Chapter 13. Clocked Circuits SEQUENTIAL VS. COMBINATIONAL CMOS TG LATCHES, FLIP FLOPS. Baker Ch. 13 Clocked Circuits. Introduction to VLSI
|
|
|
- Rosanna Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 13 Clocked Circuits SEQUENTIAL VS. COMBINATIONAL CMOS TG LATCHES, FLIP FLOPS SET-RESET (SR) ARBITER LATCHES FLIP FLOPS EDGE TRIGGERED DFF FF TIMING Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 1
2 o Baker Ch. 13 Clocked Circuits CLK D Q In SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS DESCRIPTION VTC V o1 Combinational Logic Circuit Combinational V i1 t su V o1 = V i 2 V o2 = V i 1 DATA STABLE V i2 = V o1 Out V "Adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits, A Design Perspective, i1 = V o2 Rabaey, Chandrakasan, and Nikolic, Copyright 2003 Prentice Hall/Pearson." V o2 t hold t c 2 q V i1 A V i2 In DATA STABLE C t t t B Combinational Logic Circuit State Sequential Register D V o2 Q CLK Out COMBINATIONAL INPUTS DETERMINE OUTPUT SEQUENTIAL FEEDBACK FROM OUTPUT EXAMPLES OF SEQUENTIAL CKTS REGISTERS COUNTERS OSCILLATORS MEMORIES GENERIC TERMINOLOGY SETUP TIME DATA VALID BEFORE CLOCK CHG HOLD TIME DATA VALID AFTER CLOCK CHG LATCH OUT=IN, OR OUT=STABLE LEVEL-SENSITIVE REGISTER OUT=IN WHEN CLOCK TRANSITIONS EDGE-SENSITIVE BISTABLE TWO VALID STATES Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 2
3 CMOS TG DESCRIPTION NEED BOTH N & P TO PASS DATA WHAT IS THE BENEFIT? WHAT IS THE DRAWBACK? APPLICATION 4 TO 1 MUX 2 M = N M NUMBER OF CONTROL LINES N NUMBER OF INPUTS CHOOSES 1 OF 4 INPUTS M=2, N=4 WHERE IS THIS USED? S1 S2 Z S1=AB VS CD 0 0 D S2=A VS B, C VS D 0 1 C 1 0 B 1 1 A Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 3
4 CMOS TG VS PG VS NOR DESCRIPTION Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 4
5 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS STATIC* LATCHES LEVEL SENSITIVE DELAY DUE TO CONTENTION AFFECTS SENSE AMPS WEAKEN ONE INVERTER SR (SET-RESET) LATCH NAND, NOR BASED S-HIGH, R-LOW, RESETS OUTPUT R-HIGH, S-LOW, SETS OUTPUT BAR BASIC BLOCK FOR DFF, MEMORY ARBITER LATCH USED IN ASYNCHRONOUS DESIGNS, CLOCK SYNCHRONIZATION ONLY ONE OUTPUT HIGH OUTPUT DEPENDS ON WHICH INPUT IS FIRST TO GO HIGH OUT2 NO VDD WHEN IN1=1 *NOT USING PARASITIC CAP IN CKT Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 5
6 LATCHES DESCRIPTION LEVEL SENSITIVE LATCH CLOCK HIGH, D INPUT Q OUT WHERE IS THE DELAY? WHY DOES I2 HAVE LONG L? Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 6
7 SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS STATIC* REGISTER MASTER-SLAVE REGISTER (DFF) DESCRIPTION EDGE TRIGGERED, E.G., REGISTER USES TG TO CLOCK MASTER, SLAVE OPERATION TWO LEVEL SENSITIVES LATCHES CLOCK=L, B TRACKS D, Q HELD CLOCK=H, B GOES TO SLAVE TIMING CLOCK RISE TIME MUST BE SMALL BUFFERS IN SERIES WITH CLK POOR QA EXAMPLE CLK L H Q FOLLOWS D *NOT USING PARASITIC CAP IN CKT Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 7
8 FLIP FLOPS DESCRIPTION TG RESISTANCE IS Rp Rn NODE A CAP: CA = (1) C OXN /2 + C OXP /2 + (2) 3/2 (C OXN + C OXP ) #1 IS NODE A CAP DUE TO TG #2 IS INPUT CAP OF I1 WHAT IS MISSING? NODE B CAP: CB = (1) 3/2 (C OXN + C OXP ) (2) C OXN /2 + C OXP /2 + #1 IS INPUT CAP OF I2 #2 IS OUT CAP OF I1 WHAT IS MISSING? HAND CALCULATION VS SIM 4.5ps VS. 30ps 13.5ps VS. 90ps MUST SIMULATE Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 8
9 TIMING OF FLIP FLOPS DESCRIPTION Need to simulate various t s / t h Delay Degradation Percent 10% 0% Failure of D Q T (setup/hold) When t s / t h is marginal, delay changes Ex. D input is rising as clock is changing Node B is set to a 0 Node B starts to see a 1 state Clock changes Slave sees a partial 1 Q inverter takes longer to change D ts CLK 5 1 Q td 1 5 Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 9
10 Kaeslin, Top-Down Digital VLSI Design, Chpt. 8, Figure 8.13 Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky; Modeling MTS, Cypress Semiconductor 10
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 18 CMOS Sequential Circuits - 1 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic Designing Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
CMPEN 411. Spring Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 18: Static Sequential Circuits [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements: Lecture material adapted from R. Katz, G. Borriello, Contemporary Logic esign (second edition), Prentice-Hall/Pearson
Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. November Digital Integrated Circuits 2nd Sequential Circuits
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning i Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning i Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Naming Conventions In our text: a latch is level sensitive
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Naming Conventions In our text: a latch is level sensitive
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC
igital Integrated Circuits A esign Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic esigning Sequential Logic Circuits November 2002 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers)
 L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
L4: Sequential Building Blocks (Flip-flops, Latches and Registers) Acknowledgements:., Materials in this lecture are courtesy of the following people and used with permission. - Randy H. Katz (University
GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
9/18/2008 GMU, ECE 680 Physical VLSI Design
 ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
ECE680: Physical VLSI esign Chapter IV esigning Sequential Logic Circuits (Chapter 7) 1 Sequential Logic Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs Next state 2 storage mechanisms positive
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits. Reading: CH 7
 Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits Reading: CH 7 Sequential Logic FSM (Finite-state machine) Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs = f(current, inputs) Next state 2 storage mechanisms
Lecture 9: Sequential Logic Circuits Reading: CH 7 Sequential Logic FSM (Finite-state machine) Inputs Current State COMBINATIONAL LOGIC Registers Outputs = f(current, inputs) Next state 2 storage mechanisms
Sequential vs. Combinational
 Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
Hold Time Illustrations
 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.1 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.2 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential
Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.1 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential Logic.2 Pingqiang, ShanghaiTech, 2018 Hold Time Illustrations EE213-L09-Sequential
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic
 Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Chapter 7 Sequential Logic SKEE2263 Digital Systems Mun im/ismahani/izam {munim@utm.my,e-izam@utm.my,ismahani@fke.utm.my} March 28, 2016 Table of Contents 1 Intro 2 Bistable Circuits 3 FF Characteristics
Chapter 11. Inverter. DC AC, Switching. Layout. Sizing PASS GATES (CHPT 10) Other Inverters. Baker Ch. 11 The Inverter. Introduction to VLSI
 Chapter 11 Inverter DC AC, Switching Ring Oscillator Dynamic Power Dissipation Layout LATCHUP Sizing PASS GATES (CHPT 10) Other Inverters Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky;
Chapter 11 Inverter DC AC, Switching Ring Oscillator Dynamic Power Dissipation Layout LATCHUP Sizing PASS GATES (CHPT 10) Other Inverters Joseph A. Elias, Ph.D. Adjunct Professor, University of Kentucky;
EE141- Spring 2007 Digital Integrated Circuits
 EE141- Spring 27 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 19 Sequential Circuits 1 Administrative Stuff Project Ph. 2 due Tu. 5pm 24 Cory box + email ee141- project@bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu Hw 8 Posts this Fr.,
EE141- Spring 27 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 19 Sequential Circuits 1 Administrative Stuff Project Ph. 2 due Tu. 5pm 24 Cory box + email ee141- project@bwrc.eecs.berkeley.edu Hw 8 Posts this Fr.,
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
Synchronous Sequential Logic
 1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
1 IT 201 DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN MODULE4 NOTES Synchronous Sequential Logic Sequential Circuits - A sequential circuit consists of a combinational circuit and a feedback through the storage elements in
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics. Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D.
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Sequential Logic. Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS. Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan,
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2012 Lecture 17: Dynamic Sequential Circuits And Timing Issues [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan,
P2 (10 points): Given the circuit below, answer the following questions:
 P1 (10 points): Given the function f(a, b, c, d) = m(3,4,5,10,14) + D(6,7): A: Fill in the timing diagram for f. B: Implement f using only 2-1 MUXes. Your circuit should not include more than four 2-1
P1 (10 points): Given the function f(a, b, c, d) = m(3,4,5,10,14) + D(6,7): A: Fill in the timing diagram for f. B: Implement f using only 2-1 MUXes. Your circuit should not include more than four 2-1
ΗΜΥ 307 ΨΗΦΙΑΚΑ ΟΛΟΚΛΗΡΩΜΕΝΑ ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2018
 ΗΜΥ 307 ΨΗΦΙΑΚΑ ΟΛΟΚΛΗΡΩΜΕΝΑ ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2018 ΔΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 12-13: esigning ynamic and Static CMOS Sequential Circuits ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙΔΗΣ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) (ack: Prof. Mary Jane Irwin and
ΗΜΥ 307 ΨΗΦΙΑΚΑ ΟΛΟΚΛΗΡΩΜΕΝΑ ΚΥΚΛΩΜΑΤΑ Εαρινό Εξάμηνο 2018 ΔΙΑΛΕΞΕΙΣ 12-13: esigning ynamic and Static CMOS Sequential Circuits ΧΑΡΗΣ ΘΕΟΧΑΡΙΔΗΣ (ttheocharides@ucy.ac.cy) (ack: Prof. Mary Jane Irwin and
Topics. CMOS Design Multi-input delay analysis. John A. Chandy Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 Topics CMO Design Multi-input delay analysis pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT Z OUT Z pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT When is low, the output is at high impedance When is high, the output follows However,
Topics CMO Design Multi-input delay analysis pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT Z OUT Z pring 25 Transmission Gate OUT When is low, the output is at high impedance When is high, the output follows However,
Chapter 4. Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Topics. Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control. John A. Chandy Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 Topics Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control Dynamic CMOS In static circuits at every point in time (except when switching) the output is connected to either GND or V DD via a low resistance
Topics Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control Dynamic CMOS In static circuits at every point in time (except when switching) the output is connected to either GND or V DD via a low resistance
MODULE 5 Chapter 7. Clocked Storage Elements
 MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
MODULE 5 Chapter 7 Clocked Storage Elements 3/9/2015 1 Outline Background Clocked Storage Elements Timing, terminology, classification Static CSEs Latches Registers Dynamic CSEs Latches Registers 3/9/2015
UMBC. At the system level, DFT includes boundary scan and analog test bus. The DFT techniques discussed focus on improving testability of SAFs.
 Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements.
 1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
Y. Tsiatouhas. VLSI Systems and Computer Architecture Lab
 CMOS INTEGRATE CIRCUIT ESIGN TECHNIUES University of Ioannina Memory Elements and other Circuits ept. of Computer Science and Engineering Y. Tsiatouhas CMOS Integrated Circuit esign Techniques Overview.
CMOS INTEGRATE CIRCUIT ESIGN TECHNIUES University of Ioannina Memory Elements and other Circuits ept. of Computer Science and Engineering Y. Tsiatouhas CMOS Integrated Circuit esign Techniques Overview.
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
EE141Microelettronica. CMOS Logic
 Microelettronica CMOS Logic CMOS logic Power consumption in CMOS logic gates Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit
Microelettronica CMOS Logic CMOS logic Power consumption in CMOS logic gates Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques](/thumbs/90/103932933.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i) Derive AND gate and OR gate
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CO/CM/IF/CD/CW] Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12] Q.1(a) (i) Derive AND gate and OR gate
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
Lecture 9: Clocking, Clock Skew, Clock Jitter, Clock Distribution and some FM
 Lecture 9: Clocking, Clock Skew, Clock Jitter, Clock Distribution and some FM Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin 9/27/18 VLSI-1 Class Notes Why Clocking?
Lecture 9: Clocking, Clock Skew, Clock Jitter, Clock Distribution and some FM Mark McDermott Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin 9/27/18 VLSI-1 Class Notes Why Clocking?
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits
 Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential circuits Introduction to the concept of the
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
DEPARTMENT: ECE MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL ELECTRONICS UNIT : Design of Sequential Circuits PART A ( Marks). Draw the logic diagram 4: Multiplexer.(AUC
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/79/79145081.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Digital Circuits and Design Prelim uestion Paper Solution. (a) Static Hazard Static hazards have two cases: static and static. static- hazard exists when the output variable should
Problem Set 9 Solutions
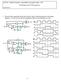 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
5. Sequential Logic x Computation Structures Part 1 Digital Circuits. Copyright 2015 MIT EECS
 5. Sequential Logic 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 igital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L5: Sequential Logic, Slide #1 Something We Can t Build (Yet) What if you were
5. Sequential Logic 6.004x Computation Structures Part 1 igital Circuits Copyright 2015 MIT EECS 6.004 Computation Structures L5: Sequential Logic, Slide #1 Something We Can t Build (Yet) What if you were
Designing Sequential Logic Circuits
 igital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 5: esigning Sequential Logic Circuits Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: r. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 26 April 2017 isclaimer: This course was
igital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 5: esigning Sequential Logic Circuits Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: r. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 26 April 2017 isclaimer: This course was
Reducing Delay Uncertainty in Deeply Scaled Integrated Circuits Using Interdependent Timing Constraints
 Reducing Delay Uncertainty in Deeply Scaled Integrated Circuits Using Interdependent Timing Constraints Emre Salman and Eby G. Friedman Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Rochester
Reducing Delay Uncertainty in Deeply Scaled Integrated Circuits Using Interdependent Timing Constraints Emre Salman and Eby G. Friedman Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Rochester
ALU A functional unit
 ALU A functional unit that performs arithmetic operations such as ADD, SUB, MPY logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, NOT on given data types: 8-,16-,32-, or 64-bit values A n-1 A n-2... A 1 A 0 B n-1
ALU A functional unit that performs arithmetic operations such as ADD, SUB, MPY logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, NOT on given data types: 8-,16-,32-, or 64-bit values A n-1 A n-2... A 1 A 0 B n-1
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops
 Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
Chapter 14 Sequential logic, Latches and Flip-Flops Flops Lesson 4 JK Flip Flop Ch14L4-"Digital Principles and Design", Raj Kamal, Pearson Education, 2006 2 JK Flip-Flop ve edge triggered Output Q and
MOSIS REPORT. Spring MOSIS Report 1. MOSIS Report 2. MOSIS Report 3
 MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering. Jungli, Taiwan
 Chapter 7 Sequential Circuits Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. epartment of Electrical Engineering National Central University it Jungli, Taiwan Outline Latches & Registers Sequencing Timing
Chapter 7 Sequential Circuits Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. epartment of Electrical Engineering National Central University it Jungli, Taiwan Outline Latches & Registers Sequencing Timing
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
I. Motivation & Examples
 I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
Lecture Outline. ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals. Total Power. Energy and Power Optimization. Worksheet Problem 1
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 16: March 20, 2018 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization " Tradeoffs! Design
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 16: March 20, 2018 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization " Tradeoffs! Design
EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1
 EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1 FF s and some Definitions Clock Input: FF s are controlled by a trigger or Clock signal. All FF s have a clock input. If a device which attempts to do a FF s task does not
EET 310 Flip-Flops 11/17/2011 1 FF s and some Definitions Clock Input: FF s are controlled by a trigger or Clock signal. All FF s have a clock input. If a device which attempts to do a FF s task does not
Clock Strategy. VLSI System Design NCKUEE-KJLEE
 Clock Strategy Clocked Systems Latch and Flip-flops System timing Clock skew High speed latch design Phase locked loop ynamic logic Multiple phase Clock distribution Clocked Systems Most VLSI systems are
Clock Strategy Clocked Systems Latch and Flip-flops System timing Clock skew High speed latch design Phase locked loop ynamic logic Multiple phase Clock distribution Clocked Systems Most VLSI systems are
Experiment 9 Sequential Circuits
 Introduction to Counters Experiment 9 Sequential Circuits The aim of this experiment is to familiarize you, frst with the basic sequential circuit device called a fip fop, and then, with the design and
Introduction to Counters Experiment 9 Sequential Circuits The aim of this experiment is to familiarize you, frst with the basic sequential circuit device called a fip fop, and then, with the design and
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
CHAPTER 9: SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques](/thumbs/82/86792063.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
Methodology to Achieve Higher Tolerance to Delay Variations in Synchronous Circuits
 Methodology to Achieve Higher Tolerance to Delay Variations in Synchronous Circuits Emre Salman and Eby G. Friedman Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Rochester Rochester,
Methodology to Achieve Higher Tolerance to Delay Variations in Synchronous Circuits Emre Salman and Eby G. Friedman Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Rochester Rochester,
Lecture 5. MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects
 Lecture 5 MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects Introduction C load = (C gd,n + C gd,p + C db,n + C db,p ) + (C int + C g ) Lumped linear capacitance intrinsic cap. extrinsic
Lecture 5 MOS Inverter: Switching Characteristics and Interconnection Effects Introduction C load = (C gd,n + C gd,p + C db,n + C db,p ) + (C int + C g ) Lumped linear capacitance intrinsic cap. extrinsic
ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops
 CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
CSE14: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems ALU, Latches and Flip-Flops Tajana Simunic Rosing Where we are. Last time: ALUs Plan for today: ALU example, latches and flip flops Exam #1 grades
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring Lecture 21: Shifters, Decoders, Muxes
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 21: Shifters, Decoders, Muxes [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 21: Shifters, Decoders, Muxes [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN
Introduction EE 224: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER DESIGN. Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 5/9/2010
 EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
Reg. No. Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Second Semester. Computer Science and Engineering
 Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
Sp 6 Reg. No. Question Paper Code : 27156 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2015. Second Semester Computer Science and Engineering CS 6201 DIGITAL PRINCIPLES AND SYSTEM DESIGN (Common
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. FSMs 9/11/2007
 EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
Synchronous Sequential Circuit
 Synchronous Sequential Circuit The change of internal state occurs in response to the synchronized clock pulses. Data are read during the clock pulse (e.g. rising-edge triggered) It is supposed to wait
Synchronous Sequential Circuit The change of internal state occurs in response to the synchronized clock pulses. Data are read during the clock pulse (e.g. rising-edge triggered) It is supposed to wait
CPE/EE 422/522. Chapter 1 - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. 1.1 Combinational Logic
 CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
Lecture 7: Logic design. Combinational logic circuits
 /24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
/24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
Sample Test Paper - I
 Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Scheme G Sample Test Paper - I Course Name : Computer Engineering Group Marks : 25 Hours: 1 Hrs. Q.1) Attempt any THREE: 09 Marks a) Define i) Propagation delay ii) Fan-in iii) Fan-out b) Convert the following:
Computers also need devices capable of Storing data and information Performing mathematical operations on such data
 Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
Sequential Machines Introduction Logic devices examined so far Combinational Output function of input only Output valid as long as input true Change input change output Computers also need devices capable
Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Sequential Logic Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 2017 State-Holding Elements Bistable Elements S Latch Latch Positive-Edge-Triggered Flip-Flop Flip-Flop with
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) State any two Boolean laws. (Any 2 laws 1 mark each)
 Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 27 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 27 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits. Bistable Devices. S-R Latches. Consider the following element. Readings : Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.
 Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Bistable Devices Readings : Consider the following element Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential
Topic 8: Sequential Circuits Bistable Devices Readings : Consider the following element Patterson & Hennesy, Appendix B.4 - B.6 Goals Basic Principles behind Memory Elements Clocks Applications of sequential
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu CPE100: Digital Logic Design I Midterm02 Review http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe100/ 2 Logistics Thursday Nov. 16 th In normal lecture (13:00-14:15)
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4
 Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
Digital Logic Design - Chapter 4 1. Analyze the latch circuit shown below by obtaining timing diagram for the circuit; include propagation delays. Y This circuit has two external input and one feedback
Unit 7 Sequential Circuits (Flip Flop, Registers)
 College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Science CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 7 Sequential Circuits (Flip Flop, Registers) 2 SR Flip-Flop The SR flip-flop, also known
College of Computer and Information Sciences Department of Computer Science CSC 220: Computer Organization Unit 7 Sequential Circuits (Flip Flop, Registers) 2 SR Flip-Flop The SR flip-flop, also known
Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design
 Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design Section 5. -To achieve correct operation of integrated logic gates, we need to satisfy 1. Functional specification. Temporal (timing) constraint. (1) In CMOS, incorrect
Chapter 5 CMOS Logic Gate Design Section 5. -To achieve correct operation of integrated logic gates, we need to satisfy 1. Functional specification. Temporal (timing) constraint. (1) In CMOS, incorrect
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Review for the Midterm Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 22 The Midterm 75 minutes 4 5 problems Closed book Simple calculators are OK, but unnecessary One double-sided
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Review for the Midterm Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Spring 22 The Midterm 75 minutes 4 5 problems Closed book Simple calculators are OK, but unnecessary One double-sided
I. Motivation & Examples
 I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
I. Motivation & Examples Output depends on current input and past history of inputs. State embodies all the information about the past needed to predict current output based on current input. State variables,
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
Implementation of Optimized Reversible Sequential and Combinational Circuits for VLSI Applications
 V. G. Santhi Swaroop et al Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Implementation of Optimized Reversible Sequential and Combinational Circuits for VLSI Applications
V. G. Santhi Swaroop et al Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Implementation of Optimized Reversible Sequential and Combinational Circuits for VLSI Applications
Gates and Flip-Flops
 Gates and Flip-Flops Chris Kervick (11355511) With Evan Sheridan and Tom Power December 2012 On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely is it that this question is using binary?...4? What s a 4? Abstract The operation
Gates and Flip-Flops Chris Kervick (11355511) With Evan Sheridan and Tom Power December 2012 On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely is it that this question is using binary?...4? What s a 4? Abstract The operation
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 6 DEPARTMENT: EEE QUESTION BANK SUBJECT NAME: DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE: EE55 SEMESTER IV UNIT : Design of Synchronous Sequential Circuits PART
Unit II Chapter 4:- Digital Logic Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4
 Unit II Chapter 4:- Digital Logic Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4 4.1.1 Signal... 4 4.1.2 Comparison of Analog and Digital Signal... 7 4.2 Number Systems... 7 4.2.1 Decimal Number System... 7 4.2.2 Binary
Unit II Chapter 4:- Digital Logic Contents 4.1 Introduction... 4 4.1.1 Signal... 4 4.1.2 Comparison of Analog and Digital Signal... 7 4.2 Number Systems... 7 4.2.1 Decimal Number System... 7 4.2.2 Binary
Fault Modeling. 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee. Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan. VLSI Testing Class
 Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Registers, Counters, RAM
 Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Registers, Counters, RAM Register - a group of binary storage elements suitable for holding binary info A group of FFs constitutes a register Commonly used as temporary storage
Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Registers, Counters, RAM Register - a group of binary storage elements suitable for holding binary info A group of FFs constitutes a register Commonly used as temporary storage
CPE100: Digital Logic Design I
 Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
Chapter 3 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/cpe1/ CPE1: Digital Logic Design I Section 14: Dr. Morris Sequential Logic Design Chapter 3 Chapter
WORKBOOK. Try Yourself Questions. Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics. Detailed Explanations of
 27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
27 WORKBOOK Detailed Eplanations of Try Yourself Questions Electrical Engineering Digital Electronics Number Systems and Codes T : Solution Converting into decimal number system 2 + 3 + 5 + 8 2 + 4 8 +
Fundamentals of Computer Systems
 Fundamentals of Computer Systems Review for the Final Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 25 The Final 2 hours 8 problems Closed book Simple calculators are OK, but unnecessary One double-sided
Fundamentals of Computer Systems Review for the Final Stephen A. Edwards Columbia University Summer 25 The Final 2 hours 8 problems Closed book Simple calculators are OK, but unnecessary One double-sided
Module - 19 Gated Latches
 Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay And Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of
Digital Circuits and Systems Prof. Shankar Balachandran Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay And Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 19: Timing Analysis
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
Chapter 20. Current Mirrors. Basics. Cascoding. Biasing Circuits. Baker Ch. 20 Current Mirrors. Introduction to VLSI
 Chapter 20 Current Mirrors Basics Long Channel Matching Biasing Short Channel Temperature Subthreshold Cascoding Simple Low Voltage, Wide Swing Wide Swing, Short Channel Regulated Drain Biasing Circuits
Chapter 20 Current Mirrors Basics Long Channel Matching Biasing Short Channel Temperature Subthreshold Cascoding Simple Low Voltage, Wide Swing Wide Swing, Short Channel Regulated Drain Biasing Circuits
Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits combinational circuits state gate delay
 Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are those with memory, also called feedback. In this, they differ from combinational circuits, which have no memory. The stable output of a combinational circuit
Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are those with memory, also called feedback. In this, they differ from combinational circuits, which have no memory. The stable output of a combinational circuit
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Midterm Information. Instructor: Mohsen Imani. Sources: TSR, Katz, Boriello & Vahid
 CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
CSE140: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Midterm Information Instructor: Mohsen Imani Midterm Topics In general: everything that was covered in homework 1 and 2 and related lectures,
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design
 EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006
 COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
Timing Issues. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolić. January 2003
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolić Timing Issues January 2003 1 Synchronous Timing CLK In R Combinational 1 R Logic 2 C in C out Out 2
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolić Timing Issues January 2003 1 Synchronous Timing CLK In R Combinational 1 R Logic 2 C in C out Out 2
