q(m, n) -- q(m + 1, n) = p(m, n), n >~ 1. (2)
|
|
|
- Lester Golden
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL THEORY 7, (1969) A New Symmetry of Partitions FREEMAN J. DYSON* Belfer Graduate School of Science, Yeshiva University, New York, New York Communicated by D. Younger Received March 27, 1968 ABSTRACT A simple combinatorial argument, based upon the graphic representation of partitions, leads to an explicit formula for the number of partitions of an integer with a given difference between the largest part and the number of parts. Euler's formula for the reciprocal of the partition generating function is an immediate corollary. The "rank" of a partition of an integer into integer parts is defined as the greatest part minus the number of parts [1,2]. Let p(m, n) be the number of partitions of n into positive integer parts with rank m. Thus p(m, n) = 0 if either m >~ n or m ~< --n. There is a well-known symmetry of partitions, called conjugation [3], which interchanges the greatest part with the number of parts, and thus implies p(m, n) = p(--m, n). (1) In this paper we exhibit a second symmetry of partitions, distinct from (1), and deduce various consequences from the simultaneous existence of the two symmetries. We define q(m, n) to be the number of partitions of n into non-negative integer parts with rank m. As the addition of zero parts to a partition decreases the rank without changing the sum, we have q(m, n) -- q(m + 1, n) = p(m, n), n >~ 1. (2) However, it is important that (2) does not hold for n = 0. Since there are no partitions of zero into positive parts, p(m, 0) ~ 0, all m. (3) * On leave of absence from The Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, N. J. 56
2 A NEW SYMMETRY OF PARTITIONS 57 On the other hand, there exists an infinite sequence of partitions of zero into non-negative (zero) parts, so that q(m, O)= 1, m <~ --1, q(m, O) = O, m ~ O. (4) Therefore (2) holds everywhere except for the single pair of values m = --1, n = 0. Tables 1 and 2 show values ofp(m, n) and q(m, n), from which it is clear that the mismatch at the point (--1, 0) is not accidental. The values of p(m, n) are centered around the line m = 0, whereas those of q(m, n) are centered around m -- --I. TABLE 1 VALUES OF p(m, n) I I l TABLE 2 VALUES OF q(m, n) m n\ " * I * * * " "
3 58 DYSON A closer inspection of Table 2 reveals that the values lie symmetrically about the column m =---l on each line: 2n m constant. For example, the values marked with an asterisk have 2n--m- 8. The second symmetry of partitions is thus q(m, n) ~= q(-.m -- 2, n -- m -- l). (5) We can give a simple combinatorial proof of (5). Let P be any partition of n into non-negative parts, with rank m. We can define an "adjoint" partition P' as follows. From P we derive a partition P1 with strictly positive parts by adding 1 to each part in P. Let Ps be the conjugate of P1. Then P' is derived from P~ by subtracting 1 from each part. This procedure establishes a one-to-one symmetric relationship between partitions P and P' into non-negative parts. The rank of P' is (--m -- 2) and its sum is (n -- m -- 1). Thus (5) is merely a statement of the "adjoint" symmetry. Let p(n) be the total number of partitions of n into positive parts. As is customary, we make the convention p(0) = 1, in spite of (3). The definition of q(m, n) then implies q(m,/7) -- p(n), m < n, (6) q(m, n) -- O, m ~ n, (7) except for the mismatch which occurs when n -- 0, m = 0 or 1. The symmetry (1) together with (2) gives q(m,n) +q(1 -- m,/l),- q(1 -+ re, n) q q(--m,n), (8) except for n 0, m = il. Consequently, either side of (8) is a number independent of m. The value of this number is p(n) by (6) and (7). Thus q(m, n) + q(1 -- m, n) p(n), (9) except for n 0, m = 0 or 1. This together with (5) implies q(m,n) -- p(n)-- q(m -- 3, n ~- m -- 2), (lo) except for n -= 0, m -- 0 or 1, or equivalently q(m,n) =p(n m-- 1)-- q(m-~ 3, n - m-- 1), (11) except for m -= --2, n = -1 or m = --3, n --2.
4 A NEW SYMMETRY OF PARTITIONS 59 Either (I0) or (11) gives at once an explicit formula for q(m, n) in terms of p(n). Using (l 1) repeatedly, we find q(m, n) -- p(n -- m -- 1) -- p(n -- 2m -- 5) q-q(mq-6, n--2m--5) ---p(n--m-- l) -- p(n -- 2m -- 5) + p(n -- 3m -- 12) --p(n -- 4m -- 22) q... = ~ (--l)k-lp(rt - - km )). (12) k=l The series comes to an end after a finite number of terms, as soon as lk(3k -- l) + km > n. In the same way (10) gives q(m, n) = p(n) -- p(n q- m -- 2) q- p(n + 2m -- 7) -- p(n v- 3rn -- 15) -1- "" = ~ (--lf~p(n + km if- 1)). (13) I,:=0 Both (12) and (13) hold subject to the proviso that the exceptional case should not arise in (11) or (10), respectively. The exceptional case in (11) will arise only if for some k >~ 1 or n = ), m = 1--3k, n = i), m = 3k. (14) In case (14) holds, the term (--l)~-lp(0) is to be omitted from the right side of (12). Similarly, the exceptional case in (10) will arise only if for some k >~ 0 or n = -- lk(3k -- 1), m 3k, n lk(3k + 1), m = 3k + 1. (15) In case (15) holds, the term (--1) ~ p(o) on the right side of (13) is to be omitted. In particular, both (12) and (13) hold as written for all m ifn is positive, (12) holds for all n if m is non-negative, and (13) holds for all n if m is negative. It is now easy to deduce from (12) and (13) the explicit form of the generating functions Q~,(x) = ~ q(m, n)x '~. (16) n=o
5 60 DYSON We write also P(x) -= ~ p(n)x% (17) ~0 Then (12), with the correction applied whenever (14) holds, gives the result Qm(x) = P(x) ~ (-1)~-lx~*n+ 89 k~l (18) if either m >~ 0 or m -- 2 (mod 3), and Qm(x) = P(x) ~ (-1)k-ix km+ 89 (-1)~X -ll/6)~nlm-1), (19) if m < 0 and m = 1 n- 3p or m = 3p. Similarly, (13) with (15) gives Q,~(x) = P(x) ~ (--1)kx -k~+ 89 (20) k=0 if either m < 0 or m ~ 2 (mod 3), and Qm(x) = P(x) ~ (-1)kx -k'n+~j~(ak+l) - (-1)~x-(1/~)'"~-1), (21) k=0 ifm ~>0andm = 1 +3porm = 3p. The simple generating functions for q(m, n) are (18) for m ~> 0 and (20) for m < 0. These are consistent with the generating functions for p(m, n) derived earlier [1, 2]. Also, (18) and (20) are related through the identity Q,~(x) = xx+,~q... z(x), (22) which is a restatement of the basic symmetry (5). Finally we can equate (19) with (20) or (18) with (21). The result is P(x) ~ (--1)kX-k' (--1)~'X-(1/6)"'-1), (23) when m = t + 3p or m = 3p. In particular, taking m = p = 0, we have Euler's formula [P(x)]-1= ~ (--1)kx 89 k(~k+l). (24) k~--oo
6 A NEW SYMMETRY OF PARTITIONS 6i This combinatorial derivation of Euler's formula is less direct, but perhaps more illuminating, than the well-known combinatorial proof by Franklin [4]. REFERENCES 1. F. J. DYSON, Eureka 8 (1944), A. O. L. ATKIN AND P. SWINNERTON-DYER, Proe. London Math. Soc. (3) 4 (1953), G. H. HARDY AND E. M. WRIGHT, An Introduction to the Theory of Numbers, 1st ed., University Press, Oxford, 1938, p F. FRAr~KLIN, Cornpt. Rend. Acad. Sci. Paris 92 (1881), See also G. H. HARDY AND E. M. WRIGHT [3, p. 284].
The part-frequency matrices of a partition
 The part-frequency matrices of a partition William J. Keith, Michigan Tech Michigan Technological University Kliakhandler Conference 2015 August 28, 2015 A partition of an integer n is a sequence λ = (λ
The part-frequency matrices of a partition William J. Keith, Michigan Tech Michigan Technological University Kliakhandler Conference 2015 August 28, 2015 A partition of an integer n is a sequence λ = (λ
CONGRUENCES IN ORDERED PAIRS OF PARTITIONS
 IJMMS 2004:47, 2509 252 PII. S0672043439 http://ijmms.hindawi.com Hindawi Publishing Corp. CONGRUENCES IN ORDERED PAIRS OF PARTITIONS PAUL HAMMOND and RICHARD LEWIS Received 28 November 2003 and in revised
IJMMS 2004:47, 2509 252 PII. S0672043439 http://ijmms.hindawi.com Hindawi Publishing Corp. CONGRUENCES IN ORDERED PAIRS OF PARTITIONS PAUL HAMMOND and RICHARD LEWIS Received 28 November 2003 and in revised
= i 0. a i q i. (1 aq i ).
 SIEVED PARTITIO FUCTIOS AD Q-BIOMIAL COEFFICIETS Fran Garvan* and Dennis Stanton** Abstract. The q-binomial coefficient is a polynomial in q. Given an integer t and a residue class r modulo t, a sieved
SIEVED PARTITIO FUCTIOS AD Q-BIOMIAL COEFFICIETS Fran Garvan* and Dennis Stanton** Abstract. The q-binomial coefficient is a polynomial in q. Given an integer t and a residue class r modulo t, a sieved
The spt-crank for Ordinary Partitions
 The spt-crank for Ordinary Partitions William Y.C. Chen a,b, Kathy Q. Ji a and Wenston J.T. Zang a a Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P.R. China b Center for Applied
The spt-crank for Ordinary Partitions William Y.C. Chen a,b, Kathy Q. Ji a and Wenston J.T. Zang a a Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P.R. China b Center for Applied
What is the crank of a partition? Daniel Glasscock, July 2014
 What is the crank of a partition? Daniel Glasscock, July 2014 These notes complement a talk given for the What is...? seminar at the Ohio State University. Introduction The crank of an integer partition
What is the crank of a partition? Daniel Glasscock, July 2014 These notes complement a talk given for the What is...? seminar at the Ohio State University. Introduction The crank of an integer partition
DYSON'S CRANK OF A PARTITION
 BULLETIN (New Series) OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 8, Number, April 988 DYSON'S CRANK OF A PARTITION GEORGE E. ANDREWS AND F. G. GARVAN. Introduction. In [], F. J. Dyson defined the rank
BULLETIN (New Series) OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 8, Number, April 988 DYSON'S CRANK OF A PARTITION GEORGE E. ANDREWS AND F. G. GARVAN. Introduction. In [], F. J. Dyson defined the rank
A lattice path approach to countingpartitions with minimum rank t
 Discrete Mathematics 249 (2002) 31 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc A lattice path approach to countingpartitions with minimum rank t Alexander Burstein a, Sylvie Corteel b, Alexander Postnikov c, d; ;1
Discrete Mathematics 249 (2002) 31 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc A lattice path approach to countingpartitions with minimum rank t Alexander Burstein a, Sylvie Corteel b, Alexander Postnikov c, d; ;1
Generating Functions of Partitions
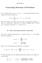 CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
Congruences in ordered pairs of partitions
 Congruences in ordered pairs of partitions Article Unspecified) Hammond, Paul and Lewis, Richard 2004) Congruences in ordered pairs of partitions. International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical
Congruences in ordered pairs of partitions Article Unspecified) Hammond, Paul and Lewis, Richard 2004) Congruences in ordered pairs of partitions. International Journal of Mathematics and Mathematical
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF GENERATING FUNCTION IDENTITIES FOR F-PARTITIONS
 COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF GENERATING FUNCTION IDENTITIES FOR F-PARTITIONS AE JA YEE 1 Abstract In his memoir in 1984 George E Andrews introduces many general classes of Frobenius partitions (simply F-partitions)
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF GENERATING FUNCTION IDENTITIES FOR F-PARTITIONS AE JA YEE 1 Abstract In his memoir in 1984 George E Andrews introduces many general classes of Frobenius partitions (simply F-partitions)
arxiv:math/ v2 [math.co] 19 Sep 2005
![arxiv:math/ v2 [math.co] 19 Sep 2005 arxiv:math/ v2 [math.co] 19 Sep 2005](/thumbs/75/72213461.jpg) A COMBINATORIAL PROOF OF THE ROGERS-RAMANUJAN AND SCHUR IDENTITIES arxiv:math/04072v2 [math.co] 9 Sep 2005 CILANNE BOULET AND IGOR PAK Abstract. We give a combinatorial proof of the first Rogers-Ramanujan
A COMBINATORIAL PROOF OF THE ROGERS-RAMANUJAN AND SCHUR IDENTITIES arxiv:math/04072v2 [math.co] 9 Sep 2005 CILANNE BOULET AND IGOR PAK Abstract. We give a combinatorial proof of the first Rogers-Ramanujan
ON CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF CONSECUTIVE VALUES OF P(N, M) Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, University at Albany, Albany, New York, 12222
 INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (007), #A16 ON CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF CONSECUTIVE VALUES OF P(N, M) Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, University at Albany, Albany,
INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (007), #A16 ON CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF CONSECUTIVE VALUES OF P(N, M) Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, University at Albany, Albany,
Nearly Equal Distributions of the Rank and the Crank of Partitions
 Nearly Equal Distributions of the Rank and the Crank of Partitions William Y.C. Chen, Kathy Q. Ji and Wenston J.T. Zang Dedicated to Professor Krishna Alladi on the occasion of his sixtieth birthday Abstract
Nearly Equal Distributions of the Rank and the Crank of Partitions William Y.C. Chen, Kathy Q. Ji and Wenston J.T. Zang Dedicated to Professor Krishna Alladi on the occasion of his sixtieth birthday Abstract
From cutting pancakes to Szemeredi-Trotter (and Ham Sandwiches too)
 From cutting pancakes to Szemeredi-Trotter (and Ham Sandwiches too) Po-Lam Yung March 14, 2017 How would you cut the following pancake into two equal halves using a knife (a straight line)? (Throughout
From cutting pancakes to Szemeredi-Trotter (and Ham Sandwiches too) Po-Lam Yung March 14, 2017 How would you cut the following pancake into two equal halves using a knife (a straight line)? (Throughout
On Partition Functions and Divisor Sums
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 5 (2002), Article 02.1.4 On Partition Functions and Divisor Sums Neville Robbins Mathematics Department San Francisco State University San Francisco,
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 5 (2002), Article 02.1.4 On Partition Functions and Divisor Sums Neville Robbins Mathematics Department San Francisco State University San Francisco,
R u t c o r Research R e p o r t. Uniform partitions and Erdös-Ko-Rado Theorem a. Vladimir Gurvich b. RRR , August, 2009
 R u t c o r Research R e p o r t Uniform partitions and Erdös-Ko-Rado Theorem a Vladimir Gurvich b RRR 16-2009, August, 2009 RUTCOR Rutgers Center for Operations Research Rutgers University 640 Bartholomew
R u t c o r Research R e p o r t Uniform partitions and Erdös-Ko-Rado Theorem a Vladimir Gurvich b RRR 16-2009, August, 2009 RUTCOR Rutgers Center for Operations Research Rutgers University 640 Bartholomew
Notes on Sets, Relations and Functions
 PURE MTH 3002 Topology & Analysis III (3246) 2002 Notes on Sets, Relations and Functions These are some notes taken from Mathematical Applications (now Mathematics for Information Technology (MIT)). They
PURE MTH 3002 Topology & Analysis III (3246) 2002 Notes on Sets, Relations and Functions These are some notes taken from Mathematical Applications (now Mathematics for Information Technology (MIT)). They
EXACT ENUMERATION OF GARDEN OF EDEN PARTITIONS. Brian Hopkins Department of Mathematics and Physics, Saint Peter s College, Jersey City, NJ 07306, USA
 EXACT ENUMERATION OF GARDEN OF EDEN PARTITIONS Brian Hopkins Department of Mathematics and Physics, Saint Peter s College, Jersey City, NJ 07306, USA bhopkins@spc.edu James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics,
EXACT ENUMERATION OF GARDEN OF EDEN PARTITIONS Brian Hopkins Department of Mathematics and Physics, Saint Peter s College, Jersey City, NJ 07306, USA bhopkins@spc.edu James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics,
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Nov 2018](/thumbs/91/104922308.jpg) The Unimodality of the Crank on Overpartitions Wenston J.T. Zang and Helen W.J. Zhang 2 arxiv:8.003v [math.co] 25 Nov 208 Institute of Advanced Study of Mathematics Harbin Institute of Technology, Heilongjiang
The Unimodality of the Crank on Overpartitions Wenston J.T. Zang and Helen W.J. Zhang 2 arxiv:8.003v [math.co] 25 Nov 208 Institute of Advanced Study of Mathematics Harbin Institute of Technology, Heilongjiang
Course : Algebraic Combinatorics
 Course 18.31: Algebraic Combinatorics Lecture Notes # 10 Addendum by Gregg Musiker (Based on Lauren Williams Notes for Math 19 at Harvard) February 5th - 7th, 009 1 Introduction to Partitions A partition
Course 18.31: Algebraic Combinatorics Lecture Notes # 10 Addendum by Gregg Musiker (Based on Lauren Williams Notes for Math 19 at Harvard) February 5th - 7th, 009 1 Introduction to Partitions A partition
NON-VANISHING OF THE PARTITION FUNCTION MODULO SMALL PRIMES
 NON-VANISHING OF THE PARTITION FUNCTION MODULO SMALL PRIMES MATTHEW BOYLAN Abstract Let pn be the ordinary partition function We show, for all integers r and s with s 1 and 0 r < s, that #{n : n r mod
NON-VANISHING OF THE PARTITION FUNCTION MODULO SMALL PRIMES MATTHEW BOYLAN Abstract Let pn be the ordinary partition function We show, for all integers r and s with s 1 and 0 r < s, that #{n : n r mod
Integer Partitions With Even Parts Below Odd Parts and the Mock Theta Functions
 Integer Partitions With Even Parts Below Odd Parts and the Mock Theta Functions by George E. Andrews Key Words: Partitions, mock theta functions, crank AMS Classification Numbers: P84, P83, P8, 33D5 Abstract
Integer Partitions With Even Parts Below Odd Parts and the Mock Theta Functions by George E. Andrews Key Words: Partitions, mock theta functions, crank AMS Classification Numbers: P84, P83, P8, 33D5 Abstract
Cranks in Ramanujan s Lost Notebook
 Cranks in Ramanujan s Lost Notebook Manjil P. Saikia Department of Mathematical Sciences, Tezpur University, Napaam Dist. - Sonitpur, Pin - 784028 India manjil@gonitsora.com January 22, 2014 Abstract We
Cranks in Ramanujan s Lost Notebook Manjil P. Saikia Department of Mathematical Sciences, Tezpur University, Napaam Dist. - Sonitpur, Pin - 784028 India manjil@gonitsora.com January 22, 2014 Abstract We
1 2 3 style total. Circle the correct answer; no explanation is required. Each problem in this section counts 5 points.
 1 2 3 style total Math 415 Examination 3 Please print your name: Answer Key 1 True/false Circle the correct answer; no explanation is required. Each problem in this section counts 5 points. 1. The rings
1 2 3 style total Math 415 Examination 3 Please print your name: Answer Key 1 True/false Circle the correct answer; no explanation is required. Each problem in this section counts 5 points. 1. The rings
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 998 Comments to the author at krm@mathsuqeduau All contents copyright c 99 Keith
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 998 Comments to the author at krm@mathsuqeduau All contents copyright c 99 Keith
1. A Little Set Theory
 . A Little Set Theory I see it, but I don t believe it. Cantor to Dedekind 29 June 877 Functions are the single most important idea pervading modern mathematics. We will assume the informal definition
. A Little Set Theory I see it, but I don t believe it. Cantor to Dedekind 29 June 877 Functions are the single most important idea pervading modern mathematics. We will assume the informal definition
NOTES Edited by William Adkins. On Goldbach s Conjecture for Integer Polynomials
 NOTES Edited by William Adkins On Goldbach s Conjecture for Integer Polynomials Filip Saidak 1. INTRODUCTION. We give a short proof of the fact that every monic polynomial f (x) in Z[x] can be written
NOTES Edited by William Adkins On Goldbach s Conjecture for Integer Polynomials Filip Saidak 1. INTRODUCTION. We give a short proof of the fact that every monic polynomial f (x) in Z[x] can be written
RANK DIFFERENCES FOR OVERPARTITIONS
 RANK DIFFERENCES FOR OVERPARTITIONS JEREMY LOVEJOY AND ROBERT OSBURN Abstract In 1954 Atkin Swinnerton-Dyer proved Dyson s conjectures on the rank of a partition by establishing formulas for the generating
RANK DIFFERENCES FOR OVERPARTITIONS JEREMY LOVEJOY AND ROBERT OSBURN Abstract In 1954 Atkin Swinnerton-Dyer proved Dyson s conjectures on the rank of a partition by establishing formulas for the generating
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K. R. MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND Second Online Version, December 1998 Comments to the author at krm@maths.uq.edu.au Contents 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS
Congruences for Fishburn numbers modulo prime powers
 Congruences for Fishburn numbers modulo prime powers Partitions, q-series, and modular forms AMS Joint Mathematics Meetings, San Antonio January, 205 University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign ξ(3) = 5
Congruences for Fishburn numbers modulo prime powers Partitions, q-series, and modular forms AMS Joint Mathematics Meetings, San Antonio January, 205 University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign ξ(3) = 5
FOUR IDENTITIES RELATED TO THIRD ORDER MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS IN RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK HAMZA YESILYURT
 FOUR IDENTITIES RELATED TO THIRD ORDER MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS IN RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK HAMZA YESILYURT Abstract. We prove, for the first time, a series of four related identities from Ramanujan s lost
FOUR IDENTITIES RELATED TO THIRD ORDER MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS IN RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK HAMZA YESILYURT Abstract. We prove, for the first time, a series of four related identities from Ramanujan s lost
a 11 x 1 + a 12 x a 1n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x a 2n x n = b 2.
 Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
Chapter 1 LINEAR EQUATIONS 11 Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x 1, x,, x n is an equation of the form a 1 x 1 + a x + + a n x n = b, where a 1, a,, a n, b are given real
An identity involving the least common multiple of binomial coefficients and its application
 Amer. Math. Monthly, 116 (2009, p. 836-839. An identity involving the least common multiple of binomial coefficients and its application Bair FARHI bair.farhi@gmail.com Abstract In this paper, we prove
Amer. Math. Monthly, 116 (2009, p. 836-839. An identity involving the least common multiple of binomial coefficients and its application Bair FARHI bair.farhi@gmail.com Abstract In this paper, we prove
Homework #2 solutions Due: June 15, 2012
 All of the following exercises are based on the material in the handout on integers found on the class website. 1. Find d = gcd(475, 385) and express it as a linear combination of 475 and 385. That is
All of the following exercises are based on the material in the handout on integers found on the class website. 1. Find d = gcd(475, 385) and express it as a linear combination of 475 and 385. That is
SPECTRAL ASYMMETRY AND RIEMANNIAN GEOMETRY
 SPECTRAL ASYMMETRY AND RIEMANNIAN GEOMETRY M. F. ATIYAH, V. K. PATODI AND I. M. SINGER 1 Main Theorems If A is a positive self-adjoint elliptic (linear) differential operator on a compact manifold then
SPECTRAL ASYMMETRY AND RIEMANNIAN GEOMETRY M. F. ATIYAH, V. K. PATODI AND I. M. SINGER 1 Main Theorems If A is a positive self-adjoint elliptic (linear) differential operator on a compact manifold then
THE DENOMINATORS OF POWER SUMS OF ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS. Bernd C. Kellner Göppert Weg 5, Göttingen, Germany
 #A95 INTEGERS 18 (2018) THE DENOMINATORS OF POWER SUMS OF ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Bernd C. Kellner Göppert Weg 5, 37077 Göttingen, Germany b@bernoulli.org Jonathan Sondow 209 West 97th Street, New Yor,
#A95 INTEGERS 18 (2018) THE DENOMINATORS OF POWER SUMS OF ARITHMETIC PROGRESSIONS Bernd C. Kellner Göppert Weg 5, 37077 Göttingen, Germany b@bernoulli.org Jonathan Sondow 209 West 97th Street, New Yor,
arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 9 Apr 2015
![arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 9 Apr 2015 arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 9 Apr 2015](/thumbs/75/72198575.jpg) CONGRUENCES FOR PARTITION PAIRS WITH CONDITIONS arxiv:408506v2 mathnt 9 Apr 205 CHRIS JENNINGS-SHAFFER Abstract We prove congruences for the number of partition pairs π,π 2 such that π is nonempty, sπ
CONGRUENCES FOR PARTITION PAIRS WITH CONDITIONS arxiv:408506v2 mathnt 9 Apr 205 CHRIS JENNINGS-SHAFFER Abstract We prove congruences for the number of partition pairs π,π 2 such that π is nonempty, sπ
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA
 ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND First Printing, 99 Chapter LINEAR EQUATIONS Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x,
ELEMENTARY LINEAR ALGEBRA K R MATTHEWS DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS UNIVERSITY OF QUEENSLAND First Printing, 99 Chapter LINEAR EQUATIONS Introduction to linear equations A linear equation in n unknowns x,
A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES
 A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES MATTHEW S. MIZUHARA, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND HOLLY SWISHER Abstract. Ramanujan s celebrated congruences of the partition function p(n have inspired a vast
A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES MATTHEW S. MIZUHARA, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND HOLLY SWISHER Abstract. Ramanujan s celebrated congruences of the partition function p(n have inspired a vast
THE MODULAR CURVE X O (169) AND RATIONAL ISOGENY
 THE MODULAR CURVE X O (169) AND RATIONAL ISOGENY M. A. KENKU 1. Introduction Let N be an integer ^ 1. The affine modular curve Y 0 (N) parametrizes isomorphism classes of pairs (E ; C N ) where E is an
THE MODULAR CURVE X O (169) AND RATIONAL ISOGENY M. A. KENKU 1. Introduction Let N be an integer ^ 1. The affine modular curve Y 0 (N) parametrizes isomorphism classes of pairs (E ; C N ) where E is an
MODULAR FORMS ARISING FROM Q(n) AND DYSON S RANK
 MODULAR FORMS ARISING FROM Q(n) AND DYSON S RANK MARIA MONKS AND KEN ONO Abstract Let R(w; q) be Dyson s generating function for partition ranks For roots of unity ζ it is known that R(ζ; q) and R(ζ; /q)
MODULAR FORMS ARISING FROM Q(n) AND DYSON S RANK MARIA MONKS AND KEN ONO Abstract Let R(w; q) be Dyson s generating function for partition ranks For roots of unity ζ it is known that R(ζ; q) and R(ζ; /q)
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF RAMANUJAN S 1 ψ 1 SUMMATION AND THE q-gauss SUMMATION
 COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF RAMANUJAN S 1 ψ 1 SUMMATION AND THE q-gauss SUMMATION AE JA YEE 1 Abstract. Theorems in the theory of partitions are closely related to basic hypergeometric series. Some identities
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF RAMANUJAN S 1 ψ 1 SUMMATION AND THE q-gauss SUMMATION AE JA YEE 1 Abstract. Theorems in the theory of partitions are closely related to basic hypergeometric series. Some identities
ANALOGUES OF THE TRIPLE PRODUCT IDENTITY, LEBESGUE S IDENTITY AND EULER S PENTAGONAL NUMBER THEOREM
 q-hypergeometric PROOFS OF POLYNOMIAL ANALOGUES OF THE TRIPLE PRODUCT IDENTITY, LEBESGUE S IDENTITY AND EULER S PENTAGONAL NUMBER THEOREM S OLE WARNAAR Abstract We present alternative, q-hypergeometric
q-hypergeometric PROOFS OF POLYNOMIAL ANALOGUES OF THE TRIPLE PRODUCT IDENTITY, LEBESGUE S IDENTITY AND EULER S PENTAGONAL NUMBER THEOREM S OLE WARNAAR Abstract We present alternative, q-hypergeometric
#A69 INTEGERS 13 (2013) OPTIMAL PRIMITIVE SETS WITH RESTRICTED PRIMES
 #A69 INTEGERS 3 (203) OPTIMAL PRIMITIVE SETS WITH RESTRICTED PRIMES William D. Banks Department of Mathematics, University of Missouri, Columbia, Missouri bankswd@missouri.edu Greg Martin Department of
#A69 INTEGERS 3 (203) OPTIMAL PRIMITIVE SETS WITH RESTRICTED PRIMES William D. Banks Department of Mathematics, University of Missouri, Columbia, Missouri bankswd@missouri.edu Greg Martin Department of
Basic Algebra. Final Version, August, 2006 For Publication by Birkhäuser Boston Along with a Companion Volume Advanced Algebra In the Series
 Basic Algebra Final Version, August, 2006 For Publication by Birkhäuser Boston Along with a Companion Volume Advanced Algebra In the Series Cornerstones Selected Pages from Chapter I: pp. 1 15 Anthony
Basic Algebra Final Version, August, 2006 For Publication by Birkhäuser Boston Along with a Companion Volume Advanced Algebra In the Series Cornerstones Selected Pages from Chapter I: pp. 1 15 Anthony
Divisibility. 1.1 Foundations
 1 Divisibility 1.1 Foundations The set 1, 2, 3,...of all natural numbers will be denoted by N. There is no need to enter here into philosophical questions concerning the existence of N. It will suffice
1 Divisibility 1.1 Foundations The set 1, 2, 3,...of all natural numbers will be denoted by N. There is no need to enter here into philosophical questions concerning the existence of N. It will suffice
A RESULT ON RAMANUJAN-LIKE CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF THE RESTRICTED PARTITION FUNCTION p(n, m) ACROSS BOTH VARIABLES
 #A63 INTEGERS 1 (01) A RESULT ON RAMANUJAN-LIKE CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF THE RESTRICTED PARTITION FUNCTION p(n, m) ACROSS BOTH VARIABLES Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, Whittier College, Whittier,
#A63 INTEGERS 1 (01) A RESULT ON RAMANUJAN-LIKE CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF THE RESTRICTED PARTITION FUNCTION p(n, m) ACROSS BOTH VARIABLES Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, Whittier College, Whittier,
arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 14 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 14 Nov 2017 arxiv: v1 [math.cv] 14 Nov 2017](/thumbs/87/95416418.jpg) EXTENDING A FUNCTION JUST BY MULTIPLYING AND DIVIDING FUNCTION VALUES: SMOOTHNESS AND PRIME IDENTITIES arxiv:1711.07887v1 [math.cv] 14 Nov 2017 PATRICK ARTHUR MILLER ABSTRACT. We describe a purely-multiplicative
EXTENDING A FUNCTION JUST BY MULTIPLYING AND DIVIDING FUNCTION VALUES: SMOOTHNESS AND PRIME IDENTITIES arxiv:1711.07887v1 [math.cv] 14 Nov 2017 PATRICK ARTHUR MILLER ABSTRACT. We describe a purely-multiplicative
Factorization of integer-valued polynomials with square-free denominator
 accepted by Comm. Algebra (2013) Factorization of integer-valued polynomials with square-free denominator Giulio Peruginelli September 9, 2013 Dedicated to Marco Fontana on the occasion of his 65th birthday
accepted by Comm. Algebra (2013) Factorization of integer-valued polynomials with square-free denominator Giulio Peruginelli September 9, 2013 Dedicated to Marco Fontana on the occasion of his 65th birthday
2 Arithmetic. 2.1 Greatest common divisors. This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}.
 2 Arithmetic This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. (See [Houston, Chapters 27 & 28]) 2.1 Greatest common divisors Definition 2.16. If a, b are integers, we say
2 Arithmetic This chapter is about properties of the integers Z = {..., 2, 1, 0, 1, 2,...}. (See [Houston, Chapters 27 & 28]) 2.1 Greatest common divisors Definition 2.16. If a, b are integers, we say
Ramsey-type problem for an almost monochromatic K 4
 Ramsey-type problem for an almost monochromatic K 4 Jacob Fox Benny Sudakov Abstract In this short note we prove that there is a constant c such that every k-edge-coloring of the complete graph K n with
Ramsey-type problem for an almost monochromatic K 4 Jacob Fox Benny Sudakov Abstract In this short note we prove that there is a constant c such that every k-edge-coloring of the complete graph K n with
RAMANUJAN S MOST BEAUTIFUL IDENTITY
 RAMANUJAN S MOST BEAUTIFUL IDENTITY MICHAEL D. HIRSCHHORN Abstract We give a simple proof of the identity which for Hardy represented the best of Ramanujan. On the way, we give a new proof of an important
RAMANUJAN S MOST BEAUTIFUL IDENTITY MICHAEL D. HIRSCHHORN Abstract We give a simple proof of the identity which for Hardy represented the best of Ramanujan. On the way, we give a new proof of an important
Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums of binomial coefficients
 Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums of binomial coefficients Tamás Mathematics Department Occidental College 29th Journées Arithmétiques JA2015, July 6-10, 2015 Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums
Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums of binomial coefficients Tamás Mathematics Department Occidental College 29th Journées Arithmétiques JA2015, July 6-10, 2015 Arithmetic properties of lacunary sums
How many units can a commutative ring have?
 How many units can a commutative ring have? Sunil K. Chebolu and Keir Locridge Abstract. László Fuchs posed the following problem in 960, which remains open: classify the abelian groups occurring as the
How many units can a commutative ring have? Sunil K. Chebolu and Keir Locridge Abstract. László Fuchs posed the following problem in 960, which remains open: classify the abelian groups occurring as the
THE PRESERVATION OF CONVERGENCE OF MEASURABLE FUNCTIONS UNDER COMPOSITION
 THE PRESERVATION OF CONVERGENCE OF MEASURABLE FUNCTIONS UNDER COMPOSITION ROBERT G. BARTLE AND JAMES T. JOICHI1 Let / be a real-valued measurable function on a measure space (S,, p.) and let
THE PRESERVATION OF CONVERGENCE OF MEASURABLE FUNCTIONS UNDER COMPOSITION ROBERT G. BARTLE AND JAMES T. JOICHI1 Let / be a real-valued measurable function on a measure space (S,, p.) and let
A RELATION BETWEEN SCHUR P AND S. S. Leidwanger. Universite de Caen, CAEN. cedex FRANCE. March 24, 1997
 A RELATION BETWEEN SCHUR P AND S FUNCTIONS S. Leidwanger Departement de Mathematiques, Universite de Caen, 0 CAEN cedex FRANCE March, 997 Abstract We dene a dierential operator of innite order which sends
A RELATION BETWEEN SCHUR P AND S FUNCTIONS S. Leidwanger Departement de Mathematiques, Universite de Caen, 0 CAEN cedex FRANCE March, 997 Abstract We dene a dierential operator of innite order which sends
EXTRA CREDIT FOR MATH 39
 EXTRA CREDIT FOR MATH 39 This is the second, theoretical, part of an extra credit homework. This homework in not compulsory. If you do it, you can get up to 6 points (3 points for each part) of extra credit
EXTRA CREDIT FOR MATH 39 This is the second, theoretical, part of an extra credit homework. This homework in not compulsory. If you do it, you can get up to 6 points (3 points for each part) of extra credit
#A22 INTEGERS 17 (2017) NEW CONGRUENCES FOR `-REGULAR OVERPARTITIONS
 #A22 INTEGERS 7 (207) NEW CONGRUENCES FOR `-REGULAR OVERPARTITIONS Shane Chern Department of Mathematics, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania shanechern@psu.edu Received: 0/6/6,
#A22 INTEGERS 7 (207) NEW CONGRUENCES FOR `-REGULAR OVERPARTITIONS Shane Chern Department of Mathematics, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania shanechern@psu.edu Received: 0/6/6,
Prime and irreducible elements of the ring of integers modulo n
 Prime and irreducible elements of the ring of integers modulo n M. H. Jafari and A. R. Madadi Department of Pure Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematical Sciences University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran Abstract
Prime and irreducible elements of the ring of integers modulo n M. H. Jafari and A. R. Madadi Department of Pure Mathematics, Faculty of Mathematical Sciences University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran Abstract
SYLVESTER S WAVE THEORY OF PARTITIONS
 SYLVESTER S WAVE THEORY OF PARTITIONS Georgia Southern University DIMACS July 11, 2011 A partition of an integer n is a representation of n as a sum of positive integers where order of summands (parts)
SYLVESTER S WAVE THEORY OF PARTITIONS Georgia Southern University DIMACS July 11, 2011 A partition of an integer n is a representation of n as a sum of positive integers where order of summands (parts)
On the lines passing through two conjugates of a Salem number
 Under consideration for publication in Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1 On the lines passing through two conjugates of a Salem number By ARTŪRAS DUBICKAS Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius
Under consideration for publication in Math. Proc. Camb. Phil. Soc. 1 On the lines passing through two conjugates of a Salem number By ARTŪRAS DUBICKAS Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius
Chapter 2 Subspaces of R n and Their Dimensions
 Chapter 2 Subspaces of R n and Their Dimensions Vector Space R n. R n Definition.. The vector space R n is a set of all n-tuples (called vectors) x x 2 x =., where x, x 2,, x n are real numbers, together
Chapter 2 Subspaces of R n and Their Dimensions Vector Space R n. R n Definition.. The vector space R n is a set of all n-tuples (called vectors) x x 2 x =., where x, x 2,, x n are real numbers, together
CONGRUENT NUMBERS AND ELLIPTIC CURVES
 CONGRUENT NUMBERS AND ELLIPTIC CURVES JIM BROWN Abstract. In this short paper we consider congruent numbers and how they give rise to elliptic curves. We will begin with very basic notions before moving
CONGRUENT NUMBERS AND ELLIPTIC CURVES JIM BROWN Abstract. In this short paper we consider congruent numbers and how they give rise to elliptic curves. We will begin with very basic notions before moving
The Maximum Dimension of a Subspace of Nilpotent Matrices of Index 2
 The Maximum Dimension of a Subspace of Nilpotent Matrices of Index L G Sweet Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Prince Edward Island Charlottetown, PEI C1A4P, Canada sweet@upeica J
The Maximum Dimension of a Subspace of Nilpotent Matrices of Index L G Sweet Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Prince Edward Island Charlottetown, PEI C1A4P, Canada sweet@upeica J
11-Dissection and Modulo 11 Congruences Properties for Partition Generating Function
 Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 1, 1-10 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.310116 11-Dissection and Modulo 11 Congruences Properties for Partition Generating
Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sciences, Vol. 9, 2014, no. 1, 1-10 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ijcms.2014.310116 11-Dissection and Modulo 11 Congruences Properties for Partition Generating
SOME FINITE IDENTITIES CONNECTED WITH POISSON'S SUMMATION FORMULA
 SOME FINITE IDENTITIES CONNECTED WITH POISSON'S SUMMATION FORMULA by A. P. GUINAND (Received 1st September 1959) 1. Introduction It is known that there is a connexion between the functional equation of
SOME FINITE IDENTITIES CONNECTED WITH POISSON'S SUMMATION FORMULA by A. P. GUINAND (Received 1st September 1959) 1. Introduction It is known that there is a connexion between the functional equation of
On certain Regular Maps with Automorphism group PSL(2, p) Martin Downs
 BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 53, 2007 (59 67) On certain Regular Maps with Automorphism group PSL(2, p) Martin Downs Received 18/04/2007 Accepted 03/10/2007 Abstract Let p be any prime
BULLETIN OF THE GREEK MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 53, 2007 (59 67) On certain Regular Maps with Automorphism group PSL(2, p) Martin Downs Received 18/04/2007 Accepted 03/10/2007 Abstract Let p be any prime
HAMBURGER BEITRÄGE ZUR MATHEMATIK
 HAMBURGER BEITRÄGE ZUR MATHEMATIK Heft 8 Degree Sequences and Edge Connectivity Matthias Kriesell November 007 Degree sequences and edge connectivity Matthias Kriesell November 9, 007 Abstract For each
HAMBURGER BEITRÄGE ZUR MATHEMATIK Heft 8 Degree Sequences and Edge Connectivity Matthias Kriesell November 007 Degree sequences and edge connectivity Matthias Kriesell November 9, 007 Abstract For each
SELF-CONJUGATE VECTOR PARTITIONS AND THE PARITY OF THE SPT-FUNCTION
 SELF-CONJUGATE VECTOR PARTITIONS AND THE PARITY OF THE SPT-FUNCTION GEORGE E ANDREWS FRANK G GARVAN AND JIE LIANG Abstract Let sptn denote the total number of appearances of the smallest parts in all the
SELF-CONJUGATE VECTOR PARTITIONS AND THE PARITY OF THE SPT-FUNCTION GEORGE E ANDREWS FRANK G GARVAN AND JIE LIANG Abstract Let sptn denote the total number of appearances of the smallest parts in all the
Congruences of Restricted Partition Functions
 Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Rose-Hulman Scholar Mathematical Sciences Technical Reports (MSTR) Mathematics 6-2002 Congruences of Restricted Partition Functions Matthew Culek Amanda Knecht Advisors:
Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology Rose-Hulman Scholar Mathematical Sciences Technical Reports (MSTR) Mathematics 6-2002 Congruences of Restricted Partition Functions Matthew Culek Amanda Knecht Advisors:
A combinatorial problem related to Mahler s measure
 A combinatorial problem related to Mahler s measure W. Duke ABSTRACT. We give a generalization of a result of Myerson on the asymptotic behavior of norms of certain Gaussian periods. The proof exploits
A combinatorial problem related to Mahler s measure W. Duke ABSTRACT. We give a generalization of a result of Myerson on the asymptotic behavior of norms of certain Gaussian periods. The proof exploits
Mini-Course on Limits and Sequences. Peter Kwadwo Asante. B.S., Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Ghana, 2014 A REPORT
 Mini-Course on Limits and Sequences by Peter Kwadwo Asante B.S., Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Ghana, 204 A REPORT submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Mini-Course on Limits and Sequences by Peter Kwadwo Asante B.S., Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, Ghana, 204 A REPORT submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
A PARTITION IDENTITY AND THE UNIVERSAL MOCK THETA FUNCTION g 2
 A PARTITION IDENTITY AND THE UNIVERSAL MOCK THETA FUNCTION g KATHRIN BRINGMANN, JEREMY LOVEJOY, AND KARL MAHLBURG Abstract. We prove analytic and combinatorial identities reminiscent of Schur s classical
A PARTITION IDENTITY AND THE UNIVERSAL MOCK THETA FUNCTION g KATHRIN BRINGMANN, JEREMY LOVEJOY, AND KARL MAHLBURG Abstract. We prove analytic and combinatorial identities reminiscent of Schur s classical
= (q) M+N (q) M (q) N
 A OVERPARTITIO AALOGUE OF THE -BIOMIAL COEFFICIETS JEHAE DOUSSE AD BYUGCHA KIM Abstract We define an overpartition analogue of Gaussian polynomials (also known as -binomial coefficients) as a generating
A OVERPARTITIO AALOGUE OF THE -BIOMIAL COEFFICIETS JEHAE DOUSSE AD BYUGCHA KIM Abstract We define an overpartition analogue of Gaussian polynomials (also known as -binomial coefficients) as a generating
CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES FOR THE PARTITION FUNCTION. Department of Mathematics Department of Mathematics. Urbana, Illinois Madison, WI 53706
 CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES FOR THE PARTITION FUNCTION Scott Ahlgren Ken Ono Department of Mathematics Department of Mathematics University of Illinois University of Wisconsin Urbana, Illinois 61801 Madison,
CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES FOR THE PARTITION FUNCTION Scott Ahlgren Ken Ono Department of Mathematics Department of Mathematics University of Illinois University of Wisconsin Urbana, Illinois 61801 Madison,
SYMMETRIC CHAIN DECOMPOSITION FOR CYCLIC QUOTIENTS OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRAS AND RELATION TO CYCLIC CRYSTALS
 SYMMETRIC CHAIN DECOMPOSITION FOR CYCLIC QUOTIENTS OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRAS AND RELATION TO CYCLIC CRYSTALS PATRICIA HERSH AND ANNE SCHILLING Abstract. The quotient of a Boolean algebra by a cyclic group is
SYMMETRIC CHAIN DECOMPOSITION FOR CYCLIC QUOTIENTS OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRAS AND RELATION TO CYCLIC CRYSTALS PATRICIA HERSH AND ANNE SCHILLING Abstract. The quotient of a Boolean algebra by a cyclic group is
ASYMPTOTICS FOR RANK AND CRANK MOMENTS
 ASYMPTOTICS FOR RANK AND CRANK MOMENTS KATHRIN BRINGMANN, KARL MAHLBURG, AND ROBERT C. RHOADES Abstract. Moments of the partition rank and crank statistics have been studied for their connections to combinatorial
ASYMPTOTICS FOR RANK AND CRANK MOMENTS KATHRIN BRINGMANN, KARL MAHLBURG, AND ROBERT C. RHOADES Abstract. Moments of the partition rank and crank statistics have been studied for their connections to combinatorial
A Search for Large Twin Prime Pairs. By R. E. Crandall and M. A. Penk. Abstract. Two methods are discussed for finding large integers m such that m I
 MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION, VOLUME 33, NUMBER 145 JANUARY 1979, PAGES 383-388 A Search for Large Twin Prime Pairs By R. E. Crandall and M. A. Penk Abstract. Two methods are discussed for finding large
MATHEMATICS OF COMPUTATION, VOLUME 33, NUMBER 145 JANUARY 1979, PAGES 383-388 A Search for Large Twin Prime Pairs By R. E. Crandall and M. A. Penk Abstract. Two methods are discussed for finding large
Successive Derivatives and Integer Sequences
 2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol 4 (20, Article 73 Successive Derivatives and Integer Sequences Rafael Jaimczu División Matemática Universidad Nacional de Luján Buenos Aires Argentina jaimczu@mailunlueduar
2 3 47 6 23 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol 4 (20, Article 73 Successive Derivatives and Integer Sequences Rafael Jaimczu División Matemática Universidad Nacional de Luján Buenos Aires Argentina jaimczu@mailunlueduar
An example of elliptic curve over Q with rank equal to Introduction. Andrej Dujella
 An example of elliptic curve over Q with rank equal to 15 Andrej Dujella Abstract We construct an elliptic curve over Q with non-trivial 2-torsion point and rank exactly equal to 15. 1 Introduction Let
An example of elliptic curve over Q with rank equal to 15 Andrej Dujella Abstract We construct an elliptic curve over Q with non-trivial 2-torsion point and rank exactly equal to 15. 1 Introduction Let
IMPROVEMENT OF A THEOREM OF LINNIK AND WALFISZ 423 IMPROVEMENT OF A THEOREM OF LINNIK AND WALFISZ. By S. CHOWLA
 IMPROVEMENT OF A THEOREM OF LINNIK AND WALFISZ 423 IMPROVEMENT OF A THEOREM OF LINNIK AND WALFISZ By S. CHOWLA [Received 19 November 1946 Read 19 December 1946] 1. On the basis of the hitherto unproved
IMPROVEMENT OF A THEOREM OF LINNIK AND WALFISZ 423 IMPROVEMENT OF A THEOREM OF LINNIK AND WALFISZ By S. CHOWLA [Received 19 November 1946 Read 19 December 1946] 1. On the basis of the hitherto unproved
Math 412: Number Theory Lecture 13 Applications of
 Math 412: Number Theory Lecture 13 Applications of Gexin Yu gyu@wm.edu College of William and Mary Partition of integers A partition λ of the positive integer n is a non increasing sequence of positive
Math 412: Number Theory Lecture 13 Applications of Gexin Yu gyu@wm.edu College of William and Mary Partition of integers A partition λ of the positive integer n is a non increasing sequence of positive
The rank of certain subfamilies of the elliptic curve Y 2 = X 3 X + T 2
 Annales Mathematicae et Informaticae 40 2012) pp. 145 15 http://ami.ektf.hu The rank of certain subfamilies of the elliptic curve Y 2 = X X + T 2 Petra Tadić Institute of Analysis and Computational Number
Annales Mathematicae et Informaticae 40 2012) pp. 145 15 http://ami.ektf.hu The rank of certain subfamilies of the elliptic curve Y 2 = X X + T 2 Petra Tadić Institute of Analysis and Computational Number
Singular Overpartitions
 Singular Overpartitions George E. Andrews Dedicated to the memory of Paul Bateman and Heini Halberstam. Abstract The object in this paper is to present a general theorem for overpartitions analogous to
Singular Overpartitions George E. Andrews Dedicated to the memory of Paul Bateman and Heini Halberstam. Abstract The object in this paper is to present a general theorem for overpartitions analogous to
1. Definition of a Polynomial
 1. Definition of a Polynomial What is a polynomial? A polynomial P(x) is an algebraic expression of the form Degree P(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 3 x 3 + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 Leading
1. Definition of a Polynomial What is a polynomial? A polynomial P(x) is an algebraic expression of the form Degree P(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 + a n 2 x n 2 + + a 3 x 3 + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 Leading
Abstract In this paper I give an elementary proof of congruence identity p(11n + 6) 0(mod11).
 An Elementary Proof that p(11n + 6) 0(mod 11) By: Syrous Marivani, Ph.D. LSU Alexandria Mathematics Department 8100 HWY 71S Alexandria, LA 71302 Email: smarivani@lsua.edu Abstract In this paper I give
An Elementary Proof that p(11n + 6) 0(mod 11) By: Syrous Marivani, Ph.D. LSU Alexandria Mathematics Department 8100 HWY 71S Alexandria, LA 71302 Email: smarivani@lsua.edu Abstract In this paper I give
Some new representation problems involving primes
 A talk given at Hong Kong Univ. (May 3, 2013) and 2013 ECNU q-series Workshop (Shanghai, July 30) Some new representation problems involving primes Zhi-Wei Sun Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, P. R.
A talk given at Hong Kong Univ. (May 3, 2013) and 2013 ECNU q-series Workshop (Shanghai, July 30) Some new representation problems involving primes Zhi-Wei Sun Nanjing University Nanjing 210093, P. R.
Notes on Paths, Trees and Lagrange Inversion
 Notes on Paths, Trees and Lagrange Inversion Today we are going to start with a problem that may seem somewhat unmotivated, and solve it in two ways. From there, we will proceed to discuss applications
Notes on Paths, Trees and Lagrange Inversion Today we are going to start with a problem that may seem somewhat unmotivated, and solve it in two ways. From there, we will proceed to discuss applications
Quizzes for Math 401
 Quizzes for Math 401 QUIZ 1. a) Let a,b be integers such that λa+µb = 1 for some inetegrs λ,µ. Prove that gcd(a,b) = 1. b) Use Euclid s algorithm to compute gcd(803, 154) and find integers λ,µ such that
Quizzes for Math 401 QUIZ 1. a) Let a,b be integers such that λa+µb = 1 for some inetegrs λ,µ. Prove that gcd(a,b) = 1. b) Use Euclid s algorithm to compute gcd(803, 154) and find integers λ,µ such that
Additional Practice Lessons 2.02 and 2.03
 Additional Practice Lessons 2.02 and 2.03 1. There are two numbers n that satisfy the following equations. Find both numbers. a. n(n 1) 306 b. n(n 1) 462 c. (n 1)(n) 182 2. The following function is defined
Additional Practice Lessons 2.02 and 2.03 1. There are two numbers n that satisfy the following equations. Find both numbers. a. n(n 1) 306 b. n(n 1) 462 c. (n 1)(n) 182 2. The following function is defined
Primal, completely irreducible, and primary meet decompositions in modules
 Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 54(102) No. 4, 2011, 297 311 Primal, completely irreducible, and primary meet decompositions in modules by Toma Albu and Patrick F. Smith Abstract This paper was
Bull. Math. Soc. Sci. Math. Roumanie Tome 54(102) No. 4, 2011, 297 311 Primal, completely irreducible, and primary meet decompositions in modules by Toma Albu and Patrick F. Smith Abstract This paper was
Topics in Algorithms. 1 Generation of Basic Combinatorial Objects. Exercises. 1.1 Generation of Subsets. 1. Consider the sum:
 Topics in Algorithms Exercises 1 Generation of Basic Combinatorial Objects 1.1 Generation of Subsets 1. Consider the sum: (ε 1,...,ε n) {0,1} n f(ε 1,..., ε n ) (a) Show that it may be calculated in O(n)
Topics in Algorithms Exercises 1 Generation of Basic Combinatorial Objects 1.1 Generation of Subsets 1. Consider the sum: (ε 1,...,ε n) {0,1} n f(ε 1,..., ε n ) (a) Show that it may be calculated in O(n)
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Prep-Year Math Program Math Term 161 Recitation (R1, R2)
 Math 001 - Term 161 Recitation (R1, R) Question 1: How many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1? (a) 1 (b) Finite (c) 0 (d) Infinite (e) Question : A will contain how many elements
Math 001 - Term 161 Recitation (R1, R) Question 1: How many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1? (a) 1 (b) Finite (c) 0 (d) Infinite (e) Question : A will contain how many elements
Ken Ono. 1 if N = m(m+1) Q(N 2ω(k)) + Q(N 2ω( k)) =
 PARTITIONS INTO DISTINCT PARTS AND ELLIPTIC CURVES Ken Ono Abstract. Let QN denote the number of partitions of N into distinct parts. If ωk : 3k2 +k, 2 then it is well known that X QN + 1 k 1 if N mm+1
PARTITIONS INTO DISTINCT PARTS AND ELLIPTIC CURVES Ken Ono Abstract. Let QN denote the number of partitions of N into distinct parts. If ωk : 3k2 +k, 2 then it is well known that X QN + 1 k 1 if N mm+1
A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F. The symbol
 Chapter MATRICES Matrix arithmetic A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F The symbol M m n (F ) denotes the collection of all m n matrices over F Matrices will usually be denoted
Chapter MATRICES Matrix arithmetic A matrix over a field F is a rectangular array of elements from F The symbol M m n (F ) denotes the collection of all m n matrices over F Matrices will usually be denoted
RANKS OF PARTITIONS AND DURFEE SYMBOLS
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Mathematics RANKS OF PARTITIONS AND DURFEE SYMBOLS A Thesis in Mathematics by William J. Keith c 2007 William J. Keith Submitted in Partial
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Mathematics RANKS OF PARTITIONS AND DURFEE SYMBOLS A Thesis in Mathematics by William J. Keith c 2007 William J. Keith Submitted in Partial
Character Polynomials
 Character Polynomials Problem From Stanley s Positivity Problems in Algebraic Combinatorics Problem : Give a combinatorial interpretation of the row sums of the character table for S n (combinatorial proof
Character Polynomials Problem From Stanley s Positivity Problems in Algebraic Combinatorics Problem : Give a combinatorial interpretation of the row sums of the character table for S n (combinatorial proof
Almost perfect powers in consecutive integers (II)
 Indag. Mathem., N.S., 19 (4), 649 658 December, 2008 Almost perfect powers in consecutive integers (II) by N. Saradha and T.N. Shorey School of Mathematics, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Homi
Indag. Mathem., N.S., 19 (4), 649 658 December, 2008 Almost perfect powers in consecutive integers (II) by N. Saradha and T.N. Shorey School of Mathematics, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Homi
FORMAL GROUPS OF CERTAIN Q-CURVES OVER QUADRATIC FIELDS
 Sairaiji, F. Osaka J. Math. 39 (00), 3 43 FORMAL GROUPS OF CERTAIN Q-CURVES OVER QUADRATIC FIELDS FUMIO SAIRAIJI (Received March 4, 000) 1. Introduction Let be an elliptic curve over Q. We denote by ˆ
Sairaiji, F. Osaka J. Math. 39 (00), 3 43 FORMAL GROUPS OF CERTAIN Q-CURVES OVER QUADRATIC FIELDS FUMIO SAIRAIJI (Received March 4, 000) 1. Introduction Let be an elliptic curve over Q. We denote by ˆ
Maximal non-commuting subsets of groups
 Maximal non-commuting subsets of groups Umut Işık March 29, 2005 Abstract Given a finite group G, we consider the problem of finding the maximal size nc(g) of subsets of G that have the property that no
Maximal non-commuting subsets of groups Umut Işık March 29, 2005 Abstract Given a finite group G, we consider the problem of finding the maximal size nc(g) of subsets of G that have the property that no
