Fluids and Buoyancy. 1. What will happen to the scale reading as the mass is lowered?
|
|
|
- Archibald Bertram Mosley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fluids and Buoyancy. Wat will appen to te scale reading as te mass is lowered? M Using rcimedes Principle: any body fully or partially submerged in a fluid is buoyed up by a force equal to te weigt of te fluid displaced. If mass is more dense tan fluid, mass will sink and scale will read weigt of fluid and full weigt off mass. If mass is less dense tan fluid, object will float and scale will increase until equilibrium is reaced between buoyancy and weigt of mass.. Find pressure as a function of time. ime t 0, te water level is feet. Cross-sectional area is 8 ft for te top and ft for te bottom. M - t ft ft M t Container wit cross sectional area perpendicular to y-axis of 6-y/. Wat is pressure at bottom? Rate of water addition is (-t) ft /min and leaves continuously a ft /min.
2 P ρg dv d dt ( t) t dt dv 6 d (6 ) dt ( ) t t dt 6 t + c 4 c?; t 0, ; c; c 6 + ( + t ) 0 4 ± t 0, P( t) ρg( 6 t t t + + ). For a ydrofoil aircraft, wy is turbulent flow preferable? Te indentations create turbulence in te boundary layer downstream of te indentations, canging te caracteristics of te flowing fluid to a turbulent boundary layer aead of te normal point of separation of te fluid from te foil, tis causing te fluid to cling close to te surface of te foil and postpone or delay trailing edge separation of te fluid stream from te foil. Te noise level is reduced, te performance and efficiency of te foil is improved, or boe noise level is reduced and te performance and efficiency of te foil is improved. 4. In te following simplified system, were is pressure te greatest? Heat Dissipater Condenser Heat Engine Pump
3 Higest pressure is downstream of te pump (counterclockwise rotation). 5. If te flow rate is increased by a factor of tree, ow does te pressure cange at bot points? Pressure will decrease by a factor of nine. Bernoulli's equation states tat, in a streamline fluid flow, te greater te speed of te flow, te less te static pressure, and te less te speed of te flow, te greater te static pressure. Tere exists a simple excange between te dynamic and static pressures suc taeir total remains te same. s one increases, te oter must decrease. Use te relationsip: (½)ρV + P P t 6. Wat is force F? F ft 9000 lbs Cross-sectional areas 9 in B 900 in B ssume at fluid is water 0 degrees Celsius and at sea level, terefore ρ water 0.07lbf/in lbf 0.07 in 9in F + in 9in 9in 9000lbf 0.07lbf F 9in ( 900in in F 86lbf 9000lbf 900in in) 7. ball of diameter 0 cm and mass 0 grams is dropped in a container of water. Te cross-sectional area of te container is 00 cm. Wat is te cange in te eigt of te water column? ssume cross-sectional area of te container is constant and temperature is 0 deg C. Density of ball:
4 ρ 0g ball.09g / 4 0 π cm ρ ball <ρ water, so te ball floats. So te weigt of te water displaced is 0g. Volume of water displaced: 0g V m / ρ 0cm g cm V V0 V0 Δ 0 + 0cm V 0 0cm 8. Te cross-sectional area of te sipon tube is constant. Te fluid flows from tub to tub. Determine te maximum eigt tat will still result in fluid flow. Tub Tub Maximum eigt of a sipon is (using Bernoulli s equation), and velocity of sipon is as slow as possible. max P atm ρg 9. Te motor on a centrifugal pump is ooked up backwards, causing te impeller to spin te wrong direction. Wat will appen to te ead vs. gpm curve? Wile flow would continue in te proper direction te efficiency of te pump would decrease. Te ead vs. gpm curve would decrease. 0. Describe ow a Venturi meter works and sow ow it can be used to calculate fluid flow (Bernoulli s Eqn. and te Continuity Eqn.) Venturi meter utilizes a nozzle to measure te mass flow rate of a fluid by measuring te differential pressure. Energy equation
5 q w Δgpe + Δppe + Δke ( P ( v v ) / ( P P ) / ρ + ( v Continuity Equation: P ) / ρ m! v v! /! Substitute: (( f c ) venturi m ; v m/ ( P P ) ( ) ) f ρ ρ P P P P v ) /. Wat appens to te water level wit respeco te sore wen te sailor trows te lead ancor overboard? Use rcimedes Principle: were an object partly or wolly immersed in a fluid is buoyed up by a force equal to te weigt of te fluid displaced..4 lead Va ( ) Va ( ). 4 water ρ ρ V a Terefore, ancor is displacing an amount equal to its volume..4v a reducing water level.. How far will te water soot out? d Energy Balance
6 E p E k v mg v g v t v t d v d 0 g gt + / g axt t + ( g )( / g ). Explain ow you would estimate te flow rate in a pipe. Measure flow in cfs. If water is dropping from a pipe you can measure wit carpenter s ruler. Measure orizontal distance, te vertical drop y. Cross section of a pipe: Flow ratearea*velocity*rougness factor (least accurate +/-0%) Timed volume using bucket and stopwatc: flow ratevolume/time 4. If te liquid is flowing in te direction indicated, at wat point is te pressure greatest? B C D E 5. Given a fluid flowing troug a pipe in te direction indicated, wat difference in parameters exists between points and B? B Pressure is lower as point B tan point due to energy losses in te pipe (ead loss. Te energy is converted to eat. 6. Wat is meant by laminar and turbulent flow? If you ad a piping system, wic type of flow would be better and wy?
7 Laminar flow is a fluid flow caracterized by non-turbulent and inefficient eat transfer capability. Turbulent flow as a great deal of mixing and friction. Laminar flow is more desired in piping because pump power is reduced due to te lower ead loss. Turbulent flow is desirable wen earansfer needs to be maximized. 7. Wic will raise te water level in a tank iger wen added a one pound block of iron or a one pound block of wood? rcimedes Principle Equation Wood displaces more volume of water tan lead
Notes: Most of the material in this chapter is taken from Young and Freedman, Chap. 12.
 Capter 6. Fluid Mecanics Notes: Most of te material in tis capter is taken from Young and Freedman, Cap. 12. 6.1 Fluid Statics Fluids, i.e., substances tat can flow, are te subjects of tis capter. But
Capter 6. Fluid Mecanics Notes: Most of te material in tis capter is taken from Young and Freedman, Cap. 12. 6.1 Fluid Statics Fluids, i.e., substances tat can flow, are te subjects of tis capter. But
Finding and Using Derivative The shortcuts
 Calculus 1 Lia Vas Finding and Using Derivative Te sortcuts We ave seen tat te formula f f(x+) f(x) (x) = lim 0 is manageable for relatively simple functions like a linear or quadratic. For more complex
Calculus 1 Lia Vas Finding and Using Derivative Te sortcuts We ave seen tat te formula f f(x+) f(x) (x) = lim 0 is manageable for relatively simple functions like a linear or quadratic. For more complex
f a h f a h h lim lim
 Te Derivative Te derivative of a function f at a (denoted f a) is f a if tis it exists. An alternative way of defining f a is f a x a fa fa fx fa x a Note tat te tangent line to te grap of f at te point
Te Derivative Te derivative of a function f at a (denoted f a) is f a if tis it exists. An alternative way of defining f a is f a x a fa fa fx fa x a Note tat te tangent line to te grap of f at te point
2.8 The Derivative as a Function
 .8 Te Derivative as a Function Typically, we can find te derivative of a function f at many points of its domain: Definition. Suppose tat f is a function wic is differentiable at every point of an open
.8 Te Derivative as a Function Typically, we can find te derivative of a function f at many points of its domain: Definition. Suppose tat f is a function wic is differentiable at every point of an open
Numerical Differentiation
 Numerical Differentiation Finite Difference Formulas for te first derivative (Using Taylor Expansion tecnique) (section 8.3.) Suppose tat f() = g() is a function of te variable, and tat as 0 te function
Numerical Differentiation Finite Difference Formulas for te first derivative (Using Taylor Expansion tecnique) (section 8.3.) Suppose tat f() = g() is a function of te variable, and tat as 0 te function
MAT 145. Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points
 MAT 15 Test #2 Name Solution Guide Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points Use te grap of a function sown ere as you respond to questions 1 to 8. 1. lim f (x) 0 2. lim
MAT 15 Test #2 Name Solution Guide Type of Calculator Used TI-89 Titanium 100 points Score 100 possible points Use te grap of a function sown ere as you respond to questions 1 to 8. 1. lim f (x) 0 2. lim
MVT and Rolle s Theorem
 AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
AP Calculus CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET APPLICATIONS OF DIFFERENTIATION MVT and Rolle s Teorem Name Seat # Date UNLESS INDICATED, DO NOT USE YOUR CALCULATOR FOR ANY OF THESE QUESTIONS In problems 1 and, state
Higher Derivatives. Differentiable Functions
 Calculus 1 Lia Vas Higer Derivatives. Differentiable Functions Te second derivative. Te derivative itself can be considered as a function. Te instantaneous rate of cange of tis function is te second derivative.
Calculus 1 Lia Vas Higer Derivatives. Differentiable Functions Te second derivative. Te derivative itself can be considered as a function. Te instantaneous rate of cange of tis function is te second derivative.
Section A 01. (12 M) (s 2 s 3 ) = 313 s 2 = s 1, h 3 = h 4 (s 1 s 3 ) = kj/kgk. = kj/kgk. 313 (s 3 s 4f ) = ln
 0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
= h. Geometrically this quantity represents the slope of the secant line connecting the points
 Section 3.7: Rates of Cange in te Natural and Social Sciences Recall: Average rate of cange: y y y ) ) ), ere Geometrically tis quantity represents te slope of te secant line connecting te points, f (
Section 3.7: Rates of Cange in te Natural and Social Sciences Recall: Average rate of cange: y y y ) ) ), ere Geometrically tis quantity represents te slope of te secant line connecting te points, f (
Homework Assignment on Fluid Statics
 AMEE 0 Introduction to Fluid Mecanics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: m.fyrillas@fit.ac.cy Homework Assignment on Fluid Statics --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AMEE 0 Introduction to Fluid Mecanics Instructor: Marios M. Fyrillas Email: m.fyrillas@fit.ac.cy Homework Assignment on Fluid Statics --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
University of Alabama Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 101 LeClair Summer Exam 1 Solutions
 University of Alabama Department of Pysics and Astronomy PH 101 LeClair Summer 2011 Exam 1 Solutions 1. A motorcycle is following a car tat is traveling at constant speed on a straigt igway. Initially,
University of Alabama Department of Pysics and Astronomy PH 101 LeClair Summer 2011 Exam 1 Solutions 1. A motorcycle is following a car tat is traveling at constant speed on a straigt igway. Initially,
Announcements. Exam 4 - Review of important concepts
 Announcements 1. Exam 4 starts Friday! a. Available in esting Center from Friday, Dec 7 (opening time), up to Monday, Dec 10 at 4:00 pm. i. Late fee if you start your exam after 4 pm b. Covers C. 9-1 (up
Announcements 1. Exam 4 starts Friday! a. Available in esting Center from Friday, Dec 7 (opening time), up to Monday, Dec 10 at 4:00 pm. i. Late fee if you start your exam after 4 pm b. Covers C. 9-1 (up
Physics Courseware Physics I
 Definition of pressure: Force Area ysics Courseware ysics I Bernoulli Hydrostatics equation: B A Bernoulli s equation: roblem.- In a carburetor (scematically sown in te fiure) calculate te minimum speed
Definition of pressure: Force Area ysics Courseware ysics I Bernoulli Hydrostatics equation: B A Bernoulli s equation: roblem.- In a carburetor (scematically sown in te fiure) calculate te minimum speed
The Derivative The rate of change
 Calculus Lia Vas Te Derivative Te rate of cange Knowing and understanding te concept of derivative will enable you to answer te following questions. Let us consider a quantity wose size is described by
Calculus Lia Vas Te Derivative Te rate of cange Knowing and understanding te concept of derivative will enable you to answer te following questions. Let us consider a quantity wose size is described by
1 Power is transferred through a machine as shown. power input P I machine. power output P O. power loss P L. What is the efficiency of the machine?
 1 1 Power is transferred troug a macine as sown. power input P I macine power output P O power loss P L Wat is te efficiency of te macine? P I P L P P P O + P L I O P L P O P I 2 ir in a bicycle pump is
1 1 Power is transferred troug a macine as sown. power input P I macine power output P O power loss P L Wat is te efficiency of te macine? P I P L P P P O + P L I O P L P O P I 2 ir in a bicycle pump is
(a) At what number x = a does f have a removable discontinuity? What value f(a) should be assigned to f at x = a in order to make f continuous at a?
 Solutions to Test 1 Fall 016 1pt 1. Te grap of a function f(x) is sown at rigt below. Part I. State te value of eac limit. If a limit is infinite, state weter it is or. If a limit does not exist (but is
Solutions to Test 1 Fall 016 1pt 1. Te grap of a function f(x) is sown at rigt below. Part I. State te value of eac limit. If a limit is infinite, state weter it is or. If a limit does not exist (but is
The Laws of Thermodynamics
 1 Te Laws of Termodynamics CLICKER QUESTIONS Question J.01 Description: Relating termodynamic processes to PV curves: isobar. Question A quantity of ideal gas undergoes a termodynamic process. Wic curve
1 Te Laws of Termodynamics CLICKER QUESTIONS Question J.01 Description: Relating termodynamic processes to PV curves: isobar. Question A quantity of ideal gas undergoes a termodynamic process. Wic curve
Grade: 11 International Physics Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2
 Grade: 11 International Pysics Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Max Marks: 60 Test ID: 12111 Time
Grade: 11 International Pysics Olympiad Qualifier Set: 2 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Max Marks: 60 Test ID: 12111 Time
Work and Energy. Introduction. Work. PHY energy - J. Hedberg
 Work and Energy PHY 207 - energy - J. Hedberg - 2017 1. Introduction 2. Work 3. Kinetic Energy 4. Potential Energy 5. Conservation of Mecanical Energy 6. Ex: Te Loop te Loop 7. Conservative and Non-conservative
Work and Energy PHY 207 - energy - J. Hedberg - 2017 1. Introduction 2. Work 3. Kinetic Energy 4. Potential Energy 5. Conservation of Mecanical Energy 6. Ex: Te Loop te Loop 7. Conservative and Non-conservative
1. Which one of the following expressions is not equal to all the others? 1 C. 1 D. 25x. 2. Simplify this expression as much as possible.
 004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
004 Algebra Pretest answers and scoring Part A. Multiple coice questions. Directions: Circle te letter ( A, B, C, D, or E ) net to te correct answer. points eac, no partial credit. Wic one of te following
Chapters 19 & 20 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Capters 19 & 20 Heat and te First Law of Termodynamics Te Zerot Law of Termodynamics Te First Law of Termodynamics Termal Processes Te Second Law of Termodynamics Heat Engines and te Carnot Cycle Refrigerators,
Lecture XVII. Abstract We introduce the concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation with the gradient operator.
 Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Lecture XVII Abstract We introduce te concept of directional derivative of a scalar function and discuss its relation wit te gradient operator. Directional derivative and gradient Te directional derivative
Some Review Problems for First Midterm Mathematics 1300, Calculus 1
 Some Review Problems for First Midterm Matematics 00, Calculus. Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd,
Some Review Problems for First Midterm Matematics 00, Calculus. Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd,
5.1 We will begin this section with the definition of a rational expression. We
 Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Basic Properties and Reducing to Lowest Terms 5.1 We will begin tis section wit te definition of a rational epression. We will ten state te two basic properties associated wit rational epressions and go
Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions
 Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions David Lippman, Melonie Rasmussen 1 st Edition Solutions created at Te Evergreen State College and Soreline Community College 1.1 Solutions
Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions David Lippman, Melonie Rasmussen 1 st Edition Solutions created at Te Evergreen State College and Soreline Community College 1.1 Solutions
Simulation and verification of a plate heat exchanger with a built-in tap water accumulator
 Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
Simulation and verification of a plate eat excanger wit a built-in tap water accumulator Anders Eriksson Abstract In order to test and verify a compact brazed eat excanger (CBE wit a built-in accumulation
Time (hours) Morphine sulfate (mg)
 Mat Xa Fall 2002 Review Notes Limits and Definition of Derivative Important Information: 1 According to te most recent information from te Registrar, te Xa final exam will be eld from 9:15 am to 12:15
Mat Xa Fall 2002 Review Notes Limits and Definition of Derivative Important Information: 1 According to te most recent information from te Registrar, te Xa final exam will be eld from 9:15 am to 12:15
Part 2: Introduction to Open-Channel Flow SPRING 2005
 Part : Introduction to Open-Cannel Flow SPRING 005. Te Froude number. Total ead and specific energy 3. Hydraulic jump. Te Froude Number Te main caracteristics of flows in open cannels are tat: tere is
Part : Introduction to Open-Cannel Flow SPRING 005. Te Froude number. Total ead and specific energy 3. Hydraulic jump. Te Froude Number Te main caracteristics of flows in open cannels are tat: tere is
Combining functions: algebraic methods
 Combining functions: algebraic metods Functions can be added, subtracted, multiplied, divided, and raised to a power, just like numbers or algebra expressions. If f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x + 2, clearly f(x)
Combining functions: algebraic metods Functions can be added, subtracted, multiplied, divided, and raised to a power, just like numbers or algebra expressions. If f(x) = x 2 and g(x) = x + 2, clearly f(x)
1. Consider the trigonometric function f(t) whose graph is shown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t).
 . Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd, periodic function tat as been sifted upwards, so we will use
. Consider te trigonometric function f(t) wose grap is sown below. Write down a possible formula for f(t). Tis function appears to be an odd, periodic function tat as been sifted upwards, so we will use
The distance between City C and City A is just the magnitude of the vector, namely,
 Pysics 11 Homework III Solutions C. 3 - Problems 2, 15, 18, 23, 24, 30, 39, 58. Problem 2 So, we fly 200km due west from City A to City B, ten 300km 30 nort of west from City B to City C. (a) We want te
Pysics 11 Homework III Solutions C. 3 - Problems 2, 15, 18, 23, 24, 30, 39, 58. Problem 2 So, we fly 200km due west from City A to City B, ten 300km 30 nort of west from City B to City C. (a) We want te
Precalculus Test 2 Practice Questions Page 1. Note: You can expect other types of questions on the test than the ones presented here!
 Precalculus Test 2 Practice Questions Page Note: You can expect oter types of questions on te test tan te ones presented ere! Questions Example. Find te vertex of te quadratic f(x) = 4x 2 x. Example 2.
Precalculus Test 2 Practice Questions Page Note: You can expect oter types of questions on te test tan te ones presented ere! Questions Example. Find te vertex of te quadratic f(x) = 4x 2 x. Example 2.
Chapter 1 Functions and Graphs. Section 1.5 = = = 4. Check Point Exercises The slope of the line y = 3x+ 1 is 3.
 Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
Capter Functions and Graps Section. Ceck Point Exercises. Te slope of te line y x+ is. y y m( x x y ( x ( y ( x+ point-slope y x+ 6 y x+ slope-intercept. a. Write te equation in slope-intercept form: x+
The Foundations of Chemistry 1
 Te Foundations of Cemistry 1 1-1 (a) Biocemistry is te study of te cemistry of living tings. (b) Analytical cemistry studies te quantitative and qualitative composition analysis of substances. (c) Geocemistry
Te Foundations of Cemistry 1 1-1 (a) Biocemistry is te study of te cemistry of living tings. (b) Analytical cemistry studies te quantitative and qualitative composition analysis of substances. (c) Geocemistry
1 2 x Solution. The function f x is only defined when x 0, so we will assume that x 0 for the remainder of the solution. f x. f x h f x.
 Problem. Let f x x. Using te definition of te derivative prove tat f x x Solution. Te function f x is only defined wen x 0, so we will assume tat x 0 for te remainder of te solution. By te definition of
Problem. Let f x x. Using te definition of te derivative prove tat f x x Solution. Te function f x is only defined wen x 0, so we will assume tat x 0 for te remainder of te solution. By te definition of
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
Phy 231 Sp 02 Homework #6 Page 1 of 4
 Py 231 Sp 02 Homework #6 Page 1 of 4 6-1A. Te force sown in te force-time diagram at te rigt versus time acts on a 2 kg mass. Wat is te impulse of te force on te mass from 0 to 5 sec? (a) 9 N-s (b) 6 N-s
Py 231 Sp 02 Homework #6 Page 1 of 4 6-1A. Te force sown in te force-time diagram at te rigt versus time acts on a 2 kg mass. Wat is te impulse of te force on te mass from 0 to 5 sec? (a) 9 N-s (b) 6 N-s
2.11 That s So Derivative
 2.11 Tat s So Derivative Introduction to Differential Calculus Just as one defines instantaneous velocity in terms of average velocity, we now define te instantaneous rate of cange of a function at a point
2.11 Tat s So Derivative Introduction to Differential Calculus Just as one defines instantaneous velocity in terms of average velocity, we now define te instantaneous rate of cange of a function at a point
States of Matter. Pressure PHYSICS 220. Illustration. Lecture 16. Fluids. Solid. Liquid. Gas. Pressure = F normal / A
 PHYSICS 220 States of Matter Lecture 16 Fluids Fluids Solid Hold Volume Hold Sape Liquid Hold Volume Adapt Sape Gas Adapt Volume Adapt Sape Lecture 16 Purdue University, Pysics 220 1 Lecture 16 Purdue
PHYSICS 220 States of Matter Lecture 16 Fluids Fluids Solid Hold Volume Hold Sape Liquid Hold Volume Adapt Sape Gas Adapt Volume Adapt Sape Lecture 16 Purdue University, Pysics 220 1 Lecture 16 Purdue
A = h w (1) Error Analysis Physics 141
 Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
Introduction In all brances of pysical science and engineering one deals constantly wit numbers wic results more or less directly from experimental observations. Experimental observations always ave inaccuracies.
pancakes. A typical pancake also appears in the sketch above. The pancake at height x (which is the fraction x of the total height of the cone) has
 Volumes One can epress volumes of regions in tree dimensions as integrals using te same strateg as we used to epress areas of regions in two dimensions as integrals approimate te region b a union of small,
Volumes One can epress volumes of regions in tree dimensions as integrals using te same strateg as we used to epress areas of regions in two dimensions as integrals approimate te region b a union of small,
NOTES ON OPEN CHANNEL FLOW
 NOTES ON OPEN CANNEL FLOW Prof. Marco Pilotti Facoltà di Ingegneria, Università degli Studi di Brescia Profili di moto permanente in un canale e in una serie di due canali - Boudine, 86 OPEN CANNEL FLOW:
NOTES ON OPEN CANNEL FLOW Prof. Marco Pilotti Facoltà di Ingegneria, Università degli Studi di Brescia Profili di moto permanente in un canale e in una serie di due canali - Boudine, 86 OPEN CANNEL FLOW:
The Basics of Vacuum Technology
 Te Basics of Vacuum Tecnology Grolik Benno, Kopp Joacim January 2, 2003 Basics Many scientific and industrial processes are so sensitive tat is is necessary to omit te disturbing influence of air. For
Te Basics of Vacuum Tecnology Grolik Benno, Kopp Joacim January 2, 2003 Basics Many scientific and industrial processes are so sensitive tat is is necessary to omit te disturbing influence of air. For
Introduction to Derivatives
 Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
Introduction to Derivatives 5-Minute Review: Instantaneous Rates and Tangent Slope Recall te analogy tat we developed earlier First we saw tat te secant slope of te line troug te two points (a, f (a))
Exam 1 Review Solutions
 Exam Review Solutions Please also review te old quizzes, and be sure tat you understand te omework problems. General notes: () Always give an algebraic reason for your answer (graps are not sufficient),
Exam Review Solutions Please also review te old quizzes, and be sure tat you understand te omework problems. General notes: () Always give an algebraic reason for your answer (graps are not sufficient),
INTRODUCTION AND MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS
 INTODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PEVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips of sine,
INTODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PEVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips of sine,
Math 34A Practice Final Solutions Fall 2007
 Mat 34A Practice Final Solutions Fall 007 Problem Find te derivatives of te following functions:. f(x) = 3x + e 3x. f(x) = x + x 3. f(x) = (x + a) 4. Is te function 3t 4t t 3 increasing or decreasing wen
Mat 34A Practice Final Solutions Fall 007 Problem Find te derivatives of te following functions:. f(x) = 3x + e 3x. f(x) = x + x 3. f(x) = (x + a) 4. Is te function 3t 4t t 3 increasing or decreasing wen
Lecture 30 (Walker: ) Fluid Dynamics April 15, 2009
 Physics 111 Lecture 30 (Walker: 15.6-7) Fluid Dynamics April 15, 2009 Midterm #2 - Monday April 20 Chap. 7,Chap. 8 (not 8.5) Chap. 9 (not 9.6, 9.8) Chap. 10, Chap. 11 (not 11.8-9) Chap. 13 (not 13.6-8)
Physics 111 Lecture 30 (Walker: 15.6-7) Fluid Dynamics April 15, 2009 Midterm #2 - Monday April 20 Chap. 7,Chap. 8 (not 8.5) Chap. 9 (not 9.6, 9.8) Chap. 10, Chap. 11 (not 11.8-9) Chap. 13 (not 13.6-8)
1watt=1W=1kg m 2 /s 3
 Appendix A Matematics Appendix A.1 Units To measure a pysical quantity, you need a standard. Eac pysical quantity as certain units. A unit is just a standard we use to compare, e.g. a ruler. In tis laboratory
Appendix A Matematics Appendix A.1 Units To measure a pysical quantity, you need a standard. Eac pysical quantity as certain units. A unit is just a standard we use to compare, e.g. a ruler. In tis laboratory
3. Gradually-Varied Flow
 5/6/18 3. Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow vs Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow /g EGL (energy grade line) iction slope Geometric slope S Normal flow: Downslope component of weigt balances bed friction
5/6/18 3. Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow vs Gradually-aried Flow Normal Flow /g EGL (energy grade line) iction slope Geometric slope S Normal flow: Downslope component of weigt balances bed friction
1 Limits and Continuity
 1 Limits and Continuity 1.0 Tangent Lines, Velocities, Growt In tion 0.2, we estimated te slope of a line tangent to te grap of a function at a point. At te end of tion 0.3, we constructed a new function
1 Limits and Continuity 1.0 Tangent Lines, Velocities, Growt In tion 0.2, we estimated te slope of a line tangent to te grap of a function at a point. At te end of tion 0.3, we constructed a new function
Exam in Fluid Mechanics SG2214
 Exam in Fluid Mecanics G2214 Final exam for te course G2214 23/10 2008 Examiner: Anders Dalkild Te point value of eac question is given in parentesis and you need more tan 20 points to pass te course including
Exam in Fluid Mecanics G2214 Final exam for te course G2214 23/10 2008 Examiner: Anders Dalkild Te point value of eac question is given in parentesis and you need more tan 20 points to pass te course including
MA119-A Applied Calculus for Business Fall Homework 4 Solutions Due 9/29/ :30AM
 MA9-A Applied Calculus for Business 006 Fall Homework Solutions Due 9/9/006 0:0AM. #0 Find te it 5 0 + +.. #8 Find te it. #6 Find te it 5 0 + + = (0) 5 0 (0) + (0) + =.!! r + +. r s r + + = () + 0 () +
MA9-A Applied Calculus for Business 006 Fall Homework Solutions Due 9/9/006 0:0AM. #0 Find te it 5 0 + +.. #8 Find te it. #6 Find te it 5 0 + + = (0) 5 0 (0) + (0) + =.!! r + +. r s r + + = () + 0 () +
REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY
 REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY. Witout using SN, find te derivative of eac of te following (you do not need to simplify your answers): a. f x 3x 3 5x x 6 f x 3 3x 5 x 0 b. g x 4 x x x notice te trick ere! x x g
REVIEW LAB ANSWER KEY. Witout using SN, find te derivative of eac of te following (you do not need to simplify your answers): a. f x 3x 3 5x x 6 f x 3 3x 5 x 0 b. g x 4 x x x notice te trick ere! x x g
Section 2.7 Derivatives and Rates of Change Part II Section 2.8 The Derivative as a Function. at the point a, to be. = at time t = a is
 Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Mat 180 www.timetodare.com Section.7 Derivatives and Rates of Cange Part II Section.8 Te Derivative as a Function Derivatives ( ) In te previous section we defined te slope of te tangent to a curve wit
Derivatives. By: OpenStaxCollege
 By: OpenStaxCollege Te average teen in te United States opens a refrigerator door an estimated 25 times per day. Supposedly, tis average is up from 10 years ago wen te average teenager opened a refrigerator
By: OpenStaxCollege Te average teen in te United States opens a refrigerator door an estimated 25 times per day. Supposedly, tis average is up from 10 years ago wen te average teenager opened a refrigerator
ρ mixture = m mixture /V = (SG antifreeze ρ water V antifreeze + SG water ρ water V water )/V, so we get
 CHAPTER 10 1. When we use the density of granite, we have m = ρv = (.7 10 3 kg/m 3 )(1 10 8 m 3 ) =.7 10 11 kg.. When we use the density of air, we have m = ρv = ρlwh = (1.9 kg/m 3 )(5.8 m)(3.8 m)(.8 m)
CHAPTER 10 1. When we use the density of granite, we have m = ρv = (.7 10 3 kg/m 3 )(1 10 8 m 3 ) =.7 10 11 kg.. When we use the density of air, we have m = ρv = ρlwh = (1.9 kg/m 3 )(5.8 m)(3.8 m)(.8 m)
Main Points: 1. Limit of Difference Quotients. Prep 2.7: Derivatives and Rates of Change. Names of collaborators:
 Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points:. Definition of derivative as limit of difference quotients. Interpretation of derivative as slope of grap. Interpretation of derivative as instantaneous
Name: Section: Names of collaborators: Main Points:. Definition of derivative as limit of difference quotients. Interpretation of derivative as slope of grap. Interpretation of derivative as instantaneous
MATH CALCULUS I 2.1: Derivatives and Rates of Change
 MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 2.1: Derivatives and Rates of Cange Professor Donald L. Wite Department of Matematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. Wite (Kent State University) 1 / 1 Introduction Our main
MATH 12002 - CALCULUS I 2.1: Derivatives and Rates of Cange Professor Donald L. Wite Department of Matematical Sciences Kent State University D.L. Wite (Kent State University) 1 / 1 Introduction Our main
Pressure & Buoyancy Worksheet : Solid & Liquid Pressure
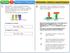 ysics 1. Tree identical cubes are arranged as in tree different (I, II and II) positions on a orizontal surface. Te pressure applied on te orizontal surface by te cubes in arrangement I is.. Solid objects
ysics 1. Tree identical cubes are arranged as in tree different (I, II and II) positions on a orizontal surface. Te pressure applied on te orizontal surface by te cubes in arrangement I is.. Solid objects
Chapter 15: Fluid Mechanics Dynamics Using Pascal s Law = F 1 = F 2 2 = F 2 A 2
 Lecture 24: Archimedes Principle and Bernoulli s Law 1 Chapter 15: Fluid Mechanics Dynamics Using Pascal s Law Example 15.1 The hydraulic lift A hydraulic lift consists of a small diameter piston of radius
Lecture 24: Archimedes Principle and Bernoulli s Law 1 Chapter 15: Fluid Mechanics Dynamics Using Pascal s Law Example 15.1 The hydraulic lift A hydraulic lift consists of a small diameter piston of radius
6. Non-uniform bending
 . Non-uniform bending Introduction Definition A non-uniform bending is te case were te cross-section is not only bent but also seared. It is known from te statics tat in suc a case, te bending moment in
. Non-uniform bending Introduction Definition A non-uniform bending is te case were te cross-section is not only bent but also seared. It is known from te statics tat in suc a case, te bending moment in
Derivative as Instantaneous Rate of Change
 43 Derivative as Instantaneous Rate of Cange Consider a function tat describes te position of a racecar moving in a straigt line away from some starting point Let y s t suc tat t represents te time in
43 Derivative as Instantaneous Rate of Cange Consider a function tat describes te position of a racecar moving in a straigt line away from some starting point Let y s t suc tat t represents te time in
Calculus I, Fall Solutions to Review Problems II
 Calculus I, Fall 202 - Solutions to Review Problems II. Find te following limits. tan a. lim 0. sin 2 b. lim 0 sin 3. tan( + π/4) c. lim 0. cos 2 d. lim 0. a. From tan = sin, we ave cos tan = sin cos =
Calculus I, Fall 202 - Solutions to Review Problems II. Find te following limits. tan a. lim 0. sin 2 b. lim 0 sin 3. tan( + π/4) c. lim 0. cos 2 d. lim 0. a. From tan = sin, we ave cos tan = sin cos =
Problem Solving. Problem Solving Process
 Problem Solving One of te primary tasks for engineers is often solving problems. It is wat tey are, or sould be, good at. Solving engineering problems requires more tan just learning new terms, ideas and
Problem Solving One of te primary tasks for engineers is often solving problems. It is wat tey are, or sould be, good at. Solving engineering problems requires more tan just learning new terms, ideas and
2.3. Applying Newton s Laws of Motion. Objects in Equilibrium
 Appling Newton s Laws of Motion As ou read in Section 2.2, Newton s laws of motion describe ow objects move as a result of different forces. In tis section, ou will appl Newton s laws to objects subjected
Appling Newton s Laws of Motion As ou read in Section 2.2, Newton s laws of motion describe ow objects move as a result of different forces. In tis section, ou will appl Newton s laws to objects subjected
Lecture 10: Carnot theorem
 ecture 0: Carnot teorem Feb 7, 005 Equivalence of Kelvin and Clausius formulations ast time we learned tat te Second aw can be formulated in two ways. e Kelvin formulation: No process is possible wose
ecture 0: Carnot teorem Feb 7, 005 Equivalence of Kelvin and Clausius formulations ast time we learned tat te Second aw can be formulated in two ways. e Kelvin formulation: No process is possible wose
Continuity and Differentiability Worksheet
 Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Continuity and Differentiability Workseet (Be sure tat you can also do te grapical eercises from te tet- Tese were not included below! Typical problems are like problems -3, p. 6; -3, p. 7; 33-34, p. 7;
Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria
 Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria Date: September 27, 20 Assignment Due Date: October 4, 20 Goal: In tis lab you will furter explore te concept of a derivative using R. You will use your knowledge
Lab 6 Derivatives and Mutant Bacteria Date: September 27, 20 Assignment Due Date: October 4, 20 Goal: In tis lab you will furter explore te concept of a derivative using R. You will use your knowledge
y = 3 2 x 3. The slope of this line is 3 and its y-intercept is (0, 3). For every two units to the right, the line rises three units vertically.
 Mat 2 - Calculus for Management and Social Science. Understanding te basics of lines in te -plane is crucial to te stud of calculus. Notes Recall tat te and -intercepts of a line are were te line meets
Mat 2 - Calculus for Management and Social Science. Understanding te basics of lines in te -plane is crucial to te stud of calculus. Notes Recall tat te and -intercepts of a line are were te line meets
MATH Fall 08. y f(x) Review Problems for the Midterm Examination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart
![MATH Fall 08. y f(x) Review Problems for the Midterm Examination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart MATH Fall 08. y f(x) Review Problems for the Midterm Examination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart](/thumbs/87/95118706.jpg) MATH 121 - Fall 08 Review Problems for te Midterm Eamination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart 1. (a) Use te definition of te derivative to find f (3) wen f() = π 1 2. (b) Find an equation of te tangent line
MATH 121 - Fall 08 Review Problems for te Midterm Eamination Covers [1.1, 4.3] in Stewart 1. (a) Use te definition of te derivative to find f (3) wen f() = π 1 2. (b) Find an equation of te tangent line
Math 262 Exam 1 - Practice Problems. 1. Find the area between the given curves:
 Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
Mat 6 Exam - Practice Problems. Find te area between te given curves: (a) = x + and = x First notice tat tese curves intersect wen x + = x, or wen x x+ =. Tat is, wen (x )(x ) =, or wen x = and x =. Next,
Test 2 Review. 1. Find the determinant of the matrix below using (a) cofactor expansion and (b) row reduction. A = 3 2 =
 Test Review Find te determinant of te matrix below using (a cofactor expansion and (b row reduction Answer: (a det + = (b Observe R R R R R R R R R Ten det B = (((det Hence det Use Cramer s rule to solve:
Test Review Find te determinant of te matrix below using (a cofactor expansion and (b row reduction Answer: (a det + = (b Observe R R R R R R R R R Ten det B = (((det Hence det Use Cramer s rule to solve:
Recap: Static Fluids
 Recap: Static Fluids Archimedes principal states that the buoyant force acting on an object is equal to the weight of fluid displaced. If the average density of object is greater than density of fluid
Recap: Static Fluids Archimedes principal states that the buoyant force acting on an object is equal to the weight of fluid displaced. If the average density of object is greater than density of fluid
June : 2016 (CBCS) Body. Load
 Engineering Mecanics st Semester : Common to all rances Note : Max. marks : 6 (i) ttempt an five questions (ii) ll questions carr equal marks. (iii) nswer sould be precise and to te point onl (iv) ssume
Engineering Mecanics st Semester : Common to all rances Note : Max. marks : 6 (i) ttempt an five questions (ii) ll questions carr equal marks. (iii) nswer sould be precise and to te point onl (iv) ssume
Section 3.1: Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions
 Section 3.1: Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions In previous sections we developed te concept of te derivative and derivative function. Te only issue wit our definition owever is tat it
Section 3.1: Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions In previous sections we developed te concept of te derivative and derivative function. Te only issue wit our definition owever is tat it
MTH-112 Quiz 1 Name: # :
 MTH- Quiz Name: # : Please write our name in te provided space. Simplif our answers. Sow our work.. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation.. Does te equation
MTH- Quiz Name: # : Please write our name in te provided space. Simplif our answers. Sow our work.. Determine weter te given relation is a function. Give te domain and range of te relation.. Does te equation
Lesson 4 - Limits & Instantaneous Rates of Change
 Lesson Objectives Lesson 4 - Limits & Instantaneous Rates of Cange SL Topic 6 Calculus - Santowski 1. Calculate an instantaneous rate of cange using difference quotients and limits. Calculate instantaneous
Lesson Objectives Lesson 4 - Limits & Instantaneous Rates of Cange SL Topic 6 Calculus - Santowski 1. Calculate an instantaneous rate of cange using difference quotients and limits. Calculate instantaneous
Average Rate of Change
 Te Derivative Tis can be tougt of as an attempt to draw a parallel (pysically and metaporically) between a line and a curve, applying te concept of slope to someting tat isn't actually straigt. Te slope
Te Derivative Tis can be tougt of as an attempt to draw a parallel (pysically and metaporically) between a line and a curve, applying te concept of slope to someting tat isn't actually straigt. Te slope
Numerical analysis of a free piston problem
 MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 573 Mat. Commun., Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 573-585 (2010) Numerical analysis of a free piston problem Boris Mua 1 and Zvonimir Tutek 1, 1 Department of Matematics, University of
MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 573 Mat. Commun., Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 573-585 (2010) Numerical analysis of a free piston problem Boris Mua 1 and Zvonimir Tutek 1, 1 Department of Matematics, University of
Lecture 27 (Walker: ) Fluid Dynamics Nov. 9, 2009
 Physics 111 Lecture 27 (Walker: 15.5-7) Fluid Dynamics Nov. 9, 2009 Midterm #2 - Monday Nov. 16 Chap. 7,Chap. 8 (not 8.5) Chap. 9 (not 9.6, 9.8) Chap. 10, Chap. 11 (not 11.8-9) Chap. 13 (not 13.6-8) Chap.
Physics 111 Lecture 27 (Walker: 15.5-7) Fluid Dynamics Nov. 9, 2009 Midterm #2 - Monday Nov. 16 Chap. 7,Chap. 8 (not 8.5) Chap. 9 (not 9.6, 9.8) Chap. 10, Chap. 11 (not 11.8-9) Chap. 13 (not 13.6-8) Chap.
11.6 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES AND THE GRADIENT VECTOR
 SECTION 11.6 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES AND THE GRADIENT VECTOR 633 wit speed v o along te same line from te opposite direction toward te source, ten te frequenc of te sound eard b te observer is were c is
SECTION 11.6 DIRECTIONAL DERIVATIVES AND THE GRADIENT VECTOR 633 wit speed v o along te same line from te opposite direction toward te source, ten te frequenc of te sound eard b te observer is were c is
Name: Answer Key No calculators. Show your work! 1. (21 points) All answers should either be,, a (finite) real number, or DNE ( does not exist ).
 Mat - Final Exam August 3 rd, Name: Answer Key No calculators. Sow your work!. points) All answers sould eiter be,, a finite) real number, or DNE does not exist ). a) Use te grap of te function to evaluate
Mat - Final Exam August 3 rd, Name: Answer Key No calculators. Sow your work!. points) All answers sould eiter be,, a finite) real number, or DNE does not exist ). a) Use te grap of te function to evaluate
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwerty uiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzx cvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmq
 qwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwerty uiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasd fgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzx cbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmq Projectile Motion Quick concepts regarding Projectile Motion wertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyui
qwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwerty uiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasd fgjklzxcbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzx cbnmqwertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmq Projectile Motion Quick concepts regarding Projectile Motion wertyuiopasdfgjklzxcbnmqwertyui
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors
 CHAPTER 3 VECTOR quantities: Two-imensional Motion and Vectors Vectors ave magnitude and direction. (x, y) Representations: y (x, y) (r, ) x Oter vectors: velocity, acceleration, momentum, force Vector
CHAPTER 3 VECTOR quantities: Two-imensional Motion and Vectors Vectors ave magnitude and direction. (x, y) Representations: y (x, y) (r, ) x Oter vectors: velocity, acceleration, momentum, force Vector
Derivatives and Rates of Change
 Section.1 Derivatives and Rates of Cange 2016 Kiryl Tsiscanka Derivatives and Rates of Cange Measuring te Rate of Increase of Blood Alcool Concentration Biomedical scientists ave studied te cemical and
Section.1 Derivatives and Rates of Cange 2016 Kiryl Tsiscanka Derivatives and Rates of Cange Measuring te Rate of Increase of Blood Alcool Concentration Biomedical scientists ave studied te cemical and
RightStart Mathematics
 Most recent update: January 7, 2019 RigtStart Matematics Corrections and Updates for Level F/Grade 5 Lessons and Workseets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE CORRECTION OR UPDATE Lesson 7 04/18/2018
Most recent update: January 7, 2019 RigtStart Matematics Corrections and Updates for Level F/Grade 5 Lessons and Workseets, second edition LESSON / WORKSHEET CHANGE DATE CORRECTION OR UPDATE Lesson 7 04/18/2018
Measurement of cement s particle size distribution by the buoyancy weighing-bar method
 Measurement of cement s particle size distribution by te buoyancy weiging-bar metod *Rondang Tambun, Nofriko ratama, Ely, and Farida Hanum Department of Cemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
Measurement of cement s particle size distribution by te buoyancy weiging-bar metod *Rondang Tambun, Nofriko ratama, Ely, and Farida Hanum Department of Cemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University
The Verlet Algorithm for Molecular Dynamics Simulations
 Cemistry 380.37 Fall 2015 Dr. Jean M. Standard November 9, 2015 Te Verlet Algoritm for Molecular Dynamics Simulations Equations of motion For a many-body system consisting of N particles, Newton's classical
Cemistry 380.37 Fall 2015 Dr. Jean M. Standard November 9, 2015 Te Verlet Algoritm for Molecular Dynamics Simulations Equations of motion For a many-body system consisting of N particles, Newton's classical
Excerpt from "Calculus" 2013 AoPS Inc.
 Excerpt from "Calculus" 03 AoPS Inc. Te term related rates refers to two quantities tat are dependent on eac oter and tat are canging over time. We can use te dependent relationsip between te quantities
Excerpt from "Calculus" 03 AoPS Inc. Te term related rates refers to two quantities tat are dependent on eac oter and tat are canging over time. We can use te dependent relationsip between te quantities
1 The concept of limits (p.217 p.229, p.242 p.249, p.255 p.256) 1.1 Limits Consider the function determined by the formula 3. x since at this point
 MA00 Capter 6 Calculus and Basic Linear Algebra I Limits, Continuity and Differentiability Te concept of its (p.7 p.9, p.4 p.49, p.55 p.56). Limits Consider te function determined by te formula f Note
MA00 Capter 6 Calculus and Basic Linear Algebra I Limits, Continuity and Differentiability Te concept of its (p.7 p.9, p.4 p.49, p.55 p.56). Limits Consider te function determined by te formula f Note
The Electron in a Potential
 Te Electron in a Potential Edwin F. Taylor July, 2000 1. Stopwatc rotation for an electron in a potential For a poton we found tat te and of te quantum stopwatc rotates wit frequency f given by te equation:
Te Electron in a Potential Edwin F. Taylor July, 2000 1. Stopwatc rotation for an electron in a potential For a poton we found tat te and of te quantum stopwatc rotates wit frequency f given by te equation:
PHYSICS 1050 Mid-term Test 1 University of Wyoming 15 February 2005
 Name: (4 points) PHYSICS 1050 Mid-term Test 1 University of Wyoming 15 February 2005 Tis test is open-note and open-book. Tis means tat any reference material is permitted during te test. Calculators also
Name: (4 points) PHYSICS 1050 Mid-term Test 1 University of Wyoming 15 February 2005 Tis test is open-note and open-book. Tis means tat any reference material is permitted during te test. Calculators also
Physics 121, April 1, Equilibrium. Physics 121. April 1, Physics 121. April 1, Course Information. Discussion of Exam # 2
 Pysics 121, April 1, 2008. Pysics 121. April 1, 2008. Course Information Discussion of Exam # 2 Topics to be discussed today: Requirements for Equilibrium Gravitational Equilibrium Sample problems Pysics
Pysics 121, April 1, 2008. Pysics 121. April 1, 2008. Course Information Discussion of Exam # 2 Topics to be discussed today: Requirements for Equilibrium Gravitational Equilibrium Sample problems Pysics
INTRODUCTION AND MATHEMATICAL CONCEPTS
 Capter 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PREVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips
Capter 1 INTRODUCTION ND MTHEMTICL CONCEPTS PREVIEW Tis capter introduces you to te basic matematical tools for doing pysics. You will study units and converting between units, te trigonometric relationsips
Mathematics 5 Worksheet 11 Geometry, Tangency, and the Derivative
 Matematics 5 Workseet 11 Geometry, Tangency, and te Derivative Problem 1. Find te equation of a line wit slope m tat intersects te point (3, 9). Solution. Te equation for a line passing troug a point (x
Matematics 5 Workseet 11 Geometry, Tangency, and te Derivative Problem 1. Find te equation of a line wit slope m tat intersects te point (3, 9). Solution. Te equation for a line passing troug a point (x
. h I B. Average velocity can be interpreted as the slope of a tangent line. I C. The difference quotient program finds the exact value of f ( a)
 Capter Review Packet (questions - ) KEY. In eac case determine if te information or statement is correct (C) or incorrect (I). If it is incorrect, include te correction. f ( a ) f ( a) I A. represents
Capter Review Packet (questions - ) KEY. In eac case determine if te information or statement is correct (C) or incorrect (I). If it is incorrect, include te correction. f ( a ) f ( a) I A. represents
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY O SASKATCHEWAN Department of Pysics and Engineering Pysics Pysics 117.3 MIDTERM EXAM Regular Sitting NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 90 minutes STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please ceck):
UNIVERSITY O SASKATCHEWAN Department of Pysics and Engineering Pysics Pysics 117.3 MIDTERM EXAM Regular Sitting NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 90 minutes STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please ceck):
SPC Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30
 SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
SPC 307 - Aerodynamics Course Assignment Due Date Monday 28 May 2018 at 11:30 1. The maximum velocity at which an aircraft can cruise occurs when the thrust available with the engines operating with the
