Mathematics 13: Lecture 4
|
|
|
- Phyllis Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mathematics 13: Lecture Planes Dan Sloughter Furman University January 10, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
2 Planes in R n Suppose v and w are nonzero vectors in R n which are not parallel. Given any third vector p 0 in R n, we call the set of all points P where s and t are scalars, a plane. p = p 0 + s v + t w, Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
3 Planes in R n Suppose v and w are nonzero vectors in R n which are not parallel. Given any third vector p 0 in R n, we call the set of all points P where s and t are scalars, a plane. p = p 0 + s v + t w, We call this equation a vector equation for P. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
4 Parametric equations If then x 1 p 1 x 2 p =., p p 2 0 =., v = v 2 w 2, and w =.., x n p n v n w n v 1 w 1 x 1 = p 1 + sv 1 + tw 1, x 2 = p 2 + sv 2 + tw 2,. =. x n = p n + sv n + tw n, which are the scalar, or parametric, equations for P. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
5 Example Let P be the plane in R 3 which contains the points p 0 = 1, q = 2, and r = Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, 2008 / 10
6 Example Let P be the plane in R 3 which contains the points p 0 = 1, q = 2, and r = Then 0 2 v = q p 0 = 3 and w = r p 0 = are vectors which lie on P. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, 2008 / 10
7 Example (cont d) So the vector equation of P is p = 1 + s 3 + t 2, and the parametric equations are x = 1 2t, y = 1 + 3s + 2t, z = 1 + s + 2t. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
8 Normal form in R 3 Suppose P is a plane in R 3 with vector equation p = p 0 + s v + t w. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
9 Normal form in R 3 Suppose P is a plane in R 3 with vector equation p = p 0 + s v + t w. Analogous to the case with lines in R 2, if n is perpendicular to both v and w, then we may describe P as the set of all p in R 3 satisfying n ( p p 0 ) = 0. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
10 Normal form in R 3 Suppose P is a plane in R 3 with vector equation p = p 0 + s v + t w. Analogous to the case with lines in R 2, if n is perpendicular to both v and w, then we may describe P as the set of all p in R 3 satisfying n ( p p 0 ) = 0. This is the normal equation of P. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
11 Example Suppose P is a plane passing through 1 p 0 = 1 1 with normal vector n = 2. 6 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
12 Example Suppose P is a plane passing through 1 p 0 = 1 1 with normal vector n = 2. 6 The normal form of the equation for P is x 1 2 y 1 = 0. 6 z 1 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
13 Example Suppose P is a plane passing through 1 p 0 = 1 1 with normal vector n = 2. 6 The normal form of the equation for P is x 1 2 y 1 = 0. 6 z 1 Or, equivalently, x 2y + 6z = 12. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
14 Distance to a plane Let P be a plane in R 3 with normal equation n ( p p 0 ) = 0. Let D be the shortest distance from a point q to P. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
15 Distance to a plane Let P be a plane in R 3 with normal equation n ( p p 0 ) = 0. Let D be the shortest distance from a point q to P. Let v = q p 0. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
16 Distance to a plane Let P be a plane in R 3 with normal equation n ( p p 0 ) = 0. Let D be the shortest distance from a point q to P. Let v = q p 0. Note: the component of v in the direction of n is n v n = n q n p 0. n Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
17 Distance to a plane Let P be a plane in R 3 with normal equation n ( p p 0 ) = 0. Let D be the shortest distance from a point q to P. Let v = q p 0. Note: the component of v in the direction of n is n v n = n q n p 0. n Hence D = n q n p 0. n Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
18 Distance to a plane Let P be a plane in R 3 with normal equation n ( p p 0 ) = 0. Let D be the shortest distance from a point q to P. Let v = q p 0. Note: the component of v in the direction of n is n v n = n q n p 0. n Hence D = n q n p 0. n Note: the point on P closest to q is q proj n v. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
19 Distance to a plane Let P be a plane in R 3 with normal equation n ( p p 0 ) = 0. Let D be the shortest distance from a point q to P. Let v = q p 0. Note: the component of v in the direction of n is n v n = n q n p 0. n Hence D = n q n p 0. n Note: the point on P closest to q is q proj n v. Note: an analogous formula works for the distance from a point to a line in R 2. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
20 Example Suppose P is a plane with equation x + 2y + z = 8 and 3 q = 3. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
21 Example Suppose P is a plane with equation x + 2y + z = 8 and 3 q = 3. Note: is a normal vector for P. n = 2 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
22 Example Suppose P is a plane with equation x + 2y + z = 8 and 3 q = 3. Note: is a normal vector for P. n = 2 Moreover, for any point p 0 on P, n p 0 = 8. Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
23 Example Suppose P is a plane with equation x + 2y + z = 8 and 3 q = 3. Note: is a normal vector for P. n = 2 Moreover, for any point p 0 on P, n p 0 = 8. Hence the shortest distance D from q to P is D = n q 8 n = = Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
24 Example (cont d) Note: If v = q p 0, where p 0 is some point on P, then proj n v = 26 2 = Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
25 Example (cont d) Note: If v = q p 0, where p 0 is some point on P, then proj n v = 26 2 = So the point on P closest to q is q proj n v = Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture January 10, / 10
Mathematics 22: Lecture 5
 Mathematics 22: Lecture 5 Autonomous Equations Dan Sloughter Furman University January 11, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 5 January 11, 2008 1 / 11 Solving the logistics
Mathematics 22: Lecture 5 Autonomous Equations Dan Sloughter Furman University January 11, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 5 January 11, 2008 1 / 11 Solving the logistics
Mathematics 22: Lecture 7
 Mathematics 22: Lecture 7 Separation of Variables Dan Sloughter Furman University January 15, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 7 January 15, 2008 1 / 8 Separable equations
Mathematics 22: Lecture 7 Separation of Variables Dan Sloughter Furman University January 15, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 7 January 15, 2008 1 / 8 Separable equations
Pivotal Quantities. Mathematics 47: Lecture 16. Dan Sloughter. Furman University. March 30, 2006
 Pivotal Quantities Mathematics 47: Lecture 16 Dan Sloughter Furman University March 30, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Pivotal Quantities March 30, 2006 1 / 10 Pivotal quantities Definition Suppose
Pivotal Quantities Mathematics 47: Lecture 16 Dan Sloughter Furman University March 30, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Pivotal Quantities March 30, 2006 1 / 10 Pivotal quantities Definition Suppose
Mathematics 22: Lecture 12
 Mathematics 22: Lecture 12 Second-order Linear Equations Dan Sloughter Furman University January 28, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 12 January 28, 2008 1 / 14 Definition
Mathematics 22: Lecture 12 Second-order Linear Equations Dan Sloughter Furman University January 28, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 12 January 28, 2008 1 / 14 Definition
Mathematics 22: Lecture 4
 Mathematics 22: Lecture 4 Population Models Dan Sloughter Furman University January 10, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 4 January 10, 2008 1 / 6 Malthusian growth model Let
Mathematics 22: Lecture 4 Population Models Dan Sloughter Furman University January 10, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 4 January 10, 2008 1 / 6 Malthusian growth model Let
Some Trigonometric Limits
 Some Trigonometric Limits Mathematics 11: Lecture 7 Dan Sloughter Furman University September 20, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Some Trigonometric Limits September 20, 2007 1 / 14 The squeeze
Some Trigonometric Limits Mathematics 11: Lecture 7 Dan Sloughter Furman University September 20, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Some Trigonometric Limits September 20, 2007 1 / 14 The squeeze
Mathematics 13: Lecture 10
 Mathematics 13: Lecture 10 Matrices Dan Sloughter Furman University January 25, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture 10 January 25, 2008 1 / 19 Matrices Recall: A matrix is a
Mathematics 13: Lecture 10 Matrices Dan Sloughter Furman University January 25, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 13: Lecture 10 January 25, 2008 1 / 19 Matrices Recall: A matrix is a
Calculus: Area. Mathematics 15: Lecture 22. Dan Sloughter. Furman University. November 12, 2006
 Calculus: Area Mathematics 15: Lecture 22 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 12, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Calculus: Area November 12, 2006 1 / 7 Area Note: formulas for the areas of
Calculus: Area Mathematics 15: Lecture 22 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 12, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Calculus: Area November 12, 2006 1 / 7 Area Note: formulas for the areas of
Mathematics 22: Lecture 19
 Mathematics 22: Lecture 19 Legendre s Equation Dan Sloughter Furman University February 5, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 19 February 5, 2008 1 / 11 Example: Legendre s
Mathematics 22: Lecture 19 Legendre s Equation Dan Sloughter Furman University February 5, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 19 February 5, 2008 1 / 11 Example: Legendre s
Antiderivatives. Mathematics 11: Lecture 30. Dan Sloughter. Furman University. November 7, 2007
 Antiderivatives Mathematics 11: Lecture 30 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 7, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Antiderivatives November 7, 2007 1 / 9 Definition Recall: Suppose F and f are
Antiderivatives Mathematics 11: Lecture 30 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 7, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Antiderivatives November 7, 2007 1 / 9 Definition Recall: Suppose F and f are
Sampling Distributions
 Sampling Distributions Mathematics 47: Lecture 9 Dan Sloughter Furman University March 16, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Sampling Distributions March 16, 2006 1 / 10 Definition We call the probability
Sampling Distributions Mathematics 47: Lecture 9 Dan Sloughter Furman University March 16, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Sampling Distributions March 16, 2006 1 / 10 Definition We call the probability
Mathematics 22: Lecture 10
 Mathematics 22: Lecture 10 Euler s Method Dan Sloughter Furman University January 22, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 10 January 22, 2008 1 / 14 Euler s method Consider the
Mathematics 22: Lecture 10 Euler s Method Dan Sloughter Furman University January 22, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 10 January 22, 2008 1 / 14 Euler s method Consider the
Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals
 Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals Mathematics 11: Lecture 39 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 29, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals November
Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals Mathematics 11: Lecture 39 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 29, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Change of Variables: Indefinite Integrals November
Mathematics 22: Lecture 11
 Mathematics 22: Lecture 11 Runge-Kutta Dan Sloughter Furman University January 25, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 11 January 25, 2008 1 / 11 Order of approximations One
Mathematics 22: Lecture 11 Runge-Kutta Dan Sloughter Furman University January 25, 2008 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Mathematics 22: Lecture 11 January 25, 2008 1 / 11 Order of approximations One
Nonparametric Tests. Mathematics 47: Lecture 25. Dan Sloughter. Furman University. April 20, 2006
 Nonparametric Tests Mathematics 47: Lecture 25 Dan Sloughter Furman University April 20, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Nonparametric Tests April 20, 2006 1 / 14 The sign test Suppose X 1, X 2,...,
Nonparametric Tests Mathematics 47: Lecture 25 Dan Sloughter Furman University April 20, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Nonparametric Tests April 20, 2006 1 / 14 The sign test Suppose X 1, X 2,...,
Example. Mathematics 255: Lecture 17. Example. Example (cont d) Consider the equation. d 2 y dt 2 + dy
 Mathematics 255: Lecture 17 Undetermined Coefficients Dan Sloughter Furman University October 10, 2008 6y = 5e 4t. so the general solution of 0 = r 2 + r 6 = (r + 3)(r 2), 6y = 0 y(t) = c 1 e 3t + c 2
Mathematics 255: Lecture 17 Undetermined Coefficients Dan Sloughter Furman University October 10, 2008 6y = 5e 4t. so the general solution of 0 = r 2 + r 6 = (r + 3)(r 2), 6y = 0 y(t) = c 1 e 3t + c 2
The Geometry. Mathematics 15: Lecture 20. Dan Sloughter. Furman University. November 6, 2006
 The Geometry Mathematics 15: Lecture 20 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 6, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) The Geometry November 6, 2006 1 / 18 René Descartes 1596-1650 Dan Sloughter (Furman
The Geometry Mathematics 15: Lecture 20 Dan Sloughter Furman University November 6, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) The Geometry November 6, 2006 1 / 18 René Descartes 1596-1650 Dan Sloughter (Furman
The Chain Rule. Mathematics 11: Lecture 18. Dan Sloughter. Furman University. October 10, 2007
 The Chain Rule Mathematics 11: Lecture 18 Dan Sloughter Furman University October 10, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) The Chain Rule October 10, 2007 1 / 15 Example Suppose that a pebble is dropped
The Chain Rule Mathematics 11: Lecture 18 Dan Sloughter Furman University October 10, 2007 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) The Chain Rule October 10, 2007 1 / 15 Example Suppose that a pebble is dropped
if b is a linear combination of u, v, w, i.e., if we can find scalars r, s, t so that ru + sv + tw = 0.
 Solutions Review # Math 7 Instructions: Use the following problems to study for Exam # which will be held Wednesday Sept For a set of nonzero vectors u v w} in R n use words and/or math expressions to
Solutions Review # Math 7 Instructions: Use the following problems to study for Exam # which will be held Wednesday Sept For a set of nonzero vectors u v w} in R n use words and/or math expressions to
R n : The Cross Product
 A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler R n : The Cross Product Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
A FIRST COURSE IN LINEAR ALGEBRA An Open Text by Ken Kuttler R n : The Cross Product Lecture Notes by Karen Seyffarth Adapted by LYRYX SERVICE COURSE SOLUTION Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA)
Goodness of Fit Tests: Homogeneity
 Goodness of Fit Tests: Homogeneity Mathematics 47: Lecture 35 Dan Sloughter Furman University May 11, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Goodness of Fit Tests: Homogeneity May 11, 2006 1 / 13 Testing
Goodness of Fit Tests: Homogeneity Mathematics 47: Lecture 35 Dan Sloughter Furman University May 11, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Goodness of Fit Tests: Homogeneity May 11, 2006 1 / 13 Testing
Vectors. Section 3: Using the vector product
 Vectors Section 3: Using the vector product Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Using the vector product in finding the equation of a plane The intersection of two planes The distance
Vectors Section 3: Using the vector product Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Using the vector product in finding the equation of a plane The intersection of two planes The distance
How can we find the distance between a point and a plane in R 3? Between two lines in R 3? Between two planes? Between a plane and a line?
 Overview Yesterday we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r = r 0 + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrary points r in terms of a specific point r 0 and the direction
Overview Yesterday we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r = r 0 + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrary points r in terms of a specific point r 0 and the direction
MAC Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II
 MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
MAC 2103 Module 5 Vectors in 2-Space and 3-Space II 1 Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Determine the cross product of a vector in R 3. 2. Determine a scalar triple
Created by T. Madas VECTOR PRACTICE Part B Created by T. Madas
 VECTOR PRACTICE Part B THE CROSS PRODUCT Question 1 Find in each of the following cases a) a = 2i + 5j + k and b = 3i j b) a = i + 2j + k and b = 3i j k c) a = 3i j 2k and b = i + 3j + k d) a = 7i + j
VECTOR PRACTICE Part B THE CROSS PRODUCT Question 1 Find in each of the following cases a) a = 2i + 5j + k and b = 3i j b) a = i + 2j + k and b = 3i j k c) a = 3i j 2k and b = i + 3j + k d) a = 7i + j
MTH 2310, FALL Introduction
 MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
MTH 2310, FALL 2011 SECTION 6.2: ORTHOGONAL SETS Homework Problems: 1, 5, 9, 13, 17, 21, 23 1, 27, 29, 35 1. Introduction We have discussed previously the benefits of having a set of vectors that is linearly
MATH 19520/51 Class 2
 MATH 19520/51 Class 2 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-09-27 1 Review dot product. 2 Angles between vectors and orthogonality. 3 Projection of one vector onto another. 4 Cross product and its
MATH 19520/51 Class 2 Minh-Tam Trinh University of Chicago 2017-09-27 1 Review dot product. 2 Angles between vectors and orthogonality. 3 Projection of one vector onto another. 4 Cross product and its
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II
 Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Lecture 3: Linear Algebra Review, Part II Brian Borchers January 4, Linear Independence Definition The vectors v, v,..., v n are linearly independent if the system of equations c v + c v +...+ c n v n
Review of Coordinate Systems
 Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
Vector in 2 R and 3 R Review of Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Common coordinate systems are: Cartesian Polar Cartesian Coordinate System Also called rectangular coordinate
VECTORS IN A STRAIGHT LINE
 A. The Equation of a Straight Line VECTORS P3 VECTORS IN A STRAIGHT LINE A particular line is uniquely located in space if : I. It has a known direction, d, and passed through a known fixed point, or II.
A. The Equation of a Straight Line VECTORS P3 VECTORS IN A STRAIGHT LINE A particular line is uniquely located in space if : I. It has a known direction, d, and passed through a known fixed point, or II.
Section 6.1. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality
 Section 6. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Almost solve the equation Ax = b Problem: In the real world, data is imperfect. x v u But due to measurement error, the measured x is not
Section 6. Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Almost solve the equation Ax = b Problem: In the real world, data is imperfect. x v u But due to measurement error, the measured x is not
Name: ID: Math 233 Exam 1. Page 1
 Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
Page 1 Name: ID: This exam has 20 multiple choice questions, worth 5 points each. You are allowed to use a scientific calculator and a 3 5 inch note card. 1. Which of the following pairs of vectors are
(iii) converting between scalar product and parametric forms. (ii) vector perpendicular to two given (3D) vectors
 Vector Theory (15/3/2014) www.alevelmathsng.co.uk Contents (1) Equation of a line (i) parametric form (ii) relation to Cartesian form (iii) vector product form (2) Equation of a plane (i) scalar product
Vector Theory (15/3/2014) www.alevelmathsng.co.uk Contents (1) Equation of a line (i) parametric form (ii) relation to Cartesian form (iii) vector product form (2) Equation of a plane (i) scalar product
Worksheet for Lecture 25 Section 6.4 Gram-Schmidt Process
 Worksheet for Lecture Name: Section.4 Gram-Schmidt Process Goal For a subspace W = Span{v,..., v n }, we want to find an orthonormal basis of W. Example Let W = Span{x, x } with x = and x =. Give an orthogonal
Worksheet for Lecture Name: Section.4 Gram-Schmidt Process Goal For a subspace W = Span{v,..., v n }, we want to find an orthonormal basis of W. Example Let W = Span{x, x } with x = and x =. Give an orthogonal
Linear Algebra: Homework 3
 Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Linear Algebra: Homework 3 Alvin Lin August 206 - December 206 Section.2 Exercise 48 Find all values of the scalar k for which the two vectors are orthogonal. [ ] [ ] 2 k + u v 3 k u v 0 2(k + ) + 3(k
Lecture 5. Equations of Lines and Planes. Dan Nichols MATH 233, Spring 2018 University of Massachusetts.
 Lecture 5 Equations of Lines and Planes Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 Universit of Massachusetts Februar 6, 2018 (2) Upcoming midterm eam First midterm: Wednesda Feb. 21, 7:00-9:00
Lecture 5 Equations of Lines and Planes Dan Nichols nichols@math.umass.edu MATH 233, Spring 2018 Universit of Massachusetts Februar 6, 2018 (2) Upcoming midterm eam First midterm: Wednesda Feb. 21, 7:00-9:00
Chapter 6. Orthogonality and Least Squares
 Chapter 6 Orthogonality and Least Squares Section 6.1 Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Recall: This course is about learning to: Solve the matrix equation Ax = b Solve the matrix equation
Chapter 6 Orthogonality and Least Squares Section 6.1 Inner Product, Length, and Orthogonality Orientation Recall: This course is about learning to: Solve the matrix equation Ax = b Solve the matrix equation
Math 261 Lecture Notes: Sections 6.1, 6.2, 6.3 and 6.4 Orthogonal Sets and Projections
 Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
Math 6 Lecture Notes: Sections 6., 6., 6. and 6. Orthogonal Sets and Projections We will not cover general inner product spaces. We will, however, focus on a particular inner product space the inner product
FINDING THE INTERSECTION OF TWO LINES
 FINDING THE INTERSECTION OF TWO LINES REALTIONSHIP BETWEEN LINES 2 D: D: the lines are coplanar (they lie in the same plane). They could be: intersecting parallel coincident the lines are not coplanar
FINDING THE INTERSECTION OF TWO LINES REALTIONSHIP BETWEEN LINES 2 D: D: the lines are coplanar (they lie in the same plane). They could be: intersecting parallel coincident the lines are not coplanar
Mathematics 2203, Test 1 - Solutions
 Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Mathematics 220, Test 1 - Solutions F, 2010 Philippe B. Laval Name 1. Determine if each statement below is True or False. If it is true, explain why (cite theorem, rule, property). If it is false, explain
Overview. Distances in R 3. Distance from a point to a plane. Question
 Overview Yesterda we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrar points r in terms of a specific point and the direction vector v.
Overview Yesterda we introduced equations to describe lines and planes in R 3 : r + tv The vector equation for a line describes arbitrar points r in terms of a specific point and the direction vector v.
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./ Orthonormal Sets A set of vectors {u, u,...,
Math 9 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture : Orthogonal Projections, Gram-Schmidt Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 9Applied Linear Algebra p./ Orthonormal Sets A set of vectors {u, u,...,
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8
 MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
MAT 1339-S14 Class 8 July 28, 2014 Contents 7.2 Review Dot Product........................... 2 7.3 Applications of the Dot Product..................... 4 7.4 Vectors in Three-Space.........................
Section 6.2, 6.3 Orthogonal Sets, Orthogonal Projections
 Section 6. 6. Orthogonal Sets Orthogonal Projections Main Ideas in these sections: Orthogonal set = A set of mutually orthogonal vectors. OG LI. Orthogonal Projection of y onto u or onto an OG set {u u
Section 6. 6. Orthogonal Sets Orthogonal Projections Main Ideas in these sections: Orthogonal set = A set of mutually orthogonal vectors. OG LI. Orthogonal Projection of y onto u or onto an OG set {u u
Last week we presented the following expression for the angles between two vectors u and v in R n ( ) θ = cos 1 u v
 Orthogonality (I) Last week we presented the following expression for the angles between two vectors u and v in R n ( ) θ = cos 1 u v u v which brings us to the fact that θ = π/2 u v = 0. Definition (Orthogonality).
Orthogonality (I) Last week we presented the following expression for the angles between two vectors u and v in R n ( ) θ = cos 1 u v u v which brings us to the fact that θ = π/2 u v = 0. Definition (Orthogonality).
Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in
 Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in R 2 In this section, we begin with a discussion about how to find the vector and parametric equations of a line in R 2. To find the vector and parametric
Section 8.1 Vector and Parametric Equations of a Line in R 2 In this section, we begin with a discussion about how to find the vector and parametric equations of a line in R 2. To find the vector and parametric
Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors.
 Vectors summary Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors. AB is the position vector of B relative to A and is the vector
Vectors summary Quantities which have only magnitude are called scalars. Quantities which have magnitude and direction are called vectors. AB is the position vector of B relative to A and is the vector
APPM 2350 Section Exam points Wednesday September 26, 6:00pm 7:30pm, 2018
 APPM 2350 Section Exam 1 140 points Wednesday September 26, 6:00pm 7:30pm, 2018 ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: (1) your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) lecture section/time (4) your instructor
APPM 2350 Section Exam 1 140 points Wednesday September 26, 6:00pm 7:30pm, 2018 ON THE FRONT OF YOUR BLUEBOOK write: (1) your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) lecture section/time (4) your instructor
Section 5.8. Taylor Series
 Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 5.8 Taylor Series In this section we will put together much of the work of Sections 5.-5.7 in the context of a discussion of Taylor series. We begin
Difference Equations to Differential Equations Section 5.8 Taylor Series In this section we will put together much of the work of Sections 5.-5.7 in the context of a discussion of Taylor series. We begin
Chapter 2: Vector Geometry
 Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Daniel Chan UNSW Semester 1 2018 Daniel Chan (UNSW) Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Semester 1 2018 1 / 32 Goals of this chapter In this chapter, we will answer the following geometric
Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Daniel Chan UNSW Semester 1 2018 Daniel Chan (UNSW) Chapter 2: Vector Geometry Semester 1 2018 1 / 32 Goals of this chapter In this chapter, we will answer the following geometric
Announcements Wednesday, November 15
 3π 4 Announcements Wednesday, November 15 Reviews today: Recitation Style Solve and discuss Practice problems in groups Preparing for the exam tips and strategies It is not mandatory Eduardo at Culc 141,
3π 4 Announcements Wednesday, November 15 Reviews today: Recitation Style Solve and discuss Practice problems in groups Preparing for the exam tips and strategies It is not mandatory Eduardo at Culc 141,
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 1.2 Echelon Forms Math 2331 Linear Algebra 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ January 22, 2018 Shang-Huan
1.2 Echelon Forms Math 2331 Linear Algebra 1.2 Row Reduction and Echelon Forms Shang-Huan Chiu Department of Mathematics, University of Houston schiu@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ schiu/ January 22, 2018 Shang-Huan
Can a Machine Think?
 Can a Machine Think? Mathematics 15: Lecture 27 Dan Sloughter Furman University December 4, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Can a Machine Think? December 4, 2006 1 / 8 Alan Turing 1912-1954 Dan
Can a Machine Think? Mathematics 15: Lecture 27 Dan Sloughter Furman University December 4, 2006 Dan Sloughter (Furman University) Can a Machine Think? December 4, 2006 1 / 8 Alan Turing 1912-1954 Dan
8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]
![8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4] 8. Find r a! r b. a) r a = [3, 2, 7], r b = [ 1, 4, 5] b) r a = [ 5, 6, 7], r b = [2, 7, 4]](/thumbs/95/122742655.jpg) Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
Chapter 8 Prerequisite Skills BLM 8-1.. Linear Relations 1. Make a table of values and graph each linear function a) y = 2x b) y = x + 5 c) 2x + 6y = 12 d) x + 7y = 21 2. Find the x- and y-intercepts of
6.1.1 Angle between Two Lines Intersection of Two lines Shortest Distance from a Point to a Line
 CHAPTER 6 : VECTORS 6. Lines in Space 6.. Angle between Two Lines 6.. Intersection of Two lines 6..3 Shortest Distance from a Point to a Line 6. Planes in Space 6.. Intersection of Two Planes 6.. Angle
CHAPTER 6 : VECTORS 6. Lines in Space 6.. Angle between Two Lines 6.. Intersection of Two lines 6..3 Shortest Distance from a Point to a Line 6. Planes in Space 6.. Intersection of Two Planes 6.. Angle
Math 2433 Notes Week The Dot Product. The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b
 Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
Math 2433 Notes Week 2 11.3 The Dot Product The angle between two vectors is found with this formula: cosθ = a b a b 3) Given, a = 4i + 4j, b = i - 2j + 3k, c = 2i + 2k Find the angle between a and c Projection
SUPPLEMENT I. Example. Graph the vector 4, 3. Definition. Given two points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ), the vector represented by # AB is # AB =,
 SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
SUPPLEMENT I 1. Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both a magnitude and a direction. A twodimensional vector is an ordered pair a = a 1, a 2 of real numbers. The numbers a 1 and a 2 are
Chapter 6: Orthogonality
 Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Chapter 6: Orthogonality (Last Updated: November 7, 7) These notes are derived primarily from Linear Algebra and its applications by David Lay (4ed). A few theorems have been moved around.. Inner products
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10
 Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
Linear Algebra I Lecture 10 Xi Chen 1 1 University of Alberta January 30, 2019 Outline 1 Gauss-Jordan Algorithm ] Let A = [a ij m n be an m n matrix. To reduce A to a reduced row echelon form using elementary
A Primer in Econometric Theory
 A Primer in Econometric Theory Lecture 1: Vector Spaces John Stachurski Lectures by Akshay Shanker May 5, 2017 1/104 Overview Linear algebra is an important foundation for mathematics and, in particular,
A Primer in Econometric Theory Lecture 1: Vector Spaces John Stachurski Lectures by Akshay Shanker May 5, 2017 1/104 Overview Linear algebra is an important foundation for mathematics and, in particular,
12.1. Cartesian Space
 12.1. Cartesian Space In most of your previous math classes, we worked with functions on the xy-plane only meaning we were working only in 2D. Now we will be working in space, or rather 3D. Now we will
12.1. Cartesian Space In most of your previous math classes, we worked with functions on the xy-plane only meaning we were working only in 2D. Now we will be working in space, or rather 3D. Now we will
Math 2331 Linear Algebra
 6. Orthogonal Projections Math 2 Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonal Projections Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math2 Jiwen He, University of
6. Orthogonal Projections Math 2 Linear Algebra 6. Orthogonal Projections Jiwen He Department of Mathematics, University of Houston jiwenhe@math.uh.edu math.uh.edu/ jiwenhe/math2 Jiwen He, University of
Matrices. A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. Cells in a matrix can be referenced in the form.
 Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Matrices A matrix is a method of writing a set of numbers using rows and columns. 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 7 2 5 4 2 0 5 10 12 8 4 9 25 30 1 1 Reading Information from a Matrix Cells in a matrix can be referenced
Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems. Three-Dimensional Coordinate Systems
 To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
To locate a point in a plane, two numbers are necessary. We know that any point in the plane can be represented as an ordered pair (a, b) of real numbers, where a is the x-coordinate and b is the y-coordinate.
MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11
 MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11 August 7 & 11, 2014 Contents 8 Lines and Planes 1 8.1 Equations of Lines in Two-Space and Three-Space............ 1 8.2 Equations of Planes........................... 5 8.3 Properties
MAT 1339-S14 Class 10 & 11 August 7 & 11, 2014 Contents 8 Lines and Planes 1 8.1 Equations of Lines in Two-Space and Three-Space............ 1 8.2 Equations of Planes........................... 5 8.3 Properties
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes
 12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
12.5 Equations of Lines and Planes Equation of Lines Vector Equation of Lines Parametric Equation of Lines Symmetric Equation of Lines Relation Between Two Lines Equations of Planes Vector Equation of
MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II
 MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Alistair Savage Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Winter 2015 Lecture 19 Alistair Savage (uottawa) MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Winter 2015 Lecture
MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Alistair Savage Mathematics and Statistics University of Ottawa Winter 2015 Lecture 19 Alistair Savage (uottawa) MAT 1302B Mathematical Methods II Winter 2015 Lecture
6.4 Vectors and Dot Products
 6.4 Vectors and Dot Products Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Find the dot product of two vectors and use the properties of the dot product. Find the angle between
6.4 Vectors and Dot Products Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn Find the dot product of two vectors and use the properties of the dot product. Find the angle between
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP Contents. 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2
 MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
MATH 12 CLASS 2 NOTES, SEP 23 2011 Contents 1. Dot product: definition, basic properties 1 2. Dot product: determining the angle between two vectors 2 Quick links to definitions/theorems Dot product definition
Announcements Monday, November 20
 Announcements Monday, November 20 You already have your midterms! Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be awarded depends on many factors, and
Announcements Monday, November 20 You already have your midterms! Course grades will be curved at the end of the semester. The percentage of A s, B s, and C s to be awarded depends on many factors, and
15. LECTURE 15. I can calculate the dot product of two vectors and interpret its meaning. I can find the projection of one vector onto another one.
 5. LECTURE 5 Objectives I can calculate the dot product of two vectors and interpret its meaning. I can find the projection of one vector onto another one. In the last few lectures, we ve learned that
5. LECTURE 5 Objectives I can calculate the dot product of two vectors and interpret its meaning. I can find the projection of one vector onto another one. In the last few lectures, we ve learned that
Math 3191 Applied Linear Algebra
 Math 191 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture 1: Inner Products, Length, Orthogonality Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 191Applied Linear Algebra p.1/ Motivation Not all linear systems have
Math 191 Applied Linear Algebra Lecture 1: Inner Products, Length, Orthogonality Stephen Billups University of Colorado at Denver Math 191Applied Linear Algebra p.1/ Motivation Not all linear systems have
2013/2014 SEMESTER 1 MID-TERM TEST. 1 October :30pm to 9:30pm PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY:
 2013/2014 SEMESTER 1 MID-TERM TEST MA1505 MATHEMATICS I 1 October 2013 8:30pm to 9:30pm PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY: 1. This test paper consists of TEN (10) multiple choice questions
2013/2014 SEMESTER 1 MID-TERM TEST MA1505 MATHEMATICS I 1 October 2013 8:30pm to 9:30pm PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY: 1. This test paper consists of TEN (10) multiple choice questions
4.3 Equations in 3-space
 4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
4.3 Equations in 3-space istance can be used to define functions from a 3-space R 3 to the line R. Let P be a fixed point in the 3-space R 3 (say, with coordinates P (2, 5, 7)). Consider a function f :
Vector equations of lines in the plane and 3-space (uses vector addition & scalar multiplication).
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.6: Lines and Planes From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Plotting points, sketching vectors. Be able to find the component form a vector given
Inner products. Theorem (basic properties): Given vectors u, v, w in an inner product space V, and a scalar k, the following properties hold:
 Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Inner products Definition: An inner product on a real vector space V is an operation (function) that assigns to each pair of vectors ( u, v) in V a scalar u, v satisfying the following axioms: 1. u, v
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 26, 2012
 Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
Study guide for Exam 1. by William H. Meeks III October 2, 2012 1 Basics. First we cover the basic definitions and then we go over related problems. Note that the material for the actual midterm may include
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1
 11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
11.4 Dot Product Contemporary Calculus 1 11.4 DOT PRODUCT In the previous sections we looked at the meaning of vectors in two and three dimensions, but the only operations we used were addition and subtraction
Announcements Wednesday, November 15
 Announcements Wednesday, November 15 The third midterm is on this Friday, November 17. The exam covers 3.1, 3.2, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.5. About half the problems will be conceptual, and the other half computational.
Announcements Wednesday, November 15 The third midterm is on this Friday, November 17. The exam covers 3.1, 3.2, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.5. About half the problems will be conceptual, and the other half computational.
7. Dimension and Structure.
 7. Dimension and Structure 7.1. Basis and Dimension Bases for Subspaces Example 2 The standard unit vectors e 1, e 2,, e n are linearly independent, for if we write (2) in component form, then we obtain
7. Dimension and Structure 7.1. Basis and Dimension Bases for Subspaces Example 2 The standard unit vectors e 1, e 2,, e n are linearly independent, for if we write (2) in component form, then we obtain
MTAEA Vectors in Euclidean Spaces
 School of Economics, Australian National University January 25, 2010 Vectors. Economists usually work in the vector space R n. A point in this space is called a vector, and is typically defined by its
School of Economics, Australian National University January 25, 2010 Vectors. Economists usually work in the vector space R n. A point in this space is called a vector, and is typically defined by its
Vector Calculus. Lecture Notes
 Vector Calculus Lecture Notes Adolfo J. Rumbos c Draft date November 23, 211 2 Contents 1 Motivation for the course 5 2 Euclidean Space 7 2.1 Definition of n Dimensional Euclidean Space........... 7 2.2
Vector Calculus Lecture Notes Adolfo J. Rumbos c Draft date November 23, 211 2 Contents 1 Motivation for the course 5 2 Euclidean Space 7 2.1 Definition of n Dimensional Euclidean Space........... 7 2.2
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T. KEMP)
 MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
MATH 20F: LINEAR ALGEBRA LECTURE B00 (T KEMP) Definition 01 If T (x) = Ax is a linear transformation from R n to R m then Nul (T ) = {x R n : T (x) = 0} = Nul (A) Ran (T ) = {Ax R m : x R n } = {b R m
5. A triangle has sides represented by the vectors (1, 2) and (5, 6). Determine the vector representing the third side.
 Vectors EXAM review Problem 1 = 8 and = 1 a) Find the net force, assume that points North, and points East b) Find the equilibrant force 2 = 15, = 7, and the angle between and is 60 What is the magnitude
Vectors EXAM review Problem 1 = 8 and = 1 a) Find the net force, assume that points North, and points East b) Find the equilibrant force 2 = 15, = 7, and the angle between and is 60 What is the magnitude
1.2 LECTURE 2. Scalar Product
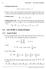 6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
6 CHAPTER 1. VECTOR ALGEBRA Pythagean theem. cos 2 α 1 + cos 2 α 2 + cos 2 α 3 = 1 There is a one-to-one crespondence between the components of the vect on the one side and its magnitude and the direction
Math 241, Exam 1 Information.
 Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
Math 241, Exam 1 Information. 2/13/13, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. Exam 1 will be based on: Sections 12.1-12.5, 14.2. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241sp13/241.html)
10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products
 Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Worksheet for Lecture 23 (due December 4) Section 6.1 Inner product, length, and orthogonality
 Worksheet for Lecture (due December 4) Name: Section 6 Inner product, length, and orthogonality u Definition Let u = u n product or dot product to be and v = v v n be vectors in R n We define their inner
Worksheet for Lecture (due December 4) Name: Section 6 Inner product, length, and orthogonality u Definition Let u = u n product or dot product to be and v = v v n be vectors in R n We define their inner
9 Mixed Exercise. vector equation is. 4 a
 9 Mixed Exercise a AB r i j k j k c OA AB 7 i j 7 k A7,, and B,,8 8 AB 6 A vector equation is 7 r x 7 y z (i j k) j k a x y z a a 7, Pearson Education Ltd 7. Copying permitted for purchasing institution
9 Mixed Exercise a AB r i j k j k c OA AB 7 i j 7 k A7,, and B,,8 8 AB 6 A vector equation is 7 r x 7 y z (i j k) j k a x y z a a 7, Pearson Education Ltd 7. Copying permitted for purchasing institution
BSc (Hons) in Computer Games Development. vi Calculate the components a, b and c of a non-zero vector that is orthogonal to
 1 APPLIED MATHEMATICS INSTRUCTIONS Full marks will be awarded for the correct solutions to ANY FIVE QUESTIONS. This paper will be marked out of a TOTAL MAXIMUM MARK OF 100. Credit will be given for clearly
1 APPLIED MATHEMATICS INSTRUCTIONS Full marks will be awarded for the correct solutions to ANY FIVE QUESTIONS. This paper will be marked out of a TOTAL MAXIMUM MARK OF 100. Credit will be given for clearly
Chapter. Triangles. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.5 Inequalities in a Triangle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Inequalities in a Triangle Important inequality relationships
Chapter 3 Triangles Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.5 Inequalities in a Triangle Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Inequalities in a Triangle Important inequality relationships
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 6
 Mathematical Economics: Lecture 6 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University October 10, 2012 Outline Chapter 11 Linear Independence 1 Chapter 11 Linear Independence New Section Chapter 11: Linear Independence Linear
Mathematical Economics: Lecture 6 Yu Ren WISE, Xiamen University October 10, 2012 Outline Chapter 11 Linear Independence 1 Chapter 11 Linear Independence New Section Chapter 11: Linear Independence Linear
Solutions to Math 51 First Exam October 13, 2015
 Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
Solutions to Math First Exam October 3, 2. (8 points) (a) Find an equation for the plane in R 3 that contains both the x-axis and the point (,, 2). The equation should be of the form ax + by + cz = d.
Euclidean Spaces. Euclidean Spaces. Chapter 10 -S&B
 Chapter 10 -S&B The Real Line: every real number is represented by exactly one point on the line. The plane (i.e., consumption bundles): Pairs of numbers have a geometric representation Cartesian plane
Chapter 10 -S&B The Real Line: every real number is represented by exactly one point on the line. The plane (i.e., consumption bundles): Pairs of numbers have a geometric representation Cartesian plane
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering
 Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13-14, Tuesday 11 th November 2014 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Eigenvectors
Maths for Signals and Systems Linear Algebra in Engineering Lectures 13-14, Tuesday 11 th November 2014 DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Eigenvectors
Solutions to Math 51 First Exam April 21, 2011
 Solutions to Math 5 First Exam April,. ( points) (a) Give the precise definition of a (linear) subspace V of R n. (4 points) A linear subspace V of R n is a subset V R n which satisfies V. If x, y V then
Solutions to Math 5 First Exam April,. ( points) (a) Give the precise definition of a (linear) subspace V of R n. (4 points) A linear subspace V of R n is a subset V R n which satisfies V. If x, y V then
The Calculus of Vec- tors
 Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Physics 2460 Electricity and Magnetism I, Fall 2007, Lecture 3 1 The Calculus of Vec- Summary: tors 1. Calculus of Vectors: Limits and Derivatives 2. Parametric representation of Curves r(t) = [x(t), y(t),
Matrix-Vector Products and the Matrix Equation Ax = b
 Matrix-Vector Products and the Matrix Equation Ax = b A. Havens Department of Mathematics University of Massachusetts, Amherst January 31, 2018 Outline 1 Matrices Acting on Vectors Linear Combinations
Matrix-Vector Products and the Matrix Equation Ax = b A. Havens Department of Mathematics University of Massachusetts, Amherst January 31, 2018 Outline 1 Matrices Acting on Vectors Linear Combinations
The Electric Potential
 Lecture 6 Chapter 25 The Electric Potential Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 25: Section 25.4-7 Electric Potential Quantities
Lecture 6 Chapter 25 The Electric Potential Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsii Today we are going to discuss: Chapter 25: Section 25.4-7 Electric Potential Quantities
web: HOMEWORK 1
 MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
MAT 207 LINEAR ALGEBRA I 2009207 Dokuz Eylül University, Faculty of Science, Department of Mathematics Instructor: Engin Mermut web: http://kisideuedutr/enginmermut/ HOMEWORK VECTORS IN THE n-dimensional
