Chapter - 1. Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
|
|
|
- Heather Stokes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter - 1 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Dr. Rajesh Sathiyamoorthy Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Kanpur hsrajesh@iitk.ac.in; Condition for Rigid-Body Equilibrium A rigid body is subjected to an external force and couple moment system that is the result of the effects of gravitational, electrical, magnetic, or contact forces caused by adjacent bodies. The force and couple moment system acting on a body can be reduced to an equivalent resultant force and resultant couple moment at any arbitrary point O on or off the body If this resultant force and couple moment are both equal to zero, then the body is said to be in equilibrium In statics, we deal primarily with bodies at rest (i.e. they are in the state of static equilibrium ). 1
2 Equilibrium of a system All physical bodies are inherently 3D, but many may be treated as 2D or sometimes 1D the heart () of mechanics R M Fi 0 M 0 i System Idealisation R F i 0 Equilibrium of Objects Particles (2D & 3D) 2D Rigid Bodies 3D Rigid Bodies Particle Ideal particle can not rotate. (no couple acting on it) 3 Equilibrium conditions A body is in equilibrium if all forces and moments applied to it are in balance Category 1: equilibrium of collinear forces, clearly requires only the one force equation in the direction of the forces (x- direction), since all other equations are automatically satisfied. Category 2: equilibrium of forces which lie in a plane (x-y plane) and are concurrent at a point O, requires the two force equations only, since the moment sum about O, that is, about a z-axis through O, is necessarily zero. Category 3: equilibrium of parallel forces in a plane, requires the one force equation in the direction of the forces (x-direction) and one moment equation about an axis (z-axis) normal to the plane of the forces. Category 4: equilibrium of a general system of forces in a plane (x-y), requires the two force equations in the plane and one moment equation about an axis (z-axis) normal to the plane. 2D Eq. system 3D Eq. system 2
3 Idealisation of a System A complex system can be simplified by enforcing some simplifying assumption. This process is called Idealisation of system Member Loading condition Support reactions Idealisation of a System Internal forces are not essential because these forces cancel each other. They will not create an external effect on the body Suitable idealisation of support and loading conditions, and materials used 3
4 External Loads A body is subjected to only two types of external loads; namely, surface forces or body forces. A body force is developed when one body exerts a force on another body without direct physical contact between the bodies. Surface forces are caused by the direct contact of one body with the surface of another. In all cases these forces are distributed over the area of contact between the bodies. If this area is small in comparison with the total surface area of the body, then the surface force can be idealized d as a single concentrated force, which is applied to a point on the body. If the surface loading is applied along a narrow strip of area, the loading can be idealized as a linear distributed load. Support Reactions If a support prevents the translation of a body in a given direction, then a force is developed on the body in that direction. If rotation is prevented, a couple moment is exerted on the body. 1) Roller supports N - Roller, rocker, or ball transmits a compressive force normal to the supporting surface N 4
5 Support Reactions 2) Pin connection Pin free to turn Pin not free to turn R R x R R x M R y R y 3) Built-in or fixed support F M V Weld A A A 9 4) Flexible cable, belt, chain, or rope Support Reactions T always away from the body T tangent to the cable 5) Spring action x F For linear springs, F = kx Normal distance 10 5
6 6) Contact surfaces Smooth surfaces N - Contact force at contact point normal to the surface/contact plane N - always compressive Rough surfaces F R N -A rough surface can produce a tangential ti force (F, friction) as well as a normal force (N) - direction of F depend on situations 11 Support Reactions Summary of 2D support reactions 6
7 Support Reactions Summary of 3D support reactions Support Reactions 7
8 System Isolation - All physical bodies are inherently 3D, but many may be treated as 2D; e.g. when all forces are on the same plane. Mechanical system isolation R F i 0 - Before we apply the equilibrium conditions M M 0 we need to know what force or moment are involved. F F F F Isolate body i - Draw Free Body Diagram (FBD) FBD is used to isolate body (or bodies / system of bodies) so that force/couple acting on it can be identified. 15 Construction of FBD 1) Pick body/combination of bodies to be isolated 2) Isolating the body. Draw complete external boundary of the isolated body 3) Add all forces and moments Label all the known and unknown force magnitudes and directions on the diagram The sense of a force having an unknown magnitude can be assumed 4) Indicate a coordinate system 5) Indicate necessary dimensions y F x 150 cm 50 cm body of interest Free Body Diagram N mg Most important step is solving problems in mechanics. *** If an FBD is not drawn (when it is needed), you will get no credit (0 point) for the whole problem!!!! *** 8
9 Free Body Diagram W FBD of A 17 F 1 F 2 F 3 y F V F 1 F 2 F 3 P P A mass m B mass m A M No internal force is shown in FBD y x x P F P V M W=mg W=mg y x N M Correct? A B m N F V T not always mg 18 9
10 Free Body Diagram - Examples The sphere has a mass of 6 kg and is supported as shown. Draw a free-body diagram of the sphere, the cord CE, and the knot at C. 19 How many unknowns? How many Equations? o Fx 0 FCBAcos60 FCD 0 o Fy 0 FCBAsin 60 F CE 0 F CE 58.9 FCBA o o sin 60 sin 60 o o F F cos cot 60 CD CE 58.9 F F N F CE F CE Fy 0 FCE F CE 0 y x 0 F F y CE F CE 58.9 N F F 58.9 N CE CE Action-reaction pair - use same symbol - opposite direction 10
11 Example Determine the tension in cables BA and BC necessary to support the 60-kg cylinder 3D -> 2D Force Equilibrium is sufficient to solve the problem! Example Determine the tension in each cord used to support the 100-kg crate Force Equilibrium is sufficient to solve the problem! 3D 11
12 Free Body Diagram - Examples Two smooth pipes, each having a mass of 300 kg, are supported by the forks of the tractor. Draw the FBDs for each pipe and both pipes together. 23 Two- and Three Force Members The solutions to some equilibrium problems can be simplified by recognizing members that are subjected to only two or three forces. Two-Force Members: If a member is subjected to only two forces, it is called a two-force member.. Two force member Due to Force equilibrium Due to Moment equilibrium For any two-force member to be in equilibrium, the two forces acting on the member must have the same magnitude, act in opposite directions, and have the same line of action, directed along the line joining the two points where these forces act. 12
13 Two- and Three Force Members The solutions to some equilibrium problems can be simplified by recognizing members that are subjected to only two or three forces. Three-Force Members: If a member is subjected to only three forces, it is called a threeforce member. Due to Moment equilibrium i Moment equilibrium can be satisfied only if the three forces form a concurrent or parallel force system. Example The lever ABC is pin supported at A and connected to a short link BD. If the weight of the members is negligible, determine the force of the pin on the lever at A. Two Force Member Three Force Member 26 13
14 Example The cord shown in figure supports a force of 100 N and wraps over the frictionless pulley. Determine the tension in the cord at C and the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at pin A. 0.5m 0.5m 100 N 100 N FBD of Cord FBD of Pulley 100 N FBD of combined cord and pulley 27 Example The wing of the jet aircraft is subjected to a thrust of T = 8 kn from its engine and the resultant lift force L = 45 kn. If the mass of the wing is 2.1 Mg and the mass center is at G, determine the x, y, z components of reaction where the wing is fixed to the fuselage A. 14
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 3 Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter Objectives To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a particle To show how to solve particle equilibrium
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 3 Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter Objectives To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a particle To show how to solve particle equilibrium
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis. Lecture 13
 ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 13 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free-body
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 13 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free-body
EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS
 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free-body diagram. In-Class Activities: Check Homework Reading
Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY & FREE-BODY DIAGRAMS a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free-body diagram. In-Class Activities: Check Homework Reading
Equilibrium of a Particle
 ME 108 - Statics Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter 3 Applications For a spool of given weight, what are the forces in cables AB and AC? Applications For a given weight of the lights, what are the forces
ME 108 - Statics Equilibrium of a Particle Chapter 3 Applications For a spool of given weight, what are the forces in cables AB and AC? Applications For a given weight of the lights, what are the forces
Ishik University / Sulaimani Architecture Department. Structure. ARCH 214 Chapter -5- Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
 Ishik University / Sulaimani Architecture Department 1 Structure ARCH 214 Chapter -5- Equilibrium of a Rigid Body CHAPTER OBJECTIVES To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce
Ishik University / Sulaimani Architecture Department 1 Structure ARCH 214 Chapter -5- Equilibrium of a Rigid Body CHAPTER OBJECTIVES To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce
EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES
 EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES Equilibrium A body in equilibrium is at rest or can translate with constant velocity F = 0 M = 0 EQUILIBRIUM IN TWO DIMENSIONS Case where the force system acting on a rigid
EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES Equilibrium A body in equilibrium is at rest or can translate with constant velocity F = 0 M = 0 EQUILIBRIUM IN TWO DIMENSIONS Case where the force system acting on a rigid
3.1 CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM
 3.1 CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM Consider rigid body fixed in the x, y and z reference and is either at rest or moves with reference at constant velocity Two types of forces that act on it, the
3.1 CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM Consider rigid body fixed in the x, y and z reference and is either at rest or moves with reference at constant velocity Two types of forces that act on it, the
Chapter Objectives. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education South Asia Pte Ltd
 Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using
EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES IN TWO DIMENSIONS
 EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES IN TWO DIMENSIONS If the resultant of all external forces acting on a rigid body is zero, then the body is said to be in equilibrium. Therefore, in order for the rigid body
EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES IN TWO DIMENSIONS If the resultant of all external forces acting on a rigid body is zero, then the body is said to be in equilibrium. Therefore, in order for the rigid body
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body Concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body Concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body
Announcements. Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
 Announcements Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Today s Objectives Identify support reactions Draw a free body diagram Class Activities Applications Support reactions Free body diagrams Examples Engr221 Chapter
Announcements Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Today s Objectives Identify support reactions Draw a free body diagram Class Activities Applications Support reactions Free body diagrams Examples Engr221 Chapter
where x and y are any two non-parallel directions in the xy-plane. iii) One force equation and one moment equation.
 Concurrent Force System ( of Particles) Recall that the resultant of a concurrent force system is a force F R that passes through the point of concurrency, which we label as point O. The moment equation,
Concurrent Force System ( of Particles) Recall that the resultant of a concurrent force system is a force F R that passes through the point of concurrency, which we label as point O. The moment equation,
The case where there is no net effect of the forces acting on a rigid body
 The case where there is no net effect of the forces acting on a rigid body Outline: Introduction and Definition of Equilibrium Equilibrium in Two-Dimensions Special cases Equilibrium in Three-Dimensions
The case where there is no net effect of the forces acting on a rigid body Outline: Introduction and Definition of Equilibrium Equilibrium in Two-Dimensions Special cases Equilibrium in Three-Dimensions
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body. Engineering Mechanics: Statics
 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter Objectives Revising equations of equilibrium of a rigid body in 2D and 3D for the general case. To introduce the concept of the free-body
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Engineering Mechanics: Statics Chapter Objectives Revising equations of equilibrium of a rigid body in 2D and 3D for the general case. To introduce the concept of the free-body
TUTORIAL SHEET 1. magnitude of P and the values of ø and θ. Ans: ø =74 0 and θ= 53 0
 TUTORIAL SHEET 1 1. The rectangular platform is hinged at A and B and supported by a cable which passes over a frictionless hook at E. Knowing that the tension in the cable is 1349N, determine the moment
TUTORIAL SHEET 1 1. The rectangular platform is hinged at A and B and supported by a cable which passes over a frictionless hook at E. Knowing that the tension in the cable is 1349N, determine the moment
When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero.
 When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero. 0 0 0 0 k M j M i M M k R j R i R F R z y x z y x Forces and moments acting on a rigid body could be
When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero. 0 0 0 0 k M j M i M M k R j R i R F R z y x z y x Forces and moments acting on a rigid body could be
Equilibrium. Rigid Bodies VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS. Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 Eighth E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies Contents Introduction
Eighth E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies Contents Introduction
When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero.
 When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero. 0 0 0 0 k M j M i M M k R j R i R F R z y x z y x Forces and moments acting on a rigid body could be
When a rigid body is in equilibrium, both the resultant force and the resultant couple must be zero. 0 0 0 0 k M j M i M M k R j R i R F R z y x z y x Forces and moments acting on a rigid body could be
STATICS. Bodies. Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Design of a support
 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e
 Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 3 Equilibrium of a Particle 1 Chapter Objectives Concept of the free-body diagram for a particle Solve particle equilibrium problems using the equations
Engineering Mechanics: Statics in SI Units, 12e 3 Equilibrium of a Particle 1 Chapter Objectives Concept of the free-body diagram for a particle Solve particle equilibrium problems using the equations
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS
 EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and, b) Recognize two-force members. In-Class
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and, b) Recognize two-force members. In-Class
MEE224: Engineering Mechanics Lecture 4
 Lecture 4: Structural Analysis Part 1: Trusses So far we have only analysed forces and moments on a single rigid body, i.e. bars. Remember that a structure is a formed by and this lecture will investigate
Lecture 4: Structural Analysis Part 1: Trusses So far we have only analysed forces and moments on a single rigid body, i.e. bars. Remember that a structure is a formed by and this lecture will investigate
Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
 Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body Concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body Solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using the equations
Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body Concept of the free-body diagram for a rigid body Solve rigid-body equilibrium problems using the equations
Statics deal with the condition of equilibrium of bodies acted upon by forces.
 Mechanics It is defined as that branch of science, which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. Engineering mechanics applies the principle of mechanics
Mechanics It is defined as that branch of science, which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under the action of forces. Engineering mechanics applies the principle of mechanics
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO-AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS
 EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO-AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and, b) Recognize two-force members. READING
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO-AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and, b) Recognize two-force members. READING
5.2 Rigid Bodies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems
 5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems 5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 1 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Equilibrium
5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems 5.2 Rigid odies and Two-Dimensional Force Systems Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 1 Procedures and Strategies for Solving Problems Involving Equilibrium
Eng Sample Test 4
 1. An adjustable tow bar connecting the tractor unit H with the landing gear J of a large aircraft is shown in the figure. Adjusting the height of the hook F at the end of the tow bar is accomplished by
1. An adjustable tow bar connecting the tractor unit H with the landing gear J of a large aircraft is shown in the figure. Adjusting the height of the hook F at the end of the tow bar is accomplished by
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS
 EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and b) Recognize two-force members. In-Class
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMEBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and b) Recognize two-force members. In-Class
ME Statics. Structures. Chapter 4
 ME 108 - Statics Structures Chapter 4 Outline Applications Simple truss Method of joints Method of section Germany Tacoma Narrows Bridge http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-323172185412005564&q=bruce+lee&pl=true
ME 108 - Statics Structures Chapter 4 Outline Applications Simple truss Method of joints Method of section Germany Tacoma Narrows Bridge http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=-323172185412005564&q=bruce+lee&pl=true
Chapter 6: Structural Analysis
 Chapter 6: Structural Analysis Chapter Objectives To show how to determine the forces in the members of a truss using the method of joints and the method of sections. To analyze the forces acting on the
Chapter 6: Structural Analysis Chapter Objectives To show how to determine the forces in the members of a truss using the method of joints and the method of sections. To analyze the forces acting on the
The centroid of an area is defined as the point at which (12-2) The distance from the centroid of a given area to a specified axis may be found by
 Unit 12 Centroids Page 12-1 The centroid of an area is defined as the point at which (12-2) The distance from the centroid of a given area to a specified axis may be found by (12-5) For the area shown
Unit 12 Centroids Page 12-1 The centroid of an area is defined as the point at which (12-2) The distance from the centroid of a given area to a specified axis may be found by (12-5) For the area shown
Engineering Mechanics Statics
 Mechanical Systems Engineering _ 2016 Engineering Mechanics Statics 7. Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Dr. Rami Zakaria Conditions for Rigid-Body Equilibrium Forces on a particle Forces on a rigid body The
Mechanical Systems Engineering _ 2016 Engineering Mechanics Statics 7. Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Dr. Rami Zakaria Conditions for Rigid-Body Equilibrium Forces on a particle Forces on a rigid body The
Course Overview. Statics (Freshman Fall) Dynamics: x(t)= f(f(t)) displacement as a function of time and applied force
 Course Overview Statics (Freshman Fall) Engineering Mechanics Dynamics (Freshman Spring) Strength of Materials (Sophomore Fall) Mechanism Kinematics and Dynamics (Sophomore Spring ) Aircraft structures
Course Overview Statics (Freshman Fall) Engineering Mechanics Dynamics (Freshman Spring) Strength of Materials (Sophomore Fall) Mechanism Kinematics and Dynamics (Sophomore Spring ) Aircraft structures
Lecture 0. Statics. Module 1. Overview of Mechanics Analysis. IDeALab. Prof. Y.Y.KIM. Solid Mechanics
 Lecture 0. Statics Module 1. Overview of Mechanics Analysis Overview of Mechanics Analysis Procedure of Solving Mechanics Problems Objective : Estimate the force required in the flexor muscle Crandall,
Lecture 0. Statics Module 1. Overview of Mechanics Analysis Overview of Mechanics Analysis Procedure of Solving Mechanics Problems Objective : Estimate the force required in the flexor muscle Crandall,
Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
 Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of a free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve
Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of a free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve
The Laws of Motion. Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples
 The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
The Laws of Motion Newton s first law Force Mass Newton s second law Gravitational Force Newton s third law Examples Gravitational Force Gravitational force is a vector Expressed by Newton s Law of Universal
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK UNIT I - PART-A
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
Chapter 04 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
 Chapter 04 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies Application Engineers designing this crane will need to determine the forces that act on this body under various conditions. 4-2 Introduction For a rigid body, the
Chapter 04 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies Application Engineers designing this crane will need to determine the forces that act on this body under various conditions. 4-2 Introduction For a rigid body, the
Chapter 6: Structural Analysis
 Chapter 6: Structural Analysis APPLICATIONS Trusses are commonly used to support a roof. For a given truss geometry and load, how can we determine the forces in the truss members and select their sizes?
Chapter 6: Structural Analysis APPLICATIONS Trusses are commonly used to support a roof. For a given truss geometry and load, how can we determine the forces in the truss members and select their sizes?
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3
 Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
Statics Chapter II Fall 2018 Exercises Corresponding to Sections 2.1, 2.2, and 2.3 2 3 Determine the magnitude of the resultant force FR = F1 + F2 and its direction, measured counterclockwise from the
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMBERS
 EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and, b) Recognize two-force members. APPLICATIONS
EQUATIONS OF EQUILIBRIUM & TWO- AND THREE-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Apply equations of equilibrium to solve for unknowns, and, b) Recognize two-force members. APPLICATIONS
Announcements. Trusses Method of Joints
 Announcements Mountain Dew is an herbal supplement Today s Objectives Define a simple truss Trusses Method of Joints Determine the forces in members of a simple truss Identify zero-force members Class
Announcements Mountain Dew is an herbal supplement Today s Objectives Define a simple truss Trusses Method of Joints Determine the forces in members of a simple truss Identify zero-force members Class
To show how to determine the forces in the members of a truss using the method of joints and the method of sections.
 5 Chapter Objectives To show how to determine the forces in the members of a truss using the method of joints and the method of sections. To analyze the forces acting on the members of frames and machines
5 Chapter Objectives To show how to determine the forces in the members of a truss using the method of joints and the method of sections. To analyze the forces acting on the members of frames and machines
MEM202 Engineering Mechanics - Statics MEM
 E Engineering echanics - Statics E hapter 6 Equilibrium of Rigid odies k j i k j i R z z r r r r r r r r z z E Engineering echanics - Statics Equilibrium of Rigid odies E Pin Support N w N/m 5 N m 6 m
E Engineering echanics - Statics E hapter 6 Equilibrium of Rigid odies k j i k j i R z z r r r r r r r r z z E Engineering echanics - Statics Equilibrium of Rigid odies E Pin Support N w N/m 5 N m 6 m
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
Physics 101 Lecture 5 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department The Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law qfrictional forces q Examples
11.1 Virtual Work Procedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2
 11.1 Virtual Work 11.1 Virtual Work rocedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 rocedures and Strategies for Solving roblems Involving Virtual Work 1. Identify a single coordinate, q, that will completely define
11.1 Virtual Work 11.1 Virtual Work rocedures and Strategies, page 1 of 2 rocedures and Strategies for Solving roblems Involving Virtual Work 1. Identify a single coordinate, q, that will completely define
SRSD 2093: Engineering Mechanics 2SRRI SECTION 19 ROOM 7, LEVEL 14, MENARA RAZAK
 SRSD 2093: Engineering Mechanics 2SRRI SECTION 19 ROOM 7, LEVEL 14, MENARA RAZAK SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Define a simple
SRSD 2093: Engineering Mechanics 2SRRI SECTION 19 ROOM 7, LEVEL 14, MENARA RAZAK SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Define a simple
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis. Lecture 19
 ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 19 SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: In-Class Activities: a) Define a simple
ENGR-1100 Introduction to Engineering Analysis Lecture 19 SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: In-Class Activities: a) Define a simple
ENGINEERING MECHANICS BAA1113
 ENGINEERING MECHANICS BAA1113 Chapter 3: Equilibrium of a Particle (Static) by Pn Rokiah Bt Othman Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources rokiah@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims To explain the
ENGINEERING MECHANICS BAA1113 Chapter 3: Equilibrium of a Particle (Static) by Pn Rokiah Bt Othman Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources rokiah@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Aims To explain the
What is a Force? Free-Body diagrams. Contact vs. At-a-Distance 11/28/2016. Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion
 Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
Forces and Newton s Laws of Motion What is a Force? In generic terms: a force is a push or a pull exerted on an object that could cause one of the following to occur: A linear acceleration of the object
SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS
 SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Define a simple truss. b) Determine the forces in members of a simple truss. c) Identify zero-force
SIMPLE TRUSSES, THE METHOD OF JOINTS, & ZERO-FORCE MEMBERS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Define a simple truss. b) Determine the forces in members of a simple truss. c) Identify zero-force
Engineering Mechanics: Statics STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS. by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2007 ENES 110 Statics
 CHAPTER Engineering Mechanics: Statics STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Tenth Edition 6a by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2007 ENES 110 Statics Department
CHAPTER Engineering Mechanics: Statics STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS College of Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering Tenth Edition 6a by Dr. Ibrahim A. Assakkaf SPRING 2007 ENES 110 Statics Department
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY
 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free diagram. APPLICATIONS A 200 kg platform is suspended off an oil rig. How do we
EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY Today s Objectives: Students will be able to a) Identify support reactions, and, b) Draw a free diagram. APPLICATIONS A 200 kg platform is suspended off an oil rig. How do we
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies
 Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies 1 2 Contents Introduction Free-Bod Diagram Reactions at Supports and Connections for a wo-dimensional Structure Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod in wo Dimensions Staticall Indeterminate
Equilibrium of Rigid Bodies 1 2 Contents Introduction Free-Bod Diagram Reactions at Supports and Connections for a wo-dimensional Structure Equilibrium of a Rigid Bod in wo Dimensions Staticall Indeterminate
SOLUTION 8 1. a+ M B = 0; N A = 0. N A = kn = 16.5 kn. Ans. + c F y = 0; N B = 0
 8 1. The mine car and its contents have a total mass of 6 Mg and a center of gravity at G. If the coefficient of static friction between the wheels and the tracks is m s = 0.4 when the wheels are locked,
8 1. The mine car and its contents have a total mass of 6 Mg and a center of gravity at G. If the coefficient of static friction between the wheels and the tracks is m s = 0.4 when the wheels are locked,
Similar to trusses, frames are generally fixed, load carrying structures.
 Similar to trusses, frames are generally fixed, load carrying structures. The main difference between a frame and a truss is that in a frame at least one member is a multi force member (çoklu kuvvet elemanı).
Similar to trusses, frames are generally fixed, load carrying structures. The main difference between a frame and a truss is that in a frame at least one member is a multi force member (çoklu kuvvet elemanı).
6.6 FRAMES AND MACHINES APPLICATIONS. Frames are commonly used to support various external loads.
 6.6 FRAMES AND MACHINES APPLICATIONS Frames are commonly used to support various external loads. How is a frame different than a truss? How can you determine the forces at the joints and supports of a
6.6 FRAMES AND MACHINES APPLICATIONS Frames are commonly used to support various external loads. How is a frame different than a truss? How can you determine the forces at the joints and supports of a
CHAPTER 2: EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES
 For a rigid body to be in equilibrium, the net force as well as the net moment about any arbitrary point O must be zero Summation of all external forces. Equilibrium: Sum of moments of all external forces.
For a rigid body to be in equilibrium, the net force as well as the net moment about any arbitrary point O must be zero Summation of all external forces. Equilibrium: Sum of moments of all external forces.
Statics - TAM 211. Lecture 14 October 19, 2018
 Statics - TAM 211 Lecture 14 October 19, 2018 Announcements Students are encouraged to practice drawing FBDs, writing out equilibrium equations, and solving these by hand using your calculator. Expending
Statics - TAM 211 Lecture 14 October 19, 2018 Announcements Students are encouraged to practice drawing FBDs, writing out equilibrium equations, and solving these by hand using your calculator. Expending
EQUILIBRIUM OF A PARTICLE, THE FREE-BODY DIAGRAM & COPLANAR FORCE SYSTEMS
 EQUILIBRIUM OF PRTICLE, THE FREE-BODY DIGRM & COPLNR FORCE SYSTEMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to : a) Draw a free body diagram (FBD), and, b) pply equations of equilibrium to solve a 2-D
EQUILIBRIUM OF PRTICLE, THE FREE-BODY DIGRM & COPLNR FORCE SYSTEMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to : a) Draw a free body diagram (FBD), and, b) pply equations of equilibrium to solve a 2-D
STATICS. Bodies VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Ninth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 N E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
N E 4 Equilibrium CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University of Rigid Bodies 2010 The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Announcements. Equilibrium of a Particle in 2-D
 nnouncements Equilibrium of a Particle in 2-D Today s Objectives Draw a free body diagram (FBD) pply equations of equilibrium to solve a 2-D problem Class ctivities pplications What, why, and how of a
nnouncements Equilibrium of a Particle in 2-D Today s Objectives Draw a free body diagram (FBD) pply equations of equilibrium to solve a 2-D problem Class ctivities pplications What, why, and how of a
If the solution does not follow a logical thought process, it will be assumed in error.
 Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam. If I detect cheating I will write a note on my exam and raise
Please review the following statement: I certify that I have not given unauthorized aid nor have I received aid in the completion of this exam. If I detect cheating I will write a note on my exam and raise
STATICS. Friction VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: Eighth Edition CHAPTER. Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr.
 Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
Eighth E 8 Friction CHAPTER VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STATICS Ferdinand P. Beer E. Russell Johnston, Jr. Lecture Notes: J. Walt Oler Texas Tech University Contents Introduction Laws of Dry Friction.
READING QUIZ. 2. When using the method of joints, typically equations of equilibrium are applied at every joint. A) Two B) Three C) Four D) Six
 READING QUIZ 1. One of the assumptions used when analyzing a simple truss is that the members are joined together by. A) Welding B) Bolting C) Riveting D) Smooth pins E) Super glue 2. When using the method
READING QUIZ 1. One of the assumptions used when analyzing a simple truss is that the members are joined together by. A) Welding B) Bolting C) Riveting D) Smooth pins E) Super glue 2. When using the method
Check Homework. Reading Quiz Applications Equations of Equilibrium Example Problems Concept Questions Group Problem Solving Attention Quiz
 THREE-DIMENSIONAL FORCE SYSTEMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to solve 3-D particle equilibrium problems by a) Drawing a 3-D free body diagram, and, b) Applying the three scalar equations (based
THREE-DIMENSIONAL FORCE SYSTEMS Today s Objectives: Students will be able to solve 3-D particle equilibrium problems by a) Drawing a 3-D free body diagram, and, b) Applying the three scalar equations (based
PROBLEMS ON EQUILIBRIUM OF PARTICLES
 O EQUILIBRIUM O PRICLES 1. ind the angle of tilt q with the horiontal so that the contact force at B will be one-half that at for the smooth clinder. (3/15) q?, contact force at B will be one-half that
O EQUILIBRIUM O PRICLES 1. ind the angle of tilt q with the horiontal so that the contact force at B will be one-half that at for the smooth clinder. (3/15) q?, contact force at B will be one-half that
Plane Trusses Trusses
 TRUSSES Plane Trusses Trusses- It is a system of uniform bars or members (of various circular section, angle section, channel section etc.) joined together at their ends by riveting or welding and constructed
TRUSSES Plane Trusses Trusses- It is a system of uniform bars or members (of various circular section, angle section, channel section etc.) joined together at their ends by riveting or welding and constructed
FRAMES AND MACHINES Learning Objectives 1). To evaluate the unknown reactions at the supports and the interaction forces at the connection points of a
 FRAMES AND MACHINES Learning Objectives 1). To evaluate the unknown reactions at the supports and the interaction forces at the connection points of a rigid frame in equilibrium by solving the equations
FRAMES AND MACHINES Learning Objectives 1). To evaluate the unknown reactions at the supports and the interaction forces at the connection points of a rigid frame in equilibrium by solving the equations
7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES
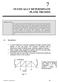 7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with the definition of a truss and briefly explains various types of plane truss. The determinancy and stability of a truss also will
7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with the definition of a truss and briefly explains various types of plane truss. The determinancy and stability of a truss also will
Problems (Equilibrium of Particles)
 1. he 4kg block rests on the rough surface. Length of the spring is 18 mm in the position shown. Unstretched length of the spring is 2 mm. Determine the coefficient of friction required for the equilibrium.
1. he 4kg block rests on the rough surface. Length of the spring is 18 mm in the position shown. Unstretched length of the spring is 2 mm. Determine the coefficient of friction required for the equilibrium.
ENGINEERING MECHANICS SOLUTIONS UNIT-I
 LONG QUESTIONS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SOLUTIONS UNIT-I 1. A roller shown in Figure 1 is mass 150 Kg. What force P is necessary to start the roller over the block A? =90+25 =115 = 90+25.377 = 115.377 = 360-(115+115.377)
LONG QUESTIONS ENGINEERING MECHANICS SOLUTIONS UNIT-I 1. A roller shown in Figure 1 is mass 150 Kg. What force P is necessary to start the roller over the block A? =90+25 =115 = 90+25.377 = 115.377 = 360-(115+115.377)
FE Sta'cs Review. Torch Ellio0 (801) MCE room 2016 (through 2000B door)
 FE Sta'cs Review h0p://www.coe.utah.edu/current- undergrad/fee.php Scroll down to: Sta'cs Review - Slides Torch Ellio0 ellio0@eng.utah.edu (801) 587-9016 MCE room 2016 (through 2000B door) Posi'on and
FE Sta'cs Review h0p://www.coe.utah.edu/current- undergrad/fee.php Scroll down to: Sta'cs Review - Slides Torch Ellio0 ellio0@eng.utah.edu (801) 587-9016 MCE room 2016 (through 2000B door) Posi'on and
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017
 Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Physics 2211 ABC Quiz #3 Solutions Spring 2017 I. (16 points) A block of mass m b is suspended vertically on a ideal cord that then passes through a frictionless hole and is attached to a sphere of mass
Newton s Third Law Newton s Third Law: For each action there is an action and opposite reaction F
 FRAMES AND MACHINES Learning Objectives 1). To evaluate the unknown reactions at the supports and the interaction forces at the connection points of a rigid frame in equilibrium by solving the equations
FRAMES AND MACHINES Learning Objectives 1). To evaluate the unknown reactions at the supports and the interaction forces at the connection points of a rigid frame in equilibrium by solving the equations
Sara Rwentambo. PHYS 1007 AB
 Topics: Free body diagrams (FBDs) Static friction and kinetic friction Tension and acceleration of a system Tension in dynamic equilibrium (bonus question) Opener: Find Your Free Body Diagram Group Activity!
Topics: Free body diagrams (FBDs) Static friction and kinetic friction Tension and acceleration of a system Tension in dynamic equilibrium (bonus question) Opener: Find Your Free Body Diagram Group Activity!
1. If it is known that the center pin A supports one-half of the vertical loading shown, determine the force in member BF.
 1. If it is known that the center pin A supports one-half of the vertical loading shown, determine the force in member B. Joint A AB A I. Cut D D B A 26 kn A I. Cut H 13 kn D B D A H 13 kn 2. Determine
1. If it is known that the center pin A supports one-half of the vertical loading shown, determine the force in member B. Joint A AB A I. Cut D D B A 26 kn A I. Cut H 13 kn D B D A H 13 kn 2. Determine
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body. Chapter 5
 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter 5 Overview Rigid Body Equilibrium Free Body Diagrams Equations of Equilibrium 2 and 3-Force Members Statical Determinacy CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM Recall
Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter 5 Overview Rigid Body Equilibrium Free Body Diagrams Equations of Equilibrium 2 and 3-Force Members Statical Determinacy CONDITIONS FOR RIGID-BODY EQUILIBRIUM Recall
Vector Mechanics: Statics
 PDHOnline Course G492 (4 PDH) Vector Mechanics: Statics Mark A. Strain, P.E. 2014 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org www.pdhcenter.com
PDHOnline Course G492 (4 PDH) Vector Mechanics: Statics Mark A. Strain, P.E. 2014 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org www.pdhcenter.com
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws
 Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
Physics 111 Lecture 4 Newton`s Laws Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com he Laws of Motion q Newton s first law q Force q Mass q Newton s second law q Newton s third law q Examples Isaac
DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF FORCES
 DEINITION AND CLASSIICATION O ORCES As defined before, force is an action of one body on another. It is a vector quantity since its effect depends on the direction as well as on the magnitude of the action.
DEINITION AND CLASSIICATION O ORCES As defined before, force is an action of one body on another. It is a vector quantity since its effect depends on the direction as well as on the magnitude of the action.
Chapter 10: Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without
 Chapter 10: Friction 10-1 Chapter 10 Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without trials. Lucius Annaeus Seneca (4 BC - 65 AD) 10.1 Overview When two bodies are
Chapter 10: Friction 10-1 Chapter 10 Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without trials. Lucius Annaeus Seneca (4 BC - 65 AD) 10.1 Overview When two bodies are
ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATIC
 Trusses Simple trusses The basic element of a truss is the triangle, three bars joined by pins at their ends, fig. a below, constitutes a rigid frame. The term rigid is used to mean noncollapsible and
Trusses Simple trusses The basic element of a truss is the triangle, three bars joined by pins at their ends, fig. a below, constitutes a rigid frame. The term rigid is used to mean noncollapsible and
Equilibrium & Elasticity
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 12 Equilibrium & Elasticity Static equilibrium Elasticity 1. A uniform steel bar of length 3.0 m and weight 20 N rests on two supports (A and B) at its ends. A block
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 12 Equilibrium & Elasticity Static equilibrium Elasticity 1. A uniform steel bar of length 3.0 m and weight 20 N rests on two supports (A and B) at its ends. A block
However, the friction forces are limited in magnitude and will not prevent motion if sufficiently large forces are applied.
 FRICTION 1 Introduction In preceding chapters, it was assumed that surfaces in contact were either frictionless (surfaces could move freely with respect to each other) or rough (tangential forces prevent
FRICTION 1 Introduction In preceding chapters, it was assumed that surfaces in contact were either frictionless (surfaces could move freely with respect to each other) or rough (tangential forces prevent
(35+70) 35 g (m 1+m 2)a=m1g a = 35 a= =3.27 g 105
 Coordinator: Dr. W. L-Basheer Monday, March 16, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. 70 N block and a 35 N block are connected by a massless inextendable string which is wrapped over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure
Coordinator: Dr. W. L-Basheer Monday, March 16, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. 70 N block and a 35 N block are connected by a massless inextendable string which is wrapped over a frictionless pulley as shown in Figure
Static Equilibrium; Torque
 Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5
 1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
1 / 36 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 25: Ch.17, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa Date: 2 / 36 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: ROTATION
STATICS. FE Review. Statics, Fourteenth Edition R.C. Hibbeler. Copyright 2016 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 STATICS FE Review 1. Resultants of force systems VECTOR OPERATIONS (Section 2.2) Scalar Multiplication and Division VECTOR ADDITION USING EITHER THE PARALLELOGRAM LAW OR TRIANGLE Parallelogram Law: Triangle
STATICS FE Review 1. Resultants of force systems VECTOR OPERATIONS (Section 2.2) Scalar Multiplication and Division VECTOR ADDITION USING EITHER THE PARALLELOGRAM LAW OR TRIANGLE Parallelogram Law: Triangle
Lecture 14 February 16, 2018
 Statics - TAM 210 & TAM 211 Lecture 14 February 16, 2018 SoonTrending.com Announcements Structured office hours of working through practice problems will be held during Sunday office hours, starting Sunday
Statics - TAM 210 & TAM 211 Lecture 14 February 16, 2018 SoonTrending.com Announcements Structured office hours of working through practice problems will be held during Sunday office hours, starting Sunday
NAME: Section: RIN: Tuesday, May 19, :00 11:00. Problem Points Score Total 100
 RENSSELAER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE TROY, NY FINAL EXAM INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING ANALYSIS (ENGR-1100) NAME: Section: RIN: Tuesday, May 19, 2015 8:00 11:00 Problem Points Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20
RENSSELAER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE TROY, NY FINAL EXAM INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING ANALYSIS (ENGR-1100) NAME: Section: RIN: Tuesday, May 19, 2015 8:00 11:00 Problem Points Score 1 20 2 20 3 20 4 20 5 20
Physics 170 Week 5, Lecture 2
 Physics 170 Week 5, Lecture 2 http://www.phas.ubc.ca/ gordonws/170 Physics 170 Week 5 Lecture 2 1 Textbook Chapter 5:Section 5.5-5.7 Physics 170 Week 5 Lecture 2 2 Learning Goals: Review the condition
Physics 170 Week 5, Lecture 2 http://www.phas.ubc.ca/ gordonws/170 Physics 170 Week 5 Lecture 2 1 Textbook Chapter 5:Section 5.5-5.7 Physics 170 Week 5 Lecture 2 2 Learning Goals: Review the condition
CHAPTER 5 ANALYSIS OF STRUCTURES. Expected Outcome:
 CHAPTER ANALYSIS O STRUCTURES Expected Outcome: Able to analyze the equilibrium of structures made of several connected parts, using the concept of the equilibrium of a particle or of a rigid body, in
CHAPTER ANALYSIS O STRUCTURES Expected Outcome: Able to analyze the equilibrium of structures made of several connected parts, using the concept of the equilibrium of a particle or of a rigid body, in
Chapter 5. The Laws of Motion
 Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in motion included its position, velocity, and acceleration. There was no consideration of what might influence that motion.
Chapter 5 The Laws of Motion The Laws of Motion The description of an object in motion included its position, velocity, and acceleration. There was no consideration of what might influence that motion.
3. A piece of candy is accelerated at 3.0 m/s 2 in the direction shown by a, over a frictionless horizontal surface. The acceleration is caused by 3
 3. A piece of candy is accelerated at 3.0 m/s 2 in the direction shown by a, over a frictionless horizontal surface. The acceleration is caused by 3 forces, 2 of which are shown. F 1 has a magnitude of
3. A piece of candy is accelerated at 3.0 m/s 2 in the direction shown by a, over a frictionless horizontal surface. The acceleration is caused by 3 forces, 2 of which are shown. F 1 has a magnitude of
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body
 EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: GENERAL PLANE MOTION (Section 17.5) Today s Objectives: Students will be able to analyze the planar kinetics of a rigid body undergoing general plane motion. APPLICATIONS As the soil
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74
 PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
PHY 1150 Doug Davis Chapter 8; Static Equilibrium 8.3, 10, 22, 29, 52, 55, 56, 74 8.3 A 2-kg ball is held in position by a horizontal string and a string that makes an angle of 30 with the vertical, as
AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice
 AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice 1981M2. A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing
AP Physics C: Work, Energy, and Power Practice 1981M2. A swing seat of mass M is connected to a fixed point P by a massless cord of length L. A child also of mass M sits on the seat and begins to swing
PAT 101 FUNDAMENTAL OF ENGINEERING MECHANICS EQUILIBREQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY IUM OF A RIGID BODY
 PAT 101 FUNDAMENTAL OF ENGINEERING MECHANICS EQUILIBREQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY IUM OF A RIGID BODY MARDHIAH FARHANA BINT OMAR Week 5-6 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY Conditions for Rigid Equilibrium Free-Body
PAT 101 FUNDAMENTAL OF ENGINEERING MECHANICS EQUILIBREQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY IUM OF A RIGID BODY MARDHIAH FARHANA BINT OMAR Week 5-6 EQUILIBRIUM OF A RIGID BODY Conditions for Rigid Equilibrium Free-Body
