Perturbation Theory, Zeeman Effect, Stark Effect
|
|
|
- Primrose Gaines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 8 Perturbatio Theory, Zeea Effect, Stark Effect Ufortuately, apart fro a few siple exaples, the Schrödiger equatio is geerally ot exactly solvable ad we therefore have to rely upo approxiative ethods to deal with ore realistic situatios. Such ethods iclude perturbatio theory, the variatioal ethod ad the WKB -approxiatio. I our Scriptu we, however, just cope with perturbatio theory i its siplest versio. It is a systeatic procedure for obtaiig approxiate solutios to the uperturbed proble which is assued to be kow exactly. 8. Tie Idepedet Perturbatio Theory The ethod of perturbatio theory is that we defor slightly perturb a kow Hailtoia H by a ew Hailtoia H I, soe potetial resposible for a iteractio of the syste, ad try to solve the Schrödiger equatio approxiately sice, i geeral, we will be uable to solve it exactly. Thus we start with a Hailtoia of the followig for H = H + λ H I where λ [, ], (8.) where the Hailtoia H is perturbed by a saller ter, the iteractio H I with λ sall. The uperturbed Hailtoia is assued to be solved ad has well-kow eigefuctios ad eigevalues, i.e. H = E (), (8.2) where the eigefuctios are chose to be oralized = δ. (8.3) The superscript deotes the eigefuctios ad eigevalues of the uperturbed syste H, ad we furtherore require the uperturbed eigevalues to be o-degeerate, aed after Wetzel, Kraers ad Brilloui. E () E (), (8.4) 5
2 52CHAPTER 8. PERTURBATION THEORY, ZEEMAN EFFECT, STARK EFFECT otherwise we would use a differet ethod leadig to the so-called degeerate perturbatio theory. What we are ow goig to ivestigate are the eigevalues E ad eigefuctios of the total Hailtoia H H = E. (8.5) The basic idea of perturbatio theory the is to expad the eigevalues ad eigefuctios i a power series, without takig care of the correspodig covergece properties. I ay cases, cosiderig just the first few ters of the power series gives us reasoable results, eve if the whole power series ca be show to be diverget. Let us therefore start with a power series i the paraeter λ, which is a good approxiatio for sall λ E = E () + λ E () + λ 2 E (2) + (8.6) = + λ + λ 2 2 +, (8.7) where we have coefficiet fuctios of labda, the uperturbed ter, first ad secod order perturbative correctios ad so o. Isertig these expasios ito the Schrödiger equatio (8.5) together with Hailtoia (8.), we get = (H + λ H I ) ( + λ + λ ) = ( ) E () + λ E () + λ 2 E (2) + ( + λ + λ ). (8.8) Equatig coefficiets we obtai the followig relatios: λ : H = E () (8.9) λ : H + H I = E () + E () (8.) λ 2 : H 2 + H I = E () 2 + E () + E (2). (8.) Additioally, it is coveiet to oralize the followig trasitio aplitude for the perturbed eergy eigestate = (8.2) 8.. First Order Correctios λ + λ = (8.3) = 2 = =. (8.4) To derive the first order correctios we ultiply the first order coefficiet equatio (Eq. 8.) with fro the left ad let the heritia, uperturbed Hailtoia H = H act to the left o E () } {{ } + HI = E () } {{ } + E () } {{ }. (8.5) This leads us directly to the followig fudaetal result, which is already a sufficiet correctio for ay cases to reproduce physical observatios:
3 8.. TIME INDEPENDENT PERTURBATION THEORY 53 Theore 8. The perturbative eergy correctios of first order are give by the expectatio value of the perturbig Hailtoia i the uperturbed states E () = HI Although we ow have the eergy correctio we are iterested i, we are curious as to how the state itself is perturbed. We therefore expad the first order expasio state ito a coplete orthooral syste { } =, (8.6) where all the ters for = vaish due to our choice of oralizatio (Eq. 8.4). We are the iterested i the expasio coefficiet, which we calculate by usig agai Eq. (8.). This tie, however, we ultiply the equatio with E () + HI = E () + E (). (8.7) Though the last ter o the right side of Eq. (8.7) would be ozero if =, the state expasio excludes this case i the suatio ad therefore we ca igore this ter, which allows us to express the expasio coefficiet as = H I E () E (), (8.8) where the atrix eleet H I has to be calculated. So the iportat result for the first order state correctio is: Theore 8.2 The perturbative state correctios of first order are give by the superpositio of all uperturbed states with eergies differet fro the cosidered state = H I E () E () Reark: Due to the eergy deoiator the adjacet eergy levels cotribute i this approxiatio stroger to the correctios of the state (assuig early costat atrix eleets) tha the ore reote oes, what is ituitively expected.
4 54CHAPTER 8. PERTURBATION THEORY, ZEEMAN EFFECT, STARK EFFECT 8..2 Secod Order Correctios To fid the correctios of secod order, we start siilar as i the last subsectio, by this tie ultiplyig Eq. (8.) by E () 2 + HI = E () 2 + E () + E (2). }{{}}{{}}{{}}{{} (8.9) Further isertig our result of Sectio 8.. (Theore 8.2), we get E (2) = HI H I E () E (), (8.2) the we iediately fid the result for the secod order eergy correctio as: Theore 8.3 The perturbative eergy correctios of secod order are deteried by all uperturbed states with eergy differet fro the cosidered state E (2) = H I 2 E () E () Reark I: Agai, the adjacet eergy levels cotribute to the ajority of the correctio if the atrix eleets are assued to be of approxiately the sae order. Reark II: For the groud state the eergy correctio of secod order is always egative, i.e. E (2) <, sice E () < E (). 8.2 Zeea Effect The eergy levels of particles carryig a agetic dipole oet, e.g. the H-ato, i a exterior (hoogeeous) agetic field are further split up, i.e., the degeeracy of the eergy eigevalues is reoved. The Hailtoia of the electro i the H-ato therefore has a additioal ter, the Zeea ter H Z, perturbig the already kow ter H Coul. which cotais the Coulob potetial (Eq. 6.95). We thus have the total Hailtoia H = H Coul. + H Z, (8.2) where the Zeea ter is the scalar product of the agetic dipole oet µ ad the exterior agetic field B, see Eq. (7.4) H Z = µ B = q ( ) L + g S B. (8.22) 2 c
5 8.3. STARK EFFECT 55 We ow assue without loss of geerality that the agetic field is orieted alog the z-directio, where it has the stregth B ext., ad isert the electro ass e, charge e = e ad g-factor g e = 2 H Z = e 2 e c ( L z + 2 S z ) B ext.. (8.23) We further assue that the agetic field is sufficietly strog, such that the orbital agular oetu L ad the spi S decouple ad the uperturbed states are product states of the for, l, l ad, l, l, (8.24) which is called the Pasche Back Effect. The (first order) eergy correctios E to the pure Coulob eergy are the give by Theore 8., where we iediately see that E (), l, l, s = e 2 e c ( l + 2 }{{} s ) B ext.. (8.25) ± Thus every, util ow degeerate, l-level is split up by the eergy correctio ter, depedig o the spi orietatio. Whe recallig the eergy levels of the Coulob potetial (Eq. 6.4) E, Coul. l = E I 3, 6 ev =, (8.26) 2 2 ad Bohr s ageto µ B µ B = e 2 e c = 5, ev / Tesla, (8.27) we see that the Zeea eergy ter is a sall correctio with respect to the Coulob eergy, eve for very strog agetic fields (B ext. Tesla). 8.3 Stark Effect The Stark effect is the electric aalogue to the Zeea effect, i.e., a particle carryig a electric dipole oet, like the H-ato, will get a splittig of its eergy levels whe subjected to a exterior electric field. The Hailtoia of the H-ato thus has (aother) additioal ter, the Stark ter H Stark, which is perturbig the Coulob Hailtoia H Stark = E µ el = q }{{} e E x = e E z, (8.28) where E deotes the exteral electric field which, without loss of geerality, we choose alog the z-directio, ad µ el is the electrical dipole oet. For the siple case of a electro of charge e placed at a distace x of the oppositely charged proto, restig at the origi, the electric dipole oet reduces to µ el = e x.
6 56CHAPTER 8. PERTURBATION THEORY, ZEEMAN EFFECT, STARK EFFECT To calculate the eergy correctios of first (Theore 8.) ad secod (Theore 8.3) order, we eed to cosider expectatio values or scalar products of the Stark ter i the Coulob states of the for, l, l. This is, however, ore coplicated tha the situatio we studied before. To ake the proble ore precise, let us calculate the followig scalar product, where we already kow fro Eq. (6.5) that L z ad z coute, l, l [ L z, z ], l, l = ( }{{} l l ), l, l z, l, l =. (8.29) = Sice the coutator of L z ad z is zero we ca coclude that the states, l, l ad z, l, l ust be orthogoal for l l, ad sice we are oly iterested i ozero atrix eleets we choose l l. (8.3) At the sae tie, however, for the scalar product to be ozero, we have to require that the aziuthal quatu ubers be uequal, i.e. l l. The reaso for this is the parity of the z operator. We reeber fro Theore 4.2 that a basis of states ca be chose for a syetric potetial, such as the Coulob potetial (Eq. (6.95)), that cosists etirely of eve ad odd fuctios, which i this case are the Legedre polyoials P l (cos θ). These are polyoials of order l i cos θ = z ad thus alterately eve ad odd r fuctios. Therefore, if the fuctios ψ, l, l ad ψ, l, l have the sae aziuthal quatu uber, i.e. parity, their product has parity +. The z operator however chages its sig uder a spatial iversio ad the itegratio of the scalar product vaishes, because We ca the assue that +a a dx f(x) g(x) }{{}}{{} eve odd. (8.3) l = l ±, (8.32) which is a reasoable choice sice the electric dipole iteracts with the electric field by exchagig photos of spi, so the agular oetu of the electro ust decrease or icrease by. The Stark effect will therefore oly occur for atrix eleets of the for, l, l z, (l ± ), l =. (8.33) Let us ow cosider the eergy correctio for the groud state of the hydroge ato, the first order correctio is E (),, = e E,, z,, =. (8.34) It vaishes due to the requireet of Eq. (8.32) ad we thus see that there is o liear Stark effect for the hydroge groud state. The effect of secod order is of the for E (2),, = e 2 E 2,, z,, 2, (8.35) E () E () = 2
7 8.3. STARK EFFECT 57 where the uperturbed eergy levels E () are give by Eq. (6.5). This expressio ca be calculated usig perturbative ethods, which leads to the result E (2),, = 9 4 where r B is the Bohr radius (Eq. (6.97)). 2 e e 2 E 2 = 9 4 r B E 2, (8.36) The first excited state, i cotrast to the groud state, is four-fold degeerate, i.e. there are 4 states 2,,, 2,,, 2,, ad 2,,, that belog to the pricipal quatu uber = 2. I this case oe has to cosider degeerate perturbatio theory, which leads to calculatig the eigevalues of a o-diagoal atrix. Because of the requireet of Eq. (8.3) we oly cosider eleets with equal agetic quatu uber, which is oly the case for the states 2,, ad 2,,. It leaves us a 2 2 atrix to diagoalize. The secod requireet (Eq. (8.32)) rids us of the diagoal eleets of the atrix. The reaiig ozero off-diagoal eleets are 2,, z 2,, = 2,, z 2,,. (8.37) The ozero eigevalues ca thus be easily calculated ad we coclude that the excited state has a liear Stark effect correctio with the result E () 2, l, l = ± e r B E. (8.38) Further splittig of the excited hydroge eergy levels ca be see i Fig. 8..
8 58CHAPTER 8. PERTURBATION THEORY, ZEEMAN EFFECT, STARK EFFECT Figure 8.: Stark Effect i Hydroge: The util the degeerate excited eergy levels are split up if a exterior electric field is applied. Figure fro: splittig.pg
X. Perturbation Theory
 X. Perturbatio Theory I perturbatio theory, oe deals with a ailtoia that is coposed Ĥ that is typically exactly solvable of two pieces: a referece part ad a perturbatio ( Ĥ ) that is assued to be sall.
X. Perturbatio Theory I perturbatio theory, oe deals with a ailtoia that is coposed Ĥ that is typically exactly solvable of two pieces: a referece part ad a perturbatio ( Ĥ ) that is assued to be sall.
8.3 Perturbation theory
 8.3 Perturbatio theory Slides: Video 8.3.1 Costructig erturbatio theory Text referece: Quatu Mechaics for Scietists ad gieers Sectio 6.3 (u to First order erturbatio theory ) Perturbatio theory Costructig
8.3 Perturbatio theory Slides: Video 8.3.1 Costructig erturbatio theory Text referece: Quatu Mechaics for Scietists ad gieers Sectio 6.3 (u to First order erturbatio theory ) Perturbatio theory Costructig
( ) Time-Independent Perturbation Theory. Michael Fowler 2/16/06
 Tie-Idepedet Perturbatio Theory Michael Fowler /6/6 Itroductio If a ato (ot ecessarily i its groud state) is placed i a exteral electric field, the eergy levels shift, ad the wave fuctios are distorted
Tie-Idepedet Perturbatio Theory Michael Fowler /6/6 Itroductio If a ato (ot ecessarily i its groud state) is placed i a exteral electric field, the eergy levels shift, ad the wave fuctios are distorted
Lecture 25 (Dec. 6, 2017)
 Lecture 5 8.31 Quatum Theory I, Fall 017 106 Lecture 5 (Dec. 6, 017) 5.1 Degeerate Perturbatio Theory Previously, whe discussig perturbatio theory, we restricted ourselves to the case where the uperturbed
Lecture 5 8.31 Quatum Theory I, Fall 017 106 Lecture 5 (Dec. 6, 017) 5.1 Degeerate Perturbatio Theory Previously, whe discussig perturbatio theory, we restricted ourselves to the case where the uperturbed
Bernoulli Polynomials Talks given at LSBU, October and November 2015 Tony Forbes
 Beroulli Polyoials Tals give at LSBU, October ad Noveber 5 Toy Forbes Beroulli Polyoials The Beroulli polyoials B (x) are defied by B (x), Thus B (x) B (x) ad B (x) x, B (x) x x + 6, B (x) dx,. () B 3
Beroulli Polyoials Tals give at LSBU, October ad Noveber 5 Toy Forbes Beroulli Polyoials The Beroulli polyoials B (x) are defied by B (x), Thus B (x) B (x) ad B (x) x, B (x) x x + 6, B (x) dx,. () B 3
(s)h(s) = K( s + 8 ) = 5 and one finite zero is located at z 1
 ROOT LOCUS TECHNIQUE 93 should be desiged differetly to eet differet specificatios depedig o its area of applicatio. We have observed i Sectio 6.4 of Chapter 6, how the variatio of a sigle paraeter like
ROOT LOCUS TECHNIQUE 93 should be desiged differetly to eet differet specificatios depedig o its area of applicatio. We have observed i Sectio 6.4 of Chapter 6, how the variatio of a sigle paraeter like
Orthogonal Functions
 Royal Holloway Uiversity of odo Departet of Physics Orthogoal Fuctios Motivatio Aalogy with vectors You are probably failiar with the cocept of orthogoality fro vectors; two vectors are orthogoal whe they
Royal Holloway Uiversity of odo Departet of Physics Orthogoal Fuctios Motivatio Aalogy with vectors You are probably failiar with the cocept of orthogoality fro vectors; two vectors are orthogoal whe they
Hydrogen (atoms, molecules) in external fields. Static electric and magnetic fields Oscyllating electromagnetic fields
 Hydroge (atoms, molecules) i exteral fields Static electric ad magetic fields Oscyllatig electromagetic fields Everythig said up to ow has to be modified more or less strogly if we cosider atoms (ad ios)
Hydroge (atoms, molecules) i exteral fields Static electric ad magetic fields Oscyllatig electromagetic fields Everythig said up to ow has to be modified more or less strogly if we cosider atoms (ad ios)
Chapter 4 Postulates & General Principles of Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 4 Postulates & Geeral Priciples of Quatu Mechaics Backgroud: We have bee usig quite a few of these postulates already without realizig it. Now it is tie to forally itroduce the. State of a Syste
Chapter 4 Postulates & Geeral Priciples of Quatu Mechaics Backgroud: We have bee usig quite a few of these postulates already without realizig it. Now it is tie to forally itroduce the. State of a Syste
c z c z c z c z c c c c a a c A P( a ) a c a z c x z R j z z, z z z z I
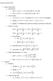 . Quatu Spi States State Vectors c c i Ier Products: * * c c oralied. orthogoal c c c c c c * * i ii Probability that a particle i state ca be foud i state. c. States i S -basis y i i Geeral States. c
. Quatu Spi States State Vectors c c i Ier Products: * * c c oralied. orthogoal c c c c c c * * i ii Probability that a particle i state ca be foud i state. c. States i S -basis y i i Geeral States. c
Orthogonal Function Solution of Differential Equations
 Royal Holloway Uiversity of Loo Departet of Physics Orthogoal Fuctio Solutio of Differetial Equatios trouctio A give oriary ifferetial equatio will have solutios i ters of its ow fuctios Thus, for eaple,
Royal Holloway Uiversity of Loo Departet of Physics Orthogoal Fuctio Solutio of Differetial Equatios trouctio A give oriary ifferetial equatio will have solutios i ters of its ow fuctios Thus, for eaple,
Physics 219 Summary of linear response theory
 1 Physics 219 Suary of liear respose theory I. INTRODUCTION We apply a sall perturbatio of stregth f(t) which is switched o gradually ( adiabatically ) fro t =, i.e. the aplitude of the perturbatio grows
1 Physics 219 Suary of liear respose theory I. INTRODUCTION We apply a sall perturbatio of stregth f(t) which is switched o gradually ( adiabatically ) fro t =, i.e. the aplitude of the perturbatio grows
Summer MA Lesson 13 Section 1.6, Section 1.7 (part 1)
 Suer MA 1500 Lesso 1 Sectio 1.6, Sectio 1.7 (part 1) I Solvig Polyoial Equatios Liear equatio ad quadratic equatios of 1 variable are specific types of polyoial equatios. Soe polyoial equatios of a higher
Suer MA 1500 Lesso 1 Sectio 1.6, Sectio 1.7 (part 1) I Solvig Polyoial Equatios Liear equatio ad quadratic equatios of 1 variable are specific types of polyoial equatios. Soe polyoial equatios of a higher
Integrals of Functions of Several Variables
 Itegrals of Fuctios of Several Variables We ofte resort to itegratios i order to deterie the exact value I of soe quatity which we are uable to evaluate by perforig a fiite uber of additio or ultiplicatio
Itegrals of Fuctios of Several Variables We ofte resort to itegratios i order to deterie the exact value I of soe quatity which we are uable to evaluate by perforig a fiite uber of additio or ultiplicatio
6.4 Binomial Coefficients
 64 Bioial Coefficiets Pascal s Forula Pascal s forula, aed after the seveteeth-cetury Frech atheaticia ad philosopher Blaise Pascal, is oe of the ost faous ad useful i cobiatorics (which is the foral ter
64 Bioial Coefficiets Pascal s Forula Pascal s forula, aed after the seveteeth-cetury Frech atheaticia ad philosopher Blaise Pascal, is oe of the ost faous ad useful i cobiatorics (which is the foral ter
The Binomial Multi-Section Transformer
 4/15/2010 The Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforer preset.doc 1/24 The Bioial Multi-Sectio Trasforer Recall that a ulti-sectio atchig etwork ca be described usig the theory of sall reflectios as: where:
4/15/2010 The Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforer preset.doc 1/24 The Bioial Multi-Sectio Trasforer Recall that a ulti-sectio atchig etwork ca be described usig the theory of sall reflectios as: where:
5.6 Binomial Multi-section Matching Transformer
 4/14/21 5_6 Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforers 1/1 5.6 Bioial Multi-sectio Matchig Trasforer Readig Assiget: pp. 246-25 Oe way to axiize badwidth is to costruct a ultisectio Γ f that is axially flat.
4/14/21 5_6 Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforers 1/1 5.6 Bioial Multi-sectio Matchig Trasforer Readig Assiget: pp. 246-25 Oe way to axiize badwidth is to costruct a ultisectio Γ f that is axially flat.
1st order Perturbation Theory
 Perturbatio Theory Although quatu echaics is beautiful stuff, it suffers fro the fact that there are relatively few, aalytically solveable exaples. The classical solvable exaples are basically piecewise
Perturbatio Theory Although quatu echaics is beautiful stuff, it suffers fro the fact that there are relatively few, aalytically solveable exaples. The classical solvable exaples are basically piecewise
19.1 The dictionary problem
 CS125 Lecture 19 Fall 2016 19.1 The dictioary proble Cosider the followig data structural proble, usually called the dictioary proble. We have a set of ites. Each ite is a (key, value pair. Keys are i
CS125 Lecture 19 Fall 2016 19.1 The dictioary proble Cosider the followig data structural proble, usually called the dictioary proble. We have a set of ites. Each ite is a (key, value pair. Keys are i
Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
Math 160 www.timetodare.com 4.5 4.6 Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered with fidig the solutios of polyomial equatios of ay degree
Assignment 2 Solutions SOLUTION. ϕ 1 Â = 3 ϕ 1 4i ϕ 2. The other case can be dealt with in a similar way. { ϕ 2 Â} χ = { 4i ϕ 1 3 ϕ 2 } χ.
 PHYSICS 34 QUANTUM PHYSICS II (25) Assigmet 2 Solutios 1. With respect to a pair of orthoormal vectors ϕ 1 ad ϕ 2 that spa the Hilbert space H of a certai system, the operator  is defied by its actio
PHYSICS 34 QUANTUM PHYSICS II (25) Assigmet 2 Solutios 1. With respect to a pair of orthoormal vectors ϕ 1 ad ϕ 2 that spa the Hilbert space H of a certai system, the operator  is defied by its actio
distinct distinct n k n k n! n n k k n 1 if k n, identical identical p j (k) p 0 if k > n n (k)
 THE TWELVEFOLD WAY FOLLOWING GIAN-CARLO ROTA How ay ways ca we distribute objects to recipiets? Equivaletly, we wat to euerate equivalece classes of fuctios f : X Y where X = ad Y = The fuctios are subject
THE TWELVEFOLD WAY FOLLOWING GIAN-CARLO ROTA How ay ways ca we distribute objects to recipiets? Equivaletly, we wat to euerate equivalece classes of fuctios f : X Y where X = ad Y = The fuctios are subject
A string of not-so-obvious statements about correlation in the data. (This refers to the mechanical calculation of correlation in the data.
 STAT-UB.003 NOTES for Wedesday 0.MAY.0 We will use the file JulieApartet.tw. We ll give the regressio of Price o SqFt, show residual versus fitted plot, save residuals ad fitted. Give plot of (Resid, Price,
STAT-UB.003 NOTES for Wedesday 0.MAY.0 We will use the file JulieApartet.tw. We ll give the regressio of Price o SqFt, show residual versus fitted plot, save residuals ad fitted. Give plot of (Resid, Price,
PHY4905: Nearly-Free Electron Model (NFE)
 PHY4905: Nearly-Free Electro Model (NFE) D. L. Maslov Departmet of Physics, Uiversity of Florida (Dated: Jauary 12, 2011) 1 I. REMINDER: QUANTUM MECHANICAL PERTURBATION THEORY A. No-degeerate eigestates
PHY4905: Nearly-Free Electro Model (NFE) D. L. Maslov Departmet of Physics, Uiversity of Florida (Dated: Jauary 12, 2011) 1 I. REMINDER: QUANTUM MECHANICAL PERTURBATION THEORY A. No-degeerate eigestates
Curious problem using the variational method to find the ground state energy of the Harmonic oscillator.
 Curious proble usig the variatioal ethod to fid the groud state eergy of the Haroic oscillator. Origially appeared at: http://sites.google.co/site/peeterjoot/ath211/variatioharoicoscillator.pdf Peeter
Curious proble usig the variatioal ethod to fid the groud state eergy of the Haroic oscillator. Origially appeared at: http://sites.google.co/site/peeterjoot/ath211/variatioharoicoscillator.pdf Peeter
x !1! + 1!2!
 4 Euler-Maclauri Suatio Forula 4. Beroulli Nuber & Beroulli Polyoial 4.. Defiitio of Beroulli Nuber Beroulli ubers B (,,3,) are defied as coefficiets of the followig equatio. x e x - B x! 4.. Expreesio
4 Euler-Maclauri Suatio Forula 4. Beroulli Nuber & Beroulli Polyoial 4.. Defiitio of Beroulli Nuber Beroulli ubers B (,,3,) are defied as coefficiets of the followig equatio. x e x - B x! 4.. Expreesio
We have also learned that, thanks to the Central Limit Theorem and the Law of Large Numbers,
 Cofidece Itervals III What we kow so far: We have see how to set cofidece itervals for the ea, or expected value, of a oral probability distributio, both whe the variace is kow (usig the stadard oral,
Cofidece Itervals III What we kow so far: We have see how to set cofidece itervals for the ea, or expected value, of a oral probability distributio, both whe the variace is kow (usig the stadard oral,
Binomial transform of products
 Jauary 02 207 Bioial trasfor of products Khristo N Boyadzhiev Departet of Matheatics ad Statistics Ohio Norther Uiversity Ada OH 4580 USA -boyadzhiev@ouedu Abstract Give the bioial trasfors { b } ad {
Jauary 02 207 Bioial trasfor of products Khristo N Boyadzhiev Departet of Matheatics ad Statistics Ohio Norther Uiversity Ada OH 4580 USA -boyadzhiev@ouedu Abstract Give the bioial trasfors { b } ad {
Lecture Outline. 2 Separating Hyperplanes. 3 Banach Mazur Distance An Algorithmist s Toolkit October 22, 2009
 18.409 A Algorithist s Toolkit October, 009 Lecture 1 Lecturer: Joatha Keler Scribes: Alex Levi (009) 1 Outlie Today we ll go over soe of the details fro last class ad ake precise ay details that were
18.409 A Algorithist s Toolkit October, 009 Lecture 1 Lecturer: Joatha Keler Scribes: Alex Levi (009) 1 Outlie Today we ll go over soe of the details fro last class ad ake precise ay details that were
5.6 Binomial Multi-section Matching Transformer
 4/14/2010 5_6 Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforers 1/1 5.6 Bioial Multi-sectio Matchig Trasforer Readig Assiget: pp. 246-250 Oe way to axiize badwidth is to costruct a ultisectio Γ f that is axially flat.
4/14/2010 5_6 Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforers 1/1 5.6 Bioial Multi-sectio Matchig Trasforer Readig Assiget: pp. 246-250 Oe way to axiize badwidth is to costruct a ultisectio Γ f that is axially flat.
Supplementary Information
 Suppleetary Iforatio -Breakdow of cotiuu fracture echaics at the aoscale- Takahiro Shiada,,* Keji Ouchi, Yuu Chihara, ad Takayuki Kitaura Departet of echaical Egieerig ad Sciece, Kyoto Uiversity, Nishikyo-ku,
Suppleetary Iforatio -Breakdow of cotiuu fracture echaics at the aoscale- Takahiro Shiada,,* Keji Ouchi, Yuu Chihara, ad Takayuki Kitaura Departet of echaical Egieerig ad Sciece, Kyoto Uiversity, Nishikyo-ku,
Physics 232 Gauge invariance of the magnetic susceptibilty
 Physics 232 Gauge ivariace of the magetic susceptibilty Peter Youg (Dated: Jauary 16, 2006) I. INTRODUCTION We have see i class that the followig additioal terms appear i the Hamiltoia o addig a magetic
Physics 232 Gauge ivariace of the magetic susceptibilty Peter Youg (Dated: Jauary 16, 2006) I. INTRODUCTION We have see i class that the followig additioal terms appear i the Hamiltoia o addig a magetic
1. Hydrogen Atom: 3p State
 7633A QUANTUM MECHANICS I - solutio set - autum. Hydroge Atom: 3p State Let us assume that a hydroge atom is i a 3p state. Show that the radial part of its wave fuctio is r u 3(r) = 4 8 6 e r 3 r(6 r).
7633A QUANTUM MECHANICS I - solutio set - autum. Hydroge Atom: 3p State Let us assume that a hydroge atom is i a 3p state. Show that the radial part of its wave fuctio is r u 3(r) = 4 8 6 e r 3 r(6 r).
HE ATOM & APPROXIMATION METHODS MORE GENERAL VARIATIONAL TREATMENT. Examples:
 5.6 4 Lecture #3-4 page HE ATOM & APPROXIMATION METHODS MORE GENERAL VARIATIONAL TREATMENT Do t restrict the wavefuctio to a sigle term! Could be a liear combiatio of several wavefuctios e.g. two terms:
5.6 4 Lecture #3-4 page HE ATOM & APPROXIMATION METHODS MORE GENERAL VARIATIONAL TREATMENT Do t restrict the wavefuctio to a sigle term! Could be a liear combiatio of several wavefuctios e.g. two terms:
AVERAGE MARKS SCALING
 TERTIARY INSTITUTIONS SERVICE CENTRE Level 1, 100 Royal Street East Perth, Wester Australia 6004 Telephoe (08) 9318 8000 Facsiile (08) 95 7050 http://wwwtisceduau/ 1 Itroductio AVERAGE MARKS SCALING I
TERTIARY INSTITUTIONS SERVICE CENTRE Level 1, 100 Royal Street East Perth, Wester Australia 6004 Telephoe (08) 9318 8000 Facsiile (08) 95 7050 http://wwwtisceduau/ 1 Itroductio AVERAGE MARKS SCALING I
The Binomial Multi- Section Transformer
 4/4/26 The Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforer /2 The Bioial Multi- Sectio Trasforer Recall that a ulti-sectio atchig etwork ca be described usig the theory of sall reflectios as: where: ( ω ) = + e +
4/4/26 The Bioial Multisectio Matchig Trasforer /2 The Bioial Multi- Sectio Trasforer Recall that a ulti-sectio atchig etwork ca be described usig the theory of sall reflectios as: where: ( ω ) = + e +
Bertrand s postulate Chapter 2
 Bertrad s postulate Chapter We have see that the sequece of prie ubers, 3, 5, 7,... is ifiite. To see that the size of its gaps is ot bouded, let N := 3 5 p deote the product of all prie ubers that are
Bertrad s postulate Chapter We have see that the sequece of prie ubers, 3, 5, 7,... is ifiite. To see that the size of its gaps is ot bouded, let N := 3 5 p deote the product of all prie ubers that are
New Version of the Rayleigh Schrödinger Perturbation Theory: Examples
 New Versio of the Rayleigh Schrödiger Perturbatio Theory: Examples MILOŠ KALHOUS, 1 L. SKÁLA, 1 J. ZAMASTIL, 1 J. ČÍŽEK 2 1 Charles Uiversity, Faculty of Mathematics Physics, Ke Karlovu 3, 12116 Prague
New Versio of the Rayleigh Schrödiger Perturbatio Theory: Examples MILOŠ KALHOUS, 1 L. SKÁLA, 1 J. ZAMASTIL, 1 J. ČÍŽEK 2 1 Charles Uiversity, Faculty of Mathematics Physics, Ke Karlovu 3, 12116 Prague
A PROBABILITY PROBLEM
 A PROBABILITY PROBLEM A big superarket chai has the followig policy: For every Euros you sped per buy, you ear oe poit (suppose, e.g., that = 3; i this case, if you sped 8.45 Euros, you get two poits,
A PROBABILITY PROBLEM A big superarket chai has the followig policy: For every Euros you sped per buy, you ear oe poit (suppose, e.g., that = 3; i this case, if you sped 8.45 Euros, you get two poits,
The Non-homogeneous Diffusion Equation
 The No-hoogeeous Diffusio Equatio The o-hoogeeous diffusio equatio, with sources, has the geeral for, 2 r,t a 2 r,t Fr,t t a 2 is real ad The hoogeeous diffusio equatio, 2 r,t a 2 t r,t ca be solved by
The No-hoogeeous Diffusio Equatio The o-hoogeeous diffusio equatio, with sources, has the geeral for, 2 r,t a 2 r,t Fr,t t a 2 is real ad The hoogeeous diffusio equatio, 2 r,t a 2 t r,t ca be solved by
1 Adiabatic and diabatic representations
 1 Adiabatic ad diabatic represetatios 1.1 Bor-Oppeheimer approximatio The time-idepedet Schrödiger equatio for both electroic ad uclear degrees of freedom is Ĥ Ψ(r, R) = E Ψ(r, R), (1) where the full molecular
1 Adiabatic ad diabatic represetatios 1.1 Bor-Oppeheimer approximatio The time-idepedet Schrödiger equatio for both electroic ad uclear degrees of freedom is Ĥ Ψ(r, R) = E Ψ(r, R), (1) where the full molecular
Math 4707 Spring 2018 (Darij Grinberg): midterm 2 page 1. Math 4707 Spring 2018 (Darij Grinberg): midterm 2 with solutions [preliminary version]
![Math 4707 Spring 2018 (Darij Grinberg): midterm 2 page 1. Math 4707 Spring 2018 (Darij Grinberg): midterm 2 with solutions [preliminary version] Math 4707 Spring 2018 (Darij Grinberg): midterm 2 page 1. Math 4707 Spring 2018 (Darij Grinberg): midterm 2 with solutions [preliminary version]](/thumbs/85/91691469.jpg) Math 4707 Sprig 08 Darij Griberg: idter page Math 4707 Sprig 08 Darij Griberg: idter with solutios [preliiary versio] Cotets 0.. Coutig first-eve tuples......................... 3 0.. Coutig legal paths
Math 4707 Sprig 08 Darij Griberg: idter page Math 4707 Sprig 08 Darij Griberg: idter with solutios [preliiary versio] Cotets 0.. Coutig first-eve tuples......................... 3 0.. Coutig legal paths
Generating Functions and Their Applications
 Geeratig Fuctios ad Their Applicatios Agustius Peter Sahaggau MIT Matheatics Departet Class of 2007 18.104 Ter Paper Fall 2006 Abstract. Geeratig fuctios have useful applicatios i ay fields of study. I
Geeratig Fuctios ad Their Applicatios Agustius Peter Sahaggau MIT Matheatics Departet Class of 2007 18.104 Ter Paper Fall 2006 Abstract. Geeratig fuctios have useful applicatios i ay fields of study. I
The time evolution of the state of a quantum system is described by the time-dependent Schrödinger equation (TDSE): ( ) ( ) 2m "2 + V ( r,t) (1.
 Adrei Tokmakoff, MIT Departmet of Chemistry, 2/13/2007 1-1 574 TIME-DEPENDENT QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 INTRODUCTION 11 Time-evolutio for time-idepedet Hamiltoias The time evolutio of the state of a quatum system
Adrei Tokmakoff, MIT Departmet of Chemistry, 2/13/2007 1-1 574 TIME-DEPENDENT QUANTUM MECHANICS 1 INTRODUCTION 11 Time-evolutio for time-idepedet Hamiltoias The time evolutio of the state of a quatum system
Jacobi symbols. p 1. Note: The Jacobi symbol does not necessarily distinguish between quadratic residues and nonresidues. That is, we could have ( a
 Jacobi sybols efiitio Let be a odd positive iteger If 1, the Jacobi sybol : Z C is the costat fuctio 1 1 If > 1, it has a decopositio ( as ) a product of (ot ecessarily distict) pries p 1 p r The Jacobi
Jacobi sybols efiitio Let be a odd positive iteger If 1, the Jacobi sybol : Z C is the costat fuctio 1 1 If > 1, it has a decopositio ( as ) a product of (ot ecessarily distict) pries p 1 p r The Jacobi
A Generalization of Ince s Equation
 Joural of Applied Matheatics ad Physics 7-8 Published Olie Deceber i SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/oural/ap http://dx.doi.org/.36/ap..337 A Geeralizatio of Ice s Equatio Ridha Moussa Uiversity of Wiscosi
Joural of Applied Matheatics ad Physics 7-8 Published Olie Deceber i SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/oural/ap http://dx.doi.org/.36/ap..337 A Geeralizatio of Ice s Equatio Ridha Moussa Uiversity of Wiscosi
Chapter 2. Asymptotic Notation
 Asyptotic Notatio 3 Chapter Asyptotic Notatio Goal : To siplify the aalysis of ruig tie by gettig rid of details which ay be affected by specific ipleetatio ad hardware. [1] The Big Oh (O-Notatio) : It
Asyptotic Notatio 3 Chapter Asyptotic Notatio Goal : To siplify the aalysis of ruig tie by gettig rid of details which ay be affected by specific ipleetatio ad hardware. [1] The Big Oh (O-Notatio) : It
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 20
 ECE 6341 Sprig 016 Prof. David R. Jackso ECE Dept. Notes 0 1 Spherical Wave Fuctios Cosider solvig ψ + k ψ = 0 i spherical coordiates z φ θ r y x Spherical Wave Fuctios (cot.) I spherical coordiates we
ECE 6341 Sprig 016 Prof. David R. Jackso ECE Dept. Notes 0 1 Spherical Wave Fuctios Cosider solvig ψ + k ψ = 0 i spherical coordiates z φ θ r y x Spherical Wave Fuctios (cot.) I spherical coordiates we
PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS SEPARATION OF VARIABLES
 Diola Bagayoko (0 PARTAL DFFERENTAL EQUATONS SEPARATON OF ARABLES. troductio As discussed i previous lectures, partial differetial equatios arise whe the depedet variale, i.e., the fuctio, varies with
Diola Bagayoko (0 PARTAL DFFERENTAL EQUATONS SEPARATON OF ARABLES. troductio As discussed i previous lectures, partial differetial equatios arise whe the depedet variale, i.e., the fuctio, varies with
The Hypergeometric Coupon Collection Problem and its Dual
 Joural of Idustrial ad Systes Egieerig Vol., o., pp -7 Sprig 7 The Hypergeoetric Coupo Collectio Proble ad its Dual Sheldo M. Ross Epstei Departet of Idustrial ad Systes Egieerig, Uiversity of Souther
Joural of Idustrial ad Systes Egieerig Vol., o., pp -7 Sprig 7 The Hypergeoetric Coupo Collectio Proble ad its Dual Sheldo M. Ross Epstei Departet of Idustrial ad Systes Egieerig, Uiversity of Souther
Note that the argument inside the second square root is always positive since R L > Z 0. The series reactance can be found as
 Ipedace Matchig Ipedace Matchig Itroductio Ipedace atchig is the process to atch the load to a trasissio lie by a atchig etwork, as depicted i Fig Recall that the reflectios are eliiated uder the atched
Ipedace Matchig Ipedace Matchig Itroductio Ipedace atchig is the process to atch the load to a trasissio lie by a atchig etwork, as depicted i Fig Recall that the reflectios are eliiated uder the atched
Define a Markov chain on {1,..., 6} with transition probability matrix P =
 Pla Group Work 0. The title says it all Next Tie: MCMC ad Geeral-state Markov Chais Midter Exa: Tuesday 8 March i class Hoework 4 due Thursday Uless otherwise oted, let X be a irreducible, aperiodic Markov
Pla Group Work 0. The title says it all Next Tie: MCMC ad Geeral-state Markov Chais Midter Exa: Tuesday 8 March i class Hoework 4 due Thursday Uless otherwise oted, let X be a irreducible, aperiodic Markov
Name Period ALGEBRA II Chapter 1B and 2A Notes Solving Inequalities and Absolute Value / Numbers and Functions
 Nae Period ALGEBRA II Chapter B ad A Notes Solvig Iequalities ad Absolute Value / Nubers ad Fuctios SECTION.6 Itroductio to Solvig Equatios Objectives: Write ad solve a liear equatio i oe variable. Solve
Nae Period ALGEBRA II Chapter B ad A Notes Solvig Iequalities ad Absolute Value / Nubers ad Fuctios SECTION.6 Itroductio to Solvig Equatios Objectives: Write ad solve a liear equatio i oe variable. Solve
5.76 Lecture #33 5/08/91 Page 1 of 10 pages. Lecture #33: Vibronic Coupling
 5.76 Lecture #33 5/8/9 Page of pages Lecture #33: Vibroic Couplig Last time: H CO A A X A Electroically forbidde if A -state is plaar vibroically allowed to alterate v if A -state is plaar iertial defect
5.76 Lecture #33 5/8/9 Page of pages Lecture #33: Vibroic Couplig Last time: H CO A A X A Electroically forbidde if A -state is plaar vibroically allowed to alterate v if A -state is plaar iertial defect
Physics 324, Fall Dirac Notation. These notes were produced by David Kaplan for Phys. 324 in Autumn 2001.
 Physics 324, Fall 2002 Dirac Notatio These otes were produced by David Kapla for Phys. 324 i Autum 2001. 1 Vectors 1.1 Ier product Recall from liear algebra: we ca represet a vector V as a colum vector;
Physics 324, Fall 2002 Dirac Notatio These otes were produced by David Kapla for Phys. 324 i Autum 2001. 1 Vectors 1.1 Ier product Recall from liear algebra: we ca represet a vector V as a colum vector;
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS 4786)
 Machie Learig for Data Sciece CS 4786) Lecture & 3: Pricipal Compoet Aalysis The text i black outlies high level ideas. The text i blue provides simple mathematical details to derive or get to the algorithm
Machie Learig for Data Sciece CS 4786) Lecture & 3: Pricipal Compoet Aalysis The text i black outlies high level ideas. The text i blue provides simple mathematical details to derive or get to the algorithm
Chapter 4. Fourier Series
 Chapter 4. Fourier Series At this poit we are ready to ow cosider the caoical equatios. Cosider, for eample the heat equatio u t = u, < (4.) subject to u(, ) = si, u(, t) = u(, t) =. (4.) Here,
Chapter 4. Fourier Series At this poit we are ready to ow cosider the caoical equatios. Cosider, for eample the heat equatio u t = u, < (4.) subject to u(, ) = si, u(, t) = u(, t) =. (4.) Here,
Answer Key, Problem Set 1, Written
 Cheistry 1 Mies, Sprig, 018 Aswer Key, Proble Set 1, Writte 1. 14.3;. 14.34 (add part (e): Estiate / calculate the iitial rate of the reactio); 3. NT1; 4. NT; 5. 14.37; 6. 14.39; 7. 14.41; 8. NT3; 9. 14.46;
Cheistry 1 Mies, Sprig, 018 Aswer Key, Proble Set 1, Writte 1. 14.3;. 14.34 (add part (e): Estiate / calculate the iitial rate of the reactio); 3. NT1; 4. NT; 5. 14.37; 6. 14.39; 7. 14.41; 8. NT3; 9. 14.46;
) is a square matrix with the property that for any m n matrix A, the product AI equals A. The identity matrix has a ii
 square atrix is oe that has the sae uber of rows as colus; that is, a atrix. he idetity atrix (deoted by I, I, or [] I ) is a square atrix with the property that for ay atrix, the product I equals. he
square atrix is oe that has the sae uber of rows as colus; that is, a atrix. he idetity atrix (deoted by I, I, or [] I ) is a square atrix with the property that for ay atrix, the product I equals. he
Chapter 8 Approximation Methods, Hueckel Theory
 Witer 3 Chem 356: Itroductory Quatum Mechaics Chapter 8 Approximatio Methods, Huecel Theory... 8 Approximatio Methods... 8 The Liear Variatioal Priciple... Chapter 8 Approximatio Methods, Huecel Theory
Witer 3 Chem 356: Itroductory Quatum Mechaics Chapter 8 Approximatio Methods, Huecel Theory... 8 Approximatio Methods... 8 The Liear Variatioal Priciple... Chapter 8 Approximatio Methods, Huecel Theory
The Growth of Functions. Theoretical Supplement
 The Growth of Fuctios Theoretical Supplemet The Triagle Iequality The triagle iequality is a algebraic tool that is ofte useful i maipulatig absolute values of fuctios. The triagle iequality says that
The Growth of Fuctios Theoretical Supplemet The Triagle Iequality The triagle iequality is a algebraic tool that is ofte useful i maipulatig absolute values of fuctios. The triagle iequality says that
ECE 901 Lecture 4: Estimation of Lipschitz smooth functions
 ECE 9 Lecture 4: Estiatio of Lipschitz sooth fuctios R. Nowak 5/7/29 Cosider the followig settig. Let Y f (X) + W, where X is a rado variable (r.v.) o X [, ], W is a r.v. o Y R, idepedet of X ad satisfyig
ECE 9 Lecture 4: Estiatio of Lipschitz sooth fuctios R. Nowak 5/7/29 Cosider the followig settig. Let Y f (X) + W, where X is a rado variable (r.v.) o X [, ], W is a r.v. o Y R, idepedet of X ad satisfyig
5. Quantum Nature of the Nano-world ( Fundamental of. Quantum mechanics)
 5. Quatu Nature of the Nao-world Fudaetal of What is the defiitio of aoaterials?? Quatu echaics i Origial: quatu size effect where the electroic properties of solids are altered with great reductios i
5. Quatu Nature of the Nao-world Fudaetal of What is the defiitio of aoaterials?? Quatu echaics i Origial: quatu size effect where the electroic properties of solids are altered with great reductios i
Recurrence Relations
 Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
Recurrece Relatios Aalysis of recursive algorithms, such as: it factorial (it ) { if (==0) retur ; else retur ( * factorial(-)); } Let t be the umber of multiplicatios eeded to calculate factorial(). The
Chapter 5 Vibrational Motion
 Fall 4 Chapter 5 Vibratioal Motio... 65 Potetial Eergy Surfaces, Rotatios ad Vibratios... 65 Harmoic Oscillator... 67 Geeral Solutio for H.O.: Operator Techique... 68 Vibratioal Selectio Rules... 7 Polyatomic
Fall 4 Chapter 5 Vibratioal Motio... 65 Potetial Eergy Surfaces, Rotatios ad Vibratios... 65 Harmoic Oscillator... 67 Geeral Solutio for H.O.: Operator Techique... 68 Vibratioal Selectio Rules... 7 Polyatomic
Optimal Estimator for a Sample Set with Response Error. Ed Stanek
 Optial Estiator for a Saple Set wit Respose Error Ed Staek Itroductio We develop a optial estiator siilar to te FP estiator wit respose error tat was cosidered i c08ed63doc Te first 6 pages of tis docuet
Optial Estiator for a Saple Set wit Respose Error Ed Staek Itroductio We develop a optial estiator siilar to te FP estiator wit respose error tat was cosidered i c08ed63doc Te first 6 pages of tis docuet
Automated Proofs for Some Stirling Number Identities
 Autoated Proofs for Soe Stirlig Nuber Idetities Mauel Kauers ad Carste Scheider Research Istitute for Sybolic Coputatio Johaes Kepler Uiversity Altebergerstraße 69 A4040 Liz, Austria Subitted: Sep 1, 2007;
Autoated Proofs for Soe Stirlig Nuber Idetities Mauel Kauers ad Carste Scheider Research Istitute for Sybolic Coputatio Johaes Kepler Uiversity Altebergerstraße 69 A4040 Liz, Austria Subitted: Sep 1, 2007;
3.2 Properties of Division 3.3 Zeros of Polynomials 3.4 Complex and Rational Zeros of Polynomials
 Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
Math 60 www.timetodare.com 3. Properties of Divisio 3.3 Zeros of Polyomials 3.4 Complex ad Ratioal Zeros of Polyomials I these sectios we will study polyomials algebraically. Most of our work will be cocered
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 116C. Problem Set 4. Benjamin Stahl. November 6, 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 6C Problem Set 4 Bejami Stahl November 6, 4 BOAS, P. 63, PROBLEM.-5 The Laguerre differetial equatio, x y + ( xy + py =, will be solved
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA - SANTA CRUZ DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS PHYS 6C Problem Set 4 Bejami Stahl November 6, 4 BOAS, P. 63, PROBLEM.-5 The Laguerre differetial equatio, x y + ( xy + py =, will be solved
Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors
 5 Eigevalues ad Eigevectors 5.3 DIAGONALIZATION DIAGONALIZATION Example 1: Let. Fid a formula for A k, give that P 1 1 = 1 2 ad, where Solutio: The stadard formula for the iverse of a 2 2 matrix yields
5 Eigevalues ad Eigevectors 5.3 DIAGONALIZATION DIAGONALIZATION Example 1: Let. Fid a formula for A k, give that P 1 1 = 1 2 ad, where Solutio: The stadard formula for the iverse of a 2 2 matrix yields
Math 2784 (or 2794W) University of Connecticut
 ORDERS OF GROWTH PAT SMITH Math 2784 (or 2794W) Uiversity of Coecticut Date: Mar. 2, 22. ORDERS OF GROWTH. Itroductio Gaiig a ituitive feel for the relative growth of fuctios is importat if you really
ORDERS OF GROWTH PAT SMITH Math 2784 (or 2794W) Uiversity of Coecticut Date: Mar. 2, 22. ORDERS OF GROWTH. Itroductio Gaiig a ituitive feel for the relative growth of fuctios is importat if you really
q-fibonacci polynomials and q-catalan numbers Johann Cigler [ ] (4) I don t know who has observed this well-known fact for the first time.
![q-fibonacci polynomials and q-catalan numbers Johann Cigler [ ] (4) I don t know who has observed this well-known fact for the first time. q-fibonacci polynomials and q-catalan numbers Johann Cigler [ ] (4) I don t know who has observed this well-known fact for the first time.](/thumbs/79/80173725.jpg) -Fiboacci polyoials ad -Catala ubers Joha Cigler The Fiboacci polyoials satisfy the recurrece F ( x s) = s x = () F ( x s) = xf ( x s) + sf ( x s) () with iitial values F ( x s ) = ad F( x s ) = These
-Fiboacci polyoials ad -Catala ubers Joha Cigler The Fiboacci polyoials satisfy the recurrece F ( x s) = s x = () F ( x s) = xf ( x s) + sf ( x s) () with iitial values F ( x s ) = ad F( x s ) = These
Statistics and Data Analysis in MATLAB Kendrick Kay, February 28, Lecture 4: Model fitting
 Statistics ad Data Aalysis i MATLAB Kedrick Kay, kedrick.kay@wustl.edu February 28, 2014 Lecture 4: Model fittig 1. The basics - Suppose that we have a set of data ad suppose that we have selected the
Statistics ad Data Aalysis i MATLAB Kedrick Kay, kedrick.kay@wustl.edu February 28, 2014 Lecture 4: Model fittig 1. The basics - Suppose that we have a set of data ad suppose that we have selected the
Application 10.5D Spherical Harmonic Waves
 Applicatio 10.5D Spherical Haroic Waves I probles ivolvig regios that ejoy spherical syetry about the origi i space, it is appropriate to use spherical coordiates. The 3-diesioal Laplacia for a fuctio
Applicatio 10.5D Spherical Haroic Waves I probles ivolvig regios that ejoy spherical syetry about the origi i space, it is appropriate to use spherical coordiates. The 3-diesioal Laplacia for a fuctio
Lecture 19. Curve fitting I. 1 Introduction. 2 Fitting a constant to measured data
 Lecture 9 Curve fittig I Itroductio Suppose we are preseted with eight poits of easured data (x i, y j ). As show i Fig. o the left, we could represet the uderlyig fuctio of which these data are saples
Lecture 9 Curve fittig I Itroductio Suppose we are preseted with eight poits of easured data (x i, y j ). As show i Fig. o the left, we could represet the uderlyig fuctio of which these data are saples
PAPER : IIT-JAM 2010
 MATHEMATICS-MA (CODE A) Q.-Q.5: Oly oe optio is correct for each questio. Each questio carries (+6) marks for correct aswer ad ( ) marks for icorrect aswer.. Which of the followig coditios does NOT esure
MATHEMATICS-MA (CODE A) Q.-Q.5: Oly oe optio is correct for each questio. Each questio carries (+6) marks for correct aswer ad ( ) marks for icorrect aswer.. Which of the followig coditios does NOT esure
1 Generating functions for balls in boxes
 Math 566 Fall 05 Some otes o geeratig fuctios Give a sequece a 0, a, a,..., a,..., a geeratig fuctio some way of represetig the sequece as a fuctio. There are may ways to do this, with the most commo ways
Math 566 Fall 05 Some otes o geeratig fuctios Give a sequece a 0, a, a,..., a,..., a geeratig fuctio some way of represetig the sequece as a fuctio. There are may ways to do this, with the most commo ways
Bertrand s Postulate
 Bertrad s Postulate Lola Thompso Ross Program July 3, 2009 Lola Thompso (Ross Program Bertrad s Postulate July 3, 2009 1 / 33 Bertrad s Postulate I ve said it oce ad I ll say it agai: There s always a
Bertrad s Postulate Lola Thompso Ross Program July 3, 2009 Lola Thompso (Ross Program Bertrad s Postulate July 3, 2009 1 / 33 Bertrad s Postulate I ve said it oce ad I ll say it agai: There s always a
The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j
![The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j The z-transform. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 The z-transform Derivation of the z-transform: x[n] = z n LTI system, h[n] z = re j](/thumbs/82/85448534.jpg) The -Trasform 7. Itroductio Geeralie the complex siusoidal represetatio offered by DTFT to a represetatio of complex expoetial sigals. Obtai more geeral characteristics for discrete-time LTI systems. 7.
The -Trasform 7. Itroductio Geeralie the complex siusoidal represetatio offered by DTFT to a represetatio of complex expoetial sigals. Obtai more geeral characteristics for discrete-time LTI systems. 7.
Math 475, Problem Set #12: Answers
 Math 475, Problem Set #12: Aswers A. Chapter 8, problem 12, parts (b) ad (d). (b) S # (, 2) = 2 2, sice, from amog the 2 ways of puttig elemets ito 2 distiguishable boxes, exactly 2 of them result i oe
Math 475, Problem Set #12: Aswers A. Chapter 8, problem 12, parts (b) ad (d). (b) S # (, 2) = 2 2, sice, from amog the 2 ways of puttig elemets ito 2 distiguishable boxes, exactly 2 of them result i oe
Properties and Tests of Zeros of Polynomial Functions
 Properties ad Tests of Zeros of Polyomial Fuctios The Remaider ad Factor Theorems: Sythetic divisio ca be used to fid the values of polyomials i a sometimes easier way tha substitutio. This is show by
Properties ad Tests of Zeros of Polyomial Fuctios The Remaider ad Factor Theorems: Sythetic divisio ca be used to fid the values of polyomials i a sometimes easier way tha substitutio. This is show by
42 Dependence and Bases
 42 Depedece ad Bases The spa s(a) of a subset A i vector space V is a subspace of V. This spa ay be the whole vector space V (we say the A spas V). I this paragraph we study subsets A of V which spa V
42 Depedece ad Bases The spa s(a) of a subset A i vector space V is a subspace of V. This spa ay be the whole vector space V (we say the A spas V). I this paragraph we study subsets A of V which spa V
Contents Two Sample t Tests Two Sample t Tests
 Cotets 3.5.3 Two Saple t Tests................................... 3.5.3 Two Saple t Tests Setup: Two Saples We ow focus o a sceario where we have two idepedet saples fro possibly differet populatios. Our
Cotets 3.5.3 Two Saple t Tests................................... 3.5.3 Two Saple t Tests Setup: Two Saples We ow focus o a sceario where we have two idepedet saples fro possibly differet populatios. Our
SECTION 2.6 THE SECOND ALTERNATIVE
 54 SECTION 2.6 THE SECOND ALTERNATIVE We ow discuss the probles where the Secod Alterative holds. The suppositio is that there is a otrivial solutio for L(y) =, B (y) = B 2 (y) =. The Fredhol Theores assure
54 SECTION 2.6 THE SECOND ALTERNATIVE We ow discuss the probles where the Secod Alterative holds. The suppositio is that there is a otrivial solutio for L(y) =, B (y) = B 2 (y) =. The Fredhol Theores assure
On the transcendence of infinite sums of values of rational functions
 O the trascedece of ifiite sus of values of ratioal fuctios N. Saradha ad R. Tijdea Abstract P () = We ivestigate coverget sus T = Q() ad U = P (X), Q(X) Q[X], ad Q(X) has oly siple ratioal roots. = (
O the trascedece of ifiite sus of values of ratioal fuctios N. Saradha ad R. Tijdea Abstract P () = We ivestigate coverget sus T = Q() ad U = P (X), Q(X) Q[X], ad Q(X) has oly siple ratioal roots. = (
The state space model needs 5 parameters, so it is not as convenient to use in this control study.
 Trasfer fuctio for of the odel G θ K ω 2 θ / v θ / v ( s) = = 2 2 vi s + 2ζωs + ω The followig slides detail a derivatio of this aalog eter odel both as state space odel ad trasfer fuctio (TF) as show
Trasfer fuctio for of the odel G θ K ω 2 θ / v θ / v ( s) = = 2 2 vi s + 2ζωs + ω The followig slides detail a derivatio of this aalog eter odel both as state space odel ad trasfer fuctio (TF) as show
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS 4786)
 Machie Learig for Data Sciece CS 4786) Lecture 9: Pricipal Compoet Aalysis The text i black outlies mai ideas to retai from the lecture. The text i blue give a deeper uderstadig of how we derive or get
Machie Learig for Data Sciece CS 4786) Lecture 9: Pricipal Compoet Aalysis The text i black outlies mai ideas to retai from the lecture. The text i blue give a deeper uderstadig of how we derive or get
x a x a Lecture 2 Series (See Chapter 1 in Boas)
 Lecture Series (See Chapter i Boas) A basic ad very powerful (if pedestria, recall we are lazy AD smart) way to solve ay differetial (or itegral) equatio is via a series expasio of the correspodig solutio
Lecture Series (See Chapter i Boas) A basic ad very powerful (if pedestria, recall we are lazy AD smart) way to solve ay differetial (or itegral) equatio is via a series expasio of the correspodig solutio
A new sequence convergent to Euler Mascheroni constant
 You ad Che Joural of Iequalities ad Applicatios 08) 08:7 https://doi.org/0.86/s3660-08-670-6 R E S E A R C H Ope Access A ew sequece coverget to Euler Mascheroi costat Xu You * ad Di-Rog Che * Correspodece:
You ad Che Joural of Iequalities ad Applicatios 08) 08:7 https://doi.org/0.86/s3660-08-670-6 R E S E A R C H Ope Access A ew sequece coverget to Euler Mascheroi costat Xu You * ad Di-Rog Che * Correspodece:
Wavelet Transform Theory. Prof. Mark Fowler Department of Electrical Engineering State University of New York at Binghamton
 Wavelet Trasfor Theory Prof. Mark Fowler Departet of Electrical Egieerig State Uiversity of New York at Bighato What is a Wavelet Trasfor? Decopositio of a sigal ito costituet parts Note that there are
Wavelet Trasfor Theory Prof. Mark Fowler Departet of Electrical Egieerig State Uiversity of New York at Bighato What is a Wavelet Trasfor? Decopositio of a sigal ito costituet parts Note that there are
Lanczos-Haydock Recursion
 Laczos-Haydock Recursio Bor: Feb 893 i Székesehérvár, Hugary- Died: 5 Jue 974 i Budapest, Hugary Corelius Laczos From a abstract mathematical viewpoit, the method for puttig a symmetric matrix i three-diagoal
Laczos-Haydock Recursio Bor: Feb 893 i Székesehérvár, Hugary- Died: 5 Jue 974 i Budapest, Hugary Corelius Laczos From a abstract mathematical viewpoit, the method for puttig a symmetric matrix i three-diagoal
The Born-Oppenheimer approximation
 The Bor-Oppeheimer approximatio 1 Re-writig the Schrödiger equatio We will begi from the full time-idepedet Schrödiger equatio for the eigestates of a molecular system: [ P 2 + ( Pm 2 + e2 1 1 2m 2m m
The Bor-Oppeheimer approximatio 1 Re-writig the Schrödiger equatio We will begi from the full time-idepedet Schrödiger equatio for the eigestates of a molecular system: [ P 2 + ( Pm 2 + e2 1 1 2m 2m m
a for a 1 1 matrix. a b a b 2 2 matrix: We define det ad bc 3 3 matrix: We define a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a a
 Math S-b Lecture # Notes This wee is all about determiats We ll discuss how to defie them, how to calculate them, lear the allimportat property ow as multiliearity, ad show that a square matrix A is ivertible
Math S-b Lecture # Notes This wee is all about determiats We ll discuss how to defie them, how to calculate them, lear the allimportat property ow as multiliearity, ad show that a square matrix A is ivertible
Complex Analysis Spring 2001 Homework I Solution
 Complex Aalysis Sprig 2001 Homework I Solutio 1. Coway, Chapter 1, sectio 3, problem 3. Describe the set of poits satisfyig the equatio z a z + a = 2c, where c > 0 ad a R. To begi, we see from the triagle
Complex Aalysis Sprig 2001 Homework I Solutio 1. Coway, Chapter 1, sectio 3, problem 3. Describe the set of poits satisfyig the equatio z a z + a = 2c, where c > 0 ad a R. To begi, we see from the triagle
SphericalHarmonicY. Notations. Primary definition. Specific values. Traditional name. Traditional notation. Mathematica StandardForm notation
 SphericalHaroicY Notatios Traditioal ae Spherical haroic Traditioal otatio Y, φ Matheatica StadardFor otatio SphericalHaroicY,,, φ Priary defiitio 05.0.0.000.0 Y, φ φ P cos ; 05.0.0.000.0 Y 0 k, φ k k
SphericalHaroicY Notatios Traditioal ae Spherical haroic Traditioal otatio Y, φ Matheatica StadardFor otatio SphericalHaroicY,,, φ Priary defiitio 05.0.0.000.0 Y, φ φ P cos ; 05.0.0.000.0 Y 0 k, φ k k
LOWER BOUNDS FOR MOMENTS OF ζ (ρ) 1. Introduction
 LOWER BOUNDS FOR MOMENTS OF ζ ρ MICAH B. MILINOVICH AND NATHAN NG Abstract. Assuig the Riea Hypothesis, we establish lower bouds for oets of the derivative of the Riea zeta-fuctio averaged over the otrivial
LOWER BOUNDS FOR MOMENTS OF ζ ρ MICAH B. MILINOVICH AND NATHAN NG Abstract. Assuig the Riea Hypothesis, we establish lower bouds for oets of the derivative of the Riea zeta-fuctio averaged over the otrivial
Michail Zak Senior Research Scientist (Emeritus) Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 91109, USA.
 Solvig NP-coplete proble by siulatios. Michail Zak Seior Research Scietist (Eeritus) Jet Propulsio Laboratory Califoria Istitute of Techology Pasadea, CA 99, USA. Abstract. The atheatical foralis of uatu
Solvig NP-coplete proble by siulatios. Michail Zak Seior Research Scietist (Eeritus) Jet Propulsio Laboratory Califoria Istitute of Techology Pasadea, CA 99, USA. Abstract. The atheatical foralis of uatu
GROUPOID CARDINALITY AND EGYPTIAN FRACTIONS
 GROUPOID CARDINALITY AND EGYPTIAN FRACTIONS JULIA E. BERGNER AND CHRISTOPHER D. WALKER Abstract. I this paper we show that two very ew questios about the cardiality of groupoids reduce to very old questios
GROUPOID CARDINALITY AND EGYPTIAN FRACTIONS JULIA E. BERGNER AND CHRISTOPHER D. WALKER Abstract. I this paper we show that two very ew questios about the cardiality of groupoids reduce to very old questios
1 (12 points) Red-Black trees and Red-Purple trees
 CS6 Hoework 3 Due: 29 April 206, 2 oo Subit o Gradescope Haded out: 22 April 206 Istructios: Please aswer the followig questios to the best of your ability. If you are asked to desig a algorith, please
CS6 Hoework 3 Due: 29 April 206, 2 oo Subit o Gradescope Haded out: 22 April 206 Istructios: Please aswer the followig questios to the best of your ability. If you are asked to desig a algorith, please
Chapter 6 Infinite Series
 Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
Chapter 6 Ifiite Series I the previous chapter we cosidered itegrals which were improper i the sese that the iterval of itegratio was ubouded. I this chapter we are goig to discuss a topic which is somewhat
