Digital Pendulum Control Experiments
|
|
|
- David Jenkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EE-341L CONTROL SYSTEMS LAB 2013 Digital Pendulum Control Experiments Ahmed Zia Sheikh M. Salman Khalid Suleman Belal Kazi
2 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT...2 PENDULUM OVERVIEW...3 EXERCISE 1 NONLINEAR MODEL...3 EXERCISE 2 LINEAR MODEL...5 EXERCISE 3 STATIC FRICTION COEFFICIENTS...6 EXERCISE 4 CART MODEL IDENTIFICATION...7 EXERCISE 5 CRANE LINEAR MODEL IDENTIFICATION...9 EXERCISE 6 INVERTED PENDULUM LINEAR MODEL IDENTIFICATION EXERCISE 7 PID CONTROL OF CART MODEL POSITION (SIMULATED) EXERCISE 8 PID CONTROL OF CART MODEL POSITION (REALTIME) EXERCISE 9 MODEL SWING UP CONTROL (SIMULATION): EXERCISE 10 SWING UP CONTROL (REAL-TIME): EXERCISE 11 PENDULUM STABILIZATION USING THE NONLINEAR MODEL (SIMULATION) EXERCISE 12 PENDULUM REAL TIME STABILIZATION EXERCISE 13 CRANE CONTROL EXERCISE 14 SWING UP AND HOLD CONTROL EXERCISE 15 UP AND DOWN
3 ABSTRACT The Digital Pendulum is a modern version of a classical control problem; that of erecting and balancing a free swinging pendulum in its inverted position or moving a hanging pendulum in a controlled manner. The cart on the track is digitally controlled to swing up and to balance the pendulum into an upright sustained position or to move the cart with pendulum in an unperturbed down position. The cart track is of limited length, imposing constraints on the control algorithm. In pendulum mode the system is used to control the twin arm pendulum from an initial position, hanging at rest with the cart in the center of its travel along the track, to a final position with the pendulum upright and the cart restored to its central position. In crane mode the control problem is to move the position of the cart without undue movement of the pendulum. This problem is typical of that experienced when controlling a gantry crane.. 2
4 PENDULUM OVERVIEW Exercise 1 Nonlinear model In this experiment, the pendulum is modeled in Simulink using it s equations of motions and then simulated to see the output. Equations of the pendulum (Non-Linear) from Instruction manual: In the simulation no voltage is given to the motor, and only an initial angle is set, below are the results Figure 1 Results for an initial angle of zero (Inverted Pendulum) 3
5 Figure 2 Initial Angle of 0.01 (Very slight disturbance from vertical) The pendulum parameters in the simulation were adjustable; all of the graphs were obtained using the approximate values specified in the datasheet as shown below Figure 3 Pendulum Simulation Parameters 4
6 Exercise 2 Linear model For small values of theta, the equations of motion in Exercise 1 take on the form: In this experiment, the pendulum is modelled using non-linear equations for both theta=0 and theta=pi i.e. Inverted and hanging respectively. Results for both are shown below: Figure 4 Linear Model for initial angle =π (Crane Mode) As can be seen the linear model applies very well to small oscillations about the theta=pi position. The next graph shows the linear model for a small disturbance for theta=0 5
7 Figure 5 Linear Model for inverted Pendulum theta=0 In this case the linear model fails as the system is unstable and a small disturbance causes a large change in theta thus making our assumptions void. Exercise 3 Static Friction Coefficients Figure 6 Static Friction Offsets 6
8 Because of the static friction forces (also called stiction); with very small values of control signal the cart will not move. Furthermore the static friction force may not be symmetrical. We can compensate for that simply by adding an additional voltage offset value to the cart control signal. Measurement of the value of the offset is the purpose of this exercise. RESULTS: Static friction in: Positive Direction: 0.2 Negative direction: PROBLEMS: Several problems were faced in this experiment, according to the manual the values of the friction in both directions should have been almost the same however even after numerous attempts and readjustments of the pendulum our values differed by almost 100%, moreover upon further experimentation it was found that the pendulum was behaving erratically using these values, so the values used in all subsequent experiments were: Positive Direction: 0.1 Negative directions: 0.4 Exercise 4 Cart model identification In this experiment we identify the linear model between the control signal u and the cart position x Figure 7 Experiment To Identify Cart Model 7
9 After using the real-time model to get the required data, Matlab identification interface was used to get the transfer function of the cart. Figure 8 Figure 9 8
10 Figure 10 The pendulum had to be immobilized or else the cart would veer off to one direction due to excess swing. Finally, the transfer function for the cart, generated using Matlab was: Exercise 5 Crane linear model identification Crane refers to the pendulum in the stable position (theta=pi), in this experiment a transfer function for the crane mode is found. The excitation signal is applied for the first 10 seconds then the pendulum is allowed to swing freely for 80 seconds to identify the damping effect. 9
11 Figure 11 Crane Identification experiment The transfer function derived in Matlab for the crane mode: Figure 12 Measured Vs. Estimated Response 10
12 Figure 13 Peak Shows Natural Frequency Figure 14 Pole Zero Plot: Poles slightly to right of jw axis show error 11
13 Exercise 6 Inverted pendulum linear model identification Figure 15 Response of inverted Pendulum In the case of this experiment, a vital file Mextract.m which was required for extracting the transfer function of the inverted pendulum was missing; we tried to use a file of the same name from the Maglev experiment but failed. We ed Feedback systems about this omission, they have not replied till the publishing of this report. Since we could not develop a model for the inverted pendulum, due to which some of the further experiments of the inverted pendulum control were performed using the pre-specified model. Exercise 7 PID control of cart model position (SIMULATED) Using the cart model identified in previous experiments, a PID controller was designed for controlling the cart position. Various values of PID were tested for different experiments. 12
14 Figure 16 Unmodified Root Locus Figure 17 Root Locus Of the Cart System after adjustment 13
15 Figure 16 Simulated Step Response of the adjusted system P=27.84 I=36 D= 4.5 Figure 17 Response of the PID Compensated system 14
16 Exercise 8 PID control of cart model position (REALTIME) Figure 18 Real Time Results with P=10 I=25 D=2 Figure 19 Real Time Results with P=27.84 I=36 D=4.5 15
17 Exercise 9 Model swing up control (SIMULATION): Figure 20 Simulation of Model Swing up control with default parameters Exercise 10 Swing up control (REAL-TIME): Figure 21 Real Time Swing up Control 16
18 Exercise 11 Pendulum stabilization using the nonlinear model (SIMULATION) Figure 22 Pendulum Stabilization (Simulation) Assuming pendulum is at 0 degrees whilst starting Exercise 12 Pendulum real time stabilization Figure 23 Real Time Pendulum Stabilization 17
19 Exercise 13 Crane control SIMULATION: Figure 24 Desired Angle is pi (perfectly still pendulum) 18
20 Figure 25 Simulation for another control Signal REAL-TIME: Figure 26 Default Settings: Sine wave 0.1 Hz, 0.2v Amplitude 19
21 Figure 27 Sawtooth 0.2Hz 0.4v Amplitude Exercise 14 Swing up and hold control Figure 28 Square 0.1Hz, 0.2 Amplitude 20
22 Figure 29 Simulation Results Figure 30 Real Time Trial 1 (FAILURE) Cart hits end of track 21
23 Figure 32 First Success Swing up and Hold in Real Time In the real time trials it was observed that as the initial voltage of the square wave which slowly increases the pendulum s oscillations is increased two things occur: 1. The pendulum reaches the top point more quickly. 2. The pendulum becomes less stable at the top inverted position, and in extreme cases fails to balance Figure 31 Swing up and hold with decreased initial voltage, extremely stable 22
24 Exercise 15 Up and down Figure 33 Graph of Final Experiment This is the final experiment in the study of the inverted pendulum and involves a combination or culmination of all previous experiments into one. First the pendulum is started from a rest position and made to balance in the inverted position after which it is allowed to fall down into the crane mode and settled as quickly as possible. 23
Contents. PART I METHODS AND CONCEPTS 2. Transfer Function Approach Frequency Domain Representations... 42
 Contents Preface.............................................. xiii 1. Introduction......................................... 1 1.1 Continuous and Discrete Control Systems................. 4 1.2 Open-Loop
Contents Preface.............................................. xiii 1. Introduction......................................... 1 1.1 Continuous and Discrete Control Systems................. 4 1.2 Open-Loop
Lab 6d: Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulum (SEIP)
 Lab 6d: Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulum (SEIP) Arthur Schopen- Life swings like a pendulum backward and forward between pain and boredom. hauer 1 Objectives The goal of this project is to design a controller
Lab 6d: Self-Erecting Inverted Pendulum (SEIP) Arthur Schopen- Life swings like a pendulum backward and forward between pain and boredom. hauer 1 Objectives The goal of this project is to design a controller
Project Lab Report. Michael Hall. Hao Zhu. Neil Nevgi. Station 6. Ta: Yan Cui
 Project Lab Report Michael Hall Hao Zhu Neil Nevgi Station 6 Ta: Yan Cui Nov. 12 th 2012 Table of Contents: Executive Summary 3 Modeling Report.4-7 System Identification 7-11 Control Design..11-15 Simulation
Project Lab Report Michael Hall Hao Zhu Neil Nevgi Station 6 Ta: Yan Cui Nov. 12 th 2012 Table of Contents: Executive Summary 3 Modeling Report.4-7 System Identification 7-11 Control Design..11-15 Simulation
Controlling the Inverted Pendulum
 Controlling the Inverted Pendulum Steven A. P. Quintero Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara Email: squintero@umail.ucsb.edu Abstract The strategies
Controlling the Inverted Pendulum Steven A. P. Quintero Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara Email: squintero@umail.ucsb.edu Abstract The strategies
EE 4443/5329. LAB 3: Control of Industrial Systems. Simulation and Hardware Control (PID Design) The Torsion Disks. (ECP Systems-Model: 205)
 EE 4443/539 LAB 3: Control of Industrial Systems Simulation and Hardware Control (PID Design) The Torsion Disks (ECP Systems-Model: 05) Compiled by: Nitin Swamy Email: nswamy@lakeshore.uta.edu Email: okuljaca@lakeshore.uta.edu
EE 4443/539 LAB 3: Control of Industrial Systems Simulation and Hardware Control (PID Design) The Torsion Disks (ECP Systems-Model: 05) Compiled by: Nitin Swamy Email: nswamy@lakeshore.uta.edu Email: okuljaca@lakeshore.uta.edu
Inverted Pendulum. Objectives
 Inverted Pendulum Objectives The objective of this lab is to experiment with the stabilization of an unstable system. The inverted pendulum problem is taken as an example and the animation program gives
Inverted Pendulum Objectives The objective of this lab is to experiment with the stabilization of an unstable system. The inverted pendulum problem is taken as an example and the animation program gives
Table of Contents 1.0 OBJECTIVE APPARATUS PROCEDURE LAB PREP WORK POLE-PLACEMENT DESIGN
 LAB 4 ENGI 38: ADVANCED CONTROLS -------------------------------------------------------------------- Lab Partners: (Alphabetically) Figliomeni, Dan Malyshev, Andrey McGrath, Adam TO: WARREN PAJU ELECTRICAL
LAB 4 ENGI 38: ADVANCED CONTROLS -------------------------------------------------------------------- Lab Partners: (Alphabetically) Figliomeni, Dan Malyshev, Andrey McGrath, Adam TO: WARREN PAJU ELECTRICAL
Stabilizing the dual inverted pendulum
 Stabilizing the dual inverted pendulum Taylor W. Barton Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139 USA (e-mail: tbarton@mit.edu) Abstract: A classical control approach to stabilizing a
Stabilizing the dual inverted pendulum Taylor W. Barton Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA 02139 USA (e-mail: tbarton@mit.edu) Abstract: A classical control approach to stabilizing a
State Feedback MAE 433 Spring 2012 Lab 7
 State Feedback MAE 433 Spring 1 Lab 7 Prof. C. Rowley and M. Littman AIs: Brandt Belson, onathan Tu Princeton University April 4-7, 1 1 Overview This lab addresses the control of an inverted pendulum balanced
State Feedback MAE 433 Spring 1 Lab 7 Prof. C. Rowley and M. Littman AIs: Brandt Belson, onathan Tu Princeton University April 4-7, 1 1 Overview This lab addresses the control of an inverted pendulum balanced
Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #02: DC Motor Position Control. DC Motor Control Trainer (DCMCT) Student Manual
 Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #02: DC Motor Position Control DC Motor Control Trainer (DCMCT) Student Manual Table of Contents 1 Laboratory Objectives1 2 References1 3 DCMCT Plant
Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #02: DC Motor Position Control DC Motor Control Trainer (DCMCT) Student Manual Table of Contents 1 Laboratory Objectives1 2 References1 3 DCMCT Plant
DC Motor Position: System Modeling
 1 of 7 01/03/2014 22:07 Tips Effects TIPS ABOUT BASICS INDEX NEXT INTRODUCTION CRUISE CONTROL MOTOR SPEED MOTOR POSITION SUSPENSION INVERTED PENDULUM SYSTEM MODELING ANALYSIS DC Motor Position: System
1 of 7 01/03/2014 22:07 Tips Effects TIPS ABOUT BASICS INDEX NEXT INTRODUCTION CRUISE CONTROL MOTOR SPEED MOTOR POSITION SUSPENSION INVERTED PENDULUM SYSTEM MODELING ANALYSIS DC Motor Position: System
Example: Modeling DC Motor Position Physical Setup System Equations Design Requirements MATLAB Representation and Open-Loop Response
 Page 1 of 5 Example: Modeling DC Motor Position Physical Setup System Equations Design Requirements MATLAB Representation and Open-Loop Response Physical Setup A common actuator in control systems is the
Page 1 of 5 Example: Modeling DC Motor Position Physical Setup System Equations Design Requirements MATLAB Representation and Open-Loop Response Physical Setup A common actuator in control systems is the
DC-motor PID control
 DC-motor PID control This version: November 1, 2017 REGLERTEKNIK Name: P-number: AUTOMATIC LINKÖPING CONTROL Date: Passed: Chapter 1 Introduction The purpose of this lab is to give an introduction to
DC-motor PID control This version: November 1, 2017 REGLERTEKNIK Name: P-number: AUTOMATIC LINKÖPING CONTROL Date: Passed: Chapter 1 Introduction The purpose of this lab is to give an introduction to
MEAM 510 Fall 2011 Bruce D. Kothmann
 Balancing g Robot Control MEAM 510 Fall 2011 Bruce D. Kothmann Agenda Bruce s Controls Resume Simple Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) of the Balancing Robot Basic Ideas About Feedback & Stability Effects
Balancing g Robot Control MEAM 510 Fall 2011 Bruce D. Kothmann Agenda Bruce s Controls Resume Simple Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) of the Balancing Robot Basic Ideas About Feedback & Stability Effects
EE 422G - Signals and Systems Laboratory
 EE 4G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 9 PID Control Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 April, 04 Objectives: Identify the
EE 4G - Signals and Systems Laboratory Lab 9 PID Control Kevin D. Donohue Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Kentucky Lexington, KY 40506 April, 04 Objectives: Identify the
Double Inverted Pendulum (DBIP)
 Linear Motion Servo Plant: IP01_2 Linear Experiment #15: LQR Control Double Inverted Pendulum (DBIP) All of Quanser s systems have an inherent open architecture design. It should be noted that the following
Linear Motion Servo Plant: IP01_2 Linear Experiment #15: LQR Control Double Inverted Pendulum (DBIP) All of Quanser s systems have an inherent open architecture design. It should be noted that the following
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department
 YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Date: Lab
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Date: Lab
Laboratory 11 Control Systems Laboratory ECE3557. State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Joint
 Laboratory 11 State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Joint 11.1 Objective The objective of this laboratory is to design a full state feedback controller for endpoint position control
Laboratory 11 State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Joint 11.1 Objective The objective of this laboratory is to design a full state feedback controller for endpoint position control
FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL Vs. CONVENTIONAL PID CONTROL OF AN INVERTED PENDULUM ROBOT
 http:// FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL Vs. CONVENTIONAL PID CONTROL OF AN INVERTED PENDULUM ROBOT 1 Ms.Mukesh Beniwal, 2 Mr. Davender Kumar 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Asst.Prof, Department of Electronics and Communication
http:// FUZZY LOGIC CONTROL Vs. CONVENTIONAL PID CONTROL OF AN INVERTED PENDULUM ROBOT 1 Ms.Mukesh Beniwal, 2 Mr. Davender Kumar 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Asst.Prof, Department of Electronics and Communication
SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 7. Rotary Inverted Pendulum. Student Handout
 SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 7 Rotary Inverted Pendulum Student Handout SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 7 Rotary Inverted Pendulum Student Handout 1. Objectives The objective in this experiment is
SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 7 Rotary Inverted Pendulum Student Handout SRV02-Series Rotary Experiment # 7 Rotary Inverted Pendulum Student Handout 1. Objectives The objective in this experiment is
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department
 YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Report
YTÜ Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture of Special Laboratory of Machine Theory, System Dynamics and Control Division Coupled Tank 1 Level Control with using Feedforward PI Controller Lab Report
MEAM 510 Fall 2012 Bruce D. Kothmann
 Balancing g Robot Control MEAM 510 Fall 2012 Bruce D. Kothmann Agenda Bruce s Controls Resume Simple Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) of the Balancing Robot Basic Ideas About Feedback & Stability Effects
Balancing g Robot Control MEAM 510 Fall 2012 Bruce D. Kothmann Agenda Bruce s Controls Resume Simple Mechanics (Statics & Dynamics) of the Balancing Robot Basic Ideas About Feedback & Stability Effects
Lab 4 Numerical simulation of a crane
 Lab 4 Numerical simulation of a crane Agenda Time 10 min Item Review agenda Introduce the crane problem 95 min Lab activity I ll try to give you a 5- minute warning before the end of the lab period to
Lab 4 Numerical simulation of a crane Agenda Time 10 min Item Review agenda Introduce the crane problem 95 min Lab activity I ll try to give you a 5- minute warning before the end of the lab period to
Lab 6a: Pole Placement for the Inverted Pendulum
 Lab 6a: Pole Placement for the Inverted Pendulum Idiot. Above her head was the only stable place in the cosmos, the only refuge from the damnation of the Panta Rei, and she guessed it was the Pendulum
Lab 6a: Pole Placement for the Inverted Pendulum Idiot. Above her head was the only stable place in the cosmos, the only refuge from the damnation of the Panta Rei, and she guessed it was the Pendulum
Hands-on Lab. Damped Compound Pendulum System ID (Experimental and Simulation) L Bar length m d Pivot to CG distance m m Mass of pendulum kg
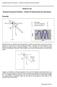 Hands-on Lab Damped Compound Pendulum System ID (Experimental and Simulation) Preamble: c d dt d L Bar length m d Pivot to CG distance m m Mass of pendulum kg L L m g L Sketched above is a damped compound
Hands-on Lab Damped Compound Pendulum System ID (Experimental and Simulation) Preamble: c d dt d L Bar length m d Pivot to CG distance m m Mass of pendulum kg L L m g L Sketched above is a damped compound
Analysis and Synthesis of Single-Input Single-Output Control Systems
 Lino Guzzella Analysis and Synthesis of Single-Input Single-Output Control Systems l+kja» \Uja>)W2(ja»\ um Contents 1 Definitions and Problem Formulations 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Definitions 1 1.2.1 Systems
Lino Guzzella Analysis and Synthesis of Single-Input Single-Output Control Systems l+kja» \Uja>)W2(ja»\ um Contents 1 Definitions and Problem Formulations 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Definitions 1 1.2.1 Systems
MEM04: Rotary Inverted Pendulum
 MEM4: Rotary Inverted Pendulum Interdisciplinary Automatic Controls Laboratory - ME/ECE/CHE 389 April 8, 7 Contents Overview. Configure ELVIS and DC Motor................................ Goals..............................................3
MEM4: Rotary Inverted Pendulum Interdisciplinary Automatic Controls Laboratory - ME/ECE/CHE 389 April 8, 7 Contents Overview. Configure ELVIS and DC Motor................................ Goals..............................................3
1. In Activity 1-1, part 3, how do you think graph a will differ from graph b? 3. Draw your graph for Prediction 2-1 below:
 PRE-LAB PREPARATION SHEET FOR LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION (Due at the beginning of Lab 1) Directions: Read over Lab 1 and then answer the following questions about the procedures. 1. In Activity 1-1,
PRE-LAB PREPARATION SHEET FOR LAB 1: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION (Due at the beginning of Lab 1) Directions: Read over Lab 1 and then answer the following questions about the procedures. 1. In Activity 1-1,
LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION
 Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
Name Date Partners L02-1 LAB 2 - ONE DIMENSIONAL MOTION OBJECTIVES Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise To learn how to use a motion detector and gain more familiarity
State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Link
 Laboratory 12 Control Systems Laboratory ECE3557 Laboratory 12 State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Link 12.1 Objective The objective of this laboratory is to design a full state
Laboratory 12 Control Systems Laboratory ECE3557 Laboratory 12 State Feedback Controller for Position Control of a Flexible Link 12.1 Objective The objective of this laboratory is to design a full state
Rotary Inverted Pendulum
 Rotary Inverted Pendulum Eric Liu 1 Aug 2013 1 1 State Space Derivations 1.1 Electromechanical Derivation Consider the given diagram. We note that the voltage across the motor can be described by: e b
Rotary Inverted Pendulum Eric Liu 1 Aug 2013 1 1 State Space Derivations 1.1 Electromechanical Derivation Consider the given diagram. We note that the voltage across the motor can be described by: e b
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. When a spring is compressed 10 cm, compared to its
Application of Neural Networks for Control of Inverted Pendulum
 Application of Neural Networks for Control of Inverted Pendulum VALERI MLADENOV Department of Theoretical Electrical Engineering Technical University of Sofia Sofia, Kliment Ohridski blvd. 8; BULARIA valerim@tu-sofia.bg
Application of Neural Networks for Control of Inverted Pendulum VALERI MLADENOV Department of Theoretical Electrical Engineering Technical University of Sofia Sofia, Kliment Ohridski blvd. 8; BULARIA valerim@tu-sofia.bg
Target Tracking Using Double Pendulum
 Target Tracking Using Double Pendulum Brian Spackman 1, Anusna Chakraborty 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Utah State University Abstract: This paper deals with the design, implementation
Target Tracking Using Double Pendulum Brian Spackman 1, Anusna Chakraborty 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Utah State University Abstract: This paper deals with the design, implementation
DOUBLE ARM JUGGLING SYSTEM Progress Presentation ECSE-4962 Control Systems Design
 DOUBLE ARM JUGGLING SYSTEM Progress Presentation ECSE-4962 Control Systems Design Group Members: John Kua Trinell Ball Linda Rivera Introduction Where are we? Bulk of Design and Build Complete Testing
DOUBLE ARM JUGGLING SYSTEM Progress Presentation ECSE-4962 Control Systems Design Group Members: John Kua Trinell Ball Linda Rivera Introduction Where are we? Bulk of Design and Build Complete Testing
ECE-320: Linear Control Systems Homework 8. 1) For one of the rectilinear systems in lab, I found the following state variable representations:
 ECE-30: Linear Control Systems Homework 8 Due: Thursday May 6, 00 at the beginning of class ) For one of the rectilinear systems in lab, I found the following state variable representations: 0 0 q q+ 74.805.6469
ECE-30: Linear Control Systems Homework 8 Due: Thursday May 6, 00 at the beginning of class ) For one of the rectilinear systems in lab, I found the following state variable representations: 0 0 q q+ 74.805.6469
Neural Network Control of an Inverted Pendulum on a Cart
 Neural Network Control of an Inverted Pendulum on a Cart VALERI MLADENOV, GEORGI TSENOV, LAMBROS EKONOMOU, NICHOLAS HARKIOLAKIS, PANAGIOTIS KARAMPELAS Department of Theoretical Electrical Engineering Technical
Neural Network Control of an Inverted Pendulum on a Cart VALERI MLADENOV, GEORGI TSENOV, LAMBROS EKONOMOU, NICHOLAS HARKIOLAKIS, PANAGIOTIS KARAMPELAS Department of Theoretical Electrical Engineering Technical
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics
 UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Modeling and Control of a Flexishaft System March 19, 2003 Christopher Lum Travis Reisner Amanda Stephens Brian Hass AA/EE-448 Controls
UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Modeling and Control of a Flexishaft System March 19, 2003 Christopher Lum Travis Reisner Amanda Stephens Brian Hass AA/EE-448 Controls
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems. Process Dynamics and Control
 Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
Feedback Control of Linear SISO systems Process Dynamics and Control 1 Open-Loop Process The study of dynamics was limited to open-loop systems Observe process behavior as a result of specific input signals
PID Control. Objectives
 PID Control Objectives The objective of this lab is to study basic design issues for proportional-integral-derivative control laws. Emphasis is placed on transient responses and steady-state errors. The
PID Control Objectives The objective of this lab is to study basic design issues for proportional-integral-derivative control laws. Emphasis is placed on transient responses and steady-state errors. The
The output voltage is given by,
 71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
71 The output voltage is given by, = (3.1) The inductor and capacitor values of the Boost converter are derived by having the same assumption as that of the Buck converter. Now the critical value of the
Laboratory Exercise 1 DC servo
 Laboratory Exercise DC servo Per-Olof Källén ø 0,8 POWER SAT. OVL.RESET POS.RESET Moment Reference ø 0,5 ø 0,5 ø 0,5 ø 0,65 ø 0,65 Int ø 0,8 ø 0,8 Σ k Js + d ø 0,8 s ø 0 8 Off Off ø 0,8 Ext. Int. + x0,
Laboratory Exercise DC servo Per-Olof Källén ø 0,8 POWER SAT. OVL.RESET POS.RESET Moment Reference ø 0,5 ø 0,5 ø 0,5 ø 0,65 ø 0,65 Int ø 0,8 ø 0,8 Σ k Js + d ø 0,8 s ø 0 8 Off Off ø 0,8 Ext. Int. + x0,
Nonlinear Op-amp Circuits
 deba21pratim@gmail.com Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Bombay May 3, 2013 Overview of op-amp operating regions Linear Region Occurs when the op-amp output is stable i.e.
deba21pratim@gmail.com Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Bombay May 3, 2013 Overview of op-amp operating regions Linear Region Occurs when the op-amp output is stable i.e.
Video 5.1 Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh
 Video 5.1 Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.1 1 The Purpose of Control Input/Stimulus/ Disturbance System or Plant Output/ Response Understand the Black Box Evaluate the Performance Change the Behavior
Video 5.1 Vijay Kumar and Ani Hsieh Robo3x-1.1 1 The Purpose of Control Input/Stimulus/ Disturbance System or Plant Output/ Response Understand the Black Box Evaluate the Performance Change the Behavior
ES205 Analysis and Design of Engineering Systems: Lab 1: An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK
 ES205 Analysis and Design of Engineering Systems: Lab 1: An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK What is SIMULINK? SIMULINK is a software package for modeling, simulating, and analyzing
ES205 Analysis and Design of Engineering Systems: Lab 1: An Introductory Tutorial: Getting Started with SIMULINK What is SIMULINK? SIMULINK is a software package for modeling, simulating, and analyzing
Inverted Pendulum System
 Introduction Inverted Pendulum System This lab experiment consists of two experimental procedures, each with sub parts. Experiment 1 is used to determine the system parameters needed to implement a controller.
Introduction Inverted Pendulum System This lab experiment consists of two experimental procedures, each with sub parts. Experiment 1 is used to determine the system parameters needed to implement a controller.
Chapter 7 Control. Part Classical Control. Mobile Robotics - Prof Alonzo Kelly, CMU RI
 Chapter 7 Control 7.1 Classical Control Part 1 1 7.1 Classical Control Outline 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.2 Virtual Spring Damper 7.1.3 Feedback Control 7.1.4 Model Referenced and Feedforward Control Summary
Chapter 7 Control 7.1 Classical Control Part 1 1 7.1 Classical Control Outline 7.1.1 Introduction 7.1.2 Virtual Spring Damper 7.1.3 Feedback Control 7.1.4 Model Referenced and Feedforward Control Summary
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology. EEE 402: Control System I Laboratory
 Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department EEE 402: Control System I Laboratory Experiment No. 4 a) Effect of input waveform, loop gain, and system
Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department EEE 402: Control System I Laboratory Experiment No. 4 a) Effect of input waveform, loop gain, and system
Non-Linear Swing-Up and Stabilizing Control of an Inverted Pendulum System
 EUROCON 3 Ljubljana, Slovenia Non-Linear Swing-Up and Stabilizing Control of an Inverted Pendulum System Marvin Bugeja Faculty of Engineering University of Malta Msida (MSD6) Malta email: merv@ieee.org
EUROCON 3 Ljubljana, Slovenia Non-Linear Swing-Up and Stabilizing Control of an Inverted Pendulum System Marvin Bugeja Faculty of Engineering University of Malta Msida (MSD6) Malta email: merv@ieee.org
1 An Overview and Brief History of Feedback Control 1. 2 Dynamic Models 23. Contents. Preface. xiii
 Contents 1 An Overview and Brief History of Feedback Control 1 A Perspective on Feedback Control 1 Chapter Overview 2 1.1 A Simple Feedback System 3 1.2 A First Analysis of Feedback 6 1.3 Feedback System
Contents 1 An Overview and Brief History of Feedback Control 1 A Perspective on Feedback Control 1 Chapter Overview 2 1.1 A Simple Feedback System 3 1.2 A First Analysis of Feedback 6 1.3 Feedback System
1 Introduction. 2 Process description
 1 Introduction This document describes the backround and theory of the Rotary Inverted Pendulum laboratory excercise. The purpose of this laboratory excercise is to familiarize the participants with state
1 Introduction This document describes the backround and theory of the Rotary Inverted Pendulum laboratory excercise. The purpose of this laboratory excercise is to familiarize the participants with state
FUZZY SWING-UP AND STABILIZATION OF REAL INVERTED PENDULUM USING SINGLE RULEBASE
 005-010 JATIT All rights reserved wwwjatitorg FUZZY SWING-UP AND STABILIZATION OF REAL INVERTED PENDULUM USING SINGLE RULEBASE SINGH VIVEKKUMAR RADHAMOHAN, MONA SUBRAMANIAM A, DR MJNIGAM Indian Institute
005-010 JATIT All rights reserved wwwjatitorg FUZZY SWING-UP AND STABILIZATION OF REAL INVERTED PENDULUM USING SINGLE RULEBASE SINGH VIVEKKUMAR RADHAMOHAN, MONA SUBRAMANIAM A, DR MJNIGAM Indian Institute
Lab 5a: Pole Placement for the Inverted Pendulum
 Lab 5a: Pole Placement for the Inverted Pendulum November 1, 2011 1 Purpose The objective of this lab is to achieve simultaneous control of both the angular position of the pendulum and horizontal position
Lab 5a: Pole Placement for the Inverted Pendulum November 1, 2011 1 Purpose The objective of this lab is to achieve simultaneous control of both the angular position of the pendulum and horizontal position
Mechatronic System Case Study: Rotary Inverted Pendulum Dynamic System Investigation
 Mechatronic System Case Study: Rotary Inverted Pendulum Dynamic System Investigation Dr. Kevin Craig Greenheck Chair in Engineering Design & Professor of Mechanical Engineering Marquette University K.
Mechatronic System Case Study: Rotary Inverted Pendulum Dynamic System Investigation Dr. Kevin Craig Greenheck Chair in Engineering Design & Professor of Mechanical Engineering Marquette University K.
CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Control and Dynamical Systems
 CDS 101 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.3 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 3. Åström and Murray, Exercise 2.6, parts (a) and (b) CDS 110a 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise
CDS 101 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.3 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 3. Åström and Murray, Exercise 2.6, parts (a) and (b) CDS 110a 1. Åström and Murray, Exercise 1.4 2. Åström and Murray, Exercise
Cascade Control of a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
 Journal of Applied and Industrial Sciences, 213, 1 (4): 16-23, ISSN: 2328-4595 (PRINT), ISSN: 2328-469 (ONLINE) Research Article Cascade Control of a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) 16 A. O. Ahmed
Journal of Applied and Industrial Sciences, 213, 1 (4): 16-23, ISSN: 2328-4595 (PRINT), ISSN: 2328-469 (ONLINE) Research Article Cascade Control of a Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR) 16 A. O. Ahmed
Index. Index. More information. in this web service Cambridge University Press
 A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
A-type elements, 4 7, 18, 31, 168, 198, 202, 219, 220, 222, 225 A-type variables. See Across variable ac current, 172, 251 ac induction motor, 251 Acceleration rotational, 30 translational, 16 Accumulator,
The control of a gantry
 The control of a gantry AAE 364L In this experiment we will design a controller for a gantry or crane. Without a controller the pendulum of crane will swing for a long time. The idea is to use control
The control of a gantry AAE 364L In this experiment we will design a controller for a gantry or crane. Without a controller the pendulum of crane will swing for a long time. The idea is to use control
Forced oscillation - Pohl s pendulum with measure Dynamics. Equipment TEP
 Forced oscillation - Pohl s pendulum TEP Related topics Angular velocity, characteristic frequency, resonance frequency, torsional pendulum, torsional oscillation, restoring torque, damped/undamped free
Forced oscillation - Pohl s pendulum TEP Related topics Angular velocity, characteristic frequency, resonance frequency, torsional pendulum, torsional oscillation, restoring torque, damped/undamped free
CHAPTER 1 Basic Concepts of Control System. CHAPTER 6 Hydraulic Control System
 CHAPTER 1 Basic Concepts of Control System 1. What is open loop control systems and closed loop control systems? Compare open loop control system with closed loop control system. Write down major advantages
CHAPTER 1 Basic Concepts of Control System 1. What is open loop control systems and closed loop control systems? Compare open loop control system with closed loop control system. Write down major advantages
The Control of an Inverted Pendulum
 The Control of an Inverted Pendulum AAE 364L This experiment is devoted to the inverted pendulum. Clearly, the inverted pendulum will fall without any control. We will design a controller to balance the
The Control of an Inverted Pendulum AAE 364L This experiment is devoted to the inverted pendulum. Clearly, the inverted pendulum will fall without any control. We will design a controller to balance the
(Refer Slide Time: 1:42)
 Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 21 Basic Principles of Feedback Control (Contd..) Friends, let me get started
Control Engineering Prof. Madan Gopal Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 21 Basic Principles of Feedback Control (Contd..) Friends, let me get started
Example: DC Motor Speed Modeling
 Page 1 of 5 Example: DC Motor Speed Modeling Physical setup and system equations Design requirements MATLAB representation and open-loop response Physical setup and system equations A common actuator in
Page 1 of 5 Example: DC Motor Speed Modeling Physical setup and system equations Design requirements MATLAB representation and open-loop response Physical setup and system equations A common actuator in
FEEDBACK CONTROL SYSTEMS
 FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
FEEDBAC CONTROL SYSTEMS. Control System Design. Open and Closed-Loop Control Systems 3. Why Closed-Loop Control? 4. Case Study --- Speed Control of a DC Motor 5. Steady-State Errors in Unity Feedback Control
QNET Experiment #04: Inverted Pendulum Control. Rotary Pendulum (ROTPEN) Inverted Pendulum Trainer. Instructor Manual
 Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #04: Inverted Pendulum Control Rotary Pendulum (ROTPEN) Inverted Pendulum Trainer Instructor Manual Table of Contents 1 Laboratory Objectives1 2
Quanser NI-ELVIS Trainer (QNET) Series: QNET Experiment #04: Inverted Pendulum Control Rotary Pendulum (ROTPEN) Inverted Pendulum Trainer Instructor Manual Table of Contents 1 Laboratory Objectives1 2
Lab 3: Model based Position Control of a Cart
 I. Objective Lab 3: Model based Position Control of a Cart The goal of this lab is to help understand the methodology to design a controller using the given plant dynamics. Specifically, we would do position
I. Objective Lab 3: Model based Position Control of a Cart The goal of this lab is to help understand the methodology to design a controller using the given plant dynamics. Specifically, we would do position
D(s) G(s) A control system design definition
 R E Compensation D(s) U Plant G(s) Y Figure 7. A control system design definition x x x 2 x 2 U 2 s s 7 2 Y Figure 7.2 A block diagram representing Eq. (7.) in control form z U 2 s z Y 4 z 2 s z 2 3 Figure
R E Compensation D(s) U Plant G(s) Y Figure 7. A control system design definition x x x 2 x 2 U 2 s s 7 2 Y Figure 7.2 A block diagram representing Eq. (7.) in control form z U 2 s z Y 4 z 2 s z 2 3 Figure
CYBER EXPLORATION LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS
 CYBER EXPLORATION LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS 1 2 Cyber Exploration oratory Experiments Chapter 2 Experiment 1 Objectives To learn to use MATLAB to: (1) generate polynomial, (2) manipulate polynomials, (3)
CYBER EXPLORATION LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS 1 2 Cyber Exploration oratory Experiments Chapter 2 Experiment 1 Objectives To learn to use MATLAB to: (1) generate polynomial, (2) manipulate polynomials, (3)
Design and Comparison of Different Controllers to Stabilize a Rotary Inverted Pendulum
 ISSN (Online): 347-3878, Impact Factor (5): 3.79 Design and Comparison of Different Controllers to Stabilize a Rotary Inverted Pendulum Kambhampati Tejaswi, Alluri Amarendra, Ganta Ramesh 3 M.Tech, Department
ISSN (Online): 347-3878, Impact Factor (5): 3.79 Design and Comparison of Different Controllers to Stabilize a Rotary Inverted Pendulum Kambhampati Tejaswi, Alluri Amarendra, Ganta Ramesh 3 M.Tech, Department
Digital Control Semester Project
 Digital Control Semester Project Part I: Transform-Based Design 1 Introduction For this project you will be designing a digital controller for a system which consists of a DC motor driving a shaft with
Digital Control Semester Project Part I: Transform-Based Design 1 Introduction For this project you will be designing a digital controller for a system which consists of a DC motor driving a shaft with
EE C128 / ME C134 Fall 2014 HW 6.2 Solutions. HW 6.2 Solutions
 EE C28 / ME C34 Fall 24 HW 6.2 Solutions. PI Controller For the system G = K (s+)(s+3)(s+8) HW 6.2 Solutions in negative feedback operating at a damping ratio of., we are going to design a PI controller
EE C28 / ME C34 Fall 24 HW 6.2 Solutions. PI Controller For the system G = K (s+)(s+3)(s+8) HW 6.2 Solutions in negative feedback operating at a damping ratio of., we are going to design a PI controller
The Control of an Inverted Pendulum
 The Control of an Inverted Pendulum AAE 364L This experiment is devoted to the inverted pendulum. Clearly, the inverted pendulum will fall without any control. We will design a controller to balance the
The Control of an Inverted Pendulum AAE 364L This experiment is devoted to the inverted pendulum. Clearly, the inverted pendulum will fall without any control. We will design a controller to balance the
Motor Controller. A block diagram for the motor with a feedback controller is shown below
 Motor Controller A block diagram for the motor with a feedback controller is shown below A few things to note 1. In this modeling problem, there is no established method or set of criteria for selecting
Motor Controller A block diagram for the motor with a feedback controller is shown below A few things to note 1. In this modeling problem, there is no established method or set of criteria for selecting
THE REACTION WHEEL PENDULUM
 THE REACTION WHEEL PENDULUM By Ana Navarro Yu-Han Sun Final Report for ECE 486, Control Systems, Fall 2013 TA: Dan Soberal 16 December 2013 Thursday 3-6pm Contents 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Sensors (Encoders)...
THE REACTION WHEEL PENDULUM By Ana Navarro Yu-Han Sun Final Report for ECE 486, Control Systems, Fall 2013 TA: Dan Soberal 16 December 2013 Thursday 3-6pm Contents 1. Introduction... 1 1.1 Sensors (Encoders)...
Lab 4 Motion in One-Dimension Part 2: Position, Velocity and Acceleration Graphically and Statistically (pre-requisite Lab3)
 Lab 4 Motion in One-Dimension Part 2: Position, Velocity and Acceleration Graphically and Statistically (pre-requisite Lab3) Objectives: To obtain an understanding of position, velocity, and acceleration
Lab 4 Motion in One-Dimension Part 2: Position, Velocity and Acceleration Graphically and Statistically (pre-requisite Lab3) Objectives: To obtain an understanding of position, velocity, and acceleration
R a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies.
 SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 01 1. a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies..
SET - 1 II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 01 1. a) Compare open loop and closed loop control systems. b) Clearly bring out, from basics, Force-current and Force-Voltage analogies..
6.1 Sketch the z-domain root locus and find the critical gain for the following systems K., the closed-loop characteristic equation is K + z 0.
 6. Sketch the z-domain root locus and find the critical gain for the following systems K (i) Gz () z 4. (ii) Gz K () ( z+ 9. )( z 9. ) (iii) Gz () Kz ( z. )( z ) (iv) Gz () Kz ( + 9. ) ( z. )( z 8. ) (i)
6. Sketch the z-domain root locus and find the critical gain for the following systems K (i) Gz () z 4. (ii) Gz K () ( z+ 9. )( z 9. ) (iii) Gz () Kz ( z. )( z ) (iv) Gz () Kz ( + 9. ) ( z. )( z 8. ) (i)
9.1 Harmonic Motion. Motion in cycles. linear motion - motion that goes from one place to another without repeating.
 9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
9.1 Harmonic Motion A bicyclist pedaling past you on the street moves in linear motion. Linear motion gets us from one place to another (Figure 9.1A). This chapter is about another kind of motion called
Lecture 25: Tue Nov 27, 2018
 Lecture 25: Tue Nov 27, 2018 Reminder: Lab 3 moved to Tuesday Dec 4 Lecture: review time-domain characteristics of 2nd-order systems intro to control: feedback open-loop vs closed-loop control intro to
Lecture 25: Tue Nov 27, 2018 Reminder: Lab 3 moved to Tuesday Dec 4 Lecture: review time-domain characteristics of 2nd-order systems intro to control: feedback open-loop vs closed-loop control intro to
CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Sixth Edition International Student Version
 CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Sixth Edition International Student Version Norman S. Nise California State Polytechnic University, Pomona John Wiley fir Sons, Inc. Contents PREFACE, vii 1. INTRODUCTION, 1
CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING Sixth Edition International Student Version Norman S. Nise California State Polytechnic University, Pomona John Wiley fir Sons, Inc. Contents PREFACE, vii 1. INTRODUCTION, 1
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 1 Fall 2006 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION I
 PHYSICS 289 Experiment 1 Fall 2006 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION I (A short report is required for this lab. Just fill in the worksheet, make the graphs, and provide answers to the questions. Be sure to include
PHYSICS 289 Experiment 1 Fall 2006 SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION I (A short report is required for this lab. Just fill in the worksheet, make the graphs, and provide answers to the questions. Be sure to include
THE FLOATING DUTCHMEN Three Dimensional Driven-Arm Inverted Pendulum
 THE FLOATING DUTCHMEN Three Dimensional Driven-Arm Inverted Pendulum Final Report for ECSE-496 Control Systems Design Team Teresa Bernardi Brian Lewis Matthew Rosmarin Monday, May 8, 6 Rensselaer Polytechnic
THE FLOATING DUTCHMEN Three Dimensional Driven-Arm Inverted Pendulum Final Report for ECSE-496 Control Systems Design Team Teresa Bernardi Brian Lewis Matthew Rosmarin Monday, May 8, 6 Rensselaer Polytechnic
FRICTION AND FRICTION COMPENSATION IN THE FURUTA PENDULUM
 FRICTION AND FRICTION COMPENSATION IN THE FURUTA PENDULUM M. Gäfvert, J. Svensson and K. J. Åström Department of Automatic Control Lund Institute of Technology, Box 8, S- Lund, Sweden Fax:+4646388,E-mail:{magnus,kja}@control.lth.se
FRICTION AND FRICTION COMPENSATION IN THE FURUTA PENDULUM M. Gäfvert, J. Svensson and K. J. Åström Department of Automatic Control Lund Institute of Technology, Box 8, S- Lund, Sweden Fax:+4646388,E-mail:{magnus,kja}@control.lth.se
Transitioning to Chaos in a Simple Mechanical Oscillator
 Transitioning to Chaos in a Simple Mechanical Oscillator Hwan Bae Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 69, USA (Dated: May 9, 8) We vary the magnetic damping, driver frequency, and
Transitioning to Chaos in a Simple Mechanical Oscillator Hwan Bae Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 69, USA (Dated: May 9, 8) We vary the magnetic damping, driver frequency, and
Mechatronics Engineering. Li Wen
 Mechatronics Engineering Li Wen Bio-inspired robot-dc motor drive Unstable system Mirko Kovac,EPFL Modeling and simulation of the control system Problems 1. Why we establish mathematical model of the control
Mechatronics Engineering Li Wen Bio-inspired robot-dc motor drive Unstable system Mirko Kovac,EPFL Modeling and simulation of the control system Problems 1. Why we establish mathematical model of the control
EE 474 Lab Part 2: Open-Loop and Closed-Loop Control (Velocity Servo)
 Contents EE 474 Lab Part 2: Open-Loop and Closed-Loop Control (Velocity Servo) 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Discovery learning in the Controls Teaching Laboratory.............. 1 1.2 A Laboratory Notebook...............................
Contents EE 474 Lab Part 2: Open-Loop and Closed-Loop Control (Velocity Servo) 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Discovery learning in the Controls Teaching Laboratory.............. 1 1.2 A Laboratory Notebook...............................
Design of Fuzzy PD-Controlled Overhead Crane System with Anti-Swing Compensation
 Engineering, 2011, 3, 755-762 doi:10.4236/eng.2011.37091 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Design of Fuzzy PD-Controlled Overhead Crane System with Anti-Swing Compensation Abstract
Engineering, 2011, 3, 755-762 doi:10.4236/eng.2011.37091 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Design of Fuzzy PD-Controlled Overhead Crane System with Anti-Swing Compensation Abstract
Matlab-Based Tools for Analysis and Control of Inverted Pendula Systems
 Matlab-Based Tools for Analysis and Control of Inverted Pendula Systems Slávka Jadlovská, Ján Sarnovský Dept. of Cybernetics and Artificial Intelligence, FEI TU of Košice, Slovak Republic sjadlovska@gmail.com,
Matlab-Based Tools for Analysis and Control of Inverted Pendula Systems Slávka Jadlovská, Ján Sarnovský Dept. of Cybernetics and Artificial Intelligence, FEI TU of Košice, Slovak Republic sjadlovska@gmail.com,
B1-1. Closed-loop control. Chapter 1. Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology. Festo Didactic Process Control System
 B1-1 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology B1-2 This chapter outlines the differences between closed-loop and openloop control and gives an introduction to closed-loop control technology.
B1-1 Chapter 1 Fundamentals of closed-loop control technology B1-2 This chapter outlines the differences between closed-loop and openloop control and gives an introduction to closed-loop control technology.
Simulink Modeling Tutorial
 Simulink Modeling Tutorial Train system Free body diagram and Newton's law Model Construction Running the Model Obtaining MATLAB Model In Simulink, it is very straightforward to represent a physical system
Simulink Modeling Tutorial Train system Free body diagram and Newton's law Model Construction Running the Model Obtaining MATLAB Model In Simulink, it is very straightforward to represent a physical system
Inverted Pendulum: State-Space Methods for Controller Design
 1 de 12 18/10/2015 22:45 Tips Effects TIPS ABOUT BASICS HARDWARE INDEX NEXT INTRODUCTION CRUISE CONTROL MOTOR SPEED MOTOR POSITION SYSTEM MODELING ANALYSIS Inverted Pendulum: State-Space Methods for Controller
1 de 12 18/10/2015 22:45 Tips Effects TIPS ABOUT BASICS HARDWARE INDEX NEXT INTRODUCTION CRUISE CONTROL MOTOR SPEED MOTOR POSITION SYSTEM MODELING ANALYSIS Inverted Pendulum: State-Space Methods for Controller
EE 3CL4: Introduction to Control Systems Lab 4: Lead Compensation
 EE 3CL4: Introduction to Control Systems Lab 4: Lead Compensation Tim Davidson Ext. 27352 davidson@mcmaster.ca Objective To use the root locus technique to design a lead compensator for a marginally-stable
EE 3CL4: Introduction to Control Systems Lab 4: Lead Compensation Tim Davidson Ext. 27352 davidson@mcmaster.ca Objective To use the root locus technique to design a lead compensator for a marginally-stable
Single-Input-Single-Output Systems
 TF 502 Single-Input-Single-Output Systems SIST, ShanghaiTech Introduction Open-Loop Control-Response Proportional Control General PID Control Boris Houska 1-1 Contents Introduction Open-Loop Control-Response
TF 502 Single-Input-Single-Output Systems SIST, ShanghaiTech Introduction Open-Loop Control-Response Proportional Control General PID Control Boris Houska 1-1 Contents Introduction Open-Loop Control-Response
Physics General Physics. Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems. Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones
 Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Physics 22000 General Physics Lecture 24 Oscillating Systems Fall 2016 Semester Prof. Matthew Jones 1 2 Oscillating Motion We have studied linear motion objects moving in straight lines at either constant
Experiment P09: Acceleration of a Dynamics Cart I (Smart Pulley)
 PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P09-1 Experiment P09: (Smart Pulley) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton s Laws 30 m 500 or 700 P09 Cart Acceleration 1 P09_CAR1.SWS EQUIPMENT
PASCO scientific Physics Lab Manual: P09-1 Experiment P09: (Smart Pulley) Concept Time SW Interface Macintosh file Windows file Newton s Laws 30 m 500 or 700 P09 Cart Acceleration 1 P09_CAR1.SWS EQUIPMENT
Balancing of an Inverted Pendulum with a SCARA Robot
 Balancing of an Inverted Pendulum with a SCARA Robot Bernhard Sprenger, Ladislav Kucera, and Safer Mourad Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETHZ Institute of Robotics 89 Zurich, Switzerland
Balancing of an Inverted Pendulum with a SCARA Robot Bernhard Sprenger, Ladislav Kucera, and Safer Mourad Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETHZ Institute of Robotics 89 Zurich, Switzerland
CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS
 CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS 7.1 Period and Frequency Anything that vibrates or repeats its motion regularly is said to have oscillatory motion (sometimes called harmonic
CHAPTER 7: OSCILLATORY MOTION REQUIRES A SET OF CONDITIONS 7.1 Period and Frequency Anything that vibrates or repeats its motion regularly is said to have oscillatory motion (sometimes called harmonic
Energy in a Simple Harmonic Oscillator. Class 30. Simple Harmonic Motion
 Simple Harmonic Motion Class 30 Here is a simulation of a mass hanging from a spring. This is a case of stable equilibrium in which there is a large extension in which the restoring force is linear in
Simple Harmonic Motion Class 30 Here is a simulation of a mass hanging from a spring. This is a case of stable equilibrium in which there is a large extension in which the restoring force is linear in
CONTROL * ~ SYSTEMS ENGINEERING
 CONTROL * ~ SYSTEMS ENGINEERING H Fourth Edition NormanS. Nise California State Polytechnic University, Pomona JOHN WILEY& SONS, INC. Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction, 2 1.2 A History of Control
CONTROL * ~ SYSTEMS ENGINEERING H Fourth Edition NormanS. Nise California State Polytechnic University, Pomona JOHN WILEY& SONS, INC. Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Introduction, 2 1.2 A History of Control
LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION
 Lab 2 - Introduction to Motion 3 Name Date Partners LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise Objectives To explore how various motions are represented
Lab 2 - Introduction to Motion 3 Name Date Partners LAB 2: INTRODUCTION TO MOTION Slow and steady wins the race. Aesop s fable: The Hare and the Tortoise Objectives To explore how various motions are represented
