Reteach 2-3. Graphing Linear Functions. 22 Holt Algebra 2. Name Date Class
|
|
|
- Caitlin Marlene Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 -3 Graphing Linear Functions Use intercepts to sketch the graph of the function 3x 6y 1. The x-intercept is where the graph crosses the x-axis. To find the x-intercept, set y 0 and solve for x. 3x 6y 1 3x 6(0) 1 3x 1 x 4 The y-intercept is where the graph crosses the y-axis. To find the y-intercept, set x 0 and solve for y. 3x 6y 1 3(0) 6y 1 6y 1 y The y-intercept occurs at the point 0,. Plot the points ( 4, 0) and ( 0, ). Draw a line connecting the points. The x-intercept occurs at the point 4, 0. Find the intercepts and graph each line. 1. 3x y 6 a. 3x 6 x-intercept b. 3 y 6 y-intercept. 6x 3y 1 a. 6x 3 1 x-intercept b. 6 3y 1 y-intercept Holt Algebra
2 -3 Graphing Linear Functions (continued) Use the slope and the y-intercept to graph a linear function. To write y x 6 in slope-intercept form, solve for y. y x 6 x x y x 6 y x 6 y x 3 Compare y x 3 to y mx b. m, so the slope is. b 3, so the y-intercept is 3. y mx b is the slope-intercept form. m represents the slope and b represents the y-intercept. Write each function in slope-intercept form. Use m and b to graph. 3. x y 1 a. y x 4. y x 1 a. y b. m b. m c. b c. b 3 Holt Algebra
3 -4 Writing Linear Functions Write the equation of the line shown in the graph in slope-intercept form. Slope-intercept form: y mx b The point, 4 lies on the line. From 0, 1, move 3 units down, or a rise of 3 units, and units right, or a run of units, to, 4. m rise run 3 3 Note that when the rise is a drop the slope is negative. Substitute m 3 and b 1 into y mx b to get the equation y 3 x 1. Write the equation of each line in slope-intercept form b b b m rise run 1 m rise run 1 m rise run y x y y 30 Holt Algebra
4 -4 Writing Linear Functions (continued) The slopes of parallel and perpendicular lines have a special relationship. The slopes of parallel lines are equal. y x 1 and y x are parallel lines since both equations have a slope of. Note: The slopes of parallel vertical lines are undefined. The slopes of perpendicular lines are negative reciprocals. Their product is 1. y x 1 and y x 1 are perpendicular since 1. The point-slope form of the equation of a line is y y 1 m x x 1. The line has slope m and passes through the point x 1, y 1. Write the equation of the line perpendicular to y x through, 5. 3 Substitute values for m and x 1, y 1 in y y 1 m x x 1. x 1, y 1, 5, so x 1, y 1 5, and m 3 y y 1 m x x 1 y 5 3 x y 5 3x 6 y 3x 11 The negative reciprocal of 3 is 3 because Write the equation of each line. 4. parallel to y 4x 3 through the point 1, m x 1, y 1, y y 1 m x x 1 y x y 5. perpendicular to y x 4 through the point 1, 1 m x 1, y 1, y y 1 m x x 1 y x y 31 Holt Algebra
5 -6 Transforming Linear Functions Translating linear functions vertically or horizontally changes the intercepts of the function. It does NOT change the slope. Let f x 3x 1. Read the rule for each translation. Horizontal Translation B Think: Add to x, go west. Use f x r f x h. Translation units right c g x f x g x 3 x 1 Rule: g x 3x 5 Translation units left V h x f x f x h x 3 x 1 Rule: h x 3x 7 Let f x x 1. Write the rule for g x. Vertical Translation n Think: Add to y, go high. Use f x r f x k. Translation units up M g x f x g x 3x 1 Rule: g x 3x 3 Translation units down m h x f x f x h x 3x 1 Rule: h x 3x 1 1. horizontal translation 5 units right. vertical translation 4 units down g x f x g x f x g x x 1 g x g x g x 3. vertical translation 3 units up 4. horizontal translation 1 unit left g x f x g x f x g x g x 1 g x g x 5. vertical translation 7 units down 6. horizontal translation 9 units right 7. vertical translation 1 unit up 8. horizontal translation unit to the left 46 Holt Algebra
6 -6 Transforming Linear Functions (continued) Compressing or stretching linear functions changes the slope. Let f x 3x 1. Read the rule for each translation. Horizontal stretch or compression by a factor of b Use f x r f b x. Horizontal stretch by a factor of g x f b x f x g x 3 x 1 Rule: g x 3 x 1 Horizontal compression by a factor of h x f b x f 1 h x 3 x 1 Rule: h x 6x 1 x f x Vertical stretch or compression by a factor of a Use f x r a f x. Vertical stretch by a factor of g x a f x f x g x 3x 1 Rule: g x 6x Vertical compression by a factor of h x a f x f x h x 3x 1 Rule: h x 3 x Let f x x 1. Write the rule for g x. 7. vertical compression by a factor of 4 f x r g x g x 8. horizontal stretch by a factor of 3 4 f x f x r f 1 3 x 4 x 1 g x 1 3 x 1 x 1 4 g x 3 x 1 9. horizontal compression by a factor of 3 f x r 3 1 x vertical stretch by a factor of 5 f x r 5 x 1 g x 6x 1 g x r g x 10x 5 47 Holt Algebra
7 -7 Curve Fitting with Linear Models Use a scatter plot to identify a correlation. If the variables appear correlated, then find a line of fit. Positive correlation Negative correlation No correlation The table shows the relationship between two variables. Identify the correlation, sketch a line of fit, and find its equation. x y Step 1 Step Step 3 Step 4 Step 5 Make a scatter plot of the data. As x increases, y decreases. The data is negatively correlated. Use a straightedge to draw a line. There will be some points above and below the line. Choose two points on the line to find the equation: 1, 16 and 7,. Use the points to find the slope: m change in y change in x Use the point-slope form to find the equation of a line that models the data. y y 1 m x x 1 y 7 3 x 7 y 7 x 18 3 Use the scatter plot of the data to solve. 1. The correlation is Positive.. Choose two points on the line and find the slope. 4, 8 and 6, 11 ; m 3 3. Find the equation of a line that models the data. y 3 x 54 Holt Algebra
8 -7 Curve Fitting with Linear Models (continued) A line of best fit can be used to predict data. Use the correlation coefficient, r, to measure how well the data fits. If r is near 1, data is modeled by a line with a negative slope. 1 r 1 If r is near 0, data has no correlation. If r is near 1, data is modeled by a line with a positive slope. Use a graphing calculator to find the correlation coefficient of the data and the line of best fit. Use STAT EDIT to enter the data. x y Use LinReg from the STAT CALC menu to find the line of best fit and the correlation coefficient. LinReg y ax b a.0 b r.9308 r.9648 The correlation coefficient is The data is very close to linear with a negative slope. Use the linear regression model to predict y when x 3.5. y.x y y Use a calculator and the scatter plot of the data to solve. 4. Find the correlation coefficient, r Find the equation of the line of best fit. y 1.38x.9 6. Predict y when x.6. y Predict y when x 5.3. y Holt Algebra
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8)
 Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Characteristics of Linear Functions (pp. 1 of 8) Algebra 2 Parent Function Table Linear Parent Function: x y y = Domain: Range: What patterns do you observe in the table and graph of the linear parent
Sect The Slope-Intercept Form
 0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
0 Concepts # and # Sect. - The Slope-Intercept Form Slope-Intercept Form of a line Recall the following definition from the beginning of the chapter: Let a, b, and c be real numbers where a and b are not
Graphing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form 4.1. Positive Slope Negative Slope 0 slope No Slope
 Slope-Intercept Form y = mx + b m = slope b = y-intercept Graphing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form 4.1 Positive Slope Negative Slope 0 slope No Slope Example 1 Write an equation in slope-intercept form
Slope-Intercept Form y = mx + b m = slope b = y-intercept Graphing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form 4.1 Positive Slope Negative Slope 0 slope No Slope Example 1 Write an equation in slope-intercept form
Chapters 1 and 2 Test
 Class: Date: Chapters 1 and 2 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. 2r 9 6 Solve the inequality. Graph the solution set. a. r 1 1 2 c. r
Class: Date: Chapters 1 and 2 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. 2r 9 6 Solve the inequality. Graph the solution set. a. r 1 1 2 c. r
x and y, called the coordinates of the point.
 P.1 The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane (also called the rectangular coordinate system) is the plane that allows you to represent ordered pairs of real numbers by points. It is
P.1 The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane The Cartesian Plane (also called the rectangular coordinate system) is the plane that allows you to represent ordered pairs of real numbers by points. It is
The coordinates of the vertex of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the parabola opens upward. If a < 0, the parabola opens downward.
 Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 8 Quadratic Relations in Vertex Form The expression y ax p q defines a quadratic relation in form. The coordinates of the of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the
Mathematics 10 Page 1 of 8 Quadratic Relations in Vertex Form The expression y ax p q defines a quadratic relation in form. The coordinates of the of the corresponding parabola are p, q. If a > 0, the
MA.8.1 Students will apply properties of the real number system to simplify algebraic expressions and solve linear equations.
 Focus Statement: Students will solve multi-step linear, quadratic, and compound equations and inequalities using the algebraic properties of the real number system. They will also graph linear and quadratic
Focus Statement: Students will solve multi-step linear, quadratic, and compound equations and inequalities using the algebraic properties of the real number system. They will also graph linear and quadratic
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part I
 Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part I This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the first part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
Intermediate Algebra Summary - Part I This is an overview of the key ideas we have discussed during the first part of this course. You may find this summary useful as a study aid, but remember that the
Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions
 Analyze and graph relations. Find functional values. Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions We are familiar with a number line. A number line enables us to locate points, denoted by numbers, and find distances
Analyze and graph relations. Find functional values. Chapter 2.1 Relations and Functions We are familiar with a number line. A number line enables us to locate points, denoted by numbers, and find distances
Review of Section 1.1. Mathematical Models. Review of Section 1.1. Review of Section 1.1. Functions. Domain and range. Piecewise functions
 Review of Section 1.1 Functions Mathematical Models Domain and range Piecewise functions January 19, 2017 Even and odd functions Increasing and decreasing functions Mathematical Models January 19, 2017
Review of Section 1.1 Functions Mathematical Models Domain and range Piecewise functions January 19, 2017 Even and odd functions Increasing and decreasing functions Mathematical Models January 19, 2017
Linear Equations. Find the domain and the range of the following set. {(4,5), (7,8), (-1,3), (3,3), (2,-3)}
 Linear Equations Domain and Range Domain refers to the set of possible values of the x-component of a point in the form (x,y). Range refers to the set of possible values of the y-component of a point in
Linear Equations Domain and Range Domain refers to the set of possible values of the x-component of a point in the form (x,y). Range refers to the set of possible values of the y-component of a point in
1.2 Graphs and Lines. Cartesian Coordinate System
 1.2 Graphs and Lines Cartesian Coordinate System Note that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the points in a plane and the elements in the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) of real numbers. Graphs
1.2 Graphs and Lines Cartesian Coordinate System Note that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the points in a plane and the elements in the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) of real numbers. Graphs
Algebra I Assessment. Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Algebra I Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Algebra I Assessment Reporting Category 1: Functional Relationships The student will describe functional relationships in a variety
Algebra I Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Algebra I Assessment Reporting Category 1: Functional Relationships The student will describe functional relationships in a variety
Section 1.6. Functions
 Section 1.6 Functions Definitions Relation, Domain, Range, and Function The table describes a relationship between the variables x and y. This relationship is also described graphically. x y 3 2 4 1 5
Section 1.6 Functions Definitions Relation, Domain, Range, and Function The table describes a relationship between the variables x and y. This relationship is also described graphically. x y 3 2 4 1 5
Section 1.4. Meaning of Slope for Equations, Graphs, and Tables
 Section 1.4 Meaning of Slope for Equations, Graphs, and Tables Finding Slope from a Linear Equation Finding Slope from a Linear Equation Example Find the slope of the line Solution Create a table using
Section 1.4 Meaning of Slope for Equations, Graphs, and Tables Finding Slope from a Linear Equation Finding Slope from a Linear Equation Example Find the slope of the line Solution Create a table using
Cartesian Plane. Analytic Geometry. Unit Name
 3.1cartesian Unit Name Analytic Geometry Unit Goals 1. Create table of values in order to graph &/or determine if a relation is linear. Determine slope 3. Calculate missing information for linearelationships.
3.1cartesian Unit Name Analytic Geometry Unit Goals 1. Create table of values in order to graph &/or determine if a relation is linear. Determine slope 3. Calculate missing information for linearelationships.
GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Represent a linear function. Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Interpret slope
GUIDED NOTES 4.1 LINEAR FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Represent a linear function. Determine whether a linear function is increasing, decreasing, or constant. Interpret slope
Reteach Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
 8-2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Examples of rational expressions: 3 x, x 1, and x 3 x 2 2 x 2 Undefined at x 0 Undefined at x 0 Undefined at x 2 When simplifying a rational expression:
8-2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Examples of rational expressions: 3 x, x 1, and x 3 x 2 2 x 2 Undefined at x 0 Undefined at x 0 Undefined at x 2 When simplifying a rational expression:
Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3
 Section 3.1: Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3 Note: Make sure you already printed the graphing papers Plotting Points, Quadrant s signs, x-intercepts and y-intercepts Example 1: Plot the following
Section 3.1: Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 3 Note: Make sure you already printed the graphing papers Plotting Points, Quadrant s signs, x-intercepts and y-intercepts Example 1: Plot the following
Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review 3.1, 3.3, & 4.4. Name: Date: Period:
 Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review.1,., 4.1-4. & 4.4 Algebra I Name: Date: Period: Quest Topics Section.1 linear versus nonlinear rewrite linear equations in standard form: Ax By C find and use
Graphing and Writing Linear Equations Review.1,., 4.1-4. & 4.4 Algebra I Name: Date: Period: Quest Topics Section.1 linear versus nonlinear rewrite linear equations in standard form: Ax By C find and use
Finite Mathematics Chapter 1
 Finite Mathematics Chapter 1 Section 1.2 Straight Lines The equation of a horizontal line is of the form y # (namely b ), since m 0. The equation of a vertical line is of the form x # (namely the x -intercept
Finite Mathematics Chapter 1 Section 1.2 Straight Lines The equation of a horizontal line is of the form y # (namely b ), since m 0. The equation of a vertical line is of the form x # (namely the x -intercept
GUIDED NOTES 6.4 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS
 GUIDED NOTES 6.4 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. FINDING THE DOMAIN OF A LOGARITHMIC
GUIDED NOTES 6.4 GRAPHS OF LOGARITHMIC FUNCTIONS LEARNING OBJECTIVES In this section, you will: Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. FINDING THE DOMAIN OF A LOGARITHMIC
Period: Date: Lesson 3B: Properties of Dilations and Equations of lines
 Name: Period: Date: : Properties of Dilations and Equations of lines Learning Targets I can identify the properties of dilation mentioned as followed: dilation takes a line not passing through the center
Name: Period: Date: : Properties of Dilations and Equations of lines Learning Targets I can identify the properties of dilation mentioned as followed: dilation takes a line not passing through the center
BIOSTATISTICS NURS 3324
 Simple Linear Regression and Correlation Introduction Previously, our attention has been focused on one variable which we designated by x. Frequently, it is desirable to learn something about the relationship
Simple Linear Regression and Correlation Introduction Previously, our attention has been focused on one variable which we designated by x. Frequently, it is desirable to learn something about the relationship
AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment Attached is an assignment for students entering AP Calculus BC in the fall. Next year we will focus more on concepts and thinking outside of the box. We will not have time
AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment Attached is an assignment for students entering AP Calculus BC in the fall. Next year we will focus more on concepts and thinking outside of the box. We will not have time
Math 1 Unit 1 EOC Review
 Math 1 Unit 1 EOC Review Solving Equations (including Literal Equations) - Get the variable to show what it equals to satisfy the equation or inequality - Steps (each step only where necessary): 1. Distribute
Math 1 Unit 1 EOC Review Solving Equations (including Literal Equations) - Get the variable to show what it equals to satisfy the equation or inequality - Steps (each step only where necessary): 1. Distribute
Reminder: Univariate Data. Bivariate Data. Example: Puppy Weights. You weigh the pups and get these results: 2.5, 3.5, 3.3, 3.1, 2.6, 3.6, 2.
 TP: To review Standard Deviation, Residual Plots, and Correlation Coefficients HW: Do a journal entry on each of the calculator tricks in this lesson. Lesson slides will be posted with notes. Do Now: Write
TP: To review Standard Deviation, Residual Plots, and Correlation Coefficients HW: Do a journal entry on each of the calculator tricks in this lesson. Lesson slides will be posted with notes. Do Now: Write
Lesson 4 Linear Functions and Applications
 In this lesson, we take a close look at Linear Functions and how real world situations can be modeled using Linear Functions. We study the relationship between Average Rate of Change and Slope and how
In this lesson, we take a close look at Linear Functions and how real world situations can be modeled using Linear Functions. We study the relationship between Average Rate of Change and Slope and how
Mini Lecture 2.1 Introduction to Functions
 Mini Lecture.1 Introduction to Functions 1. Find the domain and range of a relation.. Determine whether a relation is a function. 3. Evaluate a function. 1. Find the domain and range of the relation. a.
Mini Lecture.1 Introduction to Functions 1. Find the domain and range of a relation.. Determine whether a relation is a function. 3. Evaluate a function. 1. Find the domain and range of the relation. a.
HMH Fuse Algebra correlated to the. Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics High School Algebra 1
 HMH Fuse Algebra 1 2012 correlated to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics High School Algebra 1 111.32. Algebra I (b) Knowledge and skills. (1) Foundations for functions. The student
HMH Fuse Algebra 1 2012 correlated to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics High School Algebra 1 111.32. Algebra I (b) Knowledge and skills. (1) Foundations for functions. The student
7. The set of all points for which the x and y coordinates are negative is quadrant III.
 SECTION - 67 CHAPTER Section -. To each point P in the plane there corresponds a single ordered pair of numbers (a, b) called the coordinates of the point. To each ordered pair of numbers (a, b) there
SECTION - 67 CHAPTER Section -. To each point P in the plane there corresponds a single ordered pair of numbers (a, b) called the coordinates of the point. To each ordered pair of numbers (a, b) there
AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMNET NAME: READ THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY
 AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMNET NAME: READ THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This packet is to be handed in on the first day of school. 2. All work must be shown in the space provided in the packet.
AP CALCULUS AB SUMMER ASSIGNMNET NAME: READ THE FOLLOWING DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY 1. This packet is to be handed in on the first day of school. 2. All work must be shown in the space provided in the packet.
Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient. Sign of Leading Coefficient
 Chapter 1 PRE-TEST REVIEW Polynomial Functions MHF4U Jensen Section 1: 1.1 Power Functions 1) State the degree and the leading coefficient of each polynomial Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient y = 2x
Chapter 1 PRE-TEST REVIEW Polynomial Functions MHF4U Jensen Section 1: 1.1 Power Functions 1) State the degree and the leading coefficient of each polynomial Polynomial Degree Leading Coefficient y = 2x
Equation. A mathematical sentence formed by setting two expressions equal to each other. Example 1: 3 6 = 18 Example 2: 7 + x = 12
 Equation A mathematical sentence formed by setting two expressions equal to each other Example 1: 3 6 = 18 Example 2: 7 + x = 12 Variable A symbol, usually a letter, that is used to represent one or more
Equation A mathematical sentence formed by setting two expressions equal to each other Example 1: 3 6 = 18 Example 2: 7 + x = 12 Variable A symbol, usually a letter, that is used to represent one or more
Use slope and y-intercept to write an equation. Write an equation of the line with a slope of 1 } 2. Write slope-intercept form.
 5.1 Study Guide For use with pages 282 291 GOAL Write equations of lines. EXAMPLE 1 Use slope and y-intercept to write an equation Write an equation of the line with a slope of 1 } 2 and a y-intercept
5.1 Study Guide For use with pages 282 291 GOAL Write equations of lines. EXAMPLE 1 Use slope and y-intercept to write an equation Write an equation of the line with a slope of 1 } 2 and a y-intercept
(a) Write down the value of q and of r. (2) Write down the equation of the axis of symmetry. (1) (c) Find the value of p. (3) (Total 6 marks)
 1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
1. Let f(x) = p(x q)(x r). Part of the graph of f is shown below. The graph passes through the points ( 2, 0), (0, 4) and (4, 0). (a) Write down the value of q and of r. (b) Write down the equation of
Section 1: Introduction to Functions and Graphs
 Section 1: Introduction to Functions and Graphs The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics TAC 111.42(c). 1.01 Lines Precalculus (1)(A) Precalculus
Section 1: Introduction to Functions and Graphs The following maps the videos in this section to the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Mathematics TAC 111.42(c). 1.01 Lines Precalculus (1)(A) Precalculus
Geometry Summer Assignment 2018
 Geometry Summer Assignment 2018 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in Geometry this year. You are advised to be familiar with each
Geometry Summer Assignment 2018 The following packet contains topics and definitions that you will be required to know in order to succeed in Geometry this year. You are advised to be familiar with each
2-1: Relations and Functions. Mr. Gallo Algebra 2. What is a Relation
 -1: Relations and Functions Mr. Gallo Algebra What is a Relation 1 In 000, the 4 most populous states(in millions), were CA {3}, TX {1}, NY {19} and FL {16}. The numbers of U.S. Representatives were CA
-1: Relations and Functions Mr. Gallo Algebra What is a Relation 1 In 000, the 4 most populous states(in millions), were CA {3}, TX {1}, NY {19} and FL {16}. The numbers of U.S. Representatives were CA
ANSWER KEY. Checklist Do I understand? Test Date: A-Day 2/7. Algebra 1 Benchmark Review study guide is due on test day!
 ANSWER KEY Name: Algebra 1 Benchmark Review study guide is due on test day! Test Date: A-Day 2/7 Checklist Do I understand? Unit 1 Solving Equations and Inequalities Two Step Equations Properties of Real
ANSWER KEY Name: Algebra 1 Benchmark Review study guide is due on test day! Test Date: A-Day 2/7 Checklist Do I understand? Unit 1 Solving Equations and Inequalities Two Step Equations Properties of Real
Chapter 2 Linear Relations and Functions
 Chapter Linear Relations and Functions I. Relations and Functions A. Definitions 1. Relation. Domain the variable ( ) 3. Range the variable ( ). Function a) A relationship between ( ) and ( ). b) The output
Chapter Linear Relations and Functions I. Relations and Functions A. Definitions 1. Relation. Domain the variable ( ) 3. Range the variable ( ). Function a) A relationship between ( ) and ( ). b) The output
a) Do you see a pattern in the scatter plot, or does it look like the data points are
 Aim #93: How do we distinguish between scatter plots that model a linear versus a nonlinear equation and how do we write the linear regression equation for a set of data using our calculator? Homework:
Aim #93: How do we distinguish between scatter plots that model a linear versus a nonlinear equation and how do we write the linear regression equation for a set of data using our calculator? Homework:
ALGEBRA 2 MIDTERM REVIEW. Simplify and evaluate the expression for the given value of the variable:
 ALGEBRA 2 MIDTERM REVIEW Evaluating Expressions: 1.) -3 + 3(-2+ 5) 2 2.) ( -5 ) 2 3.) -5 2 Simplify and evaluate the expression for the given value of the variable: 4.) f(x) = x 2 + x 8; find f(-2) 5.)
ALGEBRA 2 MIDTERM REVIEW Evaluating Expressions: 1.) -3 + 3(-2+ 5) 2 2.) ( -5 ) 2 3.) -5 2 Simplify and evaluate the expression for the given value of the variable: 4.) f(x) = x 2 + x 8; find f(-2) 5.)
Mathematical Modeling
 Mathematical Modeling Sample Problem: The chart below gives the profit for a company for the years 1990 to 1999, where 0 corresponds to 1990 and the profit is in millions of dollars. Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Mathematical Modeling Sample Problem: The chart below gives the profit for a company for the years 1990 to 1999, where 0 corresponds to 1990 and the profit is in millions of dollars. Year 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate System Graphs of Equations in Two Variables x-intercepts and y-intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the
CHAPTER 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models
 CHAPTER 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models 1.1 Introduction to Graphing 1.2 Functions and Graphs 1.3 Linear Functions, Slope, and Applications 1.4 Equations of Lines and Modeling 1.5 Linear Equations, Functions,
CHAPTER 1: Graphs, Functions, and Models 1.1 Introduction to Graphing 1.2 Functions and Graphs 1.3 Linear Functions, Slope, and Applications 1.4 Equations of Lines and Modeling 1.5 Linear Equations, Functions,
Session 4 2:40 3:30. If neither the first nor second differences repeat, we need to try another
 Linear Quadratics & Exponentials using Tables We can classify a table of values as belonging to a particular family of functions based on the math operations found on any calculator. First differences
Linear Quadratics & Exponentials using Tables We can classify a table of values as belonging to a particular family of functions based on the math operations found on any calculator. First differences
MINI LESSON. Lesson 2a Linear Functions and Applications
 MINI LESSON Lesson 2a Linear Functions and Applications Lesson Objectives: 1. Compute AVERAGE RATE OF CHANGE 2. Explain the meaning of AVERAGE RATE OF CHANGE as it relates to a given situation 3. Interpret
MINI LESSON Lesson 2a Linear Functions and Applications Lesson Objectives: 1. Compute AVERAGE RATE OF CHANGE 2. Explain the meaning of AVERAGE RATE OF CHANGE as it relates to a given situation 3. Interpret
RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW
 RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW Name: Block: Date: Total = % 2 202 Page of 4 Unit 2 . Sketch the graph of the following functions. State the domain and range. y = 2 x + 3 Domain: Range: 2. Identify
RADICAL AND RATIONAL FUNCTIONS REVIEW Name: Block: Date: Total = % 2 202 Page of 4 Unit 2 . Sketch the graph of the following functions. State the domain and range. y = 2 x + 3 Domain: Range: 2. Identify
Bivariate Data Summary
 Bivariate Data Summary Bivariate data data that examines the relationship between two variables What individuals to the data describe? What are the variables and how are they measured Are the variables
Bivariate Data Summary Bivariate data data that examines the relationship between two variables What individuals to the data describe? What are the variables and how are they measured Are the variables
Algebra One Dictionary
 Algebra One Dictionary Page 1 of 17 A Absolute Value - the distance between the number and 0 on a number line Algebraic Expression - An expression that contains numbers, operations and at least one variable.
Algebra One Dictionary Page 1 of 17 A Absolute Value - the distance between the number and 0 on a number line Algebraic Expression - An expression that contains numbers, operations and at least one variable.
Table of contents. Jakayla Robbins & Beth Kelly (UK) Precalculus Notes Fall / 53
 Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
Table of contents The Cartesian Coordinate System - Pictures of Equations Your Personal Review Graphs of Equations with Two Variables Distance Equations of Circles Midpoints Quantifying the Steepness of
LAKOTA WEST HIGH SCHOOL HONORS ALGEBRA II EXPECTATIONS ( )
 LAKOTA WEST HIGH SCHOOL HONORS ALGEBRA II EXPECTATIONS (07-08) Upon entering Honors Algebra II class at Lakota West HS it will be expected that you to have an excellent understanding of certain topics
LAKOTA WEST HIGH SCHOOL HONORS ALGEBRA II EXPECTATIONS (07-08) Upon entering Honors Algebra II class at Lakota West HS it will be expected that you to have an excellent understanding of certain topics
Lesson 3 - Linear Functions
 Lesson 3 - Linear Functions Introduction As an overview for the course, in Lesson's 1 and 2 we discussed the importance of functions to represent relationships and the associated notation of these functions
Lesson 3 - Linear Functions Introduction As an overview for the course, in Lesson's 1 and 2 we discussed the importance of functions to represent relationships and the associated notation of these functions
Name Class Date. Residuals and Linear Regression Going Deeper
 Name Class Date 4-8 and Linear Regression Going Deeper Essential question: How can you use residuals and linear regression to fit a line to data? You can evaluate a linear model s goodness of fit using
Name Class Date 4-8 and Linear Regression Going Deeper Essential question: How can you use residuals and linear regression to fit a line to data? You can evaluate a linear model s goodness of fit using
Experimental Design and Graphical Analysis of Data
 Experimental Design and Graphical Analysis of Data A. Designing a controlled experiment When scientists set up experiments they often attempt to determine how a given variable affects another variable.
Experimental Design and Graphical Analysis of Data A. Designing a controlled experiment When scientists set up experiments they often attempt to determine how a given variable affects another variable.
Rational Numbers. Integers. Irrational Numbers
 EOC Review: Pre-Algebra Unit Rational Numbers Integers Irrational Numbers Ex: Matrices: Ex 1: Ex 2: Ex 3: Unit 1 Equations Equations To solve an equation, use your calculator. STEPS: 1. Menu 2. Algebra
EOC Review: Pre-Algebra Unit Rational Numbers Integers Irrational Numbers Ex: Matrices: Ex 1: Ex 2: Ex 3: Unit 1 Equations Equations To solve an equation, use your calculator. STEPS: 1. Menu 2. Algebra
Chapter 3: Inequalities, Lines and Circles, Introduction to Functions
 QUIZ AND TEST INFORMATION: The material in this chapter is on Quiz 3 and Exam 2. You should complete at least one attempt of Quiz 3 before taking Exam 2. This material is also on the final exam and used
QUIZ AND TEST INFORMATION: The material in this chapter is on Quiz 3 and Exam 2. You should complete at least one attempt of Quiz 3 before taking Exam 2. This material is also on the final exam and used
Constant no variables, just a number. Linear Note: Same form as f () x mx b. Quadratic Note: Same form as. Cubic x to the third power
 Precalculus Notes: Section. Modeling High Degree Polnomial Functions Graphs of Polnomials Polnomial Notation f ( ) a a a... a a a is a polnomial function of degree n. n n 1 n n n1 n 1 0 n is the degree
Precalculus Notes: Section. Modeling High Degree Polnomial Functions Graphs of Polnomials Polnomial Notation f ( ) a a a... a a a is a polnomial function of degree n. n n 1 n n n1 n 1 0 n is the degree
7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS
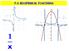 7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS x VOCABULARY Word Know It Well Have Heard It or Seen It No Clue RECIPROCAL FUNCTION ASYMPTOTE VERTICAL ASYMPTOTE HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE RECIPROCAL a mathematical expression or function
7.4 RECIPROCAL FUNCTIONS x VOCABULARY Word Know It Well Have Heard It or Seen It No Clue RECIPROCAL FUNCTION ASYMPTOTE VERTICAL ASYMPTOTE HORIZONTAL ASYMPTOTE RECIPROCAL a mathematical expression or function
OHS Algebra 2 Summer Packet
 OHS Algebra 2 Summer Packet Good Luck to: Date Started: (please print student name here) Geometry Teacher s Name: Complete each of the following exercises in this formative assessment. To receive full
OHS Algebra 2 Summer Packet Good Luck to: Date Started: (please print student name here) Geometry Teacher s Name: Complete each of the following exercises in this formative assessment. To receive full
Practice Test - Chapter 2
 Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS. Chapter 5
 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 5.1 EXPLORING THE GRAPHS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 5.2 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE EQUATIONS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What s a polynomial? A polynomial
POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 5.1 EXPLORING THE GRAPHS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS 5.2 CHARACTERISTICS OF THE EQUATIONS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS Chapter 5 POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What s a polynomial? A polynomial
To get horizontal and slant asymptotes algebraically we need to know about end behaviour for rational functions.
 Concepts: Horizontal Asymptotes, Vertical Asymptotes, Slant (Oblique) Asymptotes, Transforming Reciprocal Function, Sketching Rational Functions, Solving Inequalities using Sign Charts. Rational Function
Concepts: Horizontal Asymptotes, Vertical Asymptotes, Slant (Oblique) Asymptotes, Transforming Reciprocal Function, Sketching Rational Functions, Solving Inequalities using Sign Charts. Rational Function
x y x y 15 y is directly proportional to x. a Draw the graph of y against x.
 3 8.1 Direct proportion 1 x 2 3 5 10 12 y 6 9 15 30 36 B a Draw the graph of y against x. y 40 30 20 10 0 0 5 10 15 20 x b Write down a rule for y in terms of x.... c Explain why y is directly proportional
3 8.1 Direct proportion 1 x 2 3 5 10 12 y 6 9 15 30 36 B a Draw the graph of y against x. y 40 30 20 10 0 0 5 10 15 20 x b Write down a rule for y in terms of x.... c Explain why y is directly proportional
Chapter 1: Precalculus Review
 : Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
: Precalculus Review Math 115 17 January 2018 Overview 1 Important Notation 2 Exponents 3 Polynomials 4 Rational Functions 5 Cartesian Coordinates 6 Lines Notation Intervals: Interval Notation (a, b) (a,
Transformation of functions
 Transformation of functions Translations Dilations (from the x axis) Dilations (from the y axis) Reflections (in the x axis) Reflections (in the y axis) Summary Applying transformations Finding equations
Transformation of functions Translations Dilations (from the x axis) Dilations (from the y axis) Reflections (in the x axis) Reflections (in the y axis) Summary Applying transformations Finding equations
Chapter P. Prerequisites. Slide P- 1. Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
Slide P- 1 Chapter P Prerequisites 1 P.1 Real Numbers Quick Review 1. List the positive integers between -4 and 4.. List all negative integers greater than -4. 3. Use a calculator to evaluate the expression
SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS 1-30
 . Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
. Answer: 5 Evaluate x x + 9 for x SOLUTIONS FOR PROBLEMS - 0 When substituting x in x be sure to do the exponent before the multiplication by to get (). + 9 5 + When multiplying ( ) so that ( 7) ( ).
B.U.G. Newsletter. As one semester comes to an end by Jennifer L. Brown. December WÜA UÜÉãÇ
 B.U.G. Newsletter December 2014 THIS NEWSLETTER IS A SERVICE THAT WAS FUNDED BY "NO CHILD LEFT BEHIND" TITLE II PART A HIGHER EDUCATION IMPROVING TEACHER QUALITY HIGHER EDUCATION GRANT ADMINISTERED THROUGH
B.U.G. Newsletter December 2014 THIS NEWSLETTER IS A SERVICE THAT WAS FUNDED BY "NO CHILD LEFT BEHIND" TITLE II PART A HIGHER EDUCATION IMPROVING TEACHER QUALITY HIGHER EDUCATION GRANT ADMINISTERED THROUGH
1.5 GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF LINEAR FUNCTIONS
 Functions Modeling Change: 1.5 GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF LINEAR FUNCTIONS Interpreting the Parameters of a Example 1 Linear Function With time, t, in years, the populations of four towns, P A, P B, P C,
Functions Modeling Change: 1.5 GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF LINEAR FUNCTIONS Interpreting the Parameters of a Example 1 Linear Function With time, t, in years, the populations of four towns, P A, P B, P C,
MAC College Algebra
 MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
Sect 2.4 Linear Functions
 36 Sect 2.4 Linear Functions Objective 1: Graphing Linear Functions Definition A linear function is a function in the form y = f(x) = mx + b where m and b are real numbers. If m 0, then the domain and
36 Sect 2.4 Linear Functions Objective 1: Graphing Linear Functions Definition A linear function is a function in the form y = f(x) = mx + b where m and b are real numbers. If m 0, then the domain and
2014 Summer Review for Students Entering Algebra 2. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 1. Solving Linear Equations 2. Solving Linear Systems of Equations 3. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 4. Writing the Equation of a Line 5. Laws of Exponents and Scientific Notation 6. Solving
1. Solving Linear Equations 2. Solving Linear Systems of Equations 3. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 4. Writing the Equation of a Line 5. Laws of Exponents and Scientific Notation 6. Solving
MCR3U - Exam Review. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
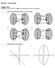 MCR3U - Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following relations is not a function? 2. Which graph is not a function?
MCR3U - Exam Review Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following relations is not a function? 2. Which graph is not a function?
4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
 590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
Sample Questions to the Final Exam in Math 1111 Chapter 2 Section 2.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs
 Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
Sample Questions to the Final Eam in Math 1111 Chapter Section.1: Basics of Functions and Their Graphs 1. Find the range of the function: y 16. a.[-4,4] b.(, 4],[4, ) c.[0, ) d.(, ) e.. Find the domain
Math Placement Test Review Sheet Louisburg College _ Summer = c = d. 5
 1. Preform indicated operations with fractions and decimals: a. 7 14 15 = b. 2 = c. 5 + 1 = d. 5 20 4 5 18 12 18 27 = 2. What is the least common denominator of fractions: 8 21 and 9 14. The fraction 9
1. Preform indicated operations with fractions and decimals: a. 7 14 15 = b. 2 = c. 5 + 1 = d. 5 20 4 5 18 12 18 27 = 2. What is the least common denominator of fractions: 8 21 and 9 14. The fraction 9
8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES
 8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES What is the standard form equation for a circle? Why do you use the distance formula when writing the equation of a circle? What general equation of a circle is
8.3 GRAPH AND WRITE EQUATIONS OF CIRCLES What is the standard form equation for a circle? Why do you use the distance formula when writing the equation of a circle? What general equation of a circle is
Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Graphs
 Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Graphs Section R Linear Equations and Inequalities Important Terms, Symbols, Concepts 1.1. Linear Equations and Inequalities A first degree, or linear, equation in one variable
Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Graphs Section R Linear Equations and Inequalities Important Terms, Symbols, Concepts 1.1. Linear Equations and Inequalities A first degree, or linear, equation in one variable
Course Readiness and Skills Review Handbook (83 topics) Course Readiness (21 topics) Course Name: Algebra Course Code: UY6JA-RATXM
 Course Name: Algebra 1 2014-15 Course Code: UY6JA-RATXM ALEKS Course: Algebra 1A Instructor: Ms. Dalton Course Dates: Begin: 11/18/2014 End: 06/18/2015 Course Content: 335 Topics (334 goal + 1 prerequisite)
Course Name: Algebra 1 2014-15 Course Code: UY6JA-RATXM ALEKS Course: Algebra 1A Instructor: Ms. Dalton Course Dates: Begin: 11/18/2014 End: 06/18/2015 Course Content: 335 Topics (334 goal + 1 prerequisite)
ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing
 ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing To be prepared for algebra two, and all subsequent math courses, you need to be able to accurately and efficiently find the slope of any line, be able to write
ALGEBRA 2 Summer Review Assignments Graphing To be prepared for algebra two, and all subsequent math courses, you need to be able to accurately and efficiently find the slope of any line, be able to write
Solve the following equations. Show all work to receive credit. No decimal answers. 8) 4x 2 = 100
 Algebra 2 1.1 Worksheet Name Solve the following equations. Show all work to receive credit. No decimal answers. 1) 3x 5(2 4x) = 18 2) 17 + 11x = -19x 25 3) 2 6x+9 b 4 = 7 4) = 2x 3 4 5) 3 = 5 7 x x+1
Algebra 2 1.1 Worksheet Name Solve the following equations. Show all work to receive credit. No decimal answers. 1) 3x 5(2 4x) = 18 2) 17 + 11x = -19x 25 3) 2 6x+9 b 4 = 7 4) = 2x 3 4 5) 3 = 5 7 x x+1
Vertex Form of a Parabola
 Verte Form of a Parabola In this investigation ou will graph different parabolas and compare them to what is known as the Basic Parabola. THE BASIC PARABOLA Equation = 2-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 verte? What s the
Verte Form of a Parabola In this investigation ou will graph different parabolas and compare them to what is known as the Basic Parabola. THE BASIC PARABOLA Equation = 2-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 verte? What s the
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS
 CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 2012, Brooks/Cole
CRASH COURSE IN PRECALCULUS Shiah-Sen Wang The graphs are prepared by Chien-Lun Lai Based on : Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus by J. Stuwart, L. Redin & S. Watson, 6th edition, 2012, Brooks/Cole
Algebra II/ Advanced Algebra II (2016)
 Algebra II/ Advanced Algebra II (2016) Course This course is intended to strengthen Algebra I skills and to develop the basic concepts of Algebra II. The course includes solving equations and inequalities
Algebra II/ Advanced Algebra II (2016) Course This course is intended to strengthen Algebra I skills and to develop the basic concepts of Algebra II. The course includes solving equations and inequalities
Chapter 1 Functions and Models
 Chapter 1 Functions and Models 1.2 Mathematical Models: A catalog of Essential Functions A mathematical model is a mathematical description of a real world situations such as the size of a population,
Chapter 1 Functions and Models 1.2 Mathematical Models: A catalog of Essential Functions A mathematical model is a mathematical description of a real world situations such as the size of a population,
Eidul- Adha Break. Darul Arqam North Scope and Sequence Revised 6/01/18 8 th Algebra I. 1 st Quarter (41 Days)
 Mc Graw Hill Mathematics, 1 st Quarter (41 Days) - Welcome Solve equations with one variable - Survey getting to Solve equations with two variables Aug 8-10 log Supplies know you 1st: (3 days) - received
Mc Graw Hill Mathematics, 1 st Quarter (41 Days) - Welcome Solve equations with one variable - Survey getting to Solve equations with two variables Aug 8-10 log Supplies know you 1st: (3 days) - received
2. The table of values shows the cost of movie tickets at a local theatre.
 Relations and Functions Practice Questions. The following distance-time graph represents the distance (in kilometres) a person bicycled during a 0-min period. Describe a possible scenario. 6 d (km) 6 9
Relations and Functions Practice Questions. The following distance-time graph represents the distance (in kilometres) a person bicycled during a 0-min period. Describe a possible scenario. 6 d (km) 6 9
Regressions of Olympic Proportions
 About the Lesson In this activity, students use the Manual-Fit and Linear Regression commands to find lines of best fit to model data from the Olympic Games. As a result, students will: Develop and evaluate
About the Lesson In this activity, students use the Manual-Fit and Linear Regression commands to find lines of best fit to model data from the Olympic Games. As a result, students will: Develop and evaluate
Pre-Calculus Summer Packet
 2013-2014 Pre-Calculus Summer Packet 1. Complete the attached summer packet, which is due on Friday, September 6, 2013. 2. The material will be reviewed in class on Friday, September 6 and Monday, September
2013-2014 Pre-Calculus Summer Packet 1. Complete the attached summer packet, which is due on Friday, September 6, 2013. 2. The material will be reviewed in class on Friday, September 6 and Monday, September
Algebra 1 Semester 1 Review Packet Name. Exam Date
 Algebra 1 Semester 1 Review Packet 2012-2013 Name Exam Date Part 1: Translate each verbal phrase into an algebraic expression: 1. The sum of a number x and the square of a number y. 2. Six less than a
Algebra 1 Semester 1 Review Packet 2012-2013 Name Exam Date Part 1: Translate each verbal phrase into an algebraic expression: 1. The sum of a number x and the square of a number y. 2. Six less than a
UNIT 2B QUADRATICS II
 UNIT 2B QUADRATICS II M2 12.1-8, M2 12.10, M1 4.4 2B.1 Quadratic Graphs Objective I will be able to identify quadratic functions and their vertices, graph them and adjust the height and width of the parabolas.
UNIT 2B QUADRATICS II M2 12.1-8, M2 12.10, M1 4.4 2B.1 Quadratic Graphs Objective I will be able to identify quadratic functions and their vertices, graph them and adjust the height and width of the parabolas.
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS ALGEBRA II. 1 st Nine Weeks,
 STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS ALGEBRA II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra II Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
STANDARDS OF LEARNING CONTENT REVIEW NOTES HONORS ALGEBRA II 1 st Nine Weeks, 2016-2017 OVERVIEW Algebra II Content Review Notes are designed by the High School Mathematics Steering Committee as a resource
Algebra I Exam Review
 Name Algebra I Exam Review Assigned on Assignment 1/17 Final Exam Practice Units 1 and Problems 1-4 1/18 Final Exam Practice Units and 4 Problems 5-5 1/19 Practice Final Exam Multiple Choice 1-16 1/ Practice
Name Algebra I Exam Review Assigned on Assignment 1/17 Final Exam Practice Units 1 and Problems 1-4 1/18 Final Exam Practice Units and 4 Problems 5-5 1/19 Practice Final Exam Multiple Choice 1-16 1/ Practice
Unit 3 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal
 Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal Asymptote Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Graphs
Five-Minute Check (over Lesson 8 3) CCSS Then/Now New Vocabulary Key Concept: Vertical and Horizontal Asymptotes Example 1: Graph with No Horizontal Asymptote Example 2: Real-World Example: Use Graphs
Algebra 2 Chapter 2 Page 1
 Mileage (MPGs) Section. Relations and Functions. To graph a relation, state the domain and range, and determine if the relation is a function.. To find the values of a function for the given element of
Mileage (MPGs) Section. Relations and Functions. To graph a relation, state the domain and range, and determine if the relation is a function.. To find the values of a function for the given element of
ALGEBRA 1 KEYSTONE. Module 1 and Module 2 both have 23 multiple choice questions and 4 CRQ questions.
 Name: ALGEBRA 1 KEYSTONE Module 1 and Module 2 both have 23 multiple choice questions and 4 CRQ questions. Module 1 Topics Numbers, Operations, Linear Equations, and Inequalities 1 Compare and order rational/irrational
Name: ALGEBRA 1 KEYSTONE Module 1 and Module 2 both have 23 multiple choice questions and 4 CRQ questions. Module 1 Topics Numbers, Operations, Linear Equations, and Inequalities 1 Compare and order rational/irrational
Steps to take to do the descriptive part of regression analysis:
 STA 2023 Simple Linear Regression: Least Squares Model Steps to take to do the descriptive part of regression analysis: A. Plot the data on a scatter plot. Describe patterns: 1. Is there a strong, moderate,
STA 2023 Simple Linear Regression: Least Squares Model Steps to take to do the descriptive part of regression analysis: A. Plot the data on a scatter plot. Describe patterns: 1. Is there a strong, moderate,
