12 th Annual Johns Hopkins Math Tournament Saturday, February 19, 2011
|
|
|
- Ursula Harrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 th Annual Johns Hopkins Math Tournament Saturay, February 19, 011 Geometry Subject Test 1. [105] Let D x,y enote the half-isk of raius 1 with its curve bounary externally tangent to the unit circle at the point (x, y, such that the straight bounary of the isk is parallel to the tangent line (so the point of tangency is the mile of the curve bounary. Fin the area of the union of the D x,y over all (x, y with x + y = 1 (that is, (x, y is on the unit circle. 4π Given any point of tangency (x, y, the points on the circle farthest away are the two iametrically opposite points on the straight bounary. The length of the segment connecting (x, y an either of these two points (pick one an call it A is because the half-isk has raius 1; the line segment can be viewe as the hypotenuse of the right triangle spanne by two raii of D x,y. As the union of the D x,y sweep aroun the unit circle, the segment from (x, y to A sweeps out an annulus of with ; that is, it sweeps out a large circle of raius 5 with an inner circle of raius 1 remove. Hence the area of the remaining region is ifference between the areas of the two circles: 5π π = 4π.. [106] Let circle O have raius 5 with iameter AE. Point F is outsie circle O such that lines AF an EF intersect circle O at points B, an D, respectively. If AF = 10 an m F AE = 0, then the perimeter of quarilateral ABDE can be expresse as a + b + c + 6, where a, b, c, are rational. Fin a + b + c After some angle chasing, we fin that m DBF = m DF B = 75, which implies that DF = DB. Hence the esire perimeter is equal to AF BF + AE + F E = 0 BF + F E. By the Law of Sines, F E sin 0 = 10 sin 75 F E = = Now, to fin BF raw the altitue from O to AB intersecting AB at P. This forms a triangle, so we can see that AP = 5 = 10 BF BF = Hence the answer is 0 + (5 6 5 (10 5 = , so the esire sum is = 15.. [108] In a unit cube ABCD EF GH, an equilateral triangle BDG cuts out a circle from the circumsphere of the cube. Fin the area of the circle. π Consier the cube of sie length an ivie the answer by 4 later. Set the coorinates 6 1
2 of the vertices of the cube to be (±1, ±1, ±1. Then the plane going through a equilateral triangle can be escribe as x + y + z = 1. The istance to the plane from the origin is 1, as ( 1, 1, 1 is the foot ( of the perpenicular from (0, 0, 0. Thus the raius of the circle is 1 1 =, so the area is π. In the case of the unit cube we shoul ivie it by 4 to get the answer π [10] Compute the largest value of r such that three non-overlapping circles of raius r can be inscribe in a unit square The three circles will be inscribe in such a way that one altitue of the equilateral triangle forme by the centers of the three circles will coincie with a iagonal of the square, as in the figure below. Inee, by the Pigeonhole Principle, one circle must lie tangent to two sies of the square, an in any orientation other than the one below, the circles can be ilate. Label the square ABCD starting in the upper left an going clockwise. The line from the center of the top left circle to A has length r, an the equilateral triangle forme by the raii has height r. Then the line from the base of the equilateral triangle to C has length ( + r. Now, raw lines from the centers of the two lower circles to C to form four triangles. Observe that these triangles are ientical, with angle π 8 in the lower right. Then ( π tan = 1 = 8 r ( + r an solving for r gives the esire answer, or some equivalent expression. 5. [1040] Let ABCD be a unit square. Point E is on BC, point F is on DC, AEF is equilateral, an GHIJ is a square in AEF such that GH is on EF. Compute the area of square GHIJ The setup is as follows: First let a be the length of AE. Then CE = a/, BE = 1 a/ so AE = a = 1 + BE = a + a /. Solving it gives a + a 4 = 0, (a + = 6 so a = 6. Next let b
3 be the length of IJ. Then AIJ is equilateral so AJ = b. Also JE = / b, so AE = a = + b, b = ( ( ( 6 = (9 5. Squaring it gives [1056] Let ABC be equilateral. Two points D an E are on sie BC (with orer B, D, E, C, an satisfy DAE = 0. If BD = an CE =, what is BC? A 0 B D E C Rotate the figure aroun A by 60 so that C comes at the place of B. Let B, C, D, E be corresponing points of the move figure. Since E AD = E AC + C AD = EAC + BAD = 0 = EAD, E A = EA an DA = D A, one has E D = ED. So BC = BD + DE + EA can be foun out if we know E D. But E D = E B + BD E B BD cos 10 = 19, so BC = = B D A E B = C D E C 7. [1088] Let ABCD be cyclic quarilateral with AB = 6, BC = 1, CD =, an DA = 6. Let E, F be the intersection of lines AB an CD, lines AD an BC, respectively. Fin EF. 10 We have ADE CBE, an ratio is AD : CB = 1 :. Let AE = p an DE = q, then we have AB = BE AE = DE AE = q p an CD = p q. Solving for p an q we have p = 4 an q = 5. Similarly we have F C = 8 an F D = 10.
4 Let B = θ, then F DE = π θ. Apply the cosine law to EBF to get EF = BE + BF BE BF cos θ = cos θ = cos θ an to EDF to get EF = DE + DF + DE DF cos θ = cos θ = cos θ. Solving for EF we get EF = [115] Two parallel lines l 1 an l are on a plane with istance. On l 1 there are infinitely many points A 1, A, A, progressing in the same istance: A n A n+1 = for all n. In aition, on l there are also infinitely many points B 1, B, B, satisfying B n B n+1 = 1 for all n. Given that A 1 B 1 is perpenicular to both l 1 an l, express the sum i=1 A ib i A i+1 in terms of. π tan 1 ( 1 Construct points C 1, C, C,... on l 1 progressing in the same irection as the A i such that C 1 = A 1 an C n C n+1 = 1. Thus we have C 1 = A 1, C = A, C 5 = A, etc., with C n 1 = A n in general. We can write A i B i A i+1 = C i 1 B i C i+1 = C i B i C i+1 C i B i C i 1. Observe that C i B i C k (for any k is a right triangle with legs of length an k i, an C i B i C k = tan 1 ( k i. So Ci B i C i+1 C i B i C i 1 = tan 1 ( i+1 which has nth partial sum so it converges to π tan 1 ( 1. i=1 ( tan 1 i 1 ( ( i + 1 i 1 tan 1 tan 1 ( n + 1 tan 1 ( + tan 1 n ( 1 tan 1. The whole sum is therefore 9. [180] In an unit square ABCD, fin the minimum of AP + BP + CP when P is an arbitrary point in ABCD. 5 Rotate the triangle AP B aroun A by 90 egree as in the following figure. Let P an B be the rotate image of P an B respectively. Then we have B P = BP, P P = AP so AP + BP + CP = CP = P P + P B CB = 5. 4
5 10. [156] Given a triangle ABC with sie lengths a = 5, b = 7, c = 8, fin the sie length of largest equilateral triangle P QR such that A, B, C are on QR, RP, P Q, respectively. Answer 4 We claim that in general, the answer is (a + b + c + 4 S, where S is the area of ABC. Suppose that P QR is a equilateral triangle satisfying the conitions. Then BP C = CQA = ARB = 60. The locus of points satisfying BXC = 60 is an part of a circle O a. Draw O b an O c similarly. Three circles meet at a single point X insie the triangle, which is the unique point satisfying BXC = CXA = AXB = 10. Then the choice of P on O a etermines Q an R: those two points shoul also be on O b an O c respectively, an P CQ an P BR shoul form the sie of triangle. Now one shoul fin the maximum of P Q uner these conitions. Note that BP X an BRX oes not epen on choice of P, so triangle P XR has same shape. Especially, the ratio of P X an P R is constant, so P R is maximize when P X is the iameter of O a. This requires P Q, QR, RP to be perpenicular to XC, XA, XB respectively. From this point there may be several ways to calculate the answer. One way is to observe P Q = (AX + BX + CX by consiering (P QR = (P XQ + (QXR + (RXP. AX + BX + CX can be compute by the usual rotation trick for the Fermat point: rotate BXA 60 aroun B to BX A. Observe that BXX is equilateral, an so A, X, X, an C are collinear. Hence, A C = AX +BX + CX, an we can apply the Law of Cosines to A BC to get that A C = c + a ac cos (B + 60 = a + c + ac sin 60 sin B ac cos 60 cos B = a + c + S 1 (a + c b = a + b + c + S = P Q = (a + b + c + 4 S (where S is again the area of ABC. Plugging in our values for a, b, an c, an using Heron s formula to fin S = 10 5 = 10, we can calculate P Q = 4. 5
SMT 2018 Geometry Test Solutions February 17, 2018
 SMT 018 Geometry Test Solutions February 17, 018 1. Consider a semi-circle with diameter AB. Let points C and D be on diameter AB such that CD forms the base of a square inscribed in the semicircle. Given
SMT 018 Geometry Test Solutions February 17, 018 1. Consider a semi-circle with diameter AB. Let points C and D be on diameter AB such that CD forms the base of a square inscribed in the semicircle. Given
RMT 2013 Geometry Test Solutions February 2, = 51.
 RMT 0 Geometry Test Solutions February, 0. Answer: 5 Solution: Let m A = x and m B = y. Note that we have two pairs of isosceles triangles, so m A = m ACD and m B = m BCD. Since m ACD + m BCD = m ACB,
RMT 0 Geometry Test Solutions February, 0. Answer: 5 Solution: Let m A = x and m B = y. Note that we have two pairs of isosceles triangles, so m A = m ACD and m B = m BCD. Since m ACD + m BCD = m ACB,
Physics 505 Electricity and Magnetism Fall 2003 Prof. G. Raithel. Problem Set 3. 2 (x x ) 2 + (y y ) 2 + (z + z ) 2
 Physics 505 Electricity an Magnetism Fall 003 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 3 Problem.7 5 Points a): Green s function: Using cartesian coorinates x = (x, y, z), it is G(x, x ) = 1 (x x ) + (y y ) + (z z
Physics 505 Electricity an Magnetism Fall 003 Prof. G. Raithel Problem Set 3 Problem.7 5 Points a): Green s function: Using cartesian coorinates x = (x, y, z), it is G(x, x ) = 1 (x x ) + (y y ) + (z z
Collinearity/Concurrence
 Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
2008 Euclid Contest. Solutions. Canadian Mathematics Competition. Tuesday, April 15, c 2008 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
the coordinates of C (3) Find the size of the angle ACB. Give your answer in degrees to 2 decimal places. (4)
 . The line l has equation, 2 4 3 2 + = λ r where λ is a scalar parameter. The line l 2 has equation, 2 0 5 3 9 0 + = µ r where μ is a scalar parameter. Given that l and l 2 meet at the point C, find the
. The line l has equation, 2 4 3 2 + = λ r where λ is a scalar parameter. The line l 2 has equation, 2 0 5 3 9 0 + = µ r where μ is a scalar parameter. Given that l and l 2 meet at the point C, find the
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Concurrency and Collinearity
 Concurrency and Collinearity Victoria Krakovna vkrakovna@gmail.com 1 Elementary Tools Here are some tips for concurrency and collinearity questions: 1. You can often restate a concurrency question as a
Concurrency and Collinearity Victoria Krakovna vkrakovna@gmail.com 1 Elementary Tools Here are some tips for concurrency and collinearity questions: 1. You can often restate a concurrency question as a
INVERSION IN THE PLANE BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE
 INVERSION IN THE PLANE BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA MILLS COLLEGE/UC BERKELEY SEPTEMBER 26TH 2004 Contents 1. Definition of Inversion in the Plane 1 Properties of Inversion 2 Problems 2 2.
INVERSION IN THE PLANE BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE ZVEZDELINA STANKOVA MILLS COLLEGE/UC BERKELEY SEPTEMBER 26TH 2004 Contents 1. Definition of Inversion in the Plane 1 Properties of Inversion 2 Problems 2 2.
(D) (A) Q.3 To which of the following circles, the line y x + 3 = 0 is normal at the point ? 2 (A) 2
 CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
CIRCLE [STRAIGHT OBJECTIVE TYPE] Q. The line x y + = 0 is tangent to the circle at the point (, 5) and the centre of the circles lies on x y = 4. The radius of the circle is (A) 3 5 (B) 5 3 (C) 5 (D) 5
Higher Geometry Problems
 Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1
 Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
Calgary Math Circles: Triangles, Concurrency and Quadrilaterals 1 1 Triangles: Basics This section will cover all the basic properties you need to know about triangles and the important points of a triangle.
Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? A. (1,10) B. (2,7) C. (3,5) D. (4,3) E.
 April 9, 01 Standards: MM1Ga, MM1G1b Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? (1,10) B. (,7) C. (,) (,) (,1). Points P, Q, R, and S lie on a line
April 9, 01 Standards: MM1Ga, MM1G1b Practice Test Geometry 1. Which of the following points is the greatest distance from the y-axis? (1,10) B. (,7) C. (,) (,) (,1). Points P, Q, R, and S lie on a line
VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER)
 BY:Prof. RAHUL MISHRA Class :- X QNo. VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CIRCLES Subject :- Maths General Instructions Questions M:9999907099,9818932244 1 In the adjoining figures, PQ
BY:Prof. RAHUL MISHRA Class :- X QNo. VAISHALI EDUCATION POINT (QUALITY EDUCATION PROVIDER) CIRCLES Subject :- Maths General Instructions Questions M:9999907099,9818932244 1 In the adjoining figures, PQ
UNC Charlotte 2005 Comprehensive March 7, 2005
 March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
March 7, 2005 1. The numbers x and y satisfy 2 x = 15 and 15 y = 32. What is the value xy? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6 (E) none of A, B, C or D Solution: C. Note that (2 x ) y = 15 y = 32 so 2 xy = 2 5 and
chapter 1 vector geometry solutions V Consider the parallelogram shown alongside. Which of the following statements are true?
 chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
 UNIT-8 SIMILAR TRIANGLES Geometry is the right foundation of all painting, I have decided to teach its rudiments and principles to all youngsters eager for art. 1. ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled
UNIT-8 SIMILAR TRIANGLES Geometry is the right foundation of all painting, I have decided to teach its rudiments and principles to all youngsters eager for art. 1. ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled
 = ( +1) BP AC = AP + (1+ )BP Proved UNIT-9 CIRCLES 1. Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is rhombus. Ans Given : ABCD is a parallelogram circumscribing a circle. To prove : - ABCD is
= ( +1) BP AC = AP + (1+ )BP Proved UNIT-9 CIRCLES 1. Prove that the parallelogram circumscribing a circle is rhombus. Ans Given : ABCD is a parallelogram circumscribing a circle. To prove : - ABCD is
( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear.
 Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Problems 01 - POINT Page 1 ( 1 ) Show that P ( a, b + c ), Q ( b, c + a ) and R ( c, a + b ) are collinear. ( ) Prove that the two lines joining the mid-points of the pairs of opposite sides and the line
Exercises for Unit I I I (Basic Euclidean concepts and theorems)
 Exercises for Unit I I I (Basic Euclidean concepts and theorems) Default assumption: All points, etc. are assumed to lie in R 2 or R 3. I I I. : Perpendicular lines and planes Supplementary background
Exercises for Unit I I I (Basic Euclidean concepts and theorems) Default assumption: All points, etc. are assumed to lie in R 2 or R 3. I I I. : Perpendicular lines and planes Supplementary background
MATH 13200/58: Trigonometry
 MATH 00/58: Trigonometry Minh-Tam Trinh For the trigonometry unit, we will cover the equivalent of 0.7,.4,.4 in Purcell Rigon Varberg.. Right Triangles Trigonometry is the stuy of triangles in the plane
MATH 00/58: Trigonometry Minh-Tam Trinh For the trigonometry unit, we will cover the equivalent of 0.7,.4,.4 in Purcell Rigon Varberg.. Right Triangles Trigonometry is the stuy of triangles in the plane
Worksheet A VECTORS 1 G H I D E F A B C
 Worksheet A G H I D E F A B C The diagram shows three sets of equally-spaced parallel lines. Given that AC = p that AD = q, express the following vectors in terms of p q. a CA b AG c AB d DF e HE f AF
Worksheet A G H I D E F A B C The diagram shows three sets of equally-spaced parallel lines. Given that AC = p that AD = q, express the following vectors in terms of p q. a CA b AG c AB d DF e HE f AF
2018 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST
 08 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST. A right triangle has hypotenuse 9 and one leg. What is the length of the other leg?. Don is /3 of the way through his run. After running another / mile, he
08 LEHIGH UNIVERSITY HIGH SCHOOL MATH CONTEST. A right triangle has hypotenuse 9 and one leg. What is the length of the other leg?. Don is /3 of the way through his run. After running another / mile, he
International Mathematical Olympiad. Preliminary Selection Contest 2017 Hong Kong. Outline of Solutions 5. 3*
 International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers: 06 0000 * 6 97 7 6 8 7007 9 6 0 6 8 77 66 7 7 0 6 7 7 6 8 9 8 0 0 8 *See the remar after the solution
International Mathematical Olympiad Preliminary Selection Contest Hong Kong Outline of Solutions Answers: 06 0000 * 6 97 7 6 8 7007 9 6 0 6 8 77 66 7 7 0 6 7 7 6 8 9 8 0 0 8 *See the remar after the solution
Solutions to Math 41 Second Exam November 4, 2010
 Solutions to Math 41 Secon Exam November 4, 2010 1. (13 points) Differentiate, using the metho of your choice. (a) p(t) = ln(sec t + tan t) + log 2 (2 + t) (4 points) Using the rule for the erivative of
Solutions to Math 41 Secon Exam November 4, 2010 1. (13 points) Differentiate, using the metho of your choice. (a) p(t) = ln(sec t + tan t) + log 2 (2 + t) (4 points) Using the rule for the erivative of
HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICAL COMPETITON PROBLEMS
 HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICAL COMPETITON PROBLEMS HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2006... 3 1.1.1
HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICAL COMPETITON PROBLEMS HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2006... 3 1.1.1
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars
 SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
SMT Power Round Solutions : Poles and Polars February 18, 011 1 Definition and Basic Properties 1 Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They just make the graphs look nicer. (1).0
Higher Geometry Problems
 Higher Geometry Problems (1 Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Higher Geometry Problems (1 Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Mathematics. Circles. hsn.uk.net. Higher. Contents. Circles 1. CfE Edition
 Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Representing a Circle A 1 Testing a Point A 3 The General Equation of a Circle A 4 Intersection of a Line an a Circle A 4 5 Tangents to A 5 6 Equations of Tangents to A
Higher Mathematics Contents 1 1 Representing a Circle A 1 Testing a Point A 3 The General Equation of a Circle A 4 Intersection of a Line an a Circle A 4 5 Tangents to A 5 6 Equations of Tangents to A
Maharashtra State Board Class X Mathematics Geometry Board Paper 2015 Solution. Time: 2 hours Total Marks: 40
 Maharashtra State Board Class X Mathematics Geometry Board Paper 05 Solution Time: hours Total Marks: 40 Note:- () Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. ()Use of calculator is not allowed.
Maharashtra State Board Class X Mathematics Geometry Board Paper 05 Solution Time: hours Total Marks: 40 Note:- () Solve all questions. Draw diagrams wherever necessary. ()Use of calculator is not allowed.
Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths
![Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths Topic 2 [312 marks] The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle. Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths](/thumbs/86/93150791.jpg) Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
Topic 2 [312 marks] 1 The rectangle ABCD is inscribed in a circle Sides [AD] and [AB] have lengths [12 marks] 3 cm and (\9\) cm respectively E is a point on side [AB] such that AE is 3 cm Side [DE] is
Math Implicit Differentiation. We have discovered (and proved) formulas for finding derivatives of functions like
 Math 400 3.5 Implicit Differentiation Name We have iscovere (an prove) formulas for fining erivatives of functions like f x x 3x 4x. 3 This amounts to fining y for 3 y x 3x 4x. Notice that in this case,
Math 400 3.5 Implicit Differentiation Name We have iscovere (an prove) formulas for fining erivatives of functions like f x x 3x 4x. 3 This amounts to fining y for 3 y x 3x 4x. Notice that in this case,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE
 QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
QUESTION BANK ON STRAIGHT LINE AND CIRCLE Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. If the lines x + y + = 0 ; 4x + y + 4 = 0 and x + αy + β = 0, where α + β =, are concurrent then α =,
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca Euclid Contest. Tuesday, April 12, 2016
 The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 016 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 1, 016 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, April 13, 016 (outside of North America
The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING cemc.uwaterloo.ca 016 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 1, 016 (in North America and South America) Wednesday, April 13, 016 (outside of North America
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Math Notes on differentials, the Chain Rule, gradients, directional derivative, and normal vectors
 Math 18.02 Notes on ifferentials, the Chain Rule, graients, irectional erivative, an normal vectors Tangent plane an linear approximation We efine the partial erivatives of f( xy, ) as follows: f f( x+
Math 18.02 Notes on ifferentials, the Chain Rule, graients, irectional erivative, an normal vectors Tangent plane an linear approximation We efine the partial erivatives of f( xy, ) as follows: f f( x+
Related Rates. Introduction. We are familiar with a variety of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especially geometric ones.
 Relate Rates Introuction We are familiar with a variety of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especially geometric ones For example, for the sies of a right triangle we have a 2 + b 2 = c 2 or
Relate Rates Introuction We are familiar with a variety of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especially geometric ones For example, for the sies of a right triangle we have a 2 + b 2 = c 2 or
1) Exercise 1 In the diagram, ABC = AED, AD = 3, DB = 2 and AE = 2. Determine the length of EC. Solution:
 1) Exercise 1 In the diagram, ABC = AED, AD = 3, DB = 2 and AE = 2. Determine the length of EC. Solution: First, we show that AED and ABC are similar. Since DAE = BAC and ABC = AED, we have that AED is
1) Exercise 1 In the diagram, ABC = AED, AD = 3, DB = 2 and AE = 2. Determine the length of EC. Solution: First, we show that AED and ABC are similar. Since DAE = BAC and ABC = AED, we have that AED is
Academic Challenge 2009 Regional Mathematics Solution Set. #2 Ans. C. Let a be the side of the cube. Then its surface area equals 6a = 10, so
 Academic Challenge 009 Regional Mathematics Solution Set #1 Ans. C: x 4 = x 9 = -5 # Ans. C. Let a be the side of the cube. Then its surface area equals 6a = 10, so a = 10 / 6 and volume V = a = ( 10 /
Academic Challenge 009 Regional Mathematics Solution Set #1 Ans. C: x 4 = x 9 = -5 # Ans. C. Let a be the side of the cube. Then its surface area equals 6a = 10, so a = 10 / 6 and volume V = a = ( 10 /
Exam 2 Review Solutions
 Exam Review Solutions 1. True or False, an explain: (a) There exists a function f with continuous secon partial erivatives such that f x (x, y) = x + y f y = x y False. If the function has continuous secon
Exam Review Solutions 1. True or False, an explain: (a) There exists a function f with continuous secon partial erivatives such that f x (x, y) = x + y f y = x y False. If the function has continuous secon
SMT 2011 General Test and Solutions February 19, F (x) + F = 1 + x. 2 = 3. Now take x = 2 2 F ( 1) = F ( 1) = 3 2 F (2)
 SMT 0 General Test and Solutions February 9, 0 Let F () be a real-valued function defined for all real 0, such that ( ) F () + F = + Find F () Answer: Setting =, we find that F () + F ( ) = Now take =,
SMT 0 General Test and Solutions February 9, 0 Let F () be a real-valued function defined for all real 0, such that ( ) F () + F = + Find F () Answer: Setting =, we find that F () + F ( ) = Now take =,
RMT 2014 Geometry Test Solutions February 15, 2014
 RMT 014 Geometry Test Solutions February 15, 014 1. The coordinates of three vertices of a parallelogram are A(1, 1), B(, 4), and C( 5, 1). Compute the area of the parallelogram. Answer: 18 Solution: Note
RMT 014 Geometry Test Solutions February 15, 014 1. The coordinates of three vertices of a parallelogram are A(1, 1), B(, 4), and C( 5, 1). Compute the area of the parallelogram. Answer: 18 Solution: Note
12 th Annual Johns Hopkins Math Tournament Saturday, February 19, 2011 Power Round-Poles and Polars
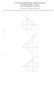 1 th Annual Johns Hopkins Math Tournaent Saturday, February 19, 011 Power Round-Poles and Polars 1. Definition and Basic Properties 1. Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They
1 th Annual Johns Hopkins Math Tournaent Saturday, February 19, 011 Power Round-Poles and Polars 1. Definition and Basic Properties 1. Note that the unit circles are not necessary in the solutions. They
11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers, and Hints
 view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
view.php3 (JPEG Image, 840x888 pixels) - Scaled (71%) https://mail.ateneo.net/horde/imp/view.php3?mailbox=inbox&inde... 1 of 1 11/5/2008 5:02 PM 11 th Philippine Mathematical Olympiad Questions, Answers,
Figure 1: Problem 1 diagram. Figure 2: Problem 2 diagram
 Geometry A Solutions 1. Note that the solid formed is a generalized cylinder. It is clear from the diagram that the area of the base of this cylinder (i.e., a vertical cross-section of the log) is composed
Geometry A Solutions 1. Note that the solid formed is a generalized cylinder. It is clear from the diagram that the area of the base of this cylinder (i.e., a vertical cross-section of the log) is composed
0113ge. Geometry Regents Exam In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC?
 0113ge 1 If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest side of VWX? 1) XV ) WX 3) VW 4) NP 4 In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC? In circle
0113ge 1 If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest side of VWX? 1) XV ) WX 3) VW 4) NP 4 In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC? In circle
Alg. (( Sheet 1 )) [1] Complete : 1) =.. 3) =. 4) 3 a 3 =.. 5) X 3 = 64 then X =. 6) 3 X 6 =... 7) 3
![Alg. (( Sheet 1 )) [1] Complete : 1) =.. 3) =. 4) 3 a 3 =.. 5) X 3 = 64 then X =. 6) 3 X 6 =... 7) 3 Alg. (( Sheet 1 )) [1] Complete : 1) =.. 3) =. 4) 3 a 3 =.. 5) X 3 = 64 then X =. 6) 3 X 6 =... 7) 3](/thumbs/88/117811617.jpg) Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch [1] Complete : 1) 3 216 =.. Alg. (( Sheet 1 )) 1 8 2) 3 ( ) 2 =..
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch [1] Complete : 1) 3 216 =.. Alg. (( Sheet 1 )) 1 8 2) 3 ( ) 2 =..
3.7 Implicit Differentiation -- A Brief Introduction -- Student Notes
 Fin these erivatives of these functions: y.7 Implicit Differentiation -- A Brief Introuction -- Stuent Notes tan y sin tan = sin y e = e = Write the inverses of these functions: y tan y sin How woul we
Fin these erivatives of these functions: y.7 Implicit Differentiation -- A Brief Introuction -- Stuent Notes tan y sin tan = sin y e = e = Write the inverses of these functions: y tan y sin How woul we
nx + 1 = (n + 1)x 13(n + 1) and nx = (n + 1)x + 27(n + 1).
 1. (Answer: 630) 001 AIME SOLUTIONS Let a represent the tens digit and b the units digit of an integer with the required property. Then 10a + b must be divisible by both a and b. It follows that b must
1. (Answer: 630) 001 AIME SOLUTIONS Let a represent the tens digit and b the units digit of an integer with the required property. Then 10a + b must be divisible by both a and b. It follows that b must
Answer Key. 9.1 Parts of Circles. Chapter 9 Circles. CK-12 Geometry Concepts 1. Answers. 1. diameter. 2. secant. 3. chord. 4.
 9.1 Parts of Circles 1. diameter 2. secant 3. chord 4. point of tangency 5. common external tangent 6. common internal tangent 7. the center 8. radius 9. chord 10. The diameter is the longest chord in
9.1 Parts of Circles 1. diameter 2. secant 3. chord 4. point of tangency 5. common external tangent 6. common internal tangent 7. the center 8. radius 9. chord 10. The diameter is the longest chord in
Practice Assessment Task SET 3
 PRACTICE ASSESSMENT TASK 3 655 Practice Assessment Task SET 3 Solve m - 5m + 6 $ 0 0 Find the locus of point P that moves so that it is equidistant from the points A^-3, h and B ^57, h 3 Write x = 4t,
PRACTICE ASSESSMENT TASK 3 655 Practice Assessment Task SET 3 Solve m - 5m + 6 $ 0 0 Find the locus of point P that moves so that it is equidistant from the points A^-3, h and B ^57, h 3 Write x = 4t,
sin A cos A Georgia Milestones Geometry EOC Study/Resource Guide for Students and Parents Page 73 of 182
 UNIT 3: RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY This unit investigates the properties of right triangles. The trigonometric ratios sine, cosine, an tangent along with the Pythagorean theorem are use to solve right
UNIT 3: RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY This unit investigates the properties of right triangles. The trigonometric ratios sine, cosine, an tangent along with the Pythagorean theorem are use to solve right
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 2015
 Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 215 I. (17 points) The magnetic fiel at point P ue to a current through the wire is 5. µt into the page. The curve portion of the wire is a semicircle of raius 2.
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #4 Solutions Fall 215 I. (17 points) The magnetic fiel at point P ue to a current through the wire is 5. µt into the page. The curve portion of the wire is a semicircle of raius 2.
Vectors - Applications to Problem Solving
 BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 00-003 Vectors - Applications to Problem Solving Zvezdelina Stankova Mills College& UC Berkeley 1. Well-known Facts (1) Let A 1 and B 1 be the midpoints of the sides BC and AC of ABC.
BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 00-003 Vectors - Applications to Problem Solving Zvezdelina Stankova Mills College& UC Berkeley 1. Well-known Facts (1) Let A 1 and B 1 be the midpoints of the sides BC and AC of ABC.
Final Exam Study Guide and Practice Problems Solutions
 Final Exam Stuy Guie an Practice Problems Solutions Note: These problems are just some of the types of problems that might appear on the exam. However, to fully prepare for the exam, in aition to making
Final Exam Stuy Guie an Practice Problems Solutions Note: These problems are just some of the types of problems that might appear on the exam. However, to fully prepare for the exam, in aition to making
HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICS COMPETITON PROBLEMS
 HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICS COMPETITON PROBLEMS 2006-2013 HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 2006...
HANOI MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY NGUYEN VAN MAU HANOI OPEN MATHEMATICS COMPETITON PROBLEMS 2006-2013 HANOI - 2013 Contents 1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 3 1.1 Hanoi Open Mathematics Competition 2006...
CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY. 1. Find the points on the y axis whose distances from the points (6, 7) and (4,-3) are in the. ratio 1:2.
 UNIT- CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY Mathematics is the tool specially suited for dealing with abstract concepts of any ind and there is no limit to its power in this field.. Find the points on the y axis whose
UNIT- CO-ORDINATE GEOMETRY Mathematics is the tool specially suited for dealing with abstract concepts of any ind and there is no limit to its power in this field.. Find the points on the y axis whose
1 Lecture 20: Implicit differentiation
 Lecture 20: Implicit ifferentiation. Outline The technique of implicit ifferentiation Tangent lines to a circle Derivatives of inverse functions by implicit ifferentiation Examples.2 Implicit ifferentiation
Lecture 20: Implicit ifferentiation. Outline The technique of implicit ifferentiation Tangent lines to a circle Derivatives of inverse functions by implicit ifferentiation Examples.2 Implicit ifferentiation
0809ge. Geometry Regents Exam Based on the diagram below, which statement is true?
 0809ge 1 Based on the diagram below, which statement is true? 3 In the diagram of ABC below, AB AC. The measure of B is 40. 1) a b ) a c 3) b c 4) d e What is the measure of A? 1) 40 ) 50 3) 70 4) 100
0809ge 1 Based on the diagram below, which statement is true? 3 In the diagram of ABC below, AB AC. The measure of B is 40. 1) a b ) a c 3) b c 4) d e What is the measure of A? 1) 40 ) 50 3) 70 4) 100
23 Implicit differentiation
 23 Implicit ifferentiation 23.1 Statement The equation y = x 2 + 3x + 1 expresses a relationship between the quantities x an y. If a value of x is given, then a corresponing value of y is etermine. For
23 Implicit ifferentiation 23.1 Statement The equation y = x 2 + 3x + 1 expresses a relationship between the quantities x an y. If a value of x is given, then a corresponing value of y is etermine. For
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry. Tan
 Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
Part (1) Second : Trigonometry (1) Complete the following table : The angle Ratio 42 12 \ Sin 0.3214 Cas 0.5321 Tan 2.0625 (2) Complete the following : 1) 46 36 \ 24 \\ =. In degrees. 2) 44.125 = in degrees,
Name Date Period Notes Formal Geometry Chapter 8 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8.1 Geometric Mean. A. Definitions: 1.
 Name Date Period Notes Formal Geometry Chapter 8 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8.1 Geometric Mean A. Definitions: 1. Geometric Mean: 2. Right Triangle Altitude Similarity Theorem: If the altitude is
Name Date Period Notes Formal Geometry Chapter 8 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8.1 Geometric Mean A. Definitions: 1. Geometric Mean: 2. Right Triangle Altitude Similarity Theorem: If the altitude is
1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Electrostatics 1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity. A soli conucting sphere is given a positive charge Q.
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Electrostatics 1. The electron volt is a measure of (A) charge (B) energy (C) impulse (D) momentum (E) velocity. A soli conucting sphere is given a positive charge Q.
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1
 1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
Geometry Honors Review for Midterm Exam
 Geometry Honors Review for Midterm Exam Format of Midterm Exam: Scantron Sheet: Always/Sometimes/Never and Multiple Choice 40 Questions @ 1 point each = 40 pts. Free Response: Show all work and write answers
Geometry Honors Review for Midterm Exam Format of Midterm Exam: Scantron Sheet: Always/Sometimes/Never and Multiple Choice 40 Questions @ 1 point each = 40 pts. Free Response: Show all work and write answers
Math 9 Chapter 8 Practice Test
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Math 9 Chapter 8 Practice Test Short Answer 1. O is the centre of this circle and point Q is a point of tangency. Determine the value of t. If necessary, give your answer to the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Math 9 Chapter 8 Practice Test Short Answer 1. O is the centre of this circle and point Q is a point of tangency. Determine the value of t. If necessary, give your answer to the
Lecture XII. where Φ is called the potential function. Let us introduce spherical coordinates defined through the relations
 Lecture XII Abstract We introuce the Laplace equation in spherical coorinates an apply the metho of separation of variables to solve it. This will generate three linear orinary secon orer ifferential equations:
Lecture XII Abstract We introuce the Laplace equation in spherical coorinates an apply the metho of separation of variables to solve it. This will generate three linear orinary secon orer ifferential equations:
Table of Common Derivatives By David Abraham
 Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
Prouct an Quotient Rules: Table of Common Derivatives By Davi Abraham [ f ( g( ] = [ f ( ] g( + f ( [ g( ] f ( = g( [ f ( ] g( g( f ( [ g( ] Trigonometric Functions: sin( = cos( cos( = sin( tan( = sec
Additional Math (4047) Paper 1(80 marks)
 Aitional Math (07) Prepare b Mr Ang, Nov 07 A curve is such that 6 8 an the point P(, 8) lies on the curve. The graient of the curve at P is. Fin the equation of the curve. [6] C where C is an integration
Aitional Math (07) Prepare b Mr Ang, Nov 07 A curve is such that 6 8 an the point P(, 8) lies on the curve. The graient of the curve at P is. Fin the equation of the curve. [6] C where C is an integration
(A) 2S + 3 (B) 3S + 2 (C) 3S + 6 (D) 2S + 6 (E) 2S + 12
 1 The sum of two numbers is S Suppose 3 is added to each number and then each of the resulting numbers is doubled What is the sum of the final two numbers? (A) S + 3 (B) 3S + (C) 3S + 6 (D) S + 6 (E) S
1 The sum of two numbers is S Suppose 3 is added to each number and then each of the resulting numbers is doubled What is the sum of the final two numbers? (A) S + 3 (B) 3S + (C) 3S + 6 (D) S + 6 (E) S
The Alberta High School Mathematics Competition Solution to Part I, 2014.
 The Alberta High School Mathematics Competition Solution to Part I, 2014. Question 1. When the repeating decimal 0.6 is divided by the repeating decimal 0.3, the quotient is (a) 0.2 (b) 2 (c) 0.5 (d) 0.5
The Alberta High School Mathematics Competition Solution to Part I, 2014. Question 1. When the repeating decimal 0.6 is divided by the repeating decimal 0.3, the quotient is (a) 0.2 (b) 2 (c) 0.5 (d) 0.5
Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2017
 Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2017 Junior Section Saturday, 4 March 2017 08h30-11h30 Important: Answer to all 15 questions. Write your answers on the answer sheets provided. For the multiple choice
Hanoi Open Mathematical Competition 2017 Junior Section Saturday, 4 March 2017 08h30-11h30 Important: Answer to all 15 questions. Write your answers on the answer sheets provided. For the multiple choice
Triangles. 3.In the following fig. AB = AC and BD = DC, then ADC = (A) 60 (B) 120 (C) 90 (D) none 4.In the Fig. given below, find Z.
 Triangles 1.Two sides of a triangle are 7 cm and 10 cm. Which of the following length can be the length of the third side? (A) 19 cm. (B) 17 cm. (C) 23 cm. of these. 2.Can 80, 75 and 20 form a triangle?
Triangles 1.Two sides of a triangle are 7 cm and 10 cm. Which of the following length can be the length of the third side? (A) 19 cm. (B) 17 cm. (C) 23 cm. of these. 2.Can 80, 75 and 20 form a triangle?
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep Nozha Language Schools Geometry Revision Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. In the parallelogram, each
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep Nozha Language Schools Geometry Revision Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. In the parallelogram, each
LLT Education Services
 8. The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle. (a) 4 cm (b) 3 cm (c) 6 cm (d) 5 cm 9. From a point P, 10 cm away from the
8. The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle. (a) 4 cm (b) 3 cm (c) 6 cm (d) 5 cm 9. From a point P, 10 cm away from the
Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse
 Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 2: Ellipse Oct 2017 1 / 24 Introduction Problem 2.1 Let A, F 1 and F 2 be three points that form a triangle F 2
Conic Sections Session 2: Ellipse Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 2: Ellipse Oct 2017 1 / 24 Introduction Problem 2.1 Let A, F 1 and F 2 be three points that form a triangle F 2
It is known that the length of the tangents drawn from an external point to a circle is equal.
 CBSE -MATHS-SET 1-2014 Q1. The first three terms of an AP are 3y-1, 3y+5 and 5y+1, respectively. We need to find the value of y. We know that if a, b and c are in AP, then: b a = c b 2b = a + c 2 (3y+5)
CBSE -MATHS-SET 1-2014 Q1. The first three terms of an AP are 3y-1, 3y+5 and 5y+1, respectively. We need to find the value of y. We know that if a, b and c are in AP, then: b a = c b 2b = a + c 2 (3y+5)
10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]
![10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152] 10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]](/thumbs/94/121826807.jpg) foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that
 1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that g(x)(x 2 3x + 2) = h(x)(x 2 + 3x + 2) and f(x) = g(x)h(x) + (x 4 5x 2 + 4). Prove that f(x) has at least four real roots. 2. Let M be
1. Let g(x) and h(x) be polynomials with real coefficients such that g(x)(x 2 3x + 2) = h(x)(x 2 + 3x + 2) and f(x) = g(x)h(x) + (x 4 5x 2 + 4). Prove that f(x) has at least four real roots. 2. Let M be
History of Mathematics Workbook
 History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
History of Mathematics Workbook Paul Yiu Department of Mathematics Florida Atlantic University Last Update: April 7, 2014 Student: Spring 2014 Problem A1. Given a square ABCD, equilateral triangles ABX
Math Chapter 2 Essentials of Calculus by James Stewart Prepared by Jason Gaddis
 Math 231 - Chapter 2 Essentials of Calculus by James Stewart Prepare by Jason Gais Chapter 2 - Derivatives 21 - Derivatives an Rates of Change Definition A tangent to a curve is a line that intersects
Math 231 - Chapter 2 Essentials of Calculus by James Stewart Prepare by Jason Gais Chapter 2 - Derivatives 21 - Derivatives an Rates of Change Definition A tangent to a curve is a line that intersects
 CONCURRENT LINES- PROPERTIES RELATED TO A TRIANGLE THEOREM The medians of a triangle are concurrent. Proof: Let A(x 1, y 1 ), B(x, y ), C(x 3, y 3 ) be the vertices of the triangle A(x 1, y 1 ) F E B(x,
CONCURRENT LINES- PROPERTIES RELATED TO A TRIANGLE THEOREM The medians of a triangle are concurrent. Proof: Let A(x 1, y 1 ), B(x, y ), C(x 3, y 3 ) be the vertices of the triangle A(x 1, y 1 ) F E B(x,
Circle and Cyclic Quadrilaterals. MARIUS GHERGU School of Mathematics and Statistics University College Dublin
 Circle and Cyclic Quadrilaterals MARIUS GHERGU School of Mathematics and Statistics University College Dublin 3 Basic Facts About Circles A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the
Circle and Cyclic Quadrilaterals MARIUS GHERGU School of Mathematics and Statistics University College Dublin 3 Basic Facts About Circles A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the
Second Major Solution Q1. The three capacitors in the figure have an equivalent capacitance of 2.77 µf. What is C 2?
 Secon Major Solution Q1. The three capacitors in the figure have an equivalent capacitance of.77 µf. What is C? C 4.0 µf.0 µf A) 7 µf B) µf C) 4 µf D) 3 µf E) 6 µf Q. When the potential ifference across
Secon Major Solution Q1. The three capacitors in the figure have an equivalent capacitance of.77 µf. What is C? C 4.0 µf.0 µf A) 7 µf B) µf C) 4 µf D) 3 µf E) 6 µf Q. When the potential ifference across
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 03 (2017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) BLUE PRINT : CLASS X Unit Chapter VSA (1 mark) SA I (2 marks) SA II (3 marks) LA (4 marks) Total Unit
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, HYDERABAD REGION SAMPLE PAPER 03 (2017-18) SUBJECT: MATHEMATICS(041) BLUE PRINT : CLASS X Unit Chapter VSA (1 mark) SA I (2 marks) SA II (3 marks) LA (4 marks) Total Unit
Related Rates. Introduction
 Relate Rates Introuction We are familiar with a variet of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especiall geometric ones For eample, for the sies of a right triangle we have a 2 + b 2 = c 2 or the
Relate Rates Introuction We are familiar with a variet of mathematical or quantitative relationships, especiall geometric ones For eample, for the sies of a right triangle we have a 2 + b 2 = c 2 or the
1. The unit vector perpendicular to both the lines. Ans:, (2)
 1. The unit vector perpendicular to both the lines x 1 y 2 z 1 x 2 y 2 z 3 and 3 1 2 1 2 3 i 7j 7k i 7j 5k 99 5 3 1) 2) i 7j 5k 7i 7j k 3) 4) 5 3 99 i 7j 5k Ans:, (2) 5 3 is Solution: Consider i j k a
1. The unit vector perpendicular to both the lines x 1 y 2 z 1 x 2 y 2 z 3 and 3 1 2 1 2 3 i 7j 7k i 7j 5k 99 5 3 1) 2) i 7j 5k 7i 7j k 3) 4) 5 3 99 i 7j 5k Ans:, (2) 5 3 is Solution: Consider i j k a
u t v t v t c a u t b a v t u t v t b a
 Nonlinear Dynamical Systems In orer to iscuss nonlinear ynamical systems, we must first consier linear ynamical systems. Linear ynamical systems are just systems of linear equations like we have been stuying
Nonlinear Dynamical Systems In orer to iscuss nonlinear ynamical systems, we must first consier linear ynamical systems. Linear ynamical systems are just systems of linear equations like we have been stuying
NEW YORK CITY INTERSCHOLASTIC MATHEMATICS LEAGUE Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1
 Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1 PART I FALL 2011 CONTEST 1 TIME: 10 MINUTES F11A1 Larry selects a 13-digit number while David selects a 10-digit number. Let be the number of digits in the product of
Senior A Division CONTEST NUMBER 1 PART I FALL 2011 CONTEST 1 TIME: 10 MINUTES F11A1 Larry selects a 13-digit number while David selects a 10-digit number. Let be the number of digits in the product of
The Advantage Testing Foundation Solutions
 The Advantage Testing Foundation 2016 Problem 1 Let T be a triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. If P is a point in or on T, what is the greatest possible sum of the distances from P to each of the three
The Advantage Testing Foundation 2016 Problem 1 Let T be a triangle with side lengths 3, 4, and 5. If P is a point in or on T, what is the greatest possible sum of the distances from P to each of the three
Math Contest, Fall 2017 BC EXAM , z =
 Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why. (a b)(a c)(a d)(b c)(b d)(c d) a 2 + ab b = 2018.
 New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
New Zealand Mathematical Olympiad Committee Camp Selection Problems 2018 Solutions Due: 28th September 2018 1. Suppose that a, b, c and d are four different integers. Explain why must be a multiple of
6 CHAPTER. Triangles. A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
 6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
Power Round: Geometry Revisited
 Power Round: Geometry Revisited Stobaeus (one of Euclid s students): But what shall I get by learning these things? Euclid to his slave: Give him three pence, since he must make gain out of what he learns.
Power Round: Geometry Revisited Stobaeus (one of Euclid s students): But what shall I get by learning these things? Euclid to his slave: Give him three pence, since he must make gain out of what he learns.
Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 9
 9A. Vectors an Forces Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 9. F = 5 sin 5.9 an F = 5 cos 5 4.8.. a. By the Pythagorean theorem, the length of the vector from to (, ) is + = 5. So the magnitue of the force
9A. Vectors an Forces Solutions to the Exercises of Chapter 9. F = 5 sin 5.9 an F = 5 cos 5 4.8.. a. By the Pythagorean theorem, the length of the vector from to (, ) is + = 5. So the magnitue of the force
 Note : This document might take a little longer time to print. more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more
Note : This document might take a little longer time to print. more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more exam papers at : more
The sum x 1 + x 2 + x 3 is (A): 4 (B): 6 (C): 8 (D): 14 (E): None of the above. How many pairs of positive integers (x, y) are there, those satisfy
 Important: Answer to all 15 questions. Write your answers on the answer sheets provided. For the multiple choice questions, stick only the letters (A, B, C, D or E) of your choice. No calculator is allowed.
Important: Answer to all 15 questions. Write your answers on the answer sheets provided. For the multiple choice questions, stick only the letters (A, B, C, D or E) of your choice. No calculator is allowed.
14 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 12 February 2011
 14 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 1 February 011 1. Let a, b, and c be positive real numbers. etermine the largest total number of real roots that the following three polynomials
14 th Annual Harvard-MIT Mathematics Tournament Saturday 1 February 011 1. Let a, b, and c be positive real numbers. etermine the largest total number of real roots that the following three polynomials
7.5 Proportionality Relationships
 www.ck12.org Chapter 7. Similarity 7.5 Proportionality Relationships Learning Objectives Identify proportional segments when two sides of a triangle are cut by a segment parallel to the third side. Extend
www.ck12.org Chapter 7. Similarity 7.5 Proportionality Relationships Learning Objectives Identify proportional segments when two sides of a triangle are cut by a segment parallel to the third side. Extend
Math Day at the Beach 2017 Solutions
 Math Day at the Beach 07 Solutions Mike Bao, Brendan Brzycki, Benjamin Chen, Samuel Cui, Michael Diao, Ayush Kamat, Emma Qin, Jack Sun, Jason Ye, Xuyang Yu, Beckman Math Club Individual Round Problem.
Math Day at the Beach 07 Solutions Mike Bao, Brendan Brzycki, Benjamin Chen, Samuel Cui, Michael Diao, Ayush Kamat, Emma Qin, Jack Sun, Jason Ye, Xuyang Yu, Beckman Math Club Individual Round Problem.
