The analysis method for construction problems in the dynamic geometry
|
|
|
- Emil Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The analysis method for construction problems in the dynamic geometry Hee-chan Lew Korea National University of Education SEMEO-RECSAM University of Tsukuba of Tsukuba Joint Seminar Feb. 15, 2016, Tokyo
2 Key word Analysis: A working backward strategy to find a construction or deductive proof methods in geometric problems Pappus, the Greek mathematician in AD 3 rd century, systemized in his book The Collections It has not been used after his era, in my opinion, because of the lack of drawing tools to operate the method efficiently.
3 Conclusion DG is a very good environment for students to find a construction method by themselves for geometric construction problems and to prove that it is a proper method deductively. DG is an environment to revive the analysis method of Pappus who criticized Euclid s deductive method so called synthesis
4 Euclid Elements In BC 3rd century Euclid wrote the great books so called Elements based on mathematical activities of 300 years from BC 6 th to BC 3 rd century It has been a typical geometry textbook of mankind for over 2000 years
5 Euclid Elements It was written by an axiomatic and deductive method It has been used as an unique textbook to develop students deductive proof ability since Greek era.
6 Euclid Elements It was edited as a textbook for a small group of elite students at the time of BC 3rd Century. It might be not proper for ordinary students, like in nowadays, who dislike mathematics seriously, particularly dislike proof.
7 Educational Defect Elements does not show the process of mathematical discovery as follows: imagination, experimentation, reasonable guess, analogy, trial and error, (sometimes) mistakes and failure etc
8 Educational Defect It gives only final results by mathematicians without showing the behind story. It makes normal teachers easy to explain the proof process appeared in the books one by one It is difficult for students to get the reason why the particular proof method was selected. It makes students think mathematics a very difficult subject
9 New Direction for Euclidean Geometry Students must reconstruct the construction process and design its proving process by themselves rather than absorbing the proceeses from teachers. Students must think independently and productively. Intuition, guessing, investigation, measuring, and trial and error.
10 New Method It is almost impossible in Paper and Pencil environment. Furthermore DG does not guarantee the success. We need a special method in DG to improve deductive proof abilities of ordinary students.
11 Analysis The analysis can provide an alternative teaching method for Euclidean geometry which is very difficult to normal students The Oldest strategy among the mathematics heuristics Pythagorean school also emphasized the analysis but, in Elements not appeared. In AD 3 rd century, Pappus systemized it in his famous book, the collections.
12 Definition of Analysis In analysis, we assume that which is sought as if it were already done and we inquire what it is from which this results and again until we come up something already known or belonging to the class of first principles
13 Definition of Synthesis In synthesis, reversing the analysis, we take as already done that which was last arrived at in the analysis and we arrive finally at the construction of what was sought
14 Dialectic unity Greek thought the dialectic integration of analysis and synthesis as a substance of mathematical thought. However, Euclid s Elements considered the synthesis to reduce theorems from the foundation as a way to guarantee the truth of mathematics.
15 Example 1 Prove that every triangle has one inscribed circle.
16 Analysis Assume that triangle ABC has one inscribed circle. Triangle ABC has one circle contacted at one point of each three sides of the triangle Triangle ABC has one point D from which the distances to three sides of the triangle are same. This D is an intersection of two sets; 1) the set of points whose distance from AB and AC are same and 2) the set of points whose distance from CB and CA. This is an intersection of the bisector of angle A and the bisector of angle C. A B D
17 Synthesis Draw an angle bisector of angle BAC and BCA The intersection point D is such that the distances from three sides of the triangle are same. E D B F ED = DG = DF There is one inscribed circle D A G C
18 Example 2 There is a circle O and there are two lines m and n which are perpendicular each other like the following figure. O n Construct a circle whose center is located on the line n and to which the circle O and the line m are tangent m
19 Analysis Assume that the circle P is constructed satisfying the given conditions. O n P m
20 Analysis Draw a circle P with radius OP Let F is an intersection point of the line n and the circle The triangle is an isosceles. O n P Draw a line perpendicular to OF passing through P E F m E is a mid point of OF
21 Synthesis Draw a circle H with radius OG Let F is the intersection point n Draw a perpendicular bisector of OF O P P is an intersection of the perpendicular bisector and line n G E H m Draw a circle P with radius PH F
22 Problem 1: Tangent line Draw a tangent line of Circle A through point B B A
23 Analysis Assume that the line BC is a tangent line of the circle A C B A
24 Analysis Draw segments AC and AB B Triangle ABC is a right triangle C D Let D is a midpoint of the segment AB A DC = DA = DB
25 Synthesis Draw a segment AB and let D is a midpoint of AB B Draw a circle D with radius DA and let C is a intersection point of the two circles C A D AC is the tangent line to find
26 Problem 2: The Shortest path Someone wants to move from A to B via one point on the seashore through the shortest path. Find the point on the seashore.
27 Analysis Determine the point C such that the sum of two segments is least by using length and calculation function in measurement menu and by dragging a point C. Assume that the point C is what we want to find.
28 Draw a line AC Draw a perpendicular line BD to the seashore CE Two triangles CBE and CED are congruent BE = ED Analysis
29 Synthesis Draw a perpendicular line BE Draw a circle E with the radius BE D is an intersection point of the circle and the line Draw a line AD C is the point to find
30 Problem 3: Fermat point In the interior part of triangle ABC, find a point F such that the sum of the length of three segments AF, BF, CF is least. A F We call the point Fermat point. B C
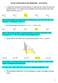
31 Analysis Determine the point F such that the sum of three segments is least by using length and calculation function in measurement menu and by dragging a point F. Assume that the point is the Fermat point. A FA = cm FB = cm FC = cm FA+FB+FC = cm F B C
32 Analysis Construct a circle F, I, J of which radii are AF, BF, CF respectively. Two triangles AHB, AGC are equilateral. H A G I J F B C
33 Synthesis Construct equilateral triangles AHB and AGC Draw lines HC and GB The intersection point F is the Fermat point. G H A F B C
34 Please construct a point the sum of distances to the following points A and B is same as the given segment as below. A B
35 Analysis
36 Synthesis
37 Problem 5: Hypobola Please construct a point the difference of distances to the following points A and B is same as the given segment as below. A B
38 Analysis
39 Synthesis
40 Problem 6: Parabola Please construct a point from which distances to point A and the below line is same. A
41 Analysis
42 Synthesis
43 DG as a tool for analysis DG can help students draw a precise figure. To find more easily a series of necessary conditions of final conclusion, students have to show relations among components in the problem situation. In a figure roughly drawn on the paper it is very difficult for students to find the relation.
44 DG as a tool of analysis DG has a measure function. It makes students determine the good starting point for analysis by measuring length or angle etc continuously while dragging the point continuously. In paper circumstance, it is very difficult for students to make a precise measuring enough to find the good starting point for analysis.
45 DG as a tool of analysis DG is dynamic It can make student perform various experiment to find necessary conditions by drawing, erasing and manipulating figures easily as well as dynamically. In paper and pencil circumstance, it is almost impossible to perform analysis because the figure drawn on the paper cannot be manipulated.
46 DG as a tool of analysis DG is a reflective tool If the relation among components is preserved while dragging the picture constructed by synthesis, the construction process can be considered as a right procedure. In paper and pencil circumstance, there is no way to check whether the construction process is right or not.
47 Conclusion In the late of 1980s, Cabri and GSP were designed as a dynamic tool for students to investigate the properties and relation within and between figures through operating figures on the computer screen directly.
48 Conclusion More than traditional construction by normal compasses and ruler Construct, erase, drag and transform figures Measure segments and angles DG: A dynamic method for Euclidean geometry proposed by Clairaut, French mathematician in the 17 th century But, then he also had not the proper tool
49 Conclusion In DG, students can make a conjecture to geometric properties and confirm them informally and feel the need to prove the conjectured and informally confirmed geometric facts. In DG, students can improve their proof abilities by using the analysis method.
50 Conclusion DG is a very excellent tool for the analysis method which is a good mathematical strategy proposed by Greek mathematicians but forgotten for a long time because of maybe a lack of proper tool.
51 Conclusion In mathematics textbooks, the conclusion is a conclusion. In mathematics education, the conclusion should be a starting point rather than a conclusion. DG can provide a better and safe route from the starting point to the development of deductive proof of normal students.
52 Suggestion There need to be various LS experiment in which students can actually perform analysis well by using DG. We have to investigate students thought process of analysis in various construction problems.
Pappus in a Modern Dynamic Geometry: An Honest Way for Deductive Proof Hee-chan Lew Korea National University of Education
 Pappus in a Modern Dynamic Geometry: An Honest Way for Deductive Proof Hee-chan Lew Korea National University of Education hclew@knue.ac.kr Abstract. This study shows that dynamic geometry using the "analysis"
Pappus in a Modern Dynamic Geometry: An Honest Way for Deductive Proof Hee-chan Lew Korea National University of Education hclew@knue.ac.kr Abstract. This study shows that dynamic geometry using the "analysis"
(RC3) Constructing the point which is the intersection of two existing, non-parallel lines.
 The mathematical theory of ruller and compass constructions consists on performing geometric operation with a ruler and a compass. Any construction starts with two given points, or equivalently a segment
The mathematical theory of ruller and compass constructions consists on performing geometric operation with a ruler and a compass. Any construction starts with two given points, or equivalently a segment
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Ismailia Road Branch
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep. Nozha Language Schools Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. in the parallelogram, each two opposite
Objectives. Cabri Jr. Tools
 ^Åíáîáíó=NQ Objectives To investigate relationships between angle measurements and sides of a triangle To investigate relationships among the three sides of a triangle Cabri Jr. Tools fåíêççìåíáçå qêá~åöäé=fåéèì~äáíó
^Åíáîáíó=NQ Objectives To investigate relationships between angle measurements and sides of a triangle To investigate relationships among the three sides of a triangle Cabri Jr. Tools fåíêççìåíáçå qêá~åöäé=fåéèì~äáíó
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions
 Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions Quiz #1. Tuesday, 17 January, 2012. [10 minutes] 1. Given a line segment AB, use (some of) Postulates I V,
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Winter 2012 Quiz Solutions Quiz #1. Tuesday, 17 January, 2012. [10 minutes] 1. Given a line segment AB, use (some of) Postulates I V,
Euclidean Geometry Proofs
 Euclidean Geometry Proofs History Thales (600 BC) First to turn geometry into a logical discipline. Described as the first Greek philosopher and the father of geometry as a deductive study. Relied on rational
Euclidean Geometry Proofs History Thales (600 BC) First to turn geometry into a logical discipline. Described as the first Greek philosopher and the father of geometry as a deductive study. Relied on rational
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Student Name:
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, January 27, 2011 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Thursday, January 27, 2011 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name
USA Mathematical Talent Search Solutions to Problem 5/3/16
 Solutions to Problem 5//16 5//16. Consider an isosceles triangle ABC with side lengths AB = AC = 10 2 and BC = 10. Construct semicircles P, Q, and R with diameters AB, AC, BC respectively, such that the
Solutions to Problem 5//16 5//16. Consider an isosceles triangle ABC with side lengths AB = AC = 10 2 and BC = 10. Construct semicircles P, Q, and R with diameters AB, AC, BC respectively, such that the
2007 Hypatia Contest
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 007 Hypatia Contest Wednesday, April 18, 007 Solutions c
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 007 Hypatia Contest Wednesday, April 18, 007 Solutions c
7.5 Proportionality Relationships
 www.ck12.org Chapter 7. Similarity 7.5 Proportionality Relationships Learning Objectives Identify proportional segments when two sides of a triangle are cut by a segment parallel to the third side. Extend
www.ck12.org Chapter 7. Similarity 7.5 Proportionality Relationships Learning Objectives Identify proportional segments when two sides of a triangle are cut by a segment parallel to the third side. Extend
Mathematics 3210 Spring Semester, 2005 Homework notes, part 8 April 15, 2005
 Mathematics 3210 Spring Semester, 2005 Homework notes, part 8 April 15, 2005 The underlying assumption for all problems is that all points, lines, etc., are taken within the Poincaré plane (or Poincaré
Mathematics 3210 Spring Semester, 2005 Homework notes, part 8 April 15, 2005 The underlying assumption for all problems is that all points, lines, etc., are taken within the Poincaré plane (or Poincaré
2016 State Mathematics Contest Geometry Test
 2016 State Mathematics Contest Geometry Test In each of the following, choose the BEST answer and record your choice on the answer sheet provided. To ensure correct scoring, be sure to make all erasures
2016 State Mathematics Contest Geometry Test In each of the following, choose the BEST answer and record your choice on the answer sheet provided. To ensure correct scoring, be sure to make all erasures
Triangles. Example: In the given figure, S and T are points on PQ and PR respectively of PQR such that ST QR. Determine the length of PR.
 Triangles Two geometric figures having the same shape and size are said to be congruent figures. Two geometric figures having the same shape, but not necessarily the same size, are called similar figures.
Triangles Two geometric figures having the same shape and size are said to be congruent figures. Two geometric figures having the same shape, but not necessarily the same size, are called similar figures.
Unit 5: Congruency. Part 1 of 3: Intro to Congruency & Proof Pieces. Lessons 5-1 through 5-4
 Name: Geometry Period Unit 5: Congruency Part 1 of 3: Intro to Congruency & Proof Pieces Lessons 5-1 through 5-4 In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please
Name: Geometry Period Unit 5: Congruency Part 1 of 3: Intro to Congruency & Proof Pieces Lessons 5-1 through 5-4 In this unit you must bring the following materials with you to class every day: Please
Integrated Math II. IM2.1.2 Interpret given situations as functions in graphs, formulas, and words.
 Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Standard 1: Algebra and Functions Students graph linear inequalities in two variables and quadratics. They model data with linear equations. IM2.1.1 Graph a linear inequality in two variables. IM2.1.2
Activity Sheet 1: Constructions
 Name ctivity Sheet 1: Constructions Date 1. Constructing a line segment congruent to a given line segment: Given a line segment B, B a. Use a straightedge to draw a line, choose a point on the line, and
Name ctivity Sheet 1: Constructions Date 1. Constructing a line segment congruent to a given line segment: Given a line segment B, B a. Use a straightedge to draw a line, choose a point on the line, and
Objectives. Cabri Jr. Tools
 ^Åíáîáíó=R püçêíéëí=aáëí~ååé _ÉíïÉÉå=mçáåíë ~åç=iáåéë Objectives To investigate the shortest distance between two points To investigate the shortest distance between a line and a point To investigate the
^Åíáîáíó=R püçêíéëí=aáëí~ååé _ÉíïÉÉå=mçáåíë ~åç=iáåéë Objectives To investigate the shortest distance between two points To investigate the shortest distance between a line and a point To investigate the
Euclidean Geometry. The Elements of Mathematics
 Euclidean Geometry The Elements of Mathematics Euclid, We Hardly Knew Ye Born around 300 BCE in Alexandria, Egypt We really know almost nothing else about his personal life Taught students in mathematics
Euclidean Geometry The Elements of Mathematics Euclid, We Hardly Knew Ye Born around 300 BCE in Alexandria, Egypt We really know almost nothing else about his personal life Taught students in mathematics
0113ge. Geometry Regents Exam In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC?
 0113ge 1 If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest side of VWX? 1) XV ) WX 3) VW 4) NP 4 In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC? In circle
0113ge 1 If MNP VWX and PM is the shortest side of MNP, what is the shortest side of VWX? 1) XV ) WX 3) VW 4) NP 4 In the diagram below, under which transformation is A B C the image of ABC? In circle
Power Round: Geometry Revisited
 Power Round: Geometry Revisited Stobaeus (one of Euclid s students): But what shall I get by learning these things? Euclid to his slave: Give him three pence, since he must make gain out of what he learns.
Power Round: Geometry Revisited Stobaeus (one of Euclid s students): But what shall I get by learning these things? Euclid to his slave: Give him three pence, since he must make gain out of what he learns.
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Review. Show all work for full credit. 5. In the drawing, what is the measure of angle y?
 Triangle Congruence and Similarity Review Score Name: Date: Show all work for full credit. 1. In a plane, lines that never meet are called. 5. In the drawing, what is the measure of angle y? A. parallel
Triangle Congruence and Similarity Review Score Name: Date: Show all work for full credit. 1. In a plane, lines that never meet are called. 5. In the drawing, what is the measure of angle y? A. parallel
UNIT 3 CIRCLES AND VOLUME Lesson 1: Introducing Circles Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: performing operations with fractions understanding slope, both algebraically and graphically understanding the relationship of
TRIANGLES CHAPTER 7. (A) Main Concepts and Results. (B) Multiple Choice Questions
 CHAPTER 7 TRIANGLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Triangles and their parts, Congruence of triangles, Congruence and correspondence of vertices, Criteria for Congruence of triangles: (i) SAS (ii) ASA (iii)
CHAPTER 7 TRIANGLES (A) Main Concepts and Results Triangles and their parts, Congruence of triangles, Congruence and correspondence of vertices, Criteria for Congruence of triangles: (i) SAS (ii) ASA (iii)
triangles in neutral geometry three theorems of measurement
 lesson 10 triangles in neutral geometry three theorems of measurement 112 lesson 10 in this lesson we are going to take our newly created measurement systems, our rulers and our protractors, and see what
lesson 10 triangles in neutral geometry three theorems of measurement 112 lesson 10 in this lesson we are going to take our newly created measurement systems, our rulers and our protractors, and see what
EXPLORING CHORDS. Q1. Draw and label a radius on the circle. How does a chord compare with a radius? What are their similarities and differences?
 EXPLORING CHORDS Name: Date: In this activity you will be using Geogebra to explore some properties associated with chords within a circle. Please answer each question throughout the activity marked Q#
EXPLORING CHORDS Name: Date: In this activity you will be using Geogebra to explore some properties associated with chords within a circle. Please answer each question throughout the activity marked Q#
2008 Euclid Contest. Solutions. Canadian Mathematics Competition. Tuesday, April 15, c 2008 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing
 Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
Canadian Mathematics Competition An activity of the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, Ontario 008 Euclid Contest Tuesday, April 5, 008 Solutions c 008
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXMINTION GEOMETRY Thursday, January 26, 2012 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: Notice School Name: Print your name and the
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXMINTION GEOMETRY Thursday, January 26, 2012 9:15 a.m. to 12:15 p.m., only Student Name: Notice School Name: Print your name and the
JANE LONG ACADEMY HIGH SCHOOL MATH SUMMER PREVIEW PACKET SCHOOL YEAR. Geometry
 JANE LONG ACADEMY HIGH SCHOOL MATH SUMMER PREVIEW PACKET 2015-2016 SCHOOL YEAR Geometry STUDENT NAME: THE PARTS BELOW WILL BE COMPLETED ON THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL: DUE DATE: MATH TEACHER: PERIOD: Algebra
JANE LONG ACADEMY HIGH SCHOOL MATH SUMMER PREVIEW PACKET 2015-2016 SCHOOL YEAR Geometry STUDENT NAME: THE PARTS BELOW WILL BE COMPLETED ON THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL: DUE DATE: MATH TEACHER: PERIOD: Algebra
Math 1230, Notes 2. Aug. 28, Math 1230, Notes 2 Aug. 28, / 17
 Math 1230, Notes 2 Aug. 28, 2014 Math 1230, Notes 2 Aug. 28, 2014 1 / 17 This fills in some material between pages 10 and 11 of notes 1. We first discuss the relation between geometry and the quadratic
Math 1230, Notes 2 Aug. 28, 2014 Math 1230, Notes 2 Aug. 28, 2014 1 / 17 This fills in some material between pages 10 and 11 of notes 1. We first discuss the relation between geometry and the quadratic
Foundations of Neutral Geometry
 C H A P T E R 12 Foundations of Neutral Geometry The play is independent of the pages on which it is printed, and pure geometries are independent of lecture rooms, or of any other detail of the physical
C H A P T E R 12 Foundations of Neutral Geometry The play is independent of the pages on which it is printed, and pure geometries are independent of lecture rooms, or of any other detail of the physical
Geometry - An Olympiad Approach
 Geometry - An Olympiad Approach Manjil P. Saikia Department of Mathematical Sciences Tezpur University manjil@gonitsora.com April 19, 2013 UGC Sponsored Workshop for High School Students and Teachers Women
Geometry - An Olympiad Approach Manjil P. Saikia Department of Mathematical Sciences Tezpur University manjil@gonitsora.com April 19, 2013 UGC Sponsored Workshop for High School Students and Teachers Women
Vectors - Applications to Problem Solving
 BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 00-003 Vectors - Applications to Problem Solving Zvezdelina Stankova Mills College& UC Berkeley 1. Well-known Facts (1) Let A 1 and B 1 be the midpoints of the sides BC and AC of ABC.
BERKELEY MATH CIRCLE 00-003 Vectors - Applications to Problem Solving Zvezdelina Stankova Mills College& UC Berkeley 1. Well-known Facts (1) Let A 1 and B 1 be the midpoints of the sides BC and AC of ABC.
Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep
 Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep Nozha Language Schools Geometry Revision Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. In the parallelogram, each
Cairo Governorate Department : Maths Nozha Directorate of Education Form : 2 nd Prep Nozha Language Schools Geometry Revision Sheet Ismailia Road Branch Sheet ( 1) 1-Complete 1. In the parallelogram, each
1 Line n intersects lines l and m, forming the angles shown in the diagram below. 4 In the diagram below, MATH is a rhombus with diagonals AH and MT.
 1 Line n intersects lines l and m, forming the angles shown in the diagram below. 4 In the diagram below, MATH is a rhombus with diagonals AH and MT. Which value of x would prove l m? 1) 2.5 2) 4.5 3)
1 Line n intersects lines l and m, forming the angles shown in the diagram below. 4 In the diagram below, MATH is a rhombus with diagonals AH and MT. Which value of x would prove l m? 1) 2.5 2) 4.5 3)
6 CHAPTER. Triangles. A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle.
 6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
6 CHAPTER We are Starting from a Point but want to Make it a Circle of Infinite Radius A plane figure bounded by three line segments is called a triangle We denote a triangle by the symbol In fig ABC has
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1
 1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
1 What is the solution of the system of equations graphed below? y = 2x + 1 3 As shown in the diagram below, when hexagon ABCDEF is reflected over line m, the image is hexagon A'B'C'D'E'F'. y = x 2 + 2x
0616geo. Geometry CCSS Regents Exam x 2 + 4x = (y 2 20)
 0616geo 1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
0616geo 1 A student has a rectangular postcard that he folds in half lengthwise. Next, he rotates it continuously about the folded edge. Which three-dimensional object below is generated by this rotation?
1 Solution of Final. Dr. Franz Rothe December 25, Figure 1: Dissection proof of the Pythagorean theorem in a special case
 Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe December 25, 2012 Name: 1 Solution of Final Figure 1: Dissection proof of the Pythagorean theorem in a special case 10 Problem 1. Given is a right triangle ABC with angle α =
Math 3181 Dr. Franz Rothe December 25, 2012 Name: 1 Solution of Final Figure 1: Dissection proof of the Pythagorean theorem in a special case 10 Problem 1. Given is a right triangle ABC with angle α =
Class IX : Math Chapter 11: Geometric Constructions Top Concepts 1. To construct an angle equal to a given angle. Given : Any POQ and a point A.
 1 Class IX : Math Chapter 11: Geometric Constructions Top Concepts 1. To construct an angle equal to a given angle. Given : Any POQ and a point A. Required : To construct an angle at A equal to POQ. 1.
1 Class IX : Math Chapter 11: Geometric Constructions Top Concepts 1. To construct an angle equal to a given angle. Given : Any POQ and a point A. Required : To construct an angle at A equal to POQ. 1.
Answer Key. 9.1 Parts of Circles. Chapter 9 Circles. CK-12 Geometry Concepts 1. Answers. 1. diameter. 2. secant. 3. chord. 4.
 9.1 Parts of Circles 1. diameter 2. secant 3. chord 4. point of tangency 5. common external tangent 6. common internal tangent 7. the center 8. radius 9. chord 10. The diameter is the longest chord in
9.1 Parts of Circles 1. diameter 2. secant 3. chord 4. point of tangency 5. common external tangent 6. common internal tangent 7. the center 8. radius 9. chord 10. The diameter is the longest chord in
1) Exercise 1 In the diagram, ABC = AED, AD = 3, DB = 2 and AE = 2. Determine the length of EC. Solution:
 1) Exercise 1 In the diagram, ABC = AED, AD = 3, DB = 2 and AE = 2. Determine the length of EC. Solution: First, we show that AED and ABC are similar. Since DAE = BAC and ABC = AED, we have that AED is
1) Exercise 1 In the diagram, ABC = AED, AD = 3, DB = 2 and AE = 2. Determine the length of EC. Solution: First, we show that AED and ABC are similar. Since DAE = BAC and ABC = AED, we have that AED is
Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry)
 Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry) V.1 : Facts from spherical geometry Ryan : pp. 84 123 [ Note : Hints for the first two exercises are given in math133f07update08.pdf. ] 1.
Exercises for Unit V (Introduction to non Euclidean geometry) V.1 : Facts from spherical geometry Ryan : pp. 84 123 [ Note : Hints for the first two exercises are given in math133f07update08.pdf. ] 1.
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes
 Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #1. Wednesday, 13 September. [10 minutes] 1. Suppose you are given a line (segment) AB. Using
Mathematics 2260H Geometry I: Euclidean geometry Trent University, Fall 2016 Solutions to the Quizzes Quiz #1. Wednesday, 13 September. [10 minutes] 1. Suppose you are given a line (segment) AB. Using
0609ge. Geometry Regents Exam AB DE, A D, and B E.
 0609ge 1 Juliann plans on drawing ABC, where the measure of A can range from 50 to 60 and the measure of B can range from 90 to 100. Given these conditions, what is the correct range of measures possible
0609ge 1 Juliann plans on drawing ABC, where the measure of A can range from 50 to 60 and the measure of B can range from 90 to 100. Given these conditions, what is the correct range of measures possible
Lecture 1: Axioms and Models
 Lecture 1: Axioms and Models 1.1 Geometry Although the study of geometry dates back at least to the early Babylonian and Egyptian societies, our modern systematic approach to the subject originates in
Lecture 1: Axioms and Models 1.1 Geometry Although the study of geometry dates back at least to the early Babylonian and Egyptian societies, our modern systematic approach to the subject originates in
Math Contest, Fall 2017 BC EXAM , z =
 Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
Math Contest, Fall 017 BC EXAM 1. List x, y, z in order from smallest to largest fraction: x = 111110 111111, y = 1 3, z = 333331 333334 Consider 1 x = 1 111111, 1 y = thus 1 x > 1 z > 1 y, and so x
Understand and Apply Theorems about Circles
 UNIT 4: CIRCLES AND VOLUME This unit investigates the properties of circles and addresses finding the volume of solids. Properties of circles are used to solve problems involving arcs, angles, sectors,
UNIT 4: CIRCLES AND VOLUME This unit investigates the properties of circles and addresses finding the volume of solids. Properties of circles are used to solve problems involving arcs, angles, sectors,
0610ge. Geometry Regents Exam The diagram below shows a right pentagonal prism.
 0610ge 1 In the diagram below of circle O, chord AB chord CD, and chord CD chord EF. 3 The diagram below shows a right pentagonal prism. Which statement must be true? 1) CE DF 2) AC DF 3) AC CE 4) EF CD
0610ge 1 In the diagram below of circle O, chord AB chord CD, and chord CD chord EF. 3 The diagram below shows a right pentagonal prism. Which statement must be true? 1) CE DF 2) AC DF 3) AC CE 4) EF CD
 UNIT-8 SIMILAR TRIANGLES Geometry is the right foundation of all painting, I have decided to teach its rudiments and principles to all youngsters eager for art. 1. ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled
UNIT-8 SIMILAR TRIANGLES Geometry is the right foundation of all painting, I have decided to teach its rudiments and principles to all youngsters eager for art. 1. ABC is a right-angled triangle, right-angled
A Lab Dethroned Ed s Chimera 1 Bobby Hanson October 17, 2007
 A Lab Dethroned Ed s Chimera 1 Bobby Hanson October 17, 2007 The mathematician s patterns, like the painter s or the poet s must be beautiful; the ideas like the colours or the words, must fit together
A Lab Dethroned Ed s Chimera 1 Bobby Hanson October 17, 2007 The mathematician s patterns, like the painter s or the poet s must be beautiful; the ideas like the colours or the words, must fit together
0114ge. Geometry Regents Exam 0114
 0114ge 1 The midpoint of AB is M(4, 2). If the coordinates of A are (6, 4), what are the coordinates of B? 1) (1, 3) 2) (2, 8) 3) (5, 1) 4) (14, 0) 2 Which diagram shows the construction of a 45 angle?
0114ge 1 The midpoint of AB is M(4, 2). If the coordinates of A are (6, 4), what are the coordinates of B? 1) (1, 3) 2) (2, 8) 3) (5, 1) 4) (14, 0) 2 Which diagram shows the construction of a 45 angle?
chapter 1 vector geometry solutions V Consider the parallelogram shown alongside. Which of the following statements are true?
 chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
chapter vector geometry solutions V. Exercise A. For the shape shown, find a single vector which is equal to a)!!! " AB + BC AC b)! AD!!! " + DB AB c)! AC + CD AD d)! BC + CD!!! " + DA BA e) CD!!! " "
2005 Palm Harbor February Invitational Geometry Answer Key
 005 Palm Harbor February Invitational Geometry Answer Key Individual 1. B. D. C. D 5. C 6. D 7. B 8. B 9. A 10. E 11. D 1. C 1. D 1. C 15. B 16. B 17. E 18. D 19. C 0. C 1. D. C. C. A 5. C 6. C 7. A 8.
005 Palm Harbor February Invitational Geometry Answer Key Individual 1. B. D. C. D 5. C 6. D 7. B 8. B 9. A 10. E 11. D 1. C 1. D 1. C 15. B 16. B 17. E 18. D 19. C 0. C 1. D. C. C. A 5. C 6. C 7. A 8.
SOLUTIONS FOR. MTH 338 Final, June A 3 5 note card allowed. Closed book. No calculator. You may also use your list of the first 15 SMGS axioms.
 SOLUTIONS FOR MTH 338 Final, June 2009 A 3 5 note card allowed. Closed book. No calculator. You may also use your list of the first 15 SMGS axioms. 1. In neutral geometry and without a compass, prove that
SOLUTIONS FOR MTH 338 Final, June 2009 A 3 5 note card allowed. Closed book. No calculator. You may also use your list of the first 15 SMGS axioms. 1. In neutral geometry and without a compass, prove that
SM2H Unit 6 Circle Notes
 Name: Period: SM2H Unit 6 Circle Notes 6.1 Circle Vocabulary, Arc and Angle Measures Circle: All points in a plane that are the same distance from a given point, called the center of the circle. Chord:
Name: Period: SM2H Unit 6 Circle Notes 6.1 Circle Vocabulary, Arc and Angle Measures Circle: All points in a plane that are the same distance from a given point, called the center of the circle. Chord:
Chapter (Circle) * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in
 Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Chapter - 10 (Circle) Key Concept * Circle - circle is locus of such points which are at equidistant from a fixed point in a plane. * Concentric circle - Circle having same centre called concentric circle.
Class 9 Quadrilaterals
 ID : in-9-quadrilaterals [1] Class 9 Quadrilaterals For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) The diameter of circumcircle of a rectangle is 13 cm and rectangle's width
ID : in-9-quadrilaterals [1] Class 9 Quadrilaterals For more such worksheets visit www.edugain.com Answer t he quest ions (1) The diameter of circumcircle of a rectangle is 13 cm and rectangle's width
Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 Example 1: Tell how many common tangents the circles have and draw them.
 Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 EQ: How can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Circle: Center: Radius: Chord: Diameter: Secant: Tangent: Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 Example 1: Tell how
Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 EQ: How can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Circle: Center: Radius: Chord: Diameter: Secant: Tangent: Tangent Lines Unit 10 Lesson 1 Example 1: Tell how
GeoGebra as a tool to explore, conjecture, verify, justify, and prove: The case of a circle
 14 North American GeoGebra Journal (ISSN: 2162-3856) Vol. 2, No. 1, 2013 GeoGebra as a tool to explore, conjecture, verify, justify, and prove: The case of a circle Yip-Cheung Chan Abstract: GeoGebra is
14 North American GeoGebra Journal (ISSN: 2162-3856) Vol. 2, No. 1, 2013 GeoGebra as a tool to explore, conjecture, verify, justify, and prove: The case of a circle Yip-Cheung Chan Abstract: GeoGebra is
Geometry and axiomatic Method
 Chapter 1 Geometry and axiomatic Method 1.1 Origin of Geometry The word geometry has its roots in the Greek word geometrein, which means earth measuring. Before the time of recorded history, geometry originated
Chapter 1 Geometry and axiomatic Method 1.1 Origin of Geometry The word geometry has its roots in the Greek word geometrein, which means earth measuring. Before the time of recorded history, geometry originated
STAAR STANDARDS ALGEBRA I ALGEBRA II GEOMETRY
 STANDARDS ALGEBRA I ALGEBRA II GEOMETRY STANDARDS ALGEBRA I TEKS Snapshot Algebra I (New TEKS 2015-16) Mathematical Process Standards A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes
STANDARDS ALGEBRA I ALGEBRA II GEOMETRY STANDARDS ALGEBRA I TEKS Snapshot Algebra I (New TEKS 2015-16) Mathematical Process Standards A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes
10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]
![10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152] 10. Show that the conclusion of the. 11. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.4.7, p 148] 4. Prove the above Theorem. [Th 6.5.3, p152]](/thumbs/94/121826807.jpg) foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
foot of the altitude of ABM from M and let A M 1 B. Prove that then MA > MB if and only if M 1 A > M 1 B. 8. If M is the midpoint of BC then AM is called a median of ABC. Consider ABC such that AB < AC.
Chapter 10. Properties of Circles
 Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
Chapter 10 Properties of Circles 10.1 Use Properties of Tangents Objective: Use properties of a tangent to a circle. Essential Question: how can you verify that a segment is tangent to a circle? Terminology:
MEI Conference Squaring the Circle and Other Shapes
 MEI Conference 2017 Squaring the Circle and Other Shapes Kevin Lord kevin.lord@mei.org.uk Can you prove that the area of the square and the rectangle are equal? Use the triangle HPN to show that area of
MEI Conference 2017 Squaring the Circle and Other Shapes Kevin Lord kevin.lord@mei.org.uk Can you prove that the area of the square and the rectangle are equal? Use the triangle HPN to show that area of
CHAPTER 5 INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID S GEOMETRY. 5.1 Introduction
 78 MATHEMATICS INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID S GEOMETRY CHAPTER 5 5.1 Introduction The word geometry comes form the Greek words geo, meaning the earth, and metrein, meaning to measure. Geometry appears to have
78 MATHEMATICS INTRODUCTION TO EUCLID S GEOMETRY CHAPTER 5 5.1 Introduction The word geometry comes form the Greek words geo, meaning the earth, and metrein, meaning to measure. Geometry appears to have
The Lunes of Hippocrates by Karen Droga Campe
 Grade level: 9-12 The Lunes of Hippocrates by Karen Droga Campe Activity overview In this activity, students will explore a figure that involves lunes the area enclosed between arcs of intersecting circles.
Grade level: 9-12 The Lunes of Hippocrates by Karen Droga Campe Activity overview In this activity, students will explore a figure that involves lunes the area enclosed between arcs of intersecting circles.
Analysis and synthesis (and other peculiarities): Euclid, Apollonius. 2 th March 2014
 Analysis and synthesis (and other peculiarities): Euclid, Apollonius 2 th March 2014 What is algebra? Algebra (today): Advanced level : Groups, rings,..., structures; Elementary level : equations. The
Analysis and synthesis (and other peculiarities): Euclid, Apollonius 2 th March 2014 What is algebra? Algebra (today): Advanced level : Groups, rings,..., structures; Elementary level : equations. The
Computer algebra systems (CAS) have been around for a number of years,
 Problem solving in calculus with symbolic geometry and CAS Philip Todd Saltire Software James Wiechmann Tualatin High School, Tualatin Oregon, USA Computer
Problem solving in calculus with symbolic geometry and CAS Philip Todd Saltire Software James Wiechmann Tualatin High School, Tualatin Oregon, USA Computer
RMT 2013 Geometry Test Solutions February 2, = 51.
 RMT 0 Geometry Test Solutions February, 0. Answer: 5 Solution: Let m A = x and m B = y. Note that we have two pairs of isosceles triangles, so m A = m ACD and m B = m BCD. Since m ACD + m BCD = m ACB,
RMT 0 Geometry Test Solutions February, 0. Answer: 5 Solution: Let m A = x and m B = y. Note that we have two pairs of isosceles triangles, so m A = m ACD and m B = m BCD. Since m ACD + m BCD = m ACB,
Ch 10 Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Ch 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the diagram shown, the measure of ADC is a. 55 b. 70 c. 90 d. 180 2. What is the measure
Ch 10 Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the diagram shown, the measure of ADC is a. 55 b. 70 c. 90 d. 180 2. What is the measure
MATHEMATICS 2017 HSC Course Assessment Task 4 (Trial Examination) Thursday, 3 August 2017
 MATHEMATICS 2017 HSC Course Assessment Task 4 (Trial Examination) Thursday, 3 August 2017 General instructions Working time 3 hours. (plus 5 minutes reading time) Write using blue or black pen. Where diagrams
MATHEMATICS 2017 HSC Course Assessment Task 4 (Trial Examination) Thursday, 3 August 2017 General instructions Working time 3 hours. (plus 5 minutes reading time) Write using blue or black pen. Where diagrams
BHP BILLITON UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE SCHOOL MATHEMATICS COMPETITION, 2003: INTERMEDIATE DIVISION
 BHP BILLITON UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE SCHOOL MATHEMATICS COMPETITION, 00: INTERMEDIATE DIVISION 1. A fraction processing machine takes a fraction f and produces a new fraction 1 f. If a fraction f = p is
BHP BILLITON UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE SCHOOL MATHEMATICS COMPETITION, 00: INTERMEDIATE DIVISION 1. A fraction processing machine takes a fraction f and produces a new fraction 1 f. If a fraction f = p is
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle.
 21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
21. Prove that If one side of the cyclic quadrilateral is produced then the exterior angle is equal to the interior opposite angle. 22. Prove that If two sides of a cyclic quadrilateral are parallel, then
Higher Geometry Problems
 Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Higher Geometry Problems (1) Look up Eucidean Geometry on Wikipedia, and write down the English translation given of each of the first four postulates of Euclid. Rewrite each postulate as a clear statement
Constructing Trig Values: The Golden Triangle and the Mathematical Magic of the Pentagram
 Constructing Trig Values: The Golden Triangle and the Mathematical Magic of the Pentagram A Play in Five Acts 1 "Mathematicians always strive to confuse their audiences; where there is no confusion there
Constructing Trig Values: The Golden Triangle and the Mathematical Magic of the Pentagram A Play in Five Acts 1 "Mathematicians always strive to confuse their audiences; where there is no confusion there
MATH TOURNAMENT 2012 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS
 MATH TOURNAMENT 0 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS. Consider the eperiment of throwing two 6 sided fair dice, where, the faces are numbered from to 6. What is the probability of the event that the sum of the values
MATH TOURNAMENT 0 PROBLEMS SOLUTIONS. Consider the eperiment of throwing two 6 sided fair dice, where, the faces are numbered from to 6. What is the probability of the event that the sum of the values
The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY. Student Name:
 GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Wednesday, August 17, 2011 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of
GEOMETRY The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GEOMETRY Wednesday, August 17, 2011 8:30 to 11:30 a.m., only Student Name: School Name: Print your name and the name of
Geometry. Commensurate and incommensurate segments. The Euclidean algorithm.
 September 24, 2017 Geometry. Commensurate and incommensurate segments. The Euclidean algorithm. Definition. Two segments, and, are commensurate if there exists a third segment,, such that it is contained
September 24, 2017 Geometry. Commensurate and incommensurate segments. The Euclidean algorithm. Definition. Two segments, and, are commensurate if there exists a third segment,, such that it is contained
13 Spherical geometry
 13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
13 Spherical geometry Let ABC be a triangle in the Euclidean plane. From now on, we indicate the interior angles A = CAB, B = ABC, C = BCA at the vertices merely by A, B, C. The sides of length a = BC
Definitions, Axioms, Postulates, Propositions, and Theorems from Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometries by Marvin Jay Greenberg
 Definitions, Axioms, Postulates, Propositions, and Theorems from Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometries by Marvin Jay Greenberg Undefined Terms: Point, Line, Incident, Between, Congruent. Incidence Axioms:
Definitions, Axioms, Postulates, Propositions, and Theorems from Euclidean and Non-Euclidean Geometries by Marvin Jay Greenberg Undefined Terms: Point, Line, Incident, Between, Congruent. Incidence Axioms:
Anticipations of Calculus - Archimedes
 Anticipations of Calculus - Archimedes Let ABC be a segment of a parabola bounded by the straight line AC and the parabola ABC, and let D be the middle point of AC. Draw the straight line DBE parallel
Anticipations of Calculus - Archimedes Let ABC be a segment of a parabola bounded by the straight line AC and the parabola ABC, and let D be the middle point of AC. Draw the straight line DBE parallel
Triangles. 3.In the following fig. AB = AC and BD = DC, then ADC = (A) 60 (B) 120 (C) 90 (D) none 4.In the Fig. given below, find Z.
 Triangles 1.Two sides of a triangle are 7 cm and 10 cm. Which of the following length can be the length of the third side? (A) 19 cm. (B) 17 cm. (C) 23 cm. of these. 2.Can 80, 75 and 20 form a triangle?
Triangles 1.Two sides of a triangle are 7 cm and 10 cm. Which of the following length can be the length of the third side? (A) 19 cm. (B) 17 cm. (C) 23 cm. of these. 2.Can 80, 75 and 20 form a triangle?
8-6. a: 110 b: 70 c: 48 d: a: no b: yes c: no d: yes e: no f: yes g: yes h: no
 Lesson 8.1.1 8-6. a: 110 b: 70 c: 48 d: 108 8-7. a: no b: yes c: no d: yes e: no f: yes g: yes h: no 8-8. b: The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the measures of its remote
Lesson 8.1.1 8-6. a: 110 b: 70 c: 48 d: 108 8-7. a: no b: yes c: no d: yes e: no f: yes g: yes h: no 8-8. b: The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle equals the sum of the measures of its remote
0612ge. Geometry Regents Exam
 0612ge 1 Triangle ABC is graphed on the set of axes below. 3 As shown in the diagram below, EF intersects planes P, Q, and R. Which transformation produces an image that is similar to, but not congruent
0612ge 1 Triangle ABC is graphed on the set of axes below. 3 As shown in the diagram below, EF intersects planes P, Q, and R. Which transformation produces an image that is similar to, but not congruent
Similarity of Triangle
 Similarity of Triangle 95 17 Similarity of Triangle 17.1 INTRODUCTION Looking around you will see many objects which are of the same shape but of same or different sizes. For examples, leaves of a tree
Similarity of Triangle 95 17 Similarity of Triangle 17.1 INTRODUCTION Looking around you will see many objects which are of the same shape but of same or different sizes. For examples, leaves of a tree
1) With a protractor (or using CABRI), carefully measure nacb and write down your result.
 4.5 The Circle Theorem Moment for Discovery: Inscribed Angles Draw a large circle and any of its chords AB, as shown. Locate three points C, C', and C'' at random on the circle and on the same side of
4.5 The Circle Theorem Moment for Discovery: Inscribed Angles Draw a large circle and any of its chords AB, as shown. Locate three points C, C', and C'' at random on the circle and on the same side of
Circle Geometry. This booklet belongs to:
 Circle Geometry This booklet belongs to: LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW TEST Questions that I find difficult Find
Circle Geometry This booklet belongs to: LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW TEST Questions that I find difficult Find
9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations
 www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
www.ck12.org Chapter 9. Circles 9.7 Extension: Writing and Graphing the Equations of Circles Learning Objectives Graph a circle. Find the equation of a circle in the coordinate plane. Find the radius and
THE CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM AND OF THE PROBLEM OF IRRATIONAL NUMBERS
 Global Journal of Advanced Research on Classical and Modern Geometries ISSN: 2284-5569, Vol.2, Issue 2, pp.59-68 THE CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM AND OF THE PROBLEM OF IRRATIONAL NUMBERS
Global Journal of Advanced Research on Classical and Modern Geometries ISSN: 2284-5569, Vol.2, Issue 2, pp.59-68 THE CRITICAL ANALYSIS OF THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM AND OF THE PROBLEM OF IRRATIONAL NUMBERS
Historic Investigation of Legendre s Proof about the 5th Postulate of. Elements for Reeducation of Mathematics Teacher
 Journal of Modern Education Review, ISSN 2155-7993, USA December 2013, Volume 3, No. 12, pp. 926 931 Academic Star Publishing Company, 2013 http://www.academicstar.us Historic Investigation of Legendre
Journal of Modern Education Review, ISSN 2155-7993, USA December 2013, Volume 3, No. 12, pp. 926 931 Academic Star Publishing Company, 2013 http://www.academicstar.us Historic Investigation of Legendre
SOLUTION. Taken together, the preceding equations imply that ABC DEF by the SSS criterion for triangle congruence.
 1. [20 points] Suppose that we have ABC and DEF in the Euclidean plane and points G and H on (BC) and (EF) respectively such that ABG DEH and AGC DHF. Prove that ABC DEF. The first congruence assumption
1. [20 points] Suppose that we have ABC and DEF in the Euclidean plane and points G and H on (BC) and (EF) respectively such that ABG DEH and AGC DHF. Prove that ABC DEF. The first congruence assumption
Tin Ka Ping Secondary School F.2 Mathematics Teaching Syllabus
 Tin Ka Ping Secondary School 05-06 F. Mathematics Syllabus Chapter Rate and Time Guide. Rates. s A. Basic Concept of s B. s of Three Quantities Learn the concept of a rate. Learn the concepts of a ratio
Tin Ka Ping Secondary School 05-06 F. Mathematics Syllabus Chapter Rate and Time Guide. Rates. s A. Basic Concept of s B. s of Three Quantities Learn the concept of a rate. Learn the concepts of a ratio
Collinearity/Concurrence
 Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
Collinearity/Concurrence Ray Li (rayyli@stanford.edu) June 29, 2017 1 Introduction/Facts you should know 1. (Cevian Triangle) Let ABC be a triangle and P be a point. Let lines AP, BP, CP meet lines BC,
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1
 Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
Correlation of 2012 Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) for Algebra I and Geometry to Moving with Math SUMS Moving with Math SUMS Algebra 1 ALGEBRA I A.1 Mathematical process standards. The student
Jakarta International School 8 th Grade AG1
 Jakarta International School 8 th Grade AG1 Practice Test - Black Points, Lines, and Planes Name: Date: Score: 40 Goal 5: Solve problems using visualization and geometric modeling Section 1: Points, Lines,
Jakarta International School 8 th Grade AG1 Practice Test - Black Points, Lines, and Planes Name: Date: Score: 40 Goal 5: Solve problems using visualization and geometric modeling Section 1: Points, Lines,
Do not open your test until instructed to do so!
 Fifth Annual Columbus State Calculus Contest-Precalculus Test Sponsored by The Columbus State University Department of Mathematics April 1 th, 017 ************************* The Columbus State University
Fifth Annual Columbus State Calculus Contest-Precalculus Test Sponsored by The Columbus State University Department of Mathematics April 1 th, 017 ************************* The Columbus State University
Chapter 3. Betweenness (ordering) A system satisfying the incidence and betweenness axioms is an ordered incidence plane (p. 118).
 Chapter 3 Betweenness (ordering) Point B is between point A and point C is a fundamental, undefined concept. It is abbreviated A B C. A system satisfying the incidence and betweenness axioms is an ordered
Chapter 3 Betweenness (ordering) Point B is between point A and point C is a fundamental, undefined concept. It is abbreviated A B C. A system satisfying the incidence and betweenness axioms is an ordered
Lecture 3: Geometry. Sadov s theorem. Morley s miracle. The butterfly theorem. E-320: Teaching Math with a Historical Perspective Oliver Knill, 2013
 E-320: Teaching Math with a Historical Perspective Oliver Knill, 2013 Lecture 3: Geometry Sadov s theorem Here is an example of a geometric theorem which has been found only 10 years ago: The quadrilateral
E-320: Teaching Math with a Historical Perspective Oliver Knill, 2013 Lecture 3: Geometry Sadov s theorem Here is an example of a geometric theorem which has been found only 10 years ago: The quadrilateral
C XZ if C XY > C YZ. Answers for the lesson Apply Properties of Chords. AC } DB therefore you can t show C BC > C CD. 4x x 1 8.
 LESSON 10.3 Answers for the lesson Apply Properties of Chords Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Skill Practice 1. Sample answer: Point Y bisects C XZ if C XY
LESSON 10.3 Answers for the lesson Apply Properties of Chords Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company. All rights reserved. Skill Practice 1. Sample answer: Point Y bisects C XZ if C XY
The Inversion Transformation
 The Inversion Transformation A non-linear transformation The transformations of the Euclidean plane that we have studied so far have all had the property that lines have been mapped to lines. Transformations
The Inversion Transformation A non-linear transformation The transformations of the Euclidean plane that we have studied so far have all had the property that lines have been mapped to lines. Transformations
