Equilibrium. For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: and no net torque:
|
|
|
- Reginald Summers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Equilibrium For an object to remain in equilibrium, two conditions must be met. The object must have no net force: F v = 0 and no net torque: v τ = 0
2 Worksheet A uniform rod with a length L and a mass m is attached to a wall by a hinge at the left end. A string will hold the rod in a horizontal position; the string can be tied to one of three points, lettered A-C, on the rod. The other end of the string can be tied to one of three hooks, numbered 1-3, above the rod. This system could be a simple model of a broken arm you want to immobilize with a sling.
3 Sling, part 1 How would you attach a string so the rod is held in a horizontal position but the hinge exerts no force at all on the rod? 1. A A A B 1 or B B C C C It can t be done.
4 Sling, part 2 How would you attach a string so the rod is held in a horizontal position while the force exerted on the rod by the hinge has no horizontal component, but has a non-zero vertical component directed straight up? 1. A A A B 1 or B B C C C It can t be done.
5 Sling, part 3 How would you attach a string so the rod is held in a horizontal position while the force exerted on the rod by the hinge has no vertical component, but has a non-zero horizontal component? 1. A A A B 1 or B B C C C It can t be done.
6 A balanced beam A uniform beam sits on two identical scales. Scale A is farther from the center than scale B, but the beam remains in equilibrium. Which scale shows a higher reading? How far to the left could scale B be moved without the beam tipping over?
7 A balanced beam A uniform beam sits on two identical scales. Scale A is farther from the center than scale B, but the beam remains in equilibrium. Which scale shows a higher reading? Scale B it is closer to the center of gravity. How far to the left could scale B be moved without the beam tipping over?
8 A balanced beam A uniform beam sits on two identical scales. Scale A is farther from the center than scale B, but the beam remains in equilibrium. Which scale shows a higher reading? Scale B it is closer to the center of gravity. How far to the left could scale B be moved without the beam tipping over? To the center of the beam, but no farther. The beam s center of gravity must be between the supports to be stable.
9 A balanced beam Could you place a weight on the beam without the reading on scale A changing? Could you place a weight on the beam and cause the reading on scale A to decrease?
10 A balanced beam Could you place a weight on the beam without the reading on scale A changing? Yes place it directly over scale B. Could you place a weight on the beam and cause the reading on scale A to decrease?
11 A balanced beam Could you place a weight on the beam without the reading on scale A changing? Yes place it directly over scale B. Could you place a weight on the beam and cause the reading on scale A to decrease? Yes put it on the beam to the right of scale B.
12 A balanced beam What happens to the scale readings when scale B is moved to the right? 1. A is unchanged, B goes up. 2. A is unchanged, B goes down. 3. Both readings decrease. 4. Both readings increase. 5. A goes up, B goes down. 6. A goes down, B goes up. 7. None of the above.
13 The human spine Equilibrium ideas can be applied to the human body, including the spine. If you bend your upper body so it is horizontal, you put a lot of stress on the lumbrosacral disk, the disk separating the lowest vertebra from the tailbone (the sacrum). Picking something up when bending this way is even worse.
14 The human spine Simulation Treat the spine as a pivoted bar. There are essentially three forces acting on this bar: The force of gravity, mg, acting on the upper body (this is about 65% of the body weight). The tension in the back muscles. This can be considered as one force T that acts at an angle of about 12 to the horizontal when the upper body is horizontal. The support force F from the tailbone, which also acts at a small angle measured from the horizontal.
15 The human spine Treat the spine as a pivoted bar. There are essentially three forces acting on this bar: The force of gravity, mg, acting on the upper body (this is about 65% of the body weight). The tension in the back muscles. This can be considered as one force T that acts at an angle of about 12 to the horizontal when the upper body is horizontal. The support force F from the tailbone, which also acts at a small angle measured from the horizontal.
16 The human spine For a person with a weight of 600 N, the upper body weighs almost 400 N. What are T and F?
17 The human spine For a person with a weight of 600 N, the upper body weighs almost 400 N. What are T and F? v How far do forces get us? F = 0 X-direction: + F T = x x 0 Y-direction: Now what? + F + T mg = y y 0
18 Let s try summing torques: The human spine v τ = 0 Choose a point where one of the unknown forces passes through to sum torques.
19 Let s try summing torques: The human spine v τ = 0 Choose a point where one of the unknown forces passes through to sum torques. In this case, choose the tailbone (the left end, below) as our axis for torques this eliminates F.
20 The human spine Take torques about the tailbone I m choosing counterclockwise to be positive for torque. Effectively, T is applied about 10% farther from the tailbone than the force of gravity. + (1.1 d)( T)(sin12 ) d( mg) = 0 mg T = 1.1(sin12 ) If mg = 400 N, T comes out to about 1700 N! The components of the support force F can be found from our force equations. F is also about 1700 N. d
21 The human spine Picking up something, which has a weight of 100 N, with your arms increases both T and F by about 600 N! The moral of the story: bend your legs instead of your back. Picking up a 100 N bag of groceries by bending at the knee produces a force of about 500 N on the bottom disk in the spine. The force is 4-5 times larger if you bend your back!
22 Newton s Second Law for Rotation v v The equation τ = I α is the rotational equivalent of v v F = ma. Torque plays the role of force. Rotational inertia plays the role of mass. Angular acceleration plays the role of the acceleration.
23 Applying Newton s Second Law A constant force of F = 8 N is applied to a string wrapped around the outside of the pulley. The pulley is a solid disk of mass M = 2.0 kg and radius R = 0.50 m, and is mounted on a horizontal frictionless axle. What is the pulley's angular acceleration? Simulation What should we do first? Why are we told that the pulley is a solid disk?
24 Applying Newton s Second Law A constant force of F = 8 N is applied to a string wrapped around the outside of the pulley. The pulley is a solid disk of mass M = 2.0 kg and radius R = 0.50 m, and is mounted on a horizontal frictionless axle. What is the pulley's angular acceleration? Simulation What should we do first? Draw a free-body diagram of the pulley. Why are we told that the pulley is a solid disk?
25 Applying Newton s Second Law A constant force of F = 8 N is applied to a string wrapped around the outside of the pulley. The pulley is a solid disk of mass M = 2.0 kg and radius R = 0.50 m, and is mounted on a horizontal frictionless axle. What is the pulley's angular acceleration? Simulation What should we do first? Draw a free-body diagram of the pulley. Why are we told that the pulley is a solid disk? So we know what to use for the rotational inertia. I = 1 MR 2 2
26 Applying Newton s Second Law v τ = v Iα RF = 1 2 MR 2 α F = 1 MRα 2 ( ) 2F N α = = = 16 rad/s MR (2.0 kg) (0.5 m) 2
27 Two pulleys Simulation We take two identical pulleys, both with string wrapped around them. On the one on the left we apply an 8 N force to the string. On the one on the right we hang an object with a weight of 8 N. Which pulley has the larger angular acceleration?
28 Two pulleys We take two identical pulleys, both with string wrapped around them. On the one on the left we apply an 8 N force to the string. On the one on the right we hang an object with a weight of 8 N. Which pulley has the larger angular acceleration? 1. The one on the left 2. The one on the right 3. Neither, they're equal
29 Two pulleys For the pulley on the left, the tension in the string is 8 N. Simulation For the system on the right, let s draw the free-body diagram of the weight. What does the free-body diagram tell us about the tension in the string?
30 Two pulleys For the pulley on the left, the tension in the string is 8 N. For the system on the right, let s draw the free-body diagram of the weight. What does the free-body diagram tell us about the tension in the string? For the weight to have a net force directed down, the tension must be less than the force of gravity. So, the tension is less than 8 N.
Definition. is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau)
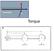 Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Torque Definition is a measure of how much a force acting on an object causes that object to rotate, symbol is, (Greek letter tau) = r F = rfsin, r = distance from pivot to force, F is the applied force
Answers to selected problems from Essential Physics, Chapter 10
 Answers to selected problems from Essential Physics, Chapter 10 1. (a) The red ones have the same speed as one another. The blue ones also have the same speed as one another, with a value twice the speed
Answers to selected problems from Essential Physics, Chapter 10 1. (a) The red ones have the same speed as one another. The blue ones also have the same speed as one another, with a value twice the speed
Torque. Physics 6A. Prepared by Vince Zaccone For Campus Learning Assistance Services at UCSB
 Physics 6A Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) For a torque
Physics 6A Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) Torque is what causes angular acceleration (just like a force causes linear acceleration) For a torque
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM. Instructor: Kazumi Tolich
 LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
LECTURE 22 EQUILIBRIUM Instructor: Kazumi Tolich Lecture 22 2 Reading chapter 11-3 to 11-4 Static equilibrium Center of mass and balance Static equilibrium 3 If a rigid object is in equilibrium (constant
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015
 Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
Physics 2210 Homework 18 Spring 2015 Charles Jui April 12, 2015 IE Sphere Incline Wording A solid sphere of uniform density starts from rest and rolls without slipping down an inclined plane with angle
Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Lecture 17, Chapter 10: Rotational Energy and Angular Momentum 1 Rotational Kinetic Energy Consider a rigid body rotating with an angular velocity ω about an axis. Clearly every point in the rigid body
Physics 111. Tuesday, November 2, Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy
 ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
ics Tuesday, ember 2, 2002 Ch 11: Rotational Dynamics Torque Angular Momentum Rotational Kinetic Energy Announcements Wednesday, 8-9 pm in NSC 118/119 Sunday, 6:30-8 pm in CCLIR 468 Announcements This
Chapter 8. Rotational Motion
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of
Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW
 Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
Pagpalain ka! (Good luck, in Filipino) Date Chapter 8 - Rotational Dynamics and Equilibrium REVIEW TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) When a rigid body
III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) Rotation. We repeat Chap. 2-8 with rotatiing objects. Eqs. of motion. Energy.
 Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Toward Exam 3 Eqs. of motion o To study angular
Static equilibrium. Objectives. Physics terms. Assessment. Brainstorm. Equations 6/3/14
 Static equilibrium Objectives State the conditions of static equilibrium in terms of forces and torques. Draw a free-body diagram of a lever showing all forces. Use the condition of equilibrium to solve
Static equilibrium Objectives State the conditions of static equilibrium in terms of forces and torques. Draw a free-body diagram of a lever showing all forces. Use the condition of equilibrium to solve
Physics for Scientist and Engineers third edition Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis Problems
 A particular bird s eye can just distinguish objects that subtend an angle no smaller than about 3 E -4 rad, A) How many degrees is this B) How small an object can the bird just distinguish when flying
A particular bird s eye can just distinguish objects that subtend an angle no smaller than about 3 E -4 rad, A) How many degrees is this B) How small an object can the bird just distinguish when flying
CHAPTER 8: ROTATIONAL OF RIGID BODY PHYSICS. 1. Define Torque
 7 1. Define Torque 2. State the conditions for equilibrium of rigid body (Hint: 2 conditions) 3. Define angular displacement 4. Define average angular velocity 5. Define instantaneous angular velocity
7 1. Define Torque 2. State the conditions for equilibrium of rigid body (Hint: 2 conditions) 3. Define angular displacement 4. Define average angular velocity 5. Define instantaneous angular velocity
 AP Physics 1- Torque, Rotational Inertia, and Angular Momentum Practice Problems FACT: The center of mass of a system of objects obeys Newton s second law- F = Ma cm. Usually the location of the center
AP Physics 1- Torque, Rotational Inertia, and Angular Momentum Practice Problems FACT: The center of mass of a system of objects obeys Newton s second law- F = Ma cm. Usually the location of the center
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Torque 1. A uniform meterstick of mass 0.20 kg is pivoted at the 40 cm mark. Where should one hang a mass of 0.50 kg to balance the stick? (A) 16 cm (B) 36 cm (C) 44
Name Student ID Score Last First. I = 2mR 2 /5 around the sphere s center of mass?
 NOTE: ignore air resistance in all Questions. In all Questions choose the answer that is the closest!! Question I. (15 pts) Rotation 1. (5 pts) A bowling ball that has an 11 cm radius and a 7.2 kg mass
NOTE: ignore air resistance in all Questions. In all Questions choose the answer that is the closest!! Question I. (15 pts) Rotation 1. (5 pts) A bowling ball that has an 11 cm radius and a 7.2 kg mass
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013
 Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
Chapter 9: Rotational Dynamics Tuesday, September 17, 2013 10:00 PM The fundamental idea of Newtonian dynamics is that "things happen for a reason;" to be more specific, there is no need to explain rest
AP Physics. Harmonic Motion. Multiple Choice. Test E
 AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
AP Physics Harmonic Motion Multiple Choice Test E A 0.10-Kg block is attached to a spring, initially unstretched, of force constant k = 40 N m as shown below. The block is released from rest at t = 0 sec.
Rotational N.2 nd Law
 Lecture 19 Chapter 12 Rotational N.2 nd Law Torque Newton 2 nd Law again!? That s it. He crossed the line! Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will
Lecture 19 Chapter 12 Rotational N.2 nd Law Torque Newton 2 nd Law again!? That s it. He crossed the line! Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Demonstrating Rotational Inertia (or Moment of Inertia)
 Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Demonstrating Rotational Inertia (or Moment of Inertia) Have you ever struggled to describe Rotational Inertia to your students? Even worse, have you ever struggled to understand
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Demonstrating Rotational Inertia (or Moment of Inertia) Have you ever struggled to describe Rotational Inertia to your students? Even worse, have you ever struggled to understand
Problem Set x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer
 8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Problem Set 10 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer (a) A thin uniform disc of mass M and radius R is mounted on an axis passing
8.01x Classical Mechanics, Fall 2016 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Problem Set 10 1. Moment of Inertia: Disc and Washer (a) A thin uniform disc of mass M and radius R is mounted on an axis passing
Rotational Dynamics continued
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.1 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics continued 9.1 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Static Equilibrium; Torque
 Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
Static Equilibrium; Torque The Conditions for Equilibrium An object with forces acting on it, but that is not moving, is said to be in equilibrium. The first condition for equilibrium is that the net force
Torque rotational force which causes a change in rotational motion. This force is defined by linear force multiplied by a radius.
 Warm up A remote-controlled car's wheel accelerates at 22.4 rad/s 2. If the wheel begins with an angular speed of 10.8 rad/s, what is the wheel's angular speed after exactly three full turns? AP Physics
Warm up A remote-controlled car's wheel accelerates at 22.4 rad/s 2. If the wheel begins with an angular speed of 10.8 rad/s, what is the wheel's angular speed after exactly three full turns? AP Physics
Chapter 8. Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics. 1. Torque. 2. Torque and Equilibrium. 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity
 Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1. Torque 2. Torque and Equilibrium 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity 4. Torque and angular acceleration 5. Rotational Kinetic energy 6. Angular
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics 1. Torque 2. Torque and Equilibrium 3. Center of Mass and Center of Gravity 4. Torque and angular acceleration 5. Rotational Kinetic energy 6. Angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PREVIEW A force acting at a perpendicular distance from a rotation point, such as pushing a doorknob and causing the door to rotate on its hinges, produces a torque. If the
Chapter 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PREVIEW A force acting at a perpendicular distance from a rotation point, such as pushing a doorknob and causing the door to rotate on its hinges, produces a torque. If the
= o + t = ot + ½ t 2 = o + 2
 Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Rotation. Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy. Torque Rolling. featuring moments of Inertia
 Rotation Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy featuring moments of Inertia Torque Rolling Angular Motion We think about rotation in the same basic way we do about linear motion How far does it go? How
Rotation Kinematics Rigid Bodies Kinetic Energy featuring moments of Inertia Torque Rolling Angular Motion We think about rotation in the same basic way we do about linear motion How far does it go? How
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes
 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes Physics 2414 - Strauss Formulas: v = l / t = r θ / t = rω a T = v / t = r ω / t =rα a C = v 2 /r = ω 2 r ω = ω 0 + αt θ = ω 0 t +(1/2)αt 2 θ = (1/2)(ω 0 +ω)t ω 2 = ω 0 2 +2αθ τ
Chapter 8 continued. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.6 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.6 The Action of Forces and Torques on Rigid Objects Chapter 8 developed the concepts of angular motion. θ : angles and radian measure for angular variables ω :
Rotational N.2 nd Law
 Lecture 0 Chapter 1 Physics I Rotational N. nd Law Torque Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics Today
Lecture 0 Chapter 1 Physics I Rotational N. nd Law Torque Course website: http://faculty.uml.edu/andriy_danylov/teaching/physicsi IN THIS CHAPTER, you will continue discussing rotational dynamics Today
CHAPTER 8 TEST REVIEW MARKSCHEME
 AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response MULTIPLE CHOICE DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM
AP PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: 50 Multiple Choice 45 Single Response 5 Multi-Response Free Response 3 Short Free Response 2 Long Free Response MULTIPLE CHOICE DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP EXAM
Moment of Inertia Race
 Review Two points, A and B, are on a disk that rotates with a uniform speed about an axis. Point A is closer to the axis than point B. Which of the following is NOT true? 1. Point B has the greater tangential
Review Two points, A and B, are on a disk that rotates with a uniform speed about an axis. Point A is closer to the axis than point B. Which of the following is NOT true? 1. Point B has the greater tangential
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 25, 2017
 Physics 8 Wednesday, October 25, 2017 HW07 due Friday. It is mainly rotation, plus a couple of basic torque questions. And there are only 8 problems this week. For today, you read (in Perusall) Onouye/Kane
Physics 8 Wednesday, October 25, 2017 HW07 due Friday. It is mainly rotation, plus a couple of basic torque questions. And there are only 8 problems this week. For today, you read (in Perusall) Onouye/Kane
Physics 101 Lecture 11 Torque
 Physics 101 Lecture 11 Torque Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Force vs. Torque q Forces cause accelerations q What cause angular accelerations? q A door is free to rotate about an axis
Physics 101 Lecture 11 Torque Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Physics Department www.aovgun.com Force vs. Torque q Forces cause accelerations q What cause angular accelerations? q A door is free to rotate about an axis
Rotation. I. Kinematics - Angular analogs
 Rotation I. Kinematics - Angular analogs II. III. IV. Dynamics - Torque and Rotational Inertia Work and Energy Angular Momentum - Bodies and particles V. Elliptical Orbits The student will be able to:
Rotation I. Kinematics - Angular analogs II. III. IV. Dynamics - Torque and Rotational Inertia Work and Energy Angular Momentum - Bodies and particles V. Elliptical Orbits The student will be able to:
are (0 cm, 10 cm), (10 cm, 10 cm), and (10 cm, 0 cm), respectively. Solve: The coordinates of the center of mass are = = = (200 g g g)
 Rotational Motion Problems Solutions.. Model: A spinning skater, whose arms are outstretched, is a rigid rotating body. Solve: The speed v rω, where r 40 / 0.70 m. Also, 80 rpm (80) π/60 rad/s 6 π rad/s.
Rotational Motion Problems Solutions.. Model: A spinning skater, whose arms are outstretched, is a rigid rotating body. Solve: The speed v rω, where r 40 / 0.70 m. Also, 80 rpm (80) π/60 rad/s 6 π rad/s.
AP Physics 1 Rotational Motion Practice Test
 AP Physics 1 Rotational Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A spinning ice skater on extremely smooth ice is able
AP Physics 1 Rotational Motion Practice Test MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A spinning ice skater on extremely smooth ice is able
It will be most difficult for the ant to adhere to the wheel as it revolves past which of the four points? A) I B) II C) III D) IV
 AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
AP Physics 1 Lesson 16 Homework Newton s First and Second Law of Rotational Motion Outcomes Define rotational inertia, torque, and center of gravity. State and explain Newton s first Law of Motion as it
Name Date Period PROBLEM SET: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
 Accelerated Physics Rotational Dynamics Problem Set Page 1 of 5 Name Date Period PROBLEM SET: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Directions: Show all work on a separate piece of paper. Box your final answer. Don t forget
Accelerated Physics Rotational Dynamics Problem Set Page 1 of 5 Name Date Period PROBLEM SET: ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Directions: Show all work on a separate piece of paper. Box your final answer. Don t forget
PHYS 185 Final Exam December 4, 2012
 PHYS 185 Final Exam December 4, 2012 Name: Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an answer, continue on the back of the page. Please make an effort
PHYS 185 Final Exam December 4, 2012 Name: Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets. If you run out of room for an answer, continue on the back of the page. Please make an effort
Physics 201 Exam 3 (Monday, November 5) Fall 2012 (Saslow)
 Physics 201 Exam 3 (Monday, November 5) Fall 2012 (Saslow) Name (printed) Lab Section(+2 pts) Name (signed as on ID) Multiple choice Section. Circle the correct answer. No work need be shown and no partial
Physics 201 Exam 3 (Monday, November 5) Fall 2012 (Saslow) Name (printed) Lab Section(+2 pts) Name (signed as on ID) Multiple choice Section. Circle the correct answer. No work need be shown and no partial
Chapter 8, Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics. 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience:
 CHAPTER 8 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience: a. a constant angular speed b. an angular acceleration c. a constant moment of inertia d. an increasing moment of inertia
CHAPTER 8 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience: a. a constant angular speed b. an angular acceleration c. a constant moment of inertia d. an increasing moment of inertia
Worksheet for Exploration 10.1: Constant Angular Velocity Equation
 Worksheet for Exploration 10.1: Constant Angular Velocity Equation By now you have seen the equation: θ = θ 0 + ω 0 *t. Perhaps you have even derived it for yourself. But what does it really mean for the
Worksheet for Exploration 10.1: Constant Angular Velocity Equation By now you have seen the equation: θ = θ 0 + ω 0 *t. Perhaps you have even derived it for yourself. But what does it really mean for the
11-2 A General Method, and Rolling without Slipping
 11-2 A General Method, and Rolling without Slipping Let s begin by summarizing a general method for analyzing situations involving Newton s Second Law for Rotation, such as the situation in Exploration
11-2 A General Method, and Rolling without Slipping Let s begin by summarizing a general method for analyzing situations involving Newton s Second Law for Rotation, such as the situation in Exploration
( )( ) ( )( ) Fall 2017 PHYS 131 Week 9 Recitation: Chapter 9: 5, 10, 12, 13, 31, 34
 Fall 07 PHYS 3 Chapter 9: 5, 0,, 3, 3, 34 5. ssm The drawing shows a jet engine suspended beneath the wing of an airplane. The weight W of the engine is 0 00 N and acts as shown in the drawing. In flight
Fall 07 PHYS 3 Chapter 9: 5, 0,, 3, 3, 34 5. ssm The drawing shows a jet engine suspended beneath the wing of an airplane. The weight W of the engine is 0 00 N and acts as shown in the drawing. In flight
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium
 Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a velocity
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a velocity
Rotation. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
Chapter 6, Problem 18. Agenda. Rotational Inertia. Rotational Inertia. Calculating Moment of Inertia. Example: Hoop vs.
 Agenda Today: Homework quiz, moment of inertia and torque Thursday: Statics problems revisited, rolling motion Reading: Start Chapter 8 in the reading Have to cancel office hours today: will have extra
Agenda Today: Homework quiz, moment of inertia and torque Thursday: Statics problems revisited, rolling motion Reading: Start Chapter 8 in the reading Have to cancel office hours today: will have extra
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_11 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1
 University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_11 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. For a wheel spinning on an axis through its center, the ratio of the radial acceleration of a point on
University Physics (Prof. David Flory) Chapt_11 Thursday, November 15, 2007 Page 1 Name: Date: 1. For a wheel spinning on an axis through its center, the ratio of the radial acceleration of a point on
Consider two students pushing with equal force on opposite sides of a desk. Looking top-down on the desk:
 1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
1 Bodies in Equilibrium Recall Newton's First Law: if there is no unbalanced force on a body (i.e. if F Net = 0), the body is in equilibrium. That is, if a body is in equilibrium, then all the forces on
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21
 PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
PHYSICS 149: Lecture 21 Chapter 8: Torque and Angular Momentum 8.2 Torque 8.4 Equilibrium Revisited 8.8 Angular Momentum Lecture 21 Purdue University, Physics 149 1 Midterm Exam 2 Wednesday, April 6, 6:30
Chapter 8 continued. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.4 Rotational Work and Energy Work to accelerate a mass rotating it by angle φ F W = F(cosθ)x x = s = rφ = Frφ Fr = τ (torque) = τφ r φ s F to s θ = 0 DEFINITION
Chapter 8 continued Rotational Dynamics 8.4 Rotational Work and Energy Work to accelerate a mass rotating it by angle φ F W = F(cosθ)x x = s = rφ = Frφ Fr = τ (torque) = τφ r φ s F to s θ = 0 DEFINITION
6. Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure about the axle through O if a = 10.0 cm and b = 25.0 cm.
 1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
AP Physics QUIZ Chapters 10
 Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
Name: 1. Torque is the rotational analogue of (A) Kinetic Energy (B) Linear Momentum (C) Acceleration (D) Force (E) Mass A 5-kilogram sphere is connected to a 10-kilogram sphere by a rigid rod of negligible
Rotation review packet. Name:
 Rotation review packet. Name:. A pulley of mass m 1 =M and radius R is mounted on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through O. A block of equal mass m =M, suspended by a cord wrapped around the
Rotation review packet. Name:. A pulley of mass m 1 =M and radius R is mounted on frictionless bearings about a fixed axis through O. A block of equal mass m =M, suspended by a cord wrapped around the
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium
 Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
Equilibrium Notes 1 Translational Equilibrium Ex. A 20.0 kg object is suspended by a rope as shown. What is the net force acting on it? Ex. Ok that was easy, now that same 20.0 kg object is lifted at a
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first
 Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Name (please print): UW ID# score last first Question I. (20 pts) Projectile motion A ball of mass 0.3 kg is thrown at an angle of 30 o above the horizontal. Ignore air resistance. It hits the ground 100
Rotational Equilibrium
 Rotational Equilibrium 6-1 Rotational Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Have you ever tried to pull a stubborn nail out of a board or develop your forearm muscles by lifting weights? Both these activities involve
Rotational Equilibrium 6-1 Rotational Equilibrium INTRODUCTION Have you ever tried to pull a stubborn nail out of a board or develop your forearm muscles by lifting weights? Both these activities involve
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion
 Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Newton s Laws for Rotation n e t I 3 rd part [N
Chap. 10: Rotational Motion I. Rotational Kinematics II. Rotational Dynamics - Newton s Law for Rotation III. Angular Momentum Conservation (Chap. 10) 1 Newton s Laws for Rotation n e t I 3 rd part [N
Webreview Torque and Rotation Practice Test
 Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium
 Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium Strike (Day 10) Prelectures, checkpoints, lectures continue with no change. Take-home quizzes this week. See Elaine Schulte s email. HW
Physics 101: Lecture 15 Torque, F=ma for rotation, and Equilibrium Strike (Day 10) Prelectures, checkpoints, lectures continue with no change. Take-home quizzes this week. See Elaine Schulte s email. HW
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium. 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction
 Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Chapter 8 Rotational Motion and Equilibrium Name 1. Give explanation of torque in own words after doing balance-the-torques lab as an inquiry introduction 1. The distance between a turning axis and the
Lecture 14. Rotational dynamics Torque. Give me a lever long enough and a fulcrum on which to place it, and I shall move the world.
 Lecture 14 Rotational dynamics Torque Give me a lever long enough and a fulcrum on which to place it, and I shall move the world. Archimedes, 87 1 BC EXAM Tuesday March 6, 018 8:15 PM 9:45 PM Today s Topics:
Lecture 14 Rotational dynamics Torque Give me a lever long enough and a fulcrum on which to place it, and I shall move the world. Archimedes, 87 1 BC EXAM Tuesday March 6, 018 8:15 PM 9:45 PM Today s Topics:
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion. Torque and angular momentum
 Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Ch. 7.3, 8.1 (KJF 3 rd ed.) Phys 114 Eyres Torque 1 Causing rotation: Torque Three factors affect the how a force can affect the rotation: The magnitude of the force The distance,
Torque and Static Equilibrium Ch. 7.3, 8.1 (KJF 3 rd ed.) Phys 114 Eyres Torque 1 Causing rotation: Torque Three factors affect the how a force can affect the rotation: The magnitude of the force The distance,
Please read this introductory material carefully; it covers topics you might not yet have seen in class.
 b Lab Physics 211 Lab 10 Torque What You Need To Know: Please read this introductory material carefully; it covers topics you might not yet have seen in class. F (a) (b) FIGURE 1 Forces acting on an object
b Lab Physics 211 Lab 10 Torque What You Need To Know: Please read this introductory material carefully; it covers topics you might not yet have seen in class. F (a) (b) FIGURE 1 Forces acting on an object
PHYSICS - CLUTCH 1E CH 12: TORQUE & ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO TORQUE TORQUE is a twist that a Force gives an object around an axis of rotation. - For example, when you push on a door, it rotates around its hinges. - When a Force acts
!! www.clutchprep.com INTRO TO TORQUE TORQUE is a twist that a Force gives an object around an axis of rotation. - For example, when you push on a door, it rotates around its hinges. - When a Force acts
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 12: TORQUE & ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com TORQUE & ACCELERATION (ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS) When a Force causes rotation, it produces a Torque. Think of TORQUE as the equivalent of FORCE! FORCE (F) TORQUE (τ) - Causes linear acceleration
!! www.clutchprep.com TORQUE & ACCELERATION (ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS) When a Force causes rotation, it produces a Torque. Think of TORQUE as the equivalent of FORCE! FORCE (F) TORQUE (τ) - Causes linear acceleration
Rotational motion problems
 Rotational motion problems. (Massive pulley) Masses m and m 2 are connected by a string that runs over a pulley of radius R and moment of inertia I. Find the acceleration of the two masses, as well as
Rotational motion problems. (Massive pulley) Masses m and m 2 are connected by a string that runs over a pulley of radius R and moment of inertia I. Find the acceleration of the two masses, as well as
Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8
 PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
Center of Gravity Pearson Education, Inc.
 Center of Gravity = The center of gravity position is at a place where the torque from one end of the object is balanced by the torque of the other end and therefore there is NO rotation. Fulcrum Point
Center of Gravity = The center of gravity position is at a place where the torque from one end of the object is balanced by the torque of the other end and therefore there is NO rotation. Fulcrum Point
θ Beam Pivot F r Figure 1. Figure 2. STATICS (Force Vectors, Tension & Torque) MBL-32 (Ver. 3/20/2006) Name: Lab Partner: Lab Partner:
 Please Circle Your Lab day: M T W T F Name: Lab Partner: Lab Partner: Project #1: Kinesthetic experiences with force vectors and torque. Project #2: How does torque depend on the lever arm? Project #1:
Please Circle Your Lab day: M T W T F Name: Lab Partner: Lab Partner: Project #1: Kinesthetic experiences with force vectors and torque. Project #2: How does torque depend on the lever arm? Project #1:
PHY 111L Activity 9 Moments of Inertia
 PHY 111L Activity 9 Moments of Inertia Name: Section: ID #: Date: Lab Partners: TA initials: Objectives 1. Introduce moment of inertia for different objects 2. Understand the moment of inertia apparatus
PHY 111L Activity 9 Moments of Inertia Name: Section: ID #: Date: Lab Partners: TA initials: Objectives 1. Introduce moment of inertia for different objects 2. Understand the moment of inertia apparatus
General Definition of Torque, final. Lever Arm. General Definition of Torque 7/29/2010. Units of Chapter 10
 Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Units of Chapter 10 Determining Moments of Inertia Rotational Kinetic Energy Rotational Plus Translational Motion; Rolling Why Does a Rolling Sphere Slow Down? General Definition of Torque, final Taking
Rotational Motion. 1 Purpose. 2 Theory 2.1 Equation of Motion for a Rotating Rigid Body
 Rotational Motion Equipment: Capstone, rotary motion sensor mounted on 80 cm rod and heavy duty bench clamp (PASCO ME-9472), string with loop at one end and small white bead at the other end (125 cm bead
Rotational Motion Equipment: Capstone, rotary motion sensor mounted on 80 cm rod and heavy duty bench clamp (PASCO ME-9472), string with loop at one end and small white bead at the other end (125 cm bead
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 13: ROTATIONAL EQUILIBRIUM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
!! www.clutchprep.com EXAMPLE: POSITION OF SECOND KID ON SEESAW EXAMPLE: A 4 m-long seesaw 50 kg in mass and of uniform mass distribution is pivoted on a fulcrum at its middle, as shown. Two kids sit on
Summer Physics 41 Pretest. Shorty Shorts (2 pts ea): Circle the best answer. Show work if a calculation is required.
 Summer Physics 41 Pretest Name: Shorty Shorts (2 pts ea): Circle the best answer. Show work if a calculation is required. 1. An object hangs in equilibrium suspended by two identical ropes. Which rope
Summer Physics 41 Pretest Name: Shorty Shorts (2 pts ea): Circle the best answer. Show work if a calculation is required. 1. An object hangs in equilibrium suspended by two identical ropes. Which rope
Static Equilibrium and Torque
 10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
10.3 Static Equilibrium and Torque SECTION OUTCOMES Use vector analysis in two dimensions for systems involving static equilibrium and torques. Apply static torques to structures such as seesaws and bridges.
Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion
 Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion What causes an angular acceleration? The effectiveness of a force at causing a rotation is called torque. QuickCheck 12.5 The four forces shown have the same strength.
Chapter 10: Dynamics of Rotational Motion What causes an angular acceleration? The effectiveness of a force at causing a rotation is called torque. QuickCheck 12.5 The four forces shown have the same strength.
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 16, 2000 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 16, 2000 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
Chapter 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics In pure translational motion, all points on an object travel on parallel paths. The most general motion is a combination of translation and rotation. 1) Torque Produces angular
Dynamics of Rotational Motion: Rotational Inertia
 Dynamics of Rotational Motion: Rotational Inertia Bởi: OpenStaxCollege If you have ever spun a bike wheel or pushed a merry-go-round, you know that force is needed to change angular velocity as seen in
Dynamics of Rotational Motion: Rotational Inertia Bởi: OpenStaxCollege If you have ever spun a bike wheel or pushed a merry-go-round, you know that force is needed to change angular velocity as seen in
TutorBreeze.com 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION. 3. If the angular velocity of a spinning body points out of the page, then describe how is the body spinning?
 1. rpm is about rad/s. 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION 2. A wheel rotates with constant angular acceleration of π rad/s 2. During the time interval from t 1 to t 2, its angular displacement is π rad. At time t 2
1. rpm is about rad/s. 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION 2. A wheel rotates with constant angular acceleration of π rad/s 2. During the time interval from t 1 to t 2, its angular displacement is π rad. At time t 2
Exam 3 Practice Solutions
 Exam 3 Practice Solutions Multiple Choice 1. A thin hoop, a solid disk, and a solid sphere, each with the same mass and radius, are at rest at the top of an inclined plane. If all three are released at
Exam 3 Practice Solutions Multiple Choice 1. A thin hoop, a solid disk, and a solid sphere, each with the same mass and radius, are at rest at the top of an inclined plane. If all three are released at
Physics 8 Friday, November 4, 2011
 Physics 8 Friday, November 4, 2011 Please turn in Homework 7. I will hand out solutions once everyone is here. The handout also includes HW8 and a page or two of updates to the equation sheet needed to
Physics 8 Friday, November 4, 2011 Please turn in Homework 7. I will hand out solutions once everyone is here. The handout also includes HW8 and a page or two of updates to the equation sheet needed to
Physics Fall Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids. Lecture 20: Rotational Motion. Slide 20-1
 Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lecture 20: Rotational Motion Slide 20-1 Recap: center of mass, linear momentum A composite system behaves as though its mass is concentrated
Physics 1501 Fall 2008 Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Fluids Lecture 20: Rotational Motion Slide 20-1 Recap: center of mass, linear momentum A composite system behaves as though its mass is concentrated
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it out of sight. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators cannot be shared.
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it out of sight. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators cannot be shared.
Review questions. Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right.
 Review questions Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right. 30 kg 70 kg v (a) Is this collision elastic? (b) Find the
Review questions Before the collision, 70 kg ball is stationary. Afterward, the 30 kg ball is stationary and 70 kg ball is moving to the right. 30 kg 70 kg v (a) Is this collision elastic? (b) Find the
Torque and Static Equilibrium
 Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Torque and Static Equilibrium Rigid Bodies Rigid body: An extended object in which the distance between any two points in the object is constant in time. Examples: sphere, disk Effect of external forces
Chapter 11. Today. Last Wednesday. Precession from Pre- lecture. Solving problems with torque
 Chapter 11 Last Wednesday Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum Conserva5on of angular momentum Today Precession from Pre- lecture Study the condi5ons for equilibrium
Chapter 11 Last Wednesday Solving problems with torque Work and power with torque Angular momentum Conserva5on of angular momentum Today Precession from Pre- lecture Study the condi5ons for equilibrium
Suggested Problems. Chapter 1
 Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Physics 111. Lecture 22 (Walker: ) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009
 Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Physics 111 Lecture 22 (Walker: 11.1-3) Torque Rotational Dynamics Static Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Lecture 22 1/26 Torque (τ) We define a quantity called torque which is a measure of twisting effort.
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium
 Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium Changes in Office-hours The following changes will take place until the end of the semester Office-hours: - Monday, 12:00-13:00h - Wednesday, 14:00-15:00h - Friday, 13:00-14:00h
Name: Date: Period: AP Physics C Rotational Motion HO19
 1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
Phys 1401: General Physics I
 1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
1. (0 Points) What course is this? a. PHYS 1401 b. PHYS 1402 c. PHYS 2425 d. PHYS 2426 2. (0 Points) Which exam is this? a. Exam 1 b. Exam 2 c. Final Exam 3. (0 Points) What version of the exam is this?
Chapter 10. Rotation
 Chapter 10 Rotation Rotation Rotational Kinematics: Angular velocity and Angular Acceleration Rotational Kinetic Energy Moment of Inertia Newton s nd Law for Rotation Applications MFMcGraw-PHY 45 Chap_10Ha-Rotation-Revised
Chapter 10 Rotation Rotation Rotational Kinematics: Angular velocity and Angular Acceleration Rotational Kinetic Energy Moment of Inertia Newton s nd Law for Rotation Applications MFMcGraw-PHY 45 Chap_10Ha-Rotation-Revised
PHYSICS 220. Lecture 15. Textbook Sections Lecture 15 Purdue University, Physics 220 1
 PHYSICS 220 Lecture 15 Angular Momentum Textbook Sections 9.3 9.6 Lecture 15 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Last Lecture Overview Torque = Force that causes rotation τ = F r sin θ Work done by torque
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 15 Angular Momentum Textbook Sections 9.3 9.6 Lecture 15 Purdue University, Physics 220 1 Last Lecture Overview Torque = Force that causes rotation τ = F r sin θ Work done by torque
