Research Article Integral Transforms of Fourier Cosine and Sine Generalized Convolution Type
|
|
|
- Grace Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 27, Article ID 9725, 11 pages doi:1.1155/27/9725 Research Article Integral Transforms of Fourier Cosine and Sine Generalized Convolution Type Nguyen Xuan Thao, Vu Kim Tuan, and Nguyen Thanh Hong Received 5 April 27; Accepted 27 August 27 Recommended by Piotr Mikusinski Integral transforms of the form f x) gx) 1 d 2 /dx 2 ){ k 1 y)[ f x + y 1 )+ f x y +1 ) f x + y +1) f x y 1 )]dy + k 2 y)[ f x + y)+ f x y )]dy} from L p R + )tol q R + ), 1 p 2, p 1 + q 1 1) are studied. Watson s and Plancherel s theorems are obtained. Copyright 27 Nguyen Xuan Thao et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 1. Introduction Let F c be the Fourier cosine transform [1] Fc f ) 2 x) cos xyfy)dy, 1.1) π and let F s be the Fourier sine transform [1] Fs f ) 2 x) sin xyfy)dy. 1.2) π In 1941, Churchill introduced the convolution of two functions f and g for the Fourier cosine transform f Fc g ) x) 1 f y) [ gx + y)+g x y )] dy, x>, 1.3) 2π and proved the following factorization equality [2]: F c f Fc g ) y) F c f ) y) F c g ) y). 1.4)
2 2 International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Using the factorization property 1.4), one can easily solve the integral equation with the Toeplitz-plus-Hankel kernel f x)+ [ k1 x + y)+k 2 x y )] f y)dy gx) 1.5) in case the Toeplitz kernel k 2 x) and the Hankel kernel k 1 x) arethesame[3, 4]. The general case is still open. The convolution of two functions f and g with the weight function γy) sin y for the Fourier sine transform was introduced by Kakichev in [5] f γ Fs g ) x) 1 2 f u) [ signx+u 1)g x+u 1 ) +signx u+1)g x u +1 ) 2π gx + u +1) signx u 1)g x u 1 )] du, x>, 1.6) where the following factorization property has been established: F s f γ Fs g ) y) sin y F s f ) y) F s g ) y). 1.7) Further properties of this convolution have been studied in [6]. Churchill was also the first author who introduced the generalized convolution for two different integral transforms. Namely, in 1941, he defined the generalized convolution of two functions f and g for the Fourier sine and cosine transforms f 1 g ) x) 1 f u) [ g x u ) gx + u) ] du, 2π x>, 1.8) and proved the following factorization identity [7]: F s f 1 g ) y) F s f ) y) F c g ) y). 1.9) It is easy to see that the integral equation with the Toeplitz-plus-Hankel kernel 1.5) can bewrittenintheform f x)+ 2π f Fc h 1 ) x)+ 2π f 1 h 2 ) x) gx), 1.1) where h 1 1/2)k 1 + k 2 )andh 2 1/2)k 2 k 1 ). So studying generalized convolutions may shed light on how to solve the integral equation with the Toeplitz-plus-Hankel kernel 1.5) in closed form. In 1998, Kakichev and Thao proposed a constructive method for defining a generalized convolution for three arbitrary integral transforms see [8]). For example, for the Fourier cosine and Fourier sine transforms, the following convolution has been introduced in [9]: f 2 g ) x) 1 2π f u) [ signu x)g u x ) + gu + x) ] du, x>. 1.11)
3 For this convolution, the following factorization equality holds [9]: Nguyen Xuan Thao et al. 3 F c f 2 g ) y) F s f ) y) F s g ) y). 1.12) Another generalized convolution with a weight function γy) sin y for the Fourier cosine and sine transforms has been studied in [1] f γ 2 g ) x) 1 2 2π It satisfies the factorization property [1] f u) [ g x + u 1 ) + g x u +1 ) gx + u +1) g x u 1 )] du, x>. 1.13) F c f γ 2 g ) y) sin y F s f ) y) F c g ) y). 1.14) In any convolution of two functions f and g, if we fix one function, say g, asthekernel, and allow the other function f vary in a certain function space, we will get an integral transform f f g. The most famous integral transforms constructed by that way are the Watson transforms that are related to the Mellin convolution and the Mellin transform [11] f x) gx) kxy) f y)dy. 1.15) Recently, a class of integral transforms that is related to the generalized convolution 1.11) has been introduced and investigated in [12]. In this paper, we will consider a class of integral transform which has a connection with the generalized convolution 1.13), namely, the transforms of the form f x) gx) 1 d2 dx 2 k 1 y) [ f x + y 1 ) + f x y +1 ) f x + y +1) f x y 1 )] dy + k 2 y) [ f x + y)+ f x y )] } dy, x>. 1.16) We show that under certain conditions on the kernels k 1 and k 2,transform1.16)admits an inverse of similar form. We find conditions on the kernels k 1 and k 2 when transform 1.16) defines a bounded operator from L p R + )tol q R + )1 p 2, p 1 + q 1 1). Moreover, Watson- and Plancherel-type theorems for transforms 1.16) inl 2 R + )are also obtained. 2. A Watson-type theorem Lemma 2.1. Let f,g L 2 R + ). Then for any x>, the following identity holds: f u) [ g x + u 1 ) + g x u +1 ) g x + u +1 ) g x u 1 )] du 2 2πF c sin y Fs f ) y) F c g ) y) ) x). 2.1)
4 4 International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Proof. Let f 1 be the odd extension of f from R + to R and g 1 the even extension of g from R + to R. ThenletFf 1 is an odd function while Fg 1 is an even function, where F is the Fourier integral transform Ff)x) 1 e ixy f y)dy. 2.2) 2π R On R +,wehaveff 1 if s f and Fg 1 F c g. The Parseval identity for the Fourier integral transform yields f u) [ g x + u 1 ) + g x u +1 ) gx + u +1) g x u 1 )] du f u)g 1 x u +1)du f u)gx + u +1)du f u)gx u 1)du+ f u)g 1 x + u 1)du f 1 u)g 1 x u +1)du f 1 u)g 1 x u 1)du ) ) Ff1 u) Fg1 u)e ix+1)u du ) ) Ff1 u) Fg1 u)e ix 1)u du ) ) ) Ff1 y) Fg1 y) cosx +1)y + i sinx +1)y dy Ff1 ) y) Fg1 ) y) cosx 1)y + i sinx 1)y ) dy. 2.3) On the other hand, note that Ff 1 )y)fg 1 )y)cosx +1)y,Ff 1 )y)fg 1 )y)cosx 1)y are odd functionsin y. Hence, their integrals over R vanish, and therefore, f u) [ g x + u 1 ) + g x u +1 ) gx + u +1) g x u 1 )] du 2i ) ) ) ) Ff1 y) Fg1 y)i sinx +1)ydy Ff1 y) Fg1 y)i sinx 1)ydy Ff1 ) y) Fg1 ) y)sin y cosxy)dy 2 2πF c sin y Fs f ) y) F c g ) y) ) x). 2.4)
5 Nguyen Xuan Thao et al. 5 This completes the proof. We assumed that all the integrals over R are interpreted as Cauchy principal value integrals, if necessary. Theorem 2.2. Let k 1,k 2 L 2 R + ). Then 2sin y ) ) F s k 1 y)+ Fc k 2 y) 1 ), 2.5) 2π 1+y 2 is a necessary and sufficient condition to ensure that the integral transform f g gx): 1 d2 dx 2 k 1 y) [ f x + y 1 ) + f x y +1 ) f x + y +1) f x y 1 )] dy+ is unitary on L 2 R + ) and the inverse transformation has the form f x) 1 d2 dx 2 k 2 y) [ f x+y)+ f x y )] } dy k 1 y) [ g x + y 1 ) + g x y +1 ) gx + y +1) g x y 1 ) ] dy+ 2.6) k 2 y) [ gx+y)+g x y ) ] } dy. 2.7) Proof Necessity. Suppose that k 1 and k 2 satisfy condition 2.5). It is well known that 1 + y 2 )hy) L 2 R), if and only if Fh)x), d/dx)fh)x)andd 2 /dx 2 )Fh)x) L 2 R)[11,Theorem 68, page 92]). Moreover, d 2 dx 2 Fh)x) F y 2 hy) ) x). 2.8) In particular, if h is an even or odd function such that 1 + y 2 )hy) L 2 R + ), then the following equalities hold: ) 1 d2 Fc dx 2 h ) x) F c 1+y 2 ) hy) ) x), ) 1 d2 Fs dx 2 h ) x) F s 1+y 2 ) hy) ) x). 2.9) Using the factorization equalities for convolutions 1.3), 1.6), we have ) gx) 1 d2 ) dx 2 F c 2 2π sin y Fs k 1 y) Fc f ) y)+ 2π ) F c k 2 y) Fc f ) y) ) x) F c 2π 1+y 2 ) 2 sin y F s k 1 ) y)+ Fc k 2 ) y) ) Fc f ) y) ) x). 2.1)
6 6 International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences By virtue of the Parseval equalities for the Fourier cosine and sine transforms f L2R +) F c f L2R +) F s f L2R +) and noting that k 1 and k 2 satisfy condition 2.5), we have g L2R +) 2π 1+y 2) 2sin y ) ) ) F s k 1 y)+ Fc k 2 y) Fc f ) y) L2R +) F c f f 2.11) L2R +) L 2R +). It follows that the transformation 2.6) is unitary. On the other hand, in view of condition 2.5), 2π1 + y 2 )2sin yf s k 1 )y) +F c k 2 )y)) is bounded, hence 2π1 + y 2 )2sin yf s k 1 )y)+f c k 2 )y))f c g)y) L 2 R + ). We have gx) F c 2π 1+y 2 ) 2sin y F s k 1 ) y)+ Fc k 2 ) y) ) Fc f ) y) ) x) F c g ) y) 2π 1+y 2) 2 sin y F s k 1 ) y)+ Fc k 2 ) y) ) Fc f ) y) F c f ) y) 2π 1+y 2) 2 sin y F s k 1 ) y)+ Fc k 2 ) y) ) Fc g ) y). 2.12) Using formula 2.9), we obtain f x) F c 2π 1+y 2 ) 2sin y ) ) F s k 1 y)+ Fc k 2 y)) Fc g ) y) ) x) ) 1 d2 dx 2 F c 2 2π sin yfsk1y) F c g ) y)+ 2π ) F ck2 y) Fc g ) y) ) 1 d2 dx 2 k 1 y) [ g x+y 1 ) +g x y+1 ) gx + y +1) g x y 1 )] dy+ k 2 y) [ gx+y)+g x y )] } dy. 2.13) Therefore, the transformation 2.6) is unitary on L 2 R + ) and the inverse transformation has the form 2.7). Sufficiency. Iftransform2.6) is unitary, then the Parseval identities for the Fourier cosine and sine transforms yield g L2R +) 2π 1+y 2) 2sin y ) ) ) F s k 1 y)+ Fc k 2 y) Fc f ) y) L2R +) F c f f 2.14) L2R +) L 2R +). The middle equality is possible if and only if k 1 and k 2 satisfy condition 2.5). This completes the proof of the theorem. Let h 1,h 2 L 2 R + ) satisfy and let k 1, k 2 be defined by ) ) F s h 1 y) Fs h 2 y) 1 1+y 2 ) 1 + sin 2 ), 2.15) y k 1 x) 1 2 γ ) h1 Fs h 2 x), k2 x) 1 ) h1 h 2 x). 2.16) 2π 2π 2
7 Nguyen Xuan Thao et al. 7 Then k 1,k 2 L 2 R + )andfrom1.7)and1.12), we have 2sin y ) ) F s k 1 y)+ Fc k 2 y) 1 sin 2 y ) ) 1 ) ) F s h 1 y) Fs h 2 y)+ Fs h 1 y) Fs h 2 y) 2π 2π sin 2 y ) ) ) 1 F s h 1 y) Fs h 2 y) ). 2π 2π 1+y ) Thus k 1 and k 2 satisfy condition 2.5). 3. A Plancherel-type theorem In order to examine the Plancherel-type theorem, we will need the following lemma. Lemma 3.1. Let f and g be L 2 R + ) functions, then f y) [ g x + y 1 ) + g x y +1 ) gx + y +1) g x y 1 )] dy gy) [ f x + y + 1) + signx y +1)f x y +1 ) signx y 1) f x y 1 ) signx + y 1) f x + y 1 )] dy, 3.1) f y) [ gx + y)+g x y )] dy gy) [ f x + y)+ f x y )] dy. 3.2) Proof. Again, let f 1 be the odd extension of f from R + to R and g 1 x) g x ) theeven extension of g from R + to R. By the Parseval equality, we have f y) [ g x + y 1 ) + g x y +1 ) gx + y +1) g x y 1 )] dy + f y)g x + y 1 ) dy+ f y)gx + y +1)dy f 1 y)g 1 x y 1)dy+ f 1 y)g 1 x y +1)dy f y)g x y +1 ) dy f y)g x y 1 ) dy f 1 y)g 1 x y +1)dy f 1 y)g 1 x y 1)dy ) ) Ff1 u) Fg1 u)e ix+1)u ) ) du Ff1 u) Fg1 u)e ix 1)u du
8 8 International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences g 1 y) f 1 x y +1)dy g 1 y) f 1 x y 1)dy g 1 y) f 1 x y +1)dy+ g 1 y) f 1 x + y +1)dy g 1 y) f 1 x y 1)dy g 1 y) f 1 x + y 1)dy gy) [ f x + y + 1) + signx y +1)f x y +1 ) signx y 1) f x y 1 ) signx + y 1) f x + y 1 )] dy. Then formula 3.1)holds.Formula3.2) follows easily from formula 1.4) 3.3) f y) [ gx + y)+g x y )] dy 2πF c [ Fc f ) y) F c g ) y) ] x) Thelemmahasbeenproved. 2πF c [ Fc g ) y) F c f ) y) ] x) gy) [ f x + y)+ f x y )] dy. 3.4) Theorem 3.2. Let k 1, k 2 be functions satisfying condition 2.5) and suppose that K 1 x) 1 d 2 /dx 2 )k 1 x) and K 2 x) 1 d 2 /dx 2 )k 2 x) are locally bounded. Let f L 2 R + ) and for each positive integer N,put g N x) K 1 y) [ f N x + y 1 ) + f N x y +1 ) f N x + y +1) f N x y 1 )] dy+ K 2 y) [ f N x + y)+ f N x y )] dy, 3.5) where f N f.χ,n), the restriction of f over,n). Then 1) g N L 2 R + ) and as N, g N converges in L 2 R + ) norm to a function g L 2 R + ) with g L2R +) f L2R +); 2) put g N g.χ,n), then f N x) K 1 y) [ g N x + y 1 ) + g N x y +1 ) g N x + y +1) g N x y 1 ) ]dy+ K 2 y)[g N x + y)+g N x y )] dy 3.6) belongs to L 2 R + ) and converges in L 2 R + ) norm to f as N.
9 Nguyen Xuan Thao et al. 9 Remark 3.3. Because of the definitions of f N and g N, these integrals are over finite intervals and therefore converge. Proof. Applying the identities 3.1)and3.2)inLemma 3.1,wehave g n x) K 1 y) [ f N x+y 1 ) + f N x y+1 ) f N x+y+1) f N x y 1 )] dy + K 2 y) [ f N x + y)+ f N x y )] dy f N y) [ K 1 x + y + 1) + signx y +1)K 1 x y +1 ) ] signx y 1)K 1 x y 1 ) signx+y 1)K1 x+y 1 ) dy + f N y) [ )] k 1 x + y)+k 1 x y dy 1 d2 dx 2 f N u) [ ) k 1 x + u + 1) + signx u +1)k 1 x u +1 ) signx u 1)k 1 x u 1 )] signx + u 1)k 1 x + u 1 du + f N y) [ )] k 1 x + y)+k 1 x y dy }. 3.7) It is legitimate to interchange the order of integration and differentiation since the integrals are actually over finite intervals. By applying Lemma 3.1 one more time, we obtain g N x) 1 d2 dx 2 k 1 y) [ f N x + y 1 ) + f N x y +1 ) f N x + y +1) f N x y 1 )] dy + k 2 y) [ f N x + y)+ f N x y )] } dy. 3.8) From this and in view of Theorem 2.2,weconcludethatg N L 2 R + ). Let g be the transform of f under the transformation 2.6). Then Theorem 2.2 guarantees that g L 2 R + ), g L2R +) f L2R +), and the reciprocal formula 2.7)holds.Forg g N,wehave g g N )x) 1 d2 dx 2 k 1 y) [ f f N ) x + y 1 ) + f f N) x y +1 ) f f N ) x + y +1) f f N ) x y 1 )] dy + k 2 y) [ f f N ) x + y)+ f f N ) x y )] } dy. 3.9)
10 1 International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Again by Theorem 2.2,g g N )x) L 2 R + )and g g N L2R +) f f N L2R +). 3.1) And since f f N L2R +) asn then g N converses in L 2 R + )normtog L 2 R + ). Similarly, one can obtain the second part of the theorem. Theorem 3.4. Let k 1 and k 2 be functions satisfying condition 2.5) and suppose that K 1 x) and K 2 x) defined as in the previous theorem are bounded on R +.Let1 p 2 and q be its conjugate exponent 1/p+1/q 1. Then the transformation f g,whereg is defined by { gx) lim N K 1 y) [ f N x + y 1 ) + f N x y +1 ) f N x + y +1) f N x y 1 )] dy+ K 2 y) [ f N x+y)+ f N x y )] } dy, 3.11) is a bounded operator from L p R + ) into L q R + ). Here the limit is understood in L q R + ) norm. Proof. From the boundedness of K 1 and K 2, it is clear that transformation 3.11) isa bounded operator from L 1 R + )intol R + ). On the other hand, Theorem 3.2 shows that transformation 3.11) defines a bounded operator from L 2 R + )intol 2 R + ). Hence, Riesz s interpolation theorem implies that 3.11)isaboundedoperatorfromL p R + ), 1 p 2, into L q R + ), where q is the conjugate exponent of p. References [1] S. Bochner and K. Chandrasekharan, Fourier Transforms, Annals of Mathematics Studies, no. 19, Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ, USA, [2] I. N. Sneddon, The Use of Integral Transforms, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, USA, [3] H. H. Kagiwada and R.Kalaba, Integral Equations via Imbedding Methods, Applied Mathematics and Computation, no. 6, Addison-Wesley, Reading, Mass, USA, [4] M.G.Kreĭn, On a new method of solution of linear integral equations of first and second kinds, Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, vol. 1, pp , 1955 Russian). [5] V. A. Kakichev, On the convolution for integral transforms, Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii. Matematika, no. 2, pp , 1967 Russian). [6] N. X. Thao and N. T. Hai, Convolutions for integral transforms and their application, Computer Centre of the Russian Academy, Moscow, 44 pages, [7] F. Al-Musallam and V. K. Tuan, A class of convolution transformations, Fractional Calculus & Applied Analysis, vol. 3, no. 3, pp , 2. [8] V. A. Kakichev and N. X. Thao, On the design method for the generalized integral convolutions, Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii. Matematika, no. 1, pp. 31 4, 1998 Russian). [9] V. A. Kakichev, N. X. Thao, and V. K. Tuan, On the generalized convolutions for Fourier cosine and sine transforms, East-West Journal of Mathematics, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 85 9, [1] N. X. Thao, V. K. Tuan, and N. M. Khoa, A generalized convolution with a weight function for the Fourier cosine and sine transforms, Fractional Calculus & Applied Analysis, vol. 7, no. 3, pp , 24.
11 Nguyen Xuan Thao et al. 11 [11] H. M. Titchmarsh, Introduction to the Theory of Fourier Integrals, Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 2nd edition, [12] F. Al-Musallam and V. K. Tuan, Integral transforms related to a generalized convolution, Results in Mathematics, vol. 38, no. 3-4, pp , 2. Nguyen Xuan Thao: Hanoi Water Resources University, 175 Tay Son, Dong Da, Hanoi, Vietnam address: thaonxbmai@yahoo.com Vu Kim Tuan: Department of Mathematics, University of West Georgia, Carrollton, GA3118, USA address: vu@westga.edu Nguyen Thanh Hong: Haiphong University, 171 Phan Dang Luu, Kien An, Haiphong, Vietnam address: hongdhsp1@yahoo.com
Research Article On the Polyconvolution with the Weight Function for the Fourier Cosine, Fourier Sine, and the Kontorovich-Lebedev Integral Transforms
 Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume, Article ID 7967, 6 pages doi:.55//7967 Research Article On the Polyconvolution with the Weight Function for the Fourier Cosine, Fourier Sine, and the Kontorovich-Lebedev
Mathematical Problems in Engineering Volume, Article ID 7967, 6 pages doi:.55//7967 Research Article On the Polyconvolution with the Weight Function for the Fourier Cosine, Fourier Sine, and the Kontorovich-Lebedev
86 On the generalized convolutions for Fourier cosine and sine transforms the convolution has the form [8] (f g)(x) = p 1 f(y)[g(j x ; y j)+g(x + y)]d
![86 On the generalized convolutions for Fourier cosine and sine transforms the convolution has the form [8] (f g)(x) = p 1 f(y)[g(j x ; y j)+g(x + y)]d 86 On the generalized convolutions for Fourier cosine and sine transforms the convolution has the form [8] (f g)(x) = p 1 f(y)[g(j x ; y j)+g(x + y)]d](/thumbs/85/92110822.jpg) East-West Journal of Mathematics: Vol. 1, No 1 (1998) pp. 85-9 ON THE GENERALIZED CONVOLUTIONS FOR FOURIER COSINE AND SINE TRANSFORMS Nguyen Xuan Thao, V.A. Kakichev Novgorod University, St. Petersburg
East-West Journal of Mathematics: Vol. 1, No 1 (1998) pp. 85-9 ON THE GENERALIZED CONVOLUTIONS FOR FOURIER COSINE AND SINE TRANSFORMS Nguyen Xuan Thao, V.A. Kakichev Novgorod University, St. Petersburg
Math 121A: Homework 6 solutions
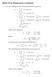 Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Math A: Homework 6 solutions. (a) The coefficients of the Fourier sine series are given by b n = π f (x) sin nx dx = x(π x) sin nx dx π = (π x) cos nx dx nπ nπ [x(π x) cos nx]π = n ( )(sin nx) dx + π n
Research Article Some Estimates of Certain Subnormal and Hyponormal Derivations
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2008, Article ID 362409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2008/362409 Research Article Some Estimates of Certain
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2008, Article ID 362409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2008/362409 Research Article Some Estimates of Certain
Examples of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 10.3). The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case.
 s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
s of the Fourier Theorem (Sect. 1.3. The Fourier Theorem: Continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem: Piecewise continuous case. : Using the Fourier Theorem. The Fourier Theorem:
On the least values of L p -norms for the Kontorovich Lebedev transform and its convolution
 Journal of Approimation Theory 131 4 31 4 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat On the least values of L p -norms for the Kontorovich Lebedev transform and its convolution Semyon B. Yakubovich Department of Pure
Journal of Approimation Theory 131 4 31 4 www.elsevier.com/locate/jat On the least values of L p -norms for the Kontorovich Lebedev transform and its convolution Semyon B. Yakubovich Department of Pure
Research Article Dunkl Translation and Uncentered Maximal Operator on the Real Line
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2007, Article ID 87808, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2007/87808 esearch Article Dunkl Translation and Uncentered
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2007, Article ID 87808, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2007/87808 esearch Article Dunkl Translation and Uncentered
Research Article On the Stability of Cubic Mappings and Quadratic Mappings in Random Normed Spaces
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2008, Article ID 902187, 11 pages doi:101155/2008/902187 Research Article On the Stability of Cubic Mappings and Quadratic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2008, Article ID 902187, 11 pages doi:101155/2008/902187 Research Article On the Stability of Cubic Mappings and Quadratic
7: FOURIER SERIES STEVEN HEILMAN
 7: FOURIER SERIES STEVE HEILMA Contents 1. Review 1 2. Introduction 1 3. Periodic Functions 2 4. Inner Products on Periodic Functions 3 5. Trigonometric Polynomials 5 6. Periodic Convolutions 7 7. Fourier
7: FOURIER SERIES STEVE HEILMA Contents 1. Review 1 2. Introduction 1 3. Periodic Functions 2 4. Inner Products on Periodic Functions 3 5. Trigonometric Polynomials 5 6. Periodic Convolutions 7 7. Fourier
Research Article On Diffraction Fresnel Transforms for Boehmians
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 20, Article ID 72746, pages doi:0.55/20/72746 esearch Article On Diffraction Fresnel Transforms for Boehmians S. K. Q. Al-Omari and A. Kılıçman 2 Department of Applied
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 20, Article ID 72746, pages doi:0.55/20/72746 esearch Article On Diffraction Fresnel Transforms for Boehmians S. K. Q. Al-Omari and A. Kılıçman 2 Department of Applied
Jim Lambers ENERGY 281 Spring Quarter Lecture 3 Notes
 Jim Lambers ENERGY 8 Spring Quarter 7-8 Lecture 3 Notes These notes are based on Rosalind Archer s PE8 lecture notes, with some revisions by Jim Lambers. Introduction The Fourier transform is an integral
Jim Lambers ENERGY 8 Spring Quarter 7-8 Lecture 3 Notes These notes are based on Rosalind Archer s PE8 lecture notes, with some revisions by Jim Lambers. Introduction The Fourier transform is an integral
On the Solution of the n-dimensional k B Operator
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 015, no. 10, 469-479 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hiari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.015.410815 On the Solution of the n-dimensional B Operator Sudprathai Bupasiri Faculty
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 9, 015, no. 10, 469-479 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hiari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.015.410815 On the Solution of the n-dimensional B Operator Sudprathai Bupasiri Faculty
Problem set 5, Real Analysis I, Spring, otherwise. (a) Verify that f is integrable. Solution: Compute since f is even, 1 x (log 1/ x ) 2 dx 1
 Problem set 5, Real Analysis I, Spring, 25. (5) Consider the function on R defined by f(x) { x (log / x ) 2 if x /2, otherwise. (a) Verify that f is integrable. Solution: Compute since f is even, R f /2
Problem set 5, Real Analysis I, Spring, 25. (5) Consider the function on R defined by f(x) { x (log / x ) 2 if x /2, otherwise. (a) Verify that f is integrable. Solution: Compute since f is even, R f /2
Research Article Commutator Length of Finitely Generated Linear Groups
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 008, Article ID 81734, 5 pages doi:10.1155/008/81734 Research Article Commutator Length of Finitely
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 008, Article ID 81734, 5 pages doi:10.1155/008/81734 Research Article Commutator Length of Finitely
Research Article A Note on Kantorovich Inequality for Hermite Matrices
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 0, Article ID 5767, 6 pages doi:0.55/0/5767 Research Article A Note on Kantorovich Inequality for Hermite Matrices Zhibing
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 0, Article ID 5767, 6 pages doi:0.55/0/5767 Research Article A Note on Kantorovich Inequality for Hermite Matrices Zhibing
Research Article Operator Representation of Fermi-Dirac and Bose-Einstein Integral Functions with Applications
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2007, Article ID 80515, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2007/80515 Research Article Operator Representation of Fermi-Dirac
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2007, Article ID 80515, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2007/80515 Research Article Operator Representation of Fermi-Dirac
Research Article Asymptotic Behavior of the Solutions of System of Difference Equations of Exponential Form
 Difference Equations Article ID 936302 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/936302 Research Article Asymptotic Behavior of the Solutions of System of Difference Equations of Exponential Form Vu Van Khuong
Difference Equations Article ID 936302 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/936302 Research Article Asymptotic Behavior of the Solutions of System of Difference Equations of Exponential Form Vu Van Khuong
ON THE KONTOROVICH- LEBEDEV TRANSFORMATION
 JOURNAL OF INTEGRAL EQUATIONS AND APPLICATIONS Volume 5, Number, Spring 3 ON THE KONTOROVICH- LEBEDEV TRANSFORMATION SEMYON B. YAKUBOVICH ABSTRACT. Further developments of the results on the Kontorovich-Lebedev
JOURNAL OF INTEGRAL EQUATIONS AND APPLICATIONS Volume 5, Number, Spring 3 ON THE KONTOROVICH- LEBEDEV TRANSFORMATION SEMYON B. YAKUBOVICH ABSTRACT. Further developments of the results on the Kontorovich-Lebedev
Research Article A Fixed Point Approach to the Stability of Quadratic Functional Equation with Involution
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Fixed Point Theory and Applications Volume 008, Article ID 73086, 11 pages doi:10.1155/008/73086 Research Article A Fixed Point Approach to the Stability of Quadratic Functional
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Fixed Point Theory and Applications Volume 008, Article ID 73086, 11 pages doi:10.1155/008/73086 Research Article A Fixed Point Approach to the Stability of Quadratic Functional
A NEW COMPOSITE IMPLICIT ITERATIVE PROCESS FOR A FINITE FAMILY OF NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS IN BANACH SPACES
 A NEW COMPOSITE IMPLICIT ITERATIVE PROCESS FOR A FINITE FAMILY OF NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS IN BANACH SPACES FENG GU AND JING LU Received 18 January 2006; Revised 22 August 2006; Accepted 23 August 2006 The
A NEW COMPOSITE IMPLICIT ITERATIVE PROCESS FOR A FINITE FAMILY OF NONEXPANSIVE MAPPINGS IN BANACH SPACES FENG GU AND JING LU Received 18 January 2006; Revised 22 August 2006; Accepted 23 August 2006 The
Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2: Differentiation Winter 2016 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 75 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Chapter 2: Differentiation Winter 2016 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 75 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Integral representations for the Dirichlet L-functions and their expansions in Meixner-Pollaczek polynomials and rising factorials
 Integral representations for the Dirichlet L-functions and their expansions in Meixner-Pollaczek polynomials and rising factorials A. Kuznetsov Dept. of Mathematical Sciences University of New Brunswick
Integral representations for the Dirichlet L-functions and their expansions in Meixner-Pollaczek polynomials and rising factorials A. Kuznetsov Dept. of Mathematical Sciences University of New Brunswick
be the set of complex valued 2π-periodic functions f on R such that
 . Fourier series. Definition.. Given a real number P, we say a complex valued function f on R is P -periodic if f(x + P ) f(x) for all x R. We let be the set of complex valued -periodic functions f on
. Fourier series. Definition.. Given a real number P, we say a complex valued function f on R is P -periodic if f(x + P ) f(x) for all x R. We let be the set of complex valued -periodic functions f on
Research Article The Weighted Fermat Triangle Problem
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2008, Article ID 283846, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2008/283846 Research Article The Weighted Fermat Triangle
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2008, Article ID 283846, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2008/283846 Research Article The Weighted Fermat Triangle
A New Approach for Solving Dual Fuzzy Nonlinear Equations Using Broyden's and Newton's Methods
 From the SelectedWorks of Dr. Mohamed Waziri Yusuf August 24, 22 A New Approach for Solving Dual Fuzzy Nonlinear Equations Using Broyden's and Newton's Methods Mohammed Waziri Yusuf, Dr. Available at:
From the SelectedWorks of Dr. Mohamed Waziri Yusuf August 24, 22 A New Approach for Solving Dual Fuzzy Nonlinear Equations Using Broyden's and Newton's Methods Mohammed Waziri Yusuf, Dr. Available at:
Chapter 2: Differentiation
 Chapter 2: Differentiation Spring 2018 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 82 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Chapter 2: Differentiation Spring 2018 Department of Mathematics Hong Kong Baptist University 1 / 82 2.1 Tangent Lines and Their Slopes This section deals with the problem of finding a straight line L
Research Article Common Fixed Points of Weakly Contractive and Strongly Expansive Mappings in Topological Spaces
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2010, Article ID 746045, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2010/746045 Research Article Common Fixed Points of Weakly Contractive and Strongly
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2010, Article ID 746045, 15 pages doi:10.1155/2010/746045 Research Article Common Fixed Points of Weakly Contractive and Strongly
MATH34032 Mid-term Test 10.00am 10.50am, 26th March 2010 Answer all six question [20% of the total mark for this course]
![MATH34032 Mid-term Test 10.00am 10.50am, 26th March 2010 Answer all six question [20% of the total mark for this course] MATH34032 Mid-term Test 10.00am 10.50am, 26th March 2010 Answer all six question [20% of the total mark for this course]](/thumbs/78/76857283.jpg) MATH3432: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1 MATH3432 Mid-term Test 1.am 1.5am, 26th March 21 Answer all six question [2% of the total mark for this course] Qu.1 (a)
MATH3432: Green s Functions, Integral Equations and the Calculus of Variations 1 MATH3432 Mid-term Test 1.am 1.5am, 26th March 21 Answer all six question [2% of the total mark for this course] Qu.1 (a)
Distribution Solutions of Some PDEs Related to the Wave Equation and the Diamond Operator
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 111, 5515-554 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.3844 Distribution Solutions of Some PDEs Related to the Wave Equation and the
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 111, 5515-554 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.3844 Distribution Solutions of Some PDEs Related to the Wave Equation and the
Lecture 16: Bessel s Inequality, Parseval s Theorem, Energy convergence
 Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. ot to be copied, used, or revised without explicit written permission from the copyright owner. ecture 6: Bessel s Inequality,
Introductory lecture notes on Partial Differential Equations - c Anthony Peirce. ot to be copied, used, or revised without explicit written permission from the copyright owner. ecture 6: Bessel s Inequality,
An Approximate Solution for Volterra Integral Equations of the Second Kind in Space with Weight Function
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11 17 no. 18 849-861 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ijma.17.771 An Approximate Solution for Volterra Integral Equations of the Second
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 11 17 no. 18 849-861 HIKARI Ltd www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.1988/ijma.17.771 An Approximate Solution for Volterra Integral Equations of the Second
Infinite-dimensional Vector Spaces and Sequences
 2 Infinite-dimensional Vector Spaces and Sequences After the introduction to frames in finite-dimensional vector spaces in Chapter 1, the rest of the book will deal with expansions in infinitedimensional
2 Infinite-dimensional Vector Spaces and Sequences After the introduction to frames in finite-dimensional vector spaces in Chapter 1, the rest of the book will deal with expansions in infinitedimensional
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 18 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 18 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 18 Nov 2016](/thumbs/88/117887558.jpg) BEURLING S THEOREM FOR THE CLIFFORD-FOURIER TRANSFORM arxiv:1611.06017v1 [math.ca] 18 Nov 016 RIM JDAY AND JAMEL EL KAMEL Abstract. We give a generalization of Beurling s theorem for the Clifford-Fourier
BEURLING S THEOREM FOR THE CLIFFORD-FOURIER TRANSFORM arxiv:1611.06017v1 [math.ca] 18 Nov 016 RIM JDAY AND JAMEL EL KAMEL Abstract. We give a generalization of Beurling s theorem for the Clifford-Fourier
The Dirac δ-function
 The Dirac δ-function Elias Kiritsis Contents 1 Definition 2 2 δ as a limit of functions 3 3 Relation to plane waves 5 4 Fourier integrals 8 5 Fourier series on the half-line 9 6 Gaussian integrals 11 Bibliography
The Dirac δ-function Elias Kiritsis Contents 1 Definition 2 2 δ as a limit of functions 3 3 Relation to plane waves 5 4 Fourier integrals 8 5 Fourier series on the half-line 9 6 Gaussian integrals 11 Bibliography
DIFFERENTIAL CRITERIA FOR POSITIVE DEFINITENESS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume, Number, Pages S -9939(XX)- DIFFERENTIAL CRITERIA FOR POSITIVE DEFINITENESS J. A. PALMER Abstract. We show how the Mellin transform can be used to
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume, Number, Pages S -9939(XX)- DIFFERENTIAL CRITERIA FOR POSITIVE DEFINITENESS J. A. PALMER Abstract. We show how the Mellin transform can be used to
λ n = L φ n = π L eınπx/l, for n Z
 Chapter 32 The Fourier Transform 32. Derivation from a Fourier Series Consider the eigenvalue problem y + λy =, y( L = y(l, y ( L = y (L. The eigenvalues and eigenfunctions are ( nπ λ n = L 2 for n Z +
Chapter 32 The Fourier Transform 32. Derivation from a Fourier Series Consider the eigenvalue problem y + λy =, y( L = y(l, y ( L = y (L. The eigenvalues and eigenfunctions are ( nπ λ n = L 2 for n Z +
1 Fourier Transformation.
 Fourier Transformation. Before stating the inversion theorem for the Fourier transformation on L 2 (R ) recall that this is the space of Lebesgue measurable functions whose absolute value is square integrable.
Fourier Transformation. Before stating the inversion theorem for the Fourier transformation on L 2 (R ) recall that this is the space of Lebesgue measurable functions whose absolute value is square integrable.
The local fractional Hilbert transform in fractal space
 The local fractional ilbert transform in fractal space Guang-Sheng Chen Department of Computer Engineering, Guangxi Modern Vocational Technology College, echi,guangxi, 547000, P.. China E-mail address:
The local fractional ilbert transform in fractal space Guang-Sheng Chen Department of Computer Engineering, Guangxi Modern Vocational Technology College, echi,guangxi, 547000, P.. China E-mail address:
Research Article Integral Means Inequalities for Fractional Derivatives of a Unified Subclass of Prestarlike Functions with Negative Coefficients
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 27, Article ID 97135, 9 pages doi:1.1155/27/97135 Research Article Integral Means Inequalities for Fractional Derivatives
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 27, Article ID 97135, 9 pages doi:1.1155/27/97135 Research Article Integral Means Inequalities for Fractional Derivatives
2.2 The derivative as a Function
 2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
2.2 The derivative as a Function Recall: The derivative of a function f at a fixed number a: f a f a+h f(a) = lim h 0 h Definition (Derivative of f) For any number x, the derivative of f is f x f x+h f(x)
2014 IJIRT Volume 1 Issue 6 ISSN : CONVOLUTION AND APPLICATIONS OF CONVOLUTION
 CONVOLUTION AND APPLICATIONS OF CONVOLUTION Akshay Behl, Akash Bhatia, Avril Puri Dronacharya College Of Engineering, GGN Abstract-We introduce an integral transform related to a Fourier sine-fourier -
CONVOLUTION AND APPLICATIONS OF CONVOLUTION Akshay Behl, Akash Bhatia, Avril Puri Dronacharya College Of Engineering, GGN Abstract-We introduce an integral transform related to a Fourier sine-fourier -
Research Article The Stability of a Quadratic Functional Equation with the Fixed Point Alternative
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2009, Article ID 907167, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2009/907167 Research Article The Stability of a Quadratic Functional Equation with the
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2009, Article ID 907167, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2009/907167 Research Article The Stability of a Quadratic Functional Equation with the
Research Article Subnormal Solutions of Second-Order Nonhomogeneous Linear Differential Equations with Periodic Coefficients
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2009, Article ID 416273, 12 pages doi:10.1155/2009/416273 Research Article Subnormal Solutions of Second-Order Nonhomogeneous
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2009, Article ID 416273, 12 pages doi:10.1155/2009/416273 Research Article Subnormal Solutions of Second-Order Nonhomogeneous
Research Article The Solution by Iteration of a Composed K-Positive Definite Operator Equation in a Banach Space
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2010, Article ID 376852, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2010/376852 Research Article The Solution by Iteration
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2010, Article ID 376852, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2010/376852 Research Article The Solution by Iteration
Research Article Brézis-Wainger Inequality on Riemannian Manifolds
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2008, Article ID 7596, 6 pages doi:0.55/2008/7596 Research Article Brézis-Wainger Inequality on Riemannian anifolds Przemysław
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 2008, Article ID 7596, 6 pages doi:0.55/2008/7596 Research Article Brézis-Wainger Inequality on Riemannian anifolds Przemysław
Research Article A Finite-Interval Uniqueness Theorem for Bilateral Laplace Transforms
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2007, Article ID 60916, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2007/60916 Research Article A Finite-Interval Uniqueness Theorem for Bilateral Laplace Transforms
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2007, Article ID 60916, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2007/60916 Research Article A Finite-Interval Uniqueness Theorem for Bilateral Laplace Transforms
2. Complex Analytic Functions
 2. Complex Analytic Functions John Douglas Moore July 6, 2011 Recall that if A and B are sets, a function f : A B is a rule which assigns to each element a A a unique element f(a) B. In this course, we
2. Complex Analytic Functions John Douglas Moore July 6, 2011 Recall that if A and B are sets, a function f : A B is a rule which assigns to each element a A a unique element f(a) B. In this course, we
MATH 124B: HOMEWORK 2
 MATH 24B: HOMEWORK 2 Suggested due date: August 5th, 26 () Consider the geometric series ( ) n x 2n. (a) Does it converge pointwise in the interval < x
MATH 24B: HOMEWORK 2 Suggested due date: August 5th, 26 () Consider the geometric series ( ) n x 2n. (a) Does it converge pointwise in the interval < x
Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. quadratic formula. absolute value. properties of absolute values
 Copyright & License Formula Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. quadratic formula absolute value properties of absolute values equation of a line in various forms equation of a circle
Copyright & License Formula Copyright c 2007 Jason Underdown Some rights reserved. quadratic formula absolute value properties of absolute values equation of a line in various forms equation of a circle
`an cos nπx. n 1. L `b
 4 Fourier Series A periodic function on a range p,q may be decomposed into a sum of sinusoidal (sine or cosine) functions. This can be written as follows gpxq 1 2 a ` ř8 `b (4.1) The aim of this chapter
4 Fourier Series A periodic function on a range p,q may be decomposed into a sum of sinusoidal (sine or cosine) functions. This can be written as follows gpxq 1 2 a ` ř8 `b (4.1) The aim of this chapter
Solutions to Chapter 17 exercises
 Solutions to Chapter 17 exercises 17.1 Let (x n ) be a Cauchy sequence in a discrete metric space (X, d). There exists N N such that d(x m,x n ) < 1 whenever m>n N,soinfactd(x m,x n ) = whenever m>n N,since
Solutions to Chapter 17 exercises 17.1 Let (x n ) be a Cauchy sequence in a discrete metric space (X, d). There exists N N such that d(x m,x n ) < 1 whenever m>n N,soinfactd(x m,x n ) = whenever m>n N,since
Research Article k-kernel Symmetric Matrices
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2009, Article ID 926217, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2009/926217 Research Article k-kernel Symmetric Matrices
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2009, Article ID 926217, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2009/926217 Research Article k-kernel Symmetric Matrices
Topics. Example. Modulation. [ ] = G(k x. ] = 1 2 G ( k % k x 0) G ( k + k x 0) ] = 1 2 j G ( k x
![Topics. Example. Modulation. [ ] = G(k x. ] = 1 2 G ( k % k x 0) G ( k + k x 0) ] = 1 2 j G ( k x Topics. Example. Modulation. [ ] = G(k x. ] = 1 2 G ( k % k x 0) G ( k + k x 0) ] = 1 2 j G ( k x](/thumbs/95/123667623.jpg) Topics Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2008 CT/Fourier Lecture 3 Modulation Modulation Transfer Function Convolution/Multiplication Revisit Projection-Slice Theorem Filtered
Topics Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2008 CT/Fourier Lecture 3 Modulation Modulation Transfer Function Convolution/Multiplication Revisit Projection-Slice Theorem Filtered
Research Article Weighted Inequalities for Potential Operators with Lipschitz and BMO Norms
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Difference quations Volume 0, Article ID 659597, pages doi:0.55/0/659597 Research Article Weighted Inequalities for Potential Operators with Lipschitz and MO
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Difference quations Volume 0, Article ID 659597, pages doi:0.55/0/659597 Research Article Weighted Inequalities for Potential Operators with Lipschitz and MO
Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-12) Solution 1 From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have.
 For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
For 2 weeks course only Mathematical Methods and its Applications (Solution of assignment-2 Solution From the definition of Fourier transforms, we have F e at2 e at2 e it dt e at2 +(it/a dt ( setting (
Research Article Taylor s Expansion Revisited: A General Formula for the Remainder
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 645736, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/645736 Research Article Taylor s Expansion Revisited: A General Formula for the Remainder José
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 2012, Article ID 645736, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/645736 Research Article Taylor s Expansion Revisited: A General Formula for the Remainder José
Methods of Mathematical Physics X1 Homework 3 Solutions
 Methods of Mathematical Physics - 556 X Homework 3 Solutions. (Problem 2.. from Keener.) Verify that l 2 is an inner product space. Specifically, show that if x, y l 2, then x, y x k y k is defined and
Methods of Mathematical Physics - 556 X Homework 3 Solutions. (Problem 2.. from Keener.) Verify that l 2 is an inner product space. Specifically, show that if x, y l 2, then x, y x k y k is defined and
Research Article On Jordan Type Inequalities for Hyperbolic Functions
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 010, Article ID 6548, 14 pages doi:10.1155/010/6548 Research Article On Jordan Type Inequalities for Hyperbolic Functions
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 010, Article ID 6548, 14 pages doi:10.1155/010/6548 Research Article On Jordan Type Inequalities for Hyperbolic Functions
ON GENERALIZATIONS OF BOEHMIAN SPACE AND HARTLEY TRANSFORM. C. Ganesan and R. Roopkumar. 1. Introduction
 MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69, 2 (2017, 133 143 June 2017 originalni nauqni rad research paper ON GENERALIZATIONS OF BOEHMIAN SPACE AND HARTLEY TRANSFORM C. Ganesan and R. Roopkumar Abstract.
MATEMATIČKI VESNIK MATEMATIQKI VESNIK 69, 2 (2017, 133 143 June 2017 originalni nauqni rad research paper ON GENERALIZATIONS OF BOEHMIAN SPACE AND HARTLEY TRANSFORM C. Ganesan and R. Roopkumar Abstract.
Research Article Uniqueness Theorems on Difference Monomials of Entire Functions
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 202, Article ID 40735, 8 pages doi:0.55/202/40735 Research Article Uniqueness Theorems on Difference Monomials of Entire Functions Gang Wang, Deng-li Han, 2 and Zhi-Tao
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 202, Article ID 40735, 8 pages doi:0.55/202/40735 Research Article Uniqueness Theorems on Difference Monomials of Entire Functions Gang Wang, Deng-li Han, 2 and Zhi-Tao
An Application of Fibonacci Sequence on Continued Fractions
 International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 0, 205, no. 2, 69-74 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/imf.205.42207 An Application of Fibonacci Sequence on Continued Fractions Ali H. Hakami
International Mathematical Forum, Vol. 0, 205, no. 2, 69-74 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/imf.205.42207 An Application of Fibonacci Sequence on Continued Fractions Ali H. Hakami
CONVOLUTION THEOREMS FOR FRACTIONAL FOURIER COSINE AND SINE TRANSFORMS AND THEIR EXTENSIONS TO BOEHMIANS
 Commun. Korean Math. Soc. 31 (16), No. 4, pp. 791 89 http://d.doi.org/1.4134/ckms.c1544 pissn: 15-1763 / eissn: 34-34 CONVOLUTION THEOREMS FOR FRACTIONAL FOURIER COSINE AND SINE TRANSFORMS AND THEIR EXTENSIONS
Commun. Korean Math. Soc. 31 (16), No. 4, pp. 791 89 http://d.doi.org/1.4134/ckms.c1544 pissn: 15-1763 / eissn: 34-34 CONVOLUTION THEOREMS FOR FRACTIONAL FOURIER COSINE AND SINE TRANSFORMS AND THEIR EXTENSIONS
Research Article On Decomposable Measures Induced by Metrics
 Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 701206, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/701206 Research Article On Decomposable Measures Induced by Metrics Dong Qiu 1 and Weiquan Zhang 2 1 College of Mathematics
Applied Mathematics Volume 2012, Article ID 701206, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/701206 Research Article On Decomposable Measures Induced by Metrics Dong Qiu 1 and Weiquan Zhang 2 1 College of Mathematics
17 The functional equation
 18.785 Number theory I Fall 16 Lecture #17 11/8/16 17 The functional equation In the previous lecture we proved that the iemann zeta function ζ(s) has an Euler product and an analytic continuation to the
18.785 Number theory I Fall 16 Lecture #17 11/8/16 17 The functional equation In the previous lecture we proved that the iemann zeta function ζ(s) has an Euler product and an analytic continuation to the
Topics. Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging. Fall Quarter 2006 CT/Fourier Lecture 2
 Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2006 CT/Fourier Lecture 2 Topics Modulation Modulation Transfer Function Convolution/Multiplication Revisit Projection-Slice Theorem Filtered
Bioengineering 280A Principles of Biomedical Imaging Fall Quarter 2006 CT/Fourier Lecture 2 Topics Modulation Modulation Transfer Function Convolution/Multiplication Revisit Projection-Slice Theorem Filtered
Calculus Summer Math Practice. 1. Find inverse functions Describe in words how you use algebra to determine the inverse function.
 1 Calculus 2017-2018: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Calculus Summer Math Practice Please see the math department document for instructions on setting
1 Calculus 2017-2018: Summer Study Guide Mr. Kevin Braun (kbraun@bdcs.org) Bishop Dunne Catholic School Calculus Summer Math Practice Please see the math department document for instructions on setting
Physics 250 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations
 Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Physics 25 Green s functions for ordinary differential equations Peter Young November 25, 27 Homogeneous Equations We have already discussed second order linear homogeneous differential equations, which
Pólya-Szegö s Principle for Nonlocal Functionals
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 12, 218, no. 5, 245-25 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.12988/ijma.218.8327 Pólya-Szegö s Principle for Nonlocal Functionals Tiziano Granucci
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 12, 218, no. 5, 245-25 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com https://doi.org/1.12988/ijma.218.8327 Pólya-Szegö s Principle for Nonlocal Functionals Tiziano Granucci
Research Article On a Class of Integrals Involving a Bessel Function Times Gegenbauer Polynomials
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 27, Article ID 7375, 5 pages doi:1.1155/27/7375 Research Article On a Class of Integrals Involving a
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 27, Article ID 7375, 5 pages doi:1.1155/27/7375 Research Article On a Class of Integrals Involving a
Chain Rule. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Spring Department of Mathematics
 3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
3.33pt Chain Rule MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2019 Single Variable Chain Rule Suppose y = g(x) and z = f (y) then dz dx = d (f (g(x))) dx = f (g(x))g (x)
ON THE BEHAVIOR OF THE SOLUTION OF THE WAVE EQUATION. 1. Introduction. = u. x 2 j
 ON THE BEHAVIO OF THE SOLUTION OF THE WAVE EQUATION HENDA GUNAWAN AND WONO SETYA BUDHI Abstract. We shall here study some properties of the Laplace operator through its imaginary powers, and apply the
ON THE BEHAVIO OF THE SOLUTION OF THE WAVE EQUATION HENDA GUNAWAN AND WONO SETYA BUDHI Abstract. We shall here study some properties of the Laplace operator through its imaginary powers, and apply the
CHAPTER VIII HILBERT SPACES
 CHAPTER VIII HILBERT SPACES DEFINITION Let X and Y be two complex vector spaces. A map T : X Y is called a conjugate-linear transformation if it is a reallinear transformation from X into Y, and if T (λx)
CHAPTER VIII HILBERT SPACES DEFINITION Let X and Y be two complex vector spaces. A map T : X Y is called a conjugate-linear transformation if it is a reallinear transformation from X into Y, and if T (λx)
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration
 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration MATH 206-01: Calculus II Department of Mathematics University of Louisville last corrected September 14, 2013 1 / 43 Chapter 7: Techniques of Integration 7.1. Integration
MATH 131P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER 12, 2012
 MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
MATH 3P: PRACTICE FINAL SOLUTIONS DECEMBER, This is a closed ook, closed notes, no calculators/computers exam. There are 6 prolems. Write your solutions to Prolems -3 in lue ook #, and your solutions to
Separable Equations (1A) Young Won Lim 3/24/15
 Separable Equations (1A) Copyright (c) 2011-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Separable Equations (1A) Copyright (c) 2011-2015 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or
Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering
 Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering Lecture notes for PDEs Sergei V. Shabanov Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611 USA CHAPTER 1 The integration theory
Mathematical Methods for Physics and Engineering Lecture notes for PDEs Sergei V. Shabanov Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32611 USA CHAPTER 1 The integration theory
Product Theorem for Quaternion Fourier Transform
 Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 8, 204, no. 2, 8-87 HIKAI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/ijma.204.3290 Product Theorem for Quaternion ourier Transform Mawardi Bahri Department of Mathematics,
Int. Journal of Math. Analysis, Vol. 8, 204, no. 2, 8-87 HIKAI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/0.2988/ijma.204.3290 Product Theorem for Quaternion ourier Transform Mawardi Bahri Department of Mathematics,
GENERALIZED WATSON TRANSFORMS I: GENERAL THEORY
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 128, Number 9, Pages 2777 2787 S 0002-9939(00)05399-5 Article electronically published on February 29, 2000 GENERALIZED WATSON TRANSFORMS I: GENERAL
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 128, Number 9, Pages 2777 2787 S 0002-9939(00)05399-5 Article electronically published on February 29, 2000 GENERALIZED WATSON TRANSFORMS I: GENERAL
Research Article Quasilinearization Technique for Φ-Laplacian Type Equations
 International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 0, Article ID 975760, pages doi:0.55/0/975760 Research Article Quasilinearization Technique for Φ-Laplacian Type Equations Inara Yermachenko and
International Mathematics and Mathematical Sciences Volume 0, Article ID 975760, pages doi:0.55/0/975760 Research Article Quasilinearization Technique for Φ-Laplacian Type Equations Inara Yermachenko and
Research Article Fourier Series of the Periodic Bernoulli and Euler Functions
 Abstract and Applied Analysis, Article ID 85649, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/85649 Research Article Fourier Series of the Periodic Bernoulli and Euler Functions Cheon Seoung Ryoo, Hyuck In Kwon, 2
Abstract and Applied Analysis, Article ID 85649, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/85649 Research Article Fourier Series of the Periodic Bernoulli and Euler Functions Cheon Seoung Ryoo, Hyuck In Kwon, 2
Math 321 Final Examination April 1995 Notation used in this exam: N. (1) S N (f,x) = f(t)e int dt e inx.
 Math 321 Final Examination April 1995 Notation used in this exam: N 1 π (1) S N (f,x) = f(t)e int dt e inx. 2π n= N π (2) C(X, R) is the space of bounded real-valued functions on the metric space X, equipped
Math 321 Final Examination April 1995 Notation used in this exam: N 1 π (1) S N (f,x) = f(t)e int dt e inx. 2π n= N π (2) C(X, R) is the space of bounded real-valued functions on the metric space X, equipped
Convex Sets Strict Separation in Hilbert Spaces
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 64, 3155-3160 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2014.44257 Convex Sets Strict Separation in Hilbert Spaces M. A. M. Ferreira 1
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 8, 2014, no. 64, 3155-3160 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2014.44257 Convex Sets Strict Separation in Hilbert Spaces M. A. M. Ferreira 1
Research Article Fixed Point Theorems of Quasicontractions on Cone Metric Spaces with Banach Algebras
 Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2013, Article ID 187348, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187348 Research Article Fixed Point Theorems of Quasicontractions on Cone Metric Spaces with Banach
Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 2013, Article ID 187348, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/187348 Research Article Fixed Point Theorems of Quasicontractions on Cone Metric Spaces with Banach
Research Article Some Identities of the Frobenius-Euler Polynomials
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 009, Article ID 639439, 7 pages doi:0.55/009/639439 Research Article Some Identities of the Frobenius-Euler Polynomials Taekyun Kim and
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Abstract and Applied Analysis Volume 009, Article ID 639439, 7 pages doi:0.55/009/639439 Research Article Some Identities of the Frobenius-Euler Polynomials Taekyun Kim and
Notes for the Physics-Based Calculus workshop
 Notes for the hysics-based Calculus workshop Adam Coffman June 9, 24 Trigonometric Functions We recall the following identities for trigonometric functions. Theorem.. For all x R, cos( x = cos(x and sin(
Notes for the hysics-based Calculus workshop Adam Coffman June 9, 24 Trigonometric Functions We recall the following identities for trigonometric functions. Theorem.. For all x R, cos( x = cos(x and sin(
Folland: Real Analysis, Chapter 8 Sébastien Picard
 Folland: Real Analysis, Chapter 8 Sébastien Picard Problem 8.3 Let η(t) = e /t for t >, η(t) = for t. a. For k N and t >, η (k) (t) = P k (/t)e /t where P k is a polynomial of degree 2k. b. η (k) () exists
Folland: Real Analysis, Chapter 8 Sébastien Picard Problem 8.3 Let η(t) = e /t for t >, η(t) = for t. a. For k N and t >, η (k) (t) = P k (/t)e /t where P k is a polynomial of degree 2k. b. η (k) () exists
Positive definite solutions of some matrix equations
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Linear Algebra and its Applications 49 (008) 40 44 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Positive definite solutions of some matrix equations Aleksandar S. Cvetković, Gradimir
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Linear Algebra and its Applications 49 (008) 40 44 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Positive definite solutions of some matrix equations Aleksandar S. Cvetković, Gradimir
f(x)e ikx dx. (1) f(k)e ikx dk. (2) e ikx dx = 2sinak. k f g(x) = g f(x) = f(s)e iks ds
 Mathematical Methods: Page 15 2 Fourier transforms 2.1 Integral transforms The Fourier transform is studied in this chapter and the Laplace transform in the next. They are both integral transforms that
Mathematical Methods: Page 15 2 Fourier transforms 2.1 Integral transforms The Fourier transform is studied in this chapter and the Laplace transform in the next. They are both integral transforms that
Research Article Bessel and Grüss Type Inequalities in Inner Product Modules over Banach -Algebras
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 011, Article ID 5693, 16 pages doi:10.1155/011/5693 Research Article Bessel and Grüss Type Inequalities in Inner Product Modules
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Inequalities and Applications Volume 011, Article ID 5693, 16 pages doi:10.1155/011/5693 Research Article Bessel and Grüss Type Inequalities in Inner Product Modules
Research Article Generalized Mann Iterations for Approximating Fixed Points of a Family of Hemicontractions
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Fixed Point Theory and Applications Volume 008, Article ID 84607, 9 pages doi:10.1155/008/84607 Research Article Generalized Mann Iterations for Approximating Fixed Points
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Fixed Point Theory and Applications Volume 008, Article ID 84607, 9 pages doi:10.1155/008/84607 Research Article Generalized Mann Iterations for Approximating Fixed Points
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 6
 MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 6 Today: 3.2 Differentiation Rules; 3.3 Derivatives of higher order. 3.4 Related rates 3.5 Chain Rule 3.6 Derivative of Trig. Functions Next: 3.7 Implicit Differentiation 4.10
MAT137 Calculus! Lecture 6 Today: 3.2 Differentiation Rules; 3.3 Derivatives of higher order. 3.4 Related rates 3.5 Chain Rule 3.6 Derivative of Trig. Functions Next: 3.7 Implicit Differentiation 4.10
On a Boundary-Value Problem for Third Order Operator-Differential Equations on a Finite Interval
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 216, no. 11, 543-548 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.216.512743 On a Boundary-Value Problem for Third Order Operator-Differential Equations
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 1, 216, no. 11, 543-548 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/1.12988/ams.216.512743 On a Boundary-Value Problem for Third Order Operator-Differential Equations
Fourier Sin and Cos Series and Least Squares Convergence
 Fourier and east Squares Convergence James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University May 7, 28 Outline et s look at the original Fourier sin
Fourier and east Squares Convergence James K. Peterson Department of Biological Sciences and Department of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University May 7, 28 Outline et s look at the original Fourier sin
Research Article Another Proof of the Faithfulness of the Lawrence-Krammer Representation of the Braid Group B 3
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Algebra Volume 01, Article ID 858959, 13 pages doi:10.540/01/858959 Research Article Another Proof of the Faithfulness of the Lawrence-Krammer Representation
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Algebra Volume 01, Article ID 858959, 13 pages doi:10.540/01/858959 Research Article Another Proof of the Faithfulness of the Lawrence-Krammer Representation
Variational iteration method for q-difference equations of second order
 Sichuan University From the SelectedWorks of G.C. Wu Summer June 6, 1 Variational iteration method for -difference euations of second order Guo-Cheng Wu Available at: https://works.bepress.com/gcwu/1/
Sichuan University From the SelectedWorks of G.C. Wu Summer June 6, 1 Variational iteration method for -difference euations of second order Guo-Cheng Wu Available at: https://works.bepress.com/gcwu/1/
A glimpse of Fourier analysis
 Chapter 7 A glimpse of Fourier analysis 7.1 Fourier series In the middle of the 18th century, mathematicians and physicists started to study the motion of a vibrating string (think of the strings of a
Chapter 7 A glimpse of Fourier analysis 7.1 Fourier series In the middle of the 18th century, mathematicians and physicists started to study the motion of a vibrating string (think of the strings of a
Analogues for Bessel Functions of the Christoffel-Darboux Identity
 Analogues for Bessel Functions of the Christoffel-Darboux Identity Mark Tygert Research Report YALEU/DCS/RR-1351 March 30, 2006 Abstract We derive analogues for Bessel functions of what is known as the
Analogues for Bessel Functions of the Christoffel-Darboux Identity Mark Tygert Research Report YALEU/DCS/RR-1351 March 30, 2006 Abstract We derive analogues for Bessel functions of what is known as the
Z. Omar. Department of Mathematics School of Quantitative Sciences College of Art and Sciences Univeristi Utara Malaysia, Malaysia. Ra ft.
 International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 9, 015, no. 46, 57-7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ijma.015.57181 Developing a Single Step Hybrid Block Method with Generalized
International Journal of Mathematical Analysis Vol. 9, 015, no. 46, 57-7 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ijma.015.57181 Developing a Single Step Hybrid Block Method with Generalized
Research Article Existence for Elliptic Equation Involving Decaying Cylindrical Potentials with Subcritical and Critical Exponent
 International Differential Equations Volume 2015, Article ID 494907, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/494907 Research Article Existence for Elliptic Equation Involving Decaying Cylindrical Potentials
International Differential Equations Volume 2015, Article ID 494907, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/494907 Research Article Existence for Elliptic Equation Involving Decaying Cylindrical Potentials
A Note on the Differential Equations with Distributional Coefficients
 MATEMATIKA, 24, Jilid 2, Bil. 2, hlm. 115 124 c Jabatan Matematik, UTM. A Note on the Differential Equations with Distributional Coefficients Adem Kilicman Department of Mathematics, Institute for Mathematical
MATEMATIKA, 24, Jilid 2, Bil. 2, hlm. 115 124 c Jabatan Matematik, UTM. A Note on the Differential Equations with Distributional Coefficients Adem Kilicman Department of Mathematics, Institute for Mathematical
