Characteristic Functions in Radar and Sonar. Southeastern Symposium on System Theory
|
|
|
- William Walters
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Characteristic Functions in Radar and Sonar Southeastern Symposium on System Theory March 18,2002 Stephen R. Addison Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Central Arkansas Conway, AR Presented By John E. Gray Code B-32 Naval Surface Warfare Center Dahlgren Division Dahlgren, VA
2 Outline FOUR QUESTIONS WHAT ARE S? SINGLE VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF CHARCTERISTIC FUNCTION. MULTI-DIMENSIONAL S RAYLEIGH PROBLEM 2
3 FOUR QUESTIONS Question 1: Given we know the density for x is Px, what is the distribution for u f x? Question 2: Given we know the density for x is P x x and the density for y is P y y, what is the distribution for u x y? Question 3: Given we know the density for x is P x x and the density for y is P y y, what is the distribution for u x y? Question 4: Given we know the density for x is P x x and the density for y is P y y, what is the distribution for u xy? 3
4 DEFINTIONS OF CHARCTERISTIC FUNCTION DEFINTION: M P e jx e jx Px dx PROPERTIES 1. M M M. 3. M M M0. ALTERNATIVE DEFINITION: M P e jx Px dx n0 jx n n! Pxdx n0 j n n! x n 4
5 DEFINTIONS OF CHARCTERISTIC FUNCTION TWO METHODS FOR CALCULATION OF MOMENTS x n x n Pxdx x n 1 j n n M P n 0 differentiation is easier than integration Fourier transform pair relationship between the PDF and CF: Px 1 2 e jx M P dx 5
6 SINGLE VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF one say would often like to know the density of a new variable, û, that is a function of the old variable: u f x Probability Density Function: Pu 1 2 e ju M u d Characteristic Function: M u e jfx e jfx Px dx Apply CF to PDF: Pu 1 2 e jfx e jx Px d dx PDF for Transformed variable: Pu u fxpxdx This solves the problem for Exercise 1. 6
7 SINGLE VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF Interpretation of Delta Function of Function gx i x x i 1 g xi fx u i x x i 1 f x i Pu i Px i f xi 7
8 SINGLE VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF Translation (Translation): Let u a x b,whatispu given we know that the PDF of x is P x x?solving for zero of the equation gives x ub a and note dx 1 a, then the distribution is Pu 1 a Px x ub 1 a a P x u b a # 8
9 SINGLE VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF Square Law Detector (Square Law Detector): Let u x 2,whatisPu given we know that the PDF of x is P x x? Answer: Solve for zeros and note 2xdx du,then*becomes If x is N0,,thenthePDFis Pu where is the unit step function x 1 x u Pxu x 1,x 2 Puu u u 1 2 u P u P u # 1 2u e u 2 2 u. x 1 x 0 0 otherwise # 9
10 SINGLE VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF The coordinate transformation y R sin apdff is onto but not one-to-one over interval,. Thus ref: * has an infinite number of zeros. It is more connivent to determine the CF directly, so the transformation of the PDF is The exponential can be written as so the CF is given by M M J n R n e jr sin f d. J n Re jn e jr sin, n e jn fd J n RFn; n which can be rewritten as M J 0 R J n RFn 1 n Fn n 1 where Fn is the Fourier transform of the PDF f evaluated at n. Depending on the problem, the CF is sufficient, but sometimes it is still useful to know the PDF. Now if we apply the identity (Abramowitz) e jt J n t dt 2j n T n 1, 1 2 where T n x is the n-th order Chebyshev polynomials, the PDF of the coordinate transformation is where a n j n Fn. f y y a 0 n 1 a n a n T n y R R 2 y 2 1 y R, # 10
11 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF Repeating the same procedure for the single dimensional case to the multi-dimensional case yields: Pu,v u fx,yv gx,ypx,y dxdy This due to Cohen, is sufficient to allow us to solve the problem of determining many of the two dimensional combinations of random variables such as those in Exercises
12 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF o the density becomes Let û fx,y,thecfis Mu e jfx,y Px,y dxdy, ntegrating out gives delta functions Pu e ju M u d Pu e jufx,y Px,y dydxd ufx,ypx,y dx. # (C) 12
13 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF EXAMPLE: Translation Let z x y, with distributions P x x and P y y (assuming they are uncorelated), then the ibution of û which is denoted by P u u is ref: C P z z z x ypxy x, y dxdy Pxyx, z x dx Px xp y z x dx (uncorrelated) # 13
14 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF EXAMPLE: Multiplication Let z x y, with distribution P xy x,y or distributions P x x and P y y (assuming they are ncorelated), then the distribution of û which is denoted by P z z is ref: C Pzz f we note that i x x i 1,so f xi z xy o f z z z xyp xyx,y dxdy. 1 x P xy y z x x z x,x dx. # 14
15 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF EXAMPLE: Division or Monopulse Ratio Let z x y, with distribution P xy x,y or distributions P x x and P y y (assuming they are uncorelated), then the distribution of z which is denoted by P z z is Pzz z x y Pxyx,y dydx. If we note that z x y y zx x so fzz x P xyzx,xdx. # 15
16 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF RAYLEIGH PROBLEM Sum of two dimension random amplitudes and phases: X N i1 x i N i1 â i cos i Arose in Scattering off Rough Surfaces, Applications in Radar, Sonar, Acoustics, Communications, Physics, etc. 16
17 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF INSTANCE OF TRACKING PROBLEM Transformations from spherical to Cartesian coordinates x r cos y r sin sin, sin, z r cos. Rewritten as: x r 2 sin sin y r 2 cos cos 17
18 MULTI-VARIABLE APPLICATIONS OF Then the distribution for z is: f z z 1 1 P r z a 0 n1 1 2 a n a n T n d. two sum case z z 1 z 2 f z z (uncorrelated) 1 Pz1 z 1 P z2 z 1 z dz 1 1 P r1 z 1 1 a 0 n1 1 1 P r2 z 2z1z 2 a n a n T n a 0 n1 a n a n T n d 1 d 2 dz 1 # Case n is obtained by repeated application of Case 2 18
19 Conclusions Demonstrated how to use CF to bypass difficulties in computing combinations of random variables using a method based on Cohen Using Fourier analysis and application of definition of Dirac delta function, combined PDF is obtained with considerable simplification Motivation engineering applications that occur in radar/sonar applications that involve combinations of probability density functions Have demonstrated simple method to obtain PDF for different combinations of random variables Rayleigh problem for i=2 solved which implies general solution for case i=n 19
Perhaps the simplest way of modeling two (discrete) random variables is by means of a joint PMF, defined as follows.
 Chapter 5 Two Random Variables In a practical engineering problem, there is almost always causal relationship between different events. Some relationships are determined by physical laws, e.g., voltage
Chapter 5 Two Random Variables In a practical engineering problem, there is almost always causal relationship between different events. Some relationships are determined by physical laws, e.g., voltage
1 Review of di erential calculus
 Review of di erential calculus This chapter presents the main elements of di erential calculus needed in probability theory. Often, students taking a course on probability theory have problems with concepts
Review of di erential calculus This chapter presents the main elements of di erential calculus needed in probability theory. Often, students taking a course on probability theory have problems with concepts
Math 416 Lecture 2 DEFINITION. Here are the multivariate versions: X, Y, Z iff P(X = x, Y = y, Z =z) = p(x, y, z) of X, Y, Z iff for all sets A, B, C,
 Math 416 Lecture 2 DEFINITION. Here are the multivariate versions: PMF case: p(x, y, z) is the joint Probability Mass Function of X, Y, Z iff P(X = x, Y = y, Z =z) = p(x, y, z) PDF case: f(x, y, z) is
Math 416 Lecture 2 DEFINITION. Here are the multivariate versions: PMF case: p(x, y, z) is the joint Probability Mass Function of X, Y, Z iff P(X = x, Y = y, Z =z) = p(x, y, z) PDF case: f(x, y, z) is
Calculus. Weijiu Liu. Department of Mathematics University of Central Arkansas 201 Donaghey Avenue, Conway, AR 72035, USA
 Calculus Weijiu Liu Department of Mathematics University of Central Arkansas 201 Donaghey Avenue, Conway, AR 72035, USA 1 Opening Welcome to your Calculus I class! My name is Weijiu Liu. I will guide you
Calculus Weijiu Liu Department of Mathematics University of Central Arkansas 201 Donaghey Avenue, Conway, AR 72035, USA 1 Opening Welcome to your Calculus I class! My name is Weijiu Liu. I will guide you
EE4601 Communication Systems
 EE4601 Communication Systems Week 2 Review of Probability, Important Distributions 0 c 2011, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect2 1) Conditional Probability Consider a sample space that consists of two
EE4601 Communication Systems Week 2 Review of Probability, Important Distributions 0 c 2011, Georgia Institute of Technology (lect2 1) Conditional Probability Consider a sample space that consists of two
' Liberty and Umou Ono and Inseparablo "
 3 5? #< q 8 2 / / ) 9 ) 2 ) > < _ / ] > ) 2 ) ) 5 > x > [ < > < ) > _ ] ]? <
3 5? #< q 8 2 / / ) 9 ) 2 ) > < _ / ] > ) 2 ) ) 5 > x > [ < > < ) > _ ] ]? <
Vector Calculus. Dr. D. Sukumar
 Vector Calculus Dr. D. Sukumar Space co-ordinates Change of variable Cartesian co-ordinates < x < Cartesian co-ordinates < x < < y < Cartesian co-ordinates < x < < y < < z < Cylindrical Cylindrical Cylindrical
Vector Calculus Dr. D. Sukumar Space co-ordinates Change of variable Cartesian co-ordinates < x < Cartesian co-ordinates < x < < y < Cartesian co-ordinates < x < < y < < z < Cylindrical Cylindrical Cylindrical
Multivariate distributions
 CHAPTER Multivariate distributions.. Introduction We want to discuss collections of random variables (X, X,..., X n ), which are known as random vectors. In the discrete case, we can define the density
CHAPTER Multivariate distributions.. Introduction We want to discuss collections of random variables (X, X,..., X n ), which are known as random vectors. In the discrete case, we can define the density
Stochastic Mode Reduction in Large Deterministic Systems
 Stochastic Mode Reduction in Large Deterministic Systems I. Timofeyev University of Houston With A. J. Majda and E. Vanden-Eijnden; NYU Related Publications: http://www.math.uh.edu/ ilya Plan Mode-Elimination
Stochastic Mode Reduction in Large Deterministic Systems I. Timofeyev University of Houston With A. J. Majda and E. Vanden-Eijnden; NYU Related Publications: http://www.math.uh.edu/ ilya Plan Mode-Elimination
1 Solution to Problem 2.1
 Solution to Problem 2. I incorrectly worked this exercise instead of 2.2, so I decided to include the solution anyway. a) We have X Y /3, which is a - function. It maps the interval, ) where X lives) onto
Solution to Problem 2. I incorrectly worked this exercise instead of 2.2, so I decided to include the solution anyway. a) We have X Y /3, which is a - function. It maps the interval, ) where X lives) onto
Mathematics 206 Solutions for HWK 23 Section 6.3 p358
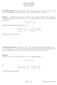 Mathematics 6 Solutions for HWK Section Problem 9. Given T(x, y, z) = (x 9y + z,6x + 5y z) and v = (,,), use the standard matrix for the linear transformation T to find the image of the vector v. Note
Mathematics 6 Solutions for HWK Section Problem 9. Given T(x, y, z) = (x 9y + z,6x + 5y z) and v = (,,), use the standard matrix for the linear transformation T to find the image of the vector v. Note
Write your Registration Number, Test Centre, Test Code and the Number of this booklet in the appropriate places on the answersheet.
 2016 Booklet No. Test Code : PSA Forenoon Questions : 30 Time : 2 hours Write your Registration Number, Test Centre, Test Code and the Number of this booklet in the appropriate places on the answersheet.
2016 Booklet No. Test Code : PSA Forenoon Questions : 30 Time : 2 hours Write your Registration Number, Test Centre, Test Code and the Number of this booklet in the appropriate places on the answersheet.
Power Series Solutions to the Legendre Equation
 Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati The Legendre equation The equation (1 x 2 )y 2xy + α(α + 1)y = 0, (1) where α is any real constant, is called Legendre s equation. When α Z +, the equation has polynomial
Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati The Legendre equation The equation (1 x 2 )y 2xy + α(α + 1)y = 0, (1) where α is any real constant, is called Legendre s equation. When α Z +, the equation has polynomial
Review session Midterm 1
 AS.110.109: Calculus II (Eng) Review session Midterm 1 Yi Wang, Johns Hopkins University Fall 2018 7.1: Integration by parts Basic integration method: u-sub, integration table Integration By Parts formula
AS.110.109: Calculus II (Eng) Review session Midterm 1 Yi Wang, Johns Hopkins University Fall 2018 7.1: Integration by parts Basic integration method: u-sub, integration table Integration By Parts formula
Physics 116C The Distribution of the Sum of Random Variables
 Physics 116C The Distribution of the Sum of Random Variables Peter Young (Dated: December 2, 2013) Consider a random variable with a probability distribution P(x). The distribution is normalized, i.e.
Physics 116C The Distribution of the Sum of Random Variables Peter Young (Dated: December 2, 2013) Consider a random variable with a probability distribution P(x). The distribution is normalized, i.e.
4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables
 4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables Setup: Consider as given the joint distribution of X 1,..., X n (i.e. consider as given f X1,...,X n and F X1,...,X n ) Consider k functions g 1 : R n
4. Distributions of Functions of Random Variables Setup: Consider as given the joint distribution of X 1,..., X n (i.e. consider as given f X1,...,X n and F X1,...,X n ) Consider k functions g 1 : R n
lim n C1/n n := ρ. [f(y) f(x)], y x =1 [f(x) f(y)] [g(x) g(y)]. (x,y) E A E(f, f),
![lim n C1/n n := ρ. [f(y) f(x)], y x =1 [f(x) f(y)] [g(x) g(y)]. (x,y) E A E(f, f), lim n C1/n n := ρ. [f(y) f(x)], y x =1 [f(x) f(y)] [g(x) g(y)]. (x,y) E A E(f, f),](/thumbs/76/73980372.jpg) 1 Part I Exercise 1.1. Let C n denote the number of self-avoiding random walks starting at the origin in Z of length n. 1. Show that (Hint: Use C n+m C n C m.) lim n C1/n n = inf n C1/n n := ρ.. Show that
1 Part I Exercise 1.1. Let C n denote the number of self-avoiding random walks starting at the origin in Z of length n. 1. Show that (Hint: Use C n+m C n C m.) lim n C1/n n = inf n C1/n n := ρ.. Show that
Sampling Distributions
 Sampling Distributions In statistics, a random sample is a collection of independent and identically distributed (iid) random variables, and a sampling distribution is the distribution of a function of
Sampling Distributions In statistics, a random sample is a collection of independent and identically distributed (iid) random variables, and a sampling distribution is the distribution of a function of
In this chapter we study elliptical PDEs. That is, PDEs of the form. 2 u = lots,
 Chapter 8 Elliptic PDEs In this chapter we study elliptical PDEs. That is, PDEs of the form 2 u = lots, where lots means lower-order terms (u x, u y,..., u, f). Here are some ways to think about the physical
Chapter 8 Elliptic PDEs In this chapter we study elliptical PDEs. That is, PDEs of the form 2 u = lots, where lots means lower-order terms (u x, u y,..., u, f). Here are some ways to think about the physical
1 Random Variable: Topics
 Note: Handouts DO NOT replace the book. In most cases, they only provide a guideline on topics and an intuitive feel. 1 Random Variable: Topics Chap 2, 2.1-2.4 and Chap 3, 3.1-3.3 What is a random variable?
Note: Handouts DO NOT replace the book. In most cases, they only provide a guideline on topics and an intuitive feel. 1 Random Variable: Topics Chap 2, 2.1-2.4 and Chap 3, 3.1-3.3 What is a random variable?
MAS113 Introduction to Probability and Statistics. Proofs of theorems
 MAS113 Introduction to Probability and Statistics Proofs of theorems Theorem 1 De Morgan s Laws) See MAS110 Theorem 2 M1 By definition, B and A \ B are disjoint, and their union is A So, because m is a
MAS113 Introduction to Probability and Statistics Proofs of theorems Theorem 1 De Morgan s Laws) See MAS110 Theorem 2 M1 By definition, B and A \ B are disjoint, and their union is A So, because m is a
Lecture 4 Filtering in the Frequency Domain. Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2016
 Lecture 4 Filtering in the Frequency Domain Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2016 Outline Background From Fourier series to Fourier transform Properties of the Fourier
Lecture 4 Filtering in the Frequency Domain Lin ZHANG, PhD School of Software Engineering Tongji University Spring 2016 Outline Background From Fourier series to Fourier transform Properties of the Fourier
First Order Differential Equations
 Chapter 2 First Order Differential Equations Introduction Any first order differential equation can be written as F (x, y, y )=0 by moving all nonzero terms to the left hand side of the equation. Of course,
Chapter 2 First Order Differential Equations Introduction Any first order differential equation can be written as F (x, y, y )=0 by moving all nonzero terms to the left hand side of the equation. Of course,
E[X n ]= dn dt n M X(t). ). What is the mgf? Solution. Found this the other day in the Kernel matching exercise: 1 M X (t) =
![E[X n ]= dn dt n M X(t). ). What is the mgf? Solution. Found this the other day in the Kernel matching exercise: 1 M X (t) = E[X n ]= dn dt n M X(t). ). What is the mgf? Solution. Found this the other day in the Kernel matching exercise: 1 M X (t) =](/thumbs/94/121808901.jpg) Chapter 7 Generating functions Definition 7.. Let X be a random variable. The moment generating function is given by M X (t) =E[e tx ], provided that the expectation exists for t in some neighborhood of
Chapter 7 Generating functions Definition 7.. Let X be a random variable. The moment generating function is given by M X (t) =E[e tx ], provided that the expectation exists for t in some neighborhood of
Series Solutions of Differential Equations
 Chapter 6 Series Solutions of Differential Equations In this chapter we consider methods for solving differential equations using power series. Sequences and infinite series are also involved in this treatment.
Chapter 6 Series Solutions of Differential Equations In this chapter we consider methods for solving differential equations using power series. Sequences and infinite series are also involved in this treatment.
Electromagnetism HW 1 math review
 Electromagnetism HW math review Problems -5 due Mon 7th Sep, 6- due Mon 4th Sep Exercise. The Levi-Civita symbol, ɛ ijk, also known as the completely antisymmetric rank-3 tensor, has the following properties:
Electromagnetism HW math review Problems -5 due Mon 7th Sep, 6- due Mon 4th Sep Exercise. The Levi-Civita symbol, ɛ ijk, also known as the completely antisymmetric rank-3 tensor, has the following properties:
Lecture Notes 3 Multiple Random Variables. Joint, Marginal, and Conditional pmfs. Bayes Rule and Independence for pmfs
 Lecture Notes 3 Multiple Random Variables Joint, Marginal, and Conditional pmfs Bayes Rule and Independence for pmfs Joint, Marginal, and Conditional pdfs Bayes Rule and Independence for pdfs Functions
Lecture Notes 3 Multiple Random Variables Joint, Marginal, and Conditional pmfs Bayes Rule and Independence for pmfs Joint, Marginal, and Conditional pdfs Bayes Rule and Independence for pdfs Functions
Lecture 2. Spring Quarter Statistical Optics. Lecture 2. Characteristic Functions. Transformation of RVs. Sums of RVs
 s of Spring Quarter 2018 ECE244a - Spring 2018 1 Function s of The characteristic function is the Fourier transform of the pdf (note Goodman and Papen have different notation) C x(ω) = e iωx = = f x(x)e
s of Spring Quarter 2018 ECE244a - Spring 2018 1 Function s of The characteristic function is the Fourier transform of the pdf (note Goodman and Papen have different notation) C x(ω) = e iωx = = f x(x)e
Two special equations: Bessel s and Legendre s equations. p Fourier-Bessel and Fourier-Legendre series. p
 LECTURE 1 Table of Contents Two special equations: Bessel s and Legendre s equations. p. 259-268. Fourier-Bessel and Fourier-Legendre series. p. 453-460. Boundary value problems in other coordinate system.
LECTURE 1 Table of Contents Two special equations: Bessel s and Legendre s equations. p. 259-268. Fourier-Bessel and Fourier-Legendre series. p. 453-460. Boundary value problems in other coordinate system.
LECTURE NOTES DISCRETE MATHEMATICS. Eusebius Doedel
 LECTURE NOTES on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel 1 LOGIC Introduction. First we introduce some basic concepts needed in our discussion of logic. These will be covered in more detail later. A set is
LECTURE NOTES on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel 1 LOGIC Introduction. First we introduce some basic concepts needed in our discussion of logic. These will be covered in more detail later. A set is
conditional cdf, conditional pdf, total probability theorem?
 6 Multiple Random Variables 6.0 INTRODUCTION scalar vs. random variable cdf, pdf transformation of a random variable conditional cdf, conditional pdf, total probability theorem expectation of a random
6 Multiple Random Variables 6.0 INTRODUCTION scalar vs. random variable cdf, pdf transformation of a random variable conditional cdf, conditional pdf, total probability theorem expectation of a random
March Algebra 2 Question 1. March Algebra 2 Question 1
 March Algebra 2 Question 1 If the statement is always true for the domain, assign that part a 3. If it is sometimes true, assign it a 2. If it is never true, assign it a 1. Your answer for this question
March Algebra 2 Question 1 If the statement is always true for the domain, assign that part a 3. If it is sometimes true, assign it a 2. If it is never true, assign it a 1. Your answer for this question
Topic 6 Continuous Random Variables
 Topic 6 page Topic 6 Continuous Random Variables Reference: Chapter 5.-5.3 Probability Density Function The Uniform Distribution The Normal Distribution Standardizing a Normal Distribution Using the Standard
Topic 6 page Topic 6 Continuous Random Variables Reference: Chapter 5.-5.3 Probability Density Function The Uniform Distribution The Normal Distribution Standardizing a Normal Distribution Using the Standard
STAT 801: Mathematical Statistics. Distribution Theory
 STAT 81: Mathematical Statistics Distribution Theory Basic Problem: Start with assumptions about f or CDF of random vector X (X 1,..., X p ). Define Y g(x 1,..., X p ) to be some function of X (usually
STAT 81: Mathematical Statistics Distribution Theory Basic Problem: Start with assumptions about f or CDF of random vector X (X 1,..., X p ). Define Y g(x 1,..., X p ) to be some function of X (usually
2 Functions of random variables
 2 Functions of random variables A basic statistical model for sample data is a collection of random variables X 1,..., X n. The data are summarised in terms of certain sample statistics, calculated as
2 Functions of random variables A basic statistical model for sample data is a collection of random variables X 1,..., X n. The data are summarised in terms of certain sample statistics, calculated as
Find the indicated derivative. 1) Find y(4) if y = 3 sin x. A) y(4) = 3 cos x B) y(4) = 3 sin x C) y(4) = - 3 cos x D) y(4) = - 3 sin x
 Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
1MA6 Partial Differentiation and Multiple Integrals: I
 1MA6/1 1MA6 Partial Differentiation and Multiple Integrals: I Dr D W Murray Michaelmas Term 1994 1. Total differential. (a) State the conditions for the expression P (x, y)dx+q(x, y)dy to be the perfect
1MA6/1 1MA6 Partial Differentiation and Multiple Integrals: I Dr D W Murray Michaelmas Term 1994 1. Total differential. (a) State the conditions for the expression P (x, y)dx+q(x, y)dy to be the perfect
Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) a n z n. n=0
 Lecture 22 Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) Recall a few facts about power series: a n z n This series in z is centered at z 0. Here z can
Lecture 22 Power series solutions for 2nd order linear ODE s (not necessarily with constant coefficients) Recall a few facts about power series: a n z n This series in z is centered at z 0. Here z can
20. Gaussian Measures
 Tutorial 20: Gaussian Measures 1 20. Gaussian Measures M n (R) isthesetofalln n-matrices with real entries, n 1. Definition 141 AmatrixM M n (R) is said to be symmetric, if and only if M = M t. M is orthogonal,
Tutorial 20: Gaussian Measures 1 20. Gaussian Measures M n (R) isthesetofalln n-matrices with real entries, n 1. Definition 141 AmatrixM M n (R) is said to be symmetric, if and only if M = M t. M is orthogonal,
p. 6-1 Continuous Random Variables p. 6-2
 Continuous Random Variables Recall: For discrete random variables, only a finite or countably infinite number of possible values with positive probability (>). Often, there is interest in random variables
Continuous Random Variables Recall: For discrete random variables, only a finite or countably infinite number of possible values with positive probability (>). Often, there is interest in random variables
DRAFT - Math 102 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
Math02 - Term72 - Guides and Exercises - DRAFT 7 Techniques of Integration A summery for the most important integrals that we have learned so far: 7. Integration by Parts The Product Rule states that if
Solutions to the Calculus and Linear Algebra problems on the Comprehensive Examination of January 28, 2011
 Solutions to the Calculus and Linear Algebra problems on the Comprehensive Examination of January 8, Solutions to Problems 5 are omitted since they involve topics no longer covered on the Comprehensive
Solutions to the Calculus and Linear Algebra problems on the Comprehensive Examination of January 8, Solutions to Problems 5 are omitted since they involve topics no longer covered on the Comprehensive
Mathematical Methods - Lecture 7
 Mathematical Methods - Lecture 7 Yuliya Tarabalka Inria Sophia-Antipolis Méditerranée, Titane team, http://www-sop.inria.fr/members/yuliya.tarabalka/ Tel.: +33 (0)4 92 38 77 09 email: yuliya.tarabalka@inria.fr
Mathematical Methods - Lecture 7 Yuliya Tarabalka Inria Sophia-Antipolis Méditerranée, Titane team, http://www-sop.inria.fr/members/yuliya.tarabalka/ Tel.: +33 (0)4 92 38 77 09 email: yuliya.tarabalka@inria.fr
Multipole moments. November 9, 2015
 Multipole moments November 9, 5 The far field expansion Suppose we have a localized charge distribution, confined to a region near the origin with r < R. Then for values of r > R, the electric field must
Multipole moments November 9, 5 The far field expansion Suppose we have a localized charge distribution, confined to a region near the origin with r < R. Then for values of r > R, the electric field must
Modified Adomian Decomposition Method for Solving Particular Third-Order Ordinary Differential Equations
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 212, no. 3, 1463-1469 Modified Adomian Decomposition Method for Solving Particular Third-Order Ordinary Differential Equations P. Pue-on 1 and N. Viriyapong 2 Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 6, 212, no. 3, 1463-1469 Modified Adomian Decomposition Method for Solving Particular Third-Order Ordinary Differential Equations P. Pue-on 1 and N. Viriyapong 2 Department
Today: Fundamentals of Monte Carlo
 Today: Fundamentals of Monte Carlo What is Monte Carlo? Named at Los Alamos in 940 s after the casino. Any method which uses (pseudo)random numbers as an essential part of the algorithm. Stochastic - not
Today: Fundamentals of Monte Carlo What is Monte Carlo? Named at Los Alamos in 940 s after the casino. Any method which uses (pseudo)random numbers as an essential part of the algorithm. Stochastic - not
LECTURE NOTES DISCRETE MATHEMATICS. Eusebius Doedel
 LECTURE NOTES on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel 1 LOGIC Introduction. First we introduce some basic concepts needed in our discussion of logic. These will be covered in more detail later. A set is
LECTURE NOTES on DISCRETE MATHEMATICS Eusebius Doedel 1 LOGIC Introduction. First we introduce some basic concepts needed in our discussion of logic. These will be covered in more detail later. A set is
LEGENDRE POLYNOMIALS AND APPLICATIONS. We construct Legendre polynomials and apply them to solve Dirichlet problems in spherical coordinates.
 LEGENDRE POLYNOMIALS AND APPLICATIONS We construct Legendre polynomials and apply them to solve Dirichlet problems in spherical coordinates.. Legendre equation: series solutions The Legendre equation is
LEGENDRE POLYNOMIALS AND APPLICATIONS We construct Legendre polynomials and apply them to solve Dirichlet problems in spherical coordinates.. Legendre equation: series solutions The Legendre equation is
Fourier Series and Transform KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #7, March 24, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Fourier Series and Transform KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #7, March 24, 20 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Fourier transform Properties Fourier transform of special function Fourier
Fourier Series and Transform KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #7, March 24, 20 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Fourier transform Properties Fourier transform of special function Fourier
1 Curvilinear Coordinates
 MATHEMATICA PHYSICS PHYS-2106/3 Course Summary Gabor Kunstatter, University of Winnipeg April 2014 1 Curvilinear Coordinates 1. General curvilinear coordinates 3-D: given or conversely u i = u i (x, y,
MATHEMATICA PHYSICS PHYS-2106/3 Course Summary Gabor Kunstatter, University of Winnipeg April 2014 1 Curvilinear Coordinates 1. General curvilinear coordinates 3-D: given or conversely u i = u i (x, y,
2.2 Separable Equations
 2.2 Separable Equations Definition A first-order differential equation that can be written in the form Is said to be separable. Note: the variables of a separable equation can be written as Examples Solve
2.2 Separable Equations Definition A first-order differential equation that can be written in the form Is said to be separable. Note: the variables of a separable equation can be written as Examples Solve
Section 3.4. Second Order Nonhomogeneous. The corresponding homogeneous equation. is called the reduced equation of (N).
 Section 3.4. Second Order Nonhomogeneous Equations y + p(x)y + q(x)y = f(x) (N) The corresponding homogeneous equation y + p(x)y + q(x)y = 0 (H) is called the reduced equation of (N). 1 General Results
Section 3.4. Second Order Nonhomogeneous Equations y + p(x)y + q(x)y = f(x) (N) The corresponding homogeneous equation y + p(x)y + q(x)y = 0 (H) is called the reduced equation of (N). 1 General Results
Homework 5 Solutions
 126/DCP126 Probability, Fall 214 Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 5 Solutions 5-Jan-215 1. Let the joint probability mass function of discrete random variables X and Y be given by { c(x + y) ifx
126/DCP126 Probability, Fall 214 Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 5 Solutions 5-Jan-215 1. Let the joint probability mass function of discrete random variables X and Y be given by { c(x + y) ifx
CS145: Probability & Computing
 CS45: Probability & Computing Lecture 0: Continuous Bayes Rule, Joint and Marginal Probability Densities Instructor: Eli Upfal Brown University Computer Science Figure credits: Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis,
CS45: Probability & Computing Lecture 0: Continuous Bayes Rule, Joint and Marginal Probability Densities Instructor: Eli Upfal Brown University Computer Science Figure credits: Bertsekas & Tsitsiklis,
Georgia Department of Education Common Core Georgia Performance Standards Framework CCGPS Advanced Algebra Unit 2
 Polynomials Patterns Task 1. To get an idea of what polynomial functions look like, we can graph the first through fifth degree polynomials with leading coefficients of 1. For each polynomial function,
Polynomials Patterns Task 1. To get an idea of what polynomial functions look like, we can graph the first through fifth degree polynomials with leading coefficients of 1. For each polynomial function,
e x2 dxdy, e x2 da, e x2 x 3 dx = e
 STS26-4 Calculus II: The fourth exam Dec 15, 214 Please show all your work! Answers without supporting work will be not given credit. Write answers in spaces provided. You have 1 hour and 2minutes to complete
STS26-4 Calculus II: The fourth exam Dec 15, 214 Please show all your work! Answers without supporting work will be not given credit. Write answers in spaces provided. You have 1 hour and 2minutes to complete
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
Series Solution of Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 Series Solution of Linear Ordinary Differential Equations Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Aim: To study methods for determining series expansions for solutions to linear ODE with variable coefficients.
Series Solution of Linear Ordinary Differential Equations Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati Aim: To study methods for determining series expansions for solutions to linear ODE with variable coefficients.
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 G $ G 2 G ««2 ««q ) q «\ { q «««/ 6 «««««q «] «q 6 ««Z q «««Q \ Q «q «X ««G X G ««? G Q / Q Q X ««/«X X «««Q X\ «q «X \ / X G XX «««X «x «X «x X G X 29 2 ««Q G G «) 22 G XXX GG G G G G G X «x G Q «) «G
G $ G 2 G ««2 ««q ) q «\ { q «««/ 6 «««««q «] «q 6 ««Z q «««Q \ Q «q «X ««G X G ««? G Q / Q Q X ««/«X X «««Q X\ «q «X \ / X G XX «««X «x «X «x X G X 29 2 ««Q G G «) 22 G XXX GG G G G G G X «x G Q «) «G
Chapter 3: Random Variables 1
 Chapter 3: Random Variables 1 Yunghsiang S. Han Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering, National Taipei University Taiwan E-mail: yshan@mail.ntpu.edu.tw 1 Modified from the lecture notes by Prof.
Chapter 3: Random Variables 1 Yunghsiang S. Han Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering, National Taipei University Taiwan E-mail: yshan@mail.ntpu.edu.tw 1 Modified from the lecture notes by Prof.
Power Series Solutions to the Legendre Equation
 Power Series Solutions to the Legendre Equation Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati The Legendre equation The equation (1 x 2 )y 2xy + α(α + 1)y = 0, (1) where α is any real constant, is called Legendre
Power Series Solutions to the Legendre Equation Department of Mathematics IIT Guwahati The Legendre equation The equation (1 x 2 )y 2xy + α(α + 1)y = 0, (1) where α is any real constant, is called Legendre
1 Lecture 8: Interpolating polynomials.
 1 Lecture 8: Interpolating polynomials. 1.1 Horner s method Before turning to the main idea of this part of the course, we consider how to evaluate a polynomial. Recall that a polynomial is an expression
1 Lecture 8: Interpolating polynomials. 1.1 Horner s method Before turning to the main idea of this part of the course, we consider how to evaluate a polynomial. Recall that a polynomial is an expression
Topic 6a Numerical Integration
 Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu Topic 6a umerical Integration EE 4386/5301 Computational Methods in EE Outline Introduction Discrete
Course Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Office: A 337 Phone: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utep.edu Topic 6a umerical Integration EE 4386/5301 Computational Methods in EE Outline Introduction Discrete
Degree Master of Science in Mathematical Modelling and Scientific Computing Mathematical Methods I Thursday, 12th January 2012, 9:30 a.m.- 11:30 a.m.
 Degree Master of Science in Mathematical Modelling and Scientific Computing Mathematical Methods I Thursday, 12th January 2012, 9:30 a.m.- 11:30 a.m. Candidates should submit answers to a maximum of four
Degree Master of Science in Mathematical Modelling and Scientific Computing Mathematical Methods I Thursday, 12th January 2012, 9:30 a.m.- 11:30 a.m. Candidates should submit answers to a maximum of four
Curve Fitting and Approximation
 Department of Physics Cotton College State University, Panbazar Guwahati 781001, Assam December 6, 2016 Outline Curve Fitting 1 Curve Fitting Outline Curve Fitting 1 Curve Fitting Topics in the Syllabus
Department of Physics Cotton College State University, Panbazar Guwahati 781001, Assam December 6, 2016 Outline Curve Fitting 1 Curve Fitting Outline Curve Fitting 1 Curve Fitting Topics in the Syllabus
Transformation of Probability Densities
 Transformation of Probability Densities This Wikibook shows how to transform the probability density of a continuous random variable in both the one-dimensional and multidimensional case. In other words,
Transformation of Probability Densities This Wikibook shows how to transform the probability density of a continuous random variable in both the one-dimensional and multidimensional case. In other words,
Lectures 9-10: Polynomial and piecewise polynomial interpolation
 Lectures 9-1: Polynomial and piecewise polynomial interpolation Let f be a function, which is only known at the nodes x 1, x,, x n, ie, all we know about the function f are its values y j = f(x j ), j
Lectures 9-1: Polynomial and piecewise polynomial interpolation Let f be a function, which is only known at the nodes x 1, x,, x n, ie, all we know about the function f are its values y j = f(x j ), j
Q SON,' (ESTABLISHED 1879L
 ( < 5(? Q 5 9 7 00 9 0 < 6 z 97 ( # ) $ x 6 < ( ) ( ( 6( ( ) ( $ z 0 z z 0 ) { ( % 69% ( ) x 7 97 z ) 7 ) ( ) 6 0 0 97 )( 0 x 7 97 5 6 ( ) 0 6 ) 5 ) 0 ) 9%5 z» 0 97 «6 6» 96? 0 96 5 0 ( ) ( ) 0 x 6 0
( < 5(? Q 5 9 7 00 9 0 < 6 z 97 ( # ) $ x 6 < ( ) ( ( 6( ( ) ( $ z 0 z z 0 ) { ( % 69% ( ) x 7 97 z ) 7 ) ( ) 6 0 0 97 )( 0 x 7 97 5 6 ( ) 0 6 ) 5 ) 0 ) 9%5 z» 0 97 «6 6» 96? 0 96 5 0 ( ) ( ) 0 x 6 0
Chapter 3: Random Variables 1
 Chapter 3: Random Variables 1 Yunghsiang S. Han Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering, National Taipei University Taiwan E-mail: yshan@mail.ntpu.edu.tw 1 Modified from the lecture notes by Prof.
Chapter 3: Random Variables 1 Yunghsiang S. Han Graduate Institute of Communication Engineering, National Taipei University Taiwan E-mail: yshan@mail.ntpu.edu.tw 1 Modified from the lecture notes by Prof.
From Determinism to Stochasticity
 From Determinism to Stochasticity Reading for this lecture: (These) Lecture Notes. Outline of next few lectures: Probability theory Stochastic processes Measurement theory You Are Here A B C... α γ β δ
From Determinism to Stochasticity Reading for this lecture: (These) Lecture Notes. Outline of next few lectures: Probability theory Stochastic processes Measurement theory You Are Here A B C... α γ β δ
Substitutions in Multiple Integrals
 Substitutions in Multiple Integrals P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Substitutions in Multiple Integrals April 10, 2017 1 / 23 Overview In the lecture, we discuss how to evaluate
Substitutions in Multiple Integrals P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Substitutions in Multiple Integrals April 10, 2017 1 / 23 Overview In the lecture, we discuss how to evaluate
Partial Differential Equations
 Partial Differential Equations Xu Chen Assistant Professor United Technologies Engineering Build, Rm. 382 Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Connecticut xchen@engr.uconn.edu Contents 1
Partial Differential Equations Xu Chen Assistant Professor United Technologies Engineering Build, Rm. 382 Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Connecticut xchen@engr.uconn.edu Contents 1
STAT 450: Statistical Theory. Distribution Theory. Reading in Casella and Berger: Ch 2 Sec 1, Ch 4 Sec 1, Ch 4 Sec 6.
 STAT 450: Statistical Theory Distribution Theory Reading in Casella and Berger: Ch 2 Sec 1, Ch 4 Sec 1, Ch 4 Sec 6. Example: Why does t-statistic have t distribution? Ingredients: Sample X 1,...,X n from
STAT 450: Statistical Theory Distribution Theory Reading in Casella and Berger: Ch 2 Sec 1, Ch 4 Sec 1, Ch 4 Sec 6. Example: Why does t-statistic have t distribution? Ingredients: Sample X 1,...,X n from
2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review
 2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review September 10, 2018 These notes are to help you through the math used in this class. This is just a refresher, so if you never learned one of these topics you should look more
2.20 Fall 2018 Math Review September 10, 2018 These notes are to help you through the math used in this class. This is just a refresher, so if you never learned one of these topics you should look more
Math 23b Practice Final Summer 2011
 Math 2b Practice Final Summer 211 1. (1 points) Sketch or describe the region of integration for 1 x y and interchange the order to dy dx dz. f(x, y, z) dz dy dx Solution. 1 1 x z z f(x, y, z) dy dx dz
Math 2b Practice Final Summer 211 1. (1 points) Sketch or describe the region of integration for 1 x y and interchange the order to dy dx dz. f(x, y, z) dz dy dx Solution. 1 1 x z z f(x, y, z) dy dx dz
) ) = γ. and P ( X. B(a, b) = Γ(a)Γ(b) Γ(a + b) ; (x + y, ) I J}. Then, (rx) a 1 (ry) b 1 e (x+y)r r 2 dxdy Γ(a)Γ(b) D
 3 Independent Random Variables II: Examples 3.1 Some functions of independent r.v. s. Let X 1, X 2,... be independent r.v. s with the known distributions. Then, one can compute the distribution of a r.v.
3 Independent Random Variables II: Examples 3.1 Some functions of independent r.v. s. Let X 1, X 2,... be independent r.v. s with the known distributions. Then, one can compute the distribution of a r.v.
V7 Foundations of Probability Theory
 V7 Foundations of Probability Theory Probability : degree of confidence that an event of an uncertain nature will occur. Events : we will assume that there is an agreed upon space of possible outcomes
V7 Foundations of Probability Theory Probability : degree of confidence that an event of an uncertain nature will occur. Events : we will assume that there is an agreed upon space of possible outcomes
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics
 SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 14: Continuous random variables Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin www.cs.cmu.edu/
SDS 321: Introduction to Probability and Statistics Lecture 14: Continuous random variables Purnamrita Sarkar Department of Statistics and Data Science The University of Texas at Austin www.cs.cmu.edu/
MAS113 Introduction to Probability and Statistics. Proofs of theorems
 MAS113 Introduction to Probability and Statistics Proofs of theorems Theorem 1 De Morgan s Laws) See MAS110 Theorem 2 M1 By definition, B and A \ B are disjoint, and their union is A So, because m is a
MAS113 Introduction to Probability and Statistics Proofs of theorems Theorem 1 De Morgan s Laws) See MAS110 Theorem 2 M1 By definition, B and A \ B are disjoint, and their union is A So, because m is a
Let X and Y denote two random variables. The joint distribution of these random
 EE385 Class Notes 9/7/0 John Stensby Chapter 3: Multiple Random Variables Let X and Y denote two random variables. The joint distribution of these random variables is defined as F XY(x,y) = [X x,y y] P.
EE385 Class Notes 9/7/0 John Stensby Chapter 3: Multiple Random Variables Let X and Y denote two random variables. The joint distribution of these random variables is defined as F XY(x,y) = [X x,y y] P.
Problem 1. Use a line integral to find the plane area enclosed by the curve C: r = a cos 3 t i + b sin 3 t j (0 t 2π). Solution: We assume a > b > 0.
 MATH 64: FINAL EXAM olutions Problem 1. Use a line integral to find the plane area enclosed by the curve C: r = a cos 3 t i + b sin 3 t j ( t π). olution: We assume a > b >. A = 1 π (xy yx )dt = 3ab π
MATH 64: FINAL EXAM olutions Problem 1. Use a line integral to find the plane area enclosed by the curve C: r = a cos 3 t i + b sin 3 t j ( t π). olution: We assume a > b >. A = 1 π (xy yx )dt = 3ab π
LIMITS AT INFINITY MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS
 LIMITS AT INFINITY MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS RECALL: VERTICAL ASYMPTOTES Remember that for a rational function, vertical asymptotes occur at values of x = a which have infinite its (either positive or
LIMITS AT INFINITY MR. VELAZQUEZ AP CALCULUS RECALL: VERTICAL ASYMPTOTES Remember that for a rational function, vertical asymptotes occur at values of x = a which have infinite its (either positive or
Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point
 Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background We will find a power series solution to the equation:
Series Solutions Near a Regular Singular Point MATH 365 Ordinary Differential Equations J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Background We will find a power series solution to the equation:
QMUL, School of Physics and Astronomy Date: 18/01/2019
 QMUL, School of Physics and stronomy Date: 8//9 PHY Mathematical Techniques Solutions for Exercise Class Script : Coordinate Systems and Double Integrals. Calculate the integral: where the region is defined
QMUL, School of Physics and stronomy Date: 8//9 PHY Mathematical Techniques Solutions for Exercise Class Script : Coordinate Systems and Double Integrals. Calculate the integral: where the region is defined
Teacher: Mr. Chafayay. Name: Class & Block : Date: ID: A. 3 Which function is represented by the graph?
 Teacher: Mr hafayay Name: lass & lock : ate: I: Midterm Exam Math III H Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question Which function is represented by the
Teacher: Mr hafayay Name: lass & lock : ate: I: Midterm Exam Math III H Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question Which function is represented by the
Final Exam May 4, 2016
 1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
1 Math 425 / AMCS 525 Dr. DeTurck Final Exam May 4, 2016 You may use your book and notes on this exam. Show your work in the exam book. Work only the problems that correspond to the section that you prepared.
Multiple Random Variables
 Multiple Random Variables Joint Probability Density Let X and Y be two random variables. Their joint distribution function is F ( XY x, y) P X x Y y. F XY ( ) 1, < x
Multiple Random Variables Joint Probability Density Let X and Y be two random variables. Their joint distribution function is F ( XY x, y) P X x Y y. F XY ( ) 1, < x
MATH2111 Higher Several Variable Calculus Integration
 MATH2 Higher Several Variable Calculus Integration Dr. Jonathan Kress School of Mathematics and Statistics University of New South Wales Semester, 26 [updated: April 3, 26] JM Kress (UNSW Maths & Stats)
MATH2 Higher Several Variable Calculus Integration Dr. Jonathan Kress School of Mathematics and Statistics University of New South Wales Semester, 26 [updated: April 3, 26] JM Kress (UNSW Maths & Stats)
Power Series and Analytic Function
 Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 21 Some Reviews of Power Series Differentiation and Integration of a Power Series
Dr Mansoor Alshehri King Saud University MATH204-Differential Equations Center of Excellence in Learning and Teaching 1 / 21 Some Reviews of Power Series Differentiation and Integration of a Power Series
arxiv:math.ca/ v2 17 Jul 2000
 NECESSARY AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR DIFFERENTIABILITY OF A FUNCTION OF SEVERAL VARIABLES. R.P. VENKATARAMAN, #1371, 13'TH MAIN ROAD, II STAGE, FIRST PHASE, B.T.M. LAYOUT, BANGALORE 560 076.
NECESSARY AND SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR DIFFERENTIABILITY OF A FUNCTION OF SEVERAL VARIABLES. R.P. VENKATARAMAN, #1371, 13'TH MAIN ROAD, II STAGE, FIRST PHASE, B.T.M. LAYOUT, BANGALORE 560 076.
234 Review Sheet 2 Solutions
 4 Review Sheet Solutions. Find all the critical points of the following functions and apply the second derivative test. (a) f(x, y) (x y)(x + y) ( ) x f + y + (x y)x (x + y) + (x y) ( ) x + ( x)y x + x
4 Review Sheet Solutions. Find all the critical points of the following functions and apply the second derivative test. (a) f(x, y) (x y)(x + y) ( ) x f + y + (x y)x (x + y) + (x y) ( ) x + ( x)y x + x
Today: Fundamentals of Monte Carlo
 Today: Fundamentals of Monte Carlo What is Monte Carlo? Named at Los Alamos in 1940 s after the casino. Any method which uses (pseudo)random numbers as an essential part of the algorithm. Stochastic -
Today: Fundamentals of Monte Carlo What is Monte Carlo? Named at Los Alamos in 1940 s after the casino. Any method which uses (pseudo)random numbers as an essential part of the algorithm. Stochastic -
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 6 Stochastic Process
 Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 6 Stochastic Process Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Definition of stochastic process (random
Department of Electrical Engineering University of Arkansas ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 6 Stochastic Process Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Definition of stochastic process (random
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES. 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) ax 2 + bx + c = 0. x = b ± b 2 4ac 2a. i = 1.
 MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
MTH4101 CALCULUS II REVISION NOTES 1. COMPLEX NUMBERS (Thomas Appendix 7 + lecture notes) 1.1 Introduction Types of numbers (natural, integers, rationals, reals) The need to solve quadratic equations:
Supervised Learning: Non-parametric Estimation
 Supervised Learning: Non-parametric Estimation Edmondo Trentin March 18, 2018 Non-parametric Estimates No assumptions are made on the form of the pdfs 1. There are 3 major instances of non-parametric estimates:
Supervised Learning: Non-parametric Estimation Edmondo Trentin March 18, 2018 Non-parametric Estimates No assumptions are made on the form of the pdfs 1. There are 3 major instances of non-parametric estimates:
6 Second Order Linear Differential Equations
 6 Second Order Linear Differential Equations A differential equation for an unknown function y = f(x) that depends on a variable x is any equation that ties together functions of x with y and its derivatives.
6 Second Order Linear Differential Equations A differential equation for an unknown function y = f(x) that depends on a variable x is any equation that ties together functions of x with y and its derivatives.
Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus (Oxford Physics) Synopsis and Problem Sets; Hilary 2015
 Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus (Oxford Physics) Ramin Golestanian Synopsis and Problem Sets; Hilary 215 The outline of the material, which will be covered in 14 lectures, is as follows: 1. Introduction
Multiple Integrals and Vector Calculus (Oxford Physics) Ramin Golestanian Synopsis and Problem Sets; Hilary 215 The outline of the material, which will be covered in 14 lectures, is as follows: 1. Introduction
P (x). all other X j =x j. If X is a continuous random vector (see p.172), then the marginal distributions of X i are: f(x)dx 1 dx n
 JOINT DENSITIES - RANDOM VECTORS - REVIEW Joint densities describe probability distributions of a random vector X: an n-dimensional vector of random variables, ie, X = (X 1,, X n ), where all X is are
JOINT DENSITIES - RANDOM VECTORS - REVIEW Joint densities describe probability distributions of a random vector X: an n-dimensional vector of random variables, ie, X = (X 1,, X n ), where all X is are
Solution. This is a routine application of the chain rule.
 EXAM 2 SOLUTIONS 1. If z = e r cos θ, r = st, θ = s 2 + t 2, find the partial derivatives dz ds chain rule. Write your answers entirely in terms of s and t. dz and dt using the Solution. This is a routine
EXAM 2 SOLUTIONS 1. If z = e r cos θ, r = st, θ = s 2 + t 2, find the partial derivatives dz ds chain rule. Write your answers entirely in terms of s and t. dz and dt using the Solution. This is a routine
42. Change of Variables: The Jacobian
 . Change of Variables: The Jacobian It is common to change the variable(s) of integration, the main goal being to rewrite a complicated integrand into a simpler equivalent form. However, in doing so, the
. Change of Variables: The Jacobian It is common to change the variable(s) of integration, the main goal being to rewrite a complicated integrand into a simpler equivalent form. However, in doing so, the
