Write down the equation which links gravitational field strength, gravitational potential energy, height and mass.
|
|
|
- Clarence West
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q1.The figure below shows a student before and after a bungee jump. The bungee cord has an unstretched length of 20.0 m. The mass of the student is 50.0 kg. The gravitational field strength is 9.8 N / kg. (a) Write down the equation which links gravitational field strength, gravitational potential energy, height and mass.... (b) Calculate the change in gravitational potential energy from the position where the student jumps to the point 20.0 m below Change in gravitational potential energy =... J (2) Page 2
2 (c) 80% of this change in gravitational potential energy has been transferred to the student s kinetic energy store. How much has the student s kinetic energy store increased after falling 20.0 m? Kinetic energy gained =... J (d) Calculate the speed of the student after falling 20.0 m. Give your answer to two significant figures Speed =... m / s (4) (e) At the lowest point in the jump, the energy stored by the stretched bungee cord is 24.5 kj. The bungee cord behaves like a spring. Calculate the spring constant of the bungee cord. Use the correct equation from the Physics Equation Sheet Spring constant =... N / m Page 3
3 (Total 11 marks) Q2. When a gun is fired, a very large force acts on the bullet for a very short time. The change in momentum of the bullet is given by the following relationship: force (N) time(s) = change in momentum (kg m/s) (a) An average force of 4000 newton acts for 0.01 seconds on a bullet of mass 50g. Calculate the speed of the bullet. (Show your working.) Answer... m/s (4) (b) The bullet is fired horizontally. In the short time it takes for the bullet to reach its target, its horizontal speed has fallen to 80% of its initial speed. (i) Explain why the speed of the bullet decreases so quickly. (2) (ii) Calculate the percentage of its original kinetic energy the bullet still has when it reaches its target. (Show your working.) (4) (Total 10 marks) Page 4
4 Q3. (a) When an object is moving it is said to have momentum. Define momentum (b) The diagram below shows one way of measuring the velocity of a bullet. A bullet is fired into a block of wood suspended by a long thread. The bullet stops in the wooden block. The impact of the bullet makes the block swing. The velocity of the wooden block can be calculated from the distance it swings. In one such experiment the block of wood and bullet had a velocity of 2 m/s Page 5
5 immediately after impact. The mass of the bullet was 20 g and the mass of the wooden block kg. (i) Calculate the combined mass of the block of wood and bullet.... Mass... (ii) Calculate the momentum of the block of wood and bullet immediately after impact.... Momentum... (iii) State the momentum of the bullet immediately before impact. (iv) Calculate the velocity of the bullet before impact.... Velocity... m/s (v) Calculate the kinetic energy of the block of wood and bullet immediately Page 6
6 after impact.... Kinetic energy... J (vi) The kinetic energy of the bullet before the impact was 1600 joules. This is much greater than the kinetic energy of the bullet and block just after the impact. What has happened to the rest of the energy? (Total 13 marks) Page 7
7 Q4. The miners working in a salt mine use smooth wooden slides to move quickly from one level to another. (a) A miner of mass 90 kg travels down the slide. Calculate the change in gravitational potential energy of the miner when he moves 15 m vertically downwards. gravitational field strength = 10 N/kg Show clearly how you work out your answer Change in gravitational potential energy =... J (2) (b) Calculate the maximum possible speed that the miner could reach at the bottom of the slide. Show clearly how you work out your answer. Give your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures Maximum possible speed =... m/s Page 8
8 (c) The speed of the miner at the bottom of the slide is much less than the calculated maximum possible speed. Explain why (Total 8 marks) Page 9
The image below shows a student before and after a bungee jump.
 CHANGES IN ENERGY Q1. The image below shows a student before and after a bungee jump. The bungee cord has an unstretched length of 20 m. (a) For safety reasons, it is important that the bungee cord used
CHANGES IN ENERGY Q1. The image below shows a student before and after a bungee jump. The bungee cord has an unstretched length of 20 m. (a) For safety reasons, it is important that the bungee cord used
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: Q5. Q7.
 Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
Old Exams Questions Ch. 8 T072 Q2.: A ball slides without friction around a loop-the-loop (see Fig 2). A ball is released, from rest, at a height h from the left side of the loop of radius R. What is the
Energy in Collisions Problems AP Physics C
 1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
1. A bullet of mass m and velocity v 0 is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity
Healy/DiMurro. Vibrations 2016
 Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Potential energy Conservation of energy conservative forces Conservation of energy friction Conservation of energy external
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 8 Potential Energy & Conservation of Energy Potential energy Conservation of energy conservative forces Conservation of energy friction Conservation of energy external
Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015
 95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
Name ID Section. 1. One mile is equal to 1609 m; 1 hour is equal to 3600 s. The highway speed limit of 65 mph is equivalent to the speed of:
 The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
The exam is closed book and closed notes. There are 30 multiple choice questions. Make sure you put your name, section, and ID number on the SCANTRON form. The answers for the multiple choice Questions
On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam.
 Physics 201, Exam 2 Name (printed) On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam. Name (signed) The multiple-choice problems carry no partial
Physics 201, Exam 2 Name (printed) On my honor as a Texas A&M University student, I will neither give nor receive unauthorized help on this exam. Name (signed) The multiple-choice problems carry no partial
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test. Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b)2.25e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b)2 (c)1.5 (d) (e).
 AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
AP Physics Momentum Practice Test Answers: A,E,E,A,E,B,D,C,B,A,B,E,D,C 16.(a)5450,5650 (b).5e7 (c)3 (d)1.5e7 17.(a)9 (b) (c)1.5 (d)-4.75 (e).65 For multiple choice ( points) write the CAPITAL letter of
AP Physics C. Momentum. Free Response Problems
 AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
AP Physics C Momentum Free Response Problems 1. A bullet of mass m moves at a velocity v 0 and collides with a stationary block of mass M and length L. The bullet emerges from the block with a velocity
4.) A baseball that weighs 1.6 N leaves a bat with a speed of 40.0 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball. 130 J
 AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
Non-textbook problem #I: The kinetic energy of a body depends on its mass and speed as. K = 1 2 mv2 (1) m 1 v 2 1 = 1 2 m 2v 2 2 (2)
 PHY 309 K. Solutions for Problem set # 7. Non-textbook problem #I: The kinetic energy of a body depends on its mass and speed as K = 1 mv (1) Therefore, two bodies of respective masses m 1 and m and speeds
PHY 309 K. Solutions for Problem set # 7. Non-textbook problem #I: The kinetic energy of a body depends on its mass and speed as K = 1 mv (1) Therefore, two bodies of respective masses m 1 and m and speeds
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. baby bouncer consisting of a harness and elastic ropes is suspended from a doorway. When a baby of mass 10 kg is placed in the harness, the ropes stretch by 0.25 m. When the
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. baby bouncer consisting of a harness and elastic ropes is suspended from a doorway. When a baby of mass 10 kg is placed in the harness, the ropes stretch by 0.25 m. When the
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum)
 AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
AP Physics C: Mechanics Practice (Systems of Particles and Linear Momentum) 1980M2. A block of mass m slides at velocity v o across a horizontal frictionless surface toward a large curved movable ramp
Unit 2- Energy and Momentum Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Unit 2- Energy and Momentum Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Unit 2- Energy and Momentum Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)
![Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a) Chapter Work, Energy and Power. Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Ans: (a)](/thumbs/83/87594074.jpg) Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Chapter Work, Energy and Power Q1. The co-efficient of restitution e for a perfectly elastic collision is [1988] (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) (d) 1 Q2. A bullet of mass 10g leaves a rifle at an initial velocity of
Name & Surname:... No:... Class: 11 /...
 METU D. F. HIGH SCHOOL 2017-2018 ACADEMIC YEAR, 1 st SEMESTER GRADE 11 / PHYSICS REVIEW FOR GENERAL EXAM-3 UNIFORMLY ACCELERATED MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS, ENERGY, IMPULSE & MOMENTUM & TORQUE DECEMBER 2017
METU D. F. HIGH SCHOOL 2017-2018 ACADEMIC YEAR, 1 st SEMESTER GRADE 11 / PHYSICS REVIEW FOR GENERAL EXAM-3 UNIFORMLY ACCELERATED MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS, ENERGY, IMPULSE & MOMENTUM & TORQUE DECEMBER 2017
A student suspended a spring from a laboratory stand and then hung a weight from the spring. Figure 1
 A student suspended a spring from a laboratory stand and then hung a weight from the spring. Figure shows the spring before and after the weight is added. Figure (a) Which distance gives the extension
A student suspended a spring from a laboratory stand and then hung a weight from the spring. Figure shows the spring before and after the weight is added. Figure (a) Which distance gives the extension
Figure 1. Before starting the investigation the student wrote the following prediction:
 Q1.A student suspended a spring from a laboratory stand and then hung a weight from the spring. Figure 1 shows the spring before and after the weight is added. Figure 1 (a) Measure the extension of the
Q1.A student suspended a spring from a laboratory stand and then hung a weight from the spring. Figure 1 shows the spring before and after the weight is added. Figure 1 (a) Measure the extension of the
As the mass travels along the track, the maximum height it will reach above point E will be closest to A) 10. m B) 20. m C) 30. m D) 40.
 1. As a pendulum swings from position A to position B as shown in the diagram, its total mechanical energy (neglecting friction) A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same 2. Base your answer to the
1. As a pendulum swings from position A to position B as shown in the diagram, its total mechanical energy (neglecting friction) A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same 2. Base your answer to the
Fall 2009 Sample Problems Exam 2
 Sample Problems Exam 2 1. (24 points) In the table below is shown three physical situations in which two objects move and interact. The assumptions you are to make about the objects and the system are
Sample Problems Exam 2 1. (24 points) In the table below is shown three physical situations in which two objects move and interact. The assumptions you are to make about the objects and the system are
Name 09-MAR-04. Work Power and Energy
 Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
40 N 40 N. Direction of travel
 1 Two ropes are attached to a box. Each rope is pulled with a force of 40 N at an angle of 35 to the direction of travel. 40 N 35 35 40 N irection of travel The work done, in joules, is found using 2 Which
1 Two ropes are attached to a box. Each rope is pulled with a force of 40 N at an angle of 35 to the direction of travel. 40 N 35 35 40 N irection of travel The work done, in joules, is found using 2 Which
1 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?
 Page of 3 Work Power And Energy TEACHER ANSWER KEY March 09, 200. A spring has a spring constant of 20 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?. 2.
Page of 3 Work Power And Energy TEACHER ANSWER KEY March 09, 200. A spring has a spring constant of 20 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?. 2.
QUESTION TWO: BUNGY JUMPING. Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m s 2
 6 QUESTION TWO: BUNGY JUMPING Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m s Standing on a platform that is 5.0 m above a river, Emma, of height.00 m and mass m, is tied to one end of an elastic rope (the bungy)
6 QUESTION TWO: BUNGY JUMPING Acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m s Standing on a platform that is 5.0 m above a river, Emma, of height.00 m and mass m, is tied to one end of an elastic rope (the bungy)
GPE AND KE PG. 144 & 145, SYLLABUS 4.11 &
 GPE AND KE PG. 144 & 145, SYLLABUS 4.11 & 4.12 STARTER: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUIZ TODAY S LEARNING OBJECTIVES ARE TO Calculate (a) (b) The kinetic energy of objects Changes in gravitational potential energy
GPE AND KE PG. 144 & 145, SYLLABUS 4.11 & 4.12 STARTER: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUIZ TODAY S LEARNING OBJECTIVES ARE TO Calculate (a) (b) The kinetic energy of objects Changes in gravitational potential energy
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation
 Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
Physics 11 Comprehensive Exam Preparation Kinematics 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
AP Physics C Summer Assignment Kinematics 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will the motorcycle
Physics Courseware Physics I Energy Conservation
 d Work work = Fd cos F Kinetic energy linear motion K. E. = mv Gravitational potential energy P. E. = mgh Physics Courseware Physics I Energy Conservation Problem.- A block is released from position A
d Work work = Fd cos F Kinetic energy linear motion K. E. = mv Gravitational potential energy P. E. = mgh Physics Courseware Physics I Energy Conservation Problem.- A block is released from position A
Final Exam Review Topics/Problems
 Final Exam Review Topics/Problems Units/Sig Figs Look at conversions Review sig figs Motion and Forces Newton s Laws X(t), v(t), a(t) graphs: look at F, displacement, accel, average velocity Boat problems/vector
Final Exam Review Topics/Problems Units/Sig Figs Look at conversions Review sig figs Motion and Forces Newton s Laws X(t), v(t), a(t) graphs: look at F, displacement, accel, average velocity Boat problems/vector
Physics-MC Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1.
 Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PH105-007 Exam 2 VERSION A Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 1.0-kg block and a 2.0-kg block are pressed together on a horizontal
PH105-007 Exam 2 VERSION A Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 1.0-kg block and a 2.0-kg block are pressed together on a horizontal
1982B1. The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant
 1982B1. The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90 meters are run with the same velocity
1982B1. The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90 meters are run with the same velocity
Today's goal: I can explain and apply concepts of work and energy (3U) to real world applicaons.
 Lesson21.notebook September 17, 2013 Work and Energy A 3U Review Today's goal: I can explain and apply concepts of work and energy (3U) to real world applicaons. What is Work? How do we calculate it? Example:
Lesson21.notebook September 17, 2013 Work and Energy A 3U Review Today's goal: I can explain and apply concepts of work and energy (3U) to real world applicaons. What is Work? How do we calculate it? Example:
Potential energy functions used in Chapter 7
 Potential energy functions used in Chapter 7 CHAPTER 7 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Conservation of mechanical energy Conservation of total energy of a system Examples Origin of friction Gravitational potential
Potential energy functions used in Chapter 7 CHAPTER 7 CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Conservation of mechanical energy Conservation of total energy of a system Examples Origin of friction Gravitational potential
Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
 GCSE PHYSICS Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the Physics Equation Sheet (enclosed). Instructions Answer
GCSE PHYSICS Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator the Physics Equation Sheet (enclosed). Instructions Answer
Simple Harmonic Oscillator Challenge Problems
 Simple Harmonic Oscillator Challenge Problems Problem 1: Dimensional Analysis, Estimation and Concepts Imagine that one drilled a hole with smooth sides straight through the center of the earth, of radius
Simple Harmonic Oscillator Challenge Problems Problem 1: Dimensional Analysis, Estimation and Concepts Imagine that one drilled a hole with smooth sides straight through the center of the earth, of radius
SOLUTION T 1 + U 1-2 = T C(31.5)(2.5)A10 6 B(0.2)D = 1 2 (7)(v 2) 2. v 2 = 2121 m>s = 2.12 km>s. Ans. (approx.
 4 5. When a 7-kg projectile is fired from a cannon barrel that has a length of 2 m, the explosive force exerted on the projectile, while it is in the barrel, varies in the manner shown. Determine the approximate
4 5. When a 7-kg projectile is fired from a cannon barrel that has a length of 2 m, the explosive force exerted on the projectile, while it is in the barrel, varies in the manner shown. Determine the approximate
Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes
 Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall Answer Key
 Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Physics 201, Midterm Exam 2, Fall 2006 Answer Key 1) A constant force is applied to a body that is already moving. The force is directed at an angle of 60 degrees to the direction of the body s velocity.
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM
 1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
A ballistic pendulum
 A ballistic pendulum A ballistic pendulum is a device used to measure the speed of a bullet. A bullet of mass m is fired at a block of wood (mass M) hanging from a string. The bullet embeds itself in the
A ballistic pendulum A ballistic pendulum is a device used to measure the speed of a bullet. A bullet of mass m is fired at a block of wood (mass M) hanging from a string. The bullet embeds itself in the
2. What would happen to his acceleration if his speed were half? Energy The ability to do work
 1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
P2 Topic 4 - Motion and forces Higher
 Name: P2 Topic 4 - Motion and forces Higher Date: Time: Total marks available: Total marks achieved: Questions Q1. A child is stationary on a swing. (a) The child is given a push by his brother to start
Name: P2 Topic 4 - Motion and forces Higher Date: Time: Total marks available: Total marks achieved: Questions Q1. A child is stationary on a swing. (a) The child is given a push by his brother to start
THE WORK OF A FORCE, THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY & SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES
 THE WORK OF A FORCE, THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY & SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Calculate the work of a force. 2. Apply the principle of work and energy to
THE WORK OF A FORCE, THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY & SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Calculate the work of a force. 2. Apply the principle of work and energy to
Dynamics Examples. Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung. 28 th June, 2010
 Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
Dynamics Examples Robin Hughes and Anson Cheung 28 th June, 2010 1 Newton s Laws Figure 1: 3 connected blocks Figure 2: Masses on a trolley 1. Two blocks of mass m 1 = 1kg and m 2 = 2kg on a frictionless
Physics 11 Exam Preparation
 Kinematics Physics 11 Exam Preparation 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled by the
Kinematics Physics 11 Exam Preparation 1. A bike first accelerates from 0.0 m/s to 5.0 m/s in 4.5 s, then continues at this constant speed for another 4.5 s. What is the total distance traveled by the
Chapter The spring stretched (85cm - 65cm) when the force was increased.. 180N. =. Solve for k.
 Chapter 11 1. The amplitude is ½ the total vertical distance, and a simple harmonic oscillator travels twice the vertical distance in one oscillation. 2. The spring stretched (85cm - 65cm) when the force
Chapter 11 1. The amplitude is ½ the total vertical distance, and a simple harmonic oscillator travels twice the vertical distance in one oscillation. 2. The spring stretched (85cm - 65cm) when the force
Page 1. Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is A) 34 m B) 30.
 Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
frictionless horizontal surface. The bullet penetrates the block and emerges with a velocity of o
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
AP Physics Free Response Practice Momentum and Impulse 1976B2. A bullet of mass m and velocity v o is fired toward a block of mass 4m. The block is initially at rest on a v frictionless horizontal surface.
PHYS 154 Practice Test 3 Spring 2018
 The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
The actual test contains 1 multiple choice questions and 2 problems. However, for extra exercise, this practice test includes 4 problems. Questions: N.B. Make sure that you justify your answers explicitly
(A) 0 (B) mv (C) 2mv (D) 2mv sin θ (E) 2mv cos θ
 Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
Physics 1 Lesson 8 Forces and Momentum Homework Outcomes 1. Define linear momentum. 2. Determine the total linear momentum of a system. 3. Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to solve problems. 4.
s_3x03 Page 1 Physics Samples
 Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
https://njctl.org/courses/science/ap-physics-c-mechanics/attachments/summerassignment-3/
 AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
AP Physics C Summer Assignment 2017 1. Complete the problem set that is online, entitled, AP C Physics C Summer Assignment 2017. I also gave you a copy of the problem set. You may work in groups as a matter
Q1. (a) The diagram shows an athlete at the start of a race. The race is along a straight track.
 Q1. (a) The diagram shows an athlete at the start of a race. The race is along a straight track. In the first 2 seconds, the athlete accelerates constantly and reaches a speed of 9 m/s. (i) Use the equation
Q1. (a) The diagram shows an athlete at the start of a race. The race is along a straight track. In the first 2 seconds, the athlete accelerates constantly and reaches a speed of 9 m/s. (i) Use the equation
CHAPTER 6: IN AN ISOLATED SYSTEM, ENERGY IS TRANSFERRED FROM ONE OBJECT TO ANOTHER WHENEVER WORK IS DONE
 CHAPTER 6: IN AN ISOLATED SYSTEM, ENERGY IS TRANSFERRED FROM ONE OBJECT TO ANOTHER WHENEVER WORK IS DONE 6.1 Work and Energy In science, work is done when a force acts over a displacement; energy is transferred.
CHAPTER 6: IN AN ISOLATED SYSTEM, ENERGY IS TRANSFERRED FROM ONE OBJECT TO ANOTHER WHENEVER WORK IS DONE 6.1 Work and Energy In science, work is done when a force acts over a displacement; energy is transferred.
pg B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is dra
 pg 165 A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line. The net force acting on the object varies with the object's displacement as shown in the graph above. The object starts from rest at displacement x
pg 165 A 0.20 kg object moves along a straight line. The net force acting on the object varies with the object's displacement as shown in the graph above. The object starts from rest at displacement x
2 possibilities. 2.) Work is done and... 1.) Work is done and... *** The function of work is to change energy ***
 Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT VECTOR DYNAMICS MULTIPLE CHOICE / 45 OPEN ENDED / 75 TOTAL / 120 NAME: 1. Unless acted on by an external net force, an object will stay at rest
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT VECTOR DYNAMICS MULTIPLE CHOICE / 45 OPEN ENDED / 75 TOTAL / 120 NAME: 1. Unless acted on by an external net force, an object will stay at rest
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper
 Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
BROCK UNIVERSITY. Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 234 Examination date: 5 December 2014 Number of hours: 3
 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 12 Final Exam: December 2014 Number of pages: 12 (+ formula sheet) Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 234 Examination date: 5 December 2014 Number of
Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Page 1 of 12 Final Exam: December 2014 Number of pages: 12 (+ formula sheet) Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 234 Examination date: 5 December 2014 Number of
Dynamic Relationship between Bungee Cord s Length and Tension Force
 Saimon Islam, Yoko Koyoma. Professor Cumming Physics 113- Thursday morning November 15, 015. Dynamic Relationship between Bungee Cord s Length and Tension Force Introduction: The purpose of this experiment
Saimon Islam, Yoko Koyoma. Professor Cumming Physics 113- Thursday morning November 15, 015. Dynamic Relationship between Bungee Cord s Length and Tension Force Introduction: The purpose of this experiment
1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a
 Collisions Worksheet Honors: Name: Date: 1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a 9,900-kg truck moving in the same direction
Collisions Worksheet Honors: Name: Date: 1. A 1,160-kg car traveling initially with a speed of 25.0 m/s in an easterly direction crashes into the rear end of a 9,900-kg truck moving in the same direction
Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy
 Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy Key points: Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Generalized work-energy principle Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation
Phys101 Lectures 9 and 10 Conservation of Mechanical Energy Key points: Conservative and Nonconservative Forces Potential Energy Generalized work-energy principle Mechanical Energy and Its Conservation
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations
 AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
AP Physics Free Response Practice Oscillations 1975B7. A pendulum consists of a small object of mass m fastened to the end of an inextensible cord of length L. Initially, the pendulum is drawn aside through
- 1 -APPH_MidTerm. Mid - Term Exam. Part 1: Write your answers to all multiple choice questions in this space. A B C D E A B C D E
 Name - 1 -APPH_MidTerm AP Physics Date Mid - Term Exam Part 1: Write your answers to all multiple choice questions in this space. 1) 2) 3) 10) 11) 19) 20) 4) 12) 21) 5) 13) 22) 6) 7) 14) 15) 23) 24) 8)
Name - 1 -APPH_MidTerm AP Physics Date Mid - Term Exam Part 1: Write your answers to all multiple choice questions in this space. 1) 2) 3) 10) 11) 19) 20) 4) 12) 21) 5) 13) 22) 6) 7) 14) 15) 23) 24) 8)
Name Period Date. Record all givens, draw a picture, arrow all vectors, write the formula, substitute and solve. units
 Example Problems 8.4 Conservation of Energy E1. A monkey does 0.45 joule of work compressing the spring in a pop-up toy. If the mass of the toy is 0.00 kilogram, calculate the maximum vertical height that
Example Problems 8.4 Conservation of Energy E1. A monkey does 0.45 joule of work compressing the spring in a pop-up toy. If the mass of the toy is 0.00 kilogram, calculate the maximum vertical height that
GPE = m g h. GPE = w h. k = f d. PE elastic = ½ k d 2. Work = Force x distance. KE = ½ m v 2
 1 NAME PERIOD PHYSICS GUIDESHEET ENERGY CONVERSIONS POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT CLASS OVERHEAD NOTES (5 pts/page) (Plus 5 pts/page for sample questions)
1 NAME PERIOD PHYSICS GUIDESHEET ENERGY CONVERSIONS POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT CLASS OVERHEAD NOTES (5 pts/page) (Plus 5 pts/page for sample questions)
Question 3 (1 point) A rubber band stretched as far as it will go (without breaking) is a good example of an equilibrium position. a. True b.
 Name: Schoology Review Question 1 (1 point) Which answer best describes elastic potential energy? a. Elastic potential energy refers to the rigidity of an elastic material. b. Elastic potential energy
Name: Schoology Review Question 1 (1 point) Which answer best describes elastic potential energy? a. Elastic potential energy refers to the rigidity of an elastic material. b. Elastic potential energy
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum
 Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
Lab 8: Ballistic Pendulum Caution In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally across the room with sufficient speed to injure a person. Be sure the line of fire is clear before firing the
CONSERVATIVE FORCES, POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
 CONSERVATIVE FORCES, POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Use the concept of conservative forces and determine the potential energy of such forces.
CONSERVATIVE FORCES, POTENTIAL ENERGY AND CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Use the concept of conservative forces and determine the potential energy of such forces.
Phy211: General Physics I Lab page 1 of 5 PCC-Cascade
 Phy11: General Physics I Lab page 1 of 5 Experiment: The Ballistic Pendulum Objectives: Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to an inelastic collision Apply the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy
Phy11: General Physics I Lab page 1 of 5 Experiment: The Ballistic Pendulum Objectives: Apply the Law of Conservation of Momentum to an inelastic collision Apply the Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
Physics. Chapter 7 Energy
 Physics Chapter 7 Energy Work How long does a force act? Last week, we meant time as in impulse (Ft) This week, we will take how long to mean distance Force x distance (Fd) is what we call WORK W = Fd
Physics Chapter 7 Energy Work How long does a force act? Last week, we meant time as in impulse (Ft) This week, we will take how long to mean distance Force x distance (Fd) is what we call WORK W = Fd
2009 A-level Maths Tutor All Rights Reserved
 2 This book is under copyright to A-level Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents Newton s Laws 3 connected particles 9 work & energy 18 power &
2 This book is under copyright to A-level Maths Tutor. However, it may be distributed freely provided it is not sold for profit. Contents Newton s Laws 3 connected particles 9 work & energy 18 power &
St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School
 Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Time allowed:.5 hours Take g = 0 ms - if necessary. St. Joseph s Anglo-Chinese School 008 009 First Term Examination Form 6 ASL Physics Section A (40%) Answer ALL questions in this section. Write your
Physics 2211 A & B Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 2016
 Physics 22 A & B Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 206 I. (6 points) A pendulum bob of mass M is hanging at rest from an ideal string of length L. A bullet of mass m traveling horizontally at speed v 0 strikes it
Physics 22 A & B Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 206 I. (6 points) A pendulum bob of mass M is hanging at rest from an ideal string of length L. A bullet of mass m traveling horizontally at speed v 0 strikes it
Ballistic Pendulum. Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION
 Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
Ballistic Pendulum Equipment- ballistic pendulum apparatus, 2 meter ruler, 30 cm ruler, blank paper, carbon paper, masking tape, scale PRECAUTION In this experiment a steel ball is projected horizontally
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME:
 HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
HATZIC SECONDARY SCHOOL PROVINCIAL EXAMINATION ASSIGNMENT ENERGY & MOMENTUM MULTIPLE CHOICE / 30 OPEN ENDED / 79 TOTAL / 109 NAME: 1. Which of the following best represents the momentum of a small car
Base your answers to questions 5 and 6 on the information below.
 1. A car travels 90. meters due north in 15 seconds. Then the car turns around and travels 40. meters due south in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the car during this 20.-second
1. A car travels 90. meters due north in 15 seconds. Then the car turns around and travels 40. meters due south in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the car during this 20.-second
THE BALLISTIC PENDULUM AND THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY
 THE BALLISTIC PENDULUM AND THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Objectives 1) To study the laws of conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, and the elements of projectile motion using the ballistic
THE BALLISTIC PENDULUM AND THE LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY Objectives 1) To study the laws of conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, and the elements of projectile motion using the ballistic
Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School Of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Extension Division Assignment 2
 Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School Of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Extension Division Assignment 2 1. The 50-kg crate is projected along the floor with an initial
Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology School Of Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Extension Division Assignment 2 1. The 50-kg crate is projected along the floor with an initial
CIE Physics IGCSE. Topic 1: General Physics
 CIE Physics IGCSE Topic 1: General Physics Summary Notes Length and time A ruler (rule) is used to measure the length of an object between 1mm and 1m. The volume of an object of irregular shape can be
CIE Physics IGCSE Topic 1: General Physics Summary Notes Length and time A ruler (rule) is used to measure the length of an object between 1mm and 1m. The volume of an object of irregular shape can be
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that.
 Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
Extra credit assignment #4 It can be handed in up until one class before Test 4 (check your course outline). It will NOT be accepted after that. NAME: 4. Units of power include which of the following?
CHAPTER 2 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 69 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 2 TEST REVIEW 1. Samantha walks along a horizontal path in the direction shown. The curved
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: # Marks: 69 Raw Score: IB Curve: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 2 TEST REVIEW 1. Samantha walks along a horizontal path in the direction shown. The curved
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Name: Unit 4 Newton s 1 st & 3 rd Law
 Name: Period: Table #: Unit 4 Newton s 1 st & 3 rd Law 1 UNIT IV: Reading - Force Diagrams The analysis of a problem in dynamics usually involves the selection and analysis of the relevant forces acting
Name: Period: Table #: Unit 4 Newton s 1 st & 3 rd Law 1 UNIT IV: Reading - Force Diagrams The analysis of a problem in dynamics usually involves the selection and analysis of the relevant forces acting
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions
 Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
Chapter 9 Linear Momentum and Collisions The Center of Mass The center of mass of a system of particles is the point that moves as though (1) all of the system s mass were concentrated there and (2) all
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the
 23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
23. A force in the negative direction of an x-axis is applied for 27ms to a 0.40kg ball initially moving at 14m/s in the positive direction of the axis. The force varies in magnitude, and the impulse has
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. baby bouncer consisting of a harness and elastic ropes is suspended from a doorway. When a baby of mass 10 kg is placed in the harness, the ropes stretch by 0.25 m. When the
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. baby bouncer consisting of a harness and elastic ropes is suspended from a doorway. When a baby of mass 10 kg is placed in the harness, the ropes stretch by 0.25 m. When the
a) Calculate the height that m 2 moves up the bowl after the collision (measured vertically from the bottom of the bowl).
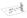 2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 BROCK UNIVERSITY
 Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
Tutorial #: Circle correct course: PHYS 1P21 or PHYS 1P91 Name: Student #: BROCK UNIVERSITY Test 7: November 2015 Number of pages: 5 Course: PHYS 1P21/1P91 Number of students: 218 Examination date: 17
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a kg pencil 0.25 m against a force of 23 N.
 Work, Power and Energy Worksheet Work and Power 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a 0.025 kg pencil 0.25 m against a
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet Work and Power 1. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a pencil 0.26 m. 2. Calculate the work done by a 47 N force pushing a 0.025 kg pencil 0.25 m against a
9.2 Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY
 9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
PROJECTILE MOTION: CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM 19 FEBRUARY 2013
 PROJECTILE MOTION: CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM 19 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Learn that an object s momentum is the amount of motion it has due to its mass and velocity. Show that
PROJECTILE MOTION: CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM 19 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Learn that an object s momentum is the amount of motion it has due to its mass and velocity. Show that
