Problem 01 C. 50. What is the length of a line segment with a slope of 4/3, measured from the y-axis to a point (6,4)? B. 25 D. 75 A.
|
|
|
- Adelia Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FE Review-Math 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 Problem 01 What is the length of a line segment with a slope of 4/3, measured from the y-axis to a point (6,4)? A. 10 B. 25 C. 50 D. 75 5
6 Problem 02 What is the general form of the equation for a line whose x-intercept is 4 and y-intercept is -6? A. 2x - 3y - 18 = 0 B. 2x + 3y + 18 = 0 C. 3x - 2y - 12 = 0 D. 3x + 2y + 12 = 0 6
7 Problem 03 Simplify and evaluate the following expression. log 3 ( %)+ log 3 (12)- log 3 (2) A B C D
8 Problem 04 For some angle 8, csc(8) = -8/5. What is cos(28)? A. 7/32 B. 1/4 C. 3/8 D. 5/8 8
9 Problem 05 The expression... csc(x )cos 3 (x) tan ( x)... is equivalent to which of the following? A. sin(x) B. cos(x) C. 1 - sin 2 (x) D. 1 + sin 2 (x) 9
10 Problem 06 What is the value of x (less than 360 ) that will satisfy the following equation? sin 2 (x)+ 4sin(x)+3 = 0 A. 45 B. 90 C. 180 D
11 Problem 07 If the rectangular coordinates of a point are (-3, -5.2), what are its polar coordinates? A. (-6, -120 ) B. (6, -120 ) C. (6, 120 ) D. (6, -150 ) 11
12 Problem 08 Determine the {x, y) coordinates of the center of the ci rcle defined by the following equation? x 2-8x + l - IO y + 25 = 0 A. (3, 2) B. (3, 4) C. (4, 5) D. (5, 4) 12
13 Problem 09 What is the slope of the following curve when it crosses the positive part of the x-axis? y = I Ox 2-3x - I A. 3/20 B. 1/5 c. 1/3 D. 7 13
14 Problem 10 What is the maximum value of the following function on the interval x < O? A B. -36 C. -5 D. 210 f (x) = 2x x 2-30x
15 Problem 11 What is the value of the following limit? lim[-sin... (5,_x)] <- >0 X A. 0 B C. 1 D. 5 15
16 Problem 12 What is the partial derivative with respect to "x" of the following function? f(x)= x 2 / +x/ +sin(x) +cos 2 (x)+sin 3 (y) A. (2x+ y)/ +3sin 2 (y)cos(y) B. ( 4x-3/)xy 2 + 3sin 2 (y)cos(y) C. ( 3x + 4/ ).ry+3sin 2 (y )cos (y) D. (2x+ y)y3 +[t-2sin(x)]cos(x) 16
17 Problem 13 What is the result of the following indefinite integral? f ( 15x 4-8xJ + ~ + 7 )dx A. 3x 5-2x 4 + In l,~+7x+ C B. 60x 3-24x 2 - x- 2 + C C. 60x 4-24x 3 -x x+ C D. (15/ 4)x 5 - (8/ 3)x 4 - x x+C 17
18 Problem 14 What is the result of the following indefinite integral? f cos 2 (x)sin(x) dx A. -2/3[sin 3 (x)] +c B. - 1/3 [ COS 3 ( X)] + C C. l/3[sin 3 (x)] +c D. l/2[sin 2 (x)cos 2 (x)] + C 18
19 Problem 15 What is the total area of the region bounded by the x-axis and the curve y = sin (x) on the interval between x = n/2 and x = 2n? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 19
20 Problem 16 What is the general solution to the following differential equation? y"-8y'+ l6y=0 A. B. C. D. y= C,e4x y=(c1 +C2x)e4. Y - Ce-4x+Ce4 " - I 2 y = C 1 e 2 x + C 2 e4x 20
21 Problem 17 For the three vectors what is the value of the following product? A (Bx C) - A = 6i + 8j + 1 Ok - B = i + 2j + 3k - C = 3i + 4j + 5k A. 0 B. 64 C. 80 D
22 Problem 18 What is the angle between the two given vectors? - A = 4i + 12j + 6k - B = 24i - 8j + 6k A B C D
23 Problem 19 What is the determinant of the following matrix? A. -8 B. -4 C. 0 D. 4 [ 2 34] A ;
24 Problem 20 The second and sixth terms of a geometric progression are 3/10 and 243/160, respectively. What is the first term of this sequence? A. 1/10 B. 1/5 C. 3/5 D. 3/2 24
25 1. To find the width of a river, a surveyor sets up a transit at point C on one river bank and sights directly across to point B on the other bank. The surveyor then walks along the bank for a distance of 275 m to point A. The angle CAB is 57 28'. B ' 275 m What is the approximate width of the river? (A) 150 m (B) 230 m (C) 330 m (D) 430 m 25
26 2. In the following illustration, angles 2 and 5 are 90, AD = 15, DC = 20, and AC= 25. D What are the lengths BC and BD, respectively? (A) 12 and 16 (B) 13 and 17 (C) 16 and 12 (D) 18 and 13 26
27 3. What is the length of the line segment with slope 4/3 that extends from the point (6, 4) to the y-axis? (A) 10 (B) 25 (C) 50 (D) Which of the following expressions is equivalent to sin 20? (A) 2 sin 0 cos 0 (B) cos sin 2 0 (C) sin 0 cos 0 (D) 1 - cos
28 5. Which of the following equations describes a circle with center at (2, 3) and passing through the point (-3, - 4)? (A) (x+ 3) 2 + (y+ 4) 2 = 85 (B) ( X + 3) 2 + ( y + 2) 2 = J74 (C) (x-3)2+(y-2)2=74 (D) ( x - 2 )2 + ( y - 3) 2 = The equation for a circle is x 2 + 4x+ y2 + 8y= 0. What are the coordinates of the circle's center? (A) (-4, - 8) (B) (-4, - 2) (C) (-2, -4) (D) (2, - 4) 28
29 7. Which of the following statements is FALSE for all noncircular ellipses? (A) The eccentricity, e, is less than one. (B) The ellipse has two foci. ( C) The sum of the two distances from the two foci to any point on the ellipse is 2 a (i.e., twice the semimajor distance). (D) The coefficients A and C preceding the x 2 and i/ terms in the general form of the equation are equal. 8. What is the area of the shaded portion of the circle shown? (A) 5n (B) (~~) (5n - 3) (C) 50n 3 (D) 49n - v'3 29
30 9. A pipe with a 20 cm inner diameter is filled to a depth equal to one-third of its diameter. What is the approximate area in flow? (A) 33 cm 2 (B) 60 cm 2 (C) 92 cm 2 (D) 100 cm 2 1 O. The equation y = a1 + ~x is an algebraic expression for which of the following? (A) a cosine expansion series (B) projectile motion ( C) a circle in polar form (D) a straight line 30
31 11. For the right triangle shown, x = 18 cm and y = 13 cm. ~v~13cm x = 18 cm Most nearly, what is csc 0? (A) 0.98 (B) 1.2 (C) 1.7 (D) A circular sector has a radius of 8 cm and an arc length of 13 cm. Most nearly, what is its area? (A) 48 cm 2 (B) 50 cm 2 (C) 52 cm 2 (D) 60 cm 2 31
32 13. The equation -3x 2-4y2 = 1 defines (A) a circle (B) an ellipse (C) a hyperbola (D) a parabola 14. What is the approximate surface area (including both side and base) of a 4 m high right circular cone with a base 3 min diameter? (A) 24 m 2 (B) 27 m 2 (C) 32 m 2 (D) 36 m 2 32
33 15. A particle moves in the x-y plane. After t s, the x and y-coordinates of the particle's location are x = 8 sin t and y = 6 cos t. Which of the following equations describes the path of the particle? (A) 36x2 + 64y 2 = 2304 (B) 36x2-64y 2 = 2304 (C) 64x y 2 = 2304 (D) 64x 2-36y 2 =
34 1. What is the name for a vector that represents the sum of two vectors? (A) scalar ' ' (B) resultant (C) tensor (D) moment 2. The second and sixth terms of a geometric progression are 3/10 and 243/160, respectively. What is the first term of this sequence? (A) 1/10 (B) 1/5 (C) 3/5 (D) 3/2 34
35 3. Using logarithmic identities, what is most nearly the numerical value for the following expression? (A) 0.95 (B) 1.33 (C) 2.00 (D) Which of the following statements is true for a power series with the general term aixi? I. An infinite power series converges for x < l. II. Power series can be added together or subtracted within their interval of convergence. III. Power series can be integrated within their interval of convergence. (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and III (D) II and III 35
36 5. What is most nearly the length of the resultant of the following vectors? (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 10 (D) 14 3i + 4j - 5k 7i + 2j + 3k -16i - 14j + 2k 6. What is the solution to the following system of simultaneous linear equations? lox + 3y + loz = 5 8x- 2y+ 9z= 3 8x + y - loz = 7 (A) X= 0.326; y = ; Z= (B) X= 0.148; y= 1.203; Z= (C) X= 0.625; y = 0.186; Z= (D) X= 0.282; y = ; Z=
37 7. What is the inverse of matrix A? (A) [ ~ l : (B) [ : ~ l (C) [ _ : - : l (D) r-: _: l 37
38 8. If the determinant of matrix A is -40, what is the determinant of matrix B? A= B= (A) -80 (B) - 40 (C) -20 (D)
39 9. Given the origin-based vector A = i + 2j + k, what is most nearly the angle between A and the x-axis? (A) 22 (B) 24 (C) 66 (D) 80 1 O. Which is a true statement about these two vectors? A = i+2j +k B = i + 3j - 7k (A) Both vectors pass through the point (0, -1, 6). (B) The vectors are parallel. ( C) The vectors are orthogonal. (D) The angle between the vectors is
40 11. What is most nearly the acute angle between vectors A = (3, 2, 1) and B = (2, 3, 2), both based at the origin? (A) 25 (B) 33 (C) 35 (D) Force vectors A, B, and C are applied at a single point. A = i+3j +4k B = 2i + 7j - k C= -i+4j + 2k What is most nearly the magnitude of the resultant force vector, R? (A) p (B) 14 (C) 15 (D) 16 40
41 13. What is the sum of j and 7-9j? (A) 19-22j (B) j (C) 25-22j (D) j 14. What is the product of the complex numbers 3 + 4j and 7-2j? (A) 10+2j (B) j (C) j (D) j 41
42 1. Which of the following is NOT a correct derivative? ', (A) -1:.._ cos x = - sin x dx (B) -1:.._ (1 - x) 3 = - 3(1 - x)2 dx (C) d l 1 (D) dxx x2 d dx csc x = - cot x 2. What is the derivative, dy/dx, of the expression x 2 y- e 2 x = sin y? (A) (B) 2e2x x2 - cosy 2e2x - 2xy x2 - cos y (C) 2 e2x - 2xy (D) x 2 - cos y 42
43 3. What is the approximate area bounded by the curves y = 8 - x 2 and y = af'? (A) 22 (B) 27 (C) 30 (D) What are the mm1mum and maximum values, respectively, of the equation f(x) = 5x 3-2af' + 1 on the interval [- 2, 2]? (A) - 47, 33 (B) - 4, 4 (C) 0.95, 1 (D) 0,
44 5. In vector calculus, a gradient is a I. vector that points in the direction of the rate of change of a scalar field II. vector whose magnitude indicates the maximum rate of change of a scalar field III. scalar that indicates the magnitude of the rate of change of a vector field in a particular direction IV. scalar that indicates the maximum magnitude of the rate of change of a vector field in any particular direction (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II (D) III and IV 6. Which of the illustrations shown represents the vector field, F(x, y) = - yi + xj? (A) (B) * / X (C) (D) 44
45 7. A peach grower estimates that if he picks his crop now, he will obtain 1000 lugs of peaches, which he can sell at $1.00 per lug. However, he estimates that his crop will increase by an additional 60 lugs of peaches for each week that he delays picking, but the price will drop at a rate of $0.025 per lug per week. In addition, he will experience a spoilage rate of approximately 10 lugs for each week he delays. In order to maximize his revenue, how many weeks should he wait before picking the peaches? (A) 2 weeks (B) 5 weeks (C) 7 weeks (D) 10 weeks 45
46 8. Determine the following indefinite integral. (A) ~ + ln I xi - j_ + C (B) (C) (D) 4 X - x 2 + log x - 8x + C x lnlxl--+ C 2 x 2 x ln lxl - -+ C 2 X 9. Find dy/ dx for the parametric equations given. X = 2t 2 - t y = t 3-2t + 1 (A) 3t2 (B) 3t2 /2 (C) 4t-1 (D) (3f - 2)/(4t- 1) 46
47 10. A two-dimensional function, f(x, y), is defined as f(x, y) = 2x 2 - y 2 + 3x - y What is the direction of the line passing through the point (1, -2) that has the maximum slope? (A) 4i + 2j (B) 7i + 3j (C) 7i + 4j (D) 9i - 7j ' 11. Evaluate the following limit.,:, " (A) 0 (B) 2 (C) 4 (D) 00 r (x 2-4) x~ x-2 47
48 11. Evaluate the following limit. (A) 0 (B) 2 (C) 4 (D) oo r (x 2-4) x~ x If f( x, y) = x 2 y 3 + xy 4 + sin x+ cos 2 x+ sin 3 y, what is of/ox? (A) (2x + y)y sin 2 ycos y (B) ( 4x- 3y 2 )xy sin 2 ycos y (C) (3x+ 4y 2 )xy+ 3 sin 2 ycos y (D) (2x + y)y 3 +(1-2sin x)cosx 48
49 13. What is dy/dx if y= (2xY? (A) (2xt(2 + ln 2x) (B) 2x(l + ln 2x? (C) (2xt(ln 2x 2 ) (D) (2xt(l+ln2x) 1. What is the solution to the following differential equation? (A) y=5x+ C (B) y= Ce- 5 x (C) y= Ce 5 x (D) either (A) or (B) y' + 5y = 0 49
50 2. What is the solution to the following linear difference equation? (k+ l)(y(k+ 1)) - ky(k) = 1 (A) y(k) = 12 -¼ (B) y(k) = 1-1 f (C) y(k) = k (D) y(k) = 3 + ¼ 3. What is the general solution to the following differential equation? (d 2 y) (dy) y=O dx2 dx (A) y = C 1 cos x + C 2 sin x (B) y = C1 ex+ C2e-x (C) y = e-x( C1 cos x - C2 sin x) (D) y = ex( C1 cos x + C2 sinx) 50
51 4. What is the general solution to the following differential equation? d 2 (A) y = C 1 sin x - d dx _Jj_ y = 0 dx2 C 2 cos x (B) y = C 1 cos x - C 2 sin x (C) y = C1 cos x + C2 sin x (D) y = e-x( C1 cos x + C2 sin x) S. What is the complementary solution to the following differential equation? y" - 4y' + 2 f y = 10 cos 8x (A) y = 2C1x + C2x - C3x (B) Y = C 1 e2 x + C 2 e1.5 x (C) y = C1e2xcosl.5x+ C2e2xsinl.5x (D) y = C 1 ex tan x + C 2 ex cot x 51
52 6. What is the general solution to the following differential equation? (A) (B) (C) (D) y"+y'+y=o y = e-½x ( C 1 cos 1 x + C 2 sin 1 x) 1 y = e -2x ( C 1 cos!x + C 2 sin!x) - y = e- 2x( C1 cos 1x + C2 sin 1x) y= e-2x(c1 cos!x+ C2sin!x) 7. What is the solution to the following differential equation if x = 1 at t= 0, and dx/ dt = 0 at t= O? (A) (B) (C) (D) x = e- 4t + 4te- 4t x = ie-2t( cos 2t + sin 2t) + i x = e- 4t + 4te-4t + i x = ie-4t +!te-4t + i 52
53 8. In the following differential equation with the initial condition x(0) = 12, what is the value of x(2)? (A) 3.4 x 10-3 (B) 4.0 X 10-3 (C) 5.1 x 10-3 (D) 6.2 X 10-3 dx + 4x = 0 dt 53
54 9. What are the three general Fourier coefficients for the sawtooth wave shown? fwc 1~.---:::::::::1~ 'IT 2'11" t (A) (B) (C) (D) -1 ao = 0, an = 0, bn = - rrn 1-1 ao = -, an = 0, bn = - 2 rrn ao = 1, an = 1, bn = - rrn ao = 2) an = 2 ) bn = rrn 1 O. The values of an unknown function follow a Fibonacci number sequence. It is known that f(l) = 4 and f(2) = 1.3. What is f(4)? (A) -4.1 (B) 0.33 (C) 2.7 (D)
FAIRFIELD COUNTY MATH LEAGUE (FCML) Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics
 Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics 1.) 6.4.) 14706.) 85 1.)The geometric mean of the numbers x 1, x, x n is defined to be n x 1 x...x n. What is the positive difference between the arithmetic
Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics 1.) 6.4.) 14706.) 85 1.)The geometric mean of the numbers x 1, x, x n is defined to be n x 1 x...x n. What is the positive difference between the arithmetic
5, tan = 4. csc = Simplify: 3. Simplify: 4. Factor and simplify: cos x sin x cos x
 Precalculus Final Review 1. Given the following values, evaluate (if possible) the other four trigonometric functions using the fundamental trigonometric identities or triangles csc = - 3 5, tan = 4 3.
Precalculus Final Review 1. Given the following values, evaluate (if possible) the other four trigonometric functions using the fundamental trigonometric identities or triangles csc = - 3 5, tan = 4 3.
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review
 Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Exam Mathematics Review Dr. Garey Fox Professor and Buchanan Endowed Chair Biosystems and Agricultural Engineering October 16, 2014 Reference Material from FE Review Instructor
Topic 3 Part 1 [449 marks]
![Topic 3 Part 1 [449 marks] Topic 3 Part 1 [449 marks]](/thumbs/90/102647102.jpg) Topic 3 Part [449 marks] a. Find all values of x for 0. x such that sin( x ) = 0. b. Find n n+ x sin( x )dx, showing that it takes different integer values when n is even and when n is odd. c. Evaluate
Topic 3 Part [449 marks] a. Find all values of x for 0. x such that sin( x ) = 0. b. Find n n+ x sin( x )dx, showing that it takes different integer values when n is even and when n is odd. c. Evaluate
5 t + t2 4. (ii) f(x) = ln(x 2 1). (iii) f(x) = e 2x 2e x + 3 4
 Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
Study Guide for Final Exam 1. You are supposed to be able to determine the domain of a function, looking at the conditions for its expression to be well-defined. Some examples of the conditions are: What
M GENERAL MATHEMATICS -2- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 1 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H
 M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
M - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 38-39 H 3 Q. Let A =, B = and C = 3 Compute (if possible) : A+B and BC A+B is impossible. ( ) BC = 3
Transweb Educational Services Pvt. Ltd Tel:
 . An aeroplane flying at a constant speed, parallel to the horizontal ground, km above it, is observed at an elevation of 6º from a point on the ground. If, after five seconds, its elevation from the same
. An aeroplane flying at a constant speed, parallel to the horizontal ground, km above it, is observed at an elevation of 6º from a point on the ground. If, after five seconds, its elevation from the same
QUESTION BANK ON. CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola)
 QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
QUESTION BANK ON CONIC SECTION (Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola) Question bank on Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola Select the correct alternative : (Only one is correct) Q. Two mutually perpendicular tangents
Consortium of Medical Engineering and Dental Colleges of Karnataka (COMEDK-2007)
 Consortium of Medical Engineering and Dental Colleges of Karnataka (COMEDK-007) MATHEMATICS. Log'f/ is equal to 7 Log 35 5. In the group (G 5 ), where G = {3, 6, 9, }; 5 is multiplication modulo 5, the
Consortium of Medical Engineering and Dental Colleges of Karnataka (COMEDK-007) MATHEMATICS. Log'f/ is equal to 7 Log 35 5. In the group (G 5 ), where G = {3, 6, 9, }; 5 is multiplication modulo 5, the
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus II.
 MTH 142 Practice Exam Chapters 9-11 Calculus II With Analytic Geometry Fall 2011 - University of Rhode Island This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus
MTH 142 Practice Exam Chapters 9-11 Calculus II With Analytic Geometry Fall 2011 - University of Rhode Island This practice exam is intended to help you prepare for the final exam for MTH 142 Calculus
Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the tangent line at P. 1) y = x2 + 11x - 15, P(1, -3)
 Final Exam Review AP Calculus AB Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the tangent line at P. 1) y = x2 + 11x - 15, P(1, -3) Use the graph to evaluate the limit. 2) lim x
Final Exam Review AP Calculus AB Find the slope of the curve at the given point P and an equation of the tangent line at P. 1) y = x2 + 11x - 15, P(1, -3) Use the graph to evaluate the limit. 2) lim x
Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed.
 Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed. Part A: (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) Do the following problems. Write the answer in the space provided. Only the answers
Sample Questions Exam II, FS2009 Paulette Saab Calculators are neither needed nor allowed. Part A: (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) Do the following problems. Write the answer in the space provided. Only the answers
Solution to Review Problems for Midterm II
 Solution to Review Problems for Midterm II Midterm II: Monday, October 18 in class Topics: 31-3 (except 34) 1 Use te definition of derivative f f(x+) f(x) (x) lim 0 to find te derivative of te functions
Solution to Review Problems for Midterm II Midterm II: Monday, October 18 in class Topics: 31-3 (except 34) 1 Use te definition of derivative f f(x+) f(x) (x) lim 0 to find te derivative of te functions
correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2
 correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2003 Introduction to Advanced Mathematics 2003 by Richard G. Brown Advanced Mathematics offers comprehensive coverage of precalculus
correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2003 Introduction to Advanced Mathematics 2003 by Richard G. Brown Advanced Mathematics offers comprehensive coverage of precalculus
Since x + we get x² + 2x = 4, or simplifying it, x² = 4. Therefore, x² + = 4 2 = 2. Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #01 Solution 1. x + = 2, then x² + = Since x + = 2, by squaring both side of the equation, (A) - (B) 0 (C) 2 (D) 4 (E) -2 we get x² + 2x 1 + 1 = 4, or simplifying it, x² + 2
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
3. Identify and find the general solution of each of the following first order differential equations.
 Final Exam MATH 33, Sample Questions. Fall 7. y = Cx 3 3 is the general solution of a differential equation. Find the equation. Answer: y = 3y + 9 xy. y = C x + C x is the general solution of a differential
Final Exam MATH 33, Sample Questions. Fall 7. y = Cx 3 3 is the general solution of a differential equation. Find the equation. Answer: y = 3y + 9 xy. y = C x + C x is the general solution of a differential
b) The trend is for the average slope at x = 1 to decrease. The slope at x = 1 is 1.
 Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
b = 2, c = 3, we get x = 0.3 for the positive root. Ans. (D) x 2-2x - 8 < 0, or (x - 4)(x + 2) < 0, Therefore -2 < x < 4 Ans. (C)
 SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
SAT II - Math Level 2 Test #02 Solution 1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E) 2.2 ± Using Quadratic formula, x =, with a = 1,
18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 3. Double Integrals 3A. Double
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 3. Double Integrals 3A. Double
ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM
 First Round : March 7, 00 Second Round: April, 00 at The University of Alabama ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM Construction of this test directed by Congxiao Liu, Alabama A&M University and Alzaki Fadl
First Round : March 7, 00 Second Round: April, 00 at The University of Alabama ALGEBRA II WITH TRIGONOMETRY EXAM Construction of this test directed by Congxiao Liu, Alabama A&M University and Alzaki Fadl
2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time is
 . If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
. If P(A) = x, P = 2x, P(A B) = 2, P ( A B) = 2 3, then the value of x is (A) 5 8 5 36 6 36 36 2. A die is rolled 3 times, the probability of getting a number larger than the previous number each time
Lone Star College-CyFair Formula Sheet
 Lone Star College-CyFair Formula Sheet The following formulas are critical for success in the indicated course. Student CANNOT bring these formulas on a formula sheet or card to tests and instructors MUST
Lone Star College-CyFair Formula Sheet The following formulas are critical for success in the indicated course. Student CANNOT bring these formulas on a formula sheet or card to tests and instructors MUST
Math 190 (Calculus II) Final Review
 Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
Math 90 (Calculus II) Final Review. Sketch the region enclosed by the given curves and find the area of the region. a. y = 7 x, y = x + 4 b. y = cos ( πx ), y = x. Use the specified method to find the
y mx 25m 25 4 circle. Then the perpendicular distance of tangent from the centre (0, 0) is the radius. Since tangent
 Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
Mathematics. The sides AB, BC and CA of ABC have, 4 and 5 interior points respectively on them as shown in the figure. The number of triangles that can be formed using these interior points is () 80 ()
π π π π Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A B C D Determine the period of 15
 Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A. 0.09 B. 0.18 C. 151.83 D. 303.67. Determine the period of y = 6cos x + 8. 15 15 A. B. C. 15 D. 30 15 3. Determine the exact value of
Trigonometry Homework Booklet 1. Convert 5.3 radians to degrees. A. 0.09 B. 0.18 C. 151.83 D. 303.67. Determine the period of y = 6cos x + 8. 15 15 A. B. C. 15 D. 30 15 3. Determine the exact value of
y = x 3 and y = 2x 2 x. 2x 2 x = x 3 x 3 2x 2 + x = 0 x(x 2 2x + 1) = 0 x(x 1) 2 = 0 x = 0 and x = (x 3 (2x 2 x)) dx
 Millersville University Name Answer Key Mathematics Department MATH 2, Calculus II, Final Examination May 4, 2, 8:AM-:AM Please answer the following questions. Your answers will be evaluated on their correctness,
Millersville University Name Answer Key Mathematics Department MATH 2, Calculus II, Final Examination May 4, 2, 8:AM-:AM Please answer the following questions. Your answers will be evaluated on their correctness,
Part D - Sample Questions
 Mathematics Placement Test Part D - Sample Questions Calculators are not permitted (An answer key is included) #1. For the parabola x = 16y + 4y + 13, for what value of y does x have a minimum? #. If sin
Mathematics Placement Test Part D - Sample Questions Calculators are not permitted (An answer key is included) #1. For the parabola x = 16y + 4y + 13, for what value of y does x have a minimum? #. If sin
PART ONE: Solve algebraically and check. Be sure to show all work.
 NAME AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2017 DIRECTIONS: Each part must be completed separately on looseleaf. All work should be shown and done in a neat and precise manner. Any questions pertaining to the
NAME AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER ASSIGNMENT 2017 DIRECTIONS: Each part must be completed separately on looseleaf. All work should be shown and done in a neat and precise manner. Any questions pertaining to the
Practice Problems for Exam 3 (Solutions) 1. Let F(x, y) = xyi+(y 3x)j, and let C be the curve r(t) = ti+(3t t 2 )j for 0 t 2. Compute F dr.
 1. Let F(x, y) xyi+(y 3x)j, and let be the curve r(t) ti+(3t t 2 )j for t 2. ompute F dr. Solution. F dr b a 2 2 F(r(t)) r (t) dt t(3t t 2 ), 3t t 2 3t 1, 3 2t dt t 3 dt 1 2 4 t4 4. 2. Evaluate the line
1. Let F(x, y) xyi+(y 3x)j, and let be the curve r(t) ti+(3t t 2 )j for t 2. ompute F dr. Solution. F dr b a 2 2 F(r(t)) r (t) dt t(3t t 2 ), 3t t 2 3t 1, 3 2t dt t 3 dt 1 2 4 t4 4. 2. Evaluate the line
Calculus I (Math 241) (In Progress)
 Calculus I (Math 241) (In Progress) The following is a collection of Calculus I (Math 241) problems. Students may expect that their final exam is comprised, more or less, of one problem from each section,
Calculus I (Math 241) (In Progress) The following is a collection of Calculus I (Math 241) problems. Students may expect that their final exam is comprised, more or less, of one problem from each section,
Find the indicated derivative. 1) Find y(4) if y = 3 sin x. A) y(4) = 3 cos x B) y(4) = 3 sin x C) y(4) = - 3 cos x D) y(4) = - 3 sin x
 Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
Assignment 5 Name Find the indicated derivative. ) Find y(4) if y = sin x. ) A) y(4) = cos x B) y(4) = sin x y(4) = - cos x y(4) = - sin x ) y = (csc x + cot x)(csc x - cot x) ) A) y = 0 B) y = y = - csc
2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with a graph. f(x) = 25 x 2
 29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
29 April PreCalculus Final Review 1. Find the slope and y-intercept (if possible) of the equation of the line. Sketch the line: y = 3x + 13 2. Determine the domain of the function. Verify your result with
Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus
 PRECALCULUS correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2004 Introduction to Precalculus 2004 by Roland E. Larson and Robert P. Hostetler Precalculus thoroughly explores topics
PRECALCULUS correlated to the Indiana Academic Standards for Precalculus CC2 6/2003 2004 Introduction to Precalculus 2004 by Roland E. Larson and Robert P. Hostetler Precalculus thoroughly explores topics
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
Math 170 Final Exam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the function at the given value of the independent variable and
FAIRFIELD COUNTY MATH LEAGUE (FCML) Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics
 Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics 1.) 2.) 3.) 1.)The geometric mean of the numbers x1, x2,..., x n is defined to be n x 1 x 2...x n. What is the positive difference between the arithmetic mean
Match 4 Round 1 Arithmetic: Basic Statistics 1.) 2.) 3.) 1.)The geometric mean of the numbers x1, x2,..., x n is defined to be n x 1 x 2...x n. What is the positive difference between the arithmetic mean
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 2007
 Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Test Codes : MIA (Objective Type) and MIB (Short Answer Type) 007 Questions will be set on the following and related topics. Algebra: Sets, operations on sets. Prime numbers, factorisation of integers
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
f(x 0 + h) f(x 0 ) h slope of secant line = m sec
 Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
Derivatives Using limits, we can define the slope of a tangent line to a function. When given a function f(x), and given a point P (x 0, f(x 0 )) on f, if we want to find the slope of the tangent line
MA 162 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring Find the angle between the vectors v = 2i + 2j + k and w = 2i + 2j k. C.
 MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
MA 6 FINAL EXAM PRACTICE PROBLEMS Spring. Find the angle between the vectors v = i + j + k and w = i + j k. cos 8 cos 5 cos D. cos 7 E. cos. Find a such that u = i j + ak and v = i + j + k are perpendicular.
f( X 3-3x )dx = x 2 --3x +C (A) 3x 2-3+C (B) 4x 4-6x 2 +C (C) x 4 3x 2 x 4 5x 3 +15x 2 +20x+25 5x 2 +15x+25 (E) 5 (D) 225 (B) (A)
 . f( X -x )dx = x -+C x -6x +C x x x --x+c ---+C x --x +C. If f(x)=x +x +x+5 and g(x)=5, then g(f(x))= 5 5x +5x+5 5 5x +5x +0x+5. The slope of the line tangent to the graph of y = In (x ) at x = e is e
. f( X -x )dx = x -+C x -6x +C x x x --x+c ---+C x --x +C. If f(x)=x +x +x+5 and g(x)=5, then g(f(x))= 5 5x +5x+5 5 5x +5x +0x+5. The slope of the line tangent to the graph of y = In (x ) at x = e is e
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic concepts: Find y(x) where x is the independent and y the dependent varible, based on an equation involving x, y(x), y 0 (x),...e.g.: y 00 (x) = 1+y(x) y0 (x) 1+x or,
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Basic concepts: Find y(x) where x is the independent and y the dependent varible, based on an equation involving x, y(x), y 0 (x),...e.g.: y 00 (x) = 1+y(x) y0 (x) 1+x or,
M GENERAL MATHEMATICS -2- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel 1 Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester H
 M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 435-436 H Q. Let A ( ) 4 and B 3 3 Compute (if possible) : AB and BA ( ) 4 AB 3 3 ( ) ( ) ++ 4+4+ 4
M 4 - GENERAL MATHEMATICS -- Dr. Tariq A. AlFadhel Solution of the First Mid-Term Exam First semester 435-436 H Q. Let A ( ) 4 and B 3 3 Compute (if possible) : AB and BA ( ) 4 AB 3 3 ( ) ( ) ++ 4+4+ 4
Dr. Sophie Marques. MAM1020S Tutorial 8 August Divide. 1. 6x 2 + x 15 by 3x + 5. Solution: Do a long division show your work.
 Dr. Sophie Marques MAM100S Tutorial 8 August 017 1. Divide 1. 6x + x 15 by 3x + 5. 6x + x 15 = (x 3)(3x + 5) + 0. 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 by 3a 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 = (4a 3 3a + a + 3)(3a ) + 0 3. 1a
Dr. Sophie Marques MAM100S Tutorial 8 August 017 1. Divide 1. 6x + x 15 by 3x + 5. 6x + x 15 = (x 3)(3x + 5) + 0. 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 by 3a 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 = (4a 3 3a + a + 3)(3a ) + 0 3. 1a
( ) as a fraction. If both numerator and denominator are
 A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
A. Limits and Horizontal Asymptotes What you are finding: You can be asked to find lim f x x a (H.A.) problem is asking you find lim f x x ( ) and lim f x x ( ). ( ) or lim f x x ± ( ). Typically, a horizontal
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW
 CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
CALCULUS ASSESSMENT REVIEW DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS CHRISTOPHER NEWPORT UNIVERSITY 1. Introduction and Topics The purpose of these notes is to give an idea of what to expect on the Calculus Readiness
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
TEST CODE: MMA (Objective type) 2015 SYLLABUS Analytical Reasoning Algebra Arithmetic, geometric and harmonic progression. Continued fractions. Elementary combinatorics: Permutations and combinations,
Final Exam SOLUTIONS MAT 131 Fall 2011
 1. Compute the following its. (a) Final Exam SOLUTIONS MAT 131 Fall 11 x + 1 x 1 x 1 The numerator is always positive, whereas the denominator is negative for numbers slightly smaller than 1. Also, as
1. Compute the following its. (a) Final Exam SOLUTIONS MAT 131 Fall 11 x + 1 x 1 x 1 The numerator is always positive, whereas the denominator is negative for numbers slightly smaller than 1. Also, as
(1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3
 Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
Math 127 Introduction and Review (1) Recap of Differential Calculus and Integral Calculus (2) Preview of Calculus in three dimensional space (3) Tools for Calculus 3 MATH 127 Introduction to Calculus III
DRAFT - Math 101 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 The Derivative of Polynomial and Exponential Functions In this section we learn how to differentiate constant functions, power functions, polynomials, and exponential functions.
TABLE OF CONTENTS 2 CHAPTER 1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Quadratics CHAPTER Functions 3 CHAPTER 3 Coordinate Geometry 3 CHAPTER 4 Circular Measure 4 CHAPTER 5 Trigonometry 4 CHAPTER 6 Vectors 5 CHAPTER 7 Series 6 CHAPTER 8 Differentiation
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Quadratics CHAPTER Functions 3 CHAPTER 3 Coordinate Geometry 3 CHAPTER 4 Circular Measure 4 CHAPTER 5 Trigonometry 4 CHAPTER 6 Vectors 5 CHAPTER 7 Series 6 CHAPTER 8 Differentiation
Solving Systems of Linear Equations. Classification by Number of Solutions
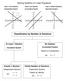 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Case 1: One Solution Case : No Solution Case 3: Infinite Solutions Independent System Inconsistent System Dependent System x = 4 y = Classification by Number of Solutions
Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
Formulas to remember
 Complex numbers Let z = x + iy be a complex number The conjugate z = x iy Formulas to remember The real part Re(z) = x = z+z The imaginary part Im(z) = y = z z i The norm z = zz = x + y The reciprocal
Complex numbers Let z = x + iy be a complex number The conjugate z = x iy Formulas to remember The real part Re(z) = x = z+z The imaginary part Im(z) = y = z z i The norm z = zz = x + y The reciprocal
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 5
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 3 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 3 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 3 1.3 Algebraic
Set 3: Multiple-Choice Questions on Differentiation
 Set 3: Multiple-Choice Questions on Differentiation 65 Set 3: Multiple-Choice Questions on Differentiation In each of Questions -5 a function is given. Choose the alternative that is the derivative, dy,
Set 3: Multiple-Choice Questions on Differentiation 65 Set 3: Multiple-Choice Questions on Differentiation In each of Questions -5 a function is given. Choose the alternative that is the derivative, dy,
Math 226 Calculus Spring 2016 Exam 2V1
 Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (35 Points) Evaluate the following integrals. (a) (7 Points) tan 5 (x) sec 3 (x) dx (b) (8 Points) cos 4 (x) dx Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (Continued) Evaluate
Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (35 Points) Evaluate the following integrals. (a) (7 Points) tan 5 (x) sec 3 (x) dx (b) (8 Points) cos 4 (x) dx Math 6 Calculus Spring 6 Exam V () (Continued) Evaluate
Math 1431 Final Exam Review
 Math 1431 Final Exam Review Comprehensive exam. I recommend you study all past reviews and practice exams as well. Know all rules/formulas. Make a reservation for the final exam. If you miss it, go back
Math 1431 Final Exam Review Comprehensive exam. I recommend you study all past reviews and practice exams as well. Know all rules/formulas. Make a reservation for the final exam. If you miss it, go back
Math 153 Final Exam Extra Review Problems
 Math 153 Final Exam Extra Review Problems This is not intended to be a comprehensive review of every type of problem you are responsible for solving, but instead is meant to give you some extra problems
Math 153 Final Exam Extra Review Problems This is not intended to be a comprehensive review of every type of problem you are responsible for solving, but instead is meant to give you some extra problems
ALGEBRA 2 X. Final Exam. Review Packet
 ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
ALGEBRA X Final Exam Review Packet Multiple Choice Match: 1) x + y = r a) equation of a line ) x = 5y 4y+ b) equation of a hyperbola ) 4) x y + = 1 64 9 c) equation of a parabola x y = 1 4 49 d) equation
Learning Objectives for Math 166
 Learning Objectives for Math 166 Chapter 6 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 6.1: Volumes Using Cross-Sections Draw and label both 2-dimensional perspectives and 3-dimensional sketches of the
Learning Objectives for Math 166 Chapter 6 Applications of Definite Integrals Section 6.1: Volumes Using Cross-Sections Draw and label both 2-dimensional perspectives and 3-dimensional sketches of the
10.1 Review of Parametric Equations
 10.1 Review of Parametric Equations Recall that often, instead of representing a curve using just x and y (called a Cartesian equation), it is more convenient to define x and y using parametric equations
10.1 Review of Parametric Equations Recall that often, instead of representing a curve using just x and y (called a Cartesian equation), it is more convenient to define x and y using parametric equations
M273Q Multivariable Calculus Spring 2017 Review Problems for Exam 3
 M7Q Multivariable alculus Spring 7 Review Problems for Exam Exam covers material from Sections 5.-5.4 and 6.-6. and 7.. As you prepare, note well that the Fall 6 Exam posted online did not cover exactly
M7Q Multivariable alculus Spring 7 Review Problems for Exam Exam covers material from Sections 5.-5.4 and 6.-6. and 7.. As you prepare, note well that the Fall 6 Exam posted online did not cover exactly
You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).
 Review You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).. Arithmetic You should know how to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and work with the integers Z = {...,,,
Review You should be comfortable with everything below (and if you aren t you d better brush up).. Arithmetic You should know how to add, subtract, multiply, divide, and work with the integers Z = {...,,,
Have a Safe and Happy Break
 Math 121 Final EF: December 10, 2013 Name Directions: 1 /15 2 /15 3 /15 4 /15 5 /10 6 /10 7 /20 8 /15 9 /15 10 /10 11 /15 12 /20 13 /15 14 /10 Total /200 1. No book, notes, or ouiji boards. You may use
Math 121 Final EF: December 10, 2013 Name Directions: 1 /15 2 /15 3 /15 4 /15 5 /10 6 /10 7 /20 8 /15 9 /15 10 /10 11 /15 12 /20 13 /15 14 /10 Total /200 1. No book, notes, or ouiji boards. You may use
Exercise. Exercise 1.1. MA112 Section : Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1
 MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Exercise Exercise 1.1 1 8 Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola and sketch its graph. 1. x = 2y 2 2. 4y +x 2 = 0 3. 4x 2 =
MA112 Section 750001: Prepared by Dr.Archara Pacheenburawana 1 Exercise Exercise 1.1 1 8 Find the vertex, focus, and directrix of the parabola and sketch its graph. 1. x = 2y 2 2. 4y +x 2 = 0 3. 4x 2 =
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET
 SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
SANDERSON HIGH SCHOOL AP CALCULUS AB/BC SUMMER REVIEW PACKET 017-018 Name: 1. This packet is to be handed in on Monday August 8, 017.. All work must be shown on separate paper attached to the packet. 3.
Pre Calculus Gary Community School Corporation Unit Planning Map
 UNIT/TIME FRAME STANDARDS Functions and Graphs (6 weeks) PC.F.1: For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities,
UNIT/TIME FRAME STANDARDS Functions and Graphs (6 weeks) PC.F.1: For a function that models a relationship between two quantities, interpret key features of graphs and tables in terms of the quantities,
Math 2413 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/2016
 Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
OR MSc Maths Revision Course
 OR MSc Maths Revision Course Tom Byrne School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh t.m.byrne@sms.ed.ac.uk 15 September 2017 General Information Today JCMB Lecture Theatre A, 09:30-12:30 Mathematics revision
OR MSc Maths Revision Course Tom Byrne School of Mathematics University of Edinburgh t.m.byrne@sms.ed.ac.uk 15 September 2017 General Information Today JCMB Lecture Theatre A, 09:30-12:30 Mathematics revision
Things you should have learned in Calculus II
 Things you should have learned in Calculus II 1 Vectors Given vectors v = v 1, v 2, v 3, u = u 1, u 2, u 3 1.1 Common Operations Operations Notation How is it calculated Other Notation Dot Product v u
Things you should have learned in Calculus II 1 Vectors Given vectors v = v 1, v 2, v 3, u = u 1, u 2, u 3 1.1 Common Operations Operations Notation How is it calculated Other Notation Dot Product v u
c) xy 3 = cos(7x +5y), y 0 = y3 + 7 sin(7x +5y) 3xy sin(7x +5y) d) xe y = sin(xy), y 0 = ey + y cos(xy) x(e y cos(xy)) e) y = x ln(3x + 5), y 0
 Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
Some Math 35 review problems With answers 2/6/2005 The following problems are based heavily on problems written by Professor Stephen Greenfield for his Math 35 class in spring 2005. His willingness to
Module 2: Reflecting on One s Problems
 MATH55 Module : Reflecting on One s Problems Main Math concepts: Translations, Reflections, Graphs of Equations, Symmetry Auxiliary ideas: Working with quadratics, Mobius maps, Calculus, Inverses I. Transformations
MATH55 Module : Reflecting on One s Problems Main Math concepts: Translations, Reflections, Graphs of Equations, Symmetry Auxiliary ideas: Working with quadratics, Mobius maps, Calculus, Inverses I. Transformations
JEE MAIN 2013 Mathematics
 JEE MAIN 01 Mathematics 1. The circle passing through (1, ) and touching the axis of x at (, 0) also passes through the point (1) (, 5) () (5, ) () (, 5) (4) ( 5, ) The equation of the circle due to point
JEE MAIN 01 Mathematics 1. The circle passing through (1, ) and touching the axis of x at (, 0) also passes through the point (1) (, 5) () (5, ) () (, 5) (4) ( 5, ) The equation of the circle due to point
Indefinite Integration
 Indefinite Integration 1 An antiderivative of a function y = f(x) defined on some interval (a, b) is called any function F(x) whose derivative at any point of this interval is equal to f(x): F'(x) = f(x)
Indefinite Integration 1 An antiderivative of a function y = f(x) defined on some interval (a, b) is called any function F(x) whose derivative at any point of this interval is equal to f(x): F'(x) = f(x)
UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE
 Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Math 250 Skills Assessment Test
 Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
Math 5 Skills Assessment Test Page Math 5 Skills Assessment Test The purpose of this test is purely diagnostic (before beginning your review, it will be helpful to assess both strengths and weaknesses).
3. Go over old quizzes (there are blank copies on my website try timing yourself!)
 final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems
 Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
Math 147 Exam II Practice Problems This review should not be used as your sole source for preparation for the exam. You should also re-work all examples given in lecture, all homework problems, all lab
worked out from first principles by parameterizing the path, etc. If however C is a A path C is a simple closed path if and only if the starting point
 III.c Green s Theorem As mentioned repeatedly, if F is not a gradient field then F dr must be worked out from first principles by parameterizing the path, etc. If however is a simple closed path in the
III.c Green s Theorem As mentioned repeatedly, if F is not a gradient field then F dr must be worked out from first principles by parameterizing the path, etc. If however is a simple closed path in the
4 Partial Differentiation
 4 Partial Differentiation Many equations in engineering, physics and mathematics tie together more than two variables. For example Ohm s Law (V = IR) and the equation for an ideal gas, PV = nrt, which
4 Partial Differentiation Many equations in engineering, physics and mathematics tie together more than two variables. For example Ohm s Law (V = IR) and the equation for an ideal gas, PV = nrt, which
1. The positive zero of y = x 2 + 2x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to
 SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
SAT II - Math Level Test #0 Solution SAT II - Math Level Test No. 1. The positive zero of y = x + x 3/5 is, to the nearest tenth, equal to (A) 0.8 (B) 0.7 + 1.1i (C) 0.7 (D) 0.3 (E). 3 b b 4ac Using Quadratic
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 2010 SYLLABUS
 TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
TEST CODE: MIII (Objective type) 200 SYLLABUS Algebra Permutations and combinations. Binomial theorem. Theory of equations. Inequalities. Complex numbers and De Moivre s theorem. Elementary set theory.
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems
 Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Solutions to old Exam 3 problems Hi students! I am putting this version of my review for the Final exam review here on the web site, place and time to be announced. Enjoy!! Best, Bill Meeks PS. There are
Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations
 Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.1.1 Solve Simple Equations Involving Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations 0.2.1 Use the
Pre-Calculus Chapter 0. Solving Equations and Inequalities 0.1 Solving Equations with Absolute Value 0.1.1 Solve Simple Equations Involving Absolute Value 0.2 Solving Quadratic Equations 0.2.1 Use the
MATHEMATICS LEARNING AREA. Methods Units 1 and 2 Course Outline. Week Content Sadler Reference Trigonometry
 MATHEMATICS LEARNING AREA Methods Units 1 and 2 Course Outline Text: Sadler Methods and 2 Week Content Sadler Reference Trigonometry Cosine and Sine rules Week 1 Trigonometry Week 2 Radian Measure Radian
MATHEMATICS LEARNING AREA Methods Units 1 and 2 Course Outline Text: Sadler Methods and 2 Week Content Sadler Reference Trigonometry Cosine and Sine rules Week 1 Trigonometry Week 2 Radian Measure Radian
Fall 2009 Math 113 Final Exam Solutions. f(x) = 1 + ex 1 e x?
 . What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
. What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
Mathematics, Algebra, and Geometry
 Mathematics, Algebra, and Geometry by Satya http://www.thesatya.com/ Contents 1 Algebra 1 1.1 Logarithms............................................ 1. Complex numbers........................................
Mathematics, Algebra, and Geometry by Satya http://www.thesatya.com/ Contents 1 Algebra 1 1.1 Logarithms............................................ 1. Complex numbers........................................
PGT Mathematics. 1. The domain of f(x) = is:-
 PGT Mathematics 1. The domain of f(x) = is:- a. (-2, + ) b. R-{-1, -2, -3} c. (-3, + )-{-1, -2} d. R-{-1, -2} 2. If f is a function such that f(0) = 2, f(1) = 3 & f(x+2) = 2f(x)-f(x + 1) for every real
PGT Mathematics 1. The domain of f(x) = is:- a. (-2, + ) b. R-{-1, -2, -3} c. (-3, + )-{-1, -2} d. R-{-1, -2} 2. If f is a function such that f(0) = 2, f(1) = 3 & f(x+2) = 2f(x)-f(x + 1) for every real
UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST Spring 2018 Calculus Test
 UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST Spring 2018 Calculus Test NAME: SCHOOL: 1. Let f be some function for which you know only that if 0 < x < 1, then f(x) 5 < 0.1. Which of the following
UNIVERSITY OF HOUSTON HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS CONTEST Spring 2018 Calculus Test NAME: SCHOOL: 1. Let f be some function for which you know only that if 0 < x < 1, then f(x) 5 < 0.1. Which of the following
Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank ( )
 Class : XI Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank (07 8) Subject : Math s Q. For all sets A and B, (A B) (A B) A. LHS (A B) (A B) [(A B) A] [(A B) B] A A B A RHS Hence, given statement is true. Q. For
Class : XI Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank (07 8) Subject : Math s Q. For all sets A and B, (A B) (A B) A. LHS (A B) (A B) [(A B) A] [(A B) B] A A B A RHS Hence, given statement is true. Q. For
Ch 4 Differentiation
 Ch 1 Partial fractions Ch 6 Integration Ch 2 Coordinate geometry C4 Ch 5 Vectors Ch 3 The binomial expansion Ch 4 Differentiation Chapter 1 Partial fractions We can add (or take away) two fractions only
Ch 1 Partial fractions Ch 6 Integration Ch 2 Coordinate geometry C4 Ch 5 Vectors Ch 3 The binomial expansion Ch 4 Differentiation Chapter 1 Partial fractions We can add (or take away) two fractions only
EXAM II CALCULUS BC SECTION I PART A Time-55 minutes Number of questions-28 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USED ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION
 6 EXAM II CALCULUS BC SECTION I PART A Time-55 minutes Number of questions-8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USE ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION irections: Solve each of the following problems, using the available
6 EXAM II CALCULUS BC SECTION I PART A Time-55 minutes Number of questions-8 A CALCULATOR MAY NOT BE USE ON THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION irections: Solve each of the following problems, using the available
Vectors, dot product, and cross product
 MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
MTH 201 Multivariable calculus and differential equations Practice problems Vectors, dot product, and cross product 1. Find the component form and length of vector P Q with the following initial point
First Degree Programme in Mathematics. Semester 1 MM 1141 Methods of Mathematics
 UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Mathematics Model Question Paper Semester 1 MM 1141 Methods of Mathematics Time: Three hours Maximum marks : 80 Section I All the first ten questions are
UNIVERSITY OF KERALA First Degree Programme in Mathematics Model Question Paper Semester 1 MM 1141 Methods of Mathematics Time: Three hours Maximum marks : 80 Section I All the first ten questions are
Candidates are expected to have available a calculator. Only division by (x + a) or (x a) will be required.
 Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
Revision Checklist Unit C2: Core Mathematics 2 Unit description Algebra and functions; coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane; sequences and series; trigonometry; exponentials and logarithms; differentiation;
y d y b x a x b Fundamentals of Engineering Review Fundamentals of Engineering Review 1 d x y Introduction - Algebra Cartesian Coordinates
 Fundamentals of Engineering Review RICHARD L. JONES FE MATH REVIEW ALGEBRA AND TRIG 8//00 Introduction - Algebra Cartesian Coordinates Lines and Linear Equations Quadratics Logs and exponents Inequalities
Fundamentals of Engineering Review RICHARD L. JONES FE MATH REVIEW ALGEBRA AND TRIG 8//00 Introduction - Algebra Cartesian Coordinates Lines and Linear Equations Quadratics Logs and exponents Inequalities
Things You Should Know Coming Into Calc I
 Things You Should Know Coming Into Calc I Algebraic Rules, Properties, Formulas, Ideas and Processes: 1) Rules and Properties of Exponents. Let x and y be positive real numbers, let a and b represent real
Things You Should Know Coming Into Calc I Algebraic Rules, Properties, Formulas, Ideas and Processes: 1) Rules and Properties of Exponents. Let x and y be positive real numbers, let a and b represent real
Pre-Calculus Team Questions Florida Regional Competition March C = ( )
 Florida Regional Competition March 08. Given: sin ( ) sin α = for 0 < α
Florida Regional Competition March 08. Given: sin ( ) sin α = for 0 < α
