Pythagoras theorem and surds
|
|
|
- Sophia Marshall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HPTER Mesurement nd Geometry Pythgors theorem nd surds In IE-EM Mthemtis Yer 8, you lernt out the remrkle reltionship etween the lengths of the sides of right-ngled tringle. This result is known s Pythgors theorem. The theorem sttes tht the squre of the length of the hypotenuse equls the sum of the squres of the lengths of the other two sides. In symols: + The onverse of this theorem is lso true. This mens tht if we hve tringle in whih the squre of one side equls the sum of the squres of the other two sides, then the tringle is right-ngled, with the longest side eing the hypotenuse. Pythgors theorem leds to the disovery of ertin irrtionl numers, suh s nd. These numers re emples of surds. In this hpter, we investigte the rithmeti of surds. Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
2 Review of Pythgors' theorem nd pplitions In Yer 8, we used Pythgors theorem to solve prolems relted to right-ngled tringles. Pythgors theorem nd its onverse In ny right-ngled tringle, the squre of the length of the hypotenuse equls the sum of the squres of the lengths of the other two sides. Emple Find the vlue of the unknown side in eh tringle. 9 + tringle with side lengths of,, whih stisfy + is right-ngled tringle. The right ngle is opposite the side of length lultors nd rounding In Emple ove, the vlues for re perfet squres nd so we ould tke the squre root esily. This is not lwys the se. In Yer 8, we found the pproimte squre roots of numers tht re not perfet squres y looking up tle of squre roots. Insted of doing this, from now on we re going to use lultor. HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
3 Review of Pythgors' theorem nd pplitions When using lultor to find squre root, try to hve in mind rough ide of wht the nswer should e. For emple, 0 should e lose to, sine nd 44. Note: 0.40 orret to deiml ples. lultor gives the pproimte vlue of squre root to lrge numer of deiml ples, fr more thn we need. We often round off deiml to required numer of deiml ples. The method for rounding to deiml ples is s follows. Look t the digit in the third deiml ple. If the digit is less thn 5, tke the two digits to the right of the deiml point. For emple,.764 eomes.76, orret to deiml ples. If the digit is more thn 4, tke the two digits to the right of the deiml point nd inrese the seond of these y one. For emple,.455 eomes.46, orret to deiml ples. Emple lultor gives Stte the vlue of orret to deiml ples. lultor gives Stte the vlue of 5 orret to deiml ples. Stte the vlue of.697, orret to deiml ples..7, sine the digit,, in the third deiml ple is less thn , sine the digit, 6, in the third deiml ple is more thn , sine the digit, 7, in the third deiml ple is more thn 4 nd 69 rounds to 70. The symol mens is pproimtely equl to. When pproimting, we should stte the numer of deiml ples to whih we hve rounded our nswer. Emple Find the length of the unknown side, orret to deiml ples (orret to deimlples) 0 4 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
4 Review of Pythgors' theorem nd pplitions In the emple on the previous pge, 044 is the et length while. is n pproimtion to the length of the side. Emple 4 Determine whether or not the three side lengths given form the sides of right-ngled tringle. 4,, 40 4,8, The squre of the length of the longest side The sum of the squres of the lengths of the other sides Sine , the tringle is right-ngled. The squre of the length of the longest side 59 The sum of the squres of the lengths of the other sides Sine 4 + 8, the tringle is not right-ngled. Emple 5 door frme hs height.7 m nd width m. Will squre piee of ord m y m fit through the doorwy? Let d m e the length of the digonl of the doorwy. Using Pythgors theorem, d d.89 d m.7 m.97 (orret to deiml ples) Hene the ord will not fit through the doorwy. m HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 5 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
5 R e v i e w o f P y t h g o rs ' t h e o rem n d pp l i t i o n s Eerise Emple Use Pythgors theorem to find the vlue of the pronumerl. 5 m m 8 m m m 6 m d m 4 m ES.6 m Use Pythgors theorem to find the vlue of the pronumerl. 5 m m d e 5 m m 45 m f 48 m m N L y m 50 m 70 m Use lultor to find, orret to deiml ples, pproimtions to these numers. Emple 74 m 6 m y m m 7 m m 8 m 5 m P Emple G. m Emple 40 m m 9 7 d Use Pythgors theorem to find the vlue of the pronumerl. lulte your nswer first s squre root nd then orret to deiml ples. m FI 4 m 7 m m 5 m d 8 m e 7 m m m y m f 8 m 0 m m y m m m 4 m 7 m 6 I E - E M M T H E M T I S YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
6 Review of Pythgors' theorem nd pplitions g h 7 m m 6 m 8 m Emple 4 Emple 5 6 m 5 Determine whether or not the tringle with the three side lengths given is right-ngled. y m 6, 0, 4 0, 4, 6 4, 6, 7 d 4.5, 7, 7.5 e 6, 0, f 0,, 9 6 In the tle elow, the side lengths of right-ngled tringles re listed. opy nd omplete the tle, giving nswers s whole numer or squre root. Lengths of the two shortest sides of right-ngled tringle Length of the hypotenuse m 4m... 5m 6m... 4m... 9m d 6m 0 m... e... 7m 0 m 7 door frme hs height.8 m nd width m. Will squre piee of ord. m wide fit through the opening? 8 trdesmn is mking the wooden retngulr frme for gte. In order to mke the frme stronger nd to keep it squre, the trdesmn will put digonl piee into the frme s shown in the digrm. If the frme is. m wide nd m high, find the length of the digonl piee of wood, in metres, orret to deiml ples. 9 signwriter lens his ldder ginst wll so tht he n pint sign. The wll is vertil nd the ground in front of the wll is horizontl. The signwriter s ldder is 4m long. If the signwriter wnts the top of the ldder to e.8 m ove the ground when lening ginst the wll, how fr, orret to deiml ple, should the foot of the ldder e pled from the wll? 0 ot uilder needs to lulte the lengths of the stys needed to support mst on yht. Two of the stys ( nd D) will e the sme length, s they go from point on the mst to eh side of the ot, s shown in the digrm. The third sty (E) will e different in length s it goes from the point on the mst to the front of the ot.. m m Front elevtion Side elevtion D E HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 7 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
7 Review of Pythgors' theorem nd pplitions If 5m, D. m nd E.9 m, find the length, to the nerest entimetre, of: one of the side stys, or D the front sty, E stinless steel wire needed to mke the three stys s prt of design, n rtist drws irle pssing through the four orners (verties) of squre. If the squre hs side lengths of 4 m, wht is the rdius, to the nerest millimetre, of the irle? If the irle hs rdius of m, wht re the side lengths, to the nerest millimetre, of the squre? prent is sked to mke some srves for the lol Sout troop. Two srves n e mde from one squre piee of mteril y utting on the digonl. If this digonl side length is to e 00 m long, wht must e the side length of the squre piee of mteril to the nerest mm? girl plnned to swim stright ross river of width 5 m. fter she hd swum ross the river, the girl found she hd een swept 4 m downstrem. How fr did she tully swim? lulte your nswer, in metres, orret to deiml ple. 4 yhtsmn wishes to uild shed with retngulr se to store his siling equipment. If the shed is to e.6 m wide nd must e le to house 4.6 m mst, whih is to e stored digonlly ross the eiling, how long must the shed e? lulte your nswer, in metres, orret to deiml ple. 5 In tringle the line D is drwn perpendiulr to. h is the length of D nd is the length of D. Show tht the length of is 6. Find the re of tringle in two wys to show tht h 0. Use Pythgors theorem to find. 4 h 0 D 8 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
8 6 In digrms nd, we hve two squres with the sme side length, +. The sides re divided up into lengths nd s shown. Prove tht the shded prt of digrm is squre. The two shded prts of digrm re lso squres. Why? Digrm Digrm y looking refully t the two digrms, show tht the re of the shded squre in digrm is the sum of the res of the shded squres in digrm. Use the result of prt to prove Pythgors theorem. Simplifying surds This setion dels only with surds tht re squre roots. If is positive integer whih is not perfet squre then is lled surd. We will look t surds more generlly in Setion I. We will now review the si rules for squre roots. If nd re positive numers then: For emple: ( ) ( ) The first two of these rules remind us tht, for positive numers, squring nd tking squre root re inverse proesses. When we write, we men. s in lger, we usully do not epliitly write the multiplition sign. HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
9 Simplifying surds Emple 6 Evlute: ( 6) ( 6) ( 6) 6 6 Emple 7 6 Evlute: Emple ( 6) d 5 0 Evlute: d 5 0 onsider the surd. We n ftor out the perfet squre 4 from, nd write: 4 4 (using ) 40 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
10 Simplifying surds Hene nd re equl. We will regrd s simpler form thn sine the numer under the squre root sign is smller. To simplify surd (or multiple of surd) we write it so tht the numer under the squre root sign hs no ftors tht re perfet squres other thn. For emple, In mthemtis, we re often instruted to leve our nswers in surd form. This simply mens tht we should not pproimte the nswer using lultor, ut leve the nswer, in simplest form, using squre roots, ue roots, et. This is lled giving the et vlue of the nswer. We n simplify surds diretly or in stges. Emple 9 Simplify the following In some prolems, we need to reverse this proess. Emple 0 Epress s the squre root of whole numer Emple Use Pythgors theorem to find the vlue of. Give your nswer s surd whih hs een simplified HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 4 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
11 Simplifying surds Emple 6 Emple 6 Emple The rithmeti of surds If nd re positive numers, then: ( ) ( 5) + ( ) surd is in its simplest form if the numer under the squre root sign hs no ftors tht re perfet squres, prt from. To simplify surd, we write it so tht the numer under the squre root sign hs no ftors tht re perfet squres, prt from. For emple, Eerise Evlute: ( 7) ( ) ( ) d ( ) Evlute: ( ) (4 ) (5 ) d ( 5) e ( 7) f (7 ) g ( ) h ( ) Epress s squre root of whole numer d e 7 f 5 g 4 h IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
12 Simplifying surds Emple 7,, d Emple 8 Emple 9 Emple 9 Emple 0 Emple 4 Epress s squre root of numer e 77 5 Evlute the produt. 4 f 40 8 g 6 4 h d e 5 f g 4 h Evlute: ( ) ( 5) ( 5) ( ) 9 d 46 d ( 7) ( ) e ( ) + ( ) f ( 5) + ( ) g 8 h i 7 Simplify eh of these surds d 4 e 7 f 44 g 50 h 54 i 0 j 98 k 6 l 60 m 6 n 68 o 75 p 99 q 8 r 4 8 Simplify eh of these surds d 88 e 48 f 80 g h 6 i 96 j 5 k 60 l 8 m 0 n 76 o 9 p 00 q 6 r 4 9 Epress eh of these surds s the squre root of whole numer. 6 7 d 6 e 4 5 f 5 7 g 4 h i 6 j 0 k 0 7 l 4 0 Evlute: e f g 5 d 6 Use Pythgors theorem to find the vlue of. Give your nswer s surd whih hs een simplified. 6 h HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 4 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
13 S i mp l i f y i n g s u r d s d e 9 f h i 5 50 G Find the length of the digonl D of the retngle D. Epress your nswer in simplest form. 0 ES g P D 6 squre hs side length. Find: the re of the squre the length of the digonl N L 4 D is squre. Find the vlue of. D FI 5 is n equilterl tringle with side length. X is the midpoint of. Find the length X. I E - E M M T H E M T I S 6 44 X YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
14 ddition nd sutrtion of surds We n sometimes simplify sums of surds. The sum n e thought of s 4 lots of 7 plus 5 lots of 7 equls 9 lots of 7. This is very similr to lger, where we write We sy 4 7 nd 5 7 re like surds sine they re oth multiples of 7. On the other hnd, in lger we nnot simplify 4 + 7y, euse 4 nd 7 y re not like terms. Similrly, it is not possile to write the sum of 4 nd 7 in simpler wy. They re unlike surds, sine one is multiple of while the other is multiple of. We n only simplify the sum or differene of like surds. Emple Simplify: d d This nnot e simplified further sine 5 nd 7 re unlike surds. When deling with epressions involving surds, we should simplify the surds first nd then look for like surds. Emple Simplify: This epression nnot e simplified further. HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 45 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
15 ddition nd sutrtion of surds Emple 4 Simplify: Emple 8 Simplify: ddition nd sutrtion of surds (Use ommon denomintor.) (Simplify the surds.) Simplify eh surd first, then look for like surds. (Use ommon denomintor.) We n simplify sums nd differenes of like surds. We nnot simplify sums nd differenes of unlike surds. Eerise d 8 e f g + 4 h 5 i Simplify: d e f g h IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
16 ddition nd sutrtion of surds Emple Emple 4 Simplify: d e f Simplify: d 8 + e 7 + f 48 + g h i Simplify: d e f g h i j k l Simplify: e Find the vlue of if: f g d h Find the vlue of nd the perimeter. M 5 d 6 5 Z N O X Y HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 47 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
17 9 In the digrm to the right, 5, X, 5 5, YX 5. X Y Z d Y Y X Z 0 In the digrm to the right, find: X X Find nd the perimeter of the retngle. qudrilterl D hs side lengths 9, 6 nd D 8. D 90 o nd the digonl 67. Find the perimeter of the qudrilterl. D Multiplition nd division of surds When we ome to multiply two surds, we simply multiply the numers outside the squre root sign together, nd similrly, multiply the numers under the squre root signs. similr rule holds for division. X D D 48 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
18 D Multiplition nd division of surds Emple 5 Find (4 8, 7 4) We n stte the proedure we just used s generl rule: d d, where nd d re positive numers. Emple 6 Find: (5 5, 5 7 5) (49 4, 7) We n stte the proedure we just used s generl rule: d, d where nd d re positive numers nd 0. s usul, we should lwys give the nswer in simplest form. Emple 7 Find HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 49 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
19 D Multiplition nd division of surds The distriutive lw We n pply the distriutive lw to epressions involving surds, just s we do in lger. Emple 8 Epnd nd simplify (4 + ). (4 + ) In lger, you lernt how to epnd rkets suh s ( + )( + d). These re known s inomil produts. You multiply eh term in the seond rket y eh term in the first, then dd. This mens you epnd out ( + d) + ( + d) to otin + d + + d. We use this ide gin when multiplying out inomil produts involving surds. Emple 9 Epnd nd simplify: ( 7 + )(5 7 4) (5 )( 4) ( 4 )(5 ) d ( )( + ) ( 7 + )(5 7 4) 7(5 7 4) + (5 7 4) (5 )( 4) 5 ( 4) ( 4) ( 4 )(5 ) (5 ) 4 (5 ) d ( )( + ) IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
20 D Multiplition nd division of surds Multiplition nd division of surds Emple 5 Emple 6 Emple 7 Emple 8 Emple 9 For positive numers nd d, d d. For positive numers nd d, d d, provided 0. Give the nswers in simplest form. We epnd inomil produts involving surds just s we do in lger: Simplify: ( + )( + d) ( + d) + ( + d) + d + + d Eerise D 5 7 d 4 7 e f 4 5 g 5 7 h Simplify: d e f g 5 7 h i j k l Simplify: d e 6 f 6 g 7 0 h Epnd nd simplify: ( 6 + ) ( 6) 5( 5) d ( ) e 5 5(4 ) f 7( 7 4) g 4 5( 5 ) h ( 5) i ( + 4 ) j 6 5( + ) k 7( 4) l 5( 5 + ) 5 Epnd nd simplify: (4 5 + )( 5 + ) (4 + 6)( + 5 6) ( + )( ) d ( + 5)(7 6 5) e ( 4)( + 5) f ( 7 )(5 7 ) g (7 + 5) h (4 ) HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 5 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
21 6 Epnd nd simplify: ( 5 + )( + ) ( )( + ) (4 + )( 7 5) d (8 4 6)( 7) e ( 7 5)( 7 + 5) f (5 )( + ) g (4 7 5)( 5 + 7) h (4 5)( 5 + ) 7 If nd y +, find: y + y + ( ) d y e y f + y g ( + )( y + ) h i + j + k + + E Speil produts In lger, you lerned the following speil epnsions. They re lled identities euse they re true for ll vlues of the pronumerls. These re espeilly importnt when deling with surds. ( + ) + + Emple 0 Epnd nd simplify ( 5 + ). ( ) + ( )( + ) ( 5 + ) ( 5) ( ) The first two identities re lled the perfet squre identities. The lst identity is known s the differene of two squres identity. You will need to e very onfident with these identities nd e le to reognise them. Sine they re true for ll numers, we n pply them to surds. Rell tht ( ) holds for ny positive numer. 5 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
22 E Speil produts Emple Epnd nd simplify ( ). ( ) ( ) + ( ) You should lwys epress your nswer in simplest form. Emple Epnd nd simplify ( + 4 6). ( + 4 6) ( ) (4 6) The following emple shows n interesting pplition of the differene of two squres identity. We will use this lter in this hpter when simplifying surds with inomil denominter. Emple Epnd nd simplify: ( 7 5)( 7 + 5) (5 6 5)( ) ( 7 5)( 7 + 5) ( 7) (5 6 5)( ) (5 6) ( 5) HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 5 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
23 E Speil produts Identities The following identities re often used in lultions involving surds. ( + ) + + ( ) + ( )( + ) Emple 0 Emple Emple Emple Eerise E Epnd nd simplify: (5 + ) ( + 6) (4 + 5) d ( + ) e ( 5 + 7) f ( + ) g (5 + ) h ( + 5) i ( ) j ( + y) k ( + y) l ( y + ) Epnd nd simplify: ( 7 ) (4 ) ( 5 ) d ( ) e ( 5 ) f ( ) g ( 4 5) h (4 7) i ( y) Epnd nd simplify: ( ) (5 6 + ) ( + ) d ( 5 + 5) e ( 0 ) f ( 0) g ( 70 0) h ( 50 5) i ( ) j ( 0 5) k ( 6) l (5 4 ) 4 Epnd nd simplify: ( 5)( + 5) ( 6 )( 6 + ) (7 + )(7 ) d ( )( + ) e ( 5 + )( 5 ) f ( )( + ) g ( 5)( + 5) h (4 5)(4 + 5) i (6 7)(6 + 7) j ( 5 6)( + 5 6) k ( )( 5 7 0) l ( + y)( y) 5 If nd y +, find: y + y d y e y f y g y h + y 54 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
24 6 Find: ( 5 + ) + ( 5 ) ( 5 + ) ( 5 ) ( + ) + ( ) d ( + ) ( ) e ( 7 ) + ( 7 + ) f ( 6 + ) ( 6 ) 7 Simplify ( + d)( d). 8 For the figures shown, find: i the vlue of ii the re of the tringle iii the perimeter of the tringle + 9 For the figures shown, find: i the perimeter ii the re n equilterl tringle hs sides length +. Find: the perimeter of the tringle the re of the tringle F Rtionlising the denomintor The epression + is untidy. The first term hs squre root in the denomintor. Frtions involving surds re esiest to del with when they re epressed in simplest form, with rtionl denomintor. When we multiply the numertor nd denomintor of frtion y the sme numer, we form n equivlent frtion. The sme hppens with quotient involving surds. HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 55 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
25 F Rtionlising the denomintor Emple 4 Epress 4 with rtionl denomintor Emple Write s quotient with rtionl denomintor Emple 6 Simplify (Multiply top nd ottom y the sme surd.) (Multiply top nd ottom y.) (Rtionlise the denomintor of the first term.) (Use ommon denomintor.) 56 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
26 F Rtionlising the denomintor Rtionlising the denomintor Rtionlising the denomintor mens onverting the denomintor into rtionl numer. We use the result, where is positive, to rtionlise the denomintor of quotient involving surds. Emple 4 Emple 5 Emple 6 Rtionlise the denomintor f Eerise F 8 6 g 5 Rtionlise the denomintor. 7 5 f 5 g h h 8 8 d 4 7 i d i e 7 j 7 e j Given tht.4 nd.7, find these vlues, orret to deiml ples, without using lultor. (First rtionlise the denomintor where pproprite.) 5 d e f 8 g h 8 4 y first rtionlising the denomintors, simplify eh epression d e 7 + f If 4 nd y 4, find nd rtionlise the denomintor. y y y d y HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 57 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
27 6 If, find nd rtionlise the denomintor. + + d 7 Find the vlue of. Epress your nswer with rtionl denomintor. 5 G 0 pplitions of Pythgors theorem in three dimensions How n we find the length of the digonl D of ue whose side length is 4 m? D is fe digonl nd sometimes D is lled spe digonl. We n pply Pythgors theorem to tringle D to find the squre of the length s m of the digonl D. s We n then pply Pythgors theorem gin to tringle D sine D is right ngle. The length d m of the digonl D is given y: d s d (orret to deiml ples) The length of the digonl D is 6.9 m orret to deiml ples. 4 m 5 4 m d m s m D 58 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
28 G pplitions of Pythgors theorem in three dimensions Emple 7 squre pyrmid hs height 5m nd squre se with side length 4m. Find the length of the edge V in this digrm. V 5 m m The se is squre with side length 4m, so: Hene E (Leve in et form to mintin ury.) Tringle VE is right-ngled, so: VE + E 5 + ( ) (orret to deiml ples) The lenth of V is 5.74 m orret to deiml ples. pplitions of Pythgors theorem in three dimensions Pythgors theorem n e used to find lengths in three-dimensionl prolems. lwys drw reful digrm identifying the pproprite right-ngled tringle(s). To mintin ury, use et vlues nd only pproimte using lultor t the end of the prolem if required. 4 m E D 4 m HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 59 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
29 G pplitions of Pythgors theorem in three dimensions Eerise G Emple 7 The retngulr prism in the digrm hs length of m, width of 5 m nd height of 6m. onsider tringle EFG. Find: i EF Find EG. Find G, orret to deiml ple. ii the size of ÐEFG Note: G is lled the spe digonl of the retngulr prism. Find the length of the spe digonl of the retngulr prism whose length, width nd height re: m,9 m, 8m m,5m,8m 0 m,4 m,7 m d 8m, 6m, 4m e 7m, m, m f m, m, m Find the length of the longest penil tht n fit inside ylindril penil se of length 5 m nd rdius m. 4 owl in the shpe of hemisphere of rdius length 5m is prtilly filled with wter. The surfe of the wter is irle of rdius 4 m when the rim of the owl is horizontl. Find the depth of the wter. 5 uilder needs to rry lengths of timer long orridor in order to get them to where he is working. There is right-ngled end in the orridor long the wy. The orridor is m wide nd the eiling is.6 m ove the floor. Wht is the longest length of timer tht the uilder n tke round the orner in the orridor? (Hint: Drw digrm.) 6 oin for n industril knitting mhine is in the shpe of trunted one. The dimeter of the top is 4m, the dimeter of the se is 6m nd the length of the slnt is 0 m. Find the height of the oin. 7 For the retngulr prism shown opposite, EH 4 m nd HG m. Find the et length of EG, giving your nswer s surd in simplest form. If E EG, find the et vlue of E. E F D H E 4 m 6 m m D G 0 m H G 6 m F 5 m 60 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
30 Find the length of: i E ii H d Wht type of tringle is tringle EH? e Show tht if EH m, HG m nd E EG, then the sides of the tringle EH re in the rtio : 4 : 5. H inomil denomintors onsider the epression. 7 5 How n we write this s quotient with rtionl denomintor? In the setion on speil produts, we sw tht: so Similrly, so ( ) ( ) ( 7 5)( 7 + 5) , whih is rtionl, (5 4)(5 + 4) (5 ) , whih gin isrtionl, Using the differene of two squres identity in this wy is n importnt tehnique. HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 6 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
31 H inomil denomintors Emple 8 Simplify the following: (5 + 5) inomil denomintors ( + )( ) 8 ( ) To rtionlise denomintor whih hs two terms, we use the differene of two squres identity: In n epression suh s In n epression suh s Eerise H 5 +, multiply top nd ottom y 5. 7, multiply top nd ottom y 7 +. The surd 7 is lled the onjugte of 7 + nd 7 + is the onjugte of 7. Simplify: ( 7 5)( 7 + 5) ( 5 )( 5 + ) (7 + 4 )(7 4 ) d (4 )(4 + ) 6 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
32 Emple 8 Rtionlise the denomintor in eh epression d 5 e f 7 5 g j m 4 7 h k n i l o Rtionlise the denomintors in these epressions nd use the deiml pproimtions.44 nd.7 to evlute them orret to deiml ples. + 4 Find the integers p nd q suh tht 5 Simplify: Simplify: I p + q Irrtionl numers nd surds We first rell some fts out frtions nd deimls. Frtions nd deimls d 5 ( 7 ) We know tht some frtions n e written s deimls tht terminte. For emple, 4 0.5, Some frtions hve deiml representtions tht do not terminte. For emple, whih we write s 0... HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 6 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
33 I Irrtionl numers nd surds The dot ove the indites tht the digit is repeted forever. Some frtions hve deiml representtions tht eventully repet. For emple, whih is written s 0.6. Other frtions hve deiml representtions with more thn one repeting digit. For emple, whih we write s , with dot ove oth of the repeting digits. nother emple is onverting deimls to frtions It is esy to write terminting deimls s frtions y using denomintor whih is power of 0. For emple, Deimls tht hve repeted sequene of digits n lso e written s frtions. For emple, 4 0. nd method for doing this is shown in the net two emples. Emple 9 Write 0.. s frtion. Let S 0.. So S Then 0S.... (Multiply y 0.) 0S Therefore 0S S + Hene 9S So S 9 Thus IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
34 I Irrtionl numers nd surds Emple 0 Write 0.. s frtion. Let S 0.. So S Then 00S... Therefore 00S + S Hene 99S So S Thus 0. Rtionl numers rtionl numer is numer tht n e written s frtion p q, where p nd q re integers nd q 0. ll integers re rtionl numers. For emple, Emple Eplin why eh of these numers is rtionl. 5 7 We will epress eh numer in the form p q (ontinued over pge) HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 65 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
35 I Irrtionl numers nd surds Let S S (Multipyy00.) 00S 4 + S Hene 99S 4 4 S Thus 0.4 Eh numer hs een epressed s frtion p, where p nd q re integers, so eh numer is rtionl. q Irrtionl numers Mthemtiins up to out 600 E thought tht ll numers were rtionl. However, when we pply Pythgors theorem, we enounter numers suh s tht re not rtionl. The numer is n emple of n irrtionl numer. n irrtionl numer is one tht is not rtionl. Hene n irrtionl numer nnot e written in the p form, where p nd q re integers nd q 0. Nor n it e written s terminting or repeting q deiml. In 00 E, Eulid proved tht mking the ssumption tht is rtionl leds to ontrdition. Hene ws shown to e irrtionl. The proof is outlined here. ssume p where p nd q re integers with highest ommon ftor. q p Squre oth sides of this eqution to otin q. We n write p q. Hene p is even nd thus p is even. We n now write, 4 k q For some whole numer k. From this, show q is lso even whih is ontrdition of our ssumption tht the highest ommon ftor is. The deiml epnsion of goes on forever ut does not repet. The vlue of n e pproimted using lultor. The sme is true of other irrtionl numers suh s, 4 nd 9. Try finding these numers on your lultor nd see wht you get. Other emples of irrtionl numers inlude:,, ππ, nd π There re infinitely mny rtionl numers euse every whole numer is rtionl. We n lso esily write down infinitely mny other frtions. For emple,,, 4, IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
36 I Irrtionl numers nd surds There re infinitely mny irrtionl numers too. For emple,,,, 4,... Every numer, whether rtionl or irrtionl, is represented y point on the numer line. onversely, we n think of eh point on the numer line s numer. π Emple rrnge these irrtionl numers in order of size on the numer line Find on pproimtion of eh numer to deiml ples using lultor Surds In Yer 8, we looked t squres, squre roots, ues nd ue roots. For emple: 5 5 nd nd The use of this nottion n e etended. For emple: nd This is red s The fourth power of 5 is 65 nd the fourth root of 65 is 5. We lso hve fifth roots, sith roots nd so on. In generl, we n tke the nth root of ny positive numer. The nth root of is the positive numer whose nth power is. The sttement n is equivlent to the sttement n. Your lultor will give you pproimtions to the nth root of. Note: For n, positive integer, 0n n 0 nd 0 0. n n irrtionl numer whih n e epressed s, where is positive whole numer, is lled surd. For emple,, 7 nd 5 re ll emples of surds, while 4 nd 9 re not surds sine they re whole numers. The numer π, lthough it is irrtionl, is not surd. This is lso diffiult to prove. 4 HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 67 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
37 I Irrtionl numers nd surds Emple Use Pythgors theorem to onstrut line of length 0. Emple 9 Emple 0 Emple Find two perfet squres tht sum to Drw perpendiulr line segments from ommon point of lengths units nd 4 units. onnet their endpoints with third line segment. 4 0 Irrtionl numers nd surds Every frtion n e written s terminting, or eventully repeting, deiml. Every terminting, or eventully repeting, deiml n e written s frtion. rtionl numer is numer whih n e epressed s p where p nd q re integers q nd q 0. Tht is, rtionl numer is n integer or frtion. There re numers suh s π nd Eerise I Write eh repeting deiml s frtion. tht re irrtionl (not rtionl). Eh rtionl nd eh irrtionl numer represents point on the numer line. Every point on the numer line represents rtionl or n irrtionl numer. n irrtionl numer whih n e epressed s numers, is lled surd. π is not surd., where n nd re positive whole d 0.4 e 0. f 0.6 Write eh repeting deiml s frtion d 0.4 e 0.6 f 0.06 g 0.4 h 0.56 i 0.00 Show tht eh numer is rtionl y writing it s frtion d 0.5 e 5 7 f. n 68 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
38 Emple Emple 4 Whih of these numers re irrtionl? d π 5 y pproimting orret to deiml ples, ple these rel numers on the sme numer line d π e 6 Whih of these numers re surds? 5 4 d 9 e 7 f 6 g 0 h i j 5 k 5 l 5 7 Use the ft tht + 5 to onstrut length 5. Use the ft tht to onstrut length 4. 8 How would you onstrut n intervl of length: 7??? 9 Show tht The epression on the right is lled ontinued frtion. Epress 5 s ontinued frtion with ll numertors. Review eerise For eh right-ngled tringle, find the vlue of the pronumerl. h m 8 m 6 m.5 m 6 m h m For eh right-ngled tringle, find the vlue of the pronumerl. m 4 m 8.5 m 6.5 m y m 6 m HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 69 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
39 REVIEW EXERISE support rket is to e pled under shelf, s shown in the digrm. If 0 m, find, orret to the nerest millimetre, the length of. 4 rod runs in n est west diretion joining towns nd, whih re 40 km prt. third town,, is situted 0 km due north of. stright rod is uilt from, to the rod etween nd nd meets it t D, whih is equidistnt from nd. Find the length of rod D. 5 irles of rdius 6 m nd m re pled in squre, s shown in the digrm opposite. Find, orret to deiml ples: E FD the length of the digonl D d the side length of the squre 6 Simplify: Simplify: Simplify: ( + ) 5 ( ) 9 Epnd nd simplify: ( + )( ) (5 )( ) 0 Simplify: d 7 e 048 f 448 g 800 h Simplify: d Epress with rtionl denomintor. 5 5 e f g 4 7 D d F 7 h E 70 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
40 REVIEW EXERISE Epress with rtionl denomintor e f g 7 4 d h 4 Epnd nd simplify ( 5 ). Simplify +, epressing your nswer with rtionl denomintor. 5 The digrm opposite shows prt of skte ord rmp. (It is prism whose ross-setion is rightngled tringle.) Use the informtion in the digrm to find: E 6 Find the length of the spe digonl of ue with side length 5m. 7 motorist deprts from town, whih is 8km due south from nother town,, nd drives due est towrds town, whih is 0 km from. fter driving distne of km, he noties tht he is the sme distne wy from oth towns nd. 8 km km D 0 km Epress the motorist s distne from in terms of (tht is, D). Epress the motorist s distne from in terms of. Find the distne he hs driven from. 8 The digrm opposite shows the logo of prtiulr ompny. The lrge irle hs entre O nd rdius m nd is dimeter. D is the entre of the middle-sized irle with dimeter O. Finlly, is the entre of the smllest irle. Wht is the rdius of the irle with entre D? If the rdius of the irle with entre is r m, epress these in terms of r. i O ii D Find the vlue of r. D 5 m O 4 m D F.5 m HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 7 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
41 9 In the digrm opposite, VD is squre-sed pyrmid with D D 0 nd V V V VD 0. Wht type of tringle is tringlev? If M is the midpoint of, find the et vlues of: i VM ii VE, the height of the pyrmid 0 Write eh repeting deiml s frtion. V M E D d 0.0 e 0.8 f 0.96 g 0.0 h Write 67 s ontinued frtion. (See Eerise I, Question 9.) 9 Write s frtion. How would you onstrut intervls of the following lengths? Disuss with your teher. 8 d 8 4 Find the length of the long digonl of the retngulr prism whose length, width nd height re: +,, 5 +, 5, 5 For nd y 5, find in simplest form. + + d y y y hllenge eerise Prove tht is irrtionl. In the tringle elow, > 8. Is the ngle θ greter or less thn 90? Eplin your nswer. 7 8 θ 4 7 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
42 HLLENGE EXERISE pollonius theorem sttes tht in ny tringle, if we join verte to the midpoint of the opposite side, nd the length of tht line is d, then + ( d + m)where m. In words it sys: In ny tringle, the sum of the squres on two sides is equl to twie the squre on hlf the third side together with twie the squre on the medin. Prove this result s follows: Drop perpendiulr E of length h from to nd let ED p. i Write E in terms of m nd p. ii Write E in terms of m nd p. y pplying Pythgors theorem to the three right-ngled tringles in the digrm, omplete these sttements: d dd the first two equtions in prt ove nd simplify. d Use the third eqution in prt to dedue pollonius theorem. e Wht hppens when the ngle t is right ngle? m h 4 retngle D hs 5 m, D 0m. point P is loted inside the retngle suh tht P 4 m nd P m. Find PD in et form. 5 E is ny point inside the retngle D. Let E, E, E nd ED. Prove tht +. d D d E p D m m HPTER Pythgors theorem nd surds 7 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
43 HLLENGE EXERISE 6 We use the ft tht every integer n e uniquely ftorised s produt of primes to give nother proof tht is irrtionl. We egin y supposing the opposite tht is, we suppose tht we n write p, where p nd q re whole numers with no q ommon ftors eept. Eplin why q is ftor of p. Eplin why q is ftor of p. Eplin how this shows tht is irrtionl. 7 Prove tht 6 is irrtionl. 8 Epnd nd simplify: ( + ) 4 ( ) 4 9 Prove tht there re infinitely mny irrtionl numers etween 0 nd. 0 Prove tht etween ny two numers, there re infinitely mny rtionl numers nd infinitely mny irrtionl numers. Rtionlise the denomintor of: ( + ) Show tht 7 < 5 < < without using lultor. Two irles with entres O nd O nd rdii r nd R meet t single point. nd re the points where the irles touh line l. Find the distne etween points nd. O r O R 74 IE-EM MTHEMTIS YER 9 Finl pges mridge University Press rown et l, 07 ISN Ph
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? IN THIS CHAPTER YOU WILL:
 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 WHAT S IN CHAPTER 1? 1 01 Squres, squre roots nd surds 1 02 Pythgors theorem 1 03 Finding the hypotenuse 1 04 Finding shorter side 1 05 Mixed prolems 1 06 Testing for right-ngled tringles
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
Nme Dte hpter 9 Mintining Mthemtil Profiieny Simplify the epression. 1. 500. 189 3. 5 4. 4 3 5. 11 5 6. 8 Solve the proportion. 9 3 14 7. = 8. = 9. 1 7 5 4 = 4 10. 0 6 = 11. 7 4 10 = 1. 5 9 15 3 = 5 +
5. Every rational number have either terminating or repeating (recurring) decimal representation.
 CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
CHAPTER NUMBER SYSTEMS Points to Rememer :. Numer used for ounting,,,,... re known s Nturl numers.. All nturl numers together with zero i.e. 0,,,,,... re known s whole numers.. All nturl numers, zero nd
GM1 Consolidation Worksheet
 Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Cmridge Essentils Mthemtis Core 8 GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet GM1 Consolidtion Worksheet 1 Clulte the size of eh ngle mrked y letter. Give resons for your nswers. or exmple, ngles on stright line dd up
Activities. 4.1 Pythagoras' Theorem 4.2 Spirals 4.3 Clinometers 4.4 Radar 4.5 Posting Parcels 4.6 Interlocking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes and Solutions
 MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
MEP: Demonstrtion Projet UNIT 4: Trigonometry UNIT 4 Trigonometry tivities tivities 4. Pythgors' Theorem 4.2 Spirls 4.3 linometers 4.4 Rdr 4.5 Posting Prels 4.6 Interloking Pipes 4.7 Sine Rule Notes nd
LESSON 11: TRIANGLE FORMULAE
 . THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
. THE SEMIPERIMETER OF TRINGLE LESSON : TRINGLE FORMULE In wht follows, will hve sides, nd, nd these will e opposite ngles, nd respetively. y the tringle inequlity, nd..() So ll of, & re positive rel numers.
CHENG Chun Chor Litwin The Hong Kong Institute of Education
 PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
PE-hing Mi terntionl onferene IV: novtion of Mthemtis Tehing nd Lerning through Lesson Study- onnetion etween ssessment nd Sujet Mtter HENG hun hor Litwin The Hong Kong stitute of Edution Report on using
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q5 of Paper 2
 Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Trigonometry Revision Sheet Q of Pper The Bsis - The Trigonometry setion is ll out tringles. We will normlly e given some of the sides or ngles of tringle nd we use formule nd rules to find the others.
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
AP Calculus BC Chapter 8: Integration Techniques, L Hopital s Rule and Improper Integrals
 AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
AP Clulus BC Chpter 8: Integrtion Tehniques, L Hopitl s Rule nd Improper Integrls 8. Bsi Integrtion Rules In this setion we will review vrious integrtion strtegies. Strtegies: I. Seprte the integrnd into
Geometry of the Circle - Chords and Angles. Geometry of the Circle. Chord and Angles. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 272.
 Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
Geometry of the irle - hords nd ngles Geometry of the irle hord nd ngles urriulum Redy MMG: 272 www.mthletis.om hords nd ngles HRS N NGLES The irle is si shpe nd so it n e found lmost nywhere. This setion
Lesson 2: The Pythagorean Theorem and Similar Triangles. A Brief Review of the Pythagorean Theorem.
 27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
27 Lesson 2: The Pythgoren Theorem nd Similr Tringles A Brief Review of the Pythgoren Theorem. Rell tht n ngle whih mesures 90º is lled right ngle. If one of the ngles of tringle is right ngle, then we
PYTHAGORAS THEOREM,TRIGONOMETRY,BEARINGS AND THREE DIMENSIONAL PROBLEMS
 PYTHGORS THEOREM,TRIGONOMETRY,ERINGS ND THREE DIMENSIONL PROLEMS 1.1 PYTHGORS THEOREM: 1. The Pythgors Theorem sttes tht the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the squres of the other two sides
PYTHGORS THEOREM,TRIGONOMETRY,ERINGS ND THREE DIMENSIONL PROLEMS 1.1 PYTHGORS THEOREM: 1. The Pythgors Theorem sttes tht the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the squres of the other two sides
Pythagoras Theorem. Pythagoras Theorem. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 222, 245.
 Pythgors Theorem Pythgors Theorem Curriulum Redy ACMMG:, 45 www.mthletis.om Fill in these spes with ny other interesting fts you n find out Pythgors. In the world of Mthemtis, Pythgors is legend. He lived
Pythgors Theorem Pythgors Theorem Curriulum Redy ACMMG:, 45 www.mthletis.om Fill in these spes with ny other interesting fts you n find out Pythgors. In the world of Mthemtis, Pythgors is legend. He lived
Surds and Indices. Surds and Indices. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 233,
 Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
Surs n Inies Surs n Inies Curriulum Rey ACMNA:, 6 www.mthletis.om Surs SURDS & & Inies INDICES Inies n surs re very losely relte. A numer uner (squre root sign) is lle sur if the squre root n t e simplifie.
Section 1.3 Triangles
 Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Se 1.3 Tringles 21 Setion 1.3 Tringles LELING TRINGLE The line segments tht form tringle re lled the sides of the tringle. Eh pir of sides forms n ngle, lled n interior ngle, nd eh tringle hs three interior
Proving the Pythagorean Theorem
 Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Proving the Pythgoren Theorem W. Bline Dowler June 30, 2010 Astrt Most people re fmilir with the formul 2 + 2 = 2. However, in most ses, this ws presented in lssroom s n solute with no ttempt t proof or
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 9: Roots, Real Numbers and The Pythagorean Theorem
 HS Pre-Alger Notes Unit 9: Roots, Rel Numers nd The Pythgoren Theorem Roots nd Cue Roots Syllus Ojetive 5.4: The student will find or pproximte squre roots of numers to 4. CCSS 8.EE.-: Evlute squre roots
HS Pre-Alger Notes Unit 9: Roots, Rel Numers nd The Pythgoren Theorem Roots nd Cue Roots Syllus Ojetive 5.4: The student will find or pproximte squre roots of numers to 4. CCSS 8.EE.-: Evlute squre roots
Chapter 8 Roots and Radicals
 Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
Chpter 8 Roots nd Rdils 7 ROOTS AND RADICALS 8 Figure 8. Grphene is n inredily strong nd flexile mteril mde from ron. It n lso ondut eletriity. Notie the hexgonl grid pttern. (redit: AlexnderAIUS / Wikimedi
3 Angle Geometry. 3.1 Measuring Angles. 1. Using a protractor, measure the marked angles.
 3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
3 ngle Geometry MEP Prtie ook S3 3.1 Mesuring ngles 1. Using protrtor, mesure the mrked ngles. () () (d) (e) (f) 2. Drw ngles with the following sizes. () 22 () 75 120 (d) 90 (e) 153 (f) 45 (g) 180 (h)
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM
 THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM The Pythgoren Theorem is one of the most well-known nd widely used theorems in mthemtis. We will first look t n informl investigtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd then pply this
THE PYTHAGOREAN THEOREM The Pythgoren Theorem is one of the most well-known nd widely used theorems in mthemtis. We will first look t n informl investigtion of the Pythgoren Theorem, nd then pply this
Shape and measurement
 C H A P T E R 5 Shpe nd mesurement Wht is Pythgors theorem? How do we use Pythgors theorem? How do we find the perimeter of shpe? How do we find the re of shpe? How do we find the volume of shpe? How do
C H A P T E R 5 Shpe nd mesurement Wht is Pythgors theorem? How do we use Pythgors theorem? How do we find the perimeter of shpe? How do we find the re of shpe? How do we find the volume of shpe? How do
April 8, 2017 Math 9. Geometry. Solving vector problems. Problem. Prove that if vectors and satisfy, then.
 pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
pril 8, 2017 Mth 9 Geometry Solving vetor prolems Prolem Prove tht if vetors nd stisfy, then Solution 1 onsider the vetor ddition prllelogrm shown in the Figure Sine its digonls hve equl length,, the prllelogrm
Naming the sides of a right-angled triangle
 6.2 Wht is trigonometry? The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (tringle) nd metron (mesurement). Thus, it literlly mens to mesure tringle. Trigonometry dels with the reltionship
6.2 Wht is trigonometry? The word trigonometry is derived from the Greek words trigonon (tringle) nd metron (mesurement). Thus, it literlly mens to mesure tringle. Trigonometry dels with the reltionship
Trigonometry. Trigonometry. labelling conventions. Evaluation of areas of non-right-angled triangles using the formulas A = 1 ab sin (C )
 8 8 Pythgors theorem 8 Pythgoren trids 8 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 8D Trigonometri rtios 8E The sine rule 8F miguous se of the sine rule 8G The osine rule 8H Speil tringles 8I re of tringles res
8 8 Pythgors theorem 8 Pythgoren trids 8 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 8D Trigonometri rtios 8E The sine rule 8F miguous se of the sine rule 8G The osine rule 8H Speil tringles 8I re of tringles res
6.5 Improper integrals
 Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
Eerpt from "Clulus" 3 AoPS In. www.rtofprolemsolving.om 6.5. IMPROPER INTEGRALS 6.5 Improper integrls As we ve seen, we use the definite integrl R f to ompute the re of the region under the grph of y =
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL. Part 1. What and Why.?
 SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
SECTION A STUDENT MATERIAL Prt Wht nd Wh.? Student Mteril Prt Prolem n > 0 n > 0 Is the onverse true? Prolem If n is even then n is even. If n is even then n is even. Wht nd Wh? Eploring Pure Mths Are
Non Right Angled Triangles
 Non Right ngled Tringles Non Right ngled Tringles urriulum Redy www.mthletis.om Non Right ngled Tringles NON RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES sin i, os i nd tn i re lso useful in non-right ngled tringles. This unit
Non Right ngled Tringles Non Right ngled Tringles urriulum Redy www.mthletis.om Non Right ngled Tringles NON RIGHT NGLED TRINGLES sin i, os i nd tn i re lso useful in non-right ngled tringles. This unit
( ) 1. 1) Let f( x ) = 10 5x. Find and simplify f( 2) and then state the domain of f(x).
 Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
Green s Theorem. (2x e y ) da. (2x e y ) dx dy. x 2 xe y. (1 e y ) dy. y=1. = y e y. y=0. = 2 e
 Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
 PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
PAIR OF LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES. Two liner equtions in the sme two vriles re lled pir of liner equtions in two vriles. The most generl form of pir of liner equtions is x + y + 0 x + y + 0 where,,,,,,
ONLINE PAGE PROOFS. Trigonometry Kick off with CAS 12.2 Trigonometry 12.3 Pythagorean triads
 12 12.1 Kik off with S 12.2 Trigonometry 12.3 Pythgoren trids Trigonometry 12.4 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 12.5 Trigonometri rtios 12.6 The sine rule 12.7 miguous se of the sine rule 12.8 The osine
12 12.1 Kik off with S 12.2 Trigonometry 12.3 Pythgoren trids Trigonometry 12.4 Three-dimensionl Pythgors theorem 12.5 Trigonometri rtios 12.6 The sine rule 12.7 miguous se of the sine rule 12.8 The osine
m m m m m m m m P m P m ( ) m m P( ) ( ). The o-ordinte of the point P( ) dividing the line segment joining the two points ( ) nd ( ) eternll in the r
 CO-ORDINTE GEOMETR II I Qudrnt Qudrnt (-.+) (++) X X - - - 0 - III IV Qudrnt - Qudrnt (--) - (+-) Region CRTESIN CO-ORDINTE SSTEM : Retngulr Co-ordinte Sstem : Let X' OX nd 'O e two mutull perpendiulr
CO-ORDINTE GEOMETR II I Qudrnt Qudrnt (-.+) (++) X X - - - 0 - III IV Qudrnt - Qudrnt (--) - (+-) Region CRTESIN CO-ORDINTE SSTEM : Retngulr Co-ordinte Sstem : Let X' OX nd 'O e two mutull perpendiulr
Similar Right Triangles
 Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
Geometry V1.noteook Ferury 09, 2012 Similr Right Tringles Cn I identify similr tringles in right tringle with the ltitude? Cn I identify the proportions in right tringles? Cn I use the geometri mens theorems
Ellipses. The second type of conic is called an ellipse.
 Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
Ellipses The seond type of oni is lled n ellipse. Definition of Ellipse An ellipse is the set of ll points (, y) in plne, the sum of whose distnes from two distint fied points (foi) is onstnt. (, y) d
12.4 Similarity in Right Triangles
 Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
Nme lss Dte 12.4 Similrit in Right Tringles Essentil Question: How does the ltitude to the hpotenuse of right tringle help ou use similr right tringles to solve prolems? Eplore Identifing Similrit in Right
A Study on the Properties of Rational Triangles
 Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Interntionl Journl of Mthemtis Reserh. ISSN 0976-5840 Volume 6, Numer (04), pp. 8-9 Interntionl Reserh Pulition House http://www.irphouse.om Study on the Properties of Rtionl Tringles M. Q. lm, M.R. Hssn
Perimeter, area and volume
 6 Perimeter, re nd volume Syllus topi M. Perimeter, re nd volume This topi will develop your skills to ompetently solve prolems involving perimeter, re, volume nd pity. Outomes Clulte the re of irles nd
6 Perimeter, re nd volume Syllus topi M. Perimeter, re nd volume This topi will develop your skills to ompetently solve prolems involving perimeter, re, volume nd pity. Outomes Clulte the re of irles nd
m A 1 1 A ! and AC 6
 REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
REVIEW SET A Using sle of m represents units, sketh vetor to represent: NON-CALCULATOR n eroplne tking off t n ngle of 8 ± to runw with speed of 6 ms displement of m in north-esterl diretion. Simplif:
Logarithms LOGARITHMS.
 Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
Logrithms LOGARITHMS www.mthletis.om.u Logrithms LOGARITHMS Logrithms re nother method to lulte nd work with eponents. Answer these questions, efore working through this unit. I used to think: In the
Integration. antidifferentiation
 9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
9 Integrtion 9A Antidifferentition 9B Integrtion of e, sin ( ) nd os ( ) 9C Integrtion reognition 9D Approimting res enlosed funtions 9E The fundmentl theorem of integrl lulus 9F Signed res 9G Further
Introduction to Olympiad Inequalities
 Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Introdution to Olympid Inequlities Edutionl Studies Progrm HSSP Msshusetts Institute of Tehnology Snj Simonovikj Spring 207 Contents Wrm up nd Am-Gm inequlity 2. Elementry inequlities......................
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday 17 October 2012 Geometry II: Side Lengths
 Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
Intermedite Mth Cirles Wednesdy 17 Otoer 01 Geometry II: Side Lengths Lst week we disussed vrious ngle properties. As we progressed through the evening, we proved mny results. This week, we will look t
Chapter 9 Definite Integrals
 Chpter 9 Definite Integrls In the previous chpter we found how to tke n ntiderivtive nd investigted the indefinite integrl. In this chpter the connection etween ntiderivtives nd definite integrls is estlished
Chpter 9 Definite Integrls In the previous chpter we found how to tke n ntiderivtive nd investigted the indefinite integrl. In this chpter the connection etween ntiderivtives nd definite integrls is estlished
Matrices SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT. Mathematics (c) 1. Definition of a Matrix
 tries Definition of tri mtri is regulr rry of numers enlosed inside rkets SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & UIL ENVIRONEN Emple he following re ll mtries: ), ) 9, themtis ), d) tries Definition of tri Size of tri
tries Definition of tri mtri is regulr rry of numers enlosed inside rkets SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & UIL ENVIRONEN Emple he following re ll mtries: ), ) 9, themtis ), d) tries Definition of tri Size of tri
Polynomials. Polynomials. Curriculum Ready ACMNA:
 Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
Polynomils Polynomils Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 66 www.mthletis.om Polynomils POLYNOMIALS A polynomil is mthemtil expression with one vrile whose powers re neither negtive nor frtions. The power in eh expression
= x x 2 = 25 2
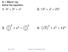 9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
9.1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 7, 2016 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 9.1
21.1 Using Formulae Construct and Use Simple Formulae Revision of Negative Numbers Substitution into Formulae
 MEP Jmi: STRAND G UNIT 1 Formule: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Alger Unit 1 Formule Student Tet Contents Setion 1.1 Using Formule 1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule 1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers 1.4
MEP Jmi: STRAND G UNIT 1 Formule: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Alger Unit 1 Formule Student Tet Contents Setion 1.1 Using Formule 1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule 1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers 1.4
UNCORRECTED. Australian curriculum MEASUREMENT AND GEOMETRY
 3 3 3C 3D 3 3F 3G 3H 3I 3J Chpter Wht you will lern Pythgors theorem Finding the shorter sides pplying Pythgors theorem Pythgors in three dimensions (tending) Trigonometri rtios Finding side lengths Solving
3 3 3C 3D 3 3F 3G 3H 3I 3J Chpter Wht you will lern Pythgors theorem Finding the shorter sides pplying Pythgors theorem Pythgors in three dimensions (tending) Trigonometri rtios Finding side lengths Solving
The Ellipse. is larger than the other.
 The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
The Ellipse Appolonius of Perg (5 B.C.) disovered tht interseting right irulr one ll the w through with plne slnted ut is not perpendiulr to the is, the intersetion provides resulting urve (oni setion)
Mathematics SKE: STRAND F. F1.1 Using Formulae. F1.2 Construct and Use Simple Formulae. F1.3 Revision of Negative Numbers
 Mthemtis SKE: STRAND F UNIT F1 Formule: Tet STRAND F: Alger F1 Formule Tet Contents Setion F1.1 Using Formule F1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule F1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers F1.4 Sustitution into Formule
Mthemtis SKE: STRAND F UNIT F1 Formule: Tet STRAND F: Alger F1 Formule Tet Contents Setion F1.1 Using Formule F1. Construt nd Use Simple Formule F1.3 Revision of Negtive Numers F1.4 Sustitution into Formule
9.1 Day 1 Warm Up. Solve the equation = x x 2 = March 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythagorean Theorem 1
 9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
9.1 Dy 1 Wrm Up Solve the eqution. 1. 4 2 + 3 2 = x 2 2. 13 2 + x 2 = 25 2 3. 3 2 2 + x 2 = 5 2 2 4. 5 2 + x 2 = 12 2 Mrh 1, 2017 Geometry 9.1 The Pythgoren Theorem 1 9.1 Dy 2 Wrm Up Use the Pythgoren
Part I: Study the theorem statement.
 Nme 1 Nme 2 Nme 3 A STUDY OF PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Instrutions: Together in groups of 2 or 3, fill out the following worksheet. You my lift nswers from the reding, or nswer on your own. Turn in one pket for
Nme 1 Nme 2 Nme 3 A STUDY OF PYTHAGORAS THEOREM Instrutions: Together in groups of 2 or 3, fill out the following worksheet. You my lift nswers from the reding, or nswer on your own. Turn in one pket for
Comparing the Pre-image and Image of a Dilation
 hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
hpter Summry Key Terms Postultes nd Theorems similr tringles (.1) inluded ngle (.2) inluded side (.2) geometri men (.) indiret mesurement (.6) ngle-ngle Similrity Theorem (.2) Side-Side-Side Similrity
Pythagoras Theorem. The area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides
 Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
Pythgors theorem nd trigonometry Pythgors Theorem The hypotenuse of right-ngled tringle is the longest side The hypotenuse is lwys opposite the right-ngle 2 = 2 + 2 or 2 = 2-2 or 2 = 2-2 The re of the
Trigonometry and Constructive Geometry
 Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
Trigonometry nd Construtive Geometry Trining prolems for M2 2018 term 1 Ted Szylowie tedszy@gmil.om 1 Leling geometril figures 1. Prtie writing Greek letters. αβγδɛθλµπψ 2. Lel the sides, ngles nd verties
SAMPLE. Trigonometry. Naming the sides of a right-angled triangle
 H P T E R 7 Trigonometry How re sin, os nd tn defined using right-ngled tringle? How n the trigonometri rtios e used to find the side lengths or ngles in right-ngled tringles? Wht is ment y n ngle of elevtion
H P T E R 7 Trigonometry How re sin, os nd tn defined using right-ngled tringle? How n the trigonometri rtios e used to find the side lengths or ngles in right-ngled tringles? Wht is ment y n ngle of elevtion
Basic Angle Rules 5. A Short Hand Geometric Reasons. B Two Reasons. 1 Write in full the meaning of these short hand geometric reasons.
 si ngle Rules 5 6 Short Hnd Geometri Resons 1 Write in full the mening of these short hnd geometri resons. Short Hnd Reson Full Mening ) se s isos Δ re =. ) orr s // lines re =. ) sum s t pt = 360. d)
si ngle Rules 5 6 Short Hnd Geometri Resons 1 Write in full the mening of these short hnd geometri resons. Short Hnd Reson Full Mening ) se s isos Δ re =. ) orr s // lines re =. ) sum s t pt = 360. d)
Plotting Ordered Pairs Using Integers
 SAMPLE Plotting Ordered Pirs Using Integers Ple two elsti nds on geoord to form oordinte xes shown on the right to help you solve these prolems.. Wht letter of the lphet does eh set of pirs nme?. (, )
SAMPLE Plotting Ordered Pirs Using Integers Ple two elsti nds on geoord to form oordinte xes shown on the right to help you solve these prolems.. Wht letter of the lphet does eh set of pirs nme?. (, )
Factorising FACTORISING.
 Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
Ftorising FACTORISING www.mthletis.om.u Ftorising FACTORISING Ftorising is the opposite of expning. It is the proess of putting expressions into rkets rther thn expning them out. In this setion you will
2.4 Linear Inequalities and Interval Notation
 .4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
.4 Liner Inequlities nd Intervl Nottion We wnt to solve equtions tht hve n inequlity symol insted of n equl sign. There re four inequlity symols tht we will look t: Less thn , Less thn or
8Similarity UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS. 8.1 Kick off with CAS 8.2 Similar objects 8.3 Linear scale factors. 8.4 Area and volume scale factors 8.
 8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8. re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review U N O R R E TE D P G E PR O O FS 8.1 Kick off with S Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims
8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8. re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review U N O R R E TE D P G E PR O O FS 8.1 Kick off with S Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims
2. There are an infinite number of possible triangles, all similar, with three given angles whose sum is 180.
 SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
SECTION 8-1 11 CHAPTER 8 Setion 8 1. There re n infinite numer of possile tringles, ll similr, with three given ngles whose sum is 180. 4. If two ngles α nd β of tringle re known, the third ngle n e found
Linear Algebra Introduction
 Introdution Wht is Liner Alger out? Liner Alger is rnh of mthemtis whih emerged yers k nd ws one of the pioneer rnhes of mthemtis Though, initilly it strted with solving of the simple liner eqution x +
Introdution Wht is Liner Alger out? Liner Alger is rnh of mthemtis whih emerged yers k nd ws one of the pioneer rnhes of mthemtis Though, initilly it strted with solving of the simple liner eqution x +
p-adic Egyptian Fractions
 p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
p-adic Egyptin Frctions Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Trditionl Egyptin Frctions nd Greedy Algorithm 2 3 Set-up 3 4 p-greedy Algorithm 5 5 p-egyptin Trditionl 10 6 Conclusion 1 Introduction An Egyptin frction
Calculus Module C21. Areas by Integration. Copyright This publication The Northern Alberta Institute of Technology All Rights Reserved.
 Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
Clculus Module C Ares Integrtion Copright This puliction The Northern Alert Institute of Technolog 7. All Rights Reserved. LAST REVISED Mrch, 9 Introduction to Ares Integrtion Sttement of Prerequisite
QUADRATIC EQUATION. Contents
 QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
QUADRATIC EQUATION Contents Topi Pge No. Theory 0-04 Exerise - 05-09 Exerise - 09-3 Exerise - 3 4-5 Exerise - 4 6 Answer Key 7-8 Syllus Qudrti equtions with rel oeffiients, reltions etween roots nd oeffiients,
Vectors. Chapter14. Syllabus reference: 4.1, 4.2, 4.5 Contents:
 hpter Vetors Syllus referene:.,.,.5 ontents: D E F G H I J K Vetors nd slrs Geometri opertions with vetors Vetors in the plne The mgnitude of vetor Opertions with plne vetors The vetor etween two points
hpter Vetors Syllus referene:.,.,.5 ontents: D E F G H I J K Vetors nd slrs Geometri opertions with vetors Vetors in the plne The mgnitude of vetor Opertions with plne vetors The vetor etween two points
BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I)
 /0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
/0 BEGINNING ALGEBRA (ALGEBRA I) SAMPLE TEST PLACEMENT EXAMINATION Downlod the omplete Study Pket: http://www.glendle.edu/studypkets Students who hve tken yer of high shool lger or its equivlent with grdes
Perimeter and Area. Mathletics Instant Workbooks. Copyright
 Perimeter nd Are Student Book - Series J- L B Mthletis Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series J Contents Topis Topi - Plne shpes Topi 2 - Perimeter of regulr shpes Topi 3 - Perimeter of irregulr
Perimeter nd Are Student Book - Series J- L B Mthletis Instnt Workooks Copyright Student Book - Series J Contents Topis Topi - Plne shpes Topi 2 - Perimeter of regulr shpes Topi 3 - Perimeter of irregulr
Bridging the gap: GCSE AS Level
 Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
Bridging the gp: GCSE AS Level CONTENTS Chpter Removing rckets pge Chpter Liner equtions Chpter Simultneous equtions 8 Chpter Fctors 0 Chpter Chnge the suject of the formul Chpter 6 Solving qudrtic equtions
1.3 SCALARS AND VECTORS
 Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
Bridge Course Phy I PUC 24 1.3 SCLRS ND VECTORS Introdution: Physis is the study of nturl phenomen. The study of ny nturl phenomenon involves mesurements. For exmple, the distne etween the plnet erth nd
This enables us to also express rational numbers other than natural numbers, for example:
 Overview Study Mteril Business Mthemtis 05-06 Alger The Rel Numers The si numers re,,3,4, these numers re nturl numers nd lso lled positive integers. The positive integers, together with the negtive integers
Overview Study Mteril Business Mthemtis 05-06 Alger The Rel Numers The si numers re,,3,4, these numers re nturl numers nd lso lled positive integers. The positive integers, together with the negtive integers
MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS 1.6
 MTHMTIS N STTISTIS 1.6 pply geometri resoning in solving prolems ternlly ssessed 4 redits S 91031 inding unknown ngles When finding the size of unknown ngles in figure, t lest two steps of resoning will
MTHMTIS N STTISTIS 1.6 pply geometri resoning in solving prolems ternlly ssessed 4 redits S 91031 inding unknown ngles When finding the size of unknown ngles in figure, t lest two steps of resoning will
Number systems: the Real Number System
 Numer systems: the Rel Numer System syllusref eferenceence Core topic: Rel nd complex numer systems In this ch chpter A Clssifiction of numers B Recurring decimls C Rel nd complex numers D Surds: suset
Numer systems: the Rel Numer System syllusref eferenceence Core topic: Rel nd complex numer systems In this ch chpter A Clssifiction of numers B Recurring decimls C Rel nd complex numers D Surds: suset
Trigonometry. cosθ. sinθ tanθ. Mathletics Instant Workbooks. Copyright
 Student Book - Series K- sinθ tnθ osθ Mtletis Instnt Workooks Copyrigt Student Book - Series K Contents Topis Topi - Nming te sides of rigt-ngled tringle Topi 2 - Te trigonometri rtios Topi 3 - Using lultor
Student Book - Series K- sinθ tnθ osθ Mtletis Instnt Workooks Copyrigt Student Book - Series K Contents Topis Topi - Nming te sides of rigt-ngled tringle Topi 2 - Te trigonometri rtios Topi 3 - Using lultor
Algebra Basics. Algebra Basics. Curriculum Ready ACMNA: 133, 175, 176, 177, 179.
 Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Curriulum Redy ACMNA: 33 75 76 77 79 www.mthletis.om Fill in the spes with nything you lredy know out Alger Creer Opportunities: Arhitets eletriins plumers et. use it to do importnt lultions. Give this
Calculus Cheat Sheet. Integrals Definitions. where F( x ) is an anti-derivative of f ( x ). Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. dx = f x dx g x dx
 Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Clulus Chet Sheet Integrls Definitions Definite Integrl: Suppose f ( ) is ontinuous Anti-Derivtive : An nti-derivtive of f ( ) on [, ]. Divide [, ] into n suintervls of is funtion, F( ), suh tht F = f.
Date Lesson Text TOPIC Homework. Solving for Obtuse Angles QUIZ ( ) More Trig Word Problems QUIZ ( )
 UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRI RTIOS Dte Lesson Text TOPI Homework pr. 4 5.1 (48) Trigonometry Review WS 5.1 # 3 5, 9 11, (1, 13)doso pr. 6 5. (49) Relted ngles omplete lesson shell & WS 5. pr. 30 5.3 (50) 5.3 5.4
UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRI RTIOS Dte Lesson Text TOPI Homework pr. 4 5.1 (48) Trigonometry Review WS 5.1 # 3 5, 9 11, (1, 13)doso pr. 6 5. (49) Relted ngles omplete lesson shell & WS 5. pr. 30 5.3 (50) 5.3 5.4
Goals: Determine how to calculate the area described by a function. Define the definite integral. Explore the relationship between the definite
 Unit #8 : The Integrl Gols: Determine how to clculte the re described by function. Define the definite integrl. Eplore the reltionship between the definite integrl nd re. Eplore wys to estimte the definite
Unit #8 : The Integrl Gols: Determine how to clculte the re described by function. Define the definite integrl. Eplore the reltionship between the definite integrl nd re. Eplore wys to estimte the definite
8 Measurement. How is measurement used in your home? 8E Area of a circle 8B Circumference of a circle. 8A Length and perimeter
 8A Length nd perimeter 8E Are of irle 8B Cirumferene of irle 8F Surfe re 8C Are of retngles nd tringles 8G Volume of prisms 8D Are of other qudrilterls 8H Are nd volume onversions SA M PL E Mesurement
8A Length nd perimeter 8E Are of irle 8B Cirumferene of irle 8F Surfe re 8C Are of retngles nd tringles 8G Volume of prisms 8D Are of other qudrilterls 8H Are nd volume onversions SA M PL E Mesurement
Proportions: A ratio is the quotient of two numbers. For example, 2 3
 Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
Proportions: rtio is the quotient of two numers. For exmple, 2 3 is rtio of 2 n 3. n equlity of two rtios is proportion. For exmple, 3 7 = 15 is proportion. 45 If two sets of numers (none of whih is 0)
Probability. b a b. a b 32.
 Proility If n event n hppen in '' wys nd fil in '' wys, nd eh of these wys is eqully likely, then proility or the hne, or its hppening is, nd tht of its filing is eg, If in lottery there re prizes nd lnks,
Proility If n event n hppen in '' wys nd fil in '' wys, nd eh of these wys is eqully likely, then proility or the hne, or its hppening is, nd tht of its filing is eg, If in lottery there re prizes nd lnks,
5Trigonometric UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS. ratios and their applications
 5Trigonometri rtios nd their pplitions 5.1 Kik off with CS 5.2 Trigonometry of right-ngled tringles 5.3 Elevtion, depression nd erings 5.4 The sine rule 5.5 The osine rule 5.6 rs, setors nd segments 5.7
5Trigonometri rtios nd their pplitions 5.1 Kik off with CS 5.2 Trigonometry of right-ngled tringles 5.3 Elevtion, depression nd erings 5.4 The sine rule 5.5 The osine rule 5.6 rs, setors nd segments 5.7
4.3 The Sine Law and the Cosine Law
 4.3 Te Sine Lw nd te osine Lw Te ee Tower is te tllest prt of nd s rliment uildings. ronze mst, wi flies te ndin flg, stnds on top of te ee Tower. From point 25 m from te foot of te tower, te ngle of elevtion
4.3 Te Sine Lw nd te osine Lw Te ee Tower is te tllest prt of nd s rliment uildings. ronze mst, wi flies te ndin flg, stnds on top of te ee Tower. From point 25 m from te foot of te tower, te ngle of elevtion
Chapter 1: Logarithmic functions and indices
 Chpter : Logrithmic functions nd indices. You cn simplify epressions y using rules of indices m n m n m n m n ( m ) n mn m m m m n m m n Emple Simplify these epressions: 5 r r c 4 4 d 6 5 e ( ) f ( ) 4
Chpter : Logrithmic functions nd indices. You cn simplify epressions y using rules of indices m n m n m n m n ( m ) n mn m m m m n m m n Emple Simplify these epressions: 5 r r c 4 4 d 6 5 e ( ) f ( ) 4
In right-angled triangles the square on the side subtending the right angle is equal to the squares on the sides containing the right angle.
 Mth 3329-Uniform Geometries Leture 06 1. Review of trigonometry While we re looking t Eulid s Elements, I d like to look t some si trigonometry. Figure 1. The Pythgoren theorem sttes tht if = 90, then
Mth 3329-Uniform Geometries Leture 06 1. Review of trigonometry While we re looking t Eulid s Elements, I d like to look t some si trigonometry. Figure 1. The Pythgoren theorem sttes tht if = 90, then
Mathematics Number: Logarithms
 plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
plce of mind F A C U L T Y O F E D U C A T I O N Deprtment of Curriculum nd Pedgogy Mthemtics Numer: Logrithms Science nd Mthemtics Eduction Reserch Group Supported y UBC Teching nd Lerning Enhncement
Exercise sheet 6: Solutions
 Eerise sheet 6: Solutions Cvet emptor: These re merel etended hints, rther thn omplete solutions. 1. If grph G hs hromti numer k > 1, prove tht its verte set n e prtitioned into two nonempt sets V 1 nd
Eerise sheet 6: Solutions Cvet emptor: These re merel etended hints, rther thn omplete solutions. 1. If grph G hs hromti numer k > 1, prove tht its verte set n e prtitioned into two nonempt sets V 1 nd
STRAND J: TRANSFORMATIONS, VECTORS and MATRICES
 Mthemtics SKE: STRN J STRN J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS nd MTRIES J3 Vectors Text ontents Section J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs * J3. Vectors nd Geometry Mthemtics SKE: STRN J J3 Vectors J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs Vectors
Mthemtics SKE: STRN J STRN J: TRNSFORMTIONS, VETORS nd MTRIES J3 Vectors Text ontents Section J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs * J3. Vectors nd Geometry Mthemtics SKE: STRN J J3 Vectors J3.1 Vectors nd Sclrs Vectors
ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS. The real numbers have the following properties: a b c ab ac
 REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
REVIEW OF ALGEBRA Here we review the bsic rules nd procedures of lgebr tht you need to know in order to be successful in clculus. ARITHMETIC OPERATIONS The rel numbers hve the following properties: b b
Triangles The following examples explore aspects of triangles:
 Tringles The following exmples explore spects of tringles: xmple 1: ltitude of right ngled tringle + xmple : tringle ltitude of the symmetricl ltitude of n isosceles x x - 4 +x xmple 3: ltitude of the
Tringles The following exmples explore spects of tringles: xmple 1: ltitude of right ngled tringle + xmple : tringle ltitude of the symmetricl ltitude of n isosceles x x - 4 +x xmple 3: ltitude of the
8Similarity ONLINE PAGE PROOFS. 8.1 Kick off with CAS 8.2 Similar objects 8.3 Linear scale factors. 8.4 Area and volume scale factors 8.
 8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8.4 re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims section of your eookplus for comprehensive step-y-step
8.1 Kick off with S 8. Similr ojects 8. Liner scle fctors 8Similrity 8.4 re nd volume scle fctors 8. Review Plese refer to the Resources t in the Prelims section of your eookplus for comprehensive step-y-step
MCH T 111 Handout Triangle Review Page 1 of 3
 Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
Hnout Tringle Review Pge of 3 In the stuy of sttis, it is importnt tht you e le to solve lgeri equtions n tringle prolems using trigonometry. The following is review of trigonometry sis. Right Tringle:
Algebraic fractions. This unit will help you to work with algebraic fractions and solve equations. rs r s 2. x x.
 Get strted 25 Algeri frtions This unit will help you to work with lgeri frtions nd solve equtions. AO1 Flueny hek 1 Ftorise 2 2 5 2 25 2 6 5 d 2 2 6 2 Simplify 2 6 3 rs r s 2 d 8 2 y 3 6 y 2 3 Write s
Get strted 25 Algeri frtions This unit will help you to work with lgeri frtions nd solve equtions. AO1 Flueny hek 1 Ftorise 2 2 5 2 25 2 6 5 d 2 2 6 2 Simplify 2 6 3 rs r s 2 d 8 2 y 3 6 y 2 3 Write s
5.2 Exponent Properties Involving Quotients
 5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
5. Eponent Properties Involving Quotients Lerning Objectives Use the quotient of powers property. Use the power of quotient property. Simplify epressions involving quotient properties of eponents. Use
K 7. Quadratic Equations. 1. Rewrite these polynomials in the form ax 2 + bx + c = 0. Identify the values of a, b and c:
 Qudrti Equtions The Null Ftor Lw Let's sy there re two numers nd. If # = then = or = (or oth re ) This mens tht if the produt of two epressions is zero, then t lest one of the epressions must e equl to
Qudrti Equtions The Null Ftor Lw Let's sy there re two numers nd. If # = then = or = (or oth re ) This mens tht if the produt of two epressions is zero, then t lest one of the epressions must e equl to
How do we solve these things, especially when they get complicated? How do we know when a system has a solution, and when is it unique?
 XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
XII. LINEAR ALGEBRA: SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS Tody we re going to tlk out solving systems of liner equtions. These re prolems tht give couple of equtions with couple of unknowns, like: 6= x + x 7=
