Università degli Studi di Bari. mechanics 1. Load system determination. Joint load. Stress-strain distribution. Biological response 2/45 3/45
|
|
|
- James Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Università degli Studi di Bari mechanics 1 Load system determination Joint load Stress-strain distribution Biological response 2/45 3/45
2 ? 4/45 The human body machine Energy transformation Work development 5/45 Bodies interaction Movement external effects Deformation internal effects 6/45
3 Material chemical bond strenght 7/45 Material properties mechanical structure of materials macrostructure 8/45 macrostructure Material is: continuous and homogeneous mechanical described by its average properties which are obtained from specimen evaluation isotropic 9/45
4 Mechanics Statics - study of systems that are in a constant state of motion, whether at rest with no motion or moving at a constant velocity without acceleration Statics involves all forces acting on the body being in balance resulting in the body being in equilibrium 10/45 The body The body is a system modelled as: point Kinetics study rigid body Static study deformable body Stress strain description Body mass 11/45 Newton s 1 st Law of Motion An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 12/45
5 load Load is the parameter which defines the effects of bodies interaction. It is a vector (four features) a quantity possessing magnitude, direction, sense and one application point A D E B C 13/45 F Load system; Stress strain distribution; Behaviour of material. Aims A D E B C E 14/45 Vector magnitude, direction, sense and one application point 15/45
6 Components of Force The magnitude or how much force is applied; direction: The way in which the force is applied; The point of application : Where the force is applied on the body; the sense of a vector is specified by the order of two points on a line parallel to the vector 16/45 Components of Force y Fx F Fy o x 17/45 Components of Force F 1 F 2 F 1 R F 1 R = F 1 + F 2 F i F n F 2 18/45
7 Newton s 2 nd Law of Motion A force or torque acting on a body will produce an acceleration proportional to the force or torque F = ma M= I α 19/45 Newton s 3 rd Law of Motion For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction (torque and/or force) 20/45 load static dynamic distributed concentrated 21/45
8 Moments of Force (Torque) The turning effect of a force is known as the moment. It is the product of the force multiplied by the perpendicular distance from the line of action of the force to the pivot or point where the object will turn. Momentum (quantity( of motion) - equal to mass times velocity F d M = F d P 22/45 Moments of Force 23/45 transport moment P C = M = F d F d P F C P global effect of F in P 24/45
9 force effects External movement force translation moment rotation Internal shape changement shape changement strain stress force linear changement moment angular changement 25/45 force effects External movement rigid body Internal shape changement deformable body 26/45 27/45
10 Rigid body Rigid body: a system of mass points where the distances between all pairs of points remain constant independently from the load applied system. If there are N free particles, there are 3N degrees of freedom For a rigid body, the number of degrees of freedom is reduced by the constraints expressed in the form: r = ij c ij How many independent coordinates does a rigid body have? 28/45 degrees of freedom independent coordinates = degrees of freedom (d.o.f.) Y A X Z A rigid body into the space has 6 d.o.f. : 3 translationals and 3 rotationals 29/45 constraints something that limits or restricts someone or something A B In order to cancel each d.o.f. a specific constraint have to be implemented 30/45
11 constraints A reaction force is developed when a constraint is active A B 31/45 constraint reaction forces? constraints A 32/45 constraints LABILE ISOSTATIC IPERSTATIC d.o.f. (3 in the plan - 6 in the space) 33/45
12 constraints ISOSTATIC BODY When constraints number is equal to d.o.f. without any omission or repetition 34/45 Ball-and-socket joint 35/45 Hinge joint 36/45
13 37/45 constraints
Dynamics. Dynamics of mechanical particle and particle systems (many body systems)
 Dynamics Dynamics of mechanical particle and particle systems (many body systems) Newton`s first law: If no net force acts on a body, it will move on a straight line at constant velocity or will stay at
Dynamics Dynamics of mechanical particle and particle systems (many body systems) Newton`s first law: If no net force acts on a body, it will move on a straight line at constant velocity or will stay at
Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis
 6-1 Introduction 6-2Newton s Law and Conservation of Momentum 6-3 Choosing a Control Volume 6-4 Forces Acting on a Control Volume 6-5Linear Momentum Equation 6-6 Angular Momentum 6-7 The Second Law of
6-1 Introduction 6-2Newton s Law and Conservation of Momentum 6-3 Choosing a Control Volume 6-4 Forces Acting on a Control Volume 6-5Linear Momentum Equation 6-6 Angular Momentum 6-7 The Second Law of
Methods of Analysis. Force or Flexibility Method
 INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix. Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed
 Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
PART I ORTHOPAEDIC BIOMATERIALS AND THEIR PROPERTIES
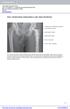 PT I OTHOPEDIC BIOMTEILS ND THEI POPETIES cetabular Cup: Polyethylene (polymer) emoral Head: Ceramic Bone Cement: Polymer emoral Stem: Metal emur: Composite emur + Stem: Composite Just as there are three
PT I OTHOPEDIC BIOMTEILS ND THEI POPETIES cetabular Cup: Polyethylene (polymer) emoral Head: Ceramic Bone Cement: Polymer emoral Stem: Metal emur: Composite emur + Stem: Composite Just as there are three
Structural Dynamics Lecture 4. Outline of Lecture 4. Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems. Formulation of Equations of Motions. Undamped Eigenvibrations.
 Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
Outline of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Systems Formulation of Equations of Motions. Newton s 2 nd Law Applied to Free Masses. D Alembert s Principle. Basic Equations of Motion for Forced Vibrations of Linear
How Can Motion be Described? and Explained?
 How Can Motion be Described? and Explained? Lesson 14: Torque and the Stability of Structures Stable Structures Explain why structures should be stable. What are the conditions for a structure to be stable?
How Can Motion be Described? and Explained? Lesson 14: Torque and the Stability of Structures Stable Structures Explain why structures should be stable. What are the conditions for a structure to be stable?
Torque and Rotation Lecture 7
 Torque and Rotation Lecture 7 ˆ In this lecture we finally move beyond a simple particle in our mechanical analysis of motion. ˆ Now we consider the so-called rigid body. Essentially, a particle with extension
Torque and Rotation Lecture 7 ˆ In this lecture we finally move beyond a simple particle in our mechanical analysis of motion. ˆ Now we consider the so-called rigid body. Essentially, a particle with extension
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery
 WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
WEEK 1 Dynamics of Machinery References Theory of Machines and Mechanisms, J.J. Uicker, G.R.Pennock ve J.E. Shigley, 2003 Makine Dinamiği, Prof. Dr. Eres SÖYLEMEZ, 2013 Uygulamalı Makine Dinamiği, Jeremy
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics
 Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
Chapter 9 TORQUE & Rotational Kinematics This motionless person is in static equilibrium. The forces acting on him add up to zero. Both forces are vertical in this case. This car is in dynamic equilibrium
UNIT IV FLEXIBILTY AND STIFFNESS METHOD
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : SA-II (13A01505) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : SA-II (13A01505) Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & I-Sem Course & Branch: B.Tech
Chapter 3. Inertia. Force. Free Body Diagram. Net Force. Mass. quantity of matter composing a body represented by m. units are kg
 Chapter 3 Mass quantity of matter composing a body represented by m Kinetic Concepts for Analyzing Human Motion units are kg Inertia tendency to resist change in state of motion proportional to mass has
Chapter 3 Mass quantity of matter composing a body represented by m Kinetic Concepts for Analyzing Human Motion units are kg Inertia tendency to resist change in state of motion proportional to mass has
Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body
 Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of a free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve
Chapter 5: Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives To develop the equations of equilibrium for a rigid body. To introduce the concept of a free-body diagram for a rigid body. To show how to solve
Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis of Flow Systems
 Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis of Flow Systems Introduction Fluid flow problems can be analyzed using one of three basic approaches: differential, experimental, and integral (or control volume). In Chap.
Chapter 6: Momentum Analysis of Flow Systems Introduction Fluid flow problems can be analyzed using one of three basic approaches: differential, experimental, and integral (or control volume). In Chap.
Engineering Mechanics Objective module 1 with solutions: A K GAIKAR
 Engineering Mechanics Objective module 1 with solutions: A K GAIKAR 1. What is the branch of engineering mechanics which refers to the study of stationary rigid body? A. Statics B. Kinetics C. Kinematics
Engineering Mechanics Objective module 1 with solutions: A K GAIKAR 1. What is the branch of engineering mechanics which refers to the study of stationary rigid body? A. Statics B. Kinetics C. Kinematics
Lecture 14. Rotational dynamics Torque. Give me a lever long enough and a fulcrum on which to place it, and I shall move the world.
 Lecture 14 Rotational dynamics Torque Give me a lever long enough and a fulcrum on which to place it, and I shall move the world. Archimedes, 87 1 BC EXAM Tuesday March 6, 018 8:15 PM 9:45 PM Today s Topics:
Lecture 14 Rotational dynamics Torque Give me a lever long enough and a fulcrum on which to place it, and I shall move the world. Archimedes, 87 1 BC EXAM Tuesday March 6, 018 8:15 PM 9:45 PM Today s Topics:
Three-Dimensional Biomechanical Analysis of Human Movement
 Three-Dimensional Biomechanical Analysis of Human Movement Anthropometric Measurements Motion Data Acquisition Force Platform Body Mass & Height Biomechanical Model Moments of Inertia and Locations of
Three-Dimensional Biomechanical Analysis of Human Movement Anthropometric Measurements Motion Data Acquisition Force Platform Body Mass & Height Biomechanical Model Moments of Inertia and Locations of
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents:
 PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
PHYS 1114, Lecture 33, April 10 Contents: 1 This class is o cially cancelled, and has been replaced by the common exam Tuesday, April 11, 5:30 PM. A review and Q&A session is scheduled instead during class
Lecture Outline Chapter 11. Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outline Chapter 11 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium Units of Chapter 11 Torque Torque and Angular Acceleration Zero Torque and Static
Lecture Outline Chapter 11 Physics, 4 th Edition James S. Walker Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium Units of Chapter 11 Torque Torque and Angular Acceleration Zero Torque and Static
Axis Balanced Forces Centripetal force. Change in velocity Circular Motion Circular orbit Collision. Conservation of Energy
 When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
General Definition of Torque, final. Lever Arm. General Definition of Torque 7/29/2010. Units of Chapter 10
 Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Rotational & Rigid-Body Mechanics. Lectures 3+4
 Rotational & Rigid-Body Mechanics Lectures 3+4 Rotational Motion So far: point objects moving through a trajectory. Next: moving actual dimensional objects and rotating them. 2 Circular Motion - Definitions
Rotational & Rigid-Body Mechanics Lectures 3+4 Rotational Motion So far: point objects moving through a trajectory. Next: moving actual dimensional objects and rotating them. 2 Circular Motion - Definitions
Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW
 Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
Rotation of Rigid Objects
 Notes 12 Rotation and Extended Objects Page 1 Rotation of Rigid Objects Real objects have "extent". The mass is spread out over discrete or continuous positions. THERE IS A DISTRIBUTION OF MASS TO "AN
Notes 12 Rotation and Extended Objects Page 1 Rotation of Rigid Objects Real objects have "extent". The mass is spread out over discrete or continuous positions. THERE IS A DISTRIBUTION OF MASS TO "AN
Table of Contents Lecture Topic Slides
 Mechanics 100 Table of Contents ecture Topic Slides 1 Fundamental Concepts 4 12 2 Force Vectors 14-20 3 Equilibrium Of Particles 22-26 4 Force Resultants 28-38 5 Equilibrium Of Rigid Bodies 40-52 6 Structural
Mechanics 100 Table of Contents ecture Topic Slides 1 Fundamental Concepts 4 12 2 Force Vectors 14-20 3 Equilibrium Of Particles 22-26 4 Force Resultants 28-38 5 Equilibrium Of Rigid Bodies 40-52 6 Structural
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS OPTION B-1A: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Essential Idea: The basic laws of mechanics have an extension when equivalent principles are applied to rotation. Actual
DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS OPTION B-1A: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Essential Idea: The basic laws of mechanics have an extension when equivalent principles are applied to rotation. Actual
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Structural Dynamics Prof. P. Banerji Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture - 1 Introduction
 Structural Dynamics Prof. P. Banerji Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 1 Introduction Hello, I am Pradipta Banerji from the department of civil engineering,
Structural Dynamics Prof. P. Banerji Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture - 1 Introduction Hello, I am Pradipta Banerji from the department of civil engineering,
Rotational Dynamics. A wrench floats weightlessly in space. It is subjected to two forces of equal and opposite magnitude: Will the wrench accelerate?
 Rotational Dynamics A wrench floats weightlessly in space. It is subjected to two forces of equal and opposite magnitude: Will the wrench accelerate? A. yes B. no C. kind of? Rotational Dynamics 10.1-3
Rotational Dynamics A wrench floats weightlessly in space. It is subjected to two forces of equal and opposite magnitude: Will the wrench accelerate? A. yes B. no C. kind of? Rotational Dynamics 10.1-3
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
E 490 FE Exam Prep. Engineering Mechanics
 E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
E 490 FE Exam Prep Engineering Mechanics 2008 E 490 Course Topics Statics Newton s Laws of Motion Resultant Force Systems Moment of Forces and Couples Equilibrium Pulley Systems Trusses Centroid of an
*Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units
 INTRODUCTION *Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under
INTRODUCTION *Definition of Mechanics *Basic Concepts *Newton s Laws *Units Mechanics may be defined as the physical science which describes and predicts the conditions of rest or motion of bodies under
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
General Physics I. Lecture 9: Vector Cross Product. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 9: Vector Cross Product Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Outline Examples of the rotation of a rigid object about a fixed axis Force/torque
General Physics I Lecture 9: Vector Cross Product Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Outline Examples of the rotation of a rigid object about a fixed axis Force/torque
AP Physics QUIZ Chapters 10
 Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium
 Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Mechanical Properties of Materials
 Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
Chapter 11. Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
AP Physics 1 Rotational Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Rotational Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A spinning ice skater on extremely smooth ice is able
AP Physics 1 Rotational Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A spinning ice skater on extremely smooth ice is able
Upthrust and Archimedes Principle
 1 Upthrust and Archimedes Principle Objects immersed in fluids, experience a force which tends to push them towards the surface of the liquid. This force is called upthrust and it depends on the density
1 Upthrust and Archimedes Principle Objects immersed in fluids, experience a force which tends to push them towards the surface of the liquid. This force is called upthrust and it depends on the density
FLEXIBILITY METHOD FOR INDETERMINATE FRAMES
 UNIT - I FLEXIBILITY METHOD FOR INDETERMINATE FRAMES 1. What is meant by indeterminate structures? Structures that do not satisfy the conditions of equilibrium are called indeterminate structure. These
UNIT - I FLEXIBILITY METHOD FOR INDETERMINATE FRAMES 1. What is meant by indeterminate structures? Structures that do not satisfy the conditions of equilibrium are called indeterminate structure. These
Chapter 8. Rotational Motion
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of
Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions. Newton s second law in terms of momentum:
 linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
Torques and Static Equilibrium
 Torques and Static Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Archimedes, Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor and astronomer, was widely regarded as the leading scientist of the ancient world. He made a study
Torques and Static Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Archimedes, Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, inventor and astronomer, was widely regarded as the leading scientist of the ancient world. He made a study
Laith Batarseh. internal forces
 Next Previous 1/8/2016 Chapter seven Laith Batarseh Home End Definitions When a member is subjected to external load, an and/or moment are generated inside this member. The value of the generated internal
Next Previous 1/8/2016 Chapter seven Laith Batarseh Home End Definitions When a member is subjected to external load, an and/or moment are generated inside this member. The value of the generated internal
Static Equilibrium. University of Arizona J. H. Burge
 Static Equilibrium Static Equilibrium Definition: When forces acting on an object which is at rest are balanced, then the object is in a state of static equilibrium. - No translations - No rotations In
Static Equilibrium Static Equilibrium Definition: When forces acting on an object which is at rest are balanced, then the object is in a state of static equilibrium. - No translations - No rotations In
2/28/2006 Statics ( F.Robilliard) 1
 2/28/2006 Statics (.Robilliard) 1 Extended Bodies: In our discussion so far, we have considered essentially only point masses, under the action of forces. We now broaden our considerations to extended
2/28/2006 Statics (.Robilliard) 1 Extended Bodies: In our discussion so far, we have considered essentially only point masses, under the action of forces. We now broaden our considerations to extended
MCAT FastPass Study Guide
 Keep your studying focused and high-yield with the ultimate MCAT study guide. This comprehensive guide includes all of the most important facts, figures, formulas, and concepts you need to master the new
Keep your studying focused and high-yield with the ultimate MCAT study guide. This comprehensive guide includes all of the most important facts, figures, formulas, and concepts you need to master the new
Vector Mechanics: Statics
 PDHOnline Course G492 (4 PDH) Vector Mechanics: Statics Mark A. Strain, P.E. 2014 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org www.pdhcenter.com
PDHOnline Course G492 (4 PDH) Vector Mechanics: Statics Mark A. Strain, P.E. 2014 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088 www.pdhonline.org www.pdhcenter.com
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction
 East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Special Topics: Physics of Movement (Biomechanics) Course(s): Special Topics: Physics of Movement (Biomechanics) Grades: 10-12 Department:
East Penn School District Curriculum and Instruction Curriculum for: Special Topics: Physics of Movement (Biomechanics) Course(s): Special Topics: Physics of Movement (Biomechanics) Grades: 10-12 Department:
Physics 125, Spring 2006 Monday, May 15, 8:00-10:30am, Old Chem 116. R01 Mon. 12:50 R02 Wed. 12:50 R03 Mon. 3:50. Final Exam
 Monday, May 15, 8:00-10:30am, Old Chem 116 Name: Recitation section (circle one) R01 Mon. 12:50 R02 Wed. 12:50 R03 Mon. 3:50 Closed book. No notes allowed. Any calculators are permitted. There are no trick
Monday, May 15, 8:00-10:30am, Old Chem 116 Name: Recitation section (circle one) R01 Mon. 12:50 R02 Wed. 12:50 R03 Mon. 3:50 Closed book. No notes allowed. Any calculators are permitted. There are no trick
Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh
 Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.3 1 Introduction to Lagrangian Mechanics Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh University of Pennsylvania Robo3x-1.3 2 Analytical Mechanics Aristotle Galileo Bernoulli
Video 2.1a Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.3 1 Introduction to Lagrangian Mechanics Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh University of Pennsylvania Robo3x-1.3 2 Analytical Mechanics Aristotle Galileo Bernoulli
STATICS--AN INVESTIGATION OF FORCES
 STTIS--N INVESTIGTION O ORES Two areas of study to investigate forces. Statics where the forces acting on a material are balanced so that the material is either stationary or in uniform motion. or fluid
STTIS--N INVESTIGTION O ORES Two areas of study to investigate forces. Statics where the forces acting on a material are balanced so that the material is either stationary or in uniform motion. or fluid
Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium Units of Chapter 11 Torque Torque and Angular Acceleration Zero Torque and Static Equilibrium Center of Mass and Balance Dynamic Applications of Torque
Chapter 11 Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium Units of Chapter 11 Torque Torque and Angular Acceleration Zero Torque and Static Equilibrium Center of Mass and Balance Dynamic Applications of Torque
Introduction to Dynamics
 Introduction to Dynamics Dynamics is that branch of mechanics which deals with the motion of bodies under the action of forces. Dynamics has two distinct parts: kinematics and kinetics. Kinematics is the
Introduction to Dynamics Dynamics is that branch of mechanics which deals with the motion of bodies under the action of forces. Dynamics has two distinct parts: kinematics and kinetics. Kinematics is the
Rotation of Rigid Objects
 Notes 12 Rotation and Extended Objects Page 1 Rotation of Rigid Objects Real objects have "extent". The mass is spread out over discrete or continuous positions. THERE IS A DISTRIBUTION OF MASS TO "AN
Notes 12 Rotation and Extended Objects Page 1 Rotation of Rigid Objects Real objects have "extent". The mass is spread out over discrete or continuous positions. THERE IS A DISTRIBUTION OF MASS TO "AN
Physics 141 Rotational Motion 2 Page 1. Rotational Motion 2
 Physics 141 Rotational Motion 2 Page 1 Rotational Motion 2 Right handers, go over there, left handers over here. The rest of you, come with me.! Yogi Berra Torque Motion of a rigid body, like motion of
Physics 141 Rotational Motion 2 Page 1 Rotational Motion 2 Right handers, go over there, left handers over here. The rest of you, come with me.! Yogi Berra Torque Motion of a rigid body, like motion of
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
 5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
5. Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies 5.1 Mass moments of inertia 5.2 General equations of motion 5.3 Translation 5.4 Fixed axis rotation 5.5 General plane motion 5.6 Work and energy relations 5.7 Impulse
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Basic Equations of Elasticity
 A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
A Basic Equations of Elasticity A.1 STRESS The state of stress at any point in a loaded bo is defined completely in terms of the nine components of stress: σ xx,σ yy,σ zz,σ xy,σ yx,σ yz,σ zy,σ zx,andσ
Chapter 11. Angular Momentum
 Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
Chapter 11 Angular Momentum Angular Momentum Angular momentum plays a key role in rotational dynamics. There is a principle of conservation of angular momentum. In analogy to the principle of conservation
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related Torque The door is free to rotate about
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics 9.1 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics 9.1 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination
Statics. Phys101 Lectures 19,20. Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain. Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5.
 Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Phys101 Lectures 19,20 Statics Key points: The Conditions for static equilibrium Solving statics problems Stress and strain Ref: 9-1,2,3,4,5. Page 1 The Conditions for Static Equilibrium An object in static
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium 8.1 Rigid Bodies, Translations, and Rotations A rigid body is an object or a system of particles in which the distances between particles are fixed (remain constant).
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium 8.1 Rigid Bodies, Translations, and Rotations A rigid body is an object or a system of particles in which the distances between particles are fixed (remain constant).
Dynamics of structures
 Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
Dynamics of structures 2.Vibrations: single degree of freedom system Arnaud Deraemaeker (aderaema@ulb.ac.be) 1 Outline of the chapter *One degree of freedom systems in real life Hypothesis Examples *Response
General Physics I. Lecture 9: Vector Cross Product. Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 )
 General Physics I Lecture 9: Vector Cross Product Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Outline Examples of the rotation of a rigid object about a fixed axis Force/torque
General Physics I Lecture 9: Vector Cross Product Prof. WAN, Xin ( 万歆 ) xinwan@zju.edu.cn http://zimp.zju.edu.cn/~xinwan/ Outline Examples of the rotation of a rigid object about a fixed axis Force/torque
Hong Kong Institute of Vocational Education (Tsing Yi) Higher Diploma in Civil Engineering Structural Mechanics. Chapter 1 PRINCIPLES OF STATICS
 PRINCIPLES OF STTICS Statics is the study of how forces act and react on rigid bodies which are at rest or not in motion. This study is the basis for the engineering principles, which guide the design
PRINCIPLES OF STTICS Statics is the study of how forces act and react on rigid bodies which are at rest or not in motion. This study is the basis for the engineering principles, which guide the design
Physics Laboratory I. Dinamics Rotational Inertia. Ins. Fatma Nur AKI
 Physics Laboratory I Dinamics Rotational Inertia Ins. Fatma Nur AKI fnaki@ticaret.edu.tr Vernier Calipers There are special devices for taking measurements. For example Vernier calipers are used to meausere
Physics Laboratory I Dinamics Rotational Inertia Ins. Fatma Nur AKI fnaki@ticaret.edu.tr Vernier Calipers There are special devices for taking measurements. For example Vernier calipers are used to meausere
Euler-Lagrange's equations in several variables
 Euler-Lagrange's equations in several variables So far we have studied one variable and its derivative Let us now consider L2:1 More:1 Taylor: 226-227 (This proof is slightly more general than Taylor's.)
Euler-Lagrange's equations in several variables So far we have studied one variable and its derivative Let us now consider L2:1 More:1 Taylor: 226-227 (This proof is slightly more general than Taylor's.)
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Static equilibrium. Biomechanics 2 Static Equilibrium. Free-Body diagram Internal forces of structures. Last week: Forces and Moments
 Static equilibrium Biomechanics 2 Static Equilibrium Free-Body diagram Internal forces of structures Last week: Forces and Moments Force F: tends to change state of rest or motion Moment M: force acting
Static equilibrium Biomechanics 2 Static Equilibrium Free-Body diagram Internal forces of structures Last week: Forces and Moments Force F: tends to change state of rest or motion Moment M: force acting
is acting on a body of mass m = 3.0 kg and changes its velocity from an initial
 PHYS 101 second major Exam Term 102 (Zero Version) Q1. A 15.0-kg block is pulled over a rough, horizontal surface by a constant force of 70.0 N acting at an angle of 20.0 above the horizontal. The block
PHYS 101 second major Exam Term 102 (Zero Version) Q1. A 15.0-kg block is pulled over a rough, horizontal surface by a constant force of 70.0 N acting at an angle of 20.0 above the horizontal. The block
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion. Torque and angular momentum
 Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Torque. Physics 6A. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 6A Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) For a torque
Physics 6A Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) For a torque
GIANCOLI READING ACTIVITY Lesson 8-4
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS 1. Big Idea(s): GIANCOLI READING ACTIVITY Lesson 8-4 a. Big Idea 3: The interactions of an object with other objects can be described
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS 1. Big Idea(s): GIANCOLI READING ACTIVITY Lesson 8-4 a. Big Idea 3: The interactions of an object with other objects can be described
TECNOLOGIE PER LA RIABILITAZIONE. lezione # 7 dinamica del corpo rigido. A body. Rigid body kinematics in summary. What do we mean with kinetics?
 TENLGIE PER LA RIABILITAZINE AA 2005-2006 Università degli Studi di Napoli "ederico II acoltà di Ingegneria orso di Laurea in Ingegneria Biomedica lezione # 7 dinamica del corpo rigido A body A body is
TENLGIE PER LA RIABILITAZINE AA 2005-2006 Università degli Studi di Napoli "ederico II acoltà di Ingegneria orso di Laurea in Ingegneria Biomedica lezione # 7 dinamica del corpo rigido A body A body is
MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 1
 MECE 3321 MECHANICS O SOLIDS CHAPTER 1 Samantha Ramirez, MSE WHAT IS MECHANICS O MATERIALS? Rigid Bodies Statics Dynamics Mechanics Deformable Bodies Solids/Mech. Of Materials luids 1 WHAT IS MECHANICS
MECE 3321 MECHANICS O SOLIDS CHAPTER 1 Samantha Ramirez, MSE WHAT IS MECHANICS O MATERIALS? Rigid Bodies Statics Dynamics Mechanics Deformable Bodies Solids/Mech. Of Materials luids 1 WHAT IS MECHANICS
PHY131H1S - Class 20. Pre-class reading quiz on Chapter 12
 PHY131H1S - Class 20 Today: Gravitational Torque Rotational Kinetic Energy Rolling without Slipping Equilibrium with Rotation Rotation Vectors Angular Momentum Pre-class reading quiz on Chapter 12 1 Last
PHY131H1S - Class 20 Today: Gravitational Torque Rotational Kinetic Energy Rolling without Slipping Equilibrium with Rotation Rotation Vectors Angular Momentum Pre-class reading quiz on Chapter 12 1 Last
W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 2009 W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions A person spins a tennis ball on a string in a horizontal circle (so that
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 Fall Term 2009 W13D1-1 Reading Quiz and Concept Questions A person spins a tennis ball on a string in a horizontal circle (so that
Physics for Scientists and Engineers. Chapter 5 Force and Motion
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
Physics for Scientists and Engineers Chapter 5 Force and Motion Spring, 2008 Ho Jung Paik Force Forces are what cause any change in the velocity of an object The net force is the vector sum of all the
The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval.
 Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Force, Friction & Gravity Notes
 Force, Friction & Gravity Notes Key Terms to Know Speed: The distance traveled by an object within a certain amount of time. Speed = distance/time Velocity: Speed in a given direction Acceleration: The
Force, Friction & Gravity Notes Key Terms to Know Speed: The distance traveled by an object within a certain amount of time. Speed = distance/time Velocity: Speed in a given direction Acceleration: The
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN
 EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
EDEXCEL NATIONAL CERTIFICATE/DIPLOMA SCIENCE FOR TECHNICIANS OUTCOME 1 - STATIC AND DYNAMIC FORCES TUTORIAL 3 STRESS AND STRAIN 1 Static and dynamic forces Forces: definitions of: matter, mass, weight,
7. The gyroscope. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 Theory. a) The gyroscope
 K 7. The gyroscope 7.1 Introduction This experiment concerns a special type of motion of a gyroscope, called precession. From the angular frequency of the precession, the moment of inertia of the spinning
K 7. The gyroscope 7.1 Introduction This experiment concerns a special type of motion of a gyroscope, called precession. From the angular frequency of the precession, the moment of inertia of the spinning
Biomechanics+Exam+3+Review+
 Biomechanics+Exam+3+Review+ Chapter(13(+(Equilibrium(and(Human(Movement( Center(of(Gravity((CG)(or(Center(of(Mass( The point around which the mass and weight of a body are balanced in all direction or
Biomechanics+Exam+3+Review+ Chapter(13(+(Equilibrium(and(Human(Movement( Center(of(Gravity((CG)(or(Center(of(Mass( The point around which the mass and weight of a body are balanced in all direction or
UNITS AND DEFINITIONS RELATED TO BIOMECHANICAL AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL MEASUREMENTS
 APPENDIX B UNITS AND DEFINITIONS RELATED TO BIOMECHANICAL AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL MEASUREMENTS All units used are SI (Système International d Unités). The system is based on seven well-defined base units
APPENDIX B UNITS AND DEFINITIONS RELATED TO BIOMECHANICAL AND ELECTROMYOGRAPHICAL MEASUREMENTS All units used are SI (Système International d Unités). The system is based on seven well-defined base units
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DEFINITIONS AND TERMINOLOGY Course Name : ENGINEERING MECHANICS Course Code : AAEB01 Program :
Equilibrium. the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant
 Equilibrium is the state of an object where: Equilibrium the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant Feb. 19, 2018 the angular momentum,, about the its center of mass, or any other point, is
Equilibrium is the state of an object where: Equilibrium the linear momentum,, of the center of mass is constant Feb. 19, 2018 the angular momentum,, about the its center of mass, or any other point, is
Application of Forces. Chapter Eight. Torque. Force vs. Torque. Torque, cont. Direction of Torque 4/7/2015
 Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Eight Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Application of Forces The point of application of a force is important This was ignored in treating objects as
Raymond A. Serway Chris Vuille Chapter Eight Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Application of Forces The point of application of a force is important This was ignored in treating objects as
AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS. Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016
 AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016 kimv@mit.edu 1.0 INTRODUCTION This paper is intended as a minimal introduction to the application of Lagrange equations
AN INTRODUCTION TO LAGRANGE EQUATIONS Professor J. Kim Vandiver October 28, 2016 kimv@mit.edu 1.0 INTRODUCTION This paper is intended as a minimal introduction to the application of Lagrange equations
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED MECHANICS LIST OF TOPICS Static s Friction Kinematics Dynamics Machines Strength of Materials Hydrostatics Hydrodynamics A STATICS 1 Solves problems involving forces
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1 Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related 2 Torque The door is free to rotate
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1 Force vs. Torque Forces cause accelerations Torques cause angular accelerations Force and torque are related 2 Torque The door is free to rotate
12. Foundations of Statics Mechanics of Manipulation
 12. Foundations of Statics Mechanics of Manipulation Matt Mason matt.mason@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mason Carnegie Mellon Lecture 12. Mechanics of Manipulation p.1 Lecture 12. Foundations of statics.
12. Foundations of Statics Mechanics of Manipulation Matt Mason matt.mason@cs.cmu.edu http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~mason Carnegie Mellon Lecture 12. Mechanics of Manipulation p.1 Lecture 12. Foundations of statics.
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY FORCE AND ACCELERATION
 PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY FORCE AND ACCELERATION I. Moment of Inertia: Since a body has a definite size and shape, an applied nonconcurrent force system may cause the body to both translate and rotate.
PLANAR KINETICS OF A RIGID BODY FORCE AND ACCELERATION I. Moment of Inertia: Since a body has a definite size and shape, an applied nonconcurrent force system may cause the body to both translate and rotate.
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration
 Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
Engineering Mechanics Prof. U. S. Dixit Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Introduction to vibration Module 15 Lecture 38 Vibration of Rigid Bodies Part-1 Today,
Physics Knowledge Organiser P8 - Forces in balance
 Scalar and vector quantities Scalar quantities have only a magnitude. Vector quantities have a magnitude and direction. Scalar Distance Speed mass Temperature Pressure Volume Work Vector Displacement Velocity
Scalar and vector quantities Scalar quantities have only a magnitude. Vector quantities have a magnitude and direction. Scalar Distance Speed mass Temperature Pressure Volume Work Vector Displacement Velocity
Physics Waves & Oscillations. Mechanics Lesson: Circular Motion. Mechanics Lesson: Circular Motion 1/18/2016. Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 5 French, Chapter 3 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Mechanics Lesson: Circular Motion Linear motion: Mass: Position: Velocity: / Momentum: Acceleration: /
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 5 French, Chapter 3 Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Mechanics Lesson: Circular Motion Linear motion: Mass: Position: Velocity: / Momentum: Acceleration: /
