Shin 1, Won-Joon
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsion smp 17, Espoo, Finland, June 2017 Study on Extrapolation Method for Self-Propulsion Test with Pre-Swirl Device * Moon-Chan Kim 1, Yong-Jin Shin 1, Won-Joon
Aalto University School of Engineering
 Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4120 Ship Structural Design (P) Lecture 8 - Local and Global Vibratory Response Kul-24.4120 Ship Structures Response Lecture 5: Tertiary Response: Bending
Aalto University School of Engineering Kul-24.4120 Ship Structural Design (P) Lecture 8 - Local and Global Vibratory Response Kul-24.4120 Ship Structures Response Lecture 5: Tertiary Response: Bending
Proceedings of the ASME th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2017 June 25-30, 2017, Trondheim, Norway
 Proceedings of the ASME 2017 36th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2017 June 25-30, 2017, Trondheim, Norway OMAE2017-61485 DETERMINING THRUSTER-HULL INTERACTION FOR
Proceedings of the ASME 2017 36th International Conference on Ocean, Offshore and Arctic Engineering OMAE2017 June 25-30, 2017, Trondheim, Norway OMAE2017-61485 DETERMINING THRUSTER-HULL INTERACTION FOR
PMarine Technology Society
 ddynamic Positioning Committee PMarine Technology Society DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 1999 DESIGN SESSION Thruster Noise Neal A. Brown NAB & Associates, Inc. & Offshore Model Basin INTRODUCTION
ddynamic Positioning Committee PMarine Technology Society DYNAMIC POSITIONING CONFERENCE October 12-13, 1999 DESIGN SESSION Thruster Noise Neal A. Brown NAB & Associates, Inc. & Offshore Model Basin INTRODUCTION
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION
 A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
A NEW WAY OF SIMULATING WHALE TAIL PROPULSION Written by: J.D. van Manen (Whale Tail Development, The Netherlands) and T. van Terwisga (MARIN, The Netherlands) Presented on 34 th WEGEMT School by: M.X.
Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array
 Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array S.Solomon Raj Dr.P.Ravinder Reddy 2. Assistant professor, department of mechanical engineering, chaitanya bharathi institute
Performance evaluation of composite marine propeller using L 8 orthogonal array S.Solomon Raj Dr.P.Ravinder Reddy 2. Assistant professor, department of mechanical engineering, chaitanya bharathi institute
Simulation of Spatial Motion of Self-propelled Mine Counter Charge
 Proceedings o the 5th WSEAS Int. Con. on System Science and Simulation in Engineering, Tenerie, Canary Islands, Spain, December 16-18, 26 1 Simulation o Spatial Motion o Sel-propelled Mine Counter Charge
Proceedings o the 5th WSEAS Int. Con. on System Science and Simulation in Engineering, Tenerie, Canary Islands, Spain, December 16-18, 26 1 Simulation o Spatial Motion o Sel-propelled Mine Counter Charge
Efficient Prediction of Crashback Performance of Controllable Pitch Propellers
 Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 217 Efficient Prediction of Crashback Performance of Controllable Pitch Propellers Markus Pergande, Keqi Wang, Jan Clemens
Fifth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors SMP 17, Espoo, Finland, June 217 Efficient Prediction of Crashback Performance of Controllable Pitch Propellers Markus Pergande, Keqi Wang, Jan Clemens
VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION OF RESISTANCE AND PROPULSION COMPUTATION
 VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION OF RESISTANCE AND PROPULSION COMPUTATION G. Deng, A. Leroyer, E. Guilmineau, P. Queutey, M. Visonneau & J. Wackers (ECN-LHEEA,CNRS, France) A. del Toro Llorens (Spanish Institution
VERIFICATION AND VALIDATION OF RESISTANCE AND PROPULSION COMPUTATION G. Deng, A. Leroyer, E. Guilmineau, P. Queutey, M. Visonneau & J. Wackers (ECN-LHEEA,CNRS, France) A. del Toro Llorens (Spanish Institution
EXCITATION OF A SUBMARINE HULL BY PROPELLER FORCES. Sydney, NSW 2052, Australia 2 Senior Visiting Research Fellow, University of New South Wales
 ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 27 EXCITATION OF A SUBMARINE HULL BY PROPELLER FORCES Sascha Merz 1, Nicole Kessissoglou 1 and Roger Kinns 2 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University
ICSV14 Cairns Australia 9-12 July, 27 EXCITATION OF A SUBMARINE HULL BY PROPELLER FORCES Sascha Merz 1, Nicole Kessissoglou 1 and Roger Kinns 2 1 School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University
developed at "Dunarea de Jos" University of Galati Presented by: BENZOHRA Abdelmalek
 Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Master Thesis presented in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the double degree: Advanced Master in Naval Architecture conferred by University of Liege "Master of Sciences in Applied Mechanics,
Thrust allocation system for Blue Lady training ship taking into account efficient work of main propeller
 Scientific Journals Maritime University of Szczecin Zeszyty Naukowe Akademia Morska w Szczecinie 013, 36(108) z. pp. 13 130 013, 36(108) z. s. 13 130 ISSN 1733-8670 Thrust allocation system for Blue Lady
Scientific Journals Maritime University of Szczecin Zeszyty Naukowe Akademia Morska w Szczecinie 013, 36(108) z. pp. 13 130 013, 36(108) z. s. 13 130 ISSN 1733-8670 Thrust allocation system for Blue Lady
Mechanical Principles
 Unit 8: Unit code Mechanical Principles F/615/1482 Unit level 4 Credit value 15 Introduction Mechanical principles have been crucial for engineers to convert the energy produced by burning oil and gas
Unit 8: Unit code Mechanical Principles F/615/1482 Unit level 4 Credit value 15 Introduction Mechanical principles have been crucial for engineers to convert the energy produced by burning oil and gas
