A note on partitions into distinct parts and odd parts
|
|
|
- Allan Phelps
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 c,, 5 () Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston. Manufactured in The Netherlands. A note on partitions into distinct parts and odd parts DONGSU KIM * AND AE JA YEE Department of Mathematics Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Taejon, Republic of Korea dskim@math.kaist.ac.kr Editor: Abstract. Bousquet-Mélou and Eriksson showed that the number of partitions of n into distinct parts whose alternating sum is k is equal to the number of partitions of n into k odd parts, which is a refinement of a well-known result by Euler. We give a different graphical interpretation of the bijection by Sylvester on partitions into distinct parts and partitions into odd parts, and show that the bijection implies the above statement. Keywords: Partitions. Introduction A finite nonincreasing sequence of positive integers, λ λ λ 2 λ l, is called an integer partition of n, where n l i λ i. We follow standard notations in []. The length of a partition λ is the number of its parts, denoted l(λ). Let λ, called the size of λ, denote the number which λ is a partition of. Though each part in a partition is positive, we sometimes allow a zero as a part. Let P d denote the set of all partitions whose parts are all distinct, and let P o denote the set of all partitions whose parts are all odd. If λ P d is a partition of odd length, then we can add a zero as the last part, which changes the length of λ into even. So we assume that each partition in P d has an even length. It is well known, originally due to Euler, that the generating function of P d is equal to that of P o, which proves that for any nonnegative integer n, the number of partitions of n into distinct parts is equal to the number of partitions of n into odd parts. In terms of generating functions, it is written as follows: λ P d q λ ( q; q) (q; q 2 ) λ P o q λ. () There are well known proofs of this identity. One of them is by Sylvester, which can be found on pages in [2] and pages 3 in [5]. It actually proves more general result that the number of partitions of n into odd parts (repetitions allowed) with exactly k distinct parts appearing is equal to the number of partitions of n * Partially supported by KOSEF : and SAMSUNG
2 2 into distinct parts such that exactly k sequences of consecutive integers occur in each partition ([], Theorem 2.2). Recently there has been another proof by Bousquet-Mélou and Eriksson, [3, ], establishing the identity q λ x λ a q λ x l(λ), (2) λ P d λ P o l(λ) where λ a denotes the alternating sum of λ, i.e. i ( )i λ i. They obtain more general results on the lecture hall partitions and show that the above identity is a limit case. But they do not give a combinatorial bijection establishing the identity (2). Identity (2) is stronger than identity (). It says that the number of partitions of n into distinct parts whose alternating sum is k is equal to the number of partitions of n into k odd parts. In this paper, we give a different description for the bijection by Sylvester and bring out a hidden property of the bijection, i.e. it is a simple, bijective proof of identity (2). Our description uses a special way of drawing a diagram associated to a partition in P d. Our diagram is different from that used by Sylvester. The existence of different diagrams shows the richness of the graphical methods in the theory of partitions. It turns out that the bijection establishes combinatorially (xq; q 2 ) i0 q 2i2 i x i, (3) which is a special case of the Cauchy formula (aq; q) i0 q i2 a i (q; q) i (aq; q) i () under the substitutions q q 2 and a x/q. The Cauchy formula itself has a combinatorial interpretation in terms of partitions given by Frobenius notation. But our result doesn t follow from it. 2. A new description of Sylvester s bijection We first describe a mapping φ from P d into P o, establishing the identity (2). This in fact coincides with the inverse of the bijection by Sylvester described in [5], Theorem 2.2. But the diagrams involved look totally different so that a separate description is worthwhile. By allowing the last part to be a zero, we may assume that any λ P d has even length. Let λ λ λ 2... λ 2k be a partition in P d. We need to obtain the unique partition φ(λ) in P o with λ a parts. We stack λ boxes in l(λ) rows as follows (Figure ). We first arrange λ boxes horizontally to form the first row. The second row consisting of λ 2 boxes is put on the top of the first row, aligning the leftmost box with the leftmost box in the row below. The third row consisting
3 3 of λ 3 boxes is put on the top of the second row, aligning the rightmost box with the rightmost box in the row below. We repeat this process, alternating between leftmost and rightmost. Then we get a diagram of height 2k, the top row of which may contain no box. It happens if λ 2k 0. We put a vertical bar through the whole diagram, called the separator, dividing the first row into two pieces, λ a boxes to the right and λ λ a boxes to the left. Then the columns to the right of the separator may be regarded as a partition into odd parts. Let π π π 2... π λ a be the partition formed with the heights of the columns to the right of the separator. It is clear that π 2k and π λ a and any odd integer between and 2k appears in π as a part at least once. We now prepare another partition µ µ µ 2... µ 2k, where µ i is the number of boxes to the left of the separator in row i. Then µ 2i µ 2i > µ 2i+. For i, 2,..., k, add 2µ 2i ( µ 2i + µ 2i ) to the rightmost 2i in π. Let σ be the partition obtained by sorting the resulting sequence. It is clear that each part in σ is odd and l(σ) λ a. Define φ(λ) σ. An example is given in Figure Figure. λ λ a. φ(λ) Theorem The mapping φ from P d into P o is a bijection such that λ φ(λ) and λ a l(φ(λ)), establishing the identity (2). Moreover, the inverse of φ is the Sylvester bijection in [5], Section 29. Proof: The above mapping φ(λ) can be defined in terms of formulas as well. Let ρ ρ ρ 2... ρ 2k be the partition defined by ρ 2i λ 2i λ 2i + λ 2i+ + λ 2k λ 2k, for i, 2,..., k and ρ 2i ρ 2i+ for i, 2,..., k. Note that ρ 2k > 0. For each i, ρ i is the length of row i to the right of the separator. Let µ µ µ 2... µ 2k be the partition defined by µ 2i λ 2i ρ 2i and µ 2i µ 2i for i, 2,..., k. Note that µ 2k 0. For each i, µ i is the length of row i to the left of the separator. Let π π π 2... π ρ be the conjugate of ρ. Then π 2k, π ρ and each odd integer between and 2k occurs in π at least once. For each 2i, add 2µ 2i 2(λ 2i ρ 2i ) to the rightmost 2i in π. Let σ be
4 the partition obtained by sorting the resulting sequence. Then φ(λ) σ. It is clear that λ σ and λ a l(σ). The inverse of φ is defined as follows. Let σ σ σ 2... σ l be a partition into odd parts. Let k be the largest integer such that σ k 2k. Sort the integers, 3,..., 2k, σ k+, σ k+2,..., σ l to get a new partition π π π 2... π l. Then π 2k and π l. Let ρ ρ ρ 2... ρ π be the conjugate of π. Since each part in π is odd, ρ 2i ρ 2i+, for i, 2,..., k ; and since 2i, for i, 2,..., k, appears in π, we obtain ρ 2i > ρ 2i, for i, 2,..., k. Let λ λ λ 2... λ 2k be the partition such that λ 2i ρ 2i + 2 (σ 2i 2i+) and λ 2i ρ 2i + 2 (σ 2i 2i+), for i, 2,..., k. Then λ 2i > λ 2i for i, 2,..., k, since ρ 2i > ρ 2i ; λ 2i > λ 2i+ for i, 2,..., k, since σ 2i (2i ) > σ 2i+ (2i + ). Then φ (σ) λ. If we examine the description of the bijection by Sylvester in [5], Section 29, we find that it coincides with the description of the inverse of φ. The diagrams which show up in the description of φ (in Figure ) can be counted directly as well. The diagram to the left of the separator is a partition λ with 2i parts, for some i, where each part appears exactly twice and 0 is allowed as a part. The diagram to the right of the separator is a partition µ with 2i 2l(λ) parts, where each part but the largest part appears exactly twice and the largest appears exactly once. A standard technique in partition theory [] gives q i2 i q i 2x i i0 as the generating function of these pairs (λ, µ), where x traces the number of columns to the right of the separator, i.e. µ, and the index i denotes the half of the height of the diagram, i.e. 2l(λ). It agrees with the righthand side of (3). So identity (3) follows from Theorem 2., since diagrams described in Figure correspond to partitions into distinct parts. 3. Remarks We may apply the same method, aligning alternatively at the left and at the right, to the partitions in which parts are different by at least 2. We obtain q λ x λ a q i2 2i x 2i (q 2 ; q 2 ) i (xq; q 2 + qx ) i λ i0 i0 q i2 +i x 2i, where the sum is over the set of partitions λ in which parts are different by at least 2. For the partitions in which parts are different by at least 2 and the smallest part is at least 2, we obtain q λ x λ a q i2 +2i x 2i (q 2 ; q 2 ) i (xq; q 2 + q 2 x 2 ) i λ i0 i0 q i2 +6i x 2i +.
5 5 But we don t know how to directly evaluate the righthand sides of these generating functions. Acknowledgments We thank George Andrews for bringing the subject of this paper to our attention. We also thank an anonymous referee who has pointed out that our bijections are identical to those by Sylvester. References. G. E. Andrews. The theory of partitions. Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 976. Encyclopedia of Mathematics and Its Applications, Vol G. E. Andrews. J. J. Sylvester, Johns Hopkins and Partitions. In A Century of Mathematics in America, Part I, pages 2 0. American Mathematical Society, M. Bousquet-Mélou and K. Eriksson. Lecture hall partitions. The Ramanujan Journal, :0, M. Bousquet-Mélou and K. Eriksson. Lecture hall partitions II. The Ramanujan Journal, :65 85, Percy A. MacMahon. Combinatory Analysis, Volume II. Chelsea Publishing Company, New York, N.Y., 98. Originally published in two volumes at Cambridge, 98. Published at New York as two volumes in one, 98.
ON PARTITION FUNCTIONS OF ANDREWS AND STANLEY
 ON PARTITION FUNCTIONS OF ANDREWS AND STANLEY AE JA YEE Abstract. G. E. Andrews has established a refinement of the generating function for partitions π according to the numbers O(π) and O(π ) of odd parts
ON PARTITION FUNCTIONS OF ANDREWS AND STANLEY AE JA YEE Abstract. G. E. Andrews has established a refinement of the generating function for partitions π according to the numbers O(π) and O(π ) of odd parts
ON THE SLACK EULER PAIR FOR VECTOR PARTITION
 #A7 INTEGERS 18 (2018 ON THE SLACK EULER PAIR FOR VECTOR PARTITION Shishuo Fu College of Mathematics and Statistics, Chongqing University, Huxi Campus, Chongqing, P.R. China. fsshuo@cqu.edu.cn Ting Hua
#A7 INTEGERS 18 (2018 ON THE SLACK EULER PAIR FOR VECTOR PARTITION Shishuo Fu College of Mathematics and Statistics, Chongqing University, Huxi Campus, Chongqing, P.R. China. fsshuo@cqu.edu.cn Ting Hua
Partition Identities
 Partition Identities Alexander D. Healy ahealy@fas.harvard.edu May 00 Introduction A partition of a positive integer n (or a partition of weight n) is a non-decreasing sequence λ = (λ, λ,..., λ k ) of
Partition Identities Alexander D. Healy ahealy@fas.harvard.edu May 00 Introduction A partition of a positive integer n (or a partition of weight n) is a non-decreasing sequence λ = (λ, λ,..., λ k ) of
Euler s partition theorem and the combinatorics of l-sequences
 Euler s partition theorem and the combinatorics of l-sequences Carla D. Savage North Carolina State University June 26, 2008 Inspiration BME1 Mireille Bousquet-Mélou, and Kimmo Eriksson, Lecture hall partitions,
Euler s partition theorem and the combinatorics of l-sequences Carla D. Savage North Carolina State University June 26, 2008 Inspiration BME1 Mireille Bousquet-Mélou, and Kimmo Eriksson, Lecture hall partitions,
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF RAMANUJAN S 1 ψ 1 SUMMATION AND THE q-gauss SUMMATION
 COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF RAMANUJAN S 1 ψ 1 SUMMATION AND THE q-gauss SUMMATION AE JA YEE 1 Abstract. Theorems in the theory of partitions are closely related to basic hypergeometric series. Some identities
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF RAMANUJAN S 1 ψ 1 SUMMATION AND THE q-gauss SUMMATION AE JA YEE 1 Abstract. Theorems in the theory of partitions are closely related to basic hypergeometric series. Some identities
Integer Partitions: An Overview
 Integer Partitions: An Overview D Singh, PhD, A M Ibrahim, PhD, J N Singh, Ph D, S M Ladan,PhD, Abstract This paper describes fundamentals of integer partitions and basic tools for their construction and
Integer Partitions: An Overview D Singh, PhD, A M Ibrahim, PhD, J N Singh, Ph D, S M Ladan,PhD, Abstract This paper describes fundamentals of integer partitions and basic tools for their construction and
On a continued fraction formula of Wall
 c Te Ramanujan Journal,, 7 () Kluwer Academic Publisers, Boston. Manufactured in Te Neterlands. On a continued fraction formula of Wall DONGSU KIM * Department of Matematics, KAIST, Taejon 305-70, Korea
c Te Ramanujan Journal,, 7 () Kluwer Academic Publisers, Boston. Manufactured in Te Neterlands. On a continued fraction formula of Wall DONGSU KIM * Department of Matematics, KAIST, Taejon 305-70, Korea
Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for The award of the degree of. Masters of Science in Mathematics and Computing
 SOME n-color COMPOSITION Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for The award of the degree of Masters of Science in Mathematics and Computing Submitted by Shelja Ratta Roll no- 301203014
SOME n-color COMPOSITION Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for The award of the degree of Masters of Science in Mathematics and Computing Submitted by Shelja Ratta Roll no- 301203014
RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK: COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF IDENTITIES ASSOCIATED WITH HEINE S TRANSFORMATION OR PARTIAL THETA FUNCTIONS
 RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK: COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF IDENTITIES ASSOCIATED WITH HEINE S TRANSFORMATION OR PARTIAL THETA FUNCTIONS BRUCE C. BERNDT, BYUNGCHAN KIM, AND AE JA YEE 2 Abstract. Combinatorial proofs
RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK: COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF IDENTITIES ASSOCIATED WITH HEINE S TRANSFORMATION OR PARTIAL THETA FUNCTIONS BRUCE C. BERNDT, BYUNGCHAN KIM, AND AE JA YEE 2 Abstract. Combinatorial proofs
On q-series Identities Arising from Lecture Hall Partitions
 On q-series Identities Arising from Lecture Hall Partitions George E. Andrews 1 Mathematics Department, The Pennsylvania State University, University Par, PA 16802, USA andrews@math.psu.edu Sylvie Corteel
On q-series Identities Arising from Lecture Hall Partitions George E. Andrews 1 Mathematics Department, The Pennsylvania State University, University Par, PA 16802, USA andrews@math.psu.edu Sylvie Corteel
Primary classes of compositions of numbers
 Annales Mathematicae et Informaticae 41 (2013) pp. 193 204 Proceedings of the 15 th International Conference on Fibonacci Numbers and Their Applications Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Eszterházy
Annales Mathematicae et Informaticae 41 (2013) pp. 193 204 Proceedings of the 15 th International Conference on Fibonacci Numbers and Their Applications Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Eszterházy
q GAUSS SUMMATION VIA RAMANUJAN AND COMBINATORICS
 q GAUSS SUMMATION VIA RAMANUJAN AND COMBINATORICS BRUCE C. BERNDT 1 and AE JA YEE 1. Introduction Recall that the q-gauss summation theorem is given by (a; q) n (b; q) ( n c ) n (c/a; q) (c/b; q) =, (1.1)
q GAUSS SUMMATION VIA RAMANUJAN AND COMBINATORICS BRUCE C. BERNDT 1 and AE JA YEE 1. Introduction Recall that the q-gauss summation theorem is given by (a; q) n (b; q) ( n c ) n (c/a; q) (c/b; q) =, (1.1)
RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK: COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF IDENTITIES ASSOCIATED WITH HEINE S TRANSFORMATION OR PARTIAL THETA FUNCTIONS
 RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK: COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF IDENTITIES ASSOCIATED WITH HEINE S TRANSFORMATION OR PARTIAL THETA FUNCTIONS BRUCE C. BERNDT, BYUNGCHAN KIM, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Combinatorial proofs
RAMANUJAN S LOST NOTEBOOK: COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF IDENTITIES ASSOCIATED WITH HEINE S TRANSFORMATION OR PARTIAL THETA FUNCTIONS BRUCE C. BERNDT, BYUNGCHAN KIM, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Combinatorial proofs
1 Introduction 1. 5 Rooted Partitions and Euler s Theorem Vocabulary of Rooted Partitions Rooted Partition Theorems...
 Contents 1 Introduction 1 Terminology of Partitions 1.1 Simple Terms.......................................... 1. Rank and Conjugate...................................... 1.3 Young Diagrams.........................................4
Contents 1 Introduction 1 Terminology of Partitions 1.1 Simple Terms.......................................... 1. Rank and Conjugate...................................... 1.3 Young Diagrams.........................................4
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF GENERATING FUNCTION IDENTITIES FOR F-PARTITIONS
 COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF GENERATING FUNCTION IDENTITIES FOR F-PARTITIONS AE JA YEE 1 Abstract In his memoir in 1984 George E Andrews introduces many general classes of Frobenius partitions (simply F-partitions)
COMBINATORIAL PROOFS OF GENERATING FUNCTION IDENTITIES FOR F-PARTITIONS AE JA YEE 1 Abstract In his memoir in 1984 George E Andrews introduces many general classes of Frobenius partitions (simply F-partitions)
A GENERALIZATION OF THE FARKAS AND KRA PARTITION THEOREM FOR MODULUS 7
 A GENERALIZATION OF THE FARKAS AND KRA PARTITION THEOREM FOR MODULUS 7 S. OLE WARNAAR Dedicated to George Andrews on the occasion of his 65th birthday Abstract. We prove generalizations of some partition
A GENERALIZATION OF THE FARKAS AND KRA PARTITION THEOREM FOR MODULUS 7 S. OLE WARNAAR Dedicated to George Andrews on the occasion of his 65th birthday Abstract. We prove generalizations of some partition
Guo, He. November 21, 2015
 Math 702 Enumerative Combinatorics Project: Introduction to a combinatorial proof of the Rogers-Ramanujan and Schur identities and an application of Rogers-Ramanujan identity Guo, He November 2, 205 Abstract
Math 702 Enumerative Combinatorics Project: Introduction to a combinatorial proof of the Rogers-Ramanujan and Schur identities and an application of Rogers-Ramanujan identity Guo, He November 2, 205 Abstract
Sequences that satisfy a(n a(n)) = 0
 Sequences that satisfy a(n a(n)) = 0 Nate Kube Frank Ruskey October 13, 2005 Abstract We explore the properties of some sequences for which a(n a(n)) = 0. Under the natural restriction that a(n) < n the
Sequences that satisfy a(n a(n)) = 0 Nate Kube Frank Ruskey October 13, 2005 Abstract We explore the properties of some sequences for which a(n a(n)) = 0. Under the natural restriction that a(n) < n the
PARTITION IDENTITIES INVOLVING GAPS AND WEIGHTS
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 349, Number 12, December 1997, Pages 5001 5019 S 0002-9947(97)01831-X PARTITION IDENTITIES INVOLVING GAPS AND WEIGHTS KRISHNASWAMI ALLADI Abstract.
TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 349, Number 12, December 1997, Pages 5001 5019 S 0002-9947(97)01831-X PARTITION IDENTITIES INVOLVING GAPS AND WEIGHTS KRISHNASWAMI ALLADI Abstract.
Research Article New Partition Theoretic Interpretations of Rogers-Ramanujan Identities
 International Combinatorics Volume 2012, Article ID 409505, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/409505 Research Article New Partition Theoretic Interpretations of Rogers-Ramanujan Identities A. K. Agarwal and M.
International Combinatorics Volume 2012, Article ID 409505, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/409505 Research Article New Partition Theoretic Interpretations of Rogers-Ramanujan Identities A. K. Agarwal and M.
arxiv:math/ v2 [math.co] 19 Sep 2005
![arxiv:math/ v2 [math.co] 19 Sep 2005 arxiv:math/ v2 [math.co] 19 Sep 2005](/thumbs/75/72213461.jpg) A COMBINATORIAL PROOF OF THE ROGERS-RAMANUJAN AND SCHUR IDENTITIES arxiv:math/04072v2 [math.co] 9 Sep 2005 CILANNE BOULET AND IGOR PAK Abstract. We give a combinatorial proof of the first Rogers-Ramanujan
A COMBINATORIAL PROOF OF THE ROGERS-RAMANUJAN AND SCHUR IDENTITIES arxiv:math/04072v2 [math.co] 9 Sep 2005 CILANNE BOULET AND IGOR PAK Abstract. We give a combinatorial proof of the first Rogers-Ramanujan
Integer Partitions With Even Parts Below Odd Parts and the Mock Theta Functions
 Integer Partitions With Even Parts Below Odd Parts and the Mock Theta Functions by George E. Andrews Key Words: Partitions, mock theta functions, crank AMS Classification Numbers: P84, P83, P8, 33D5 Abstract
Integer Partitions With Even Parts Below Odd Parts and the Mock Theta Functions by George E. Andrews Key Words: Partitions, mock theta functions, crank AMS Classification Numbers: P84, P83, P8, 33D5 Abstract
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Dec 2018](/thumbs/92/110511179.jpg) ANDREWS-GORDON TYPE SERIES FOR SCHUR S PARTITION IDENTITY KAĞAN KURŞUNGÖZ arxiv:1812.10039v1 [math.co] 25 Dec 2018 Abstract. We construct an evidently positive multiple series as a generating function
ANDREWS-GORDON TYPE SERIES FOR SCHUR S PARTITION IDENTITY KAĞAN KURŞUNGÖZ arxiv:1812.10039v1 [math.co] 25 Dec 2018 Abstract. We construct an evidently positive multiple series as a generating function
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ω(q) AND ν(q)
 CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit and Yee introduced partition
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit and Yee introduced partition
The part-frequency matrices of a partition
 The part-frequency matrices of a partition William J. Keith, Michigan Tech Michigan Technological University Kliakhandler Conference 2015 August 28, 2015 A partition of an integer n is a sequence λ = (λ
The part-frequency matrices of a partition William J. Keith, Michigan Tech Michigan Technological University Kliakhandler Conference 2015 August 28, 2015 A partition of an integer n is a sequence λ = (λ
RECURRENCE RELATION FOR COMPUTING A BIPARTITION FUNCTION
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 48, Number, 08 RECURRENCE RELATION FOR COMPUTING A BIPARTITION FUNCTION D.S. GIREESH AND M.S. MAHADEVA NAIKA ABSTRACT. Recently, Merca [4] found the recurrence
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 48, Number, 08 RECURRENCE RELATION FOR COMPUTING A BIPARTITION FUNCTION D.S. GIREESH AND M.S. MAHADEVA NAIKA ABSTRACT. Recently, Merca [4] found the recurrence
An Involution for the Gauss Identity
 An Involution for the Gauss Identity William Y. C. Chen Center for Combinatorics Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P. R. China Email: chenstation@yahoo.com Qing-Hu Hou Center for Combinatorics Nankai
An Involution for the Gauss Identity William Y. C. Chen Center for Combinatorics Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, P. R. China Email: chenstation@yahoo.com Qing-Hu Hou Center for Combinatorics Nankai
OVERPARTITIONS AND GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR GENERALIZED FROBENIUS PARTITIONS
 OVERPARTITIONS AND GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR GENERALIZED FROBENIUS PARTITIONS SYLVIE CORTEEL JEREMY LOVEJOY AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Generalized Frobenius partitions or F -partitions have recently played
OVERPARTITIONS AND GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR GENERALIZED FROBENIUS PARTITIONS SYLVIE CORTEEL JEREMY LOVEJOY AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Generalized Frobenius partitions or F -partitions have recently played
CAYLEY COMPOSITIONS, PARTITIONS, POLYTOPES, AND GEOMETRIC BIJECTIONS
 CAYLEY COMPOSITIONS, PARTITIONS, POLYTOPES, AND GEOMETRIC BIJECTIONS MATJAŽ KONVALINKA AND IGOR PAK Abstract. In 1857, Cayley showed that certain sequences, now called Cayley compositions, are equinumerous
CAYLEY COMPOSITIONS, PARTITIONS, POLYTOPES, AND GEOMETRIC BIJECTIONS MATJAŽ KONVALINKA AND IGOR PAK Abstract. In 1857, Cayley showed that certain sequences, now called Cayley compositions, are equinumerous
CONGRUENCES FOR GENERALIZED FROBENIUS PARTITIONS WITH AN ARBITRARILY LARGE NUMBER OF COLORS
 #A7 INTEGERS 14 (2014) CONGRUENCES FOR GENERALIZED FROBENIUS PARTITIONS WITH AN ARBITRARILY LARGE NUMBER OF COLORS Frank G. Garvan Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida
#A7 INTEGERS 14 (2014) CONGRUENCES FOR GENERALIZED FROBENIUS PARTITIONS WITH AN ARBITRARILY LARGE NUMBER OF COLORS Frank G. Garvan Department of Mathematics, University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida
Bilateral truncated Jacobi s identity
 Bilateral truncated Jacobi s identity Thomas Y He, Kathy Q Ji and Wenston JT Zang 3,3 Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 30007, PR China Center for Applied Mathematics Tianjin
Bilateral truncated Jacobi s identity Thomas Y He, Kathy Q Ji and Wenston JT Zang 3,3 Center for Combinatorics, LPMC-TJKLC Nankai University, Tianjin 30007, PR China Center for Applied Mathematics Tianjin
COMBINATORICS OF RAMANUJAN-SLATER TYPE IDENTITIES. James McLaughlin Department of Mathematics, West Chester University, West Chester, PA 19383, USA
 COMBINATORICS OF RAMANUJAN-SLATER TYPE IDENTITIES James McLaughlin Department of Mathematics, West Chester University, West Chester, PA 9383, USA jmclaughl@wcupa.edu Andrew V. Sills Department of Mathematical
COMBINATORICS OF RAMANUJAN-SLATER TYPE IDENTITIES James McLaughlin Department of Mathematics, West Chester University, West Chester, PA 9383, USA jmclaughl@wcupa.edu Andrew V. Sills Department of Mathematical
On an identity of Gessel and Stanton and the new little Göllnitz identities
 On an identity of Gessel and Stanton and the new little Göllnitz identities Carla D. Savage Dept. of Computer Science N. C. State University, Box 8206 Raleigh, NC 27695, USA savage@csc.ncsu.edu Andrew
On an identity of Gessel and Stanton and the new little Göllnitz identities Carla D. Savage Dept. of Computer Science N. C. State University, Box 8206 Raleigh, NC 27695, USA savage@csc.ncsu.edu Andrew
Chapter 5: Integer Compositions and Partitions and Set Partitions
 Chapter 5: Integer Compositions and Partitions and Set Partitions Prof. Tesler Math 184A Winter 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 5: Compositions and Partitions Math 184A / Winter 2017 1 / 32 5.1. Compositions A strict
Chapter 5: Integer Compositions and Partitions and Set Partitions Prof. Tesler Math 184A Winter 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 5: Compositions and Partitions Math 184A / Winter 2017 1 / 32 5.1. Compositions A strict
An Algebraic Identity of F.H. Jackson and its Implications for Partitions.
 An Algebraic Identity of F.H. Jackson and its Implications for Partitions. George E. Andrews ( and Richard Lewis (2 ( Department of Mathematics, 28 McAllister Building, Pennsylvania State University, Pennsylvania
An Algebraic Identity of F.H. Jackson and its Implications for Partitions. George E. Andrews ( and Richard Lewis (2 ( Department of Mathematics, 28 McAllister Building, Pennsylvania State University, Pennsylvania
Simple alternative to the Hardy-Ramanujan-Rademacher formula for p(n)
 Simple alternative to the Hardy-Ramanujan-Rademacher formula for p(n) N Chase hd School of Arts and Sciences assachusetts College of harmacy and Health Sciences 79 Longwood Avenue Boston A 05 USA nchase@mcpedu
Simple alternative to the Hardy-Ramanujan-Rademacher formula for p(n) N Chase hd School of Arts and Sciences assachusetts College of harmacy and Health Sciences 79 Longwood Avenue Boston A 05 USA nchase@mcpedu
Singular Overpartitions
 Singular Overpartitions George E. Andrews Dedicated to the memory of Paul Bateman and Heini Halberstam. Abstract The object in this paper is to present a general theorem for overpartitions analogous to
Singular Overpartitions George E. Andrews Dedicated to the memory of Paul Bateman and Heini Halberstam. Abstract The object in this paper is to present a general theorem for overpartitions analogous to
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ω(q) AND ν(q)
 CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit, and Yee introduced partition
CONGRUENCES RELATED TO THE RAMANUJAN/WATSON MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) GEORGE E. ANDREWS, DONNY PASSARY, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND AE JA YEE Abstract. Recently, Andrews, Dixit, and Yee introduced partition
The Bhargava-Adiga Summation and Partitions
 The Bhargava-Adiga Summation and Partitions By George E. Andrews September 12, 2016 Abstract The Bhargava-Adiga summation rivals the 1 ψ 1 summation of Ramanujan in elegance. This paper is devoted to two
The Bhargava-Adiga Summation and Partitions By George E. Andrews September 12, 2016 Abstract The Bhargava-Adiga summation rivals the 1 ψ 1 summation of Ramanujan in elegance. This paper is devoted to two
Some Restricted Plane partitions and Associated Lattice Paths S. Bedi Department of Mathematics, D.A.V College, Sector 10 Chandigarh , India
 Some Restricted Plane partitions and Associated Lattice Paths S. Bedi Department of Mathematics, D.A.V College, Sector 10 Chandigarh - 160010, India Abstract. Anand and Agarwal, (Proc. Indian Acad. Sci.
Some Restricted Plane partitions and Associated Lattice Paths S. Bedi Department of Mathematics, D.A.V College, Sector 10 Chandigarh - 160010, India Abstract. Anand and Agarwal, (Proc. Indian Acad. Sci.
Chapter 5: Integer Compositions and Partitions and Set Partitions
 Chapter 5: Integer Compositions and Partitions and Set Partitions Prof. Tesler Math 184A Fall 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 5: Compositions and Partitions Math 184A / Fall 2017 1 / 46 5.1. Compositions A strict
Chapter 5: Integer Compositions and Partitions and Set Partitions Prof. Tesler Math 184A Fall 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 5: Compositions and Partitions Math 184A / Fall 2017 1 / 46 5.1. Compositions A strict
A Generalization of the Euler-Glaisher Bijection
 A Generalization of the Euler-Glaisher Bijection p.1/48 A Generalization of the Euler-Glaisher Bijection Andrew Sills Georgia Southern University A Generalization of the Euler-Glaisher Bijection p.2/48
A Generalization of the Euler-Glaisher Bijection p.1/48 A Generalization of the Euler-Glaisher Bijection Andrew Sills Georgia Southern University A Generalization of the Euler-Glaisher Bijection p.2/48
EXACT ENUMERATION OF GARDEN OF EDEN PARTITIONS. Brian Hopkins Department of Mathematics and Physics, Saint Peter s College, Jersey City, NJ 07306, USA
 EXACT ENUMERATION OF GARDEN OF EDEN PARTITIONS Brian Hopkins Department of Mathematics and Physics, Saint Peter s College, Jersey City, NJ 07306, USA bhopkins@spc.edu James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics,
EXACT ENUMERATION OF GARDEN OF EDEN PARTITIONS Brian Hopkins Department of Mathematics and Physics, Saint Peter s College, Jersey City, NJ 07306, USA bhopkins@spc.edu James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics,
On the Ordinary and Signed Göllnitz-Gordon Partitions
 On the Ordinary and Signed Göllnitz-Gordon Partitions Andrew V. Sills Department of Mathematical Sciences Georgia Southern University Statesboro, Georgia, USA asills@georgiasouthern.edu Version of October
On the Ordinary and Signed Göllnitz-Gordon Partitions Andrew V. Sills Department of Mathematical Sciences Georgia Southern University Statesboro, Georgia, USA asills@georgiasouthern.edu Version of October
Bijective Proofs with Spotted Tilings
 Brian Hopkins, Saint Peter s University, New Jersey, USA Visiting Scholar, Mahidol University International College Editor, The College Mathematics Journal MUIC Mathematics Seminar 2 November 2016 outline
Brian Hopkins, Saint Peter s University, New Jersey, USA Visiting Scholar, Mahidol University International College Editor, The College Mathematics Journal MUIC Mathematics Seminar 2 November 2016 outline
Arithmetic Relations for Overpartitions
 Arithmetic Relations for Overpartitions Michael D. Hirschhorn School of Mathematics, UNSW, Sydney 2052, Australia m.hirschhorn@unsw.edu.au James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State
Arithmetic Relations for Overpartitions Michael D. Hirschhorn School of Mathematics, UNSW, Sydney 2052, Australia m.hirschhorn@unsw.edu.au James A. Sellers Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State
Some families of identities for the integer partition function
 MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 193 Math. Commun. 0(015), 193 00 Some families of identities for the integer partition function Ivica Martinja 1, and Dragutin Svrtan 1 Department of Physics, University of
MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 193 Math. Commun. 0(015), 193 00 Some families of identities for the integer partition function Ivica Martinja 1, and Dragutin Svrtan 1 Department of Physics, University of
THE MAJOR COUNTING OF NONINTERSECTING LATTICE PATHS AND GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR TABLEAUX Summary
 THE MAJOR COUNTING OF NONINTERSECTING LATTICE PATHS AND GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR TABLEAUX Summary (The full-length article will appear in Mem. Amer. Math. Soc.) C. Krattenthaler Institut für Mathematik
THE MAJOR COUNTING OF NONINTERSECTING LATTICE PATHS AND GENERATING FUNCTIONS FOR TABLEAUX Summary (The full-length article will appear in Mem. Amer. Math. Soc.) C. Krattenthaler Institut für Mathematik
Some congruences for Andrews Paule s broken 2-diamond partitions
 Discrete Mathematics 308 (2008) 5735 5741 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Some congruences for Andrews Paule s broken 2-diamond partitions Song Heng Chan Division of Mathematical Sciences, School of Physical
Discrete Mathematics 308 (2008) 5735 5741 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Some congruences for Andrews Paule s broken 2-diamond partitions Song Heng Chan Division of Mathematical Sciences, School of Physical
A Fine Dream. George E. Andrews (1) January 16, 2006
 A Fine Dream George E. Andrews () January 6, 2006 Abstract We shall develop further N. J. Fine s theory of three parameter non-homogeneous first order q-difference equations. The obect of our work is to
A Fine Dream George E. Andrews () January 6, 2006 Abstract We shall develop further N. J. Fine s theory of three parameter non-homogeneous first order q-difference equations. The obect of our work is to
RCC. Drew Armstrong. FPSAC 2017, Queen Mary, London. University of Miami armstrong
 RCC Drew Armstrong University of Miami www.math.miami.edu/ armstrong FPSAC 2017, Queen Mary, London Outline of the Talk 1. The Frobenius Coin Problem 2. Rational Dyck Paths 3. Core Partitions 4. The Double
RCC Drew Armstrong University of Miami www.math.miami.edu/ armstrong FPSAC 2017, Queen Mary, London Outline of the Talk 1. The Frobenius Coin Problem 2. Rational Dyck Paths 3. Core Partitions 4. The Double
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 25 Nov 2018](/thumbs/91/104922308.jpg) The Unimodality of the Crank on Overpartitions Wenston J.T. Zang and Helen W.J. Zhang 2 arxiv:8.003v [math.co] 25 Nov 208 Institute of Advanced Study of Mathematics Harbin Institute of Technology, Heilongjiang
The Unimodality of the Crank on Overpartitions Wenston J.T. Zang and Helen W.J. Zhang 2 arxiv:8.003v [math.co] 25 Nov 208 Institute of Advanced Study of Mathematics Harbin Institute of Technology, Heilongjiang
= (q) M+N (q) M (q) N
 A OVERPARTITIO AALOGUE OF THE -BIOMIAL COEFFICIETS JEHAE DOUSSE AD BYUGCHA KIM Abstract We define an overpartition analogue of Gaussian polynomials (also known as -binomial coefficients) as a generating
A OVERPARTITIO AALOGUE OF THE -BIOMIAL COEFFICIETS JEHAE DOUSSE AD BYUGCHA KIM Abstract We define an overpartition analogue of Gaussian polynomials (also known as -binomial coefficients) as a generating
ON CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF CONSECUTIVE VALUES OF P(N, M) Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, University at Albany, Albany, New York, 12222
 INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (007), #A16 ON CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF CONSECUTIVE VALUES OF P(N, M) Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, University at Albany, Albany,
INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (007), #A16 ON CONGRUENCE PROPERTIES OF CONSECUTIVE VALUES OF P(N, M) Brandt Kronholm Department of Mathematics, University at Albany, Albany,
Dept. of Computer Science. Raleigh, NC 27695, USA. May 14, Abstract. 1, u 2 q i+1 :
 Anti-Leture Hall Compositions Sylvie Corteel CNRS PRiSM, UVSQ 45 Avenue des Etats-Unis 78035 Versailles, Frane syl@prism.uvsq.fr Carla D. Savage Dept. of Computer Siene N. C. State University, Box 8206
Anti-Leture Hall Compositions Sylvie Corteel CNRS PRiSM, UVSQ 45 Avenue des Etats-Unis 78035 Versailles, Frane syl@prism.uvsq.fr Carla D. Savage Dept. of Computer Siene N. C. State University, Box 8206
Improved Bounds on the Anti-Waring Number
 1 3 47 6 3 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 0 (017, Article 17.8.7 Improved Bounds on the Anti-Waring Number Paul LeVan and David Prier Department of Mathematics Gannon University Erie, PA 16541-0001
1 3 47 6 3 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 0 (017, Article 17.8.7 Improved Bounds on the Anti-Waring Number Paul LeVan and David Prier Department of Mathematics Gannon University Erie, PA 16541-0001
arxiv:quant-ph/ v1 22 Aug 2005
 Conditions for separability in generalized Laplacian matrices and nonnegative matrices as density matrices arxiv:quant-ph/58163v1 22 Aug 25 Abstract Chai Wah Wu IBM Research Division, Thomas J. Watson
Conditions for separability in generalized Laplacian matrices and nonnegative matrices as density matrices arxiv:quant-ph/58163v1 22 Aug 25 Abstract Chai Wah Wu IBM Research Division, Thomas J. Watson
THE BAILEY TRANSFORM AND FALSE THETA FUNCTIONS
 THE BAILEY TRANSFORM AND FALSE THETA FUNCTIONS GEORGE E ANDREWS 1 AND S OLE WARNAAR 2 Abstract An empirical exploration of five of Ramanujan s intriguing false theta function identities leads to unexpected
THE BAILEY TRANSFORM AND FALSE THETA FUNCTIONS GEORGE E ANDREWS 1 AND S OLE WARNAAR 2 Abstract An empirical exploration of five of Ramanujan s intriguing false theta function identities leads to unexpected
PLACE-DIFFERENCE-VALUE PATTERNS: A GENERALIZATION OF GENERALIZED PERMUTATION AND WORD PATTERNS
 #A INTEGERS 0 (200), 29-54 PLACE-DIFFERENCE-VALUE PATTERNS: A GENERALIZATION OF GENERALIZED PERMUTATION AND WORD PATTERNS Sergey Kitaev The Mathematics Institute, School of Computer Science, Reykjavík
#A INTEGERS 0 (200), 29-54 PLACE-DIFFERENCE-VALUE PATTERNS: A GENERALIZATION OF GENERALIZED PERMUTATION AND WORD PATTERNS Sergey Kitaev The Mathematics Institute, School of Computer Science, Reykjavík
Integer Sequences Related to Compositions without 2 s
 1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 6 (2003), Article 03.2.3 Integer Sequences Related to Compositions without 2 s Phyllis Chinn Department of Mathematics Humboldt State University Arcata,
1 2 3 47 6 23 11 Journal of Integer Sequences, Vol. 6 (2003), Article 03.2.3 Integer Sequences Related to Compositions without 2 s Phyllis Chinn Department of Mathematics Humboldt State University Arcata,
arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 2 Aug 2017
![arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 2 Aug 2017 arxiv: v2 [math.nt] 2 Aug 2017](/thumbs/89/98386700.jpg) TRAPEZOIDAL NUMBERS, DIVISOR FUNCTIONS, AND A PARTITION THEOREM OF SYLVESTER arxiv:1601.07058v [math.nt] Aug 017 MELVYN B. NATHANSON To Krishnaswami Alladi on his 60th birthday Abstract. A partition of
TRAPEZOIDAL NUMBERS, DIVISOR FUNCTIONS, AND A PARTITION THEOREM OF SYLVESTER arxiv:1601.07058v [math.nt] Aug 017 MELVYN B. NATHANSON To Krishnaswami Alladi on his 60th birthday Abstract. A partition of
Nearly Equal Distributions of the Rank and the Crank of Partitions
 Nearly Equal Distributions of the Rank and the Crank of Partitions William Y.C. Chen, Kathy Q. Ji and Wenston J.T. Zang Dedicated to Professor Krishna Alladi on the occasion of his sixtieth birthday Abstract
Nearly Equal Distributions of the Rank and the Crank of Partitions William Y.C. Chen, Kathy Q. Ji and Wenston J.T. Zang Dedicated to Professor Krishna Alladi on the occasion of his sixtieth birthday Abstract
LARGE SCHRÖDER PATHS BY TYPES AND SYMMETRIC FUNCTIONS
 Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 51 (2014), No. 4, pp. 1229 1240 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2014.51.4.1229 LARGE SCHRÖDER PATHS BY TYPES AND SYMMETRIC FUNCTIONS Su Hyung An, Sen-Peng Eu, and Sangwook Kim Abstract.
Bull. Korean Math. Soc. 51 (2014), No. 4, pp. 1229 1240 http://dx.doi.org/10.4134/bkms.2014.51.4.1229 LARGE SCHRÖDER PATHS BY TYPES AND SYMMETRIC FUNCTIONS Su Hyung An, Sen-Peng Eu, and Sangwook Kim Abstract.
Enumerating multiplex juggling patterns
 Enumerating multiplex juggling patterns Steve Butler Jeongyoon Choi Kimyung Kim Kyuhyeok Seo Abstract Mathematics has been used in the exploration and enumeration of juggling patterns. In the case when
Enumerating multiplex juggling patterns Steve Butler Jeongyoon Choi Kimyung Kim Kyuhyeok Seo Abstract Mathematics has been used in the exploration and enumeration of juggling patterns. In the case when
Colored Partitions and the Fibonacci Sequence
 TEMA Tend. Mat. Apl. Comput., 7, No. 1 (006), 119-16. c Uma Publicação da Sociedade Brasileira de Matemática Aplicada e Computacional. Colored Partitions and the Fibonacci Sequence J.P.O. SANTOS 1, M.
TEMA Tend. Mat. Apl. Comput., 7, No. 1 (006), 119-16. c Uma Publicação da Sociedade Brasileira de Matemática Aplicada e Computacional. Colored Partitions and the Fibonacci Sequence J.P.O. SANTOS 1, M.
On a certain vector crank modulo 7
 On a certain vector crank modulo 7 Michael D Hirschhorn School of Mathematics and Statistics University of New South Wales Sydney, NSW, 2052, Australia mhirschhorn@unsweduau Pee Choon Toh Mathematics &
On a certain vector crank modulo 7 Michael D Hirschhorn School of Mathematics and Statistics University of New South Wales Sydney, NSW, 2052, Australia mhirschhorn@unsweduau Pee Choon Toh Mathematics &
On divisibility of Narayana numbers by primes
 On divisibility of Narayana numbers by primes Miklós Bóna Department of Mathematics, University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611, USA, bona@math.ufl.edu and Bruce E. Sagan Department of Mathematics, Michigan
On divisibility of Narayana numbers by primes Miklós Bóna Department of Mathematics, University of Florida Gainesville, FL 32611, USA, bona@math.ufl.edu and Bruce E. Sagan Department of Mathematics, Michigan
ON RECENT CONGRUENCE RESULTS OF ANDREWS AND PAULE FOR BROKEN ifc-diamonds
 BULL. AUSTRAL. MATH. SOC. VOL. 75 (2007) [121-126] 05A17, 11P83 ON RECENT CONGRUENCE RESULTS OF ANDREWS AND PAULE FOR BROKEN ifc-diamonds MICHAEL D. HIRSCHHORN AND JAMES A. SELLERS In one of their most
BULL. AUSTRAL. MATH. SOC. VOL. 75 (2007) [121-126] 05A17, 11P83 ON RECENT CONGRUENCE RESULTS OF ANDREWS AND PAULE FOR BROKEN ifc-diamonds MICHAEL D. HIRSCHHORN AND JAMES A. SELLERS In one of their most
Some Review Problems for Exam 3: Solutions
 Math 3355 Fall 018 Some Review Problems for Exam 3: Solutions I thought I d start by reviewing some counting formulas. Counting the Complement: Given a set U (the universe for the problem), if you want
Math 3355 Fall 018 Some Review Problems for Exam 3: Solutions I thought I d start by reviewing some counting formulas. Counting the Complement: Given a set U (the universe for the problem), if you want
Transitive cycle factorizations and prime parking functions
 Transitive cycle factorizations and prime parking functions Dongsu Kim Department of Mathematics KAIST, Daejeon 0-0, Korea dskim@math.kaist.ac.kr and Seunghyun Seo Department of Mathematics KAIST, Daejeon
Transitive cycle factorizations and prime parking functions Dongsu Kim Department of Mathematics KAIST, Daejeon 0-0, Korea dskim@math.kaist.ac.kr and Seunghyun Seo Department of Mathematics KAIST, Daejeon
Self-dual interval orders and row-fishburn matrices
 Self-dual interval orders and row-fishburn matrices Sherry H. F. Yan Department of Mathematics Zhejiang Normal University Jinhua 321004, P.R. China huifangyan@hotmail.com Yuexiao Xu Department of Mathematics
Self-dual interval orders and row-fishburn matrices Sherry H. F. Yan Department of Mathematics Zhejiang Normal University Jinhua 321004, P.R. China huifangyan@hotmail.com Yuexiao Xu Department of Mathematics
Packing Ferrers Shapes
 Packing Ferrers Shapes Noga Alon Miklós Bóna Joel Spencer February 22, 2002 Abstract Answering a question of Wilf, we show that if n is sufficiently large, then one cannot cover an n p(n) rectangle using
Packing Ferrers Shapes Noga Alon Miklós Bóna Joel Spencer February 22, 2002 Abstract Answering a question of Wilf, we show that if n is sufficiently large, then one cannot cover an n p(n) rectangle using
On the Sylvester Denumerants for General Restricted Partitions
 On the Sylvester Denumerants for General Restricted Partitions Geir Agnarsson Abstract Let n be a nonnegative integer and let ã = (a 1... a k be a k-tuple of positive integers. The term denumerant introduced
On the Sylvester Denumerants for General Restricted Partitions Geir Agnarsson Abstract Let n be a nonnegative integer and let ã = (a 1... a k be a k-tuple of positive integers. The term denumerant introduced
A Nekrasov-Okounkov type formula for affine C
 A Nekrasov-Okounkov type formula for affine C Mathias Pétréolle To cite this version: Mathias Pétréolle. A Nekrasov-Okounkov type formula for affine C. James Haglund; Jiang Zeng. 7th International Conference
A Nekrasov-Okounkov type formula for affine C Mathias Pétréolle To cite this version: Mathias Pétréolle. A Nekrasov-Okounkov type formula for affine C. James Haglund; Jiang Zeng. 7th International Conference
THE LECTURE HALL PARALLELEPIPED
 THE LECTURE HALL PARALLELEPIPED FU LIU AND RICHARD P. STANLEY Abstract. The s-lecture hall polytopes P s are a class of integer polytopes defined by Savage and Schuster which are closely related to the
THE LECTURE HALL PARALLELEPIPED FU LIU AND RICHARD P. STANLEY Abstract. The s-lecture hall polytopes P s are a class of integer polytopes defined by Savage and Schuster which are closely related to the
Chapter 7 Polynomial Functions. Factoring Review. We will talk about 3 Types: ALWAYS FACTOR OUT FIRST! Ex 2: Factor x x + 64
 Chapter 7 Polynomial Functions Factoring Review We will talk about 3 Types: 1. 2. 3. ALWAYS FACTOR OUT FIRST! Ex 1: Factor x 2 + 5x + 6 Ex 2: Factor x 2 + 16x + 64 Ex 3: Factor 4x 2 + 6x 18 Ex 4: Factor
Chapter 7 Polynomial Functions Factoring Review We will talk about 3 Types: 1. 2. 3. ALWAYS FACTOR OUT FIRST! Ex 1: Factor x 2 + 5x + 6 Ex 2: Factor x 2 + 16x + 64 Ex 3: Factor 4x 2 + 6x 18 Ex 4: Factor
m=1 . ( bzq; q2 ) k (zq 2 ; q 2 ) k . (1 + bzq4k 1 ) (1 + bzq 2k 1 ). Here and in what follows, we have made use of the standard notation (a) n = j=0
 PARTITIONS WITH NON-REPEATING ODD PARTS AND COMBINATORIAL IDENTITIES Krishnaswami Alladi* Abstract: Continuing our earlier work on partitions with non-repeating odd parts and q-hypergeometric identities,
PARTITIONS WITH NON-REPEATING ODD PARTS AND COMBINATORIAL IDENTITIES Krishnaswami Alladi* Abstract: Continuing our earlier work on partitions with non-repeating odd parts and q-hypergeometric identities,
Generating Functions of Partitions
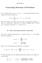 CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
CHAPTER B Generating Functions of Partitions For a complex sequence {α n n 0,, 2, }, its generating function with a complex variable q is defined by A(q) : α n q n α n [q n ] A(q). When the sequence has
A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES
 A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES MATTHEW S. MIZUHARA, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND HOLLY SWISHER Abstract. Ramanujan s celebrated congruences of the partition function p(n have inspired a vast
A PERIODIC APPROACH TO PLANE PARTITION CONGRUENCES MATTHEW S. MIZUHARA, JAMES A. SELLERS, AND HOLLY SWISHER Abstract. Ramanujan s celebrated congruences of the partition function p(n have inspired a vast
Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences
 C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 24, 343 348, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences JEONG-HEON KIM School of Electrical and
C Designs, Codes and Cryptography, 24, 343 348, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Trace Representation of Legendre Sequences JEONG-HEON KIM School of Electrical and
Elementary divisors of Cartan matrices for symmetric groups
 Elementary divisors of Cartan matrices for symmetric groups By Katsuhiro UNO and Hiro-Fumi YAMADA Abstract In this paper, we give an easy description of the elementary divisors of the Cartan matrices for
Elementary divisors of Cartan matrices for symmetric groups By Katsuhiro UNO and Hiro-Fumi YAMADA Abstract In this paper, we give an easy description of the elementary divisors of the Cartan matrices for
Postorder Preimages. arxiv: v3 [math.co] 2 Feb Colin Defant 1. 1 Introduction
![Postorder Preimages. arxiv: v3 [math.co] 2 Feb Colin Defant 1. 1 Introduction Postorder Preimages. arxiv: v3 [math.co] 2 Feb Colin Defant 1. 1 Introduction](/thumbs/72/66900964.jpg) Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science DMTCS vol. 19:1, 2017, #3 Postorder Preimages arxiv:1604.01723v3 [math.co] 2 Feb 2017 1 University of Florida Colin Defant 1 received 7 th Apr. 2016,
Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science DMTCS vol. 19:1, 2017, #3 Postorder Preimages arxiv:1604.01723v3 [math.co] 2 Feb 2017 1 University of Florida Colin Defant 1 received 7 th Apr. 2016,
arxiv: v2 [math.co] 3 May 2016
![arxiv: v2 [math.co] 3 May 2016 arxiv: v2 [math.co] 3 May 2016](/thumbs/72/67434297.jpg) VARIATION ON A THEME OF NATHAN FINE NEW WEIGHTED PARTITION IDENTITIES arxiv:16050091v [mathco] 3 May 016 ALEXANDER BERKOVICH AND ALI KEMAL UNCU Dedicated to our friend Krishna Alladi on his 60th birthday
VARIATION ON A THEME OF NATHAN FINE NEW WEIGHTED PARTITION IDENTITIES arxiv:16050091v [mathco] 3 May 016 ALEXANDER BERKOVICH AND ALI KEMAL UNCU Dedicated to our friend Krishna Alladi on his 60th birthday
Two truncated identities of Gauss
 Two truncated identities of Gauss Victor J W Guo 1 and Jiang Zeng 2 1 Department of Mathematics, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, People s Republic of China jwguo@mathecnueducn, http://mathecnueducn/~jwguo
Two truncated identities of Gauss Victor J W Guo 1 and Jiang Zeng 2 1 Department of Mathematics, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, People s Republic of China jwguo@mathecnueducn, http://mathecnueducn/~jwguo
Combinatorial Structures
 Combinatorial Structures Contents 1 Permutations 1 Partitions.1 Ferrers diagrams....................................... Skew diagrams........................................ Dominance order......................................
Combinatorial Structures Contents 1 Permutations 1 Partitions.1 Ferrers diagrams....................................... Skew diagrams........................................ Dominance order......................................
CS 468: Computational Topology Group Theory Fall b c b a b a c b a c b c c b a
 Q: What s purple and commutes? A: An abelian grape! Anonymous Group Theory Last lecture, we learned about a combinatorial method for characterizing spaces: using simplicial complexes as triangulations
Q: What s purple and commutes? A: An abelian grape! Anonymous Group Theory Last lecture, we learned about a combinatorial method for characterizing spaces: using simplicial complexes as triangulations
MacMahon s Partition Analysis V: Bijections, Recursions, and Magic Squares
 MacMahon s Partition Analysis V: Bijections, Recursions, and Magic Squares George E. Andrews, Peter Paule 2, Axel Riese 3, and Volker Strehl 4 Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State University
MacMahon s Partition Analysis V: Bijections, Recursions, and Magic Squares George E. Andrews, Peter Paule 2, Axel Riese 3, and Volker Strehl 4 Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State University
are the q-versions of n, n! and . The falling factorial is (x) k = x(x 1)(x 2)... (x k + 1).
 Lecture A jacques@ucsd.edu Notation: N, R, Z, F, C naturals, reals, integers, a field, complex numbers. p(n), S n,, b(n), s n, partition numbers, Stirling of the second ind, Bell numbers, Stirling of the
Lecture A jacques@ucsd.edu Notation: N, R, Z, F, C naturals, reals, integers, a field, complex numbers. p(n), S n,, b(n), s n, partition numbers, Stirling of the second ind, Bell numbers, Stirling of the
On p-blocks of symmetric and alternating groups with all irreducible Brauer characters of prime power degree. Christine Bessenrodt
 On p-blocks of symmetric and alternating groups with all irreducible Brauer characters of prime power degree Christine Bessenrodt Institut für Algebra, Zahlentheorie und Diskrete Mathematik Leibniz Universität
On p-blocks of symmetric and alternating groups with all irreducible Brauer characters of prime power degree Christine Bessenrodt Institut für Algebra, Zahlentheorie und Diskrete Mathematik Leibniz Universität
The part-frequency matrices of a partition
 J. Algebra Comb. Discrete Appl. 3(3) 77 86 Received: 03 November 20 Accepted: 04 January 206 Journal of Algebra Combinatorics Discrete Structures and Applications The part-frequency matrices of a partition
J. Algebra Comb. Discrete Appl. 3(3) 77 86 Received: 03 November 20 Accepted: 04 January 206 Journal of Algebra Combinatorics Discrete Structures and Applications The part-frequency matrices of a partition
LaCIM seminar, UQÀM. March 15, 2013
 (Valparaiso University) LaCIM seminar, UQÀM Montréal, Québec March 15, 2013 Conventions and Definitions s are written in one-line notation. e.g. S 3 = {123, 132, 213, 231, 312, 321} Conventions and Definitions
(Valparaiso University) LaCIM seminar, UQÀM Montréal, Québec March 15, 2013 Conventions and Definitions s are written in one-line notation. e.g. S 3 = {123, 132, 213, 231, 312, 321} Conventions and Definitions
= = = = = =
 PARTITION THEORY (notes by M. Hlynka, University of Windsor) Definition: A partition of a positive integer n is an expression of n as a sum of positive integers. Partitions are considered the same if the
PARTITION THEORY (notes by M. Hlynka, University of Windsor) Definition: A partition of a positive integer n is an expression of n as a sum of positive integers. Partitions are considered the same if the
COMBINATORICS OF RAMANUJAN-SLATER TYPE IDENTITIES
 COMBINATORICS OF RAMANUJAN-SLATER TYPE IDENTITIES James McLaughlin Department of Mathematics, West Chester University, West Chester, PA 9383, USA jmclaughl@wcupa.edu Andrew V. Sills Department of Mathematical
COMBINATORICS OF RAMANUJAN-SLATER TYPE IDENTITIES James McLaughlin Department of Mathematics, West Chester University, West Chester, PA 9383, USA jmclaughl@wcupa.edu Andrew V. Sills Department of Mathematical
Counting k-marked Durfee Symbols
 Counting k-marked Durfee Symbols Kağan Kurşungöz Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 602 kursun@math.psu.edu Submitted: May 7 200; Accepted: Feb 5 20; Published:
Counting k-marked Durfee Symbols Kağan Kurşungöz Department of Mathematics The Pennsylvania State University University Park PA 602 kursun@math.psu.edu Submitted: May 7 200; Accepted: Feb 5 20; Published:
PROBABILITY. Contents Preface 1 1. Introduction 2 2. Combinatorial analysis 5 3. Stirling s formula 8. Preface
 PROBABILITY VITTORIA SILVESTRI Contents Preface. Introduction. Combinatorial analysis 5 3. Stirling s formula 8 Preface These lecture notes are for the course Probability IA, given in Lent 09 at the University
PROBABILITY VITTORIA SILVESTRI Contents Preface. Introduction. Combinatorial analysis 5 3. Stirling s formula 8 Preface These lecture notes are for the course Probability IA, given in Lent 09 at the University
Enumerative Combinatorics with Fillings of Polyominoes
 Enumerative Combinatorics with Fillings of Polyominoes Catherine Yan Texas A&M Univesrity GSU, October, 204 2 Outline. Symmetry of the longest chains Subsequences in permutations and words Crossings and
Enumerative Combinatorics with Fillings of Polyominoes Catherine Yan Texas A&M Univesrity GSU, October, 204 2 Outline. Symmetry of the longest chains Subsequences in permutations and words Crossings and
SOME CONGRUENCES FOR PARTITION FUNCTIONS RELATED TO MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ω(q) AND ν(q) S.N. Fathima and Utpal Pore (Received October 13, 2017)
 NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 47 2017), 161-168 SOME CONGRUENCES FOR PARTITION FUNCTIONS RELATED TO MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) S.N. Fathima and Utpal Pore Received October 1, 2017) Abstract.
NEW ZEALAND JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 47 2017), 161-168 SOME CONGRUENCES FOR PARTITION FUNCTIONS RELATED TO MOCK THETA FUNCTIONS ωq) AND νq) S.N. Fathima and Utpal Pore Received October 1, 2017) Abstract.
A lattice path approach to countingpartitions with minimum rank t
 Discrete Mathematics 249 (2002) 31 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc A lattice path approach to countingpartitions with minimum rank t Alexander Burstein a, Sylvie Corteel b, Alexander Postnikov c, d; ;1
Discrete Mathematics 249 (2002) 31 39 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc A lattice path approach to countingpartitions with minimum rank t Alexander Burstein a, Sylvie Corteel b, Alexander Postnikov c, d; ;1
Compositions of n with no occurrence of k. Phyllis Chinn, Humboldt State University Silvia Heubach, California State University Los Angeles
 Compositions of n with no occurrence of k Phyllis Chinn, Humboldt State University Silvia Heubach, California State University Los Angeles Abstract A composition of n is an ordered collection of one or
Compositions of n with no occurrence of k Phyllis Chinn, Humboldt State University Silvia Heubach, California State University Los Angeles Abstract A composition of n is an ordered collection of one or
MULTI-ORDERED POSETS. Lisa Bishop Department of Mathematics, Occidental College, Los Angeles, CA 90041, United States.
 INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (2007), #A06 MULTI-ORDERED POSETS Lisa Bishop Department of Mathematics, Occidental College, Los Angeles, CA 90041, United States lbishop@oxy.edu
INTEGERS: ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF COMBINATORIAL NUMBER THEORY 7 (2007), #A06 MULTI-ORDERED POSETS Lisa Bishop Department of Mathematics, Occidental College, Los Angeles, CA 90041, United States lbishop@oxy.edu
