ECEN 474/704 Lab 2: Layout Design
|
|
|
- Emerald Weaver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECEN 474/704 Lab 2: Layout esign Objectives Learn Techniques for successful integrated circuit layout design. Introduction In this lab you will learn in detail how to generate a simple transistor layout. Next, techniques will be developed for generating optimal layouts of wide transistors and matched transistors. Layout techniques for resistors and capacitors will also be illustrated. Finally, you will use all of these techniques to produce a two stage operational amplifier layout (Lab 3). Layout Techniques for Transistors In Lab 1, you learned how to layout small size transistors. Most analog designs will not be limited to these small width transistors, thus special layout techniques need to be learned to layout large width MOFET. Luckily, wide transistors can be broken into parallel combinations of small width transistors as seen in Figure 2-1. By doing this horizontal expansion technique for the wide transistor, the drain and source area can be reduced, which decreases parasitic capacitance and resistance. G G G G Figure 2-1: Wide MO Transistor Layout Another good layout technique is to use "dummy" transistors on both ends of a transistor layout. These dummy transistors insure that the etching and diffusion processes occur equally over all segments of the transistor layout (Figure 2-2). G dummy transistor dummy transistor Figure 2-2: ummy Transistor Layout
2 Notice the gate, drain and source are connected together which keeps it from conducting any current. This shorted transistor is connected to the drain or source of the functional transistor. Another alternative for dummy transistors is to have the gate and source tied together. When laying out any device, the key is symmetry, especially when laying out fully-differential components. For matched devices, use interdigitized or common-centroid layout techniques, where two transistors need to have exactly the same geometries. Examples include current mirrors and differential pairs. An interdigitized layout is shown in Figure 2-3. Notice that the two transistors have been split into smaller size devices and are interleaved. This layout minimizes the effects of process variations on the parameters of the transistors. G1 G2 G1 G2 a) b) G G1 c) G G1 Figure 2-3: Interdigitized Layout of a ifferential Pair (a) ifferential pair (b) Horizontal pair (c) Interdigitized layout (rain areas are different. Common centroid) (d) Interdigitized layout (rain areas are equal. Not common centroid) d) The idea behind splitting a transistor up is to average the process parameter gradient over the area of the matched devices. For example, the process variation of KP and the transconductance parameter on the wafer is characterized by a global variation and a local variation. Global variations appear as gradients on the wafer as in Figure 2-4. However, local variations describe the random change in the parameter from one point on the chip to another nearby point. By using layout techniques such as interdigitized and commoncentroid, the process variation can hopefully be averaged out among the matched devices.
3 KP 27A V 2 KP 20A V 2 KP 29A V 2 KP 25A V 2 KP 33A V 2 Figure 2-4: Gradient of KP on Wafer When laying out wider matched transistors the common-centroid layout may be a better choice. This layout technique is illustrated in Figure 2-5 for the case of 8 matched M1 and M2 transistors of a differential pair. 1 G G Figure 2-5: Common-Centroid Layout of a ifferential Pair The idea behind the common-centroid layout is to average linear processing gradients that affect the transistors' electrical properties. Common-centroid layouts should have the centroid (center of mass) of each transistor positioned at the same location. The following examples (Figure 2-6) illustrate what is common-centroid and what is not common-centroid.
4 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 2 M 1 Not Common Centroid Common Centroid M 1 M 2 M 2 M 1 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 2 M 1 M 1 M 2 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 M 2 M 1 Common Centroid Better Common Centroid Additional Notes on Current Mirrors Figure 2-6: Common-Centroid Examples In this lab you will be asked to create a 64-transistor current mirror, which will require two branches each with 32 transistors. You should first create your schematic with the physical structure of the current mirror in mind. The first step is to draw a typical current mirror and add dummies to the edges, one possible configuration is shown below in Figure Figure 2-11: Current Mirror chematic
5 Next you need to decide what the dimensions of the physical current mirror shall be by setting the total width and modifying the number of fingers. uch dimensions are (in row by column format): 1x64 (2 dummies needed) 2x32 (4 dummies needed) 4x16 (8 dummies needed) 8x8 (16 dummies needed) 16x4 (32 dummies needed) 32x2 (64 dummies needed) 64x1 (128 dummies needed). This will determine your number of fingers and overall width of each row of transistors, so now choose your dimensions and draw your floor plan to match. Layout Techniques for Capacitors A capacitor is formed when an insulator separates two conducting sheets. Various types of monolithic capacitors using MOFET, MIM (metal-insulator-metal), poly-to-poly, MOM (metal-oxide-metal), etc can be fabricated on integrated circuits. In this lab MOM capacitors will be practiced. Forming a MOM capacitor is done by using lateral flux between plates formed by interdigitated finger metal layers as shown in Figure 2-7. The MOM capacitor has been widely used due to the following characteristics. High capacitance density (refer to the design manual) Low parasitic capacitance Good linearity with dimension ymmetric plate design, thus good matching characteristics No additional masks or other fabrication process, i.e. freely available with modern CMO MOM capacitors can be constructed from any number of consecutive metal levels connected in parallel with vias. The model supports variable dimensions for width (W) and length (L). Normally, the lowest metal layers (e.g. M1 - M5) with fixed metal line width and spacing are used in order to allow maximum capacitance density and high yield. In order to reduce parasitic capacitance induced between the bottom metal layer and the substrate, a lower level of metal could be removed by trading off capacitance density. Figure 2-7: Metal-Oxide-Metal Capacitor
6 Thus the total capacitance can be calculated by C total = C f W (L 2d) where: C f = capacitance density in ff/µm 2 (refer to the design manual) W = total width in µm L = total length in µm imilar to matched MOFET, the common-centroid layout technique can be employed for matched capacitors. A simplified floor plan for two equally sized, well-matched capacitors is shown in Figure 2-8. C1 C1 C1 C1 C1 C1 C1 C1 Figure 2-8: Common-Centroid Capacitor Layout Remember, the purpose of using the unit capacitor is to keep the ratio of the areas and perimeters the same. This prevents (delta) variations in capacitor dimensions from changing the capacitor ratio (see the lecture notes on the layout techniques for proof). If a non-integral number of unit capacitors are required then the perimeters and areas can still be kept the same. If the ratio of capacitors is: C 1 C 2 = I 1 C u I 2 C u + NC u where 1 < N < 2, then we can add a non-unit capacitor C nu = NC u to form C 2 and have equal perimeter/area. The unit capacitor has side length L 0 and the non-unit capacitor has the length L nu and the width W nu. Use the following formulas to calculate the side lengths of the non-unit capacitor: L nu = L 0 (N + N(N 1)) W nu = N L 0 2 Keep the unit capacitor side length L 0 in the range from 10 µm-25 µm. Also, within the capacitor array, use a consistent method of routing lines between the capacitor segments. Each unit capacitor should be surrounded by similar routing lines. Use multiple contacts to lower series resistance. For capacitors near the edge of the array, use "dummy" routing lines. Also, be sure that parasitic capacitance formed by overlapping conductors is the same for the matched capacitors. L nu
7 Additional Notes on Capacitors In this lab, you will be also asked to create an interdigitized capacitor array, complete with dummy capacitors. Figure 2-12 shows the schematic view of one possible configuration of the capacitor array that needs to be laid out. The capacitors to be used are called "vncap" and they are found in the "cmhv7sf" library. The green boxes with X's on them are an element called "noconn" found in the "basic" library. The "noconn" element is needed for the dummy elements. Another note is that once the capacitor array has been laid out, a via from RX_M1 surrounded by a layer of BP is required for the dummy transistors. Be sure to label this via "V" (Figure 2-13). Figure 2-12: chematic View of the Capacitor Array Figure 2-13: ummy Capacitor Voltage Reference for the Layout
8 Layout Techniques for Resistors Many different types of resistors are available in integrated circuits. Other than active devices biased to act as resistors, we can use the inherent resistivity of the polysilicon for diffusions to create resistors. As an example, Table 2-1 shows the typical values of a poly resistance for the IBM 180 nm process that we will be using to design circuits. Process Parameter Table 2-1: Typical Resistivity Values for the Polysilicon Layer OPRPPRE escription Min Nominal Max. Unit Rs heet Resistance(0V,25 C) kω/sq Rcon Contact Resistance kω-µm The total resistance of a monolithic resistor is the sum of the contact resistance and the ohmic resistance of the diffusion material. The following formula can be used to estimate resistance for polysilicon and diffusion resistors: where: R nom = R s L W + 2 R con W R s = resistance per square [kω/sq] for the chosen resistor type L = length [µm] of the resistor W = width [µm] of the resistor R con = contact [kω-µm] resistance A layout of one resistor made out of polysilicon from the design kit is shown in Figure 2-9. The resistor is built in by containing a strip of poly and poly-m1 contacts. The length of the OP mask determines the length of the OP resistor. Figure 2-9: Poly Resistor (OPRPPRE) Layout If the circuit operation depends on the ratio of resistances, then good matching can be obtained by using interdigitized or common-centroid techniques. When matching resistors, be sure to keep device orientation and sizes the same. Also, since contacts contribute resistance, keep the contacts in the same ratio. An interdigitized layout of resistors is illustrated in Figure Notice that the interconnecting metal is overlapping the resistor array and non-overlapping the resistor array in equal lengths for the two resistors.
9 R2 R1 R1 R2 R1 R2 R1 R2 R2 Figure 2-10: Interdigitized Resistor Layout R1 Additional Notes on Resistors In this lab, you will create an interdigitized resistor pair as well. Figure 2-14 shows a schematic of one possible configuration of the resistor pair to be laid out. The resistors to be used are "oprppres" and they are found in the "cmhv7sf" library. Note that the back plate node for all resistors needs to be set to "sub!". As in the capacitor array, the "noconn" element is needed once again for the dummy elements. Also, for the layout, a via from RX_M1 is needed with the label "sub!". o not forget to surround the via with a layer of BP (Figure 2-15). Figure 2-14: chematic View of the Resistor Array Figure 2-15: ummy Resistor Back Plate Node for the Layout
10 Prelab Answer the following questions, no computer work is required for this prelab. The prelab is due at the beginning of lab class, no late work is accepted. 1. What are the absolute minimum dimensions of a transistor? Explain your reasoning. Remember to consider minimum contact size. o we actually use this minimum size or do we use a slightly larger size for convenience? 2. raw a common-centroid layout of a simple current mirror with equal size transistors of L = 180 nm and W = 16 µm. Use a finger width of 500 nm for each transistor segment. Remember to draw the drain, source, gate and bulk connections. Use dummy transistors and all other good layout techniques learned in the lab. Include a floor plan. 3. esign a common-centroid layout for a MOM capacitor array. The capacitors have a ratio of 1.3:1. The capacitor array should consist of eight unit capacitors and one non-unit capacitor. etermine the form of the common-centroid layout and interconnect the capacitors. Each unit capacitance should have a separate top and bottom plate. o not use a common bottom plate. Use the techniques described in the lab manual to give good matching. Also, give the size of the non-unit capacitor. The unit capacitor is µm x µm (W x L). 4. esign two matched polysilicon (OPRPPRE) resistors to realize a total resistance of 12 kω each. Remember to account for contact resistance. etermine the approximate length and width of the diffusion. Use an interdigitized layout with four resistance segments. Use good layout techniques. Lab Report 1. Practice good layout techniques by laying out the following a. Current mirror from prelab question #2 b. Capacitor array from prelab question #3 c. Matched resistors from prelab question #4 2. Include in the lab report a. chematic printout b. Layout printout c. LV printout showing that the layout matches the schematic (Remember to include the NetI and timestamp in the screen capture.)
LAYOUT TECHNIQUES. Dr. Ivan Grech
 LAYOUT TECHNIQUES OUTLINE Transistor Layout Resistor Layout Capacitor Layout Floor planning Mixed A/D Layout Automatic Analog Layout Layout Techniques Main Layers in a typical Double-Poly, Double-Metal
LAYOUT TECHNIQUES OUTLINE Transistor Layout Resistor Layout Capacitor Layout Floor planning Mixed A/D Layout Automatic Analog Layout Layout Techniques Main Layers in a typical Double-Poly, Double-Metal
EE382M-14 CMOS Analog Integrated Circuit Design
 EE382M-14 CMOS Analog Integrated Circuit Design Lecture 3, MOS Capacitances, Passive Components, and Layout of Analog Integrated Circuits MOS Capacitances Type of MOS transistor capacitors Depletion capacitance
EE382M-14 CMOS Analog Integrated Circuit Design Lecture 3, MOS Capacitances, Passive Components, and Layout of Analog Integrated Circuits MOS Capacitances Type of MOS transistor capacitors Depletion capacitance
EECS240 Spring Today s Lecture. Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices. Lingkai Kong EECS. EE240 CMOS Technology
 EECS240 Spring 2013 Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Lingkai Kong EECS Today s Lecture EE240 CMOS Technology Passive devices Motivation Resistors Capacitors (Inductors) Next time: MOS transistor
EECS240 Spring 2013 Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Lingkai Kong EECS Today s Lecture EE240 CMOS Technology Passive devices Motivation Resistors Capacitors (Inductors) Next time: MOS transistor
CMOS Cross Section. EECS240 Spring Dimensions. Today s Lecture. Why Talk About Passives? EE240 Process
 EECS240 Spring 202 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 Today s Lecture
EECS240 Spring 202 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 Today s Lecture
CMOS Devices. PN junctions and diodes NMOS and PMOS transistors Resistors Capacitors Inductors Bipolar transistors
 CMOS Devices PN junctions and diodes NMOS and PMOS transistors Resistors Capacitors Inductors Bipolar transistors PN Junctions Diffusion causes depletion region D.R. is insulator and establishes barrier
CMOS Devices PN junctions and diodes NMOS and PMOS transistors Resistors Capacitors Inductors Bipolar transistors PN Junctions Diffusion causes depletion region D.R. is insulator and establishes barrier
CMOS Cross Section. EECS240 Spring Today s Lecture. Dimensions. CMOS Process. Devices. Lecture 2: CMOS Technology and Passive Devices
 EECS240 Spring 2008 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS echnology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 oday s Lecture
EECS240 Spring 2008 CMOS Cross Section Metal p - substrate p + diffusion Lecture 2: CMOS echnology and Passive Devices Poly n - well n + diffusion Elad Alon Dept. of EECS EECS240 Lecture 2 4 oday s Lecture
Lecture 210 Physical Aspects of ICs (12/15/01) Page 210-1
 Lecture 210 Physical Aspects of ICs (12/15/01) Page 210-1 LECTURE 210 PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF ICs (READING: Text-Sec. 2.5, 2.6, 2.8) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate the physical aspects of integrated circuits
Lecture 210 Physical Aspects of ICs (12/15/01) Page 210-1 LECTURE 210 PHYSICAL ASPECTS OF ICs (READING: Text-Sec. 2.5, 2.6, 2.8) INTRODUCTION Objective Illustrate the physical aspects of integrated circuits
MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics
 ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ECEN454 Digital Integrated Circuit Design MOS Transistor I-V Characteristics and Parasitics ECEN 454 Facts about Transistors So far, we have treated transistors as ideal switches An ON transistor passes
ELEN0037 Microelectronic IC Design. Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft
 ELEN0037 Microelectronic IC Design Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 2: Technological Aspects Technology Passive components Active components CMOS Process Basic Layout Scaling CMOS Technology Integrated
ELEN0037 Microelectronic IC Design Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 2: Technological Aspects Technology Passive components Active components CMOS Process Basic Layout Scaling CMOS Technology Integrated
Fundamentals of ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS: Part I.3. Technology
 Fundamentals of ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS: Part I.3 Technology January 019 Texas A&M University 1 Spring, 019 Well-Diffusion Resistor Example shows two long resistors for K range Alternatively, serpentine
Fundamentals of ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS: Part I.3 Technology January 019 Texas A&M University 1 Spring, 019 Well-Diffusion Resistor Example shows two long resistors for K range Alternatively, serpentine
MOS Transistor Properties Review
 MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
MOS Transistor Properties Review 1 VLSI Chip Manufacturing Process Photolithography: transfer of mask patterns to the chip Diffusion or ion implantation: selective doping of Si substrate Oxidation: SiO
Lecture 12 CMOS Delay & Transient Response
 EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 12 CMOS Delay & Transient Response Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 12 CMOS Delay & Transient Response Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction q Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip q Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! q Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction q Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip q Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! q Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
EE141. EE141-Spring 2006 Digital Integrated Circuits. Administrative Stuff. Class Material. Flash Memory. Read-Only Memory Cells MOS OR ROM
 EE141-pring 2006 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 29 Flash memory Administrative tuff reat job on projects and posters! Homework #10 due today Lab reports due this week Friday lab in 353 Final exam May
EE141-pring 2006 igital Integrated Circuits Lecture 29 Flash memory Administrative tuff reat job on projects and posters! Homework #10 due today Lab reports due this week Friday lab in 353 Final exam May
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. Professor Oldham Fall 1999
 UNIVERSITY OF CLIFORNI College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Professor Oldham Fall 1999 EECS 40 FINL EXM 13 December 1999 Name: Last, First Student ID: T: Kusuma
UNIVERSITY OF CLIFORNI College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Professor Oldham Fall 1999 EECS 40 FINL EXM 13 December 1999 Name: Last, First Student ID: T: Kusuma
EE 434 Lecture 12. Process Flow (wrap up) Device Modeling in Semiconductor Processes
 EE 434 Lecture 12 Process Flow (wrap up) Device Modeling in Semiconductor Processes Quiz 6 How have process engineers configured a process to assure that the thickness of the gate oxide for the p-channel
EE 434 Lecture 12 Process Flow (wrap up) Device Modeling in Semiconductor Processes Quiz 6 How have process engineers configured a process to assure that the thickness of the gate oxide for the p-channel
Lecture 040 Integrated Circuit Technology - II (5/11/03) Page ECE Frequency Synthesizers P.E. Allen
 Lecture 040 Integrated Circuit Technology - II (5/11/03) Page 040-1 LECTURE 040 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - II (Reference [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate and
Lecture 040 Integrated Circuit Technology - II (5/11/03) Page 040-1 LECTURE 040 INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TECHNOLOGY - II (Reference [7,8]) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate and
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors
 Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
Chapter 4 Field-Effect Transistors Microelectronic Circuit Design Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock 5/5/11 Chap 4-1 Chapter Goals Describe operation of MOSFETs. Define FET characteristics in operation
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture 4: CMOS Transistor Theory David Harris, Harvey Mudd College Kartik Mohanram and Steven Levitan University of Pittsburgh Outline q Introduction q MOS Capacitor q
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory
 Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Lecture 3: CMOS Transistor Theory Outline Introduction MOS Capacitor nmos I-V Characteristics pmos I-V Characteristics Gate and Diffusion Capacitance 2 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
Circuits. L5: Fabrication and Layout -2 ( ) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur. B. Mazhari, IITK. G-Number
 EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L5: Fabrication and Layout -2 (12.8.2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 44 Passive Components: Resistor Besides MOS transistors, sometimes one requires to implement passive
EE610: CMOS Analog Circuits L5: Fabrication and Layout -2 (12.8.2013) B. Mazhari Dept. of EE, IIT Kanpur 44 Passive Components: Resistor Besides MOS transistors, sometimes one requires to implement passive
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS:
 Chapter 10 FIEL EFFECT TRANITOR: MOFET The following overview gures describe important issues related to the most important electronic device. NUMBER OF ACTIVE EVICE/CHIP MOORE' LAW Gordon Moore, co-founder
Chapter 10 FIEL EFFECT TRANITOR: MOFET The following overview gures describe important issues related to the most important electronic device. NUMBER OF ACTIVE EVICE/CHIP MOORE' LAW Gordon Moore, co-founder
ECE-343 Test 1: Feb 10, :00-8:00pm, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-343 Test : Feb 0, 00 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION C Depl = C J0 + V R /V o ) m C Diff = τ F g m ω T = g m C µ + C π ω T = g m I / D C GD + C or V OV GS b = τ i τ i = R i C i ω H b Z = Z
ECE-343 Test : Feb 0, 00 6:00-8:00pm, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION C Depl = C J0 + V R /V o ) m C Diff = τ F g m ω T = g m C µ + C π ω T = g m I / D C GD + C or V OV GS b = τ i τ i = R i C i ω H b Z = Z
The K-Input Floating-Gate MOS (FGMOS) Transistor
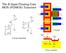 The K-Input Floating-Gate MOS (FGMOS) Transistor C 1 V D C 2 V D I V D I V S Q C 1 C 2 V S V K Q V K C K Layout V B V K C K Circuit Symbols V S Control Gate Floating Gate Interpoly Oxide Field Oxide Gate
The K-Input Floating-Gate MOS (FGMOS) Transistor C 1 V D C 2 V D I V D I V S Q C 1 C 2 V S V K Q V K C K Layout V B V K C K Circuit Symbols V S Control Gate Floating Gate Interpoly Oxide Field Oxide Gate
AE74 VLSI DESIGN JUN 2015
 Q.2 a. Write down the different levels of integration of IC industry. (4) b. With neat sketch explain briefly PMOS & NMOS enhancement mode transistor. N-MOS enhancement mode transistor:- This transistor
Q.2 a. Write down the different levels of integration of IC industry. (4) b. With neat sketch explain briefly PMOS & NMOS enhancement mode transistor. N-MOS enhancement mode transistor:- This transistor
VLSI VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 VLSI VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) SYLLABUS UNIT II VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES: VLSI Design Flow, MOS Layers, Stick Diagrams, Design Rules and Layout, 2 m CMOS Design
VLSI VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) SYLLABUS UNIT II VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN PROCESSES: VLSI Design Flow, MOS Layers, Stick Diagrams, Design Rules and Layout, 2 m CMOS Design
Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. #05 Lecture No. #02 FETS and MOSFETS (contd.) In the previous lecture, we studied the working
Electronics Fets and Mosfets Prof D C Dube Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Module No. #05 Lecture No. #02 FETS and MOSFETS (contd.) In the previous lecture, we studied the working
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 7 Interconnections 1: wire resistance, capacitance,
Federal University of Santa Catarina Center for Technology Computer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated Circuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 7 Interconnections 1: wire resistance, capacitance,
EEE598D: Analog Filter & Signal Processing Circuits
 EEE598D: Analog Filter & Signal Processing Circuits Instructor: Dr. Hongjiang Song Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University Thursday January 24, 2002 Today: Active RC & MOS-C Circuits
EEE598D: Analog Filter & Signal Processing Circuits Instructor: Dr. Hongjiang Song Department of Electrical Engineering Arizona State University Thursday January 24, 2002 Today: Active RC & MOS-C Circuits
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 13 Semiconductor Memories
 Lec 13 Semiconductor Memories 1 Semiconductor Memory Types Semiconductor Memories Read/Write (R/W) Memory or Random Access Memory (RAM) Read-Only Memory (ROM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Static RAM (SRAM) 1. Mask
Lec 13 Semiconductor Memories 1 Semiconductor Memory Types Semiconductor Memories Read/Write (R/W) Memory or Random Access Memory (RAM) Read-Only Memory (ROM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Static RAM (SRAM) 1. Mask
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor
 Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
Lecture 11: MOS Transistor Prof. Niknejad Lecture Outline Review: MOS Capacitors Regions MOS Capacitors (3.8 3.9) CV Curve Threshold Voltage MOS Transistors (4.1 4.3): Overview Cross-section and layout
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002
 CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 18-322 DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002 Final Examination, Monday Dec. 16, 2002 NAME: SECTION: Time: 180 minutes Closed
CARNEGIE MELLON UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING 18-322 DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUITS FALL 2002 Final Examination, Monday Dec. 16, 2002 NAME: SECTION: Time: 180 minutes Closed
Field-Effect (FET) transistors
 Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Barbow (Chapter 8), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and, therefore, its current-carrying
Field-Effect (FET) transistors References: Barbow (Chapter 8), Rizzoni (chapters 8 & 9) In a field-effect transistor (FET), the width of a conducting channel in a semiconductor and, therefore, its current-carrying
VLSI Design and Simulation
 VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
VLSI Design and Simulation Performance Characterization Topics Performance Characterization Resistance Estimation Capacitance Estimation Inductance Estimation Performance Characterization Inverter Voltage
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 5: Interconnect. Semester B, Lecturer: Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 1
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 5: Interconnect Semester B, 2015-16 Lecturer: Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 1 What will we learn today? 1 A First Glance at Interconnect 2 3
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 5: Interconnect Semester B, 2015-16 Lecturer: Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 1 What will we learn today? 1 A First Glance at Interconnect 2 3
EE 330 Lecture 6. Improved Switch-Level Model Propagation Delay Stick Diagrams Technology Files - Design Rules
 EE 330 Lecture 6 Improved witch-level Model Propagation elay tick iagrams Technology Files - esign Rules Review from Last Time MO Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation Bulk ource Gate
EE 330 Lecture 6 Improved witch-level Model Propagation elay tick iagrams Technology Files - esign Rules Review from Last Time MO Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation Bulk ource Gate
Lecture 9: Interconnect
 Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 9: Interconnect Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 23 May 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
Digital Integrated Circuits (83-313) Lecture 9: Interconnect Semester B, 2016-17 Lecturer: Dr. Adam Teman TAs: Itamar Levi, Robert Giterman 23 May 2017 Disclaimer: This course was prepared, in its entirety,
and V DS V GS V T (the saturation region) I DS = k 2 (V GS V T )2 (1+ V DS )
 ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
ECE 4420 Spring 2005 Page 1 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME SCORE /100 Problem 1O 2 3 4 5 6 7 Sum Points INSTRUCTIONS: This exam is closed book. You are permitted four sheets of notes (three of which are your sheets
Chapter 2. Design and Fabrication of VLSI Devices
 Chapter 2 Design and Fabrication of VLSI Devices Jason Cong 1 Design and Fabrication of VLSI Devices Objectives: To study the materials used in fabrication of VLSI devices. To study the structure of devices
Chapter 2 Design and Fabrication of VLSI Devices Jason Cong 1 Design and Fabrication of VLSI Devices Objectives: To study the materials used in fabrication of VLSI devices. To study the structure of devices
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2016
 ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 016 Lecture 5: Layout Techniques Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements Exam1 is on 9/9 It will be in WEB 36C :0-3:45PM
ECEN474/704: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 016 Lecture 5: Layout Techniques Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements Exam1 is on 9/9 It will be in WEB 36C :0-3:45PM
VLSI GATE LEVEL DESIGN UNIT - III P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, VBIT
 VLSI UNIT - III GATE LEVEL DESIGN P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents GATE LEVEL DESIGN : Logic Gates and Other complex gates, Switch logic, Alternate gate circuits, Time Delays, Driving large
VLSI UNIT - III GATE LEVEL DESIGN P.VIDYA SAGAR ( ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR) contents GATE LEVEL DESIGN : Logic Gates and Other complex gates, Switch logic, Alternate gate circuits, Time Delays, Driving large
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics. Lena Peterson
 Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
Lecture 13 MOSFET as an amplifier with an introduction to MOSFET small-signal model and small-signal schematics Lena Peterson 2015-10-13 Outline (1) Why is the CMOS inverter gain not infinite? Large-signal
ECEN474: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2010
 ECEN474: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2010 Lecture 6: Layout Techniques Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements Lab 2 next week Has a prelab Upgrading Cadence version
ECEN474: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2010 Lecture 6: Layout Techniques Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements Lab 2 next week Has a prelab Upgrading Cadence version
EE 435. Lecture 37. Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices. String DAC Parasitic Capacitances
 EE 435 Lecture 37 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices String DAC Parasitic Capacitances Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET (will initially consider two) Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET C GCH Parasitic Capacitors
EE 435 Lecture 37 Parasitic Capacitances in MOS Devices String DAC Parasitic Capacitances Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET (will initially consider two) Parasitic Capacitors in MOSFET C GCH Parasitic Capacitors
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 29, 2019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Penn ESE 570 Spring 2019 Khanna Lecture Outline! CMOS Process Enhancements! Semiconductor
Self-study problems and questions Processing and Device Technology, FFF110/FYSD13
 Self-study problems and questions Processing and Device Technology, FFF110/FYSD13 Version 2016_01 In addition to the problems discussed at the seminars and at the lectures, you can use this set of problems
Self-study problems and questions Processing and Device Technology, FFF110/FYSD13 Version 2016_01 In addition to the problems discussed at the seminars and at the lectures, you can use this set of problems
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors. Context
 Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
Lecture 12: MOS Capacitors, transistors Context In the last lecture, we discussed PN diodes, and the depletion layer into semiconductor surfaces. Small signal models In this lecture, we will apply those
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
ECE-343 Test 2: Mar 21, 2012 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION 1. (25 pts) (a) Draw a circuit diagram for a differential amplifier designed under the following constraints: Use only BJTs. (You may
nmos IC Design Report Module: EEE 112
 nmos IC Design Report Author: 1302509 Zhao Ruimin Module: EEE 112 Lecturer: Date: Dr.Zhao Ce Zhou June/5/2015 Abstract This lab intended to train the experimental skills of the layout designing of the
nmos IC Design Report Author: 1302509 Zhao Ruimin Module: EEE 112 Lecturer: Date: Dr.Zhao Ce Zhou June/5/2015 Abstract This lab intended to train the experimental skills of the layout designing of the
PURPOSE: See suggested breadboard configuration on following page!
 ECE4902 Lab 1 C2011 PURPOSE: Determining Capacitance with Risetime Measurement Reverse Biased Diode Junction Capacitance MOSFET Gate Capacitance Simulation: SPICE Parameter Extraction, Transient Analysis
ECE4902 Lab 1 C2011 PURPOSE: Determining Capacitance with Risetime Measurement Reverse Biased Diode Junction Capacitance MOSFET Gate Capacitance Simulation: SPICE Parameter Extraction, Transient Analysis
Introduction to CMOS VLSI. Chapter 2: CMOS Transistor Theory. Harris, 2004 Updated by Li Chen, Outline
 Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Introduction to MOS VLSI Design hapter : MOS Transistor Theory copyright@david Harris, 004 Updated by Li hen, 010 Outline Introduction MOS apacitor nmos IV haracteristics pmos IV haracteristics Gate and
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 08 MOS Inverters - III Hello, and welcome to today
Low Power VLSI Circuits and Systems Prof. Ajit Pal Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 08 MOS Inverters - III Hello, and welcome to today
Industrial Electricity
 Industrial Electricity PRELAB / LAB 7: Series & Parallel Circuits with Faults Name PRELAB due BEFORE beginning the lab (initials required at the bottom of page 3) PLEASE TAKE THE TIME TO READ THIS PAGE
Industrial Electricity PRELAB / LAB 7: Series & Parallel Circuits with Faults Name PRELAB due BEFORE beginning the lab (initials required at the bottom of page 3) PLEASE TAKE THE TIME TO READ THIS PAGE
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 3: MOS RC Model, CMOS Manufacturing Agenda MOS Transistor: RC Model (pp. 104-113) S R on D CMOS Manufacturing Process (pp. 36-46) S S C GS G G C GD
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering. Lecture 11 VLSI
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 11 VLSI 2005-10-6 John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) TAs: David Marquardt and Udam Saini www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Today: State Storage
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 11 VLSI 2005-10-6 John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) TAs: David Marquardt and Udam Saini www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Today: State Storage
ECEN474: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2012
 ECEN474: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2012 Lecture 5: Layout Techniques Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements HW1 due today at 5PM For grad students, confirm
ECEN474: (Analog) VLSI Circuit Design Fall 2012 Lecture 5: Layout Techniques Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Announcements HW1 due today at 5PM For grad students, confirm
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 12 VLSI II 2005-2-24 John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) TAs: Ted Hong and David Marquardt www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Last Time: Device
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 12 VLSI II 2005-2-24 John Lazzaro (www.cs.berkeley.edu/~lazzaro) TAs: Ted Hong and David Marquardt www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs152/ Last Time: Device
EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. References
 EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 26 Memory References Rabaey, Digital Integrated Circuits Memory Design and Evolution, VLSI Circuits Short Course, 1998.» Gillingham, Evolution
EE241 - Spring 2000 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 26 Memory References Rabaey, Digital Integrated Circuits Memory Design and Evolution, VLSI Circuits Short Course, 1998.» Gillingham, Evolution
Lecture 25. Semiconductor Memories. Issues in Memory
 Lecture 25 Semiconductor Memories Issues in Memory Memory Classification Memory Architectures TheMemoryCore Periphery 1 Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access
Lecture 25 Semiconductor Memories Issues in Memory Memory Classification Memory Architectures TheMemoryCore Periphery 1 Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access
Announcements. EE105 - Fall 2005 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits. Lecture Material. MOS CV Curve. MOSFET Cross Section
 Announcements EE0 - Fall 00 Microelectronic evices and Circuits ecture 7 Homework, due today Homework due net week ab this week Reading: Chapter MO Transistor ecture Material ast lecture iode currents
Announcements EE0 - Fall 00 Microelectronic evices and Circuits ecture 7 Homework, due today Homework due net week ab this week Reading: Chapter MO Transistor ecture Material ast lecture iode currents
2. (2pts) What is the major difference between an epitaxial layer and a polysilicon layer?
 EE 330 Exam 1 Spring 2017 Name Instructions: Students may bring 1 page of notes (front and back) to this exam and a calculator but the use of any device that has wireless communication capability is prohibited.
EE 330 Exam 1 Spring 2017 Name Instructions: Students may bring 1 page of notes (front and back) to this exam and a calculator but the use of any device that has wireless communication capability is prohibited.
SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORIES
 SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORIES Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable (PROM) SRAM FIFO FLASH DRAM LIFO Shift Register CAM
SEMICONDUCTOR MEMORIES Semiconductor Memory Classification RWM NVRWM ROM Random Access Non-Random Access EPROM E 2 PROM Mask-Programmed Programmable (PROM) SRAM FIFO FLASH DRAM LIFO Shift Register CAM
ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design
 SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
SLIDE 1 ENEE 359a Digital VLSI Design & Logical Effort Prof. blj@ece.umd.edu Credit where credit is due: Slides contain original artwork ( Jacob 2004) as well as material taken liberally from Irwin & Vijay
Digital Integrated Circuits. The Wire * Fuyuzhuo. *Thanks for Dr.Guoyong.SHI for his slides contributed for the talk. Digital IC.
 Digital Integrated Circuits The Wire * Fuyuzhuo *Thanks for Dr.Guoyong.SHI for his slides contributed for the talk Introduction The Wire transmitters receivers schematics physical 2 Interconnect Impact
Digital Integrated Circuits The Wire * Fuyuzhuo *Thanks for Dr.Guoyong.SHI for his slides contributed for the talk Introduction The Wire transmitters receivers schematics physical 2 Interconnect Impact
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 8: Interconnect Manufacturing and Modeling Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review
Topics to be Covered. capacitance inductance transmission lines
 Topics to be Covered Circuit Elements Switching Characteristics Power Dissipation Conductor Sizes Charge Sharing Design Margins Yield resistance capacitance inductance transmission lines Resistance of
Topics to be Covered Circuit Elements Switching Characteristics Power Dissipation Conductor Sizes Charge Sharing Design Margins Yield resistance capacitance inductance transmission lines Resistance of
! CMOS Process Enhancements. ! Semiconductor Physics. " Band gaps. " Field Effects. ! MOS Physics. " Cut-off. " Depletion.
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 9, 019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline CMOS Process Enhancements Semiconductor Physics Band gaps Field Effects
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 4: January 9, 019 MOS Transistor Theory, MOS Model Lecture Outline CMOS Process Enhancements Semiconductor Physics Band gaps Field Effects
Random Offset in CMOS IC Design
 Random Offset in CMOS C esign ECEN487/587 Analog C esign October 19, 007 Art Zirger, National Semiconductor art.zirger@nsc.com 303-845-404 Where to start? How do we choose what transistor sizes to use
Random Offset in CMOS C esign ECEN487/587 Analog C esign October 19, 007 Art Zirger, National Semiconductor art.zirger@nsc.com 303-845-404 Where to start? How do we choose what transistor sizes to use
Course Administration. CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLSI Design I L04: MOS Transistors. Review: CMOS Process at a Glance
 Course Administration CPE/EE 7, CPE 7 VLI esign I L: MO Transistors epartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Aleksandar Milenkovic ( www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka
Course Administration CPE/EE 7, CPE 7 VLI esign I L: MO Transistors epartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Aleksandar Milenkovic ( www.ece.uah.edu/~milenka
S No. Questions Bloom s Taxonomy Level UNIT-I
 GROUP-A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) S No. Questions Bloom s UNIT-I 1 Define oxidation & Classify different types of oxidation Remember 1 2 Explain about Ion implantation Understand 1 3 Describe lithography
GROUP-A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) S No. Questions Bloom s UNIT-I 1 Define oxidation & Classify different types of oxidation Remember 1 2 Explain about Ion implantation Understand 1 3 Describe lithography
Introduction and Background
 Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
Analog CMOS Integrated Circuit Design Introduction and Background Dr. Jawdat Abu-Taha Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Islamic University of Gaza jtaha@iugaza.edu.ps 1 Marking Assignments
EE 434 Lecture 13. Basic Semiconductor Processes Devices in Semiconductor Processes
 EE 434 Lecture 3 Basic Semiconductor Processes Devices in Semiconductor Processes Quiz 9 The top view of a device fabricated in a bulk CMOS process is shown in the figure below a) Identify the device b)
EE 434 Lecture 3 Basic Semiconductor Processes Devices in Semiconductor Processes Quiz 9 The top view of a device fabricated in a bulk CMOS process is shown in the figure below a) Identify the device b)
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
Page 1 of 12 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits FINAL EXAMINATION Open book. Notes: 1. Unless
ENGR890 Digital VLSI Design Fall Lecture 4: CMOS Inverter (static view)
 ENGR89 Digital VLSI Design Fall 5 Lecture 4: CMOS Inverter (static view) [Adapted from Chapter 5 of Digital Integrated Circuits, 3, J. Rabaey et al.] [Also borrowed from Vijay Narayanan and Mary Jane Irwin]
ENGR89 Digital VLSI Design Fall 5 Lecture 4: CMOS Inverter (static view) [Adapted from Chapter 5 of Digital Integrated Circuits, 3, J. Rabaey et al.] [Also borrowed from Vijay Narayanan and Mary Jane Irwin]
CMOS Inverter (static view)
 Review: Design Abstraction Levels SYSTEM CMOS Inverter (static view) + MODULE GATE [Adapted from Chapter 5. 5.3 CIRCUIT of G DEVICE Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits,, J. Rabaey et al.] S D Review:
Review: Design Abstraction Levels SYSTEM CMOS Inverter (static view) + MODULE GATE [Adapted from Chapter 5. 5.3 CIRCUIT of G DEVICE Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits,, J. Rabaey et al.] S D Review:
MOSFET: Introduction
 E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
E&CE 437 Integrated VLSI Systems MOS Transistor 1 of 30 MOSFET: Introduction Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (MOSFET) or MOS is widely used for implementing digital designs Its major
EE 330 Lecture 6. Improved Switch-Level Model Propagation Delay Stick Diagrams Technology Files
 EE 330 Lecture 6 Improved witch-level Model Propagation elay tick iagrams Technology Files Review from Last Time MO Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation Bulk ource Gate rain rain G Gate
EE 330 Lecture 6 Improved witch-level Model Propagation elay tick iagrams Technology Files Review from Last Time MO Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation Bulk ource Gate rain rain G Gate
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective
 Semiconductor Memories Adapted from Chapter 12 of Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey et al. Copyright 2003 Prentice Hall/Pearson Outline Memory Classification Memory Architectures
Semiconductor Memories Adapted from Chapter 12 of Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey et al. Copyright 2003 Prentice Hall/Pearson Outline Memory Classification Memory Architectures
Today s lecture. EE141- Spring 2003 Lecture 4. Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model
 - Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
- Spring 003 Lecture 4 Design Rules CMOS Inverter MOS Transistor Model Today s lecture Design Rules The CMOS inverter at a glance An MOS transistor model for manual analysis Important! Labs start next
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6 MOS Transistors
 ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
ECE 342 Electronic Circuits Lecture 6 MOS Transistors Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu 1 NMOS Transistor Typically L = 0.1 to 3 m, W = 0.2
Semi-Conductors insulators semi-conductors N-type Semi-Conductors P-type Semi-Conductors
 Semi-Conductors In the metal materials considered earlier, the coupling of the atoms together to form the material decouples an electron from each atom setting it free to roam around inside the material.
Semi-Conductors In the metal materials considered earlier, the coupling of the atoms together to form the material decouples an electron from each atom setting it free to roam around inside the material.
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Semiconductor. Memories. Memories
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Semiconductor Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Case Studies Semiconductor Memory Classification
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Semiconductor Chapter Overview Memory Classification Memory Architectures The Memory Core Periphery Reliability Case Studies Semiconductor Memory Classification
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Fall 2018 Lecture Notes Note Introduction to Capacitive Touchscreen
 EES 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Fall 2018 Lecture Notes Note 16 16.1 Introduction to apacitive Touchscreen We ve seen how a resistive touchscreen works by using the concept of voltage
EES 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Fall 2018 Lecture Notes Note 16 16.1 Introduction to apacitive Touchscreen We ve seen how a resistive touchscreen works by using the concept of voltage
Lecture 8. Detectors for Ionizing Particles
 Lecture 8 Detectors for Ionizing Particles Content Introduction Overview of detector systems Sources of radiation Radioactive decay Cosmic Radiation Accelerators Interaction of Radiation with Matter General
Lecture 8 Detectors for Ionizing Particles Content Introduction Overview of detector systems Sources of radiation Radioactive decay Cosmic Radiation Accelerators Interaction of Radiation with Matter General
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices
 Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Lecture 12: MOSFET Devices Gu-Yeon Wei Division of Engineering and Applied Sciences Harvard University guyeon@eecs.harvard.edu Wei 1 Overview Reading S&S: Chapter 5.1~5.4 Supplemental Reading Background
Chapter 3-7. An Exercise. Problem 1. Digital IC-Design. Problem. Problem. 1, draw the static transistor schematic for the function Q = (A+BC)D
 igital I-esign Problem Parameters rom a.35 um process hapter 3-7 n Exercise, draw the static transistor schematic or the unction (+), ind the corresponding domino gate using a PN net 3, ind the Euler path
igital I-esign Problem Parameters rom a.35 um process hapter 3-7 n Exercise, draw the static transistor schematic or the unction (+), ind the corresponding domino gate using a PN net 3, ind the Euler path
MOS Transistors. Prof. Krishna Saraswat. Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA
 MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
MOS Transistors Prof. Krishna Saraswat Department of Electrical Engineering S Stanford, CA 94305 saraswat@stanford.edu 1 1930: Patent on the Field-Effect Transistor! Julius Lilienfeld filed a patent describing
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI. Midterm Exam. Solutions
 P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
P. R. Nelson 1 ECE418 - VLSI Midterm Exam Solutions 1. (8 points) Draw the cross-section view for A-A. The cross-section view is as shown below.. ( points) Can you tell which of the metal1 regions is the
Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux telligents Microelectronics Part 1: Main CMOS circuits design rules Mohamad Sawan et al. Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! med-amine.miled@polymtl.ca!
EE141- Fall 2002 Lecture 27. Memory EE141. Announcements. We finished all the labs No homework this week Projects are due next Tuesday 9am EE141
 - Fall 2002 Lecture 27 Memory Announcements We finished all the labs No homework this week Projects are due next Tuesday 9am 1 Today s Lecture Memory:» SRAM» DRAM» Flash Memory 2 Floating-gate transistor
- Fall 2002 Lecture 27 Memory Announcements We finished all the labs No homework this week Projects are due next Tuesday 9am 1 Today s Lecture Memory:» SRAM» DRAM» Flash Memory 2 Floating-gate transistor
2. (2pts) What is the major reason that contacts from metal to poly are not allowed on top of the gate of a transistor?
 EE 330 Exam 1 Spring 2018 Name Instructions: Students may bring 1 page of notes (front and back) to this exam and a calculator but the use of any device that has wireless communication capability is prohibited.
EE 330 Exam 1 Spring 2018 Name Instructions: Students may bring 1 page of notes (front and back) to this exam and a calculator but the use of any device that has wireless communication capability is prohibited.
Charge Storage in the MOS Structure. The Inverted MOS Capacitor (V GB > V Tn )
 The Inverted MO Capacitor (V > V Tn ) We consider the surface potential as Þxed (ÒpinnedÓ) at φ s,max = - φ p φ(x).5 V. V V ox Charge torage in the MO tructure Three regions of operation: Accumulation:
The Inverted MO Capacitor (V > V Tn ) We consider the surface potential as Þxed (ÒpinnedÓ) at φ s,max = - φ p φ(x).5 V. V V ox Charge torage in the MO tructure Three regions of operation: Accumulation:
SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom. ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: Spring 2016 April 18, 2016 M. A. Alam and M.S. Lundstrom Purdue University
 NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
NAME: PUID: SECTION: Circle one: Alam Lundstrom ECE 305 Exam 5 SOLUTIONS: April 18, 2016 M A Alam and MS Lundstrom Purdue University This is a closed book exam You may use a calculator and the formula
Chapter 20. Current Mirrors. Basics. Cascoding. Biasing Circuits. Baker Ch. 20 Current Mirrors. Introduction to VLSI
 Chapter 20 Current Mirrors Basics Long Channel Matching Biasing Short Channel Temperature Subthreshold Cascoding Simple Low Voltage, Wide Swing Wide Swing, Short Channel Regulated Drain Biasing Circuits
Chapter 20 Current Mirrors Basics Long Channel Matching Biasing Short Channel Temperature Subthreshold Cascoding Simple Low Voltage, Wide Swing Wide Swing, Short Channel Regulated Drain Biasing Circuits
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
EE105 - Fall 2006 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. Jan M. Rabaey (jan@eecs) Lecture 7: MOS Transistor Some Administrative Issues Lab 2 this week Hw 2 due on We Hw 3 will be posted same day MIDTERM
The Inverter. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Inverter Revised from Digital Integrated Circuits, Jan M. Rabaey el, 2003 Propagation Delay CMOS
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Inverter Revised from Digital Integrated Circuits, Jan M. Rabaey el, 2003 Propagation Delay CMOS
The Wire. Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic. July 30, 2002
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Wire July 30, 2002 1 The Wire transmitters receivers schematics physical 2 Interconnect Impact on
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective Jan M. Rabaey Anantha Chandrakasan Borivoje Nikolic The Wire July 30, 2002 1 The Wire transmitters receivers schematics physical 2 Interconnect Impact on
Digital VLSI Design I
 The University of Toledo Section f04ms - EES:460/560 Digital VLSI Design I: Basic Subsystems Digital VLSI Design I MIDTERM EXAMINATION Problems Points. 4. 3. 5 Total Was the exam fair? yes no The University
The University of Toledo Section f04ms - EES:460/560 Digital VLSI Design I: Basic Subsystems Digital VLSI Design I MIDTERM EXAMINATION Problems Points. 4. 3. 5 Total Was the exam fair? yes no The University
EE 330 Lecture 16. MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow
 EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
EE 330 Lecture 16 MOS Device Modeling p-channel n-channel comparisons Model consistency and relationships CMOS Process Flow Review from Last Time Operation Regions by Applications Id I D 300 250 200 150
