FUZZY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD AND ITS APPLICATION
|
|
|
- Alannah Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TRENDS IN COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL MECHANICS W.A. Wall, K.U. Bletzinger and K. Schweizerhof (Eds.) CIMNE, Barcelona, Spain 2001 FUZZY FINITE ELEMENT METHOD AND ITS APPLICATION B. Möller*, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert Department of Ciil Engineering, Institute of Structural Analysis Dresden Uniersity of Technology, Dresden, Germany web page: rcswww.urz.tudresden.de/~stati/htmlhome/homest.html Abstract: In the Fuzzy Finite Element Method (FFEM) uncertain geometrical, material and loading parameters are treated as fuzzy alues. Uncertainties of the characteristic fuzziness may be obsered, e.g. in earthquae loading, impact loads, storm loading, terrorist attacs, damage processes or shortcomings in construction wor. Spatially distributed uncertainties are described in the method of finite elements using fuzzy functions. These fuzzy functions describe a bunch of functions with uncertain bunch parameters. The introduced fuzzy functions enable fuzziness to be accounted for in the principle of irtual displacements or the particular ariational principle adopted. In order to sole the system of fuzzy differential equations and the system of fuzzy equations of the FFEM αleel optimization is applied. The FFEM approach is demonstrated by way of an application example. Key words: Fuzzy finite element method (FFEM), fuzzy function, αleel optimization 1 REMARKS ON UNCERTAINTY The uncertainty of data and information may be characterized by randomness, fuzziness or fuzzyrandomness; it is also possible to distinguish between stochastic and nonstochastic uncertainty. The property randomness is lined to specific preconditions: in particular, all elements of a sample must be generated under constant reproduction conditions. Informal and lexical uncertainty as well as uncertainty associated with human error and expert nowledge, on the other hand, possess the property fuzziness. These forms of uncertainty may be obsered, e.g. in earthquae loading, impact loads, storm loading, terrorist attacs, damage and aging processes or shortcomings in construction wor. In finite element analysis geometrical, material and loading data as well as model parameters may possess uncertainty. If sufficiently reliable stochastic data are not aailable, their uncertainty may be modeled by fuzziness. When specifying fuzziness, both objectie and subjectie information is taen into consideration.
2 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert In contrast to the latter, fuzzyrandomness is exhibited by data material possessing partly random properties, whose deried random parameters cannot be modeled with absolute certainty. Fuzzyrandomness combines randomness and fuzziness and is specified by means of fuzzy probability distribution functions. Fuzzyrandomness may arise, e.g. in the following context: the stochastic data material exhibits fuzziness, i.e. the sample alues hae doubtful accuracy or were obtained under unnown or nonconstant reproduction conditions. It is presupposed in the following deeloped fuzzy finite element method that the uncertainty may be specified as fuzziness. 2 MODELING OF UNCERTAINTY WITH FUZZY FUNCTIONS Physical parameters possessing fuzziness with regard to external loading or material, geometrical and model parameters may occur at all points of a structure. Depending on the dimensionality of the structure ß 1 bar structures, ß 2 plane structures, ß 3 3D structures % it is proposed to describe fuzziness using fuzzy functions. Fuzzy functions may describe uncertainty in different ways 1. Starting from a classical function f: X 6 Y, uncertainty may be present in the argument of the function, e.g. in the form f(x ), in the function f itself, e.g. in the form f(x) or simultaneously in the argument and the function itself, e.g. in the form f (x ). The symbol ~ denotes fuzziness. f(x ) is referred to as the fuzzy extension of nonfuzzy functions and f (x) is referred to as a fuzzy function with nonfuzzy arguments. The form f (x) appears to be particularly suitable for describing the fuzziness of physical parameters within the framewor of a finite element analysis. To eery crisp point x = {x 1, x 2, x 3 } it is possible to assign an uncertain physical parameter, whose distribution in ß n is described by the fuzzy function f (x). The permissibility of introducing fuzziness, also with regard to the position ector x, requires fuzzy functions of the form f (x ). Using f(x), on the other hand, it is only possible to describe uncertain geometrical parameters with restrictions. For structures in ß 1 and ß 2 fuzziness is permitted for the coordinate x 3. All geometrical parameters dependent on x 3, such as the thicness of structure elements or leel specifications for reinforcement in a crosssection, may be expressed as fuzzy parameters. Fuzzy functions with nonfuzzy arguments may be formulated in two different ways, depending on whether the image of x 0 X is a fuzzy set of y ' f(x) on Y or whether x is mapped onto Y using a fuzzy set of functions. In the first case, socalled fuzzifying functions are obtained, whereas in the second case, a fuzzy bunch of functions is obtained. The second form enables the numerical ealuation of the goerning finite element equations to be performed using αleel optimization; this forms the basis of the following considerations. A fuzzy bunch of functions f: X 6 Y is a fuzzy set F on Y X, i.e. each function f from X to Y has a membership alue µ F (f) in F and is a crisp function, which is referred to as an original. A fuzzy bunch is thus a multialued fuzzy relationship, due to the fact that if f 1 (x) and f 2 (x) are elements of the fuzzy set F, it holds that ý x * f 1 (x) = f 2 (x) = y with µ S (f 1 ) ú µ S (f 2 ). When applying αdiscretization the fuzzy bunch of functions may be represented to adantage in the form P (x) ' P (x); µ P (x) * P (x) ' [Pmin, (x); P max, (x)]; µ P (x) ' æ ' (0;1] (1) 2
3 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert In Figure 1 a cut through the fuzzy bunch at the point i is represented for the position ector x = x i. Figure 1: Cut through the fuzzy bunch at point i The fuzzy function P (x) is approximated by means of fuzzy alues at suitably distributed interpolation nodes in ß n. Fuzzy alues at interpolation nodes are fuzzy numbers, which describe the fuzziness of the physical parameter concerned at discrete points i. These discrete points may be (but not necessarily) identical to nodes in the finite element mesh. The functional alues at the nodes must, howeer, be determinable from the P (x). Three fuzzy alues at interpolation nodes x 1, x 2, x 3 are shown in Figure 2. P (x) is linearly approximated between these points. Figure 2: Approximation of the fuzzy function P (x) in ß 1 using fuzzy numbers at x 1, x 2, x 3 3
4 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert On each αleel the P α (x) of Eqn. (1) may be expressed by the bunch parameter s α. For the fuzzy function P (x) shown in Figure 2, P α (x) between x 1 and x 2 may be expressed in the form P (x) ' s % x * s ' s min, ;s max, ; æ ' (0; 1] (2) Using the fuzzy bunch parameter s, the form P (x) ' s % x (3) is also possible. The fuzzy bunch parameter s is shown in Figure 3. If all fuzzy bunch parameters s r are combined together in a bunch parameter ector s, P (x, s) then holds. Figure 3: Fuzzy bunch parameter s 3 FUZZY FINITE ELEMENTS The introduced fuzzy functions enable fuzziness to be accounted for in the principle of irtual displacements as well as in the underlying ariation principle adopted. Fuzzy extension is demonstrated here for structures in ß 1 and ß 2 for the principle of irtual displacements. For the position ectors x = {x 1, x 2, x 3 } the coordinates x 1 and x 2 must not exhibit fuzziness; the coordinate x 3, howeer, may possess fuzziness. A displacement field (x) with fuzziness is chosen. (x) ' p with x ' (x 1,x 2 ) (e) ' p p ' A (e) (x) ' A (e) ' (e) (4) With the restriction of a linear relationship between strains and displacements, the following is obtained Moreoer, a linear material law is assumed. ḡ (x) ' p ' A (e) ' (e) (5) (x) ' ḡ (x) ' (e) (6) 4
5 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert For irtual displacements and irtual strains, the following is chosen: (x) ' p ' (e) ḡ(x) ' (e) The irtual internal fuzzy wor follows from (7) Ā i ' mv ḡ T (x) dv Ā i ' & T mv H T (e) (8) with the fuzzy element stiffness matrix K (e) ' mv H HdV (9) For the irtual external fuzzy wor the following holds under consideration of timedependent fuzzy surface forces as well as mass, inertial and damping forces possessing fuzziness: A a ' T F(e, t) T p M (x) dv % mv irtual wor of nodal forces irtual wor of mass forces % mo T p % (x, t) da O & mv T (x, t) dv irtual wor of timedependent surface forces irtual wor of inertial forces & mv T 0 (x, t) dv irtual wor of damping forces (10) Ā a Time t is still introduced into as a deterministic alue. Using the familiar abbreiations for element e, the following is obtained from Ā i & Ā a ' 0 F (e, t) ' F (e, t) % K (e, t) % M (e, t) % D 0 (e, t) (11) This yields a system of second order fuzzy differential equations for the structure which, for the static case, reduces to % 0 % ' F, (12) If nonlinearities are present, incremental forms must be used. ' F (13) 5
6 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert 4 SOLUTION TECHNIQUES The fuzziness of the n FF fuzzy functions P (x, s ), = 1, 2,..., n FF entering Eqns. (12) and (13) is expressed by the fuzzy elements of the bunch parameter ector s ' s 1,s 2,..., s j,..., s. As each fuzzy function r P(x, s) consists of a bunch ofcrisp functions f with membership alues µ P (f) the originals Eqns. (12) and (13) may be soled on an originaltooriginal wise by familiar methods. The two equations represent a mapping operator for each original of the form ' f s 1,s 2,..., s j,..., s r. (14) The goerning originals are determined for each αleel by αleel optimization 2. Figure 4: Mapping of the input alues and onto the fuzzy result alue s1 s 2 j 6
7 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert All fuzzy bunch parameters are discretized using the same number of αleels. The α leel set s j, is assigned to each bunch parameter s on the leel α, and all form j s j, the crisp subspace S. With the aid of the mapping operator of Eqn. (14), elements of the αleel set j, of the fuzzy result alue may be computed on the αleel α. The j mapping of all elements of S yields the crisp subspace V of the result space. In the case of conex fuzzy result alues it is sufficient to determine the largest and smallest element of the αleel set j,. Two points of the membership function of the result alue j are then nown on αleel α. This method is illustrated in Figure 4 for two bunch parameters s1 und s 2. 5 EXAMPLE The FFEM approach is demonstrated by way of an example. The reinforced concrete folded plate structure shown in Figure 5 is computed under consideration of the goerning nonlinearities of the reinforced concrete and fuzziness associated with the superficial load, the concrete compressie strength and the position of the reinforcement. Figure 5: Geometry, finite element model 7
8 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert The extension for eery plane of the folded plate structure in ß 2 is crisp. The system is meshed using 48 finite elements. Each element, with an oerall thicness of 10 cm, was modeled using 7 equidistant concrete layers, with two smeared mesh reinforcement layers each on the upper and lower surfaces (see Figure 5). The concrete material law according to Kupfer/Lin and a bilinear material law for reinforcement steel were applied. Tensile cracs in the concrete were accounted for in each element on a layertolayer basis according to the concept of smeared fixed cracs. The superficial load with fuzziness was increased incrementally up to the prescribed serice load. Selected result alues were computed at this stage of loading. Under consideration of the fuzziness of the uncertain input alues, the result alues are also fuzzy numbers. Inestigation 1: The superficial load and the concrete compressie strength are fuzzy input alues. The superficial load is specified as a linear fuzzy function with 3 bunch parameters, which are assigned to the fuzzy alues at interpolation nodes at the corners 3, 5, 6. The fuzzy alues at interpolation nodes are specified by the membership function µ(p) gien in Figure 6. A crisp function from the bunch of functions is shown in Figure 6 for one αleel and three alues s α =[s min, α ; s max, α ]. A linear fuzzy function is also chosen for the concrete compressie strength. Assuming that each crisp function of the respectie fuzzy bunch of functions describes a plane parallel to the folded plate planes 1 and 2 at the same distance from the folded plate planes, one bunch parameter is sufficient for the purposes of definition. This bunch parameter is assigned to the membership function µ(β R ) (Figure 6). As an example of these results the fuzzy load displacement dependency for the displacement 3 of node 63 under incremental load increase up to the serice load (ν = 1) is shown in Figure 7. Figure 6: Fuzzy function, membership functions 8
9 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert ν µ( 3 ~ ) ~ 3 [cm] Figure 7: Fuzzy loaddisplacement dependency for 3 of node 63 Inestigation 2: The fuzzy input alues in this case are position of reinforcement layer 11 and the superficial load. It is also assumed for both assigned fuzzy functions that each crisp function of the fuzzy bunch of functions describes a plane parallel to plane 2 of the folded plate. Two bunch parameters are thus required, which must be chosen from µ(h 1 ) and µ(p) (Figure 8). In this inestigation the concrete compressie strength is taen to be a deterministic alue equal to the alue of the fuzzy bunch parameter for µ(β R ) = 1. From these results the fuzzy loaddisplacement dependency for the displacement 3 of node 63 is presented (Figure 9). Figure 8: Membership functions of the input alues 9
10 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf and J.U. Sicert Figure 9: Fuzzy loaddisplacement dependency for 3 of node 63 6 REFERENCES [1] Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Fuzzy Sets and Systems Academic Press, New Yor, 1980 [2] Möller, B.; Graf, W.; Beer, M. Fuzzy structural analysis using αleel optimization Computational Mechanics 26 (2000) 6, [3] Bandemer, H.; Näther, W. Fuzzy Data Analysis Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht,
Structural Design under Fuzzy Randomness
 NSF workshop on Reliable Engineering Computing, September 15-17, 2004 Center for Reliable Engineering Computing, Georgia Tech Savannah, GA Structural Design under Fuzzy Randomness Michael Beer 1) Martin
NSF workshop on Reliable Engineering Computing, September 15-17, 2004 Center for Reliable Engineering Computing, Georgia Tech Savannah, GA Structural Design under Fuzzy Randomness Michael Beer 1) Martin
Fuzzy probabilistic method for the safety assessment
 B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf, A. Hoffmann, J.U. Sickert Fuzzy probabilistic method for the safety assessment Abstract The safety of structures may only be realistically assessed provided all input data
B. Möller, M. Beer, W. Graf, A. Hoffmann, J.U. Sickert Fuzzy probabilistic method for the safety assessment Abstract The safety of structures may only be realistically assessed provided all input data
Institute for Statics und Dynamics of Structures Fuzzy probabilistic safety assessment
 Institute for Statics und Dynamics of Structures Fuzzy probabilistic safety assessment Bernd Möller Fuzzy probabilistic safety assessment randomness fuzzy randomness fuzzyness failure Fuzzy- Probabilistik
Institute for Statics und Dynamics of Structures Fuzzy probabilistic safety assessment Bernd Möller Fuzzy probabilistic safety assessment randomness fuzzy randomness fuzzyness failure Fuzzy- Probabilistik
Fuzzy probabilistic structural analysis considering fuzzy random functions
 Fuzzy probabilistic structural analysis considering fuzzy random functions.-u. Sickert, M. Beer, W. Graf & B. Möller Institute of Structural Analysis, Dresden University of Technology, Germany Keywords:
Fuzzy probabilistic structural analysis considering fuzzy random functions.-u. Sickert, M. Beer, W. Graf & B. Möller Institute of Structural Analysis, Dresden University of Technology, Germany Keywords:
CONSTRUCTION PROCESS NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF MALLORCA CATHEDRAL
 CONSTRUCTION PROCESS NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF MALLORCA CATHEDRAL Roca, Pere 1 ; Pelà, Luca 2 ; Cerera, Miguel 3 ; Clemente, Roberto 4 1 PhD, Professor, Technical Uniersity of Catalonia
CONSTRUCTION PROCESS NUMERICAL SIMULATION AND SEISMIC ASSESSMENT OF MALLORCA CATHEDRAL Roca, Pere 1 ; Pelà, Luca 2 ; Cerera, Miguel 3 ; Clemente, Roberto 4 1 PhD, Professor, Technical Uniersity of Catalonia
Boundary Element Method Calculation of Moment Transfer Parameters in Slab-Column Connections
 ACI STRUCTURAL JOURNAL Title no. 107-S16 TECHNICAL PAPER Boundary Element Method Calculation of Moment Transfer Parameters in Slab-Column Connections by Mohammed A. Nazief, Youssef F. Rashed, and Wael
ACI STRUCTURAL JOURNAL Title no. 107-S16 TECHNICAL PAPER Boundary Element Method Calculation of Moment Transfer Parameters in Slab-Column Connections by Mohammed A. Nazief, Youssef F. Rashed, and Wael
Fuzzy Randomness. Bernd Moller Michael Beer
 Fuzzy Randomness Bernd Moller Michael Beer Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Engineering ONLINE LIBRARY springeronline.com Bernd Moller Michael Beer Fuzzy Randomne Uncertainty in Civil Engineering
Fuzzy Randomness Bernd Moller Michael Beer Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg GmbH Engineering ONLINE LIBRARY springeronline.com Bernd Moller Michael Beer Fuzzy Randomne Uncertainty in Civil Engineering
THE ANALYSIS OF THE CONVECTIVE-CONDUCTIVE HEAT TRANSFER IN THE BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS. Zbynek Svoboda
 THE NLSIS OF THE CONECTIE-CONDUCTIE HET TRNSFER IN THE BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS Zbynek Soboda Czech Technical Uniersity in Prague Faculty of Ciil Engineering 166 29 Prague 6 - Czech Republic BSTRCT The numerical
THE NLSIS OF THE CONECTIE-CONDUCTIE HET TRNSFER IN THE BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS Zbynek Soboda Czech Technical Uniersity in Prague Faculty of Ciil Engineering 166 29 Prague 6 - Czech Republic BSTRCT The numerical
Module 1. Energy Methods in Structural Analysis
 Module 1 Energy Methods in Structural Analysis esson 5 Virtual Work Instructional Objecties After studying this lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Define Virtual Work.. Differentiate between external
Module 1 Energy Methods in Structural Analysis esson 5 Virtual Work Instructional Objecties After studying this lesson, the student will be able to: 1. Define Virtual Work.. Differentiate between external
Continuum model for inelastic behaviour of masonry
 Continuum model for inelastic behaiour of masonry Luca Pelà 1, Miguel Cerera 2, Pere Roca 2 1 DICAM Department, Uniersity of Bologna, Italy E-mail: luca.pela@unibo.it 2 Technical Uniersity of Catalonia,
Continuum model for inelastic behaiour of masonry Luca Pelà 1, Miguel Cerera 2, Pere Roca 2 1 DICAM Department, Uniersity of Bologna, Italy E-mail: luca.pela@unibo.it 2 Technical Uniersity of Catalonia,
Sample Average Approximation for Stochastic Empty Container Repositioning
 Sample Aerage Approimation for Stochastic Empty Container Repositioning E Peng CHEW a, Loo Hay LEE b, Yin LOG c Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering ational Uniersity of Singapore Singapore 9260
Sample Aerage Approimation for Stochastic Empty Container Repositioning E Peng CHEW a, Loo Hay LEE b, Yin LOG c Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering ational Uniersity of Singapore Singapore 9260
Section 6: PRISMATIC BEAMS. Beam Theory
 Beam Theory There are two types of beam theory aailable to craft beam element formulations from. They are Bernoulli-Euler beam theory Timoshenko beam theory One learns the details of Bernoulli-Euler beam
Beam Theory There are two types of beam theory aailable to craft beam element formulations from. They are Bernoulli-Euler beam theory Timoshenko beam theory One learns the details of Bernoulli-Euler beam
Investigation on Ring Valve Motion and Impact Stress in Reciprocating Compressors
 Purdue Uniersity Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2010 Inestigation on Ring Vale Motion and Impact Stress in Reciprocating Compressors Yu Wang
Purdue Uniersity Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2010 Inestigation on Ring Vale Motion and Impact Stress in Reciprocating Compressors Yu Wang
Sixth World Conference on Structural Control and Monitoring
 Sixth World Conference on Structural Control and Monitoring Proceedings of the 6th edition of the World Conference of the International Association for Structural Control and Monitoring (IACSM), held in
Sixth World Conference on Structural Control and Monitoring Proceedings of the 6th edition of the World Conference of the International Association for Structural Control and Monitoring (IACSM), held in
A Regularization Framework for Learning from Graph Data
 A Regularization Framework for Learning from Graph Data Dengyong Zhou Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics Spemannstr. 38, 7076 Tuebingen, Germany Bernhard Schölkopf Max Planck Institute for
A Regularization Framework for Learning from Graph Data Dengyong Zhou Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics Spemannstr. 38, 7076 Tuebingen, Germany Bernhard Schölkopf Max Planck Institute for
Development and Validation of a Two-Phase Model for Reinforced Soil by Considering Nonlinear Behavior of Matrix
 Deelopment and Validation of a Two-Phase Model for Reinforced Soil by Considering Nonlinear Behaior of Matrix Ehsan Seyedi Hosseininia, Aff.ASCE 1 ; and Orang Farzaneh 2 Abstract: The paper presents the
Deelopment and Validation of a Two-Phase Model for Reinforced Soil by Considering Nonlinear Behaior of Matrix Ehsan Seyedi Hosseininia, Aff.ASCE 1 ; and Orang Farzaneh 2 Abstract: The paper presents the
Access from the University of Nottingham repository:
 Li, Y. and Yang, Y.M. and Roberts, G.W. and Yu, H.S. (217) Discussion: "Radial strain behaiors and stress state interpretation of soil under direct simple shear" by X. Kang, Y. Cheng, and L. Ge. Journal
Li, Y. and Yang, Y.M. and Roberts, G.W. and Yu, H.S. (217) Discussion: "Radial strain behaiors and stress state interpretation of soil under direct simple shear" by X. Kang, Y. Cheng, and L. Ge. Journal
S. Freitag, B. T. Cao, J. Ninić & G. Meschke
 SFB 837 Interaction Modeling Mechanized Tunneling S Freitag, B T Cao, J Ninić & G Meschke Institute for Structural Mechanics Ruhr University Bochum 1 Content 1 Motivation 2 Process-oriented FE model for
SFB 837 Interaction Modeling Mechanized Tunneling S Freitag, B T Cao, J Ninić & G Meschke Institute for Structural Mechanics Ruhr University Bochum 1 Content 1 Motivation 2 Process-oriented FE model for
Probabilistic Engineering Design
 Probabilistic Engineering Design Chapter One Introduction 1 Introduction This chapter discusses the basics of probabilistic engineering design. Its tutorial-style is designed to allow the reader to quickly
Probabilistic Engineering Design Chapter One Introduction 1 Introduction This chapter discusses the basics of probabilistic engineering design. Its tutorial-style is designed to allow the reader to quickly
Fuzzy analysis as alternative to stochastic methods theoretical aspects
 4. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 2005 Robustheit Fuzzy analysis as alternative to stochastic methods theoretical aspects Bernd Möller, Michael Beer, Martin Liebscher TU Dresden, Germany Abstract: A realistic
4. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Bamberg 2005 Robustheit Fuzzy analysis as alternative to stochastic methods theoretical aspects Bernd Möller, Michael Beer, Martin Liebscher TU Dresden, Germany Abstract: A realistic
DESIGN METHOD BASED ON THE CONCEPT OF EMERGENCE AND ITS APPLICATION
 DESIGN METHOD BASED ON THE CONCEPT OF EMERGENCE AND ITS APPLICATION Koichiro Sato¹ and Yoshiyuki Matsuoka 2 ¹ Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio Uniersity, Yokohama, Japan Koichiro_Sato@a7.keio.jp,
DESIGN METHOD BASED ON THE CONCEPT OF EMERGENCE AND ITS APPLICATION Koichiro Sato¹ and Yoshiyuki Matsuoka 2 ¹ Graduate School of Science and Technology, Keio Uniersity, Yokohama, Japan Koichiro_Sato@a7.keio.jp,
A. Idesman. Keywords: time integration, spurious oscillations, numerical dispersion
 COMPDYN 0 rd ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering M. Papadrakakis, M. Fragiadakis, V. Pleris (eds.) Corfu, Greece, -8 May 0 ACCURATE NUMERICAL
COMPDYN 0 rd ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering M. Papadrakakis, M. Fragiadakis, V. Pleris (eds.) Corfu, Greece, -8 May 0 ACCURATE NUMERICAL
SIMULATIONS OF CHARACTERISTICS OF TUNED LIQUID COLUMN DAMPER USING AN ELLIPTICAL FLOW PATH ESTIMATION METHOD
 October -7, 008, Beijing, China SIMULATIONS OF CHARACTERISTICS OF TUNED LIQUID COLUMN DAMPER USING AN ELLIPTICAL FLOW PATH ESTIMATION METHOD P. Chaiiriyawong, S. Limkatanyu and T. Pinkaew 3 Lecturer, Dept.
October -7, 008, Beijing, China SIMULATIONS OF CHARACTERISTICS OF TUNED LIQUID COLUMN DAMPER USING AN ELLIPTICAL FLOW PATH ESTIMATION METHOD P. Chaiiriyawong, S. Limkatanyu and T. Pinkaew 3 Lecturer, Dept.
Spectral methods for fuzzy structural dynamics: modal vs direct approach
 Spectral methods for fuzzy structural dynamics: modal vs direct approach S Adhikari Zienkiewicz Centre for Computational Engineering, College of Engineering, Swansea University, Wales, UK IUTAM Symposium
Spectral methods for fuzzy structural dynamics: modal vs direct approach S Adhikari Zienkiewicz Centre for Computational Engineering, College of Engineering, Swansea University, Wales, UK IUTAM Symposium
ULTIMATE BEARING CAPACITY OF FOOTING ON SANDY SOIL AGAINST COMBINED LOAD OF VERTICAL, HORIZONTAL AND MOMENT LOADS
 Int. J. of GEOMATE, Feb., 06, Vol. 0, No. (Sl. No. 9), pp. 649-655 Geotech., Const. Mat. and En., ISSN: 86-98(P), 86-990(O), Japan ULTIMATE BEARING CAPACITY OF FOOTING ON SANDY SOIL AGAINST COMBINED LOAD
Int. J. of GEOMATE, Feb., 06, Vol. 0, No. (Sl. No. 9), pp. 649-655 Geotech., Const. Mat. and En., ISSN: 86-98(P), 86-990(O), Japan ULTIMATE BEARING CAPACITY OF FOOTING ON SANDY SOIL AGAINST COMBINED LOAD
different formulas, depending on whether or not the vector is in two dimensions or three dimensions.
 ectors The word ector comes from the Latin word ectus which means carried. It is best to think of a ector as the displacement from an initial point P to a terminal point Q. Such a ector is expressed as
ectors The word ector comes from the Latin word ectus which means carried. It is best to think of a ector as the displacement from an initial point P to a terminal point Q. Such a ector is expressed as
Sets of Joint Probability Measures Generated by Weighted Marginal Focal Sets
 Sets of Joint Probability Measures Generated by Weighted Marginal Focal Sets Thomas Fetz Institut für Technische Mathemati, Geometrie und Bauinformati Universität Innsbruc, Austria fetz@mat.uib.ac.at Abstract
Sets of Joint Probability Measures Generated by Weighted Marginal Focal Sets Thomas Fetz Institut für Technische Mathemati, Geometrie und Bauinformati Universität Innsbruc, Austria fetz@mat.uib.ac.at Abstract
Solution to 1-D consolidation of non-homogeneous soft clay *
 Xie et al. / J Zhejiang Uni SCI 25 6A(Suppl. I):29-34 29 Journal of Zhejiang Uniersity SCIENCE ISSN 19-395 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Solution to 1-D consolidation of non-homogeneous
Xie et al. / J Zhejiang Uni SCI 25 6A(Suppl. I):29-34 29 Journal of Zhejiang Uniersity SCIENCE ISSN 19-395 http://www.zju.edu.cn/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Solution to 1-D consolidation of non-homogeneous
Sensitivity and Reliability Analysis of Nonlinear Frame Structures
 Sensitivity and Reliability Analysis of Nonlinear Frame Structures Michael H. Scott Associate Professor School of Civil and Construction Engineering Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar April 8,
Sensitivity and Reliability Analysis of Nonlinear Frame Structures Michael H. Scott Associate Professor School of Civil and Construction Engineering Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar April 8,
Mean-variance receding horizon control for discrete time linear stochastic systems
 Proceedings o the 17th World Congress The International Federation o Automatic Control Seoul, Korea, July 6 11, 008 Mean-ariance receding horizon control or discrete time linear stochastic systems Mar
Proceedings o the 17th World Congress The International Federation o Automatic Control Seoul, Korea, July 6 11, 008 Mean-ariance receding horizon control or discrete time linear stochastic systems Mar
Neural Network Based Response Surface Methods a Comparative Study
 . LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Ulm Robustheit / Optimierung II Neural Network Based Response Surface Methods a Comparative Study Wolfram Beyer, Martin Liebscher, Michael Beer, Wolfgang Graf TU Dresden, Germany
. LS-DYNA Anwenderforum, Ulm Robustheit / Optimierung II Neural Network Based Response Surface Methods a Comparative Study Wolfram Beyer, Martin Liebscher, Michael Beer, Wolfgang Graf TU Dresden, Germany
Statement: This paper will also be published during the 2017 AUTOREG conference.
 Model Predictie Control for Autonomous Lateral Vehicle Guidance M. Sc. Jochen Prof. Dr.-Ing. Steffen Müller TU Berlin, Institute of Automotie Engineering Germany Statement: This paper will also be published
Model Predictie Control for Autonomous Lateral Vehicle Guidance M. Sc. Jochen Prof. Dr.-Ing. Steffen Müller TU Berlin, Institute of Automotie Engineering Germany Statement: This paper will also be published
Damage Detection in Wind Turbine Towers using a Finite Element Model and Discrete Wavelet Transform of Strain Signals
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Damage Detection in Wind Turbine Towers using a Finite Element Model and Discrete Wavelet Transform of Strain Signals To cite this article: A Kenna
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Damage Detection in Wind Turbine Towers using a Finite Element Model and Discrete Wavelet Transform of Strain Signals To cite this article: A Kenna
Multi Criteria Analysis of the Supporting System of a Reciprocating Compressor
 Purdue Uniersity Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Multi Criteria Analysis of the Supporting System of a Reciprocating Compressor M. Lamantia
Purdue Uniersity Purdue e-pubs International Compressor Engineering Conference School of Mechanical Engineering 2000 Multi Criteria Analysis of the Supporting System of a Reciprocating Compressor M. Lamantia
Aerodynamic Admittance Function of Tall Buildings
 Aerodynamic Admittance Function o Tall Buildings in hou a Ahsan Kareem b a alou Engineering Int l, Inc., 75 W. Campbell Rd, Richardson, T, USA b Nataz odeling Laboratory, Uniersity o Notre Dame, Notre
Aerodynamic Admittance Function o Tall Buildings in hou a Ahsan Kareem b a alou Engineering Int l, Inc., 75 W. Campbell Rd, Richardson, T, USA b Nataz odeling Laboratory, Uniersity o Notre Dame, Notre
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 978-1-107-1788-3 Classical and Quantum Thermal Physics The Kinetic Theory of Gases CHAPTER 1 1.0 Kinetic Theory, Classical and Quantum Thermodynamics Two important components of the unierse are: the matter
978-1-107-1788-3 Classical and Quantum Thermal Physics The Kinetic Theory of Gases CHAPTER 1 1.0 Kinetic Theory, Classical and Quantum Thermodynamics Two important components of the unierse are: the matter
Efficient solution of interval optimization problem
 Math Meth Oper Res (212) 76:273 288 DOI 1.17/s186-12-399- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficient solution of interal optimization problem A. K. Bhurjee G. Panda Receied: 6 June 212 / Accepted: 4 August 212 / Published
Math Meth Oper Res (212) 76:273 288 DOI 1.17/s186-12-399- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficient solution of interal optimization problem A. K. Bhurjee G. Panda Receied: 6 June 212 / Accepted: 4 August 212 / Published
A fuzzy finite element analysis technique for structural static analysis based on interval fields
 A fuzzy finite element analysis technique for structural static analysis based on interval fields Wim Verhaeghe, Maarten De Munck, Wim Desmet, Dirk Vandepitte and David Moens Department of Mechanical Engineering,
A fuzzy finite element analysis technique for structural static analysis based on interval fields Wim Verhaeghe, Maarten De Munck, Wim Desmet, Dirk Vandepitte and David Moens Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Damage detection in a sandwich composite beam using wavelet transforms
 Damage detection in a sandwich composite beam using waelet transforms T. A. Dawood *a, R. A. Shenoi a, S. M. Veres a, M. Sahin a, M. J Gunning b a School of Engineering Sciences, Uniersity of Southampton,
Damage detection in a sandwich composite beam using waelet transforms T. A. Dawood *a, R. A. Shenoi a, S. M. Veres a, M. Sahin a, M. J Gunning b a School of Engineering Sciences, Uniersity of Southampton,
ROBUST DESIGN OPTIMISATION IN ADVANCED HYBRID (FIBER-METAL LAMINATED) COMPOSITE STRUCTURES
 ROBUST DESIGN OPTIMISATION IN ADVANCED HYBRID (FIBER-METAL LAMINATED) COMPOSITE STRUCTURES C. Morillo, and D.S. Lee (S. Oller, G. Bugeda, E. Oñate) International Center for Numerical Methods in Engineering
ROBUST DESIGN OPTIMISATION IN ADVANCED HYBRID (FIBER-METAL LAMINATED) COMPOSITE STRUCTURES C. Morillo, and D.S. Lee (S. Oller, G. Bugeda, E. Oñate) International Center for Numerical Methods in Engineering
0 a 3 a 2 a 3 0 a 1 a 2 a 1 0
 Chapter Flow kinematics Vector and tensor formulae This introductory section presents a brief account of different definitions of ector and tensor analysis that will be used in the following chapters.
Chapter Flow kinematics Vector and tensor formulae This introductory section presents a brief account of different definitions of ector and tensor analysis that will be used in the following chapters.
VV = voltage across voltmeter = 9 (Rs + 500) = VsRv Vs. (500) = 9 (Rs + 500) Case ii VV = 13V VS=? RV = 50kΩ / V 20v RV = 1000 kω by (1)
 1 1. A resistor has oltage drop of 110.V and current of.a. the uncertainties in the measurement of oltage and current are ± 0.V and ±0.01 respectiely calculate the uncertainty in power calculation. Ans.
1 1. A resistor has oltage drop of 110.V and current of.a. the uncertainties in the measurement of oltage and current are ± 0.V and ±0.01 respectiely calculate the uncertainty in power calculation. Ans.
Stochastic structural dynamic analysis with random damping parameters
 Stochastic structural dynamic analysis with random damping parameters K. Sepahvand 1, F. Saati Khosroshahi, C. A. Geweth and S. Marburg Chair of Vibroacoustics of Vehicles and Machines Department of Mechanical
Stochastic structural dynamic analysis with random damping parameters K. Sepahvand 1, F. Saati Khosroshahi, C. A. Geweth and S. Marburg Chair of Vibroacoustics of Vehicles and Machines Department of Mechanical
Bilinear Quadrilateral (Q4): CQUAD4 in GENESIS
 Bilinear Quadrilateral (Q4): CQUAD4 in GENESIS The Q4 element has four nodes and eight nodal dof. The shape can be any quadrilateral; we ll concentrate on a rectangle now. The displacement field in terms
Bilinear Quadrilateral (Q4): CQUAD4 in GENESIS The Q4 element has four nodes and eight nodal dof. The shape can be any quadrilateral; we ll concentrate on a rectangle now. The displacement field in terms
University of Sheffield The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire
 The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire Chaoming Yu, I. W. Burgess, Z. Huang, R. J. Plank Department of Civil and Structural Engineering StiFF 05/09/2006 3D composite structures
The development of finite elements for 3D structural analysis in fire Chaoming Yu, I. W. Burgess, Z. Huang, R. J. Plank Department of Civil and Structural Engineering StiFF 05/09/2006 3D composite structures
On general error distributions
 ProbStat Forum, Volume 6, October 3, Pages 89 95 ISSN 974-335 ProbStat Forum is an e-journal. For details please isit www.probstat.org.in On general error distributions R. Vasudea, J. Vasantha Kumari Department
ProbStat Forum, Volume 6, October 3, Pages 89 95 ISSN 974-335 ProbStat Forum is an e-journal. For details please isit www.probstat.org.in On general error distributions R. Vasudea, J. Vasantha Kumari Department
An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term
 Machine Dynamics Research 2012, Vol. 36, No 1, 15 25 Abstract An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term Mikäel Barboteu, Ahmad Ramadan, Mircea Sofonea Uniersité de Perpignan, France
Machine Dynamics Research 2012, Vol. 36, No 1, 15 25 Abstract An Elastic Contact Problem with Normal Compliance and Memory Term Mikäel Barboteu, Ahmad Ramadan, Mircea Sofonea Uniersité de Perpignan, France
BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS
 Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol.., No. 1., (2005), pp. 83 94 BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS Vladimír Kutiš and Justín Murín Department
Journal of Computational and Applied Mechanics, Vol.., No. 1., (2005), pp. 83 94 BAR ELEMENT WITH VARIATION OF CROSS-SECTION FOR GEOMETRIC NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS Vladimír Kutiš and Justín Murín Department
Chapter 11 Collision Theory
 Chapter Collision Theory Introduction. Center o Mass Reerence Frame Consider two particles o masses m and m interacting ia some orce. Figure. Center o Mass o a system o two interacting particles Choose
Chapter Collision Theory Introduction. Center o Mass Reerence Frame Consider two particles o masses m and m interacting ia some orce. Figure. Center o Mass o a system o two interacting particles Choose
Transmission lines using a distributed equivalent circuit
 Cambridge Uniersity Press 978-1-107-02600-1 - Transmission Lines Equialent Circuits, Electromagnetic Theory, and Photons Part 1 Transmission lines using a distributed equialent circuit in this web serice
Cambridge Uniersity Press 978-1-107-02600-1 - Transmission Lines Equialent Circuits, Electromagnetic Theory, and Photons Part 1 Transmission lines using a distributed equialent circuit in this web serice
Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan
 Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan Instant download and all chapters Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan https://testbandata.com/download/solution-manual-first-course-finite-elementmethod-5th-edition-logan/
Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan Instant download and all chapters Solution Manual A First Course in the Finite Element Method 5th Edition Logan https://testbandata.com/download/solution-manual-first-course-finite-elementmethod-5th-edition-logan/
TIME-DEPENDENT ANALYSIS OF PARTIALLY PRESTRESSED CONTINUOUS COMPOSITE BEAMS
 2nd Int. PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 998 Budapest IME-DEPENDEN ANAYSIS OF PARIAY PRESRESSED CONINUOUS COMPOSIE BEAMS M. Sar and Assoc. Prof. J. apos 2 Slova echnical University, Faculty of Civil
2nd Int. PhD Symposium in Civil Engineering 998 Budapest IME-DEPENDEN ANAYSIS OF PARIAY PRESRESSED CONINUOUS COMPOSIE BEAMS M. Sar and Assoc. Prof. J. apos 2 Slova echnical University, Faculty of Civil
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Contact analysis for the modelling of anchors in concrete structures H. Walter*, L. Baillet** & M. Brunet* *Laboratoire de Mecanique des Solides **Laboratoire de Mecanique des Contacts-CNRS UMR 5514 Institut
Contact analysis for the modelling of anchors in concrete structures H. Walter*, L. Baillet** & M. Brunet* *Laboratoire de Mecanique des Solides **Laboratoire de Mecanique des Contacts-CNRS UMR 5514 Institut
A-level Mathematics. MM03 Mark scheme June Version 1.0: Final
 -leel Mathematics MM0 Mark scheme 660 June 0 Version.0: Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead ssessment Writer and considered, together with the releant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
-leel Mathematics MM0 Mark scheme 660 June 0 Version.0: Final Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead ssessment Writer and considered, together with the releant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
Towards Green Distributed Storage Systems
 Towards Green Distributed Storage Systems Abdelrahman M. Ibrahim, Ahmed A. Zewail, and Aylin Yener Wireless Communications and Networking Laboratory (WCAN) Electrical Engineering Department The Pennsylania
Towards Green Distributed Storage Systems Abdelrahman M. Ibrahim, Ahmed A. Zewail, and Aylin Yener Wireless Communications and Networking Laboratory (WCAN) Electrical Engineering Department The Pennsylania
midas Civil Dynamic Analysis
 Edgar De Los Santos Midas IT August 23 rd 2017 Contents: Introduction Eigen Value Analysis Response Spectrum Analysis Pushover Analysis Time History Analysis Seismic Analysis Seismic Analysis The seismic
Edgar De Los Santos Midas IT August 23 rd 2017 Contents: Introduction Eigen Value Analysis Response Spectrum Analysis Pushover Analysis Time History Analysis Seismic Analysis Seismic Analysis The seismic
Prediction of Roof Collapse for Rectangular Underground Openings
 Prediction of Roof Collapse for Rectangular Underground Openings M Suchowerska 1, J P Hambleton 2 and J P Carter 3 STRCT In order to effectiely predict the roof collapse of underground openings using continuum
Prediction of Roof Collapse for Rectangular Underground Openings M Suchowerska 1, J P Hambleton 2 and J P Carter 3 STRCT In order to effectiely predict the roof collapse of underground openings using continuum
An Optimal Split-Plot Design for Performing a Mixture-Process Experiment
 Science Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics 217; 5(1): 15-23 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjams doi: 1.11648/j.sjams.21751.13 ISSN: 2376-9491 (Print); ISSN: 2376-9513 (Online) An Optimal
Science Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics 217; 5(1): 15-23 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjams doi: 1.11648/j.sjams.21751.13 ISSN: 2376-9491 (Print); ISSN: 2376-9513 (Online) An Optimal
Static Pile Head Impedance using 3D Nonlinear FEM Analysis
 Static Pile Head Impedance using 3D Nonlinear FEM Analysis Ichiro NAGASHIMA Technology Center, Taisei Corporation, 344-1 Nasecho, Totsuka-ku, Yokohama 245-51, Japan, ichiro.nagashima@sakura.taisei.co.jp
Static Pile Head Impedance using 3D Nonlinear FEM Analysis Ichiro NAGASHIMA Technology Center, Taisei Corporation, 344-1 Nasecho, Totsuka-ku, Yokohama 245-51, Japan, ichiro.nagashima@sakura.taisei.co.jp
Effect of Fractal Dimension of Fine Aggregates on the Concrete Chloride Resistance
 5th International Conference on Durability of Concrete Structures Jun 30 Jul 1, 2016 Shenzhen Uniersity, Shenzhen, Guangdong Proince, P.R.China Effect of Fractal Dimension of Fine Aggregates on the Concrete
5th International Conference on Durability of Concrete Structures Jun 30 Jul 1, 2016 Shenzhen Uniersity, Shenzhen, Guangdong Proince, P.R.China Effect of Fractal Dimension of Fine Aggregates on the Concrete
Noise constrained least mean absolute third algorithm
 Noise constrained least mean absolute third algorithm Sihai GUAN 1 Zhi LI 1 Abstract: he learning speed of an adaptie algorithm can be improed by properly constraining the cost function of the adaptie
Noise constrained least mean absolute third algorithm Sihai GUAN 1 Zhi LI 1 Abstract: he learning speed of an adaptie algorithm can be improed by properly constraining the cost function of the adaptie
Stress analysis of a stepped bar
 Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE RECTLINEAR MOTION: UNIFORM ACCELERATION
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE RECTLINEAR MOTION: UNIFORM ACCELERATION Predict Obsere Explain Exercise 1 Take an A4 sheet of paper and a heay object (cricket ball, basketball, brick, book, etc). Predict what will
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE RECTLINEAR MOTION: UNIFORM ACCELERATION Predict Obsere Explain Exercise 1 Take an A4 sheet of paper and a heay object (cricket ball, basketball, brick, book, etc). Predict what will
Online Companion to Pricing Services Subject to Congestion: Charge Per-Use Fees or Sell Subscriptions?
 Online Companion to Pricing Serices Subject to Congestion: Charge Per-Use Fees or Sell Subscriptions? Gérard P. Cachon Pnina Feldman Operations and Information Management, The Wharton School, Uniersity
Online Companion to Pricing Serices Subject to Congestion: Charge Per-Use Fees or Sell Subscriptions? Gérard P. Cachon Pnina Feldman Operations and Information Management, The Wharton School, Uniersity
Politecnico di Torino. Porto Institutional Repository
 Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Article] Stability analysis of transportation networks with multiscale drier decisions Original Citation: Como, Giacomo; Sala, Ketan; Acemoglu, Daron;
Politecnico di Torino Porto Institutional Repository [Article] Stability analysis of transportation networks with multiscale drier decisions Original Citation: Como, Giacomo; Sala, Ketan; Acemoglu, Daron;
Scalar multiplication and algebraic direction of a vector
 Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 1: Geometric ectors Section 5 Scalar multiplication and algebraic direction of a ector What you need to know already: of a geometric ectors. Length and geometric
Roberto s Notes on Linear Algebra Chapter 1: Geometric ectors Section 5 Scalar multiplication and algebraic direction of a ector What you need to know already: of a geometric ectors. Length and geometric
PREEMPTIVE CONTROL OF MULTIPLY ACTUATED PROCESSES: APPLICATION TO MOISTURE CONTENT CONTROL IN PAPER MANUFACTURING USING SURROGATE MEASUREMENTS
 PREEMPTIVE CONTROL OF MULTIPLY ACTUATED PROCESSES: APPLICATION TO MOISTURE CONTENT CONTROL IN PAPER MANUFACTURING USING SURROGATE MEASUREMENTS Perry Y. Li Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Uniersity of Minnesota
PREEMPTIVE CONTROL OF MULTIPLY ACTUATED PROCESSES: APPLICATION TO MOISTURE CONTENT CONTROL IN PAPER MANUFACTURING USING SURROGATE MEASUREMENTS Perry Y. Li Dept. of Mechanical Engineering Uniersity of Minnesota
3D Finite Element analysis of stud anchors with large head and embedment depth
 3D Finite Element analysis of stud anchors with large head and embedment depth G. Periškić, J. Ožbolt & R. Eligehausen Institute for Construction Materials, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany
3D Finite Element analysis of stud anchors with large head and embedment depth G. Periškić, J. Ožbolt & R. Eligehausen Institute for Construction Materials, University of Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany
Simulations of bulk phases. Periodic boundaries. Cubic boxes
 Simulations of bulk phases ChE210D Today's lecture: considerations for setting up and running simulations of bulk, isotropic phases (e.g., liquids and gases) Periodic boundaries Cubic boxes In simulations
Simulations of bulk phases ChE210D Today's lecture: considerations for setting up and running simulations of bulk, isotropic phases (e.g., liquids and gases) Periodic boundaries Cubic boxes In simulations
Nonlinear Disturbance Decoupling for a Mobile Robotic Manipulator over Uneven Terrain
 Nonlinear Disturbance Decoupling for a Mobile Robotic Manipulator oer Uneen Terrain Joel Jimenez-Lozano Bill Goodwine Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering Uniersity of Noe Dame Noe Dame IN
Nonlinear Disturbance Decoupling for a Mobile Robotic Manipulator oer Uneen Terrain Joel Jimenez-Lozano Bill Goodwine Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering Uniersity of Noe Dame Noe Dame IN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) FUZZY FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A CONDUCTION HEAT TRANSFER PROBLEM
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976-6480 (Print) ISSN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN 0976 ISSN 0976-6480 (Print) ISSN
MODELLING FLUID FLOW IN STRESS SENSITIVE PETROLEUM RESERVOIR CONSIDERING FAULT REACTIVATION PROBLEM
 Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014 ol. 1 num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/eento/10wccm MODELLING FLUID FLOW IN STRESS SENSITIVE PETROLEUM RESERVOIR CONSIDERING FAULT REACTIVATION
Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014 ol. 1 num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/eento/10wccm MODELLING FLUID FLOW IN STRESS SENSITIVE PETROLEUM RESERVOIR CONSIDERING FAULT REACTIVATION
State-space Modelling of Hysteresis-based Control Schemes
 European Control Conference (ECC) July 7-9,, Zürich, Switzerland. State-space Modelling of Hysteresis-based Control Schemes Soumya Kundu Ian A. Hiskens Abstract The paper deelops a state-space model for
European Control Conference (ECC) July 7-9,, Zürich, Switzerland. State-space Modelling of Hysteresis-based Control Schemes Soumya Kundu Ian A. Hiskens Abstract The paper deelops a state-space model for
متلب سایت MatlabSite.com
 Vehicle Velocity Estimation based on Data fusion by Kalman Filtering for ABS Melika Amiri Graduate student in electrical engineering, Islamic Azad uniersity, Science and Research ehran, Iran Melika_64@yahoo.com
Vehicle Velocity Estimation based on Data fusion by Kalman Filtering for ABS Melika Amiri Graduate student in electrical engineering, Islamic Azad uniersity, Science and Research ehran, Iran Melika_64@yahoo.com
A nonparametric confidence interval for At-Risk-of-Poverty-Rate: an example of application
 A nonparametric confidence interal for At-Ris-of-Poerty-Rate: an example of application Wojciech Zielińsi Department of Econometrics and Statistics Warsaw Uniersity of Life Sciences Nowoursynowsa 159,
A nonparametric confidence interal for At-Ris-of-Poerty-Rate: an example of application Wojciech Zielińsi Department of Econometrics and Statistics Warsaw Uniersity of Life Sciences Nowoursynowsa 159,
Parameters Identification of Equivalent Circuit Diagrams for Li-Ion Batteries
 Parameters Identification of Equialent Circuit Diagrams for Li-Ion eries Ahmad ahmoun, Helmuth Biechl Uniersity of Applied ciences Kempten Ahmad.ahmoun@stud.fh-empten.de, biechl@fh-empten.de Abstract-eries
Parameters Identification of Equialent Circuit Diagrams for Li-Ion eries Ahmad ahmoun, Helmuth Biechl Uniersity of Applied ciences Kempten Ahmad.ahmoun@stud.fh-empten.de, biechl@fh-empten.de Abstract-eries
To string together six theorems of physics by Pythagoras theorem
 To string together six theorems of physics by Pythagoras theorem H. Y. Cui Department of Applied Physics Beijing Uniersity of Aeronautics and Astronautics Beijing, 00083, China ( May, 8, 2002 ) Abstract
To string together six theorems of physics by Pythagoras theorem H. Y. Cui Department of Applied Physics Beijing Uniersity of Aeronautics and Astronautics Beijing, 00083, China ( May, 8, 2002 ) Abstract
1 Nonlinear deformation
 NONLINEAR TRUSS 1 Nonlinear deformation When deformation and/or rotation of the truss are large, various strains and stresses can be defined and related by material laws. The material behavior can be expected
NONLINEAR TRUSS 1 Nonlinear deformation When deformation and/or rotation of the truss are large, various strains and stresses can be defined and related by material laws. The material behavior can be expected
GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Autumn Lecture. 9. Nonlinear Finite Element Method & Summary
 GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Autumn 2016 Lecture. 9. Nonlinear Finite Element Method & Summary To learn today The lecture should give you overview of how non-linear problems in Finite Element Method
GEO E1050 Finite Element Method Autumn 2016 Lecture. 9. Nonlinear Finite Element Method & Summary To learn today The lecture should give you overview of how non-linear problems in Finite Element Method
VORONOI APPLIED ELEMENT METHOD FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS: THEORY AND APPLICATION FOR LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR MATERIALS
 The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 008, Beijing, China VORONOI APPLIED ELEMENT METHOD FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS: THEORY AND APPLICATION FOR LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR MATERIALS K.
The 4 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering October -7, 008, Beijing, China VORONOI APPLIED ELEMENT METHOD FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS: THEORY AND APPLICATION FOR LINEAR AND NON-LINEAR MATERIALS K.
arxiv: v1 [cs.ni] 13 Aug 2013
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ni] 13 Aug 2013 arxiv: v1 [cs.ni] 13 Aug 2013](/thumbs/80/82243585.jpg) Robotic Message Ferrying for Wireless Networks using Coarse-Grained Backpressure Control Shangxing Wang Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Uniersity of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA Email: shangxiw@usc.edu
Robotic Message Ferrying for Wireless Networks using Coarse-Grained Backpressure Control Shangxing Wang Dept. of Electrical Engineering, Uniersity of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA Email: shangxiw@usc.edu
be ye transformed by the renewing of your mind Romans 12:2
 Lecture 12: Coordinate Free Formulas for Affine and rojectie Transformations be ye transformed by the reing of your mind Romans 12:2 1. Transformations for 3-Dimensional Computer Graphics Computer Graphics
Lecture 12: Coordinate Free Formulas for Affine and rojectie Transformations be ye transformed by the reing of your mind Romans 12:2 1. Transformations for 3-Dimensional Computer Graphics Computer Graphics
HPLP300 - Plate with Young modulus function of the temperature
 Titre : HPLP300 - Plaque aec module d Young fonction de l[...] Date : 04/08/2011 Page : 1/6 HPLP300 - Plate with Young modulus function of the temperature Summarized: This thermoelastic test makes it possible
Titre : HPLP300 - Plaque aec module d Young fonction de l[...] Date : 04/08/2011 Page : 1/6 HPLP300 - Plate with Young modulus function of the temperature Summarized: This thermoelastic test makes it possible
Hasna BenSaid Faculté des sciences de Gafsa Campus Universitaire Sidi Ahmed Zarroug 2112 Gafsa, Tunisie
 On the Ealuation of Linear and Non-Linear Models Using Data of Turbulent Channel Flows Hasna BenSaid bs_hasna@yahoo.fr Faculté des sciences de Gafsa Campus Uniersitaire Sidi Ahmed Zarroug Gafsa, Tunisie
On the Ealuation of Linear and Non-Linear Models Using Data of Turbulent Channel Flows Hasna BenSaid bs_hasna@yahoo.fr Faculté des sciences de Gafsa Campus Uniersitaire Sidi Ahmed Zarroug Gafsa, Tunisie
Lifted Generalized Dual Decomposition
 Lifted Generalized Dual Decomposition Nicholas Gallo Uniersity of California Irine Irine, CA 92637-3435 ngallo1@uci.edu Alexander Ihler Uniersity of California Irine Irine, CA 92637-3435 ihler@ics.uci.edu
Lifted Generalized Dual Decomposition Nicholas Gallo Uniersity of California Irine Irine, CA 92637-3435 ngallo1@uci.edu Alexander Ihler Uniersity of California Irine Irine, CA 92637-3435 ihler@ics.uci.edu
Assignment 4 (Solutions) NPTEL MOOC (Bayesian/ MMSE Estimation for MIMO/OFDM Wireless Communications)
 Assignment 4 Solutions NPTEL MOOC Bayesian/ MMSE Estimation for MIMO/OFDM Wireless Communications The system model can be written as, y hx + The MSE of the MMSE estimate ĥ of the aboe mentioned system
Assignment 4 Solutions NPTEL MOOC Bayesian/ MMSE Estimation for MIMO/OFDM Wireless Communications The system model can be written as, y hx + The MSE of the MMSE estimate ĥ of the aboe mentioned system
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5
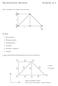 Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS
 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF THE INELASTIC SEISMIC RESPONSE OF RC STRUCTURES WITH ENERGY DISSIPATORS ABSTRACT : P Mata1, AH Barbat1, S Oller1, R Boroschek2 1 Technical University of Catalonia, Civil Engineering
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 115 A Noel Technique for Localizing the Scatterer in Inerse Profiling of Two Dimensional Circularly Symmetric Dielectric
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Symposium 2005, Hangzhou, China, August 22-26 115 A Noel Technique for Localizing the Scatterer in Inerse Profiling of Two Dimensional Circularly Symmetric Dielectric
Reduction of Random Variables in Structural Reliability Analysis
 Reduction of Random Variables in Structural Reliability Analysis S. Adhikari and R. S. Langley Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Trumpington Street Cambridge CB2 1PZ (U.K.) February 21,
Reduction of Random Variables in Structural Reliability Analysis S. Adhikari and R. S. Langley Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Trumpington Street Cambridge CB2 1PZ (U.K.) February 21,
Chapter 2 Unexpected Excessive Settlements: Kansai International Airport, Japan
 Chapter Unexpected Excessie Settlements: Kansai International Airport, Japan TABLE OF CONTENTS.1 Case Description... 4.1.1 Introduction... 4.1. Construction... 4.1.3 The history of settlements... 6.1.4
Chapter Unexpected Excessie Settlements: Kansai International Airport, Japan TABLE OF CONTENTS.1 Case Description... 4.1.1 Introduction... 4.1. Construction... 4.1.3 The history of settlements... 6.1.4
DISPENSA FEM in MSC. Nastran
 DISPENSA FEM in MSC. Nastran preprocessing: mesh generation material definitions definition of loads and boundary conditions solving: solving the (linear) set of equations components postprocessing: visualisation
DISPENSA FEM in MSC. Nastran preprocessing: mesh generation material definitions definition of loads and boundary conditions solving: solving the (linear) set of equations components postprocessing: visualisation
Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect. Synopsis. Introduction
 Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect Synopsis A simplified analysis method for a reinforced concrete shear wall structure considering strain rate effects is presented.
Dynamic analysis of a reinforced concrete shear wall with strain rate effect Synopsis A simplified analysis method for a reinforced concrete shear wall structure considering strain rate effects is presented.
The dispersion of a light solid particle in high-reynolds number homogeneous stationary turbulence: LES approach with stochastic sub-grid model
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow III 65 The dispersion of a light solid particle in high-reynolds number homogeneous stationary turbulence: ES approach with stochastic sub-grid model M. Gorokhoski
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow III 65 The dispersion of a light solid particle in high-reynolds number homogeneous stationary turbulence: ES approach with stochastic sub-grid model M. Gorokhoski
Linear Strain Triangle and other types of 2D elements. By S. Ziaei Rad
 Linear Strain Triangle and other tpes o D elements B S. Ziaei Rad Linear Strain Triangle (LST or T6 This element is also called qadratic trianglar element. Qadratic Trianglar Element Linear Strain Triangle
Linear Strain Triangle and other tpes o D elements B S. Ziaei Rad Linear Strain Triangle (LST or T6 This element is also called qadratic trianglar element. Qadratic Trianglar Element Linear Strain Triangle
Centripetal force. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Equations. Physics terms 5/13/14
 Centripetal force Objecties Describe and analyze the motion of objects moing in circular motion. Apply Newton s second law to circular motion problems. Interpret free-body force diagrams. 1. A race car
Centripetal force Objecties Describe and analyze the motion of objects moing in circular motion. Apply Newton s second law to circular motion problems. Interpret free-body force diagrams. 1. A race car
On reachability under uncertainty. A.B.Kurzhanski. Moscow State University. P.Varaiya. University of California at Berkeley
 On reachability under uncertainty A.B.Kurzhanski Moscow State Uniersity P.Varaiya Uniersity of California at Berkeley Abstract. The paper studies the problem of reachability for linear systems in the presence
On reachability under uncertainty A.B.Kurzhanski Moscow State Uniersity P.Varaiya Uniersity of California at Berkeley Abstract. The paper studies the problem of reachability for linear systems in the presence
Stochastic Simulation of Aircraft Fuselage Assembly Considering Manufacturing Uncertainties
 9th European LS-DYNA Conference 0 Stochastic Simulation of Aircraft Fuselage Assembly Considering Manufacturing Uncertainties Dietmar C. Vogt, Sönke Klostermann EADS Innovation Works, Germany Introduction
9th European LS-DYNA Conference 0 Stochastic Simulation of Aircraft Fuselage Assembly Considering Manufacturing Uncertainties Dietmar C. Vogt, Sönke Klostermann EADS Innovation Works, Germany Introduction
NON-ITERATIVE EQUIVALENT LINEAR METHOD FOR DISPLACEMENT-BASED DESIGN
 13 th World Conference on Earthquae Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Per No. 3422 NON-ITERATIVE EQUIVALENT LINEAR METHOD FOR DISPLACEMENT-BASED DESIGN Eduardo MIRANDA 1, Yu-Yuan LIN 2
13 th World Conference on Earthquae Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Per No. 3422 NON-ITERATIVE EQUIVALENT LINEAR METHOD FOR DISPLACEMENT-BASED DESIGN Eduardo MIRANDA 1, Yu-Yuan LIN 2
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS
 DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 3-7: PROJECTILE MOTION IS PARABOLIC LSN 3-8: RELATIVE VELOCITY Questions From Reading Actiity? Big Idea(s): The interactions of an object with other
DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS AP PHYSICS LSN 3-7: PROJECTILE MOTION IS PARABOLIC LSN 3-8: RELATIVE VELOCITY Questions From Reading Actiity? Big Idea(s): The interactions of an object with other
