Practice 2nd test 123
|
|
|
- Arleen Thornton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Practice 2nd test 123 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Rupel pushes a box 5.00 m by applying a 25.0-N horizontal force. What work does she do? a J b J c. 125 J d. 550 J 2. A worker pushes a sled with a force of 40 N over a level distance of 6.0 m. If a frictional force of 24 N acts on the wheelbarrow in a direction opposite to that of the worker, what net work is done on the wheelbarrow? a. 240 J b. 216 J c. 144 J d. 96 J 3. Which of the following is that form of energy associated with an object's motion? a. potential b. thermal c. bio-chemical d. kinetic 4. What is the kinetic energy of a kg baseball thrown at 40.0 m/s (90.0 mph)? a J b J c. 108 J d. 216 J 5. If both mass and velocity of a ball are tripled, the kinetic energy is increased by a factor of: a. 3. b. 6. c. 9. d A very light cart holding a 300-N box is moved at constant velocity across a 15-m level surface. What is the net work done in the process? a. zero b. 1/20 J c. 20 J d J 7. What is the minimum amount of energy required for an 80-kg climber carrying a 20-kg pack to climb Mt. Everest, m high? a MJ b MJ c MJ d MJ 8. A professional skier reaches a speed of 56 m/s on a 30 ski slope. Ignoring friction, what was the minimum distance along the slope the skier would have had to travel, starting from rest?
2 a. 110 m b. 160 m c. 320 m d. 640 m 9. As an object is lowered into a deep hole in the surface of the earth, which of the following must be assumed in regard to its potential energy? a. increase b. decrease c. remain constant d. cannot tell from the information given 10. When an object is dropped from a tower, what is the effect of the air resistance as it falls? a. does positive work b. increases the object's kinetic energy c. increases the object's potential energy d. None of the above choices are valid. 11. A 15.0-kg crate, initially at rest, slides down a ramp 2.0 m long and inclined at an angle of 20 with the horizontal. If there is no friction between ramp surface and crate, what is the kinetic energy of the crate at the bottom of the ramp? (g = 9.8 m/s 2 ) a. 220 J b. 690 J c. 10 J d. 100 J 12. A hill is 100 m long and makes an angle of 12 with the horizontal. As a 50-kg jogger runs up the hill, how much work does gravity do on the jogger? a J b J c J d. zero 13. A kg ore car rolls 50.0 m down a frictionless 10.0 incline. If there is a horizontal spring at the end of the incline, what spring constant is required to stop the ore car in a distance of 1.00 m? a. 340 kn/m b. 681 kn/m c. 980 kn/m d kn/m 14. The SI units for k, the spring constant, are equivalent to: a. J. b. J / N. c. kg / s 2. d. None of the above. 15. A Hooke's law spring is compressed 12.0 cm from equilibrium, and the potential energy stored is 72.0 J. What compression (as measured from equilibrium) would result in 100 J being stored in this case? a cm b cm c cm d. No answer is correct.
3 16. A Hooke's law spring is mounted horizontally over a frictionless surface. The spring is then compressed a distance d and is used to launch a mass m along the frictionless surface. What compression of the spring would result in the mass attaining double the speed received in the above situation? a d b d c d d d 17. A pile driver drives a post into the ground. The mass of the pile driver is kg and it is dropped through a height of 8.0 m on each stroke. If the resisting force of the ground is N, how far is the post driven in on each stroke? a. 4.9 cm b. 9.8 cm c. 16 cm d. 49 cm 18. A parachutist of mass 50.0 kg jumps out of an airplane at a height of m. The parachute deploys, and she lands on the ground with a speed of 5.0 m/s. How much energy was lost to air friction during this jump? a J b J c J d J 19. The net force acting on a 6.0-kg object is given by F x = (10 x) N, where F x is in newtons and x is in meters. How much work is done on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 10 m? a. 100 J b. 75 J c. 50 J d. 25 J 20. The net force acting on a 12.6-kg object is given by F x = (20 x) N, where F x is in newtons and x is in meters. How much work is done on the object as it moves from x = 0 to x = 10 m? a. 300 J b. 200 J c. 150 J d. 100 J 21. A valid unit for momentum is which of the following? a. kg m/s 2 b. kg/m 2 c. kg m/s d. N m 22. A 75-kg swimmer dives horizontally off a 500-kg raft. The diver's speed immediately after leaving the raft is 4.0 m/s. A micro-sensor system attached to the edge of the raft measures the time interval during which the diver applies an impulse to the raft just prior to leaving the raft surface. If the time interval is read as 0.20 s, what is the magnitude of the average horizontal force by diver on the raft? a. 900 N b. 450 N c. 525 N d N
4 23. A 0.12-kg ball is moving at 6 m/s when it is hit by a bat, causing it to reverse direction and have a speed of 14 m/s. What is the change in the magnitude of the momentum of the ball? a kg m/s b kg m/s c. 1.3 kg m/s d. 2.4 kg m/s 24. Alex throws a 0.15-kg rubber ball down onto the floor. The ball's speed just before impact is 6.5 m/s, and just after is 3.5 m/s. What is the change in the magnitude of the ball's momentum? a kg m/s b. 1.5 kg m/s c. 4.3 kg m/s d. 126 kg m/s 25. A crane drops a 0.30 kg steel ball onto a steel plate. The ball's speeds just before impact and after are 4.5 m/s and 4.2 m/s, respectively. If the ball is in contact with the plate for s, what is the magnitude of the average force that the ball exerts on the plate during impact? a. 87 N b. 133 N c. 3.0 N d. 3.5 N 26. Ann the Astronaut weighs 60 kg. She is space walking outside the space shuttle and pushes a 350-kg satellite away from the shuttle at 0.90 m/s. What speed does this give Ann as she moves toward the shuttle? a. 4.0 m/s b. 5.3 m/s c. 8.5 m/s d. 9.0 m/s 27. A uranium nucleus (mass 238 units) at rest decays into a helium nucleus (mass 4.0 units) and a thorium nucleus (mass 234 units). If the speed of the helium nucleus is m/s, what is the speed of the thorium nucleus? a m/s b m/s c m/s d m/s 28. A moderate force will break an egg. However, an egg dropped on the road usually breaks, while one dropped on the grass usually doesn't break. This is because for the egg dropped on the grass: a. the change in momentum is greater. b. the change in momentum is less. c. the time interval for stopping is greater. d. the time interval for stopping is less. 29. A billiard ball is moving in the x-direction at 30.0 cm/s and strikes another billiard ball moving in the y-direction at 40.0 cm/s. As a result of the collision, the first ball moves at 50.0 cm/s, and the second ball stops. What is the change in kinetic energy of the system as a result of the collision? a. 0 b. some positive value c. some negative value d. No answer above is correct.
5 30. In a two-body collision, if the momentum of the system is conserved, then which of the following best describes the kinetic energy after the collision? a. must be less b. must also be conserved c. may also be conserved d. is doubled in value 31. A miniature, spring-loaded, radio-controlled gun is mounted on an air puck. The gun's bullet has a mass of 5.00 g, and the gun and puck have a combined mass of 120 g. With the system initially at rest, the radio-controlled trigger releases the bullet, causing the puck and empty gun to move with a speed of m/s. Of the total kinetic energy of the gun-puck-bullet system, what percentage is in the bullet? a. 4.0% b. 50% c. 96% d. 100% 32. A neutron in a nuclear reactor makes an elastic head-on collision with a carbon atom initially at rest. (The mass of the carbon atom is 12 times that of the neutron.) What fraction of the neutron's kinetic energy is transferred to the carbon atom? a. 14.4% b. 28.4% c. 41.4% d. 56.6% 33. A billiard ball (Ball #1) moving at 5.00 m/s strikes a stationary ball (Ball #2) of the same mass. After the collision, Ball #1 moves at a speed of 4.35 m/s. Find the speed of Ball #2 after the collision. a m/s b m/s c m/s d m/s 34. A kg experimental rocket sled at rest on level frictionless rails is loaded with 50 kg of propellant. It exhausts the propellant in a 20-s "burn." The rocket moves at 150 m/s after the burn. What average force is experienced by the rocket during the burn? a N b N c N d N 35. A spool of thread has an average radius of 1.00 cm. If the spool contains 62.8 m of thread, how many turns of thread are on the spool? "Average radius" allows us to not need to treat the layering of threads on lower layers. a. 100 b c d A Ferris wheel, rotating initially at an angular speed of 0.50 rad/s, accelerates over a 7.0-s interval at a rate of rad/s 2. What is its angular speed after this 7-s interval? a rad/s b rad/s c rad/s
6 d rad/s 37. A 0.30-m-radius automobile tire accelerates from rest at a constant 2.0 rad/s 2 over a 5.0-s interval. What is the tangential component of acceleration for a point on the outer edge of the tire during the 5-s interval? a. 33 m/s 2 b. 6.7 m/s 2 c m/s 2 d m/s Consider a point on a bicycle wheel as the wheel turns about a fixed axis, neither speeding up nor slowing down. Compare the linear and angular velocities of the point. a. Both are constant. b. Only the angular velocity is constant. c. Only the linear velocity is constant. d. Neither is constant. 39. When a point on the rim of a 0.30-m-radius wheel experiences a centripetal acceleration of 4.0 m/s 2, what tangential acceleration does that point experience? a. 1.2 m/s 2 b. 2.0 m/s 2 c. 4.0 m/s 2 d. Cannot determine with the information given. 40. At what angle (relative to the horizontal) should a curve 52 m in radius be banked if no friction is required to prevent the car from slipping when traveling at 12 m/s? (g = 9.8 m/s 2 ) a. 28 b. 32 c. 16 d An airplane in a wide sweeping "outside" loop can create zero gees inside the aircraft cabin. What must be the radius of curvature of the flight path for an aircraft moving at 150 m/s to create a condition of "weightlessness" inside the aircraft? a m b m c m d m 42. The Earth is 93 million miles (mi) from the Sun and its period of revolution is 1 year = s. What is the acceleration of the Earth in its orbit about the Sun? a mi/s 2 b mi/s 2 c mi/s 2 d mi/s An object when orbiting the Earth at a height of three Earth radii from the center of the Earth has a weight of 1.00 N. What is the object's mass? (g at the surface of the Earth is 9.8 m/s 2 ) a kg b kg c kg d. 1.0 kg
7 44. An asteroid has a perihelion (the orbit's closest approach to the sun) of 1.5 AU and a period of revolution of 8.0 y. What is its greatest distance from the sun (its aphelion)? a. 8.0 AU b. 6.5 AU c. 4.0 AU d. 2.5 AU 45. At what location does an artificial Earth satellite in elliptical orbit have its greatest speed? a. nearest the Earth b. farthest from the Earth c. between Earth and Moon d. between Earth and Sun 46. An artificial Earth satellite in an elliptical orbit has its greatest centripetal acceleration when it is at what location? a. nearest the Earth b. farthest from the Earth c. between Earth and Moon d. between Earth and Sun 47. A car is going around a racetrack at constant speed. The curves around the track have different radii. In which turn is the magnitude of the car's acceleration the greatest? a. It is the greatest in the turn with the greatest radius. b. It is the greatest in the turn with the smallest radius. c. The acceleration is zero everywhere because of the constant speed. d. More information is needed to determine the answer. 48. A vault is opened by applying a force of 300 N perpendicular to the plane of the door, 0.80 m from the hinges. Find the torque due to this force about an axis through the hinges. a. 120 N m b. 240 N m c. 300 N m d. 360 N m 49. An 80-kg man is one fourth of the way up a 10-m ladder that is resting against a smooth, frictionless wall. If the ladder has a mass of 20 kg and it makes an angle of 60 with the ground, find the force of friction of the ground on the foot of the ladder. a N b N c. 50 N d N 50. The quantity "moment of inertia" (in terms of the fundamental quantities of mass, length, and time) is equivalent to: a. ML 2 T 2. b. ML. c. ML 2. d. ML 1 T If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience: a. a constant angular speed. b. an angular acceleration.
8 c. a constant moment of inertia. d. an increasing moment of inertia. 52. A majorette takes two batons and fastens them together in the middle at right angles to make an "x" shape. Each baton was 0.80 m long and each ball on the end is 0.20 kg. (Ignore the mass of the rods.) What is the moment of inertia if the arrangement is spun around an axis formed by one of the batons? a kg m 2 b kg m 2 c kg m 2 d kg m A bowling ball has a mass of 7.0 kg, a moment of inertia of kg m 2 and a radius of 0.10 m. If it rolls down the lane without slipping at a linear speed of 4.0 m/s, what is its total kinetic energy? a. 45 J b. 32 J c. 11 J d. 78 J 54. A gyroscope has a moment of inertia of 0.14 kg m 2 and an initial angular speed of 15 rad/s. Friction in the bearings causes its speed to reduce to zero in 30 s. What is the value of the average frictional torque? a N m b N m c N m d N m 55. A rotating flywheel can be used as a method to store energy. If it has J of kinetic energy when rotating at 400 rad/s, and if a frictional torque of 4.0 N m acts on the system, in what interval of time would the flywheel come to rest? a. 3.5 min b. 7.0 min c. 14 min d. 21 min 56. A cylinder (I = MR 2 /2) is rolling along the ground at 7.0 m/s. It comes to a hill and starts going up. Assuming no losses to friction, how high does it get before it stops? a. 1.2 m b. 3.7 m c. 4.2 m d. 5.9 m 57. Consider the use of the terms "rotation" and "revolution". In physics: a. the words are used interchangeably. b. the words are used interchangeably but "rotation" is the preferred word. c. the words have different meaning. d. "rotation" is the correct word and "revolution" should not be used. 58. A figure skater with arms initially extended starts spinning on the ice at 3 rad/s. She then pulls her arms in close to her body. Which of the following results? a. a smaller rotational rate b. a greater rotational rate c. a greater angular momentum d. a smaller angular momentum
9 59. A turntable has a moment of inertia of kg m 2 and spins freely on a frictionless bearing at 25 rev/min. A 0.30-kg ball of putty is dropped vertically on the turntable and sticks at a point 0.10 m from the center. By what factor does the kinetic energy of the system change after the putty is dropped onto the turntable? a b. 1.0 c d A box slides down a frictionless incline, and a hoop rolls down another incline. Both inclines have the same height, and both the box and the hoop have the same mass. If both objects start from rest, upon reaching the bottom of the incline which one will have the greater kinetic energy and which one will have the greater speed? a. The box will have both the greater kinetic energy and the greater speed. b. The hoop will have both the greater kinetic energy and the greater speed. c. Both will have the same kinetic energy but the hoop will have the greater speed. d. Both will have the same kinetic energy but the box will have the greater speed.
10 Practice 2nd test 123 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.1 Work 2. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.1 Work 3. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.2 Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem 4. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.2 Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem 5. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.2 Kinetic Energy and the Work-Energy Theorem 6. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.3 Gravitational Potential Energy 7. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.3 Gravitational Potential Energy 8. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.3 Gravitational Potential Energy 9. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.3 Gravitational Potential Energy 10. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.3 Gravitational Potential Energy 11. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.3 Gravitational Potential Energy 12. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 5.3 Gravitational Potential Energy 13. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.4 Spring Potential Energy 14. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.4 Spring Potential Energy 15. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 5.4 Spring Potential Energy 16. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 5.4 Spring Potential Energy 17. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.5 Systems and Energy Conservation 18. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 5.5 Systems and Energy Conservation 19. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 5.7 Work Done by a Varying Force 20. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 5.7 Work Done by a Varying Force 21. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 6.1 Momentum and Impulse 22. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.1 Momentum and Impulse 23. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.1 Momentum and Impulse 24. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.1 Momentum and Impulse 25. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.1 Momentum and Impulse 26. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.2 Conservation of Momentum 27. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.2 Conservation of Momentum 28. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 6.2 Conservation of Momentum 29. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.3 Collisions 6.4 Glancing Collisions 30. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 6.3 Collisions 6.4 Glancing Collisions 31. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 6.3 Collisions 6.4 Glancing Collisions 32. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 6.3 Collisions 6.4 Glancing Collisions 33. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 3
11 TOP: 6.3 Collisions 6.4 Glancing Collisions 34. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 6.5 Rocket Propulsion 35. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.1 Angular Speed and Angular Acceleration 36. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.2 Rotational Motion Under Constant Angular Acceleration 37. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 7.3 Relations Between Angular and Linear Quantities 38. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.3 Relations Between Angular and Linear Quantities 39. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.4 Centripetal Acceleration 40. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.4 Centripetal Acceleration 41. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.4 Centripetal Acceleration 42. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.4 Centripetal Acceleration 43. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.5 Newtonian Gravitation 44. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 7.6 Kepler's Laws 45. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 7.6 Kepler's Laws 46. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 7.6 Kepler's Laws 47. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: Conceptual Problems 48. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 8.1 Torque 49. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 8.2 Torque and the Two Conditions for Equilibrium 8.3 The Center of Gravity 8.4 Examples of Objects in Equilibrium 50. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 8.5 Relationship Between Torque and Angular Acceleration 51. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 8.5 Relationship Between Torque and Angular Acceleration 52. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 8.5 Relationship Between Torque and Angular Acceleration 53. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 8.6 Rotational Kinetic Energy 54. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 8.6 Rotational Kinetic Energy 55. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 8.6 Rotational Kinetic Energy 56. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 8.6 Rotational Kinetic Energy 57. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 8.6 Rotational Kinetic Energy 58. ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 8.7 Angular Momentum 59. ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 8.7 Angular Momentum 60. ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: Conceptual Problems
CHAPTER 5. Chapter 5, Energy
 CHAPTER 5 2. A very light cart holding a 300-N box is moved at constant velocity across a 15-m level surface. What is the net work done in the process? a. zero b. 1/20 J c. 20 J d. 2 000 J 4. An rock is
CHAPTER 5 2. A very light cart holding a 300-N box is moved at constant velocity across a 15-m level surface. What is the net work done in the process? a. zero b. 1/20 J c. 20 J d. 2 000 J 4. An rock is
Chapter 8, Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics. 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience:
 CHAPTER 8 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience: a. a constant angular speed b. an angular acceleration c. a constant moment of inertia d. an increasing moment of inertia
CHAPTER 8 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience: a. a constant angular speed b. an angular acceleration c. a constant moment of inertia d. an increasing moment of inertia
Webreview Torque and Rotation Practice Test
 Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
Please do not write on test. ID A Webreview - 8.2 Torque and Rotation Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A 0.30-m-radius automobile
AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice
 AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice 1. A spool of thread has an average radius of 1.00 cm. If the spool contains 62.8 m of thread, how many turns of thread are on the spool? "Average radius" allows us to
AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice 1. A spool of thread has an average radius of 1.00 cm. If the spool contains 62.8 m of thread, how many turns of thread are on the spool? "Average radius" allows us to
S15--AP Q1 Work and Energy PRACTICE
 Name: Class: Date: S15--AP Q1 Work and Energy PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Rupel pushes a box 5.00 m by applying a 25.0-N horizontal
Name: Class: Date: S15--AP Q1 Work and Energy PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Rupel pushes a box 5.00 m by applying a 25.0-N horizontal
Advanced Higher Physics. Rotational motion
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 11 Rolling, Torque & Angular Momentum Rolling motion Torque Angular momentum Conservation of angular momentum 1. A uniform hoop (ring) is rolling smoothly from the
Jordan University of Science & Technology PHYS 101A Final exam First semester 2007
 Student Name Student ID Jordan University of Science & Technology PHYS 101A Final exam First semester 2007 Approximate your answer to those given for each question. Use this table to fill in your answer
Student Name Student ID Jordan University of Science & Technology PHYS 101A Final exam First semester 2007 Approximate your answer to those given for each question. Use this table to fill in your answer
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006
 Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
Mechanics II. Which of the following relations among the forces W, k, N, and F must be true?
 Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Mechanics II 1. By applying a force F on a block, a person pulls a block along a rough surface at constant velocity v (see Figure below; directions, but not necessarily magnitudes, are indicated). Which
Exam 2--PHYS 101-Fall 2009
 ame: Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101-Fall 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this figure of a roller coaster: At which of these
ame: Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101-Fall 2009 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Consider this figure of a roller coaster: At which of these
= 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ. T.E. initial. = T.E. Final. = P.E. final. + K.E. initial. + P.E. initial. K.E. initial =
 Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Suggested Problems. Chapter 1
 Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Page 1. Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work!
 Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
PY205N Spring The vectors a, b, and c. are related by c = a b. The diagram below that best illustrates this relationship is (a) I
 PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8
 PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
3. How long must a 100 N net force act to produce a change in momentum of 200 kg m/s? (A) 0.25 s (B) 0.50 s (C) 1.0 s (D) 2.0 s (E) 4.
 AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice Momentum and Impulse 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass,
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Name: Class: Date: d. none of the above
 Name: Class: Date: H Phys quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the cause of an acceleration? a. speed b. inertia
Name: Class: Date: H Phys quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the cause of an acceleration? a. speed b. inertia
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
r r Sample Final questions for PS 150
 Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
Center of Mass & Linear Momentum
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 9 Center of Mass & Linear Momentum Center of mass Momentum of a particle Momentum of a system Impulse Conservation of momentum Elastic collisions Inelastic collisions
= o + t = ot + ½ t 2 = o + 2
 Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Chapters 8-9 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Rotational motion Rotational motion refers to the motion of an object or system that spins about an axis. The axis of rotation is the line about which the
Test 7 wersja angielska
 Test 7 wersja angielska 7.1A One revolution is the same as: A) 1 rad B) 57 rad C) π/2 rad D) π rad E) 2π rad 7.2A. If a wheel turns with constant angular speed then: A) each point on its rim moves with
Test 7 wersja angielska 7.1A One revolution is the same as: A) 1 rad B) 57 rad C) π/2 rad D) π rad E) 2π rad 7.2A. If a wheel turns with constant angular speed then: A) each point on its rim moves with
v (m/s) 10 d. displacement from 0-4 s 28 m e. time interval during which the net force is zero 0-2 s f. average velocity from 0-4 s 7 m/s x (m) 20
 Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Physics Final Exam Mechanics Review Answers 1. Use the velocity-time graph below to find the: a. velocity at 2 s 6 m/s v (m/s) 1 b. acceleration from -2 s 6 c. acceleration from 2-4 s 2 m/s 2 2 4 t (s)
Chapter 9-10 Test Review
 Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
Chapter 9-10 Test Review Chapter Summary 9.2. The Second Condition for Equilibrium Explain torque and the factors on which it depends. Describe the role of torque in rotational mechanics. 10.1. Angular
C) D) 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart.
 1. Which graph best represents the relationship between the acceleration of an object falling freely near the surface of Earth and the time that it falls? 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope
1. Which graph best represents the relationship between the acceleration of an object falling freely near the surface of Earth and the time that it falls? 2. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope
7. Two forces are applied to a 2.0-kilogram block on a frictionless horizontal surface, as shown in the diagram below.
 1. Which statement about the movement of an object with zero acceleration is true? The object must be at rest. The object must be slowing down. The object may be speeding up. The object may be in motion.
1. Which statement about the movement of an object with zero acceleration is true? The object must be at rest. The object must be slowing down. The object may be speeding up. The object may be in motion.
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, Mechanics Test
 Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, 2005 Mechanics Test Please answer the following questions on the supplied answer sheet. You may write on this test booklet,
Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, 2005 Mechanics Test Please answer the following questions on the supplied answer sheet. You may write on this test booklet,
4) Vector = and vector = What is vector = +? A) B) C) D) E)
 1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
2. What would happen to his acceleration if his speed were half? Energy The ability to do work
 1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
Slide 1 / 133. Slide 2 / 133. Slide 3 / How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m?
 1 How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? Slide 1 / 133 2 How many degrees are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius of 0.40 m? Slide 2 / 133 3 A ball rotates
1 How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? Slide 1 / 133 2 How many degrees are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius of 0.40 m? Slide 2 / 133 3 A ball rotates
Slide 2 / 133. Slide 1 / 133. Slide 3 / 133. Slide 4 / 133. Slide 5 / 133. Slide 6 / 133
 Slide 1 / 133 1 How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? Slide 2 / 133 2 How many degrees are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius of 0.40 m? Slide 3 / 133
Slide 1 / 133 1 How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? Slide 2 / 133 2 How many degrees are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius of 0.40 m? Slide 3 / 133
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
Written Homework problems. Spring (taken from Giancoli, 4 th edition)
 Written Homework problems. Spring 014. (taken from Giancoli, 4 th edition) HW1. Ch1. 19, 47 19. Determine the conversion factor between (a) km / h and mi / h, (b) m / s and ft / s, and (c) km / h and m
Written Homework problems. Spring 014. (taken from Giancoli, 4 th edition) HW1. Ch1. 19, 47 19. Determine the conversion factor between (a) km / h and mi / h, (b) m / s and ft / s, and (c) km / h and m
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
3. The diagram shows two bowling balls, A and B, each having a mass of 7.00 kilograms, placed 2.00 meters apart.
 1. Which statement describes the gravitational force and the electrostatic force between two charged particles? A) The gravitational force may be either attractive or repulsive, whereas the electrostatic
1. Which statement describes the gravitational force and the electrostatic force between two charged particles? A) The gravitational force may be either attractive or repulsive, whereas the electrostatic
Impulse,Momentum, CM Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
Name: Date: 1. A 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at a speed of 0.25 meter per second. After the speed of the cart is tripled, the inertia of the cart will be A. unchanged B. one-third as great C. three times
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
(1) +0.2 m/s (2) +0.4 m/s (3) +0.6 m/s (4) +1 m/s (5) +0.8 m/s
 77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Exam #2, Chapters 5-7 Name PHYS 101-4M MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The quantity 1/2 mv2 is A) the potential energy of the object.
Unless otherwise specified, use g = 9.80 m/s2
 Phy 111 Exam 2 March 10, 2015 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Phy 111 Exam 2 March 10, 2015 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
2014 Physics Exam Review
 Name: ate: 1. The diagrams below show a model airplane. Which energy transformation occurs in a rubber band powered model airplane when it is flown?. Thermal energy stored in the rubber band is transformed
Name: ate: 1. The diagrams below show a model airplane. Which energy transformation occurs in a rubber band powered model airplane when it is flown?. Thermal energy stored in the rubber band is transformed
A) more mass and more inertia C) the same as the magnitude of the rock's weight C) a man standing still on a bathroom scale
 1. A 15-kilogram cart is at rest on a horizontal surface. A 5-kilogram box is placed in the cart. Compared to the mass and inertia of the cart, the cart-box system has A) more mass and more inertia B)
1. A 15-kilogram cart is at rest on a horizontal surface. A 5-kilogram box is placed in the cart. Compared to the mass and inertia of the cart, the cart-box system has A) more mass and more inertia B)
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
AP Physics II Summer Packet
 Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
Name: AP Physics II Summer Packet Date: Period: Complete this packet over the summer, it is to be turned it within the first week of school. Show all work were needed. Feel free to use additional scratch
66 Chapter 6: FORCE AND MOTION II
 Chapter 6: FORCE AND MOTION II 1 A brick slides on a horizontal surface Which of the following will increase the magnitude of the frictional force on it? A Putting a second brick on top B Decreasing the
Chapter 6: FORCE AND MOTION II 1 A brick slides on a horizontal surface Which of the following will increase the magnitude of the frictional force on it? A Putting a second brick on top B Decreasing the
Study Guide For Midterm - 25 weeks Physics Exam. d. the force exerted by a towing cable on the car. c. the upward force the road exerts on the car.
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Study Guide For Midterm - 25 weeks Physics Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Study Guide For Midterm - 25 weeks Physics Exam Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following is the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam #3 Name 1) A 2000. kg car, traveling to the right at 30. m/s, collides with a brick wall and comes to rest in 0.20 s. 1) The average force the car exerts on the wall is A) 60. kn. B) 12. kn. C) 300
Exam #3 Name 1) A 2000. kg car, traveling to the right at 30. m/s, collides with a brick wall and comes to rest in 0.20 s. 1) The average force the car exerts on the wall is A) 60. kn. B) 12. kn. C) 300
Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions. Newton s second law in terms of momentum:
 linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
linear momentum: Chapter 8: Momentum, Impulse, & Collisions Newton s second law in terms of momentum: impulse: Under what SPECIFIC condition is linear momentum conserved? (The answer does not involve collisions.)
. d. v A v B. e. none of these.
 General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
General Physics I Exam 3 - Chs. 7,8,9 - Momentum, Rotation, Equilibrium Oct. 28, 2009 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show the formulas you use, the essential
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
P211 Spring 2004 Form A
 1. A 2 kg block A traveling with a speed of 5 m/s as shown collides with a stationary 4 kg block B. After the collision, A is observed to travel at right angles with respect to the initial direction with
1. A 2 kg block A traveling with a speed of 5 m/s as shown collides with a stationary 4 kg block B. After the collision, A is observed to travel at right angles with respect to the initial direction with
PHYSICS 221 SPRING EXAM 2: March 30, 2017; 8:15pm 10:15pm
 PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2017 EXAM 2: March 30, 2017; 8:15pm 10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # Student ID# INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2017 EXAM 2: March 30, 2017; 8:15pm 10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # Student ID# INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit
Physics Test Review: Mechanics Session: Name:
 Directions: For each statement or question, write in the answer box, the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below
Directions: For each statement or question, write in the answer box, the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below
Rotation Quiz II, review part A
 Rotation Quiz II, review part A 1. A solid disk with a radius R rotates at a constant rate ω. Which of the following points has the greater angular velocity? A. A B. B C. C D. D E. All points have the
Rotation Quiz II, review part A 1. A solid disk with a radius R rotates at a constant rate ω. Which of the following points has the greater angular velocity? A. A B. B C. C D. D E. All points have the
Physics 121, Sections 1 and 2, Winter 2011 Instructor: Scott Bergeson Exam #3 April 16 April 21, 2011 RULES FOR THIS TEST:
 Physics 121, Sections 1 and 2, Winter 2011 Instructor: Scott Bergeson Exam #3 April 16 April 21, 2011 RULES FOR THIS TEST: This test is closed book. You may use a dictionary. You may use your own calculator
Physics 121, Sections 1 and 2, Winter 2011 Instructor: Scott Bergeson Exam #3 April 16 April 21, 2011 RULES FOR THIS TEST: This test is closed book. You may use a dictionary. You may use your own calculator
End-of-Chapter Exercises
 End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
End-of-Chapter Exercises Exercises 1 12 are conceptual questions that are designed to see if you have understood the main concepts of the chapter. 1. Figure 11.21 shows four different cases involving a
Sample Physics Placement Exam
 Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
Sample Physics 130-1 Placement Exam A. Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A cable is used to take construction equipment from the ground to the top of a tall building. During the trip up, when (if ever) is
Midterm Prep. 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?
 Name: ate: 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?. weight and kg. velocity and m/s. speed and m/s. acceleration and m 2 /s 2. 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at
Name: ate: 1. Which combination correctly pairs a vector quantity with its corresponding unit?. weight and kg. velocity and m/s. speed and m/s. acceleration and m 2 /s 2. 12.0-kilogram cart is moving at
Phys 2210 S18 Practice Exam 3: Ch 8 10
 1. As a 1.0-kg object moves from point A to point B, it is acted upon by a single conservative force which does 40 J of work during this motion. At point A the speed of the particle is 6.0 m/s and the
1. As a 1.0-kg object moves from point A to point B, it is acted upon by a single conservative force which does 40 J of work during this motion. At point A the speed of the particle is 6.0 m/s and the
Name: Class: Date: so sliding friction is better so sliding friction is better d. µ k
 Name: Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101-F08 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. You put your book on the seat next to you. When the bus stops,
Name: Class: Date: Exam 2--PHYS 101-F08 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. You put your book on the seat next to you. When the bus stops,
A) 4.0 m/s B) 5.0 m/s C) 0 m/s D) 3.0 m/s E) 2.0 m/s. Ans: Q2.
 Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Coordinator: Dr. W. Al-Basheer Thursday, July 30, 2015 Page: 1 Q1. A constant force F ( 7.0ˆ i 2.0 ˆj ) N acts on a 2.0 kg block, initially at rest, on a frictionless horizontal surface. If the force causes
Upon collision, the clay and steel block stick together and move to the right with a speed of
 1. A 2.0-kilogram ball traveling north at 4.0 meters per second collides head on with a 1.0-kilogram ball traveling south at 8.0 meters per second. What is the magnitude of the total momentum of the two
1. A 2.0-kilogram ball traveling north at 4.0 meters per second collides head on with a 1.0-kilogram ball traveling south at 8.0 meters per second. What is the magnitude of the total momentum of the two
1. A 7.0-kg bowling ball experiences a net force of 5.0 N. What will be its acceleration? a. 35 m/s 2 c. 5.0 m/s 2 b. 7.0 m/s 2 d. 0.
 Newton's Laws 1. A 7.0-kg bowling ball experiences a net force of 5.0 N. What will be its acceleration? a. 35 m/s 2 c. 5.0 m/s 2 b. 7.0 m/s 2 d. 0.71 m/s 2 2. An astronaut applies a force of 500 N to an
Newton's Laws 1. A 7.0-kg bowling ball experiences a net force of 5.0 N. What will be its acceleration? a. 35 m/s 2 c. 5.0 m/s 2 b. 7.0 m/s 2 d. 0.71 m/s 2 2. An astronaut applies a force of 500 N to an
Name: Date: 5. A 5.0-kg ball and a 10.0-kg ball approach each other with equal speeds of 20 m/s. If
 Name: Date: 1. For this question, assume that all velocities are horizontal and that there is no friction. Two skaters A and B are on an ice surface. A and B have the same mass M = 90.5 kg. A throws a
Name: Date: 1. For this question, assume that all velocities are horizontal and that there is no friction. Two skaters A and B are on an ice surface. A and B have the same mass M = 90.5 kg. A throws a
Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy?
 Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): J. Ipser PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam April 25, 2005 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR
Instructor(s): J. Ipser PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam April 25, 2005 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination. YOUR
Rotational Mechanics Part III Dynamics. Pre AP Physics
 Rotational Mechanics Part III Dynamics Pre AP Physics We have so far discussed rotational kinematics the description of rotational motion in terms of angle, angular velocity and angular acceleration and
Rotational Mechanics Part III Dynamics Pre AP Physics We have so far discussed rotational kinematics the description of rotational motion in terms of angle, angular velocity and angular acceleration and
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014
 PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014 EXAM 2: April 3, 2014 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014 EXAM 2: April 3, 2014 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam December 13, 2011 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam December 13, 2011 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015
 95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
95.141 Physics I (Navitas) FINAL EXAM Fall 2015 Name, Last Name First Name Student Identification Number: Write your name at the top of each page in the space provided. Answer all questions, beginning
5. Use the graph below to determine the displacement of the object at the end of the first seven seconds.
 Name: Hour: 1. The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the: Sem 1 Exam Review Advanced Physics 2015-2016 2. The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: 3. The graph below
Name: Hour: 1. The slope of the tangent on a position-time graph equals the: Sem 1 Exam Review Advanced Physics 2015-2016 2. The area under the curve on a velocity-time graph equals the: 3. The graph below
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): Profs. D. Reitze, H. Chan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2 April 2, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum
 AP Physics C Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum Introduction: Rolling: In the last unit we studied the rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis. We will now extend our study to include cases where
AP Physics C Rolling, Torque, and Angular Momentum Introduction: Rolling: In the last unit we studied the rotation of a rigid body about a fixed axis. We will now extend our study to include cases where
CHAPTER 8: ROTATIONAL OF RIGID BODY PHYSICS. 1. Define Torque
 7 1. Define Torque 2. State the conditions for equilibrium of rigid body (Hint: 2 conditions) 3. Define angular displacement 4. Define average angular velocity 5. Define instantaneous angular velocity
7 1. Define Torque 2. State the conditions for equilibrium of rigid body (Hint: 2 conditions) 3. Define angular displacement 4. Define average angular velocity 5. Define instantaneous angular velocity
Centripetal acceleration ac = to2r Kinetic energy of rotation KE, = \lto2. Moment of inertia. / = mr2 Newton's second law for rotational motion t = la
 The Language of Physics Angular displacement The angle that a body rotates through while in rotational motion (p. 241). Angular velocity The change in the angular displacement of a rotating body about
The Language of Physics Angular displacement The angle that a body rotates through while in rotational motion (p. 241). Angular velocity The change in the angular displacement of a rotating body about
Exam II. Spring 2004 Serway & Jewett, Chapters Fill in the bubble for the correct answer on the answer sheet. next to the number.
 Agin/Meyer PART I: QUALITATIVE Exam II Spring 2004 Serway & Jewett, Chapters 6-10 Assigned Seat Number Fill in the bubble for the correct answer on the answer sheet. next to the number. NO PARTIAL CREDIT:
Agin/Meyer PART I: QUALITATIVE Exam II Spring 2004 Serway & Jewett, Chapters 6-10 Assigned Seat Number Fill in the bubble for the correct answer on the answer sheet. next to the number. NO PARTIAL CREDIT:
Momentum and Impulse Practice Multiple Choice
 Choose the alternative that best answers the question and record your answer on the Scantron sheet provided 1. A ball of putty is thrown at a wall and sticks to its surface. Which of the following quantities
Choose the alternative that best answers the question and record your answer on the Scantron sheet provided 1. A ball of putty is thrown at a wall and sticks to its surface. Which of the following quantities
Circular Motion & Gravitation MC Question Database
 (Questions #4,5,6,27,37,38,42 and 58 each have TWO correct answers.) 1) A record player has four coins at different distances from the center of rotation. Coin A is 1 cm away, Coin B is 2 cm away. Coin
(Questions #4,5,6,27,37,38,42 and 58 each have TWO correct answers.) 1) A record player has four coins at different distances from the center of rotation. Coin A is 1 cm away, Coin B is 2 cm away. Coin
Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class:
 Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A feather and a rock dropped at the same time from
Chapter 6 Study Questions Name: Class: Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A feather and a rock dropped at the same time from
3) An airplane has an air speed of 92.2 m/s and flies due North, but the wind blows from the Northeast to the Southwest at 66.5 m/s. What is its actua
 Review problems: This is a selection of homework and exam problems that CAPA indicated were more difficult than others. We will review these problems in class to further solidify knowledge of the course
Review problems: This is a selection of homework and exam problems that CAPA indicated were more difficult than others. We will review these problems in class to further solidify knowledge of the course
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
Forces, Momentum, & Gravity. Force and Motion Cause and Effect. Student Learning Objectives 2/16/2016
 Forces, Momentum, & Gravity (Chapter 3) Force and Motion Cause and Effect In chapter 2 we studied motion but not its cause. In this chapter we will look at both force and motion the cause and effect. We
Forces, Momentum, & Gravity (Chapter 3) Force and Motion Cause and Effect In chapter 2 we studied motion but not its cause. In this chapter we will look at both force and motion the cause and effect. We
Exam 3--PHYS 101--F15
 Name: Exam 3--PHYS 0--F5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. It takes 00 m to stop a car initially moving at 25.0 m/s. The distance required
Name: Exam 3--PHYS 0--F5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. It takes 00 m to stop a car initially moving at 25.0 m/s. The distance required
1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy?
 Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
Name: Date: 1. Which one of the following situations is an example of an object with a non-zero kinetic energy? A) a drum of diesel fuel on a parked truck B) a stationary pendulum C) a satellite in geosynchronous
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
a) Calculate the height that m 2 moves up the bowl after the collision (measured vertically from the bottom of the bowl).
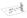 2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
2. A small mass m 1 slides in a completely frictionless spherical bowl. m 1 starts at rest at height h = ½ R above the bottom of the bowl. When it reaches the bottom of the bowl it strikes a mass m 2,
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015
 PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015 EXAM 2: April 2, 2015 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2015 EXAM 2: April 2, 2015 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
Name 09-MAR-04. Work Power and Energy
 Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
AP Physics 1: Rotational Motion & Dynamics: Problem Set
 AP Physics 1: Rotational Motion & Dynamics: Problem Set I. Axis of Rotation and Angular Properties 1. How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? 2. How many degrees are
AP Physics 1: Rotational Motion & Dynamics: Problem Set I. Axis of Rotation and Angular Properties 1. How many radians are subtended by a 0.10 m arc of a circle of radius 0.40 m? 2. How many degrees are
CPS lesson Work and Energy ANSWER KEY
 CPS lesson Work and Energy ANSWER KEY 1. A ball feeder slowly pushes a bowling ball up a 1-m ramp to a height of 0.5 m above the floor. Neglecting friction, what constant force must be exerted on the 5-kg
CPS lesson Work and Energy ANSWER KEY 1. A ball feeder slowly pushes a bowling ball up a 1-m ramp to a height of 0.5 m above the floor. Neglecting friction, what constant force must be exerted on the 5-kg
Wiley Plus. Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm!
 Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
Wiley Plus Final Assignment (5) Is Due Today: Before 11 pm! Final Exam Review December 9, 009 3 What about vector subtraction? Suppose you are given the vector relation A B C RULE: The resultant vector
Physics 116A, Section 2, Second Exam Version B, February 26, Name (Please print)
 Physics 116A, Section 2, Second Exam Version B, February 26, 2008 Name (Please print) Mulitiple choice questions are worth 3 points each. Mark your answers in the space provided at the right, and on the
Physics 116A, Section 2, Second Exam Version B, February 26, 2008 Name (Please print) Mulitiple choice questions are worth 3 points each. Mark your answers in the space provided at the right, and on the
