Algebra I. Relations and Functions. Slide 1 / 113 Slide 2 / 113. Slide 3 / 113. Slide 4 / 113. Slide 6 / 113. Slide 5 / 113.
|
|
|
- Phebe Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Slide 1 / 11 Slide 2 / 11 Algebra I Functions Slide / 11 Slide / 11 Table of Contents click on the topic to go to that section Relations and Functions Domain and Range Relations and Functions Evaluating Functions Eplicit and Recursive Functions Multiple Representations of Functions Return to Table of Contents Slide 5 / 11 Vocabular A relation is an set of ordered pairs. Slide 6 / 11 Determine if each of the relations below is a function and provide an eplanation to support our : A function is a relation where each value in the domain has eactl ONE value in the range. The -value does NOT repeat in a function.
2 Slide 7 / 11 Determine if each of the relations below is a function and provide an eplanation to support our : -2-5 X Y Slide / 11 Determine if each of the relations below is a function and provide an eplanation to support our : X Y X Y Slide 9 / 11 Graphs On a graph, a function does not have a point in the same vertical location as another point. The Vertical Line Testcan determine if a graph represents a function. Place a ruler or imaginar vertical line on the graph and move it from left to right. If the vertical line intersects onl one point at a time on the ENTIRE graph, then it represents a function. If the vertical line intersects more than one point at ANY time on the graph, then it is NOT a function. Slide 10 / 11 Equations An equation is a function onl if when a number is substituted in for, there is onl 1 output -value. Function = + Not a Function = 5 Function Not a Function = Slide 11 / 11 Determine if each of the relations below is a function and provide an eplanation to support our : Slide 12 / 11 Determine if each of the relations below is a function and provide an eplanation to support our :
3 Slide 1 / 11 1 Is the following relation a function? Slide 1 / 11 2 Is the following relation a function? Yes No {(,1), (2,-1), (1,1)} Yes No Slide 15 / 11 Is the following relation a function? Slide 16 / 11 Is the following relation a function? X Y Yes No Yes No -2 0 Slide 17 / 11 Slide 1 / 11 5 Is the following relation a function? 6 Is the following relation a function? Yes No Yes No
4 Slide 19 / 11 Slide 20 / 11 7 Is the following relation a function? Yes Domain and Range No Return to Table of Contents Slide 21 / 11 Vocabular The domain of a function/relation is the set of all possible input values (-values). Relation Domain {1,, 6} {2,, 5} Slide 22 / 11 State the domain for each eample below and tell whether the relation is a function s {1,, 1} Slide 2 / 11 State the domain for each eample below and tell whether the relation is a function. Slide 2 / 11 State the domain for each eample below and tell whether the relation is a function. X Y X Y X Y s s
5 Slide 25 / 11 Slide 26 / 11 State the domain for each eample below: s Slide 27 / 11 Slide 2 / 11 9 What is the domain of the following: (Choose all that appl) What is the domain of the following: (Choose all that appl) X Y A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers A G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers Slide 29 / 11 Slide 0 / What is the domain of the following: 12 What is the domain of the following: (Choose all that appl) (Choose all that appl) A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers
6 Slide 1 / 11 Slide 2 / 11 1 What is the domain of the following: 1 What is the domain of the following: (Choose all that appl) (Choose all that appl) A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers Slide / 11 Vocabular The range of a function/relation is the set of all possible output values (-values). Relation Domain {1,, 6} {2,, 5} Range {-1,, 7} {} Slide / 11 State the range for each eample below: s {1, } {-2, 2, 6} Slide 5 / 11 State the range for each eample below: Slide 6 / 11 State the range for each eample below: X Y X Y X Y s s
7 Slide 7 / 11 State the range for each eample below: Slide / What is the range of the following: (Choose all that appl) {(,1), (2,-1), (1,1)} s A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers Slide 9 / 11 Slide 0 / What is the range of the following: (Choose all that appl) What is the range of the following: (Choose all that appl) X Y A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers -2 0 A - G H < 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers Slide 1 / 11 Slide 2 / 11 1 What is the range of the following: 19 What is the range of the following: (Choose all that appl) (Choose all that appl) A - A - G G H < 0 H < 0 I > 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers J All Real Numbers
8 Slide / 11 Slide / What is the range of the following: 21 What is the range of the following: (Choose all that appl) (Choose all that appl) A - A - G G H < 0 H < 0 I > 0 I > 0 J All Real Numbers J All Real Numbers Slide 5 / 11 Slide 6 / 11 Function Notation Equations for relations have been in the form of = + 2 Evaluating Functions When a relation is a function, it can also be written in function notation: f() = + 2 f() = + 2 is still a line with a slope of and a -intercept of 2. Return to Table of Contents When a relation is a function, = can be substituted with the notation of f() = Function Notation is read: "f of " Slide 7 / 11 Function Notation Slide / 11 Evaluating a Function So wh the new notation? 1) It lets the reader know the relation is a function. 2) A second function can be added, such as g() = and the reader will be able to distinguish between the different functions. To Evaluate in = Form: Find the value of = when = = = 2() + 1 = 7 When is = 7 To Evaluate in Function Notation Given f() = 2 +1 find f() f() = 2() + 1 f() = 7 "f of is 7" ) The notation makes evaluating a value of easier to read. Similar methods are used to solve but function notation makes asking and ing questions more concise.
9 Slide 9 / 11 Slide 50 / 11 Slide 51 / 11 Slide 52 / Given and Find the value of. Slide 5 / 11 Slide 5 / 11 2 Given and Find the value of.
10 26 Given and Slide 55 / 11 Find the value of. 27 Given and Find the value of. Slide 56 / 11 Slide 57 / 11 Slide 5 / 11 Vocabular Arithmetic Sequence - is a sequence of numbers with a constant common difference. Eplicit and Recursive Functions a 1 - is the first term of the sequence. d - is the common difference s: (5, 7, 9, 11, 1,...) a 1 = 5 and d = 2 (2, 17, 11, 5, -1,...) a 1 = 2 and d = -6 Return to Table of Contents Eplicit and Recursive Arithmetic Sequences Video (Youtube Video) Eplicit and Recursive Arithmetic Sequences Video (Khan Academ Video) Slide 59 / 11 Eplicit Function Form - a(n) = a 1 + d(n-1) Slide 60 / 11 Write the eplicit form for the following sequences: 1) 9, 16, 2, 0,... Recursive Function Form - is written in two parts 1. The first part is the first term a 1 2. The second part is a(n) = a n-1 + d (previous term plus the common difference) Note: In the recursive formula the previous term is used to produce the net term. 2) 1,, 6,, 11,... ) 6, 57, 6, 5,...
11 Slide 61 / 11 Write the recursive form for the following sequences: 1) 9, 16, 2, 0,... 2) -2, 1,, 7, 10,... Slide 62 / 11 Write the first five terms of the sequence given the eplicit formula. a(n) = 1 - (n - 1) ) 6, 57, 6, 5,... Slide 6 / 11 Slide 6 / 11 2 What is the eplicit formula of the sequence? Write the first five terms of the sequence given the recursive formula., 2, 51, 60,... a 1 = -10 A a(n) = 9 + (n-1) a(n) = a n-1 + a(n) - 9(n-1) C a(n) = + 9(n-1) D a(n) = 9 - (n-1) Slide 65 / 11 Slide 66 / What is the recursive formula for the sequence? 11,, -5, -1,... 0 What is the sequence that corresponds to the formula? f(n) = 2 - (n-1) A a 1 = 11 a(n) = a n-1 + C a 1 = 11 a 1 = 11 a(n) = a n D a 1 = 11 A 2, 5,, 51,... 2, 9, 6,,... C 2, 6, 50, 5,... a(n) = a n a(n) = a n-1 - D 2, 9, 6,,...
12 Slide 67 / 11 1 What is the sequence that corresponds to the formula? f 1 = 77 f(n) = f n A 77, 90, 10, 116, 129,... 77, 6, 9, 5,... Slide 6 / 11 Vocabular Geometric Sequence - is a sequence of numbers with a constant common ratio. a 1 - is the first term of the sequence. r - is the common ratio s: (, 12, 6, 10,...) a 1 = and r = (2, 1, 7,.5,...) a 1 = 2 and r = 1/2 C 77, 91, 105, 119, 1,... D 77, 62, 7, 2,... Eplicit and Recursive Geometric Sequences (Youtube Video) Eplicit and Recursive Geometric Sequences (Khan Academ Video) Slide 69 / 11 Slide 70 / 11 Eplicit Formula - a 1(r) (n-1) Recursive Formula - is written in two parts 1. The first part is the first term a 1 2. The second part is a n = r a n-1 for n > 1 (common ratio times the previous term) Note: In the recursive formula the previous term is used to produce the net term. Write an eplicit formula for the following sequences: 1) 7, 5, 175, 75,... 2) 20, 5, 5/, 5/16,... ) 2.5, 5, 10, 20,... Slide 71 / 11 Write an recursive formula for the following sequences: 1) 7, 5, 175, 75,... Slide 72 / 11 Write the first five terms of the sequence given the eplicit formula. a(n) = 27(1/) n-1 2) 20, 5, 5/, 5/16,... ) 2.5, 5, 10, 20,...
13 Slide 7 / 11 Slide 7 / 11 2 What is the eplicit formula of the sequence? Write the first five terms of the sequence given the recursive formula. a 1 = -2 a(n) = (5)a n-1 for n>1 A f(n) = 2(2) n-1 2, 12, 6,,... f(n) = 2(.5) n-1 C f(n) = 2-2(n-1) D f(n) = 2(2) n-1 Slide 75 / 11 Slide 76 / 11 What is the recursive formula for the sequence? What is the sequence that corresponds to the formula?, 1, 10, 6,... f 1 = -16 A f(n) = (-1/)f n-1 for n > 1 A -16, -, -1, 1/ C D -16,, -1, 1/ 6, -, 1, -1/ D 16, -, 1, -1/ Slide 77 / 11 Slide 7 / 11 5 What is the sequence that corresponds to the formula? f(n) = 2() n-1 A 2,, 2, 12,...,, 16, 2 C 2, 1/2, 1/, 1/16 Multiple Representations of Functions D 2,, 2, 11 Return to Table of Contents
14 Slide 79 / 11 Multiple Representations An function can be written as a table, graph, verbal model, or equation. We can find the rate of change and the -intercept from an of these representations. Slide 0 / 11 Multiple Representations Look at the given table. We can use an two values to determine slope. We can find where = 0 to determine the -intercept. Remember, to find slope we can use the formula: Slope = To find the -intercept (initial value) we look to where = f() Slope = -intercept = = = = 1 Slide 1 / 11 Multiple Representations Slide 2 / 11 Multiple Representations Sometimes a table will not show the -coordinate of zero. In that case ou need to figure it out. There are a few was to do it. f() = f() There are two was to find the -intercept here. f() = f() We can simpl continue the table so that we can find when = 0. We see that the 's are moving at intervals of +. In order to work backwards to where = 0 we need to subtract from. - - (-1) = - so when = 0, = -. Note: This technique works best when the table is close to = 0 Slide / 11 Multiple Representations Slide / 11 6 What is the slope of the following table? f() = f() Another technique would be to substitute for and solve for using the equation. f() = - f(0) = (0) - f(0) = - f()
15 Slide 5 / 11 Slide 6 / 11 7 What is the -intercept of the following table? What is the slope of this table? f() f() Slide 7 / 11 Slide / 11 9 What is the -intercept of this table? f() = - 6 f() Carla puts awa a certain amount of mone per week. She started out with a certain amount. How could we figure out what she started out with and what she puts in per week? week amount in account Slide 9 / 11 Slide 90 / 11 If we look at the slope or rate of change we can figure out how much she puts in each week. So what is the slope of this table? How much did Carla start out with? # of weeks # of weeks account balance account balance
16 Slide 91 / 11 Tr One Rob is training for a marathon. He is increasing his run each week. ased on the table: Slide 92 / 11 0 Evan is buing pizza from a store that sells each pie for a given price and each topping for set price as well. Use the table to identif the cost of each topping. How much more will he run each week? How man miles was he running before training? How man weeks until he runs a full marathon 26.2 miles? # of toppings Cost # of weeks training Miles Slide 9 / 11 1 Evan is buing pizza from a store that sells each pie for a given price and each topping for set price as well. How much is a pie without an toppings. Slide 9 / 11 2 Sandra is going to a buffet. The meal is a fied price but she has to pa for each soda she drinks. What is the initial value? e prepared to eplain how it relates to the scenario # of toppings Cost Cost Number of drinks Slide 95 / 11 Sandra is going to a buffet. The meal is a fied price but she has to pa for each soda she drinks. What is the slope? Use the points (0, 15) and (6, 25). e prepared to eplain how it relates to the scenario. Cost Slide 96 / 11 What does the circled coordinate mean? A C D This tree grows feet ever ear This tree was planted when it was feet There are trees planted The tree was planted when it was ears old. Height Number of drinks Years since planting
17 Slide 97 / 11 = m + b Slide 9 / 11 Tr one!! Mica is having a pool part. The cost to rent the pool is $25 and $7.00 per person attending the part. Notice that regardless of how man people come, Mica will have to pa $25. This is the initial value, the - intercept, the "b", also known as the constant. Also notice that it costs $7.00 per person. This amount will change as the number of guests changes. This will be the slope, the rate of change, or the "m". Raul is at the gas station. He is filling up his gas tank at $.5 per gallon and is also buing $12 worth of food from the convenience store. Write an equation to show this scenario. f() = So the equation of this problem becomes: = Slide 99 / 11 Slide 100 / 11 5 Sand charges $5 per necklace that she makes and charges a flat fee of $9 for shipping. Which equation would best fit this scenario? A f() = f() = C 5 = 9 D 9 = 5 6 How much does it cost to bu 5 necklaces? A C D $9 $5 $225 $2 Sand charges $5 per necklace that she makes and charges a flat fee of $9 for shipping. Slide 101 / 11 Slide 102 / 11 7 How man necklaces can a person bu with $77? Multiple Representations A C D 6 10 We have learned how to represent a function several was: Table/Ordered Pairs Graph Equation Verbal Description (Scenario) Sand charges $5 per necklace that she makes and charges a flat fee of $9 for shipping. Net we will compare two different models to each other. We will look at the relationship between the two models in terms of the rate of change and domain.
18 Slide 10 / 11 Two Different Representations Slide 10 / 11 Greater Rate of Change In order to compare the rate of change of two different tpes of representations of functions we simpl find the rate of change of each and compare them. The higher the absolute value of the rate of change, the bigger it is. For eample, if a graph has a slope of - and an equation has a slope of, the slope of the graph is steeper because the absolute value of - = and the absolute value of =. > so The graph has a bigger slope, or rate of change. Let's tr one! Which has a greater rate of change? A f() = Slope = -5 1 (, 5) (2, ) (1, 1) Slope = = 2 1 = 2 absolute value of -5 = 5 and absolute value of 2 = 2 5>2 so A had a greater rate of change than. Slide 105 / 11 Greater Rate of Change Slide 106 / 11 Greater Rate of Change Let's tr to compare a table and a verbal model. A Chris and Shari are going to have a bowling part. It costs $10 to rent a lane and $2 per pair of shoes A Chris and Shari are going to have a bowling part. It costs $10 to rent a lane and $2 per pair of shoes. We can turn this into a function. 10 is a constant fee. 2 changes depending on the amount of people at the part. So the equation is f() = The rate of change = 2 Which has the greater rate of change? Slide 107 / 11 Greater Rate of Change Slide 10 / 11 Let's tr to compare a table and a verbal model. A Greater Rate of Change Chris and Shari are going to have a bowling part. It costs $10 to rent a lane and $2 per pair of shoes. To find the rate of change we can use the slope formula = 2 = The rate of change is Which has the greater rate of change? Rate of change of A = 2 Rate of change of = Therefore, has the greater rate of change.
19 Slide 109 / 11 Slide 110 / 11 Which has the greater rate of change? A {(1, ), (2, 6), (, ), (, 10), (5, 12)} 9 Which has the greater rate of change? A f() = 1/ + 5 The school store is selling book covers $1 for 2. Slide 111 / 11 Slide 112 / Which has the greater rate of change? 51 Which has the greatest rate of change? A f() = f() A {(1, ), (2, ), (, 5), (, 6), (5, 7)} Ran and Andrew jump down the stairs steps at a time. C f() = 1/ - 2 D Slide 11 / Which has the greatest rate of change? A A cable compan charges $12 for ever 2 premium channel. f() = C {(9, ), (6, 2), (, 1), (0, 0), (-, -1)} D
ACTIVITY: Using a Table to Plot Points
 .5 Graphing Linear Equations in Standard Form equation a + b = c? How can ou describe the graph of the ACTIVITY: Using a Table to Plot Points Work with a partner. You sold a total of $6 worth of tickets
.5 Graphing Linear Equations in Standard Form equation a + b = c? How can ou describe the graph of the ACTIVITY: Using a Table to Plot Points Work with a partner. You sold a total of $6 worth of tickets
TOPIC ESSENTIAL QUESTION
 TOPIC Topic Review TOPIC ESSENTIAL QUESTION 1. How can linear functions be used to model situations and solve problems? Vocabular Review Choose the correct term to complete each sentence.. When tends to
TOPIC Topic Review TOPIC ESSENTIAL QUESTION 1. How can linear functions be used to model situations and solve problems? Vocabular Review Choose the correct term to complete each sentence.. When tends to
8.4. If we let x denote the number of gallons pumped, then the price y in dollars can $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.
 8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
Solve each system by graphing. Check your solution. y =-3x x + y = 5 y =-7
 Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
11.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Name Class Date 11.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Essential Question: How can ou find the solution of a sstem of linear equations b graphing? Resource Locker Eplore Tpes of Sstems of Linear Equations
Essential Question How can you solve a system of linear equations? $15 per night. Cost, C (in dollars) $75 per Number of. Revenue, R (in dollars)
 5.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Essential Question How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil opens a bed-and-breakfast.
5.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Essential Question How can ou solve a sstem of linear equations? Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with a partner. Your famil opens a bed-and-breakfast.
x. 4. 2x 10 4x. 10 x
 CCGPS UNIT Semester 1 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of Reasoning with Equations and Quantities Name: Date: Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and eplain the reasoning MCC9-1.A.REI.1 Eplain
CCGPS UNIT Semester 1 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of Reasoning with Equations and Quantities Name: Date: Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and eplain the reasoning MCC9-1.A.REI.1 Eplain
Name Date. and y = 5.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
3.2 Understanding Relations and Functions-NOTES
 Name Class Date. Understanding Relations and Functions-NOTES Essential Question: How do ou represent relations and functions? Eplore A1.1.A decide whether relations represented verball, tabularl, graphicall,
Name Class Date. Understanding Relations and Functions-NOTES Essential Question: How do ou represent relations and functions? Eplore A1.1.A decide whether relations represented verball, tabularl, graphicall,
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 3 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Plot the point in a coordinate plane. Describe the location of the point. 1. A( 3, 1). B (, ) 3. C ( 1, 0). D ( 5, ) 5. Plot the point that is on
Name Date Chapter 3 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Plot the point in a coordinate plane. Describe the location of the point. 1. A( 3, 1). B (, ) 3. C ( 1, 0). D ( 5, ) 5. Plot the point that is on
Precalculus Honors - AP Calculus A Information and Summer Assignment
 Precalculus Honors - AP Calculus A Information and Summer Assignment General Information: Competenc in Algebra and Trigonometr is absolutel essential. The calculator will not alwas be available for ou
Precalculus Honors - AP Calculus A Information and Summer Assignment General Information: Competenc in Algebra and Trigonometr is absolutel essential. The calculator will not alwas be available for ou
Chapter 9 BUILD YOUR VOCABULARY
 C H A P T E R 9 BUILD YUR VCABULARY Chapter 9 This is an alphabetical list of new vocabular terms ou will learn in Chapter 9. As ou complete the stud notes for the chapter, ou will see Build Your Vocabular
C H A P T E R 9 BUILD YUR VCABULARY Chapter 9 This is an alphabetical list of new vocabular terms ou will learn in Chapter 9. As ou complete the stud notes for the chapter, ou will see Build Your Vocabular
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 5.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Widgets, Dumbbells, and Dumpsters Multiple Representations of Linear Functions Vocabular Write the term that best completes each statement.. A(n) is
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Widgets, Dumbbells, and Dumpsters Multiple Representations of Linear Functions Vocabular Write the term that best completes each statement.. A(n) is
Linear Equations Revisited Four Important Formulas: Math 8. Slope: Slope-Intercept Form: y mx b. Standard:
 Linear Equations Revisited Four Important Formulas: Slope: m x x Slope-Intercept Form: mx b Standard: Ax B C Point-Slope: m x ) ( x You should be able to convert equations easil. Example: Convert to slope-intercept
Linear Equations Revisited Four Important Formulas: Slope: m x x Slope-Intercept Form: mx b Standard: Ax B C Point-Slope: m x ) ( x You should be able to convert equations easil. Example: Convert to slope-intercept
Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing. ESSENTIAL QUESTION How can you solve a system of equations by graphing? 8.9 Slope-intercept form
 ? LESSN. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing ESSENTIAL QUESTIN How can ou solve a sstem of equations b graphing? Epressions, equations, and relationships.9 Identif and verif the values of and
? LESSN. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing ESSENTIAL QUESTIN How can ou solve a sstem of equations b graphing? Epressions, equations, and relationships.9 Identif and verif the values of and
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions
 Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Read To Go On? Skills Intervention 5-1 Using Transformations to Graph Quadratic Functions Find these vocabular words in Lesson 5-1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular quadratic function parabola verte
Fair Game Review. Chapter 2. and y = 5. Evaluate the expression when x = xy 2. 4x. Evaluate the expression when a = 9 and b = 4.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Functions. Essential Question What is a function?
 3. Functions COMMON CORE Learning Standard HSF-IF.A. Essential Question What is a function? A relation pairs inputs with outputs. When a relation is given as ordered pairs, the -coordinates are inputs
3. Functions COMMON CORE Learning Standard HSF-IF.A. Essential Question What is a function? A relation pairs inputs with outputs. When a relation is given as ordered pairs, the -coordinates are inputs
Functions. Essential Question What is a function? Work with a partner. Functions can be described in many ways.
 . Functions Essential Question What is a function? A relation pairs inputs with outputs. When a relation is given as ordered pairs, the -coordinates are inputs and the -coordinates are outputs. A relation
. Functions Essential Question What is a function? A relation pairs inputs with outputs. When a relation is given as ordered pairs, the -coordinates are inputs and the -coordinates are outputs. A relation
Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Opener. Section 4.1. Big Ideas Math Blue Worked-Out Solutions. x 2. Try It Yourself (p. 147) x 0 1. y ( ) x 2
 Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. 7). As the input decreases b, the output increases b.. Input As the input increases b, the output increases b.. As the input decreases b, the output decreases
Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. 7). As the input decreases b, the output increases b.. Input As the input increases b, the output increases b.. As the input decreases b, the output decreases
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations
 Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
For use after the chapter Graphing Linear Equations and Functions 3 D. 7. 4y 2 3x 5 4; (0, 1) x-intercept: 6 y-intercept: 3.
 Chapter Test A Write the coordinates of the point.. A. B. D. C. A. D C B.... Tell whether the ordered pair is a solution of the equation.. ; (, ) 7.. ; (, ). 7. ; (, ). Draw the line that has the given
Chapter Test A Write the coordinates of the point.. A. B. D. C. A. D C B.... Tell whether the ordered pair is a solution of the equation.. ; (, ) 7.. ; (, ). 7. ; (, ). Draw the line that has the given
Name Class Date. Solving Special Systems by Graphing. Does this linear system have a solution? Use the graph to explain.
 Name Class Date 5 Solving Special Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How do ou solve sstems with no or infinitel man solutions? 1 A-REI.3.6 EXAMPLE Solving Special Sstems b Graphing Use the graph
Name Class Date 5 Solving Special Sstems Going Deeper Essential question: How do ou solve sstems with no or infinitel man solutions? 1 A-REI.3.6 EXAMPLE Solving Special Sstems b Graphing Use the graph
Linear and Nonlinear Systems of Equations. The Method of Substitution. Equation 1 Equation 2. Check (2, 1) in Equation 1 and Equation 2: 2x y 5?
 3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
3330_070.qd 96 /5/05 Chapter 7 7. 9:39 AM Page 96 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Linear and Nonlinear Sstems of Equations What ou should learn Use the method of substitution to solve sstems of linear
THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER
 THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER ALGEBRA EOC PRACTICE Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing
THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER ALGEBRA EOC PRACTICE Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing
Lesson Remember. Finding Domain and Range from a Graph EXAMPLE. Key Vocabulary
 0. Lesson Ke Vocabular function domain range function form Functions A function is a relationship that pairs each input with eactl one output. The domain is the set of all possible input values. The range
0. Lesson Ke Vocabular function domain range function form Functions A function is a relationship that pairs each input with eactl one output. The domain is the set of all possible input values. The range
Name PD. Linear Functions
 Name PD Linear Functions Finding the Slope of a Line The steepness of the line is the ratio of rise to run, or vertical change to horizontal change, for this step. We call this ratio the slope of the line.
Name PD Linear Functions Finding the Slope of a Line The steepness of the line is the ratio of rise to run, or vertical change to horizontal change, for this step. We call this ratio the slope of the line.
Polynomial Functions. INVESTMENTS Many grandparents invest in the stock market for
 4-1 BJECTIVES Determine roots of polnomial equations. Appl the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Polnomial Functions INVESTMENTS Man grandparents invest in the stock market for their grandchildren s college
4-1 BJECTIVES Determine roots of polnomial equations. Appl the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Polnomial Functions INVESTMENTS Man grandparents invest in the stock market for their grandchildren s college
Algebra I. Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176. Slide 3 / 176. Slide 4 / 176. Slide 6 / 176. Slide 5 / 176. System of Linear Equations.
 Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176 Algebra I Sstem of Linear Equations 21-11-2 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 176 Slide 4 / 176 Table of Contents Solving Sstems b Graphing Solving Sstems b Substitution Solving Sstems
Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176 Algebra I Sstem of Linear Equations 21-11-2 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 176 Slide 4 / 176 Table of Contents Solving Sstems b Graphing Solving Sstems b Substitution Solving Sstems
b(n) = 4n, where n represents the number of students in the class. What is the independent
 Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing movie tickets that sell for $ each C The cost,, after a $ discount,
Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing movie tickets that sell for $ each C The cost,, after a $ discount,
PA CORE 8 UNIT 3 - FUNCTIONS FLEX Workbook
 PA CORE 8 UNIT - FUNCTIONS FLEX Workbook LESSON 9. INTRODUCTIONS TO FUNCTIONS 0. WORK WITH LINEAR FUNCTIONS. USE FUNCTIONS TO SOLVE PROBLEMS. USE GRAPHS TO DESCRIBE RELATIONSHIPS. COMPARE RELATIONSHIPS
PA CORE 8 UNIT - FUNCTIONS FLEX Workbook LESSON 9. INTRODUCTIONS TO FUNCTIONS 0. WORK WITH LINEAR FUNCTIONS. USE FUNCTIONS TO SOLVE PROBLEMS. USE GRAPHS TO DESCRIBE RELATIONSHIPS. COMPARE RELATIONSHIPS
Name Class Date. Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. All rights reserved. Travels in Air. Distance (miles) Time (seconds)
 Practice - Rate of Change and Slope Find the slope of each line.... O O O Find the slope of the line that passes through each pair of points.. (, ), (7, 5) 5. (8, ), (, ). (, 5), (, 7) 7. (-, 7), (, -)
Practice - Rate of Change and Slope Find the slope of each line.... O O O Find the slope of the line that passes through each pair of points.. (, ), (7, 5) 5. (8, ), (, ). (, 5), (, 7) 7. (-, 7), (, -)
Analytic Geometry 300 UNIT 9 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY. An air traffi c controller uses algebra and geometry to help airplanes get from one point to another.
 UNIT 9 Analtic Geometr An air traffi c controller uses algebra and geometr to help airplanes get from one point to another. 00 UNIT 9 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Copright 00, K Inc. All rights reserved. This material
UNIT 9 Analtic Geometr An air traffi c controller uses algebra and geometr to help airplanes get from one point to another. 00 UNIT 9 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Copright 00, K Inc. All rights reserved. This material
2. Domain: The set of all abscissas (x s) of the ordered pairs (abscissa is the first element of an ordered pair)
 . Relations and Functions. Relation: A set of ordered pairs E:,4,,5,,, 8,4. The set of all abscissas s of the ordered pairs abscissa is the first element of an ordered pair. Range: The set of all ordinates
. Relations and Functions. Relation: A set of ordered pairs E:,4,,5,,, 8,4. The set of all abscissas s of the ordered pairs abscissa is the first element of an ordered pair. Range: The set of all ordinates
Different: Arrow go different directions, circles are different, one answer is whole the other real
 a) 1.) Fatima enrolled in a traveler rewards program. She begins with 7,500 bonus points. For ever trip she takes, she collects 500 bonus points. D) When Fatima has collected 30,000 bonus points, she gets
a) 1.) Fatima enrolled in a traveler rewards program. She begins with 7,500 bonus points. For ever trip she takes, she collects 500 bonus points. D) When Fatima has collected 30,000 bonus points, she gets
Assessment Readiness. 28 Unit 1 MIXED REVIEW. 1. Look at each number. Is the number between 2π and
 MODULE 1 1. Look at each number. Is the number between π and 5? Select or for epressions A C. A. 6 _ 3 5π B. C. 3 5. Consider the number - 11 15. A. The number is rational. True False B. The number can
MODULE 1 1. Look at each number. Is the number between π and 5? Select or for epressions A C. A. 6 _ 3 5π B. C. 3 5. Consider the number - 11 15. A. The number is rational. True False B. The number can
Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences
 CONDENSED LESSON.1 Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences In this lesson, ou Write eplicit formulas for arithmetic sequences Write linear equations in intercept form You learned about recursive formulas
CONDENSED LESSON.1 Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences In this lesson, ou Write eplicit formulas for arithmetic sequences Write linear equations in intercept form You learned about recursive formulas
LESSON #11 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT 4 LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS ANSWERS FOR EXERCISES. Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 51
 MATH GRADE 8 UNIT LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS FOR EXERCISES Copright Pearson Education, Inc. Grade 8 Unit : Linear Relationships LESSON : MODELING RUNNING SPEEDS 8.EE.. A Runner A 8.EE.. D sec 8.EE.. D. m/sec
MATH GRADE 8 UNIT LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS FOR EXERCISES Copright Pearson Education, Inc. Grade 8 Unit : Linear Relationships LESSON : MODELING RUNNING SPEEDS 8.EE.. A Runner A 8.EE.. D sec 8.EE.. D. m/sec
Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs
 Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
Ch 5 Alg Note Sheet Ke Chapter 5: Quadratic Equations and Functions 5.1 Modeling Data With Quadratic Functions Quadratic Functions and Their Graphs Definition: Standard Form of a Quadratic Function The
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 NON-PROPORTIONAL LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS TOPICS COVERED:
 ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 NON-PROPORTIONAL LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS TOPICS COVERED: Representing Linear Non-Proportional Equations Slope & -Intercept Graphing Using Slope & -Intercept Proportional
ACCELERATED MATHEMATICS CHAPTER 7 NON-PROPORTIONAL LINEAR RELATIONSHIPS TOPICS COVERED: Representing Linear Non-Proportional Equations Slope & -Intercept Graphing Using Slope & -Intercept Proportional
The semester A examination for Bridge to Algebra 2 consists of two parts. Part 1 is selected response; Part 2 is short answer.
 The semester A eamination for Bridge to Algebra 2 consists of two parts. Part 1 is selected response; Part 2 is short answer. Students ma use a calculator. If a calculator is used to find points on a graph,
The semester A eamination for Bridge to Algebra 2 consists of two parts. Part 1 is selected response; Part 2 is short answer. Students ma use a calculator. If a calculator is used to find points on a graph,
c. x x < 60 d. x x =9. What are the first four terms of the sequence? a. 12, 21, 30, 39 b.
 Algebra I Unit Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities Post Test... A famil s cell phone plan costs $ per month for, minutes and cents per minute over the limit. This month, the famil paid $..
Algebra I Unit Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities Post Test... A famil s cell phone plan costs $ per month for, minutes and cents per minute over the limit. This month, the famil paid $..
Algebra 12nd 6 Weeks REVIEW
 Name: Class: Date: _ ID: A Algebra 1nd 6 Weeks REVIEW Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which graph represents a function? a. c. - x - - b.
Name: Class: Date: _ ID: A Algebra 1nd 6 Weeks REVIEW Multiple Choice Identif the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which graph represents a function? a. c. - x - - b.
Name Class Date. Inverse of Function. Understanding Inverses of Functions
 Name Class Date. Inverses of Functions Essential Question: What is an inverse function, and how do ou know it s an inverse function? A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as
Name Class Date. Inverses of Functions Essential Question: What is an inverse function, and how do ou know it s an inverse function? A..B Graph and write the inverse of a function using notation such as
RELEASED. End-of-Grade Alternate Assessment Mathematics. Grade 8. Student Booklet
 Released Form READY NCEXTEND2 End-of-Grade Alternate Assessment Mathematics Grade 8 Student Booklet Academic Services and Instructional Support Division of Accountabilit Services Copright 2013 b the North
Released Form READY NCEXTEND2 End-of-Grade Alternate Assessment Mathematics Grade 8 Student Booklet Academic Services and Instructional Support Division of Accountabilit Services Copright 2013 b the North
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
LESSON 4.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES
 LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES 9 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Linear Inequalities a. Ordered pairs as solutions of linear inequalities b. Graphing linear
LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES LESSON.3 GRAPHING INEQUALITIES 9 OVERVIEW Here s what ou ll learn in this lesson: Linear Inequalities a. Ordered pairs as solutions of linear inequalities b. Graphing linear
1. m = 3, P (3, 1) 2. m = 2, P ( 5, 8) 3. m = 1, P ( 7, 1) 4. m = m = 0, P (3, 117) 8. m = 2, P (0, 3)
 . Linear Functions 69.. Eercises To see all of the help resources associated with this section, click OSttS Chapter. In Eercises - 0, find both the point-slope form and the slope-intercept form of the
. Linear Functions 69.. Eercises To see all of the help resources associated with this section, click OSttS Chapter. In Eercises - 0, find both the point-slope form and the slope-intercept form of the
Algebra 1, Semester 1, District Final REVIEW Solve the equation.
 Algebra, Semester, District Final REVIEW 6-7 Solve the equation... - = 9. 8. The admission fee to an amusement park is $. It costs an additional d dollars to rent a locker to hold our belongings. The total
Algebra, Semester, District Final REVIEW 6-7 Solve the equation... - = 9. 8. The admission fee to an amusement park is $. It costs an additional d dollars to rent a locker to hold our belongings. The total
Solving Systems of Linear Equations
 5 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations 5. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing 5. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Substitution 5.3 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Elimination 5. Solving
5 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations 5. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing 5. Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Substitution 5.3 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Elimination 5. Solving
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
1.1. Use a Problem Solving Plan. Read a problem and make a plan. Goal p Use a problem solving plan to solve problems. VOCABULARY. Formula.
 . Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMPd, MMPa Your Notes Use a Problem Solving Plan Goal p Use a problem solving plan to solve problems. VOCABULARY Formula A PROBLEM SOLVING PLAN Step Read the problem carefull.
. Georgia Performance Standard(s) MMPd, MMPa Your Notes Use a Problem Solving Plan Goal p Use a problem solving plan to solve problems. VOCABULARY Formula A PROBLEM SOLVING PLAN Step Read the problem carefull.
Ordered pair: Domain: Range:
 Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
Sec 2.1 Relations Learning Objectives: 1. Understand relations. 2. Find the domain and the range of a relation. 3. Graph a relation defined b an equation. 1. Understand relations Relation eists when the
MATH 021 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS
 MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
Algebra 1 Honors First Semester Review
 Permitted resources: Algebra 1 Honors First Semester Review TI-108 (or similar basic four function calculator) Algebra 1 and Geometr EOC Reference Sheet 4. Identif the mapping diagram that represents the
Permitted resources: Algebra 1 Honors First Semester Review TI-108 (or similar basic four function calculator) Algebra 1 and Geometr EOC Reference Sheet 4. Identif the mapping diagram that represents the
Topic 1: Writing and Solving Equations and Inequalities
 Topic 1: Writing and Solving Equations and Inequalities In #1 3, solve each equation. Use inverse operations. 1. 8 21 5 = 15 2. 3 10 = 2(4 5) 3. 2( + 2) = 2 + 1 4. The rectangle and square have equivalent
Topic 1: Writing and Solving Equations and Inequalities In #1 3, solve each equation. Use inverse operations. 1. 8 21 5 = 15 2. 3 10 = 2(4 5) 3. 2( + 2) = 2 + 1 4. The rectangle and square have equivalent
Chapter Start Thinking! For use before Activity 6.1. For use before Activity Start Thinking! For use before Lesson
 . Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
. Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
Chapter 11. Systems of Equations Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
 Chapter 11 Sstems of Equations 11.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Learning Objectives: A. Decide whether an ordered pair is a solution of a sstem of linear equations. B. Solve a sstem of
Chapter 11 Sstems of Equations 11.1 Solving Sstems of Linear Equations b Graphing Learning Objectives: A. Decide whether an ordered pair is a solution of a sstem of linear equations. B. Solve a sstem of
CHAPTER 6: LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Name: Date: Period: CHAPTER : LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS Notes #: Section.: Solving Linear Sstems b Substitution The solution to a sstem of equations represents the where the. It would be great if
Name: Date: Period: CHAPTER : LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS Notes #: Section.: Solving Linear Sstems b Substitution The solution to a sstem of equations represents the where the. It would be great if
Name Date PD. Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Name Date PD Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Sstems of Equations Vocabular: A sstem of linear equations is A solution of a sstem of linear equations is Points of Intersection (POI) are the same thing
Name Date PD Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Sstems of Equations Vocabular: A sstem of linear equations is A solution of a sstem of linear equations is Points of Intersection (POI) are the same thing
7.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
CHAPTER 3 Graphs and Functions
 CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
CHAPTER Graphs and Functions Section. The Rectangular Coordinate Sstem............ Section. Graphs of Equations..................... 7 Section. Slope and Graphs of Linear Equations........... 7 Section.
Summary and Vocabulary
 Chapter Chapter Summar and Vocabular Equations involving percents ma be written in the form p q = r, where p is the decimal form of the percent, q is the initial quantit, and r is the resulting quantit.
Chapter Chapter Summar and Vocabular Equations involving percents ma be written in the form p q = r, where p is the decimal form of the percent, q is the initial quantit, and r is the resulting quantit.
Patterns & Graphs FPMath 70 Unit 3 Worksheet
 1. The image below shows a pattern of sections from a fence made from boards. a. Sketch the net two sections of the fence: b. Complete the following chart: Fence # (variable) # of boards 1 4 2 7 3 4 5
1. The image below shows a pattern of sections from a fence made from boards. a. Sketch the net two sections of the fence: b. Complete the following chart: Fence # (variable) # of boards 1 4 2 7 3 4 5
TOPIC 1 Domain and Range
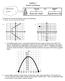 TOPIC 1 Domain and Range NEED HELP? Tr this... Determine the Domain and Range for each of the following: 1. {(3, 4), (-5, -2), (7, 6), (6, 5), (-8, 6)} 2. 3. 4. The DeWind famil lives in a rectangular
TOPIC 1 Domain and Range NEED HELP? Tr this... Determine the Domain and Range for each of the following: 1. {(3, 4), (-5, -2), (7, 6), (6, 5), (-8, 6)} 2. 3. 4. The DeWind famil lives in a rectangular
Algebra I Practice Exam
 Algebra I This practice assessment represents selected TEKS student expectations for each reporting category. These questions do not represent all the student expectations eligible for assessment. Copyright
Algebra I This practice assessment represents selected TEKS student expectations for each reporting category. These questions do not represent all the student expectations eligible for assessment. Copyright
( 7, 3) means x = 7 and y = 3. ( 7, 3) works in both equations so. Section 5 1: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Graphing
 Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
Determining Slope and y-intercept 8.4.C. Find the slope of the line using the points (0, 4) and (-3, 6).
 ? LESSON. Determining Slope and -intercept ESSENTIAL QUESTION Proportionalit 8..C Use data from a table or graph to determine the rate of change or slope and -intercept in mathematical and real-world problems.
? LESSON. Determining Slope and -intercept ESSENTIAL QUESTION Proportionalit 8..C Use data from a table or graph to determine the rate of change or slope and -intercept in mathematical and real-world problems.
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
Fair Game Review. Chapter = How many calculators are sold when the profit is $425? Solve the equation. Check your solution.
 Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
Reteaching (continued)
 Zero and Negative Eponents Eercises Write each epression as an integer, a simple fraction, or an epression that contains onl positive eponents. Simplif...3 0. 0-0,000 3. a -5. 3.7 0 a 5 5. 9-6. 3-3 9 p
Zero and Negative Eponents Eercises Write each epression as an integer, a simple fraction, or an epression that contains onl positive eponents. Simplif...3 0. 0-0,000 3. a -5. 3.7 0 a 5 5. 9-6. 3-3 9 p
Bridge-Thickness Experiment. Student 2
 Applications 1. Below are some results from the bridge-thickness eperiment. Bridge-Thickness Eperiment Thickness (laers) Breaking Weight (pennies) 15 5 5 a. Plot the (thickness, breaking weight) data.
Applications 1. Below are some results from the bridge-thickness eperiment. Bridge-Thickness Eperiment Thickness (laers) Breaking Weight (pennies) 15 5 5 a. Plot the (thickness, breaking weight) data.
LESSON #28 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #8 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
4 The Cartesian Coordinate System- Pictures of Equations
 The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem- Pictures of Equations Concepts: The Cartesian Coordinate Sstem Graphs of Equations in Two Variables -intercepts and -intercepts Distance in Two Dimensions and the Pthagorean
Algebra 2 Unit 2 Practice
 Algebra Unit Practice LESSON 7-1 1. Consider a rectangle that has a perimeter of 80 cm. a. Write a function A(l) that represents the area of the rectangle with length l.. A rectangle has a perimeter of
Algebra Unit Practice LESSON 7-1 1. Consider a rectangle that has a perimeter of 80 cm. a. Write a function A(l) that represents the area of the rectangle with length l.. A rectangle has a perimeter of
2.4 Library of Functions; Piecewise-defined Functions. 1 Graph the Functions Listed in the Library of Functions
 80 CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Problems 8 88 require the following discussion of a secant line. The slope of the secant line containing the two points, f and + h, f + h on the graph of a function
80 CHAPTER Functions and Their Graphs Problems 8 88 require the following discussion of a secant line. The slope of the secant line containing the two points, f and + h, f + h on the graph of a function
Name: Period: QVMS GTA FALL FINAL EXAM REVIEW PRE-AP ALGEBRA 1
 Name: Period: QVMS GTA FALL FINAL EXAM REVIEW PRE-AP ALGEBRA ) When simplifing an epression, ou perform operations inside grouping smbols first. a. alwas b. sometimes c. never ) The opposite of a negative
Name: Period: QVMS GTA FALL FINAL EXAM REVIEW PRE-AP ALGEBRA ) When simplifing an epression, ou perform operations inside grouping smbols first. a. alwas b. sometimes c. never ) The opposite of a negative
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
6.4 graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
 SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
SECTION 6. graphs of logarithmic functions 9 9 learning ObjeCTIveS In this section, ou will: Identif the domain of a logarithmic function. Graph logarithmic functions. 6. graphs OF logarithmic FUnCTIOnS
Chapter 4 ( 2, 2 ). Chapter 4 Opener. Section 4.1. Big Ideas Math Blue Worked-Out Solutions. Try It Yourself (p. 141) = = = = 15. The solution checks.
 Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. ). ab = ( ) = ( ) = = = =. a b = ( ). a b = = = = + = + = + 9 =, or. a ( b a ). Point Q is on the -ais, units up from the origin. So, the -coordinate is, and the
Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. ). ab = ( ) = ( ) = = = =. a b = ( ). a b = = = = + = + = + 9 =, or. a ( b a ). Point Q is on the -ais, units up from the origin. So, the -coordinate is, and the
Section 5.1: Functions
 Objective: Identif functions and use correct notation to evaluate functions at numerical and variable values. A relationship is a matching of elements between two sets with the first set called the domain
Objective: Identif functions and use correct notation to evaluate functions at numerical and variable values. A relationship is a matching of elements between two sets with the first set called the domain
4.1 Identifying and Graphing Sequences
 Name Class Date 4.1 Identifing and Graphing Sequences Essential Question: What is a sequence and how are sequences and functions related? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Sequences A go-kart racing
Name Class Date 4.1 Identifing and Graphing Sequences Essential Question: What is a sequence and how are sequences and functions related? Resource Locker Eplore Understanding Sequences A go-kart racing
LESSON #24 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
1 LESSON #4 - POWER FUNCTIONS COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Before we start to analze polnomials of degree higher than two (quadratics), we first will look at ver simple functions known as power functions. The
Linear Functions. Essential Question How can you determine whether a function is linear or nonlinear?
 . Linear Functions Essential Question How can ou determine whether a function is linear or nonlinear? Finding Patterns for Similar Figures Work with a partner. Cop and complete each table for the sequence
. Linear Functions Essential Question How can ou determine whether a function is linear or nonlinear? Finding Patterns for Similar Figures Work with a partner. Cop and complete each table for the sequence
LESSON #12 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
5 Linear Graphs and Equations
 Linear Graphs and Equations. Coordinates Firstl, we recap the concept of (, ) coordinates, illustrated in the following eamples. Eample On a set of coordinate aes, plot the points A (, ), B (0, ), C (,
Linear Graphs and Equations. Coordinates Firstl, we recap the concept of (, ) coordinates, illustrated in the following eamples. Eample On a set of coordinate aes, plot the points A (, ), B (0, ), C (,
REVIEW. Topic Essential Question. Vocabulary Review. Use Vocabulary in Writing Describe how to solve 3 7
 ? Topic Essential Question What procedures can be used to write and solve equations and inequalities? REVIEW TOPIC 4 Vocabular Review Complete each definition with a vocabular word. Vocabular dependent
? Topic Essential Question What procedures can be used to write and solve equations and inequalities? REVIEW TOPIC 4 Vocabular Review Complete each definition with a vocabular word. Vocabular dependent
Review for MIDTERM. Ensure your Survival Guides are complete and corrected. These you may use on PART #1 (but not on PART #2)
 1 M i d t e r m 10P Date: Name: Review for MIDTERM MIDTERM TASK #1 date MIDTERM TASK # date Success Criteria Students on IEP if ou will need more time to finish, arrange a ride afterschool on these das
1 M i d t e r m 10P Date: Name: Review for MIDTERM MIDTERM TASK #1 date MIDTERM TASK # date Success Criteria Students on IEP if ou will need more time to finish, arrange a ride afterschool on these das
Algebra I Final Exam Review 2016 List of Topics Covered
 Algebra I Final Exam Review 016 List of Topics Covered Know all vocabular, pa attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various tpes of directions in each of the sections of the
Algebra I Final Exam Review 016 List of Topics Covered Know all vocabular, pa attention to the highlighted words in the text, and understand the various tpes of directions in each of the sections of the
Systems of Linear Equations Monetary Systems Overload
 Sstems of Linear Equations SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Close Reading, Interactive Word Wall Have ou ever noticed that when an item is popular and man people want to bu it, the price
Sstems of Linear Equations SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Shared Reading, Close Reading, Interactive Word Wall Have ou ever noticed that when an item is popular and man people want to bu it, the price
Chapter 4 - Writing Linear Functions
 Chapter 4 - Writing Linear Functions Write an equation of the line with the given slope and y-intercept. 1. slope: 3 y-intercept: 6 a. y = 6x + 3 c. y = 6x 3 b. y = 3m + 6 d. y = 3x 6 2. D REF: Algebra
Chapter 4 - Writing Linear Functions Write an equation of the line with the given slope and y-intercept. 1. slope: 3 y-intercept: 6 a. y = 6x + 3 c. y = 6x 3 b. y = 3m + 6 d. y = 3x 6 2. D REF: Algebra
Algebra Semester 1 Final Exam Review Name: Hour: Date:
 Algebra Semester Final Exam Review Name: Hour: Date: CHAPTER Learning Target: I can appl the order of operations to evaluate expressions. Simplif the following expressions (combine like terms). x + x +
Algebra Semester Final Exam Review Name: Hour: Date: CHAPTER Learning Target: I can appl the order of operations to evaluate expressions. Simplif the following expressions (combine like terms). x + x +
Ch 3 Alg 2 Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Systems of Equations
 Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Reteaching -1. Relating Graphs to Events
 - Relating Graphs to Events The graph at the right shows the outside temperature during 6 hours of one da. You can see how the temperature changed throughout the da. The temperature rose F from A.M. to
- Relating Graphs to Events The graph at the right shows the outside temperature during 6 hours of one da. You can see how the temperature changed throughout the da. The temperature rose F from A.M. to
Comparing linear and exponential growth
 Januar 16, 2009 Comparing Linear and Exponential Growth page 1 Comparing linear and exponential growth How does exponential growth, which we ve been studing this week, compare to linear growth, which we
Januar 16, 2009 Comparing Linear and Exponential Growth page 1 Comparing linear and exponential growth How does exponential growth, which we ve been studing this week, compare to linear growth, which we
Answers. Chapter 4 A15
 . =. Sample answer:. a. B is congruent to itself. A and D have the same line of sight, and so the are congruent. Because two angles are congruent, the third angles are congruent. Because the triangles
. =. Sample answer:. a. B is congruent to itself. A and D have the same line of sight, and so the are congruent. Because two angles are congruent, the third angles are congruent. Because the triangles
Topic 16 Coordinate Geometry
 Topic 1 Coordinate Geometr Name Test Date Topic 1 Vocabular Cards coordinate grid coordinate grid A grid that makes it eas to locate points on a plane b using an ordered pair of numbers. x-axis Fold here
Topic 1 Coordinate Geometr Name Test Date Topic 1 Vocabular Cards coordinate grid coordinate grid A grid that makes it eas to locate points on a plane b using an ordered pair of numbers. x-axis Fold here
