Physics of switches. Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory
|
|
|
- Avice Webster
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physics of switches Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory
2 Logic switches A logic switch is a device that can assume physically distinct states as a result of external inputs. Usually the output of a physical system assume a continuous value (e.g. a voltage) and a threshold is used to partite the output space in two ore more states. If the states are in the number of two we have binary logic switches: this is the case of transistors for modern microprocessors.
3 Computing with binary switches Combinational switches can be easily employed do computation. Sequential switches can be easily employed to store information. Conbinational: in the absence of any external force, under equilibrium conditions, they are in the state S 0. When an external force F 01 is applied, they switch to the state S 1 and remain in that state as long as the force is present. Once the force is removed they go back to the state S 0. Sequential: They can be changed from S 0 to S 1 by applying an external force F 01. Once they are in the state S 1 they remain in this state even when the force is removed. They go from S 1 to S 0 by applying a new force F 10. Once they are in S 0 they remain in this state even when the force is removed.
4 The switch Logic gates are made by switches (presently transistors) and also memory cells can be represented in terms of switches. NAND gate
5 A physical model for the binary switch A simple switch can be represented by a physical dynamical model based on a bistable potential We need a potential barrier in order to allow for physical distinguishability of the two states
6 The switch A simple switch can be represented by a physical dynamical model based on a bistable potential Switch event
7 Questions - What is the minimum energy we have to spend if we want to produce a switch event? - Does this energy depends on the technology of the switch? - Does this energy depends on the instruction that we give to the switch? -. Some answers are still controversial
8 The Physics of switches In order to describe the physics of a switch we need to introduce a dynamical model capable of capturing the main features of a switch. The two states, in order to be dynamically stable, are separated by some energy barrier that should be surpassed in order to perform the switch event. This situation can be mathematically described by a second order differential equation like: m x = d dx U(x) mγ x + F 8
9 The Physics of switches According to this model if we want to produce a switch event we need to apply an external force F capable of bringing the particle from the left well (at rest at the bottom) into the right well (at rest at the bottom). Clearly this can be done in more than one way. As an example we start discussing what we call the first procedure: a three-step procedure based on the application of a large and constant force F=-F 0, with F 0 >0 We can ask what is the minimum work that the force F has to perform in order to make the device switch from 0 to 1 (or equivalently from 1 to 0). The work is computed as: x 2 L = F(x)dx Thus L = 2 F 0 x 1 9
10 The Physics of switches Is this the minimum work? Let s look at this other procedure (second procedure): The only work performed happened to be during step 3 where it is readily computed as L 1 = 2 F 1. Now, by the moment that F 1 << F 0 we have L 1 << L 0 10
11 The Physics of realistic switches This analysis, although correct, is quite naïve, indeed. The reason is that we have assumed that the work performed can be made arbitrarily small. IS THIS TRUE? ΔU = L - Q ΔU = 0 L = Q The second principle of thermodynamics requires that: Q TΔS Q = T ΔS + friction We might be able to make friction = 0 but what about entropy? 11
12 The Physics of realistic switches In order to be closer to a reasonable physical model we need to introduce a fluctuating force and thus a Langevin equation: m x = d U(x) mγ x +ξ(t)+ F dx The relevant quantity becomes the probability density P(x,t) and Represent the probability for our switch to assume 0 or 1 logic states This calls for a reconsideration of the equilibrium condition 12
13 The Physics of realistic switches 13
14 The Physics of realistic switches In this new physical framework we have to do with exchanges of both work and heat (constant temperature transformation approximation). Thus we have to take into account both the exchanges associate with work and the changes associated with entropy variation. Entropy here is defined according to Gibbs: Based on this new approach let s review the previous procedure: 14
15 The Physics of realistic switches Based on this new approach let s review the previous procedure: we observe a change in entropy: S 1 = S 5 = -K B ln 1 = 0 S 2 = -K B (½ ln ½ + ½ ln ½) = K B ln 2. 15
16 The Physics of realistic switches Based on these considerations we can now reformulate conditions required in order to perform the switch by spending zero energy: 1) The total work performed on the system by the external force has to be zero. 2) The switch event has to proceed with a speed arbitrarily small in order to have arbitrarily small losses due to friction. 3) The system entropy never decreases during the switch event. Is it possible? For a switch operation yes at least in principle 16
17 Operating ICT basic switches below the Landauer limit Magnetic nano dots Single cylindrical element of permalloy (NiFe) with dimensions 50 x 50 x 5 nm 3 Entropy changes Entropy stays constant More info available at Luca Gammaitoni RE.WORK Technology Berlin, June,
18 The Physics of realistic switches: the reset But let s suppose we start from an equilibrium condition In this case if we want to use the switch we need to operate a reset operation Is there a minimal cost for this operation? 18
19 THE LANDAUER LIMIT The Landauer s principle (1) states that erasing one bit of information (like in a resetting operation) comes unavoidably with a decrease in physical entropy and thus is accompanied by a minimal dissipation of energy equal to Q = k B T ln 2 More technically this is the result of a change in entropy due to a change from a random state to a defined state. Please note: this is the minimum energy required. (1) R. Landauer, Dissipation and Heat Generation in the Computing Process IBM J. Research and Develop. 5, (1961),
20 To know more Review article: Towards zero-power ICT, L Gammaitoni, D Chiuchiú, M Madami, G Carlotti Nanotechnology 26 (22), (2015) - Book: ICT - Energy - Concepts Towards Zero - Power Information and Communication Technology, InTech, February 2, Luca Gammaitoni, NiPS Laboratory, University of Perugia (IT)
Physics of switches. Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory
 Physics of switches Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory Logic switches A logic switch is a device that can assume physically dis=nct states as a result of external inputs. Usually the output of a physical
Physics of switches Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory Logic switches A logic switch is a device that can assume physically dis=nct states as a result of external inputs. Usually the output of a physical
Operating basic switches toward zero-power computing. Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory, Università di Perugia, Italy
 Operating basic switches toward zero-power computing Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory, Università di Perugia, Italy Perugia Luca Gammaitoni Helios Vocca Cristina Diamantini Florence Silvia Lombardi, Project
Operating basic switches toward zero-power computing Luca Gammaitoni NiPS Laboratory, Università di Perugia, Italy Perugia Luca Gammaitoni Helios Vocca Cristina Diamantini Florence Silvia Lombardi, Project
3 The physics of computing
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA 3 The physics of computing Luca Gammaitoni ICT-Energy Summer school 2016, Aalborg Corso di Laurea in FISICA A computer process informacon A computer is a machine = physical system
Corso di Laurea in FISICA 3 The physics of computing Luca Gammaitoni ICT-Energy Summer school 2016, Aalborg Corso di Laurea in FISICA A computer process informacon A computer is a machine = physical system
ON BROWNIAN COMPUTATION
 ON BROWNIAN COMPUTATION JOHN D. NORTON Department of History and Philosophy of Science Center for Philosophy of Science University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh PA USA 15260 jdnorton@pitt.edu Draft: October10,
ON BROWNIAN COMPUTATION JOHN D. NORTON Department of History and Philosophy of Science Center for Philosophy of Science University of Pittsburgh Pittsburgh PA USA 15260 jdnorton@pitt.edu Draft: October10,
The physics of information: from Maxwell s demon to Landauer. Eric Lutz University of Erlangen-Nürnberg
 The physics of information: from Maxwell s demon to Landauer Eric Lutz University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Outline 1 Information and physics Information gain: Maxwell and Szilard Information erasure: Landauer
The physics of information: from Maxwell s demon to Landauer Eric Lutz University of Erlangen-Nürnberg Outline 1 Information and physics Information gain: Maxwell and Szilard Information erasure: Landauer
Even if you're not burning books, destroying information generates heat.
 Even if you're not burning books, destroying information generates heat. Information and Thermodynamics: Experimental verification of Landauer's erasure principle with a colloidal particle Antoine Bérut,
Even if you're not burning books, destroying information generates heat. Information and Thermodynamics: Experimental verification of Landauer's erasure principle with a colloidal particle Antoine Bérut,
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 10 May 2018
![arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 10 May 2018 arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 10 May 2018](/thumbs/87/96225724.jpg) Cost of remembering a bit of information D. Chiuchiù, 1, M. López-Suárez, 1 I. Neri, 1,, M. C. Diamantini, 1, and L. Gammaitoni 1 arxiv:1703.05544v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 10 May 018 1 NiPS Lab, Università
Cost of remembering a bit of information D. Chiuchiù, 1, M. López-Suárez, 1 I. Neri, 1,, M. C. Diamantini, 1, and L. Gammaitoni 1 arxiv:1703.05544v3 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 10 May 018 1 NiPS Lab, Università
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER /2017
 UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
UNIVERSITY OF BOLTON TW35 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING BENG (HONS) ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EXAMINATION SEMESTER 2-2016/2017 INTERMEDIATE DIGITAL ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATIONS MODULE NO: EEE5002
Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
arxiv: v4 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 3 Mar 2017
![arxiv: v4 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 3 Mar 2017 arxiv: v4 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 3 Mar 2017](/thumbs/95/123892055.jpg) Memory Erasure using Time Multiplexed Potentials Saurav Talukdar, Shreyas Bhaban and Murti V. Salapaka University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA. (Dated: March, 7) arxiv:69.87v [cond-mat.stat-mech] Mar
Memory Erasure using Time Multiplexed Potentials Saurav Talukdar, Shreyas Bhaban and Murti V. Salapaka University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, USA. (Dated: March, 7) arxiv:69.87v [cond-mat.stat-mech] Mar
Digital Logic. CS211 Computer Architecture. l Topics. l Transistors (Design & Types) l Logic Gates. l Combinational Circuits.
 CS211 Computer Architecture Digital Logic l Topics l Transistors (Design & Types) l Logic Gates l Combinational Circuits l K-Maps Figures & Tables borrowed from:! http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_4/index.html!
CS211 Computer Architecture Digital Logic l Topics l Transistors (Design & Types) l Logic Gates l Combinational Circuits l K-Maps Figures & Tables borrowed from:! http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_4/index.html!
Basic on the physics of energy transforma2ons at micro and nanoscales
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Basic on the physics of energy transforma2ons at micro and nanoscales Luca Gammaitoni ICT-Energy Summer school 2016, Aalborg Prof. Luca Gammaitoni University of Perugia (IT) AD
Corso di Laurea in FISICA Basic on the physics of energy transforma2ons at micro and nanoscales Luca Gammaitoni ICT-Energy Summer school 2016, Aalborg Prof. Luca Gammaitoni University of Perugia (IT) AD
Thermodynamic of computing. Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2017/2018
 Thermodynamic of computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2017/2018 Landauer principle Minimum amount of energy required greater than zero Let assume the operation of bit reset # of initial states: 2 # of
Thermodynamic of computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2017/2018 Landauer principle Minimum amount of energy required greater than zero Let assume the operation of bit reset # of initial states: 2 # of
Control gates as building blocks for reversible computers
 Control gates as building blocks for reversible computers A. De Vos 1, B. Desoete 2, F. Janiak 3, and A. Nogawski 3 1 Universiteit Gent and Imec v.z.w., B-9000 Gent, Belgium 2 Universiteit Gent, B-9000
Control gates as building blocks for reversible computers A. De Vos 1, B. Desoete 2, F. Janiak 3, and A. Nogawski 3 1 Universiteit Gent and Imec v.z.w., B-9000 Gent, Belgium 2 Universiteit Gent, B-9000
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 27 Feb 1996
 Single-Electron Parametron: Reversible Computation in a Discrete State System Konstantin K. Likharev 1 and Alexander N. Korotkov 1,2 1 Department of Physics, State University of New York, arxiv:cond-mat/9602140v1
Single-Electron Parametron: Reversible Computation in a Discrete State System Konstantin K. Likharev 1 and Alexander N. Korotkov 1,2 1 Department of Physics, State University of New York, arxiv:cond-mat/9602140v1
Looking at a two binary digit sum shows what we need to extend addition to multiple binary digits.
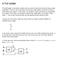 A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Sep 2018](/thumbs/87/95420526.jpg) Realizing Information Erasure in Finite Time James. Melbourne, Saurav. Talukdar, Murti. V. Salapaka arxiv:1809.09216v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Sep 2018 Abstract In this article, we focus on erasure of
Realizing Information Erasure in Finite Time James. Melbourne, Saurav. Talukdar, Murti. V. Salapaka arxiv:1809.09216v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Sep 2018 Abstract In this article, we focus on erasure of
04. Information and Maxwell's Demon. I. Dilemma for Information-Theoretic Exorcisms.
 04. Information and Maxwell's Demon. I. Dilemma for Information-Theoretic Exorcisms. Two Options: (S) (Sound). The combination of object system and demon forms a canonical thermal system. (P) (Profound).
04. Information and Maxwell's Demon. I. Dilemma for Information-Theoretic Exorcisms. Two Options: (S) (Sound). The combination of object system and demon forms a canonical thermal system. (P) (Profound).
Demons: Maxwell demon; Szilard engine; and Landauer's erasure-dissipation
 "Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not simpler." Albert Einstein Demons: Maxwell demon; Szilard engine; and Landauer's erasure-dissipation Laszlo B. Kish (1), Claes-Göran Granqvist (2),
"Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not simpler." Albert Einstein Demons: Maxwell demon; Szilard engine; and Landauer's erasure-dissipation Laszlo B. Kish (1), Claes-Göran Granqvist (2),
Maxwell s Demon. Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ (October 3, 2004)
 1 Problem Maxwell s Demon Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (October 3, 2004) This problem is prob. 2 of [1]. One of the earliest conceptual supercomputers
1 Problem Maxwell s Demon Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (October 3, 2004) This problem is prob. 2 of [1]. One of the earliest conceptual supercomputers
Implementation of Boolean Logic by Digital Circuits
 Implementation of Boolean Logic by Digital Circuits We now consider the use of electronic circuits to implement Boolean functions and arithmetic functions that can be derived from these Boolean functions.
Implementation of Boolean Logic by Digital Circuits We now consider the use of electronic circuits to implement Boolean functions and arithmetic functions that can be derived from these Boolean functions.
Thermodynamic of computing. Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016
 Thermodynamic of computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016 Landauer principle Minimum amount of energy required greater than zero Let assume the operation of bit reset # of initial states: 2 # of
Thermodynamic of computing Fisica dell Energia - a.a. 2015/2016 Landauer principle Minimum amount of energy required greater than zero Let assume the operation of bit reset # of initial states: 2 # of
Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops Prof. YingLi Tian April 11, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 17: Designing Sequential Systems Using Flip Flops Prof. YingLi Tian April 11, 2019 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
arxiv:chao-dyn/ v1 17 Feb 1999
 Entropy Generation in Computation and the Second Law of Thermodynamics arxiv:chao-dyn/9902012v1 17 Feb 1999 Shunya Ishioka Department of Information Science, Kanagawa University Hiratsuka, Kanagawa 259-1293,
Entropy Generation in Computation and the Second Law of Thermodynamics arxiv:chao-dyn/9902012v1 17 Feb 1999 Shunya Ishioka Department of Information Science, Kanagawa University Hiratsuka, Kanagawa 259-1293,
LECTURE 28. Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State
 Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
Sequential Logic. Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS. Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
CMPE12 - Notes chapter 1. Digital Logic. (Textbook Chapter 3)
 CMPE12 - Notes chapter 1 Digital Logic (Textbook Chapter 3) Transistor: Building Block of Computers Microprocessors contain TONS of transistors Intel Montecito (2005): 1.72 billion Intel Pentium 4 (2000):
CMPE12 - Notes chapter 1 Digital Logic (Textbook Chapter 3) Transistor: Building Block of Computers Microprocessors contain TONS of transistors Intel Montecito (2005): 1.72 billion Intel Pentium 4 (2000):
Statistical Physics. How to connect the microscopic properties -- lots of changes to the macroscopic properties -- not changing much.
 Statistical Physics How to connect the microscopic properties -- lots of changes to the macroscopic properties -- not changing much. We will care about: N = # atoms T = temperature V = volume U = total
Statistical Physics How to connect the microscopic properties -- lots of changes to the macroscopic properties -- not changing much. We will care about: N = # atoms T = temperature V = volume U = total
Lecture 6: Time-Dependent Behaviour of Digital Circuits
 Lecture 6: Time-Dependent Behaviour of Digital Circuits Two rather different quasi-physical models of an inverter gate were discussed in the previous lecture. The first one was a simple delay model. This
Lecture 6: Time-Dependent Behaviour of Digital Circuits Two rather different quasi-physical models of an inverter gate were discussed in the previous lecture. The first one was a simple delay model. This
Maxwell s Demon. Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ (October 3, 2004; updated September 20, 2016)
 1 Problem Maxwell s Demon Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (October 3, 2004; updated September 20, 2016) This problem is prob. 2 of [1]. One of the
1 Problem Maxwell s Demon Kirk T. McDonald Joseph Henry Laboratories, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 (October 3, 2004; updated September 20, 2016) This problem is prob. 2 of [1]. One of the
Gibbs Free Energy. Evaluating spontaneity
 Gibbs Free Energy Evaluating spontaneity Predicting Spontaneity An increase in entropy; Changing from a more structured to less structured physical state: Solid to liquid Liquid to gas Increase in temperature
Gibbs Free Energy Evaluating spontaneity Predicting Spontaneity An increase in entropy; Changing from a more structured to less structured physical state: Solid to liquid Liquid to gas Increase in temperature
Thermodynamics of computation
 C. THERMODYNAMICS OF COMPUTATION 37 C Thermodynamics of computation This lecture is based on Charles H. Bennett s The Thermodynamics of Computation a Review, Int. J. Theo. Phys., 1982 [B82]. Unattributed
C. THERMODYNAMICS OF COMPUTATION 37 C Thermodynamics of computation This lecture is based on Charles H. Bennett s The Thermodynamics of Computation a Review, Int. J. Theo. Phys., 1982 [B82]. Unattributed
2.2 Classical circuit model of computation
 Chapter 2 Classical Circuit Models for Computation 2. Introduction A computation is ultimately performed by a physical device. Thus it is a natural question to ask what are the fundamental limitations
Chapter 2 Classical Circuit Models for Computation 2. Introduction A computation is ultimately performed by a physical device. Thus it is a natural question to ask what are the fundamental limitations
Let s start by reviewing what we learned last time. Here is the basic line of reasoning for Einstein Solids
 Chapter 5 In this chapter we want to review the concept of irreversibility in more detail and see how it comes from the multiplicity of states. In addition, we want to introduce the following new topics:
Chapter 5 In this chapter we want to review the concept of irreversibility in more detail and see how it comes from the multiplicity of states. In addition, we want to introduce the following new topics:
Adequate set of connectives, logic gates and circuits
 Adequate set of connectives, logic gates and circuits Lila Kari University of Waterloo Adequate set of connectives, logic gates and circuits CS245, Logic and Computation 1 / 59 Connectives We have mentioned
Adequate set of connectives, logic gates and circuits Lila Kari University of Waterloo Adequate set of connectives, logic gates and circuits CS245, Logic and Computation 1 / 59 Connectives We have mentioned
A Novel Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM) Design Using Reversible Logic
 2015 28th International Conference 2015 on 28th VLSI International Design and Conference 2015 14th International VLSI Design Conference on Embedded Systems A Novel Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM)
2015 28th International Conference 2015 on 28th VLSI International Design and Conference 2015 14th International VLSI Design Conference on Embedded Systems A Novel Ternary Content-Addressable Memory (TCAM)
phys4.20 Page 1 - the ac Josephson effect relates the voltage V across a Junction to the temporal change of the phase difference
 Josephson Effect - the Josephson effect describes tunneling of Cooper pairs through a barrier - a Josephson junction is a contact between two superconductors separated from each other by a thin (< 2 nm)
Josephson Effect - the Josephson effect describes tunneling of Cooper pairs through a barrier - a Josephson junction is a contact between two superconductors separated from each other by a thin (< 2 nm)
The Physics of Energy
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA The Physics of Energy Luca Gammaitoni Corso di Laurea in Fisica, 2017-2018 Program Lecture 1: Energy intro and Basic thermodynamics Lecture 2: Signal analysis intro Lecture 3:
Corso di Laurea in FISICA The Physics of Energy Luca Gammaitoni Corso di Laurea in Fisica, 2017-2018 Program Lecture 1: Energy intro and Basic thermodynamics Lecture 2: Signal analysis intro Lecture 3:
Latches. October 13, 2003 Latches 1
 Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
EE241 - Spring 2003 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits
 EE241 - Spring 2003 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 16 Energy-Recovery Circuits SOI Technology and Circuits Optimal EDP Contours 1 Leakage and Switching ELk 2 = ESw Opt L ln d K tech α avg
EE241 - Spring 2003 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 16 Energy-Recovery Circuits SOI Technology and Circuits Optimal EDP Contours 1 Leakage and Switching ELk 2 = ESw Opt L ln d K tech α avg
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics. Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D.
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 2017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 1. This homework is due September 5, 2017, at 11:59AM.
 EECS 16 Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 1 This homework is due September 5, 017, at 11:59M. 1. Fundamental Theorem of Solutions to Differential
EECS 16 Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 1 This homework is due September 5, 017, at 11:59M. 1. Fundamental Theorem of Solutions to Differential
DEMONS: MAXWELL S DEMON, SZILARD S ENGINE AND LANDAUER S ERASURE DISSIPATION
 In: Proceedings of the first conference on Hot Topics in Physical Informatics (HoTPI, 2013 November). Paper is in press at International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series (2014). DEMONS: MAXWELL
In: Proceedings of the first conference on Hot Topics in Physical Informatics (HoTPI, 2013 November). Paper is in press at International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series (2014). DEMONS: MAXWELL
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Digital Electronics Part 1: Binary Logic
 Digital Electronics Part 1: Binary Logic Electronic devices in your everyday life What makes these products examples of electronic devices? What are some things they have in common? 2 How do electronics
Digital Electronics Part 1: Binary Logic Electronic devices in your everyday life What makes these products examples of electronic devices? What are some things they have in common? 2 How do electronics
Information entropy and thermal entropy: apples and oranges
 Information entropy and thermal entropy: apples and oranges L.B. Kish 1 and D.K. Ferry 2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Texas A&M University, TAMUS 3128, College Station, TX 77843-3128
Information entropy and thermal entropy: apples and oranges L.B. Kish 1 and D.K. Ferry 2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Texas A&M University, TAMUS 3128, College Station, TX 77843-3128
Introduction to Computer Engineering. CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Slides based on set prepared by
Introduction to Computer Engineering CS/ECE 252, Fall 2012 Prof. Guri Sohi Computer Sciences Department University of Wisconsin Madison Chapter 3 Digital Logic Structures Slides based on set prepared by
Second law, entropy production, and reversibility in thermodynamics of information
 Second law, entropy production, and reversibility in thermodynamics of information Takahiro Sagawa arxiv:1712.06858v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 19 Dec 2017 Abstract We present a pedagogical review of the fundamental
Second law, entropy production, and reversibility in thermodynamics of information Takahiro Sagawa arxiv:1712.06858v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 19 Dec 2017 Abstract We present a pedagogical review of the fundamental
The End of the Thermodynamics of Computation: A No Go Result
 December 22, 28, 2011 June 20, 2012 March 31, August 20, 2013 The End of the Thermodynamics of Computation: A No Go Result John D. Norton Department of History and Philosophy of Science Center for Philosophy
December 22, 28, 2011 June 20, 2012 March 31, August 20, 2013 The End of the Thermodynamics of Computation: A No Go Result John D. Norton Department of History and Philosophy of Science Center for Philosophy
Implementation of Optimized Reversible Sequential and Combinational Circuits for VLSI Applications
 V. G. Santhi Swaroop et al Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Implementation of Optimized Reversible Sequential and Combinational Circuits for VLSI Applications
V. G. Santhi Swaroop et al Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Implementation of Optimized Reversible Sequential and Combinational Circuits for VLSI Applications
The thermodynamics of cellular computation
 The thermodynamics of cellular computation Sourjik and Wingreen (2012) Cur. Opinions in Cell Bio. Pankaj Mehta Collaborators: David Schwab, Charles Fisher, Mo Khalil Cells perform complex computations
The thermodynamics of cellular computation Sourjik and Wingreen (2012) Cur. Opinions in Cell Bio. Pankaj Mehta Collaborators: David Schwab, Charles Fisher, Mo Khalil Cells perform complex computations
Energy management at micro scales
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Energy management at micro scales Luca Gammaitoni ICT- Energy Training Day, Bristol 14 Sept. 2015 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content IntroducCon to the nocon of energy. Laws of
Corso di Laurea in FISICA Energy management at micro scales Luca Gammaitoni ICT- Energy Training Day, Bristol 14 Sept. 2015 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content IntroducCon to the nocon of energy. Laws of
Problem. Problem Given a dictionary and a word. Which page (if any) contains the given word? 3 / 26
 Binary Search Introduction Problem Problem Given a dictionary and a word. Which page (if any) contains the given word? 3 / 26 Strategy 1: Random Search Randomly select a page until the page containing
Binary Search Introduction Problem Problem Given a dictionary and a word. Which page (if any) contains the given word? 3 / 26 Strategy 1: Random Search Randomly select a page until the page containing
Quantum Thermodynamics
 Quantum Thermodynamics In this chapter we wish to give some insights to quantum thermodynamics. It can be seen as an introduction to the topic, however not a broad one but rather an introduction by examples.
Quantum Thermodynamics In this chapter we wish to give some insights to quantum thermodynamics. It can be seen as an introduction to the topic, however not a broad one but rather an introduction by examples.
PHYS 414 Problem Set 4: Demonic refrigerators and eternal sunshine
 PHYS 414 Problem Set 4: Demonic refrigerators and eternal sunshine In a famous thought experiment discussing the second law of thermodynamics, James Clerk Maxwell imagined an intelligent being (a demon
PHYS 414 Problem Set 4: Demonic refrigerators and eternal sunshine In a famous thought experiment discussing the second law of thermodynamics, James Clerk Maxwell imagined an intelligent being (a demon
DESIGN OF A COMPACT REVERSIBLE READ- ONLY-MEMORY WITH MOS TRANSISTORS
 DESIGN OF A COMPACT REVERSIBLE READ- ONLY-MEMORY WITH MOS TRANSISTORS Sadia Nowrin, Papiya Nazneen and Lafifa Jamal Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Dhaka, Bangladesh ABSTRACT
DESIGN OF A COMPACT REVERSIBLE READ- ONLY-MEMORY WITH MOS TRANSISTORS Sadia Nowrin, Papiya Nazneen and Lafifa Jamal Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Dhaka, Bangladesh ABSTRACT
Lecture 6 - LANDAUER: Computing with uncertainty
 Lecture 6 - LANDAUER: Computing with uncertainty Igor Neri - NiPS Laboratory, University of Perugia July 18, 2014!! NiPS Summer School 2014 ICT-Energy: Energy management at micro and nanoscales for future
Lecture 6 - LANDAUER: Computing with uncertainty Igor Neri - NiPS Laboratory, University of Perugia July 18, 2014!! NiPS Summer School 2014 ICT-Energy: Energy management at micro and nanoscales for future
Information and Physics Landauer Principle and Beyond
 Information and Physics Landauer Principle and Beyond Ryoichi Kawai Department of Physics University of Alabama at Birmingham Maxwell Demon Lerner, 975 Landauer principle Ralf Landauer (929-999) Computational
Information and Physics Landauer Principle and Beyond Ryoichi Kawai Department of Physics University of Alabama at Birmingham Maxwell Demon Lerner, 975 Landauer principle Ralf Landauer (929-999) Computational
The Design Procedure. Output Equation Determination - Derive output equations from the state table
 The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
The Design Procedure Specification Formulation - Obtain a state diagram or state table State Assignment - Assign binary codes to the states Flip-Flop Input Equation Determination - Select flipflop types
Project Periodic Report
 Project Periodic Report Publishable Summary Grant Agreement n. 256959 Project title Nanoscale energy management for powering ICT devices Project acronym NANOPOWER Call identifier FP7-ICT-2009-5 Funding
Project Periodic Report Publishable Summary Grant Agreement n. 256959 Project title Nanoscale energy management for powering ICT devices Project acronym NANOPOWER Call identifier FP7-ICT-2009-5 Funding
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Quantum Cellular Automata: The Physics of Computing with Arrays of Quantum Dot Molecules
 Quantum Cellular Automata: The Physics of Computing with Arrays of Quantum Dot Molecules Craig. S. Lent, P. Douglas Tougaw, and Wolfgang Porod Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Notre
Quantum Cellular Automata: The Physics of Computing with Arrays of Quantum Dot Molecules Craig. S. Lent, P. Douglas Tougaw, and Wolfgang Porod Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Notre
Contents. Chapter 3 Combinational Circuits Page 1 of 36
 Chapter 3 Combinational Circuits Page of 36 Contents Combinational Circuits...2 3. Analysis of Combinational Circuits...3 3.. Using a Truth Table...3 3..2 Using a Boolean Function...6 3.2 Synthesis of
Chapter 3 Combinational Circuits Page of 36 Contents Combinational Circuits...2 3. Analysis of Combinational Circuits...3 3.. Using a Truth Table...3 3..2 Using a Boolean Function...6 3.2 Synthesis of
Basic thermodynamics
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA 1 Basic thermodynamics Luca Gammaitoni ICT- Energy Summer school 2015, Fiuggi (IT) Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content IntroducBon to the nobon of energy. Laws of energy transformabon
Corso di Laurea in FISICA 1 Basic thermodynamics Luca Gammaitoni ICT- Energy Summer school 2015, Fiuggi (IT) Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content IntroducBon to the nobon of energy. Laws of energy transformabon
XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL.
![XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL. XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL.](/thumbs/81/84726747.jpg) 2017-18 XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL HALF ADDER 1. The circuit that performs addition within the Arithmetic and Logic Unit of the CPU are called adders. 2. A unit that adds two
2017-18 XI STANDARD [ COMPUTER SCIENCE ] 5 MARKS STUDY MATERIAL HALF ADDER 1. The circuit that performs addition within the Arithmetic and Logic Unit of the CPU are called adders. 2. A unit that adds two
Circuit for Revisable Quantum Multiplier Implementation of Adders with Reversible Logic 1 KONDADASULA VEDA NAGA SAI SRI, 2 M.
 ISSN (O): 2349-7084 International Journal of Computer Engineering In Research Trends Available online at: www.ijcert.org Circuit for Revisable Quantum Multiplier Implementation of Adders with Reversible
ISSN (O): 2349-7084 International Journal of Computer Engineering In Research Trends Available online at: www.ijcert.org Circuit for Revisable Quantum Multiplier Implementation of Adders with Reversible
Digital electronics form a class of circuitry where the ability of the electronics to process data is the primary focus.
 Chapter 2 Digital Electronics Objectives 1. Understand the operation of basic digital electronic devices. 2. Understand how to describe circuits which can process digital data. 3. Understand how to design
Chapter 2 Digital Electronics Objectives 1. Understand the operation of basic digital electronic devices. 2. Understand how to describe circuits which can process digital data. 3. Understand how to design
Energy at micro scales
 Corso di Laurea in FISICA Energy at micro scales Luca Gammaitoni ERASMUS + IESRES INNOVATIVE EUROPEAN STUDIES on RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS 19 Oct 2016, Perugia Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content The microscopic
Corso di Laurea in FISICA Energy at micro scales Luca Gammaitoni ERASMUS + IESRES INNOVATIVE EUROPEAN STUDIES on RENEWABLE ENERGY SYSTEMS 19 Oct 2016, Perugia Corso di Laurea in FISICA Content The microscopic
F14 Memory Circuits. Lars Ohlsson
 Lars Ohlsson 2018-10-18 F14 Memory Circuits Outline Combinatorial vs. sequential logic circuits Analogue multivibrator circuits Noise in digital circuits CMOS latch CMOS SR flip flop 6T SRAM cell 1T DRAM
Lars Ohlsson 2018-10-18 F14 Memory Circuits Outline Combinatorial vs. sequential logic circuits Analogue multivibrator circuits Noise in digital circuits CMOS latch CMOS SR flip flop 6T SRAM cell 1T DRAM
Thermodynamics of feedback controlled systems. Francisco J. Cao
 Thermodynamics of feedback controlled systems Francisco J. Cao Open-loop and closed-loop control Open-loop control: the controller actuates on the system independently of the system state. Controller Actuation
Thermodynamics of feedback controlled systems Francisco J. Cao Open-loop and closed-loop control Open-loop control: the controller actuates on the system independently of the system state. Controller Actuation
Response to Comment on Zero and negative energy dissipation at information-theoretic erasure
 Response to Comment on Zero and negative energy dissipation at information-theoretic erasure Laszlo Bela Kish, Claes-Göran Granqvist, Sunil P. Khatri, Ferdinand Peper Abstract We prove that statistical
Response to Comment on Zero and negative energy dissipation at information-theoretic erasure Laszlo Bela Kish, Claes-Göran Granqvist, Sunil P. Khatri, Ferdinand Peper Abstract We prove that statistical
Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits combinational circuits state gate delay
 Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are those with memory, also called feedback. In this, they differ from combinational circuits, which have no memory. The stable output of a combinational circuit
Sequential Circuits Sequential circuits are those with memory, also called feedback. In this, they differ from combinational circuits, which have no memory. The stable output of a combinational circuit
Zero and negative energy dissipation at information-theoretic erasure
 In press at J. Computational Electronics. http://vixra.org/abs/1507.0221 http://arxiv.org/abs/1507.08906 Zero and negative energy dissipation at information-theoretic erasure Laszlo Bela Kish, Claes-Göran
In press at J. Computational Electronics. http://vixra.org/abs/1507.0221 http://arxiv.org/abs/1507.08906 Zero and negative energy dissipation at information-theoretic erasure Laszlo Bela Kish, Claes-Göran
Comparative analysis of non-equilibrium quantum Landauer bounds
 Comparative analysis of non-equilibrium quantum Landauer bounds Steve Campbell in collaboration with: Giacomo Guarnieri, Mauro Paternostro, and Bassano Vacchini To Appear July(ish) 2017 Landauer s Principle
Comparative analysis of non-equilibrium quantum Landauer bounds Steve Campbell in collaboration with: Giacomo Guarnieri, Mauro Paternostro, and Bassano Vacchini To Appear July(ish) 2017 Landauer s Principle
UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI-COLUMBIA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. PART I Qualifying Examination. August 20, 2013, 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m.
 UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI-COLUMBIA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PART I Qualifying Examination August 20, 2013, 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Instructions: The only material you are allowed in the examination room is a writing
UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI-COLUMBIA PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PART I Qualifying Examination August 20, 2013, 5:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Instructions: The only material you are allowed in the examination room is a writing
NAME: MA Sample Final Exam. Record all your answers on the answer sheet provided. The answer sheet is the only thing that will be graded.
 NAME: MA 300 Sample Final Exam PUID: INSTRUCTIONS There are 5 problems on 4 pages. Record all your answers on the answer sheet provided. The answer sheet is the only thing that will be graded. No books
NAME: MA 300 Sample Final Exam PUID: INSTRUCTIONS There are 5 problems on 4 pages. Record all your answers on the answer sheet provided. The answer sheet is the only thing that will be graded. No books
CMPE12 - Notes chapter 2. Digital Logic. (Textbook Chapters and 2.1)"
 CMPE12 - Notes chapter 2 Digital Logic (Textbook Chapters 3.1-3.5 and 2.1)" Truth table" The most basic representation of a logic function." Brute force representation listing the output for all possible
CMPE12 - Notes chapter 2 Digital Logic (Textbook Chapters 3.1-3.5 and 2.1)" Truth table" The most basic representation of a logic function." Brute force representation listing the output for all possible
Combinational Logic Design Principles
 Combinational Logic Design Principles Switching algebra Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Switching algebra Axioms of switching algebra Theorems
Combinational Logic Design Principles Switching algebra Doru Todinca Department of Computers Politehnica University of Timisoara Outline Introduction Switching algebra Axioms of switching algebra Theorems
Physics 132- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists II. Statistical Physics and Thermodynamics
 Physics 132- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists II Statistical Physics and Thermodynamics QUIZ 2 25 Quiz 2 20 Number of Students 15 10 5 AVG: STDEV: 5.15 2.17 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Score 1. (4 pts) A 200
Physics 132- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists II Statistical Physics and Thermodynamics QUIZ 2 25 Quiz 2 20 Number of Students 15 10 5 AVG: STDEV: 5.15 2.17 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Score 1. (4 pts) A 200
Demon Dynamics: Deterministic Chaos, the Szilard Map, & the Intelligence of Thermodynamic Systems.
 Demon Dynamics: Deterministic Chaos, the Szilard Map, & the Intelligence of Thermodynamic Systems http://csc.ucdavis.edu/~cmg/ Jim Crutchfield Complexity Sciences Center Physics Department University of
Demon Dynamics: Deterministic Chaos, the Szilard Map, & the Intelligence of Thermodynamic Systems http://csc.ucdavis.edu/~cmg/ Jim Crutchfield Complexity Sciences Center Physics Department University of
Ch. 19 Entropy and Free Energy: Spontaneous Change
 Ch. 19 Entropy and Free Energy: Spontaneous Change 19-1 Spontaneity: The Meaning of Spontaneous Change 19-2 The Concept of Entropy 19-3 Evaluating Entropy and Entropy Changes 19-4 Criteria for Spontaneous
Ch. 19 Entropy and Free Energy: Spontaneous Change 19-1 Spontaneity: The Meaning of Spontaneous Change 19-2 The Concept of Entropy 19-3 Evaluating Entropy and Entropy Changes 19-4 Criteria for Spontaneous
Chapter 4. Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 1 2 Chapter 4 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of
Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes
 Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
Thermodynamics Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes A thermodynamic system is described by an equation of state, such as the ideal gas law. The location of the state can be plotted on a p V diagram,
Biasing Brownian motion from thermal ratchets
 Mayra Vega MAE 216- Statistical Thermodynamics June 18, 2012 Introduction Biasing Brownian motion from thermal ratchets Brownian motion is the random movement of small particles however, by understanding
Mayra Vega MAE 216- Statistical Thermodynamics June 18, 2012 Introduction Biasing Brownian motion from thermal ratchets Brownian motion is the random movement of small particles however, by understanding
Lecture 23. CMOS Logic Gates and Digital VLSI I
 ecture 3 CMOS ogic Gates and Digital SI I In this lecture you will learn: Digital ogic The CMOS Inverter Charge and Discharge Dynamics Power Dissipation Digital evels and Noise NFET Inverter Cut-off Saturation
ecture 3 CMOS ogic Gates and Digital SI I In this lecture you will learn: Digital ogic The CMOS Inverter Charge and Discharge Dynamics Power Dissipation Digital evels and Noise NFET Inverter Cut-off Saturation
τ gd =Q/I=(CV)/I I d,sat =(µc OX /2)(W/L)(V gs -V TH ) 2 ESE534 Computer Organization Today At Issue Preclass 1 Energy and Delay Tradeoff
 ESE534 Computer Organization Today Day 8: February 10, 2010 Energy, Power, Reliability Energy Tradeoffs? Voltage limits and leakage? Variations Transients Thermodynamics meets Information Theory (brief,
ESE534 Computer Organization Today Day 8: February 10, 2010 Energy, Power, Reliability Energy Tradeoffs? Voltage limits and leakage? Variations Transients Thermodynamics meets Information Theory (brief,
Beyond the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 Beyond the Second Law of Thermodynamics C. Van den Broeck R. Kawai J. M. R. Parrondo Colloquium at University of Alabama, September 9, 2007 The Second Law of Thermodynamics There exists no thermodynamic
Beyond the Second Law of Thermodynamics C. Van den Broeck R. Kawai J. M. R. Parrondo Colloquium at University of Alabama, September 9, 2007 The Second Law of Thermodynamics There exists no thermodynamic
Logic Theory in Designing of Digital Circuit & Microprocessor
 Logic Theory in Designing of Digital Circuit & Microprocessor Prof.Vikram Mahendra Kakade Assistant Professor, Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Department, Prof Ram Meghe College of Engineering
Logic Theory in Designing of Digital Circuit & Microprocessor Prof.Vikram Mahendra Kakade Assistant Professor, Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Department, Prof Ram Meghe College of Engineering
1.10 (a) Function of AND, OR, NOT, NAND & NOR Logic gates and their input/output.
 Chapter 1.10 Logic Gates 1.10 (a) Function of AND, OR, NOT, NAND & NOR Logic gates and their input/output. Microprocessors are the central hardware that runs computers. There are several components that
Chapter 1.10 Logic Gates 1.10 (a) Function of AND, OR, NOT, NAND & NOR Logic gates and their input/output. Microprocessors are the central hardware that runs computers. There are several components that
VHDL DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF C.P.U BY REVERSIBLE LOGIC GATES
 VHDL DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF C.P.U BY REVERSIBLE LOGIC GATES 1.Devarasetty Vinod Kumar/ M.tech,2. Dr. Tata Jagannadha Swamy/Professor, Dept of Electronics and Commn. Engineering, Gokaraju Rangaraju
VHDL DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF C.P.U BY REVERSIBLE LOGIC GATES 1.Devarasetty Vinod Kumar/ M.tech,2. Dr. Tata Jagannadha Swamy/Professor, Dept of Electronics and Commn. Engineering, Gokaraju Rangaraju
Mark Redekopp, All rights reserved. Lecture 1 Slides. Intro Number Systems Logic Functions
 Lecture Slides Intro Number Systems Logic Functions EE 0 in Context EE 0 EE 20L Logic Design Fundamentals Logic Design, CAD Tools, Lab tools, Project EE 357 EE 457 Computer Architecture Using the logic
Lecture Slides Intro Number Systems Logic Functions EE 0 in Context EE 0 EE 20L Logic Design Fundamentals Logic Design, CAD Tools, Lab tools, Project EE 357 EE 457 Computer Architecture Using the logic
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 17: March 23, 2017 Energy and Power Optimization, Design Space Exploration, Synchronous MOS Logic Lecture Outline! Energy and Power Optimization
İlke Ercan, PhD Assistant Professor, Electrical & Electronics Eng. Dep. Boğaziçi University, İstanbul, Turkey
 ENERGY EFFICIENCY LIMITS IN BROWNIAN CIRCUITS A PHYSICAL-INFORMATION-THEORETIC APPROACH, PhD Assistant Professor, Electrical & Electronics Eng. Dep. Boğaziçi University, İstanbul, Turkey Micro Energy 2017
ENERGY EFFICIENCY LIMITS IN BROWNIAN CIRCUITS A PHYSICAL-INFORMATION-THEORETIC APPROACH, PhD Assistant Professor, Electrical & Electronics Eng. Dep. Boğaziçi University, İstanbul, Turkey Micro Energy 2017
Properties and applications of ferromagnetic nanostructures
 Properties and applications of ferromagnetic nanostructures Diego Bisero, Lucia Del Bianco, Federico Spizzo Magnetism Experimental group Outline 1.Nanostructures: some examples 2.Why ferromagnetic nanostructures?
Properties and applications of ferromagnetic nanostructures Diego Bisero, Lucia Del Bianco, Federico Spizzo Magnetism Experimental group Outline 1.Nanostructures: some examples 2.Why ferromagnetic nanostructures?
Novel Reversible Gate Based Circuit Design and Simulation Using Deep Submicron Technologies
 Novel Reversible Gate Based Circuit Design and Simulation Using Deep Submicron Technologies Abstract: The set AND, OR, and EXOR gates are not reversible as Landauer which states that for irreversible logic
Novel Reversible Gate Based Circuit Design and Simulation Using Deep Submicron Technologies Abstract: The set AND, OR, and EXOR gates are not reversible as Landauer which states that for irreversible logic
Chapter 16 Thermodynamics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 16 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics Introduction Another area of physics is thermodynamics Continues with the principle of conservation of energy
Reversible Implementation of Ternary Content Addressable Memory (TCAM) Interface with SRAM
 International Journal of Electrical Electronics Computers & Mechanical Engineering (IJEECM) ISSN: 2278-2808 Volume 5 Issue 4 ǁ April. 2017 IJEECM journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ijeecm-jec)
International Journal of Electrical Electronics Computers & Mechanical Engineering (IJEECM) ISSN: 2278-2808 Volume 5 Issue 4 ǁ April. 2017 IJEECM journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (ijeecm-jec)
Thermochemical Properties
 Thermochemical Properties Materials respond to Thermal stimuli (temperature) Chemical stimuli (composition or environment) Electromagnetic stimuli (electric or magnetic fields) Mechanical stimuli (mechanical
Thermochemical Properties Materials respond to Thermal stimuli (temperature) Chemical stimuli (composition or environment) Electromagnetic stimuli (electric or magnetic fields) Mechanical stimuli (mechanical
Sequential Logic (3.1 and is a long difficult section you really should read!)
 EECS 270, Fall 2014, Lecture 6 Page 1 of 8 Sequential Logic (3.1 and 3.2. 3.2 is a long difficult section you really should read!) One thing we have carefully avoided so far is feedback all of our signals
EECS 270, Fall 2014, Lecture 6 Page 1 of 8 Sequential Logic (3.1 and 3.2. 3.2 is a long difficult section you really should read!) One thing we have carefully avoided so far is feedback all of our signals
