Revision Materials. Functions, Quadratics & Polynomials Skills Builder
|
|
|
- Allen McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematics Higher Revision Materials Functions, Quadratics & Polynomials Skills Builder Layout and content of the Unit Assessment will be different. This is not meant to be a carbon copy of the Unit Assessment. This booklet is an opportunity to practice all of the essential skills required to pass the Unit Assessment. This booklet should be used to identify any areas for improvement before you sit the Unit assessment for the first time. Unit Assessment standard H4LD 76 Relationships and Calculus RC1.1 Applying algebraic skills to solve equations factorising a cubic polynomial expression with unitary x coefficient solving cubic polynomial equations with unitary x coefficient given the nature of the roots of an equation, use the discriminant to find an unknown RC#2.1 Interpreting a situation where mathematics can be used and identifying a valid strategy For candidates undertaking the Course, Assessment Standard 2.1 should be achieved on at least two occasions from across the Course. H4LC 76 Expressions and Functions EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions identifying and sketching related algebraic functions identifying and sketching related trigonometric functions determining composite and inverse functions (knowledge and use of the terms domain and range is expected) EF#2.1 Interpreting a situation where mathematics can be used and identifying a valid strategy For candidates undertaking the Course, Assessment Standard 2.1 should be achieved on at least two occasions from across the Course. EF#2.2 Explaining a solution and, where appropriate, relating it to context For candidates undertaking the Course, Assessment Standard 2.2 should be achieved on at least two occasions from across the Course.
2 RC1.1 Applying algebraic skills to solve equations RC#2.1 Interpreting a situation where mathematics can be used and identifying a valid strategy factorising a cubic polynomial expression with unitary x coefficient (extended to non-unitary) solving cubic polynomial equations with unitary x coefficient (extended to non-unitary) Q1 a) Show that (x 1) is a factor of f(x) = 2x 5x 2 2x + 5 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation 2x x 2 2x + = 4x 2 2 Q2 a) Show that (x ) is a factor of f(x) = x 17x x 15 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation x 15x x 14 = 2x Q a) Show that (x 1) is a factor of f(x) = 2x x 2 5x + 6 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation 2x 2x 2 + x + 1 = x 2 + 8x + 7 Q4 a) Show that (x + ) is a factor of f(x) = x + 4x 2 17x 60 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation 2x + 4x 2 17x 61 = x 1 Q5 a) Show that (x 2) is a factor of f(x) = 2x 9x 2 + 1x 6 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation 2x 1x 2 + 1x 1 = 5 4x 2 Q6 a) Show that (x + ) is a factor of f(x) = x + 20x x 12 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation x + 22x x 19 = 2x 2 7 Q7 a) Show that (x + 1) is a factor of f(x) = 2x 8x 2 + 2x + 12 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation 2x 11x 2 + x + 1 = 1 x x 2 Q8 a) Show that (x + ) is a factor of f(x) = 2x + x 2 12x + 9 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation 2x + 6x 2 1x + 9 = 5x 2 x Q9 a) Show that (x 2) is a factor of f(x) = x 2x 2 x + 2 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation x 2x 2 + 8x + 1 = 9x 1 Q10 a) Show that (x 4) is a factor of f(x) = x 25x x 16 and hence factorise f(x) fully. b) Hence solve the equation x + 5x x 15 = 0x 2 29x + 1
3 RC1.1 Applying algebraic skills to solve equations given the nature of the roots of an equation, use the discriminant to find an unknown Q11 Each of the following functions has 2 real and distinct roots. Calculate the range of values for k so that the function will maintain 2 real and distinct roots. a) f(x) = kx 2 + 6x + 8 b) f(x) = x 2 + kx + 12 c) f(x) = 4x 2 2x + k d) f(x) = kx 2 + 7x + 12 e) f(x) = 2x 2 + kx + 2 f) f(x) = 4x 2 + x + k g) f(x) = kx 2 5x + 6 h) f(x) = x 2 + kx + 8 i) f(x) = x 2 + x + k j) f(x) = kx 2 6x + 8 Q12 For what values of p does the equation x 2 2x + p = 0 have: a) equal roots b) real and distinct roots c) non real roots Q1 Q14 Find m given that x 2 + mx + x + 9 = 0 has equal roots. Find the values of a, b and c if each of the equations have equal roots a) ax 2 + 4x + 2 = 0 b) x 2 + bx + = 0 c) x 2 + 6x + c = 0 Q15 Q16 Q17 Q18 Q19 For what value of t does tx 2 + 6x + t = 0 have equal roots? Find the value of q if x 2 + (q )x + 1 = 0 has equal roots. Find the range of values of m for which 5x 2 mx + 5 = 0 has two real and distinct roots. For what value of k does the graph y = kx 2 kx + 9 touch the x axis. Find the values for n which ensure that the following equations have equal roots: a) x 2 +1 x = n b) (x 2) 2 x 2 +2 = n Q20 find k if (2k 2)x x + k = 0 has: a) equal roots b) real and distinct roots
4 EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions. identifying and sketching related algebraic functions Q21 The graph of y = f(x) is shown opposite. a) Sketch y = f(x 2) b) Sketch y = f(x) + 5 c) Sketch y = f(x 1) + 2 d) Sketch y = f( x) e) Sketch y = 2f(x 4) Q22 The graph of y = g(x) is shown opposite. a) Sketch y = g(x + ) b) Sketch y = g(x) 4 c) Sketch y = g(x 2) 1 d) Sketch y = g( x) e) Sketch y = 2g(x + 1) Q2 The graph of y = h(x) is shown opposite. a) Sketch y = h(x 1) b) Sketch y = h(x) + 2 c) Sketch y = h(x + 1) + 4 d) Sketch y = h(x) e) Sketch y = 2h(x) Q24 The graph of y = k(x) is shown opposite. a) Sketch y = k(x ) b) Sketch y = k(x) 2 c) Sketch y = k(x 1) + d) Sketch y = k(x) e) Sketch y = 4k(x )
5 EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions. identifying and sketching related algebraic functions Q25 For each of the following graphs identify the value of a. a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions. determining composite and inverse functions (knowledge and use of the terms domain and range is expected) Q26 Write down the equation of the inverse functions for the following. a) f(x) = 2 x b) f(x) = x c) f(x) = 4 x d) f(x) = 7 x e) f(x) = a x f) f(x) = 10 x g) f(x) = e x h) f(x) = 5 x i) f(x) = ( 1 2 )x j) f(x) = 9 x k) f(x) = ( 2 )x l) f(x) = ( 1 5 )x
6 EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions determining composite and inverse functions (knowledge and use of the terms domain and range is expected) Q27 Determine the inverse function for each of the following, assuming an appropriate domain and range. a) f(x) = 5x 2 b) f(x) = 4x c) f(x) = 2x + 7 d) f(x) = x 2 4 e) f(x) = 5x f) f(x) = 2(x 1) 2 g) f(x) = 5x 2 h) f(x) = (x 2) 2 i) f(x) = 2(x + 1) 2 EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions EF#2.2 Explaining a solution and, where appropriate, relating it to context determining composite and inverse functions (knowledge and use of the terms domain and range is expected) Q28 In each of the examples below, functions f and g are defined on suitable domains. For each question, obtain expressions for f(g(x)) and g(f(x)) in their simplest form. a) f(x) = x 2 g(x) = x 2 b) f(x) = 2x + 1 g(x) = x 2 2x + 1 c) f(x) = 5x g(x) = x+, explain the relationship between f(x)and g(x). 5 d) f(x) = 4 x g(x) = 4 x, explain the relationship between f(x)and g(x). e) f(x) = x g(x) = (x + 1) 2 f) f(x) = 2 x 4 g(x) = x + 6, explain the relationship between f(x)and g(x). 2 g) f(x) = 2x 2 g(x) = x 1 h) f(x) = x + 5 g(x) = 2 x+1 i) f(x) = x 2 x+1 g(x) = 1 x 2 j) f(x) = x + 4 g(x) = x 2 4, explain the relationship between f(x)and g(x).
7 EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions identifying and sketching related trigonometric functions Q29 Sketch each of the following trigonometric functions, where 0 x 2π a) y = sin x b) y = cos x c) y = 2 sin x d) y = cos x e) y = sin x + f) y = cos x 4 g) y = sin 2x h) y = cos ( 1 2 x) i) y = sin x j) y = cos x k) y = 2 sin x 1 l) y = 2 cos x EF1. Applying algebraic and trigonometric skills to functions EF#2.1 Interpreting a situation where mathematics can be used and identifying a valid strategy identifying and sketching related trigonometric functions Q0 Use the information provided in the table below to identify the equation of the curves. All equations are of the form y = a sin bx + c or y = a cos bx + c. Type of curve Domain Maximum occurs at Minimum occurs at a) sine 0 x π ( π 4, 1 ) ( π 4, 1 ) b) cosine 0 x π 2 ( 0, 1 ) ( π 2, 1 ) ( π 4, 1 ) c) sine 0 x 2π ( π, ) 2 ( π, 1 ) 2 d) cosine 0 x π ( 0, ) ( π, ) ( π, ) 2 e) sine 0 x 2π ( π, 5 ) 2 ( π, ) 2 f) cosine 0 x 2π ( π, 1 ) ( 0, ) ( 2π, ) g) sine 0 x π ( π, 5 ) 4 ( π, 1 ) 4 h) cosine 0 x π ( 0, 2) ( π, 2 ) ( π, 4 ) 2 i) sine 0 x 2π j) cosine 0 x π 2 ( π 6, 4 ) ( π 2, 2 ) ( π 4, 1 ) ( 0, ) ( π 2, ) Q1 Use your answers from Q0 to sketch the graphs of the trigonometric functions.
8 ANSWERS Q1 a) f(x) = (x + 1)(x 1)(2x 5) b) x = 1, 1, 5 2 Q2 a) f(x) = (x )(x 1)(x 5) b) x =, 1, 5 Q a) f(x) = (x 1)(x 2)(2x + ) b) x = 1, 2, 2 Q4 a) f(x) = (x + )(x + 5)(x 4) b) x =, 5, 4 Q5 a) f(x) = (x 2)(x 1)(2x ) b) x = 2, 1, 2 Q6 a) f(x) = (x + )(x + 4)(x 1) b) x =, 4, 1 Q7 a) f(x) = 2(x + 1)(x )(x 2) b) x = 1,, 2 Q8 a) f(x) = (x + )(x 1)(2x ) b) x =, 1, 2 Q9 a) f(x) = (x 2)(x 1)(x + 1) b) x = 1, 1, 2 Q10 a) f(x) = (x 4)(x 4)(x 1) b) x = 4, 1 Q11 a) k < 9 8 c) k < 1 4 b) k > 12, k < 12 d) k < e) All values of k f) k > 1 16 g) k < h) k > 4 6, k < 4 6 i) k > 1 4 j) k < 9 8 Q12 a) p = 1 b) p 1 c) p > 1 Q1 m = 5, 7 Q14 a) a = 2 b) b = ±6 c) c = 9 Q15 t = ± Q16 q = 1, 5 Q17 m 10, m 10 Q18 k = 4, k 0 as then y = 9. This line cannot touch the x axis Q19 a) n = ±2 b) n = 0, Q20 a) k = 9, 8 b) k < 8, k > 9
9 Q21 Q22
10 Q2 Q24
11 Q25 a) a = b) a = 2 c) a = 7 d) ka = e) a = 4 f) a = 2 g) a = 1 2 h) a = 1 Q26 a) y = log 2 x b) y = log x c) y = log 4 x d) y = log 7 x e) y = log a x f) y = log 10 x g) y = log e x or ln x h) y = log 5 x i) y = log1 x j) y = log 9 x 2 k) y = log2 Q27 a) f 1 (x) = x+2 5 x l) y = log1 x 5 b) f 1 (x) = x 4 d) f 1 (x) = 4x + 2 e) f 1 (x) = 2x 10 c) f 1 (x) = x 7 2 f) f 1 (x) = x+2 6 g) f 1 (x) = x 5 h) f 1 (x) = x + 2 i) f 1 (x) = 2( x 2) 6 Q28 a) f(g(x)) = x 2 2 g(f(x)) = (x 2) 2 b) f(g(x)) = 2x 2 4x + g(f(x)) = 4x 2 c) f(g(x)) = x g(f(x)) = x f(x) = g 1 (x) and f 1 (x) = g(x) (inverse of each other) d) f(g(x)) = x g(f(x)) = x f(x) = g 1 (x) and f 1 (x) = g(x) (inverse of each other) e) f(g(x)) = (x + 1) g(f(x)) = (x 2 + 2) 2 f) f(g(x)) = x g(f(x)) = x f(x) = g 1 (x) and f 1 (x) = g(x) (inverse of each other) g) f(g(x)) = 1 + 4x 2x 2 g(f(x)) = 2(1 + x)(1 x) h) f(g(x)) = 6 x g(f(x)) = 2 (x+2) i) f(g(x)) = 5 2x x 1 g(f(x)) = (x+1) (x+4) j) f(g(x)) = x g(f(x)) = x f(x) = g 1 (x) and f 1 (x) = g(x) (inverse of each other)
12 Q29
13 Q0 a) y = sin 2x b) y = cos 4x c) y = sin x + 2 d) y = cos 2x e) y = sin x + 4 f) y = cos x 2 g) y = 2sin 2x + h) y = cos 2x 1 i) y = sin x + 1 j) y = 2cos 4x 1 Q1
Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials
 Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials Higher 5. Quadratics and Polynomials Section A - Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic R1 I have
Higher Portfolio Quadratics and Polynomials Higher 5. Quadratics and Polynomials Section A - Revision Section This section will help you revise previous learning which is required in this topic R1 I have
f and radius , where is the angle between a and b sin A B sin Acos B cos Asin cos A B cos Acos B msin Asin sin 2A 2sin Acos cos 2 cos sin A A A
 FORMULAE LIST Circle: The equation 2 2 x y gx fy c 2 2 0 represents a circle centre g, f and radius 2 2 2 x a y b r The equation represents a circle centre ab, and radius r. 2 2 g f c. Scalar Product:
FORMULAE LIST Circle: The equation 2 2 x y gx fy c 2 2 0 represents a circle centre g, f and radius 2 2 2 x a y b r The equation represents a circle centre ab, and radius r. 2 2 g f c. Scalar Product:
Quadratics. SPTA Mathematics Higher Notes
 H Quadratics SPTA Mathematics Higher Notes Quadratics are expressions with degree 2 and are of the form ax 2 + bx + c, where a 0. The Graph of a Quadratic is called a Parabola, and there are 2 types as
H Quadratics SPTA Mathematics Higher Notes Quadratics are expressions with degree 2 and are of the form ax 2 + bx + c, where a 0. The Graph of a Quadratic is called a Parabola, and there are 2 types as
A Library of Functions
 LibraryofFunctions.nb 1 A Library of Functions Any study of calculus must start with the study of functions. Functions are fundamental to mathematics. In its everyday use the word function conveys to us
LibraryofFunctions.nb 1 A Library of Functions Any study of calculus must start with the study of functions. Functions are fundamental to mathematics. In its everyday use the word function conveys to us
NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018
 NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018 A] Refer to your pre-calculus notebook, the internet, or the sheets/links provided for assistance. B] Do not wait until the last minute to complete this
NAME: DATE: CLASS: AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER MATH 2018 A] Refer to your pre-calculus notebook, the internet, or the sheets/links provided for assistance. B] Do not wait until the last minute to complete this
Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet. Types of Functions
 MATH 1142 NAME Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet Types of Functions Now that we have discussed what functions are and some of their characteristics, we will explore different types of functions. Section 0.2
MATH 1142 NAME Section 0.2 & 0.3 Worksheet Types of Functions Now that we have discussed what functions are and some of their characteristics, we will explore different types of functions. Section 0.2
, g : x x 6, Sketch, in a single diagram, the graphs of y = f(x) and y = f -1 (x), making clear the
 PAST QUESTION ON FUNCTIONS 1. Express x + 4x in the form (x + a) + b, stating the numerical values of a and b. The functions f and g are defined as follows : f : x x 4x, x, g : x x 6, x R (ii) (iii) Show
PAST QUESTION ON FUNCTIONS 1. Express x + 4x in the form (x + a) + b, stating the numerical values of a and b. The functions f and g are defined as follows : f : x x 4x, x, g : x x 6, x R (ii) (iii) Show
Candidates are expected to have available a calculator. Only division by (x + a) or (x a) will be required.
 Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
C3 Revision Questions. (using questions from January 2006, January 2007, January 2008 and January 2009)
 C3 Revision Questions (using questions from January 2006, January 2007, January 2008 and January 2009) 1 2 1. f(x) = 1 3 x 2 + 3, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (a) 2 x x 1 Show that f(x) =, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (4) (b) Show
C3 Revision Questions (using questions from January 2006, January 2007, January 2008 and January 2009) 1 2 1. f(x) = 1 3 x 2 + 3, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (a) 2 x x 1 Show that f(x) =, x 2. 2 ( x 2) (4) (b) Show
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra
 Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
Test 2 Review Math 1111 College Algebra 1. Begin by graphing the standard quadratic function f(x) = x 2. Then use transformations of this graph to graph the given function. g(x) = x 2 + 2 *a. b. c. d.
Higher Mathematics Skills Checklist
 Higher Mathematics Skills Checklist 1.1 The Straight Line (APP) I know how to find the distance between 2 points using the Distance Formula or Pythagoras I know how to find gradient from 2 points, angle
Higher Mathematics Skills Checklist 1.1 The Straight Line (APP) I know how to find the distance between 2 points using the Distance Formula or Pythagoras I know how to find gradient from 2 points, angle
HEINEMANN HIGHER CHECKLIST
 St Ninian s High School HEINEMANN HIGHER CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = Name Class Teacher I do not understand this part of the course = Topic
St Ninian s High School HEINEMANN HIGHER CHECKLIST I understand this part of the course = I am unsure of this part of the course = Name Class Teacher I do not understand this part of the course = Topic
Math 110 Midterm 1 Study Guide October 14, 2013
 Name: For more practice exercises, do the study set problems in sections: 3.4 3.7, 4.1, and 4.2. 1. Find the domain of f, and express the solution in interval notation. (a) f(x) = x 6 D = (, ) or D = R
Name: For more practice exercises, do the study set problems in sections: 3.4 3.7, 4.1, and 4.2. 1. Find the domain of f, and express the solution in interval notation. (a) f(x) = x 6 D = (, ) or D = R
Core 3 (A2) Practice Examination Questions
 Core 3 (A) Practice Examination Questions Trigonometry Mr A Slack Trigonometric Identities and Equations I know what secant; cosecant and cotangent graphs look like and can identify appropriate restricted
Core 3 (A) Practice Examination Questions Trigonometry Mr A Slack Trigonometric Identities and Equations I know what secant; cosecant and cotangent graphs look like and can identify appropriate restricted
Examples 2: Composite Functions, Piecewise Functions, Partial Fractions
 Examples 2: Composite Functions, Piecewise Functions, Partial Fractions September 26, 206 The following are a set of examples to designed to complement a first-year calculus course. objectives are listed
Examples 2: Composite Functions, Piecewise Functions, Partial Fractions September 26, 206 The following are a set of examples to designed to complement a first-year calculus course. objectives are listed
Math 150 Midterm 1 Review Midterm 1 - Monday February 28
 Math 50 Midterm Review Midterm - Monday February 28 The midterm will cover up through section 2.2 as well as the little bit on inverse functions, exponents, and logarithms we included from chapter 5. Notes
Math 50 Midterm Review Midterm - Monday February 28 The midterm will cover up through section 2.2 as well as the little bit on inverse functions, exponents, and logarithms we included from chapter 5. Notes
Math 12 Final Exam Review 1
 Math 12 Final Exam Review 1 Part One Calculators are NOT PERMITTED for this part of the exam. 1. a) The sine of angle θ is 1 What are the 2 possible values of θ in the domain 0 θ 2π? 2 b) Draw these angles
Math 12 Final Exam Review 1 Part One Calculators are NOT PERMITTED for this part of the exam. 1. a) The sine of angle θ is 1 What are the 2 possible values of θ in the domain 0 θ 2π? 2 b) Draw these angles
Book 4. June 2013 June 2014 June Name :
 Book 4 June 2013 June 2014 June 2015 Name : June 2013 1. Given that 4 3 2 2 ax bx c 2 2 3x 2x 5x 4 dxe x 4 x 4, x 2 find the values of the constants a, b, c, d and e. 2. Given that f(x) = ln x, x > 0 sketch
Book 4 June 2013 June 2014 June 2015 Name : June 2013 1. Given that 4 3 2 2 ax bx c 2 2 3x 2x 5x 4 dxe x 4 x 4, x 2 find the values of the constants a, b, c, d and e. 2. Given that f(x) = ln x, x > 0 sketch
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS
 DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS A2 level Mathematics Core 3 course workbook 2015-2016 Name: Welcome to Core 3 (C3) Mathematics. We hope that you will use this workbook to give you an organised set of notes for
DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS A2 level Mathematics Core 3 course workbook 2015-2016 Name: Welcome to Core 3 (C3) Mathematics. We hope that you will use this workbook to give you an organised set of notes for
3. Use absolute value notation to write an inequality that represents the statement: x is within 3 units of 2 on the real line.
 PreCalculus Review Review Questions 1 The following transformations are applied in the given order) to the graph of y = x I Vertical Stretch by a factor of II Horizontal shift to the right by units III
PreCalculus Review Review Questions 1 The following transformations are applied in the given order) to the graph of y = x I Vertical Stretch by a factor of II Horizontal shift to the right by units III
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2013/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
Introduction Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 201/2014 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 121 - Calculus 1, Fall 201/2014! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics
Core Mathematics 1 Quadratics
 Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 1 Quadratics Quadratics September 011 C1 Note Quadratic functions and their graphs. The graph of y ax bx c. (i) a 0 (ii) a 0 The turning point can be determined
Regent College Maths Department Core Mathematics 1 Quadratics Quadratics September 011 C1 Note Quadratic functions and their graphs. The graph of y ax bx c. (i) a 0 (ii) a 0 The turning point can be determined
REQUIRED MATHEMATICAL SKILLS FOR ENTERING CADETS
 REQUIRED MATHEMATICAL SKILLS FOR ENTERING CADETS The Department of Applied Mathematics administers a Math Placement test to assess fundamental skills in mathematics that are necessary to begin the study
REQUIRED MATHEMATICAL SKILLS FOR ENTERING CADETS The Department of Applied Mathematics administers a Math Placement test to assess fundamental skills in mathematics that are necessary to begin the study
Algebra III. Mathematics Curriculum Framework. Revised 2004
 Algebra III Mathematics Curriculum Framework Revised 2004 Title: Algebra III (Fourth-year Course) Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: Teacher Licensure: Secondary Mathematics Pre-requisite: Algebra II
Algebra III Mathematics Curriculum Framework Revised 2004 Title: Algebra III (Fourth-year Course) Course/Unit Credit: 1 Course Number: Teacher Licensure: Secondary Mathematics Pre-requisite: Algebra II
Chapter 7 Algebra 2 Honors 1 Polynomials
 Chapter 7 Algebra 2 Honors 1 Polynomials Polynomial: - - Polynomials in one variable Degree Leading coefficient f(x) = 3x 3 2x + 4 f(2) = f(t) = f(y -1) = 3f(x) = Using your graphing calculator sketch/graph
Chapter 7 Algebra 2 Honors 1 Polynomials Polynomial: - - Polynomials in one variable Degree Leading coefficient f(x) = 3x 3 2x + 4 f(2) = f(t) = f(y -1) = 3f(x) = Using your graphing calculator sketch/graph
N5 R1.2 and R1.3 Quadratics - Revision
 N5 R and R3 Quadratics - Revision This revision pack covers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level for Quadratics so you can evaluate your learning of this outcome. It is important that you prepare
N5 R and R3 Quadratics - Revision This revision pack covers the skills at Unit Assessment and exam level for Quadratics so you can evaluate your learning of this outcome. It is important that you prepare
Summer Math Packet: Incoming Calculus I* students
 Summer Math Packet: Incoming Calculus I* students Directions: One of the most challenging aspects of Calculus is that it requires you to use content from all your previous math courses. You will be better
Summer Math Packet: Incoming Calculus I* students Directions: One of the most challenging aspects of Calculus is that it requires you to use content from all your previous math courses. You will be better
Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; differentiation; integration; vectors.
 Revision Checklist Unit C4: Core Mathematics 4 Unit description Assessment information Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; differentiation; integration;
Revision Checklist Unit C4: Core Mathematics 4 Unit description Assessment information Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; differentiation; integration;
Math Academy I Fall Study Guide. CHAPTER ONE: FUNDAMENTALS Due Thursday, December 8
 Name: Math Academy I Fall Study Guide CHAPTER ONE: FUNDAMENTALS Due Thursday, December 8 1-A Terminology natural integer rational real complex irrational imaginary term expression argument monomial degree
Name: Math Academy I Fall Study Guide CHAPTER ONE: FUNDAMENTALS Due Thursday, December 8 1-A Terminology natural integer rational real complex irrational imaginary term expression argument monomial degree
MODULE 1: FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS
 MODULE 1: FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. acquire competency in the application of algebraic techniques; 2. appreciate the role of exponential
MODULE 1: FOUNDATIONS OF MATHEMATICS GENERAL OBJECTIVES On completion of this Module, students should: 1. acquire competency in the application of algebraic techniques; 2. appreciate the role of exponential
Higher Maths - Expressions and Formulae Revision Questions
 Higher Maths - Expressions and Formulae Revision Questions Outcome 1.1 Applying algebraic skills to logarithms and exponentials 1. Simplify fully (a) log 42 + log 48 (b) log 3108 log 34 (c) log 318 - log
Higher Maths - Expressions and Formulae Revision Questions Outcome 1.1 Applying algebraic skills to logarithms and exponentials 1. Simplify fully (a) log 42 + log 48 (b) log 3108 log 34 (c) log 318 - log
A Level Maths summer preparation work
 A Level Maths summer preparation work Welcome to A Level Maths! We hope you are looking forward to two years of challenging and rewarding learning. You must make sure that you are prepared to study A Level
A Level Maths summer preparation work Welcome to A Level Maths! We hope you are looking forward to two years of challenging and rewarding learning. You must make sure that you are prepared to study A Level
CHAPTER 2 POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS
 CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
CHAPTER POLYNOMIALS KEY POINTS 1. Polynomials of degrees 1, and 3 are called linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials respectively.. A quadratic polynomial in x with real coefficient is of the form a x
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW
 CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
Free download from not for resale. Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle.
 Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle. Area of a triangle using trigonometry. Using the Sine Rule. Using the Cosine Rule to find a side. Using the Cosine
Apps 1.1 : Applying trigonometric skills to triangles which do not have a right angle. Area of a triangle using trigonometry. Using the Sine Rule. Using the Cosine Rule to find a side. Using the Cosine
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS
 QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic functions. Write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of functions. Find minimum and
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS AND MODELS What You Should Learn Analyze graphs of quadratic functions. Write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of functions. Find minimum and
Lesson 18: Problem Set Sample Solutions
 Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems 5 7 serve to review the process of computing f(g(x)) for given functions f and g in preparation for work with inverses of functions in Lesson 19. 1. Sketch the graphs
Problem Set Sample Solutions Problems 5 7 serve to review the process of computing f(g(x)) for given functions f and g in preparation for work with inverses of functions in Lesson 19. 1. Sketch the graphs
Tropical Polynomials
 1 Tropical Arithmetic Tropical Polynomials Los Angeles Math Circle, May 15, 2016 Bryant Mathews, Azusa Pacific University In tropical arithmetic, we define new addition and multiplication operations on
1 Tropical Arithmetic Tropical Polynomials Los Angeles Math Circle, May 15, 2016 Bryant Mathews, Azusa Pacific University In tropical arithmetic, we define new addition and multiplication operations on
SUBJECT: ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM OUTLINE LEVEL: 3 TOPIC OBJECTIVES ASSIGNMENTS / ASSESSMENT WEB-BASED RESOURCES. Online worksheet.
 TERM 1 Simultaneous Online worksheet. Week 1 Equations in two Solve two simultaneous equations where unknowns at least one is a linear equation, by http://www.tutorvista.com/mat substitution. Understand
TERM 1 Simultaneous Online worksheet. Week 1 Equations in two Solve two simultaneous equations where unknowns at least one is a linear equation, by http://www.tutorvista.com/mat substitution. Understand
Unit 3: HW3.5 Sum and Product
 Unit 3: HW3.5 Sum and Product Without solving, find the sum and product of the roots of each equation. 1. x 2 8x + 7 = 0 2. 2x + 5 = x 2 3. -7x + 4 = -3x 2 4. -10x 2 = 5x - 2 5. 5x 2 2x 3 4 6. 1 3 x2 3x
Unit 3: HW3.5 Sum and Product Without solving, find the sum and product of the roots of each equation. 1. x 2 8x + 7 = 0 2. 2x + 5 = x 2 3. -7x + 4 = -3x 2 4. -10x 2 = 5x - 2 5. 5x 2 2x 3 4 6. 1 3 x2 3x
S4 (4.3) Quadratic Functions.notebook February 06, 2018
 Daily Practice 2.11.2017 Q1. Multiply out and simplify 3g - 5(2g + 4) Q2. Simplify Q3. Write with a rational denominator Today we will be learning about quadratic functions and their graphs. Q4. State
Daily Practice 2.11.2017 Q1. Multiply out and simplify 3g - 5(2g + 4) Q2. Simplify Q3. Write with a rational denominator Today we will be learning about quadratic functions and their graphs. Q4. State
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Fall 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Fall 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Fall 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from Algebra
There are three units of study within the Pure Mathematics Specialisation. ATPPMA001 - Unit 1:
 The Pure Mathematics Specialisation applies to those who require foundation General Mathematic knowledge and skills for entrance to tertiary study in a relevant discipline or field. There are three units
The Pure Mathematics Specialisation applies to those who require foundation General Mathematic knowledge and skills for entrance to tertiary study in a relevant discipline or field. There are three units
function independent dependent domain range graph of the function The Vertical Line Test
 Functions A quantity y is a function of another quantity x if there is some rule (an algebraic equation, a graph, a table, or as an English description) by which a unique value is assigned to y by a corresponding
Functions A quantity y is a function of another quantity x if there is some rule (an algebraic equation, a graph, a table, or as an English description) by which a unique value is assigned to y by a corresponding
Course outline Mathematics: Methods ATAR Year 11
 Course outline Mathematics: Methods ATAR Year 11 Unit 1 Sequential In Unit 1 students will be provided with opportunities to: underst the concepts techniques in algebra, functions, graphs, trigonometric
Course outline Mathematics: Methods ATAR Year 11 Unit 1 Sequential In Unit 1 students will be provided with opportunities to: underst the concepts techniques in algebra, functions, graphs, trigonometric
2001 Higher Maths Non-Calculator PAPER 1 ( Non-Calc. )
 001 PAPER 1 ( Non-Calc. ) 1 1) Find the equation of the straight line which is parallel to the line with equation x + 3y = 5 and which passes through the point (, 1). Parallel lines have the same gradient.
001 PAPER 1 ( Non-Calc. ) 1 1) Find the equation of the straight line which is parallel to the line with equation x + 3y = 5 and which passes through the point (, 1). Parallel lines have the same gradient.
CALCULUS II - Self Test
 175 2- CALCULUS II - Self Test Instructor: Andrés E. Caicedo November 9, 2009 Name These questions are divided into four groups. Ideally, you would answer YES to all questions in group A, to most questions
175 2- CALCULUS II - Self Test Instructor: Andrés E. Caicedo November 9, 2009 Name These questions are divided into four groups. Ideally, you would answer YES to all questions in group A, to most questions
Pre-Calculus Summer Math Packet 2018 Multiple Choice
 Pre-Calculus Summer Math Packet 208 Multiple Choice Page A Complete all work on separate loose-leaf or graph paper. Solve problems without using a calculator. Write the answers to multiple choice questions
Pre-Calculus Summer Math Packet 208 Multiple Choice Page A Complete all work on separate loose-leaf or graph paper. Solve problems without using a calculator. Write the answers to multiple choice questions
Calculus Summer Math Practice. 1. Find inverse functions Describe in words how you use algebra to determine the inverse function.
 1 Calculus 2017-2018: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Calculus Summer Math Practice Please see the math department document for instructions on setting
1 Calculus 2017-2018: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Calculus Summer Math Practice Please see the math department document for instructions on setting
(a) Write down the value of q and of r. (2) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry. (1) (c) Find the value of p. (3) (Total 6 marks)
 1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
PART ONE: Solve algebraically and check. Be sure to show all work.
 NAME AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2017 DIRECTIONS: Each part must be completed separately on looseleaf. All work should be shown and done in a neat and precise manner. Any questions pertaining to the
NAME AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2017 DIRECTIONS: Each part must be completed separately on looseleaf. All work should be shown and done in a neat and precise manner. Any questions pertaining to the
Free download from not for resale. Apps 1.1 : Applying algebraic skills to rectilinear shapes.
 Free download from, not for resale. Apps 1.1 : Applying algebraic skills to rectilinear shapes. Gradients m = tanθ Distance Formula Midpoint Formula Parallel lines Perpendicular lines y = mx + c y - b
Free download from, not for resale. Apps 1.1 : Applying algebraic skills to rectilinear shapes. Gradients m = tanθ Distance Formula Midpoint Formula Parallel lines Perpendicular lines y = mx + c y - b
1 FUNCTIONS _ 5 _ 1.0 RELATIONS
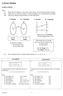 1 FUNCTIONS 1.0 RELATIONS Notes : (i) Four types of relations : one-to-one many-to-one one-to-many many-to-many. (ii) Three ways to represent relations : arrowed diagram set of ordered pairs graph. (iii)
1 FUNCTIONS 1.0 RELATIONS Notes : (i) Four types of relations : one-to-one many-to-one one-to-many many-to-many. (ii) Three ways to represent relations : arrowed diagram set of ordered pairs graph. (iii)
LESMAHAGOW HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department. National 5. Relationships Scheme of Work
 LESMAHAGOW HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department National 5 Relationships Scheme Work Relationships Main Resource (Supplementary resource Int 2 Credit Book 1/2) Applying algebraic skills to linear equations
LESMAHAGOW HIGH SCHOOL Mathematics Department National 5 Relationships Scheme Work Relationships Main Resource (Supplementary resource Int 2 Credit Book 1/2) Applying algebraic skills to linear equations
National 5 Learning Checklist - Relationships
 National 5 Learning Checklist - Relationships Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Straight Line Gradient Represented b m Measure of steepness of slope Positive gradient the line is increasing Negative gradient
National 5 Learning Checklist - Relationships Topic Skills Extra Stud / Notes Straight Line Gradient Represented b m Measure of steepness of slope Positive gradient the line is increasing Negative gradient
Name: Date: Block: FUNCTIONS TEST STUDY GUIDE
 Algebra STUDY GUIDE AII.6, AII.7 Functions Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Test covers: Graphing using transformations FUNCTIONS TEST STUDY GUIDE Analyzing functions, including finding domain/range in
Algebra STUDY GUIDE AII.6, AII.7 Functions Mrs. Grieser Name: Date: Block: Test covers: Graphing using transformations FUNCTIONS TEST STUDY GUIDE Analyzing functions, including finding domain/range in
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS GCE NORMAL ACADEMIC LEVEL (016) (Syllabus 4044) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION AIMS ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 3 USE OF CALCULATORS 3 SUBJECT CONTENT 4 MATHEMATICAL FORMULAE
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS GCE NORMAL ACADEMIC LEVEL (016) (Syllabus 4044) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION AIMS ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 3 USE OF CALCULATORS 3 SUBJECT CONTENT 4 MATHEMATICAL FORMULAE
Math 121: Calculus 1 - Winter 2012/2013 Review of Precalculus Concepts
 Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
Introduction Math 11: Calculus 1 - Winter 01/01 Review of Precalculus Concepts Welcome to Math 11 - Calculus 1, Winter 01/01! This problems in this packet are designed to help you review the topics from
King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics
 King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics Modules Algebra, Geometry and Calculus. Materials Text book: Mathematics for A-Level Hodder Education. needed Calculator. Progress objectives
King s Year 12 Medium Term Plan for LC1- A-Level Mathematics Modules Algebra, Geometry and Calculus. Materials Text book: Mathematics for A-Level Hodder Education. needed Calculator. Progress objectives
Final Exam C Name i D) 2. Solve the equation by factoring. 4) x2 = x + 72 A) {1, 72} B) {-8, 9} C) {-8, -9} D) {8, 9} 9 ± i
 Final Exam C Name First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the equation. 7 ) x + + 3 x - = 6 (x + )(x - ) ) A) No restrictions; {} B) x -, ; C) x -; {} D) x -, ; {2} Add
Final Exam C Name First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the equation. 7 ) x + + 3 x - = 6 (x + )(x - ) ) A) No restrictions; {} B) x -, ; C) x -; {} D) x -, ; {2} Add
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary GCE in Mathematics (8MA0) Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced GCE in Mathematics (9MA0)
 Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary GCE in Mathematics (8MA0) Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced GCE in Mathematics (9MA0) First teaching from September 2017 First certification from June 2018 2
Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced Subsidiary GCE in Mathematics (8MA0) Pearson Edexcel Level 3 Advanced GCE in Mathematics (9MA0) First teaching from September 2017 First certification from June 2018 2
DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS
 DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) Show by using the discriminant that the graph of the curve with equation y = x 4x + 10, does not cross the x axis. proof Question (**) Show that the quadratic
DISCRIMINANT EXAM QUESTIONS Question 1 (**) Show by using the discriminant that the graph of the curve with equation y = x 4x + 10, does not cross the x axis. proof Question (**) Show that the quadratic
Newbattle Community High School Higher Mathematics. Key Facts Q&A
 Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing to take turns reading a random question
Key Facts Q&A Ways of using this booklet: 1) Write the questions on cards with the answers on the back and test yourself. ) Work with a friend who is also doing to take turns reading a random question
Polynomial Review Problems
 Polynomial Review Problems 1. Find polynomial function formulas that could fit each of these graphs. Remember that you will need to determine the value of the leading coefficient. The point (0,-3) is on
Polynomial Review Problems 1. Find polynomial function formulas that could fit each of these graphs. Remember that you will need to determine the value of the leading coefficient. The point (0,-3) is on
Roots and Coefficients Polynomials Preliminary Maths Extension 1
 Preliminary Maths Extension Question If, and are the roots of x 5x x 0, find the following. (d) (e) Question If p, q and r are the roots of x x x 4 0, evaluate the following. pq r pq qr rp p q q r r p
Preliminary Maths Extension Question If, and are the roots of x 5x x 0, find the following. (d) (e) Question If p, q and r are the roots of x x x 4 0, evaluate the following. pq r pq qr rp p q q r r p
Unit 1 Vocabulary. A function that contains 1 or more or terms. The variables may be to any non-negative power.
 MODULE 1 1 Polynomial A function that contains 1 or more or terms. The variables may be to any non-negative power. 1 Modeling Mathematical modeling is the process of using, and to represent real world
MODULE 1 1 Polynomial A function that contains 1 or more or terms. The variables may be to any non-negative power. 1 Modeling Mathematical modeling is the process of using, and to represent real world
Core Mathematics C3 Advanced
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6665/01 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C3 Advanced Friday 12 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 6665/01 Edexcel GCE Core Mathematics C3 Advanced Friday 12 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials required for examination Mathematical Formulae
Mathematics (MEI) Advanced Subsidiary GCE Core 1 (4751) May 2010
 Link to past paper on OCR website: http://www.mei.org.uk/files/papers/c110ju_ergh.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are a school or
Link to past paper on OCR website: http://www.mei.org.uk/files/papers/c110ju_ergh.pdf These solutions are for your personal use only. DO NOT photocopy or pass on to third parties. If you are a school or
C3 PAPER JUNE 2014 *P43164A0232* 1. The curve C has equation y = f (x) where + 1. (a) Show that 9 f (x) = (3)
 PMT C3 papers from 2014 and 2013 C3 PAPER JUNE 2014 1. The curve C has equation y = f (x) where 4x + 1 f( x) =, x 2 x > 2 (a) Show that 9 f (x) = ( x ) 2 2 Given that P is a point on C such that f (x)
PMT C3 papers from 2014 and 2013 C3 PAPER JUNE 2014 1. The curve C has equation y = f (x) where 4x + 1 f( x) =, x 2 x > 2 (a) Show that 9 f (x) = ( x ) 2 2 Given that P is a point on C such that f (x)
Regents Review Session #3 Functions
 Regents Review Session #3 Functions A relation is a set of ordered pairs. A function is a relation in which each element of the domain corresponds t exactly one element in the range. (Each x value is paired
Regents Review Session #3 Functions A relation is a set of ordered pairs. A function is a relation in which each element of the domain corresponds t exactly one element in the range. (Each x value is paired
 www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com * 031 674 651 3 * UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 0606/22
www.onlineexamhelp.com www.onlineexamhelp.com * 031 674 651 3 * UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 0606/22
AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES
 AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES 1 SURDS A root such as 3 that cannot be written exactly as a fraction is IRRATIONAL An expression that involves irrational roots is in SURD FORM e.g. 2 3 3 + 2 and 3-2 are
AS PURE MATHS REVISION NOTES 1 SURDS A root such as 3 that cannot be written exactly as a fraction is IRRATIONAL An expression that involves irrational roots is in SURD FORM e.g. 2 3 3 + 2 and 3-2 are
*P43632A0120* Algebra Level 3 Calculator NOT allowed. Pearson Edexcel Award AAL30/01. P43632A 2014 Pearson Education Ltd.
 Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Award Algebra Level 3 Calculator NOT allowed Centre Number Candidate Number Monday 12 May 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Paper Reference AAL30/01 You
Write your name here Surname Other names Pearson Edexcel Award Algebra Level 3 Calculator NOT allowed Centre Number Candidate Number Monday 12 May 2014 Morning Time: 2 hours Paper Reference AAL30/01 You
Radicals: To simplify means that 1) no radicand has a perfect square factor and 2) there is no radical in the denominator (rationalize).
 Summer Review Packet for Students Entering Prealculus Radicals: To simplify means that 1) no radicand has a perfect square factor and ) there is no radical in the denominator (rationalize). Recall the
Summer Review Packet for Students Entering Prealculus Radicals: To simplify means that 1) no radicand has a perfect square factor and ) there is no radical in the denominator (rationalize). Recall the
Precalculus Lesson 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Mrs. Snow, Instructor
 Precalculus Lesson 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Mrs. Snow, Instructor Let s review the definition of a polynomial. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form P(x) = a n x n + a
Precalculus Lesson 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Mrs. Snow, Instructor Let s review the definition of a polynomial. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form P(x) = a n x n + a
Pre-calculus 12 Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours)
 Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours) Trigonometry (T) (35 40 hours) General Curriculum Outcome: Students will be expected to develop trigonometric reasoning. T01 Students will be expected to T01.01
Curriculum Outcomes Framework (110 hours) Trigonometry (T) (35 40 hours) General Curriculum Outcome: Students will be expected to develop trigonometric reasoning. T01 Students will be expected to T01.01
Year 12 Maths C1-C2-S1 2016/2017
 Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
page 1 of 14 1 for all x because f 1 = f and1 f = f. The identity for = x for all x because f
 page of 4 Entry # Inverses in General The term inverse is used in very different contexts in mathematics. For example, the multiplicative inverse of a number, the inverse of a function, and the inverse
page of 4 Entry # Inverses in General The term inverse is used in very different contexts in mathematics. For example, the multiplicative inverse of a number, the inverse of a function, and the inverse
REVIEW, pages Chapter 1: Polynomial Expressions and Functions Review Solutions DO NOT COPY. P 1.1. Write the division statement.
 REVIEW, pages 72 77 1.1 1. Use long division to divide 7x 3 + 6x 4-7x - 9x 2 + 8 by x 1. Write the division statement. Write the polynomial in descending order: 6x 4 7x 3 9x 2 7x 8 6x 4 6x 3 6x 3 13x 2
REVIEW, pages 72 77 1.1 1. Use long division to divide 7x 3 + 6x 4-7x - 9x 2 + 8 by x 1. Write the division statement. Write the polynomial in descending order: 6x 4 7x 3 9x 2 7x 8 6x 4 6x 3 6x 3 13x 2
Learning Objectives These show clearly the purpose and extent of coverage for each topic.
 Preface This book is prepared for students embarking on the study of Additional Mathematics. Topical Approach Examinable topics for Upper Secondary Mathematics are discussed in detail so students can focus
Preface This book is prepared for students embarking on the study of Additional Mathematics. Topical Approach Examinable topics for Upper Secondary Mathematics are discussed in detail so students can focus
Year 12 Maths C1-C2-S1 2017/2018
 Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
Half Term 1 5 th September 12 th September 19 th September 26 th September 3 rd October 10 th October 17 th October Basic algebra and Laws of indices Factorising expressions Manipulating surds and rationalising
MSM120 1M1 First year mathematics for civil engineers Revision notes 3
 MSM0 M First year mathematics for civil engineers Revision notes Professor Robert. Wilson utumn 00 Functions Definition of a function: it is a rule which, given a value of the independent variable (often
MSM0 M First year mathematics for civil engineers Revision notes Professor Robert. Wilson utumn 00 Functions Definition of a function: it is a rule which, given a value of the independent variable (often
ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY HOMEWORK 3
 ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY HOMEWORK 3 (1) Consider the curve Y 2 = X 2 (X + 1). (a) Sketch the curve. (b) Determine the singular point P on C. (c) For all lines through P, determine the intersection multiplicity
ALGEBRAIC GEOMETRY HOMEWORK 3 (1) Consider the curve Y 2 = X 2 (X + 1). (a) Sketch the curve. (b) Determine the singular point P on C. (c) For all lines through P, determine the intersection multiplicity
2014 Summer Review for Students Entering Algebra 2. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 1. Solving Linear Equations 2. Solving Linear Systems of Equations 3. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 4. Writing the Equation of a Line 5. Laws of Exponents and Scientific Notation 6. Solving
1. Solving Linear Equations 2. Solving Linear Systems of Equations 3. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 4. Writing the Equation of a Line 5. Laws of Exponents and Scientific Notation 6. Solving
Core Mathematics 3 Algebra
 http://kumarmathsweeblycom/ Core Mathematics 3 Algebra Edited by K V Kumaran Core Maths 3 Algebra Page Algebra fractions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Simplify
http://kumarmathsweeblycom/ Core Mathematics 3 Algebra Edited by K V Kumaran Core Maths 3 Algebra Page Algebra fractions C3 The specifications suggest that you should be able to do the following: Simplify
The Graphs of Polynomial Functions
 Section 4.3 The Graphs of Polynomial Functions Objective 1: Understanding the Definition of a Polynomial Function Definition Polynomial Function n n 1 n 2 The function f() x = anx + an 1x + an 2x + L +
Section 4.3 The Graphs of Polynomial Functions Objective 1: Understanding the Definition of a Polynomial Function Definition Polynomial Function n n 1 n 2 The function f() x = anx + an 1x + an 2x + L +
Math /Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined
 Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Math 400-001/Foundations of Algebra/Fall 2017 Numbers at the Foundations: Real Numbers In calculus, the derivative of a function f(x) is defined using limits. As a particular case, the derivative of f(x)
Semester Review Packet
 MATH 110: College Algebra Instructor: Reyes Semester Review Packet Remarks: This semester we have made a very detailed study of four classes of functions: Polynomial functions Linear Quadratic Higher degree
MATH 110: College Algebra Instructor: Reyes Semester Review Packet Remarks: This semester we have made a very detailed study of four classes of functions: Polynomial functions Linear Quadratic Higher degree
Calculus : Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun Bishop Dunne Catholic School. Calculus Summer Math Study Guide
 1 Calculus 2018-2019: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Name: Calculus Summer Math Study Guide After you have practiced the skills on Khan Academy (list
1 Calculus 2018-2019: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Name: Calculus Summer Math Study Guide After you have practiced the skills on Khan Academy (list
Dinwiddie County Subject: Trigonometry Scope and Sequence
 Dinwiddie County Subject: Trigonometry Scope and Sequence GRADE: High School 9 WKS Topics Equations (linear, quadratic, and absolute value) and Radicals (simplest radical form, including rationalizing
Dinwiddie County Subject: Trigonometry Scope and Sequence GRADE: High School 9 WKS Topics Equations (linear, quadratic, and absolute value) and Radicals (simplest radical form, including rationalizing
How many solutions are real? How many solutions are imaginary? What are the solutions? (List below):
 1 Algebra II Chapter 5 Test Review Standards/Goals: F.IF.7.c: I can identify the degree of a polynomial function. F.1.a./A.APR.1.: I can evaluate and simplify polynomial expressions and equations. F.1.b./
1 Algebra II Chapter 5 Test Review Standards/Goals: F.IF.7.c: I can identify the degree of a polynomial function. F.1.a./A.APR.1.: I can evaluate and simplify polynomial expressions and equations. F.1.b./
AP Calculus Summer Assignment Summer 2017 Expectations for Summer Assignment on the first day of the school year.
 Summer 07 Expectations for Summer Assignment This packet is to be submitted to your Calculus BC teacher on the first day of the school year. All work must be shown in the packet OR on separate paper attached
Summer 07 Expectations for Summer Assignment This packet is to be submitted to your Calculus BC teacher on the first day of the school year. All work must be shown in the packet OR on separate paper attached
2 2xdx. Craigmount High School Mathematics Department
 Π 5 3 xdx 5 cosx 4 6 3 8 Help Your Child With Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
Π 5 3 xdx 5 cosx 4 6 3 8 Help Your Child With Higher Maths Introduction We ve designed this booklet so that you can use it with your child throughout the session, as he/she moves through the Higher course,
Higher Mathematics Course Notes
 Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
Higher Mathematics Course Notes Equation of a Line (i) Collinearity: (ii) Gradient: If points are collinear then they lie on the same straight line. i.e. to show that A, B and C are collinear, show that
A101 ASSESSMENT Quadratics, Discriminant, Inequalities 1
 Do the questions as a test circle questions you cannot answer Red (1) Solve a) 7x = x 2-30 b) 4x 2-29x + 7 = 0 (2) Solve the equation x 2 6x 2 = 0, giving your answers in simplified surd form [3] (3) a)
Do the questions as a test circle questions you cannot answer Red (1) Solve a) 7x = x 2-30 b) 4x 2-29x + 7 = 0 (2) Solve the equation x 2 6x 2 = 0, giving your answers in simplified surd form [3] (3) a)
6.1 The Inverse Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions Objectives
 Objectives 1. Find the Exact Value of an Inverse Sine, Cosine, or Tangent Function. 2. Find an Approximate Value of an Inverse Sine Function. 3. Use Properties of Inverse Functions to Find Exact Values
Objectives 1. Find the Exact Value of an Inverse Sine, Cosine, or Tangent Function. 2. Find an Approximate Value of an Inverse Sine Function. 3. Use Properties of Inverse Functions to Find Exact Values
Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity
 Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity Functions Limits Continuity Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity 1 Functions Functions are the major tools for describing the real world in mathematical
Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity Functions Limits Continuity Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity 1 Functions Functions are the major tools for describing the real world in mathematical
AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet
 Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
Name Date Section AP Calculus AB Summer Math Packet This assignment is to be done at you leisure during the summer. It is meant to help you practice mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus
Precalculus Summer Assignment 2015
 Precalculus Summer Assignment 2015 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in CP Pre-calculus this year. You are advised to be familiar
Precalculus Summer Assignment 2015 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in CP Pre-calculus this year. You are advised to be familiar
Final Exam Review Problems
 Final Exam Review Problems Name: Date: June 23, 2013 P 1.4. 33. Determine whether the line x = 4 represens y as a function of x. P 1.5. 37. Graph f(x) = 3x 1 x 6. Find the x and y-intercepts and asymptotes
Final Exam Review Problems Name: Date: June 23, 2013 P 1.4. 33. Determine whether the line x = 4 represens y as a function of x. P 1.5. 37. Graph f(x) = 3x 1 x 6. Find the x and y-intercepts and asymptotes
