8 th Grade Mathematics
|
|
|
- Oswald Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8 th Grade Mathematics Unit #3: Modeling Relationships with Functions Pacing: 25 Days Unit Overview In this unit, students model functions in different ways (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions) and interpret those representations qualitatively and quantitatively. Students will grasp the concept of a function as a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. They will understand that functions describe situations where one quantity determines another. They can translate among representations and partial representations of functions (noting that tabular and graphical representations may be partial representations), and they describe how aspects of the function are reflected in the different representations. Until Grade 8, almost all of students statistical topics and investigations have dealt with univariate data, e.g., collections of counts or measurements of one characteristic. Eighth graders apply their experience with the coordinate plane and linear functions in the study of association between two variables. The Mathematical Practices should be evident throughout instruction and connected to the content addressed in this unit. For instance, understanding how functions model relationships requires that students reason abstractly and quantitatively (MP.2) while looking for and making use of structure (MP.7). Prerequisite Skills Vocabulary Mathematical Practices 1) Read numbers on a number line 2) Create t-tables and construct graphs (including scaling the axes) 3) Graph ordered pairs (x,y) 4) Evaluate Expressions 5) Compute with whole numbers and decimals, including application of order of operations 6) Understand characteristics of a proportional relationship 7) Write and solve algebraic equations Functions y-value x-value Vertical line test Input Output Intercept Linear association Dependent variable Independent variable Linear relationship Initial value Non-linear function Slope Slope- Intercept Non-linear association Relation Linear function Rate of change Relative frequency Interval notation Linear model Negative association Positive association Ordered Pair Domain Range Rise Run MP.1: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them MP.2: Reason abstractly and quantitatively MP.3: Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others MP.4: Model with mathematics MP.5: Use appropriate tools strategically MP.6: Attend to precision MP.7: Look for and make use of structure MP.8: Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning
2 Major Standards (70%) Common Core State Standards 8.SP.1 Construct and Interpret scatter plots. 8.SP.2 Know that straight lines are used to model relationships. 8.SP.4 Understand patterns of association. 8.F.1 Understand and define functions. 8.F.2 Compare properties of two functions. 8.F.3 Interpret y=mx+b as as defining a linear equation. 8.F.4 Construct a function to model a linear relationship. 8.F.5 Analyze and sketch graphs that represent the qualitative feautres of a function. According to the PARCC Model Content Framework, Standard 8.F.2 should serve as opportunity for in-depth focus: Work toward meeting this standard repositions previous work with tables and graphs in the new context of input/output rules. According to the PARCC Model Content Framework, The key advance in proportion concepts between 7 th grade and 8 th grade is: Students build on previous work with proportional relationships, unit rates, and graphing to connect these ideas and understand that the points (x,y) on a non-vertical line are the solutions of the equation y= mx+b, where m is the slope of the line as well as the unit rate of a proportional relationship (in the case b=0). Students also formalize their previous work with linear relationships by working with functions rules that assign to each input exactly one output. N/A N/A Progression of Skills 7 th Grade 8 th Grade High School 7.RP.2: Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities N/A 7.RP.2: Recognize and represent proportional relationships between quantities 8.F.1: Understand that a function is a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. The graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output. 8.F.2: Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). 8.F.3: Interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear. 8.F.4: Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities. Determine the rate of change and initial value of the function from a description of a relationship or from two (x, y) values 8.F.5: Describe qualitatively the functional relationship between two quantities by analyzing a graph (e.g., where the function is increasing or decreasing, linear or nonlinear). Sketch a graph that exhibits the qualitative features of a function HS.F.IF1A: Understand that a function from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) assigns to each element of the domain exactly one element of the range. HS.F.IF.A.2: Use function notation, evaluate functions for inputs in their domains, and interpret statements that use function notation in terms of a context. N/A HS.IF.B6: Calculate and interpret the average rate of change of a function (presented symbolically or as a table) over a specified interval. Estimate the rate of change from a graph HS.IF.B4: For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities, and sketch graphs showing key features given a verbal description of the relationship. 2 Page
3 Big Ideas What is a function? What are the different ways to represent a function? How do I determine whether a function is linear or non-linear? How can I recognize an equation that will produce a linear graph? How can a graph, table, ordered pair, or an algebraic rule help describe the relationship between two variables? How can we determine a gradual, steep or constant change between any two variables? Students Will Know/Understand A mathematical relation is a set of ordered pairs that can be listed in a table, shown on graph as points, or represented in mapping. The set of x-values is the domain and the set of y- values is the range. A function is a relation in which each element (number) of the domain is mapped to exactly one element (number) of the range. A function can be determined on a graph by using a vertical line test. Functions provide a tool for describing how variables change together. Using a function in this way is called modeling, and the function is called a model. Functions can be represented in multiple ways in algebraic symbols, graphs, verbal descriptions, tables, and so on and these representations, and the links among them, are useful in analyzing patterns of change. Some representations of a function may be more useful than others, depending on how they are used. Functions are single-valued mappings from one set the domain of the function to another its range. Functions apply to a wide range of situations. They do not have to be described by any specific expressions or follow a regular pattern. They apply to cases other than those of continuous variation. For example, sequences are functions. For functions that map real numbers to real numbers, certain patterns of covariation, or patterns in how two variables change together, indicate membership in a particular family of functions and determine the type of formula that the function has. Be Able To Describing what it means for a situation to have a functional relationship Determining the relationship between the input and output of a function Determining the different types of functions that can b used and altered to model various situations in life Representing a linear function in the context of a problem situation Representing a function using real world context Interpreting, sketching, and analyzing graphs from situations Identifying relations and functions Evaluating functions Modeling functions using rules, tables and graphs Writing function rule given table or real-world situation Using inductive reasoning in counting number patterns Writing rules for arithmetic sequences Modeling arithmetic sequence as linear function Finding input value given the output value, and vice versa 3 Page
4 Unit Sequence Student Friendly Objective SWBAT 1 Represent linear relationships using tables, graphs, equations and words Key Points/ Teaching Tips Sample Assessment Item from Exit Ticket A fitness instructor exercises about 12.5 hours per week. Write an equation to find the total number of hours h the instructor exercises in any number of weeks w. Instructional Resources My Math Chapter 4 Lessons 1-2 Key Point: The relationship between two variables is linear if the change of one variable with respect to the change in the other is constant. Weeks, w Total Hours, h Develop a conceptual understanding of functions in order to derive a formal definition of a function. Tip: A mapping diagram can help students see if a relation is a function by determining if every member of the domain has only one arrow leading to the range. A ball bounces across the schoolyard. It hits the ground at (0, 0) and bounces up and lands at (1, 0) and bounces again. The graph shows only one bounce. Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 1 (Appendix C) My Math Chapter 4 Inquiry Lab: Relations and Functions (Pages ) 1) Identify the height of the ball at the following values of t: 0, ) What is the average speed of the ball over the first 0.25 second? 4 Page
5 3 Construct and test a formal definition of a function Definitions should be based on the understanding that functions occur when there is exactly one y-value associated with any x- value. Can the table shown below represent values of a function? Explain: Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 2 (Appendix C) d.com/functionmachine.ht ml 4 Use substitution to find the value of a function. Differentiate between dependent and independent variables and organize inputs, outputs and rules in a function table Key points: Remind students that the variable y is simply another way to express the notation f(x) in a function rule or a function table. 1) Find the function value: f(-2) if f(x) = x + 4 3) How does the domain affect the range in a function? My Math Chapter 4 Lesson 3 rade-8/complete-afunction-table rade-8/write-a-rule-for-afunction-table My Math Chapter 4 Lesson 4 5 Graph linear functions from function tables and equations Determine the connection between points (x, y), functions, and the equation representing the function (y = mx + b). determine whether a set of data is continuous or discrete by the book (appendix c) may be used as an extension resource An appliance repairman charges $60 for a service call plus an additional $40 per hour to repair appliances. The function is represented by y = 40x a. Make a function table to find the total cost of 1, 2, 3 or 4 hours of repair on an appliance: b. Graph the function c. Is the function continuous or discrete? Explain By the Book (Appendix C) rade-8/graph-a-line-froma-function-table rade-8/graph-a-line-froman-equation 5 Page
6 6 Make sense of, represent and solve real world problems related to linear functions Students know that distance traveled is a function of the time spent traveling and that the total cost of an item is a function of how many items are purchased. A linear function has the table of values below. The information in the table shows the number of pages a student can read in a certain book as a function of time in minutes. Assume a constant rate: Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 3 (Appendix C) Time in minutes(x) Total # of pages read (y) a. Write the rule or equation that represents the linear function that describes the total number of pages read, y, in x minutes. b. How many pages can be read in 45 minutes? c. Do all linear functions have a constant rate of change? Explain. 7 Flex Day (Instruction Based on Data) Recommended Resources: Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 4 (Appendix C) Order Matters (Appendix C) Vending Machines (Appendix C) Secret Codes and Number Rules (Appendix C) My Math Chapter 4 Problem-Solving Investigation (Pages ) My Math Chapter 4 Mid-Chapter Check (Page 308) 6 Page
7 8 Identify a function by its graph Students must understand that the graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output. essential question: why is the graph of a function identical to the graph of a certain equation? The amount of water that flows out of a certain hose in gallons is a function of the amount of time in minutes that the faucet is turned on. The amount of water that flows out of the hose in 4 minutes is 11 gallons. Assume water flows at a constant rate. Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 5 (Appendix C) ons/1191 a. Write an equation in two variables that represents the amount of water, y, in gallons, as a function of the time in minutes, x, the faucet is turned on. b. Use the equation you wrote in part (1) to determine the amount of water that flows out of a hose in 8 minutes, 4 minutes, and 2 minutes. c. The input of the function, x, is time in minutes, and the output of the function, y, is the amount of water that flows out of the hose in gallons. Write the inputs and outputs from part (2) as ordered pairs, and plot them as points on the coordinate plane. 7 Page
8 9 Analyze and compare properties of functions Key Points: A rate of change describes how one quantity changes with another. For a linear function, the slope equals the rate of change. A function is a direct variation if the two variable quantities have a constant ratio and the graph passes through (0, 0). A museum charges $10.50 per adult ticket. The price of a student ticket is represented in the table. Student Ticket Price Tickets Price ($) Which statement(s) are true? Select all that apply. a) Both functions have the same y- intercept. b) The student ticket has a greater rate of change. c) The adult ticket has a greater rate of change. d) Both functions show a direct variation. e) Both functions have the same constant rate of change. My Math Chapter 4 Lesson 5 ons/1190-identifyfunction-properties 10 Represent real world situations by constructing a function The initial value is the same as the y- intercept or the starting amount in a real world situation. When Charlotte planted her tomato plant, it grew three inches in one week. After 5 weeks, the tomato plant was 23 inches tall. Assume the relationship is linear. My Math Chapter 4 Lesson 6 a. What was the initial value of the tomato plant? b. What is the rate of change of the tomato plant? c. Explain why a horizontal line has a rate of change of 0 8 Page
9 11 Use rate of change to determine whether or not a function is linear Students interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a line Is the function a linear function? Check at least three pairs of inputs and their corresponding outputs: Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 6 (Appendix C) Input Output What will the graph of the function from part (1) look like? Explain. Of the four linear functions represented below, which has the greatest rate of change? 12 Compare properties of at least two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically, etc.). Use rate of change to compare two functions. Providing example language for students to reference will be useful. This might consist of sentence starters, sentence frames, or a word wall. Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 7 (Appendix C) ons/1193-compare-twofunctions-by-analyzing-anequation-and-a-table 13 Differentiate between linear and non-linear functions Students may benefit from exploring these challenge exercises in small groups.(engage lesson) A function has the rule so that each input of x is assigned an output of x! 4. Do you think the function is linear or nonlinear? Explain. Engage NY Module 5 Lesson 8 (Appendix C) My Math Chapter 4 Lesson 7 9 Page
10 14 Flex Day (Instruction Based on Data) Recommended Resources: Which is Which? (Appendix C) My Math Chapter 4 Lesson 9 (Pages ) My Math Chapter 4 Inquiry Lab (Pages ) My Math Chapter 4 21 st Century Career (Pages ) 15 Make sense of, represent and solve real world 16 problems related to rate of change, linear relationships and functions Task-based lessons over the course of four days Provide an appropriate balance of independent work/think time with collaborative work/think time Emphasize the problem solving process rather than the answer (i.e. how are students making sense of and thinking about the problems; what type of solution pathways are they designing before they get started) Provide an opportunity for students to share different strategies/methods for tackling the tasks End each lesson with meaningful discussions (i.e. Socratic seminars, critiquing their peer s work, etc.) and/or written reflections Flex Days (Instruction Based on Data) Recommended Resources: Sorting Functions (Appendix C) Analyzing Linear Functions (Appendix C) Ditch Diggers (Appendix C) Engage NY Assessment (Appendix C) My Math Chapter 4 Review (Pages ) My Math Unit Project (Pages ) Battery Charging Task MAP Concept Task: Lines and Linear Equations What s My Line? MAP Task: Modeling Situations with Linear Equations Fill the Tanker (Appendix C) 20 End of Unit MCLASS Beacon Assessment Appendix B 10 Page
11 Standard 8.F.1 Understand that a function is a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. The graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output. 1 1 Function notation is not required in Grade 8. Appendix A: Unpacked Standards Guide Source: Public Schools of North Carolina NCDPI Collaborative Workspace Unpacking What do these standards mean a child will know and be able to do? 8.F.1 Students understand rules that take x as input and gives y as output is a function. Functions occur when there is exactly one y-value is associated with any x-value. Using y to represent the output we can represent this function with the equations y = x 2 + 5x + 4. Students are not expected to use the function notation f(x) at this level. Students identify functions from equations, graphs, and tables/ordered pairs. Graphs Students recognize graphs such as the one below is a function using the vertical line test, showing that each x- value has only one y-value; whereas, graphs such as the following are not functions since there are 2 y-values for multiple x-value. 11 Page
12 Tables or Ordered Pairs Students read tables or look at a set of ordered pairs to determine functions and identify equations where there is only one output (y-value) for each input (x-value). Functions Not A Function x y {(0, 2), (1, 3), (2, 5), (3, 6)} x y Equations Students recognize equations such as y = x or y = x 2 + 3x + 4 as functions; whereas, equations such as x 2 + y 2 = 25 are not functions. 8.F.2 Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). For example, given a linear function represented by a table of values and a linear function represented by an algebraic expression, determine which function has the greater rate of change. 8.F.2 Students compare two functions from different representations. Example 1: Compare the following functions to determine which has the greater rate of change. Function 1: y = 2x + 4 Function 2: x y Solution: The rate of change for function 1 is 2; the rate of change for function 2 is 3. Function 2 has the greater rate of change. Example 2: Compare the two linear functions listed below and determine which has a negative slope. 12 Page Function 1: Gift Card
13 Samantha starts with $20 on a gift card for the bookstore. She spends $3.50 per week to buy a magazine. Let y be the amount remaining as a function of the number of weeks, x. x y Function 2: Calculator rental The school bookstore rents graphing calculators for $5 per month. It also collects a non-refundable fee of $10.00 for the school year. Write the rule for the total cost (c) of renting a calculator as a function of the number of months (m). c = m Solution: Function 1 is an example of a function whose graph has a negative slope. Both functions have a positive starting amount; however, in function 1, the amount decreases 3.50 each week, while in function 2, the amount increases 5.00 each month. NOTE: Functions could be expressed in standard form. However, the intent is not to change from standard form to slope-intercept form but to use the standard form to generate ordered pairs. Substituting a zero (0) for x and y will generate two ordered pairs. From these ordered pairs, the slope could be determined. Example 3: 2x + 3y = 6 Let x = 0: 2(0) + 3y = 6 Let y = 0: 2x + 3(0) = 6 3y = 6 2x = 6 3y = 6 2x = y = 2 x = 3 Ordered pair: (0, 2) Ordered pair: (3, 0) Using (0, 2) and (3, 0) students could find the slope and make comparisons with another function. 8.F.3 Interpret the equation y = 13 Page 8.F.3 Students understand that linear functions have a constant rate of change between any two points.
14 mx + b as defining a linear function, whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear. For example, the function A = s2 giving the area of a square as a function of its side length is not linear because its graph contains the points (1,1), (2,4) and (3,9), which are not on a straight line. Students use equations, graphs and tables to categorize functions as linear or non-linear. Example 1: Determine if the functions listed below are linear or non-linear. Explain your reasoning. 1. y = -2x y = (x 2) 3. A = r X Y Solution: 1. Non-linear 2. Linear 3. Non-linear 4. Non-linear; there is not a constant rate of change 5. Non-linear; the graph curves indicating the rate of change is not constant. 8.F.4 Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities. Determine the rate of change and initial value of the function from a description of a relationship or from two (x, y) values, including reading these from a table or from a graph. Interpret the rate of change and initial value of a linear function in terms of the situation it models, and in terms of its graph or a table of values. 14 Page 8.F.4 Students identify the rate of change (slope) and initial value (y-intercept) from tables, graphs, equations or verbal descriptions to write a function (linear equation). Students understand that the equation represents the relationship between the x-value and the y-value; what math operations are performed with the x-value to give the y-value. Slopes could be undefined slopes or zero slopes. Tables: Students recognize that in a table the y-intercept is the y-value when x is equal to 0. The slope can be y determined by finding the ratio x between the change in two y-values and the change between the two corresponding x-values. Example 1:
15 Write an equation that models the linear relationship in the table below. x y Solution: The y-intercept in the table below would be (0, 2). The distance between 8 and -1 is 9 in a negative direction à -9; the distance between -2 and 1 is 3 in a positive direction. The slope is the ratio of rise to run y 9 or x or 3 = -3. The equation would be y = -3x + 2 Graphs: Using graphs, students identify the y-intercept as the point where the line crosses the y-axis and the slope as the rise. run Example 2: Write an equation that models the linear relationship in the graph below. Solution: The y-intercept is 4. The slope is ¼, found by moving up 1 and right 4 going from (0, 4) to (4, 5). The linear equation would be y = ¼ x Page
16 Equations: In a linear equation the coefficient of x is the slope and the constant is the y-intercept. Students need to be given the equations in formats other than y = mx + b, such as y = ax + b (format from graphing calculator), y = b + mx (often the format from contextual situations), etc. Point and Slope: Students write equations to model lines that pass through a given point with the given slope. Example 2: A line has a zero slope and passes through the point (-5, 4). What is the equation of the line? Solution: y = 4 Example 3: Write an equation for the line that has a slope of ½ and passes though the point (-2, 5) Solution: y = ½ x + 6 Students could multiply the slope ½ by the x-coordinate -2 to get -1. Six (6) would need to be added to get to 5, which gives the linear equation. Students also write equations given two ordered pairs. Note that point-slope form is not an expectation at this level. Students use the slope and y-intercepts to write a linear function in the form y = mx +b. Contextual Situations: In contextual situations, the y-intercept is generally the starting value or the value in the situation when the independent variable is 0. The slope is the rate of change that occurs in the problem. Rates of change can often occur over years. In these situations it is helpful for the years to be converted to 0, 1, 2, etc. For example, the years of 1960, 1970, and 1980 could be represented as 0 (for 1960), 10 (for 1970) and 20 (for 1980). Example 4: The company charges $45 a day for the car as well as charging a one-time $25 fee for the car s navigation system (GPS). Write an expression for the cost in dollars, c, as a function of the number of days, d, the car was rented. 16 Page
17 Solution: C = 45d F.5 Describe qualitatively the functional relationship between two quantities by analyzing a graph (e.g., where the function is increasing or decreasing, linear or nonlinear). Sketch a graph that exhibits the qualitative features of a function that has been described verbally. Students interpret the rate of change and the y-intercept in the context of the problem. In Example 4, the rate of change is 45 (the cost of renting the car) and that initial cost (the first day charge) also includes paying for the navigation system. Classroom discussion about one-time fees vs. recurrent fees will help students model contextual situations. 8.F.5 Given a verbal description of a situation, students sketch a graph to model that situation. Given a graph of a situation, students provide a verbal description of the situation. Example 1: The graph below shows a John s trip to school. He walks to his Sam s house and, together, they ride a bus to school. The bus stops once before arriving at school. Describe how each part A E of the graph relates to the story. Solution: A John is walking to Sam s house at a constant rate. B John gets to Sam s house and is waiting for the bus. C John and Sam are riding the bus to school. The bus is moving at a constant rate, faster than John s walking rate. D The bus stops. E The bus resumes at the same rate as in part C. Example 2: Describe the graph of the function between x = 2 and x = 5? Solution: The graph is non-linear and decreasing. 17 Page
18 18 Page
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 3: Equations Topic C: Equations in Two Variables and Their Graphs (Continued) This topic focuses on extending the
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Math Third Quarter Unit 3: Equations Topic C: Equations in Two Variables and Their Graphs (Continued) This topic focuses on extending the
8 th Grade Mathematics
 8 th Grade Mathematics Unit #2 : Understanding and Representing Linear Relationships Pacing: 40 Days Unit Overview In this unit, students will build upon informal knowledge of one-variable linear equations,
8 th Grade Mathematics Unit #2 : Understanding and Representing Linear Relationships Pacing: 40 Days Unit Overview In this unit, students will build upon informal knowledge of one-variable linear equations,
New To 8 th Grade: Moved from 8 th Grade:
 New To 8 th Grade: Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x 3 = p, where p is a positive rational number (8.EE.2) Scientific notation, including
New To 8 th Grade: Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x 2 = p and x 3 = p, where p is a positive rational number (8.EE.2) Scientific notation, including
Background Information For The Teacher
 Grade/Subject Unit Title Overview of Unit Pacing Grade 8/ Mathematics Unit 4: Functions Using functions, students will define, evaluate, and compare model relationships between quantities. Students will
Grade/Subject Unit Title Overview of Unit Pacing Grade 8/ Mathematics Unit 4: Functions Using functions, students will define, evaluate, and compare model relationships between quantities. Students will
Mathematical Practices
 Mathematical Practices 8.MP.1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 8.MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 8.MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 8.MP.6. Attend to precision.
Mathematical Practices 8.MP.1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 8.MP.2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 8.MP.5. Use appropriate tools strategically. 8.MP.6. Attend to precision.
MCS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR 8 th GRADE MATHEMATICS *
 MCS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR 8 th GRADE MATHEMATICS * Examples of Key Advances from Grade 7 to Grade 8 Students build on previous work with proportional relationships, unit rates, and graphing to connect
MCS CONTENT STANDARDS FOR 8 th GRADE MATHEMATICS * Examples of Key Advances from Grade 7 to Grade 8 Students build on previous work with proportional relationships, unit rates, and graphing to connect
3A: Solving linear equations, understanding rate of change.
 Grade/Subject Unit Title Grade 8/ Mathematics Unit 3: Linear Relationships 3A: Solving linear equations, understanding rate of change. 3B: Systems of Equations Overview of Unit Pacing In this unit, students
Grade/Subject Unit Title Grade 8/ Mathematics Unit 3: Linear Relationships 3A: Solving linear equations, understanding rate of change. 3B: Systems of Equations Overview of Unit Pacing In this unit, students
Eighth Grade - Mathematics Kentucky Core Academic Standards with Targets Student Friendly Targets
 Eighth Grade - Mathematics Kentucky Core Academic Standards with Targets Student Friendly Targets College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Math The 6-8 standards on the following pages define
Eighth Grade - Mathematics Kentucky Core Academic Standards with Targets Student Friendly Targets College and Career Readiness Anchor Standards for Math The 6-8 standards on the following pages define
Unit 5: Representations of Linear Relations
 Time Frame: Approximately 3-5 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Students build upon previous understandings of linear equations and functions and apply them to various representations of linear relationships,
Time Frame: Approximately 3-5 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Students build upon previous understandings of linear equations and functions and apply them to various representations of linear relationships,
Westbrook Public Schools Middle School Mathematics Curriculum Grade 8
 Westbrook Public Schools Middle School Mathematics Curriculum Grade 8 Unit 1: Real Numbers Anticipated Length: 8 weeks Mathematical Practices: (Practices in bold are to be emphasized in the unit.) Mathematical
Westbrook Public Schools Middle School Mathematics Curriculum Grade 8 Unit 1: Real Numbers Anticipated Length: 8 weeks Mathematical Practices: (Practices in bold are to be emphasized in the unit.) Mathematical
Mathematics Level D: Lesson 2 Representations of a Line
 Mathematics Level D: Lesson 2 Representations of a Line Targeted Student Outcomes Students graph a line specified by a linear function. Students graph a line specified by an initial value and rate of change
Mathematics Level D: Lesson 2 Representations of a Line Targeted Student Outcomes Students graph a line specified by a linear function. Students graph a line specified by an initial value and rate of change
Pacing 2 days Begin with bar models as a concrete representation (engage NY), then. inverse operations to isolate and
 28 Determine whether mathematical statements of equality and inequalities are true or false. Write three different equations that have a solution of 0. Write each equation and prove it is accurate by solving
28 Determine whether mathematical statements of equality and inequalities are true or false. Write three different equations that have a solution of 0. Write each equation and prove it is accurate by solving
Functions MCC8.F.1 MCC8.F.2 MCC8.EE.5 MCC8.EE.6 MCC8.F.3
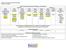 Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade - At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade - At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade
 Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade 1st Semester nd Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit Unit 9 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity Exponents
Jackson County Schools Curriculum Pacing Guide Math - Eighth Grade 1st Semester nd Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit Unit 9 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity Exponents
Big Idea(s) Essential Question(s)
 Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Math Grade/Course Algebra I Unit 4 Linear Functions Duration 20 instructional days + 4 days reteaching/enrichment Big Idea(s) Essential
Middletown Public Schools Mathematics Unit Planning Organizer Subject Math Grade/Course Algebra I Unit 4 Linear Functions Duration 20 instructional days + 4 days reteaching/enrichment Big Idea(s) Essential
My Math Chapter 1, Lesson 7
 24 Compute with numbers written in scientific notation; Apply word problem strategies to identify the appropriate operation; Evaluate a newspaper headline using exponents and scientific notation. Common
24 Compute with numbers written in scientific notation; Apply word problem strategies to identify the appropriate operation; Evaluate a newspaper headline using exponents and scientific notation. Common
Unit 3 Linear Equations and Functions
 Number of Days: 34 11/27/17 1/26/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Students learn about linear equations in two variables. Students explore concepts of slope and intercepts as they write and graph
Number of Days: 34 11/27/17 1/26/18 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Students learn about linear equations in two variables. Students explore concepts of slope and intercepts as they write and graph
Functions MCC8.F.1 MCC8.F.2 MCC8.EE.5 MCC8.EE.6 MCC8.F.3
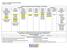 Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
Common Core Georgia Performance Standards 8 th Grade At a Glance Common Core Georgia Performance Standards: Curriculum Map Semester 1 Semester Unit 1 Unit Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit
LINEAR EQUATIONS Modeling Linear Equations Common Core Standards
 E Linear Equations, Lesson 1, Modeling Linear Functions (r. 2018) LINEAR EQUATIONS Modeling Linear Equations Common Core Standards F-BF.A.1 Write a function that describes a relationship between two quantities.
E Linear Equations, Lesson 1, Modeling Linear Functions (r. 2018) LINEAR EQUATIONS Modeling Linear Equations Common Core Standards F-BF.A.1 Write a function that describes a relationship between two quantities.
Grade-Eight Chapter. of the. Mathematics Framework. for California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade Twelve
 Grade-Eight Chapter of the Mathematics Framework for California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade Twelve Adopted by the California State Board of Education, November 2013 Published by the California
Grade-Eight Chapter of the Mathematics Framework for California Public Schools: Kindergarten Through Grade Twelve Adopted by the California State Board of Education, November 2013 Published by the California
Alta Loma Junior High 8 th Grade Math
 Alta Loma Junior High 8 th Grade Math Dear Parent(s): The following outline is being provided to better help you and your student to understand the current Common Core concepts of this trimester. Trimester
Alta Loma Junior High 8 th Grade Math Dear Parent(s): The following outline is being provided to better help you and your student to understand the current Common Core concepts of this trimester. Trimester
Math 8 Common Core. Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools
 Math 8 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 7 Common Core This course continues the trajectory towards a more
Math 8 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 7 Common Core This course continues the trajectory towards a more
BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide UNIT 7.1: THE NUMBER SYSTEM
 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content Accelerated 7th Grade BPS Suggested Planning Guide BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving
Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content Accelerated 7th Grade BPS Suggested Planning Guide BPS Accelerated 7th Grade Math Planning Guide 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving
MATHEMATICS. Perform a series of transformations and/or dilations to a figure. A FAMILY GUIDE FOR STUDENT SUCCESS 17
 MATHEMATICS In grade 8, your child will focus on three critical areas. The first is formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a
MATHEMATICS In grade 8, your child will focus on three critical areas. The first is formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a
Middle School Math Solution: Course 3
 Ohio 8.MP MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES The s for Mathematical Practice describe the skills that mathematics educators should seek to develop in their students. The descriptions of the mathematical practices
Ohio 8.MP MATHEMATICAL PRACTICES The s for Mathematical Practice describe the skills that mathematics educators should seek to develop in their students. The descriptions of the mathematical practices
, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1
 2017.18, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical
2017.18, Eighth Grade Mathematics, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical
Agile Mind Mathematics 8 Scope and Sequence, Indiana Academic Standards for Mathematics
 Prior to Grade 8, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables, and solved problems
Prior to Grade 8, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between dependent and independent variables, and solved problems
Grade 6 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map
 Grade 6 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments Common Core State Standards Standards
Grade 6 PI+ Yearlong Mathematics Map Resources: Approved from Board of Education Assessments: PARCC Assessments, Performance Series, District Benchmark Assessments Common Core State Standards Standards
Eureka Math. Grade 8, Module 5. Student File_B. Contains Exit Ticket and Assessment Materials
 A Story of Ratios Eureka Math Grade 8, Module 5 Student File_B Contains Exit Ticket and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may
A Story of Ratios Eureka Math Grade 8, Module 5 Student File_B Contains Exit Ticket and Assessment Materials Published by the non-profit Great Minds. Copyright 2015 Great Minds. No part of this work may
Math 2 Unit 4 Quadratic Functions: Modeling
 Approximate Time Frame: 2 3 Weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1, students learn how to model functions and how to interpret models of functions. Students looked at multiple representations
Approximate Time Frame: 2 3 Weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1, students learn how to model functions and how to interpret models of functions. Students looked at multiple representations
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR
 COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR Mathematics (CCSSM) Grade 8 Mathematics Grade 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and
COMMON CORE STATE STANDARDS FOR Mathematics (CCSSM) Grade 8 Mathematics Grade 8 In Grade 8, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and
Sequence of Math 7 Accelerated Units Aligned with the California Standards
 Sequence of Math 7 Accelerated Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Math Advanced 2 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations and Inequalities Ch. 1 Equations Ch. 11 Inequalities
Sequence of Math 7 Accelerated Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Math Advanced 2 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations and Inequalities Ch. 1 Equations Ch. 11 Inequalities
Common Core State Standards with California Additions 1 Standards Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program. Grade Eight Mathematics
 Common Core State s with California Additions 1 s Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program Grade Eight Mathematics Publisher 8.NS 1. 8.NS 2. Language Primary Supporting THE NUMBER SYSTEM Know that there are
Common Core State s with California Additions 1 s Map for a Basic Grade-Level Program Grade Eight Mathematics Publisher 8.NS 1. 8.NS 2. Language Primary Supporting THE NUMBER SYSTEM Know that there are
Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards
 Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Course 3 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations Ch. 1 Equations 29 days: 9/5/17 10/13/17 2. Transformational
Sequence of Math 8 SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Course 3 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations Ch. 1 Equations 29 days: 9/5/17 10/13/17 2. Transformational
MAFS.8.F.1 Define, evaluate, and compare functions. Nonlinear functions may be included for identifying a function.
 Content Standard MAFS.8.F Functions Assessment Limits Calculator s Context A table of values for x and y is shown. x y 1 5 2 7 3 9 4 11 MAFS.8.F.1 Define, evaluate, and compare functions. MAFS.8.F.1.1
Content Standard MAFS.8.F Functions Assessment Limits Calculator s Context A table of values for x and y is shown. x y 1 5 2 7 3 9 4 11 MAFS.8.F.1 Define, evaluate, and compare functions. MAFS.8.F.1.1
Mathematics Grade 8. Prepublication Version, April 2013 California Department of Education 51
 Mathematics In, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear
Mathematics In, instructional time should focus on three critical areas: (1) formulating and reasoning about expressions and equations, including modeling an association in bivariate data with a linear
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 8 Pre-Algebra 8 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 8 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 8 course, instructional time should focus on three critical
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 8 Pre-Algebra 8 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 8 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 8 course, instructional time should focus on three critical
8 th Grade Math Curriculum Guide Caldwell County Schools
 8 th Grade Math Curriculum Guide Caldwell County Schools 1 st Nine Weeks Unit 1 Linear Equations Suggested Pacing: 20 days Unit 1 Common Core Standards Domain Cluster Standard 8.EE Expressions and Equations
8 th Grade Math Curriculum Guide Caldwell County Schools 1 st Nine Weeks Unit 1 Linear Equations Suggested Pacing: 20 days Unit 1 Common Core Standards Domain Cluster Standard 8.EE Expressions and Equations
Eighth Grade Mathematics
 Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Write your answers on notebook paper. Show your work.
 UNIT 6 Getting Ready Use some or all of these exercises for formative evaluation of students readiness for Unit 6 topics. Prerequisite Skills Finding the length of the sides of special right triangles
UNIT 6 Getting Ready Use some or all of these exercises for formative evaluation of students readiness for Unit 6 topics. Prerequisite Skills Finding the length of the sides of special right triangles
Pre-Algebra 8 Overview
 Pre-Algebra 8 Overview Pre-Algebra 8 content is organized into five domains for focused study as outlined below in the column to the left. The Pre-Algebra 8 domains listed in bold print on the shaded bars
Pre-Algebra 8 Overview Pre-Algebra 8 content is organized into five domains for focused study as outlined below in the column to the left. The Pre-Algebra 8 domains listed in bold print on the shaded bars
Math 6 Common Core. Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools
 Math 6 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 5 Common Core This course begins the transition from the heavy emphasis
Math 6 Common Core Mathematics Prince George s County Public Schools 2014-2015 Course Code: Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 5 Common Core This course begins the transition from the heavy emphasis
6th Grade. Translating to Equations. Slide 1 / 65 Slide 2 / 65. Slide 4 / 65. Slide 3 / 65. Slide 5 / 65. Slide 6 / 65
 Slide 1 / 65 Slide 2 / 65 6th Grade Dependent & Independent Variables 15-11-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 65 Slide 4 / 65 Table of Contents Translating to Equations Dependent and Independent Variables Equations
Slide 1 / 65 Slide 2 / 65 6th Grade Dependent & Independent Variables 15-11-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 65 Slide 4 / 65 Table of Contents Translating to Equations Dependent and Independent Variables Equations
8 Mathematics Curriculum
 New York State Common Core 8 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E GRADE 8 MODULE 4 Table of Contents 1... 3 Topic A: Writing and Solving (8.EE.C.7)... 11 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols... 13 Lesson
New York State Common Core 8 Mathematics Curriculum G R A D E GRADE 8 MODULE 4 Table of Contents 1... 3 Topic A: Writing and Solving (8.EE.C.7)... 11 Lesson 1: Writing Equations Using Symbols... 13 Lesson
UTAH CORE STATE STANDARDS for MATHEMATICS. Mathematics Grade 7
 Mathematics Grade 7 In Grade 7, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) developing understanding of and applying proportional relationships; (2) developing understanding of operations
Mathematics Grade 7 In Grade 7, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) developing understanding of and applying proportional relationships; (2) developing understanding of operations
Agile Mind Grade 7 Scope and Sequence, Common Core State Standards for Mathematics
 In Grade 6, students developed an understanding of variables from two perspectives as placeholders for specific values and as representing sets of values represented in algebraic relationships. They applied
In Grade 6, students developed an understanding of variables from two perspectives as placeholders for specific values and as representing sets of values represented in algebraic relationships. They applied
The descriptions below provide an overview of the concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 8 th grade.
 Mathematics Grade 8 The descriptions below provide an overview of the concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 8 th grade. The Number System This is the culminating area for the number
Mathematics Grade 8 The descriptions below provide an overview of the concepts and skills that students explore throughout the 8 th grade. The Number System This is the culminating area for the number
April 2016 Draft. DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1. eureka math.org 2016 Great Minds
 DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Grade 8 April 2016 Draft DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1 Grade 8 Mathematics The majority
DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Grade 8 April 2016 Draft DRAFT New Louisiana Standards for 2016 2017 Correlation to Eureka Math Page 1 Grade 8 Mathematics The majority
PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form
 PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form Course Title: Math 8 Course Number/CBED Number: Grade Levels: Length of Course: Eighth Grade One Year Credit: 10 Meets Graduation Requirements:
PLEASANTON UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT 8 Course Outline Form Course Title: Math 8 Course Number/CBED Number: Grade Levels: Length of Course: Eighth Grade One Year Credit: 10 Meets Graduation Requirements:
Algebra 1 Scope and Sequence Standards Trajectory
 Algebra 1 Scope and Sequence Standards Trajectory Course Name Algebra 1 Grade Level High School Conceptual Category Domain Clusters Number and Quantity Algebra Functions Statistics and Probability Modeling
Algebra 1 Scope and Sequence Standards Trajectory Course Name Algebra 1 Grade Level High School Conceptual Category Domain Clusters Number and Quantity Algebra Functions Statistics and Probability Modeling
Math 2 Unit 5: Comparing Functions and Modeling
 Approximate Time Frame: 2-3 Weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1, students studied linear and exponential functions and compared them in a modeling context. Students looked at multiple representations
Approximate Time Frame: 2-3 Weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1, students studied linear and exponential functions and compared them in a modeling context. Students looked at multiple representations
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE 8 th Grade
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester
 GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester Unit 1 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity MGSE8.G.1 MGSE8.G.2 MGSE8.G.3 MGSE8.G.4 MGSE8.G.5 Unit 2 Exponents MGSE8.EE1
GSE Fulton Eighth Grade Advanced Curriculum Map 1 st Semester 2 nd Semester Unit 1 Transformations, Congruence and Similarity MGSE8.G.1 MGSE8.G.2 MGSE8.G.3 MGSE8.G.4 MGSE8.G.5 Unit 2 Exponents MGSE8.EE1
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map. Mathematics. GSE 8 th Grade
 Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Georgia Standards of Excellence Curriculum Map Mathematics GSE 8 th Grade These materials are for nonprofit educational purposes only. Any other use may constitute copyright infringement. GSE Eighth Grade
Lesson 7: Literal Equations, Inequalities, and Absolute Value
 , and Absolute Value In this lesson, we first look at literal equations, which are equations that have more than one variable. Many of the formulas we use in everyday life are literal equations. We then
, and Absolute Value In this lesson, we first look at literal equations, which are equations that have more than one variable. Many of the formulas we use in everyday life are literal equations. We then
Mathematics. Standards Plus. Grade COMMON CORE INTERVENTION SAMPLER
 Mathematics Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Grade 7 SAMPLER Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Available for Grades 1-8 Language Arts and Math Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Mathematics
Mathematics Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Grade 7 SAMPLER Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Available for Grades 1-8 Language Arts and Math Standards Plus COMMON CORE INTERVENTION Mathematics
BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide
 BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
BPS PreAlgebra Math Planning Guide 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Mathematical Practice Standards: Vehicle for All Content 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly
Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities
 - Think About a Plan Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities Skiing Sketch a graph of each situation. Are the graphs the same? Explain. a. your speed as you travel from the bottom of a ski slope to the top
- Think About a Plan Using Graphs to Relate Two Quantities Skiing Sketch a graph of each situation. Are the graphs the same? Explain. a. your speed as you travel from the bottom of a ski slope to the top
Math 3 Unit 5: Polynomial and Rational Representations and Modeling
 Approximate Time Frame: 5-6 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1 and 2, students worked with one-variable equations. They studied linear, exponential and quadratic functions and compared them
Approximate Time Frame: 5-6 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: In Math 1 and 2, students worked with one-variable equations. They studied linear, exponential and quadratic functions and compared them
Eighth Grade Algebra I Mathematics
 Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Description The Appleton Area School District middle school mathematics program provides students opportunities to develop mathematical skills in thinking and applying problem-solving strategies. The framework
Mathematics Pacing. Instruction 9/9-10/18/13 Assessment 10/21-10/25/13 Remediation 10/28 11/1/13. # STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES CCSS Resources
 CONTENT AREA: Grade 8 Mathematics Unit 1 Instruction 9/9-10/18/13 Assessment 10/21-10/25/13 Remediation 10/28 11/1/13 UNIT NAME: The Number System # STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES CCSS Resources 1 2 3 4 5
CONTENT AREA: Grade 8 Mathematics Unit 1 Instruction 9/9-10/18/13 Assessment 10/21-10/25/13 Remediation 10/28 11/1/13 UNIT NAME: The Number System # STUDENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES CCSS Resources 1 2 3 4 5
Midterm: Wednesday, January 23 rd at 8AM Midterm Review
 Name: Algebra 1 CC Period: Midterm: Wednesday, January 23 rd at 8AM Midterm Review Unit 1: Building Blocks of Algebra Number Properties (Distributive, Commutative, Associative, Additive, Multiplicative)
Name: Algebra 1 CC Period: Midterm: Wednesday, January 23 rd at 8AM Midterm Review Unit 1: Building Blocks of Algebra Number Properties (Distributive, Commutative, Associative, Additive, Multiplicative)
Moving Straight Ahead - Unit Test Review Sheet
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Moving Straight Ahead - Unit Test Review Sheet Short Answer 1. Brent's Video Shack charges $1.50 to rent a video game for a night. Mr. Buck's Entertainments opens a new store in
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Moving Straight Ahead - Unit Test Review Sheet Short Answer 1. Brent's Video Shack charges $1.50 to rent a video game for a night. Mr. Buck's Entertainments opens a new store in
CCSS MIDDLE SCHOOL PROPORTIONAL REASONING: IT S A BIG DEAL
 CCSS MIDDLE SCHOOL PROPORTIONAL REASONING: IT S A BIG DEAL Presented by Cynthia Raff cynthia@mathandteaching.org Mark Goldstein mark@mathandteaching.org The Center for Mathematics and Teaching, Inc. www.mathandteaching.org
CCSS MIDDLE SCHOOL PROPORTIONAL REASONING: IT S A BIG DEAL Presented by Cynthia Raff cynthia@mathandteaching.org Mark Goldstein mark@mathandteaching.org The Center for Mathematics and Teaching, Inc. www.mathandteaching.org
Fairfield Public Schools
 Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 7 Pre-Algebra 7 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 7 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 7 course, instructional time should focus on five critical
Mathematics Fairfield Public Schools Pre-Algebra 7 Pre-Algebra 7 BOE Approved 05/21/2013 1 PRE-ALGEBRA 7 Critical Areas of Focus In the Pre-Algebra 7 course, instructional time should focus on five critical
Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum
 Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in
Mathematics 8 Essential Curriculum The Mathematical Practices The Standards for Mathematical Practice describe varieties of expertise that mathematics educators at all levels should seek to develop in
Grade 8 + DIGITAL. EL Strategies. DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3. Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print
 Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 8 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Standards PLUS Flexible Supplemental K-8 ELA & Math Online & Print Grade 8 SAMPLER Mathematics EL Strategies DOK 1-4 RTI Tiers 1-3 15-20 Minute Lessons Assessments Consistent with CA Testing Technology
Unit 2 Linear Functions and Systems of Linear Functions Algebra 1
 Number of Days: MS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 HS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Unit 2 builds upon students prior knowledge of linear models. Students learn function notation and develop
Number of Days: MS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 HS 44 10/16/17 12/22/17 Unit Goals Stage 1 Unit Description: Unit 2 builds upon students prior knowledge of linear models. Students learn function notation and develop
Sequence of Algebra AB SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards
 Sequence of Algebra AB SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations and Inequalities Ch. 1 Solving Linear Equations
Sequence of Algebra AB SDC Units Aligned with the California Standards Year at a Glance Unit Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Textbook Chapters Dates 1. Equations and Inequalities Ch. 1 Solving Linear Equations
Unit 4: Inequalities. Inequality Symbols. Algebraic Inequality. Compound Inequality. Interval Notation
 Section 4.1: Linear Inequalities Section 4.2: Solving Linear Inequalities Section 4.3: Solving Inequalities Applications Section 4.4: Compound Inequalities Section 4.5: Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
Section 4.1: Linear Inequalities Section 4.2: Solving Linear Inequalities Section 4.3: Solving Inequalities Applications Section 4.4: Compound Inequalities Section 4.5: Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT
 HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Algebra I Semester 2 (Quarter 3) Module 3: Linear and Exponential Functions (35 days) Topic A: Linear and Exponential Sequences (7 days)
HIGLEY UNIFIED SCHOOL DISTRICT INSTRUCTIONAL ALIGNMENT 8 th Grade Algebra I Semester 2 (Quarter 3) Module 3: Linear and Exponential Functions (35 days) Topic A: Linear and Exponential Sequences (7 days)
8 th Grade Domain 2: Algebra and Functions (40%) Sara
 8 th Grade Domain 2: Algebra and Functions (40%) 1. Tara creates a budget for her weekly expenses. The graph shows how much money is in the account at different times. Find the slope of the line and tell
8 th Grade Domain 2: Algebra and Functions (40%) 1. Tara creates a budget for her weekly expenses. The graph shows how much money is in the account at different times. Find the slope of the line and tell
Relations and Functions
 Algebra 1, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Relations and Functions Overview Number of instructional days: 10 (2 assessments) (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Content to be learned Demonstrate conceptual understanding of linear
Algebra 1, Quarter 2, Unit 2.1 Relations and Functions Overview Number of instructional days: 10 (2 assessments) (1 day = 45 60 minutes) Content to be learned Demonstrate conceptual understanding of linear
Mathematics Task Arcs
 Overview of Mathematics Task Arcs: Mathematics Task Arcs A task arc is a set of related lessons which consists of eight tasks and their associated lesson guides. The lessons are focused on a small number
Overview of Mathematics Task Arcs: Mathematics Task Arcs A task arc is a set of related lessons which consists of eight tasks and their associated lesson guides. The lessons are focused on a small number
Willmar Public Schools Curriculum Map
 Note: Problem Solving Algebra Prep is an elective credit. It is not a math credit at the high school as its intent is to help students prepare for Algebra by providing students with the opportunity to
Note: Problem Solving Algebra Prep is an elective credit. It is not a math credit at the high school as its intent is to help students prepare for Algebra by providing students with the opportunity to
The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course:
 Math 8 Curriculum Overview The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1. Make
Math 8 Curriculum Overview The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1. Make
MATH GRADE 8 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient
 MATH GRADE 8 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient The Level 1 student is below proficient The Level 2 student is approaching The Level 3 student is proficient
MATH GRADE 8 PLD Standard Below Proficient Approaching Proficient Proficient Highly Proficient The Level 1 student is below proficient The Level 2 student is approaching The Level 3 student is proficient
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations. Unit Calendar
 Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
Algebra 1 Spencer Unit 4 Notes: Inequalities and Graphing Linear Equations Unit Calendar Date Topic Homework Nov 5 (A ) 6.1 Solving Linear Inequalities +/- 6.2 Solving Linear Inequalities x/ 6.3 Solving
6th Grade Unit 3 Expressions and Equations
 6th Grade Unit 3 Expressions and Equations NJ 2017 Student Learning Standards: Mathematics Grade 6 A. Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. 1. Write and evaluate
6th Grade Unit 3 Expressions and Equations NJ 2017 Student Learning Standards: Mathematics Grade 6 A. Apply and extend previous understandings of arithmetic to algebraic expressions. 1. Write and evaluate
Five District Partnership 1
 Five District Partnership 1 Grade 8 Math Year-Long Plan Overview Standards Shorthand Description Sept-Oct Nov-Dec Jan-Feb Mar-Apr May-June 8.NS.1 Rational numbers & decimal expansions X 8.NS.2 Irrational
Five District Partnership 1 Grade 8 Math Year-Long Plan Overview Standards Shorthand Description Sept-Oct Nov-Dec Jan-Feb Mar-Apr May-June 8.NS.1 Rational numbers & decimal expansions X 8.NS.2 Irrational
Danville District #118 Mathematics Transitional Algebra (PARCC Framework version) Curriculum and Scope and Sequence
 The eight Mathematical Practices will be incorporated throughout the course: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments
The eight Mathematical Practices will be incorporated throughout the course: 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 3. Construct viable arguments
In this lesson, students model filling a rectangular
 NATIONAL MATH + SCIENCE INITIATIVE Mathematics Fill It Up, Please Part III Level Algebra or Math at the end of a unit on linear functions Geometry or Math as part of a unit on volume to spiral concepts
NATIONAL MATH + SCIENCE INITIATIVE Mathematics Fill It Up, Please Part III Level Algebra or Math at the end of a unit on linear functions Geometry or Math as part of a unit on volume to spiral concepts
Bermudian Springs School District PA Core Standards Math Framework Seventh Grade Math and Pre-Algebra
 Bermudian Springs School District PA Core Standards Math Framework Seventh Grade Math and Pre-Algebra Introduction Bermudian Springs School District, in partnership with all stakeholders, recognizes the
Bermudian Springs School District PA Core Standards Math Framework Seventh Grade Math and Pre-Algebra Introduction Bermudian Springs School District, in partnership with all stakeholders, recognizes the
FOSS and Common Core Math Grade 8
 FOSS and Common Core Math Grade 8 Contents Introduction... K1 Ratios and Proportional Relationships for Grades 6 7... K4 The Number System for Grades 6 7... K8 Expressions and Equations for Grades 6 8...
FOSS and Common Core Math Grade 8 Contents Introduction... K1 Ratios and Proportional Relationships for Grades 6 7... K4 The Number System for Grades 6 7... K8 Expressions and Equations for Grades 6 8...
Accelerated Traditional Pathway: Accelerated 7 th Grade
 Accelerated Traditional Pathway: Accelerated 7 th Grade This course differs from the non-accelerated 7 th Grade course in that it contains content from 8 th grade. While coherence is retained, in that
Accelerated Traditional Pathway: Accelerated 7 th Grade This course differs from the non-accelerated 7 th Grade course in that it contains content from 8 th grade. While coherence is retained, in that
Algebra 1. Mathematics Course Syllabus
 Mathematics Algebra 1 2017 2018 Course Syllabus Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 8 or Foundations for Algebra Credits: 1.0 Math, Merit The fundamental purpose of this course is to formalize
Mathematics Algebra 1 2017 2018 Course Syllabus Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 8 or Foundations for Algebra Credits: 1.0 Math, Merit The fundamental purpose of this course is to formalize
Mathematics. Algebra Course Syllabus
 Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 8 or Foundations for Algebra Credits: 1.0 Math, Merit Mathematics Algebra 1 2018 2019 Course Syllabus Algebra I formalizes and extends the mathematics students
Prerequisites: Successful completion of Math 8 or Foundations for Algebra Credits: 1.0 Math, Merit Mathematics Algebra 1 2018 2019 Course Syllabus Algebra I formalizes and extends the mathematics students
FUNCTIONS Families of Functions Common Core Standards F-LE.A.1 Distinguish between situations that can be
 M Functions, Lesson 5, Families of Functions (r. 2018) FUNCTIONS Families of Functions Common Core Standards F-LE.A.1 Distinguish between situations that can be modeled with linear functions and with exponential
M Functions, Lesson 5, Families of Functions (r. 2018) FUNCTIONS Families of Functions Common Core Standards F-LE.A.1 Distinguish between situations that can be modeled with linear functions and with exponential
PLUMSTED TOWNSHIP SCHOOL DISTRICT Aligned to Common Core State Standards Course Title: Eighth Grade Mathematics
 Course Title: Eighth Grade Mathematics - Course 3 [Units 1-5] Pre-Algebra [Course II Units 2-5 + Course III Units 1-5] Content Area: Mathematics Grade Level(s): Eighth Course Description: This course is
Course Title: Eighth Grade Mathematics - Course 3 [Units 1-5] Pre-Algebra [Course II Units 2-5 + Course III Units 1-5] Content Area: Mathematics Grade Level(s): Eighth Course Description: This course is
Unit 1: Ratios & Proportionality
 Approximate time frame: 4 5 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Students in Grade 6 learn the concepts of ratio and unit rate as well as the precise mathematical language used to describe these relationships.
Approximate time frame: 4 5 weeks Connections to Previous Learning: Students in Grade 6 learn the concepts of ratio and unit rate as well as the precise mathematical language used to describe these relationships.
Sequenced Units for Arizona s College and Career Ready Standards MA27 Algebra I
 Sequenced Units for Arizona s College and Career Ready Standards MA27 Algebra I Year at a Glance Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1: Solving Linear Equations (12 days) Unit 2: Solving Linear Inequalities (12
Sequenced Units for Arizona s College and Career Ready Standards MA27 Algebra I Year at a Glance Semester 1 Semester 2 Unit 1: Solving Linear Equations (12 days) Unit 2: Solving Linear Inequalities (12
Unit 1.1 Equations. Quarter 1. Section Days Lesson Notes. Algebra 1 Unit & Lesson Overviews Mathematics Variables and Expressions
 Unit 1.1 Equations Quarter 1 Section Days Lesson Notes 1.1 1 Variables and Expressions 1.2 1.3 1 Solving Equations by Addition, Subtraction, Multiplying or Dividing 1.4 1 Solving Two-Step and Multi-Step
Unit 1.1 Equations Quarter 1 Section Days Lesson Notes 1.1 1 Variables and Expressions 1.2 1.3 1 Solving Equations by Addition, Subtraction, Multiplying or Dividing 1.4 1 Solving Two-Step and Multi-Step
8th Grade Common Core Math
 8th Grade Common Core Math Booklet 5 Functions Part 2 One of the Main Idea of Functions: Use functions to model relationships between quantities What are functions? Functions are like machines. You give
8th Grade Common Core Math Booklet 5 Functions Part 2 One of the Main Idea of Functions: Use functions to model relationships between quantities What are functions? Functions are like machines. You give
Grade 7 Overview. Mathematical Practices. Ratios and Proportional Relationships
 Mathematics Grade 7 In Grade 7, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) developing understanding of and applying proportional relationships; (2) developing understanding of operations
Mathematics Grade 7 In Grade 7, instructional time should focus on four critical areas: (1) developing understanding of and applying proportional relationships; (2) developing understanding of operations
TASK: WHEN IS IT NOT EQUAL?
 TASK: WHEN IS IT NOT EQUAL? ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What strategies can I use to help me understand and represent real situations using inequalities? How can I write, interpret and manipulate inequalities?
TASK: WHEN IS IT NOT EQUAL? ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What strategies can I use to help me understand and represent real situations using inequalities? How can I write, interpret and manipulate inequalities?
GRADES 7-8: ALGEBRA 1 CURRICULUM FRAMEWORKS
 NUMBER AND OPERATION (encompasses 6-8 MCA test items) Standard 1: Read, write, compare, classify and represent real numbers, and use them to solve problems in various contexts. (encompasses 6-8 MCA test
NUMBER AND OPERATION (encompasses 6-8 MCA test items) Standard 1: Read, write, compare, classify and represent real numbers, and use them to solve problems in various contexts. (encompasses 6-8 MCA test
Math 115 Syllabus (Spring 2017 Edition) By: Elementary Courses Committee Textbook: Intermediate Algebra by Aufmann & Lockwood, 9th Edition
 Math 115 Syllabus (Spring 2017 Edition) By: Elementary Courses Committee Textbook: Intermediate Algebra by Aufmann & Lockwood, 9th Edition Students have the options of either purchasing the loose-leaf
Math 115 Syllabus (Spring 2017 Edition) By: Elementary Courses Committee Textbook: Intermediate Algebra by Aufmann & Lockwood, 9th Edition Students have the options of either purchasing the loose-leaf
Unit 5: Proportions and Lines. Activities: Resources:
 Timeline: 2 nd nine weeks Vocabulary: Slope Formula, Rate of Change, Y Intercept, Slope intercept form, Vertical, Horizontal Linear Function Slope Slope of a Line Unit 5: Proportions and Lines New State
Timeline: 2 nd nine weeks Vocabulary: Slope Formula, Rate of Change, Y Intercept, Slope intercept form, Vertical, Horizontal Linear Function Slope Slope of a Line Unit 5: Proportions and Lines New State
Common Core Math Units Grade 8
 Sequenced Units for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics Prior to, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between
Sequenced Units for the Common Core State Standards in Mathematics Prior to, students have written and interpreted expressions, solved equations and inequalities, explored quantitative relationships between
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie. Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks
 Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by David Rennie Adapted from the Georgia Department of Education Frameworks Georgia Common Core GPS Coordinate Algebra Supplement: Unit 2 by
