Organization. I MCMC discussion. I project talks. I Lecture.
|
|
|
- Lesley Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Organization I MCMC discussion I project talks. I Lecture.
2 Content I Uncertainty Propagation Overview I Forward-Backward with an Ensemble I Model Reduction (Intro)
3 Uncertainty Propagation in Causal Systems X f 0 X f 1 X f 2 X f n M M(X t ; t ) X t+1 = M(X t ; t )+! t M :- Physical or Statistical Model.
4 Inference in Bayesian Networks T L P R F Q Hierarchical Bayes Found in Hierarchical Bayes, Grahical Models.
5 Belief Propagation in Undirected Graphs Grid nodes Interactions? Graphical Models
6 Inference Problems 1. Updating States 2. Estimating Parameters 3. Learning Structure Propagating Uncertainty, a first step.
7 Propagating Uncertainty Monte-Carlo Model Reduction & Interpolation I Snapshots & POD I Krylov Subspace Response Surface Models I Deterministic Equivalent Modeling Method I Stochastic Response Surface Methodology Polynomial Chaos Expansions I Generalized Polynomial Chaos
8 From Class 1 & 2 J(x 0 ):= 1 2 (x 0 x b ) T C00 1 (x 0 x b ) + mx 1 2 (y i Hx i ) T R 1 (y i Hx i )+ T i [x i M(x i 1 ; )] i=1
9 Forward Backward Forward (from ) x i = M(x i 1 ; ) 0 < i < m Backward (from x): m = H T R 1 (y m Hx m ) i i+1 + H T R 1 (y i Hx i ) ˆx 0 = x b + C 0 1
10 Uncertainty? Via Linearization Forward (you ll need this in the end) C i 1 C i 1i i 1 0 < i apple m What about backward? Convenient via information form: Î mm = H T R 1 H Î ii i Ĉ 00 = i + H T R 1 H apple C Dimensionality, Linearization challenges. 1
11 Monte-Carlo Isotropic Initial Perturbation Leading Lyapunov vectors time
12 Filter Updating NOTE THAT A f =[x f 1...x f s ] ) All at time T à f =[x f 1 x f...x f s x f ] P f = 1 s 1Ãf à ft ( Uncertainty So, propagate uncertainty via samples integrated forward.
13 No Linearization Y = h(x)+, N(0, R) Z =[Y + 1,...,Y + s ] R 1 s 1 Z Z T Perturbed Observations Also, let! f = h(a f )=[h(x f 1)...h(x f s )]! f defined similarly
14 Uncorrelated Noise Notice (! f + Z)(! ft + Z T )=(! f! ft + Z Z T ) When observation noise is uncorrelated with state an assumption Let X a be the estimate, analysis, posterior rv. A a and à a similarly, defined.
15 Easy Formulation A a = A f + Ã f! ft h! f! ft + Z Z T i 1 h Z! f i Identical to KF/EKF in linear/linearized case ) No linearization of the model ) No explicit uncertainty (covariance) propagation h! f! ft + Z Z i T 1 = [! f + Z][! ft + Z T 1 ] =(C C T ) 1
16 Solution Let C =[u s v T ] [C C T ] 1 = u s 2 u T =(u s 1 )(u s 1 ) T q = D qd T = D
17 Fast Calculation A a = A f + Ã f! ft [u s 2 u T ][Z! f ] (n, s) (n, s) (n, s)(s, n)(n, s)(s, s)(s, n)(n, s) (n, s) Return by right to left multiply, fast, low memory A a =A f + Ã f =A f (I s + ) =A f T (ENKF) A weakly nonlinear transformation (T T (A))
18 Time Dependent Example Lorenz ẋ i = x i 2 x i 1 + x i 1 x i+1 x i + u i = x i 1 [x i+1 x i 2 ] {z } Advective x i {z} Dissipative + u {z} Forcing Filter
19 Back in Time, How? Recall: A a = A f T Also, written as A a = A f All at same time t
20 Plug and Play So, x 0 x 1 y 1 A a 0 = Af 0 I s A a 1 = Af 1 1 A s 1 = A a 1I s A s 0 = Aa 0 = A a 0 1 No measurement Filter No future measurement + Ãa 0!fT 1 [u 1s 2 1 ut 1 ][Z 1! f 1 ]
21 Send me a message
22 Fixed Interval & Fixed Lag Fixed Interval Y 1 Y n 1 Y n x 0 x 1 x 2 x 3 x n 1 x n P(X 0 Y 1 Y n ) P(X 1 Y 1 Y n ). P(X n Y 1 Y n ) Smoother Filter
23 Fixed Lag Fixed Lag Y 1 Y n 1 Y n x 0 x 1 x 2 x 3 x n 1 x n Y 1 Y n 1 Y n x 0 x 1 x 2 x 3 x n 1 x n P(X 0 Y 1...Y n ) = P(X 0 Y 1...Y L ), (L < n) P(X i Y 0...Y i+l ) Smothed up to a window
24 Fixed Interval: The Dumb Way
25 Backward Recursion
26 Fixed Interval: The New Normal
27 Fixed Interval On Lorenz
28 Costs of Inference, Toy Problem
29 Fixed Lag Fixed Lag Smoother
30 Fixed Lag: The Dumb Way Computational Time (s) FBF V1-lag--->
31 Fixed Lag is FIFO A s k = A a k k+w Y j=k+1 X 5 j = A a k C k C k = X 5 1 k C k 1X 5 k+w
32 Fixed Lag: The New Normal Computational Time (s) FBF FIFO-Lag
33 Where does ensemble come from? singular vectors P f 0 P f 1 Low dimensional Subspace Span {S 0...S n } S (0) 0! L S (1) x=x0
34 Things get tough...the Tough linearize X 1 = M(X 0 ) = M( X 0 + X 0 ) = M( X X = X 0 X 0 X 1 = L X 0 S (k) 1 = LS (k) 0
35 Eigenvalue Problem Now,let C 1 be a metric on S 1 let C 0 be a metric on S 0 Maximize k: k = < LS 0, C 1 LS 0 > < S 0, C 0 S 0 > = < S 0, L # C 1 LS 0 > < S 0, C 0 S 0 > )L # C 1 LS (k) 0 = k C 0 S (k) 0 Ageneralizedeigenvalueproblem When C 1 = I &C 0 = P f 0! S 1 loading directions of P f 1
36 SV approach Notes I Adjoint & TLM not easy to calculate but one of the most robust methods available. I L may be really large too! I How can we reduce L? I Sensitivity to norm.
37 Breeding
38 It s easy to breed 1. Generate random initial perturbation 2. Let it grow; renormalize. (i.e propagate it) 3. Repeat ) Breeding vectors How many bred vectors? ) Size of L?
39 Two ways to simplify models 1. Truncate the Model: Linearize and reduce order, construct from snapshots. 2. Sample Input-Output pairs, create an auxiliary (simple) model. In Class 6
40 Truncation/Linearization
41 Another
Smoothers: Types and Benchmarks
 Smoothers: Types and Benchmarks Patrick N. Raanes Oxford University, NERSC 8th International EnKF Workshop May 27, 2013 Chris Farmer, Irene Moroz Laurent Bertino NERSC Geir Evensen Abstract Talk builds
Smoothers: Types and Benchmarks Patrick N. Raanes Oxford University, NERSC 8th International EnKF Workshop May 27, 2013 Chris Farmer, Irene Moroz Laurent Bertino NERSC Geir Evensen Abstract Talk builds
Relationship between Singular Vectors, Bred Vectors, 4D-Var and EnKF
 Relationship between Singular Vectors, Bred Vectors, 4D-Var and EnKF Eugenia Kalnay and Shu-Chih Yang with Alberto Carrasi, Matteo Corazza and Takemasa Miyoshi ECODYC10, Dresden 28 January 2010 Relationship
Relationship between Singular Vectors, Bred Vectors, 4D-Var and EnKF Eugenia Kalnay and Shu-Chih Yang with Alberto Carrasi, Matteo Corazza and Takemasa Miyoshi ECODYC10, Dresden 28 January 2010 Relationship
Data assimilation; comparison of 4D-Var and LETKF smoothers
 Data assimilation; comparison of 4D-Var and LETKF smoothers Eugenia Kalnay and many friends University of Maryland CSCAMM DAS13 June 2013 Contents First part: Forecasting the weather - we are really getting
Data assimilation; comparison of 4D-Var and LETKF smoothers Eugenia Kalnay and many friends University of Maryland CSCAMM DAS13 June 2013 Contents First part: Forecasting the weather - we are really getting
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 2950-P, Spring 2013 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 12: Gaussian Belief Propagation, State Space Models and Kalman Filters Guest Kalman Filter Lecture by
Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 2950-P, Spring 2013 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 12: Gaussian Belief Propagation, State Space Models and Kalman Filters Guest Kalman Filter Lecture by
Relationship between Singular Vectors, Bred Vectors, 4D-Var and EnKF
 Relationship between Singular Vectors, Bred Vectors, 4D-Var and EnKF Eugenia Kalnay and Shu-Chih Yang with Alberto Carrasi, Matteo Corazza and Takemasa Miyoshi 4th EnKF Workshop, April 2010 Relationship
Relationship between Singular Vectors, Bred Vectors, 4D-Var and EnKF Eugenia Kalnay and Shu-Chih Yang with Alberto Carrasi, Matteo Corazza and Takemasa Miyoshi 4th EnKF Workshop, April 2010 Relationship
9 Forward-backward algorithm, sum-product on factor graphs
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 9 Forward-backward algorithm, sum-product on factor graphs The previous
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 9 Forward-backward algorithm, sum-product on factor graphs The previous
The Kalman Filter ImPr Talk
 The Kalman Filter ImPr Talk Ged Ridgway Centre for Medical Image Computing November, 2006 Outline What is the Kalman Filter? State Space Models Kalman Filter Overview Bayesian Updating of Estimates Kalman
The Kalman Filter ImPr Talk Ged Ridgway Centre for Medical Image Computing November, 2006 Outline What is the Kalman Filter? State Space Models Kalman Filter Overview Bayesian Updating of Estimates Kalman
DATA ASSIMILATION FOR FLOOD FORECASTING
 DATA ASSIMILATION FOR FLOOD FORECASTING Arnold Heemin Delft University of Technology 09/16/14 1 Data assimilation is the incorporation of measurement into a numerical model to improve the model results
DATA ASSIMILATION FOR FLOOD FORECASTING Arnold Heemin Delft University of Technology 09/16/14 1 Data assimilation is the incorporation of measurement into a numerical model to improve the model results
Ensemble prediction and strategies for initialization: Tangent Linear and Adjoint Models, Singular Vectors, Lyapunov vectors
 Ensemble prediction and strategies for initialization: Tangent Linear and Adjoint Models, Singular Vectors, Lyapunov vectors Eugenia Kalnay Lecture 2 Alghero, May 2008 Elements of Ensemble Forecasting
Ensemble prediction and strategies for initialization: Tangent Linear and Adjoint Models, Singular Vectors, Lyapunov vectors Eugenia Kalnay Lecture 2 Alghero, May 2008 Elements of Ensemble Forecasting
Lecture 6: Bayesian Inference in SDE Models
 Lecture 6: Bayesian Inference in SDE Models Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing Point of View Simo Särkkä Aalto University Simo Särkkä (Aalto) Lecture 6: Bayesian Inference in SDEs 1 / 45 Contents 1 SDEs
Lecture 6: Bayesian Inference in SDE Models Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing Point of View Simo Särkkä Aalto University Simo Särkkä (Aalto) Lecture 6: Bayesian Inference in SDEs 1 / 45 Contents 1 SDEs
Stochastic Collocation Methods for Polynomial Chaos: Analysis and Applications
 Stochastic Collocation Methods for Polynomial Chaos: Analysis and Applications Dongbin Xiu Department of Mathematics, Purdue University Support: AFOSR FA955-8-1-353 (Computational Math) SF CAREER DMS-64535
Stochastic Collocation Methods for Polynomial Chaos: Analysis and Applications Dongbin Xiu Department of Mathematics, Purdue University Support: AFOSR FA955-8-1-353 (Computational Math) SF CAREER DMS-64535
Lecture 2: From Linear Regression to Kalman Filter and Beyond
 Lecture 2: From Linear Regression to Kalman Filter and Beyond January 18, 2017 Contents 1 Batch and Recursive Estimation 2 Towards Bayesian Filtering 3 Kalman Filter and Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing
Lecture 2: From Linear Regression to Kalman Filter and Beyond January 18, 2017 Contents 1 Batch and Recursive Estimation 2 Towards Bayesian Filtering 3 Kalman Filter and Bayesian Filtering and Smoothing
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 295-P, Spring 213 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 11: Inference & Learning Overview, Gaussian Graphical Models Some figures courtesy Michael Jordan s draft
Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 295-P, Spring 213 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 11: Inference & Learning Overview, Gaussian Graphical Models Some figures courtesy Michael Jordan s draft
Bayesian Inverse problem, Data assimilation and Localization
 Bayesian Inverse problem, Data assimilation and Localization Xin T Tong National University of Singapore ICIP, Singapore 2018 X.Tong Localization 1 / 37 Content What is Bayesian inverse problem? What is
Bayesian Inverse problem, Data assimilation and Localization Xin T Tong National University of Singapore ICIP, Singapore 2018 X.Tong Localization 1 / 37 Content What is Bayesian inverse problem? What is
Lecture 2: From Linear Regression to Kalman Filter and Beyond
 Lecture 2: From Linear Regression to Kalman Filter and Beyond Department of Biomedical Engineering and Computational Science Aalto University January 26, 2012 Contents 1 Batch and Recursive Estimation
Lecture 2: From Linear Regression to Kalman Filter and Beyond Department of Biomedical Engineering and Computational Science Aalto University January 26, 2012 Contents 1 Batch and Recursive Estimation
Lecture 7: Optimal Smoothing
 Department of Biomedical Engineering and Computational Science Aalto University March 17, 2011 Contents 1 What is Optimal Smoothing? 2 Bayesian Optimal Smoothing Equations 3 Rauch-Tung-Striebel Smoother
Department of Biomedical Engineering and Computational Science Aalto University March 17, 2011 Contents 1 What is Optimal Smoothing? 2 Bayesian Optimal Smoothing Equations 3 Rauch-Tung-Striebel Smoother
Dynamic System Identification using HDMR-Bayesian Technique
 Dynamic System Identification using HDMR-Bayesian Technique *Shereena O A 1) and Dr. B N Rao 2) 1), 2) Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Madras, Chennai 600036, Tamil Nadu, India 1) ce14d020@smail.iitm.ac.in
Dynamic System Identification using HDMR-Bayesian Technique *Shereena O A 1) and Dr. B N Rao 2) 1), 2) Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Madras, Chennai 600036, Tamil Nadu, India 1) ce14d020@smail.iitm.ac.in
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
CPSC 540: Machine Learning
 CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
CPSC 540: Machine Learning MCMC and Non-Parametric Bayes Mark Schmidt University of British Columbia Winter 2016 Admin I went through project proposals: Some of you got a message on Piazza. No news is
Stochastic Spectral Approaches to Bayesian Inference
 Stochastic Spectral Approaches to Bayesian Inference Prof. Nathan L. Gibson Department of Mathematics Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar March 4, 2011 Prof. Gibson (OSU) Spectral Approaches to
Stochastic Spectral Approaches to Bayesian Inference Prof. Nathan L. Gibson Department of Mathematics Applied Mathematics and Computation Seminar March 4, 2011 Prof. Gibson (OSU) Spectral Approaches to
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, Spis treści
 Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Parameter Selection Techniques and Surrogate Models
 Parameter Selection Techniques and Surrogate Models Model Reduction: Will discuss two forms Parameter space reduction Surrogate models to reduce model complexity Input Representation Local Sensitivity
Parameter Selection Techniques and Surrogate Models Model Reduction: Will discuss two forms Parameter space reduction Surrogate models to reduce model complexity Input Representation Local Sensitivity
Factor Analysis and Kalman Filtering (11/2/04)
 CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Factor Analysis and Kalman Filtering (11/2/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribes: Byung-Gon Chun and Sunghoon Kim 1 Factor Analysis Factor analysis is used
CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Factor Analysis and Kalman Filtering (11/2/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribes: Byung-Gon Chun and Sunghoon Kim 1 Factor Analysis Factor analysis is used
Probabilistic Graphical Networks: Definitions and Basic Results
 This document gives a cursory overview of Probabilistic Graphical Networks. The material has been gleaned from different sources. I make no claim to original authorship of this material. Bayesian Graphical
This document gives a cursory overview of Probabilistic Graphical Networks. The material has been gleaned from different sources. I make no claim to original authorship of this material. Bayesian Graphical
A Spectral Approach to Linear Bayesian Updating
 A Spectral Approach to Linear Bayesian Updating Oliver Pajonk 1,2, Bojana V. Rosic 1, Alexander Litvinenko 1, and Hermann G. Matthies 1 1 Institute of Scientific Computing, TU Braunschweig, Germany 2 SPT
A Spectral Approach to Linear Bayesian Updating Oliver Pajonk 1,2, Bojana V. Rosic 1, Alexander Litvinenko 1, and Hermann G. Matthies 1 1 Institute of Scientific Computing, TU Braunschweig, Germany 2 SPT
Stability of Ensemble Kalman Filters
 Stability of Ensemble Kalman Filters Idrissa S. Amour, Zubeda Mussa, Alexander Bibov, Antti Solonen, John Bardsley, Heikki Haario and Tuomo Kauranne Lappeenranta University of Technology University of
Stability of Ensemble Kalman Filters Idrissa S. Amour, Zubeda Mussa, Alexander Bibov, Antti Solonen, John Bardsley, Heikki Haario and Tuomo Kauranne Lappeenranta University of Technology University of
Inference in Bayesian Networks
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Inference in graphical models Description Assume we have evidence e on the state of a subset of variables E in the model (i.e. Bayesian Network)
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Inference in graphical models Description Assume we have evidence e on the state of a subset of variables E in the model (i.e. Bayesian Network)
4 Derivations of the Discrete-Time Kalman Filter
 Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Department of Electrical Engineering Estimation and Identification in Dynamical Systems (048825) Lecture Notes, Fall 2009, Prof N Shimkin 4 Derivations of the Discrete-Time
Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Department of Electrical Engineering Estimation and Identification in Dynamical Systems (048825) Lecture Notes, Fall 2009, Prof N Shimkin 4 Derivations of the Discrete-Time
Mathematical Formulation of Our Example
 Mathematical Formulation of Our Example We define two binary random variables: open and, where is light on or light off. Our question is: What is? Computer Vision 1 Combining Evidence Suppose our robot
Mathematical Formulation of Our Example We define two binary random variables: open and, where is light on or light off. Our question is: What is? Computer Vision 1 Combining Evidence Suppose our robot
Fundamentals of Data Assimilation
 National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO USA GSI Data Assimilation Tutorial - June 28-30, 2010 Acknowledgments and References WRFDA Overview (WRF Tutorial Lectures, H. Huang and D. Barker)
National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO USA GSI Data Assimilation Tutorial - June 28-30, 2010 Acknowledgments and References WRFDA Overview (WRF Tutorial Lectures, H. Huang and D. Barker)
Gaussian Process Approximations of Stochastic Differential Equations
 Gaussian Process Approximations of Stochastic Differential Equations Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning University College London c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk CSML
Gaussian Process Approximations of Stochastic Differential Equations Cédric Archambeau Centre for Computational Statistics and Machine Learning University College London c.archambeau@cs.ucl.ac.uk CSML
A new Hierarchical Bayes approach to ensemble-variational data assimilation
 A new Hierarchical Bayes approach to ensemble-variational data assimilation Michael Tsyrulnikov and Alexander Rakitko HydroMetCenter of Russia College Park, 20 Oct 2014 Michael Tsyrulnikov and Alexander
A new Hierarchical Bayes approach to ensemble-variational data assimilation Michael Tsyrulnikov and Alexander Rakitko HydroMetCenter of Russia College Park, 20 Oct 2014 Michael Tsyrulnikov and Alexander
Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter
 Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter Brian Hunt 11 June 2013 Review of Notation Forecast model: a known function M on a vector space of model states. Truth: an unknown sequence {x n } of model states
Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter Brian Hunt 11 June 2013 Review of Notation Forecast model: a known function M on a vector space of model states. Truth: an unknown sequence {x n } of model states
Forecasting and data assimilation
 Supported by the National Science Foundation DMS Forecasting and data assimilation Outline Numerical models Kalman Filter Ensembles Douglas Nychka, Thomas Bengtsson, Chris Snyder Geophysical Statistics
Supported by the National Science Foundation DMS Forecasting and data assimilation Outline Numerical models Kalman Filter Ensembles Douglas Nychka, Thomas Bengtsson, Chris Snyder Geophysical Statistics
Machine Learning 4771
 Machine Learning 4771 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 16 Undirected Graphs Undirected Separation Inferring Marginals & Conditionals Moralization Junction Trees Triangulation Undirected Graphs Separation
Machine Learning 4771 Instructor: Tony Jebara Topic 16 Undirected Graphs Undirected Separation Inferring Marginals & Conditionals Moralization Junction Trees Triangulation Undirected Graphs Separation
Linear Dynamical Systems
 Linear Dynamical Systems Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Machine Learning Course: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse574/index.html Two Models Described by Same Graph Latent variables Observations
Linear Dynamical Systems Sargur N. srihari@cedar.buffalo.edu Machine Learning Course: http://www.cedar.buffalo.edu/~srihari/cse574/index.html Two Models Described by Same Graph Latent variables Observations
Hidden Markov Models (recap BNs)
 Probabilistic reasoning over time - Hidden Markov Models (recap BNs) Applied artificial intelligence (EDA132) Lecture 10 2016-02-17 Elin A. Topp Material based on course book, chapter 15 1 A robot s view
Probabilistic reasoning over time - Hidden Markov Models (recap BNs) Applied artificial intelligence (EDA132) Lecture 10 2016-02-17 Elin A. Topp Material based on course book, chapter 15 1 A robot s view
Revision of TR-09-25: A Hybrid Variational/Ensemble Filter Approach to Data Assimilation
 Revision of TR-9-25: A Hybrid Variational/Ensemble ilter Approach to Data Assimilation Adrian Sandu 1 and Haiyan Cheng 1 Computational Science Laboratory Department of Computer Science Virginia Polytechnic
Revision of TR-9-25: A Hybrid Variational/Ensemble ilter Approach to Data Assimilation Adrian Sandu 1 and Haiyan Cheng 1 Computational Science Laboratory Department of Computer Science Virginia Polytechnic
The Ensemble Kalman Filter:
 p.1 The Ensemble Kalman Filter: Theoretical formulation and practical implementation Geir Evensen Norsk Hydro Research Centre, Bergen, Norway Based on Evensen 23, Ocean Dynamics, Vol 53, No 4 p.2 The Ensemble
p.1 The Ensemble Kalman Filter: Theoretical formulation and practical implementation Geir Evensen Norsk Hydro Research Centre, Bergen, Norway Based on Evensen 23, Ocean Dynamics, Vol 53, No 4 p.2 The Ensemble
Kalman filtering and friends: Inference in time series models. Herke van Hoof slides mostly by Michael Rubinstein
 Kalman filtering and friends: Inference in time series models Herke van Hoof slides mostly by Michael Rubinstein Problem overview Goal Estimate most probable state at time k using measurement up to time
Kalman filtering and friends: Inference in time series models Herke van Hoof slides mostly by Michael Rubinstein Problem overview Goal Estimate most probable state at time k using measurement up to time
STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 2 In our
STA 4273H: Sta-s-cal Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistical Sciences! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! h0p://www.cs.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 2 In our
The Ensemble Kalman Filter:
 p.1 The Ensemble Kalman Filter: Theoretical formulation and practical implementation Geir Evensen Norsk Hydro Research Centre, Bergen, Norway Based on Evensen, Ocean Dynamics, Vol 5, No p. The Ensemble
p.1 The Ensemble Kalman Filter: Theoretical formulation and practical implementation Geir Evensen Norsk Hydro Research Centre, Bergen, Norway Based on Evensen, Ocean Dynamics, Vol 5, No p. The Ensemble
Data assimilation in high dimensions
 Data assimilation in high dimensions David Kelly Courant Institute New York University New York NY www.dtbkelly.com February 12, 2015 Graduate seminar, CIMS David Kelly (CIMS) Data assimilation February
Data assimilation in high dimensions David Kelly Courant Institute New York University New York NY www.dtbkelly.com February 12, 2015 Graduate seminar, CIMS David Kelly (CIMS) Data assimilation February
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II
 STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
STA414/2104 Statistical Methods for Machine Learning II Murat A. Erdogdu & David Duvenaud Department of Computer Science Department of Statistical Sciences Lecture 3 Slide credits: Russ Salakhutdinov Announcements
3 Gramians and Balanced Realizations
 3 Gramians and Balanced Realizations In this lecture, we use an optimization approach to find suitable realizations for truncation and singular perturbation of G. It turns out that the recommended realizations
3 Gramians and Balanced Realizations In this lecture, we use an optimization approach to find suitable realizations for truncation and singular perturbation of G. It turns out that the recommended realizations
STA 414/2104: Machine Learning
 STA 414/2104: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 9 Sequential Data So far
STA 414/2104: Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Computer Science! Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@cs.toronto.edu! http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/ Lecture 9 Sequential Data So far
Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Sequential Planning and Decision Making
 Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Sequential Planning and Decision Making Sue Zheng, Jason Pacheco, & John Fisher Sensing, Learning, & Inference Group Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
Robust Monte Carlo Methods for Sequential Planning and Decision Making Sue Zheng, Jason Pacheco, & John Fisher Sensing, Learning, & Inference Group Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
Gaussian Filtering Strategies for Nonlinear Systems
 Gaussian Filtering Strategies for Nonlinear Systems Canonical Nonlinear Filtering Problem ~u m+1 = ~ f (~u m )+~ m+1 ~v m+1 = ~g(~u m+1 )+~ o m+1 I ~ f and ~g are nonlinear & deterministic I Noise/Errors
Gaussian Filtering Strategies for Nonlinear Systems Canonical Nonlinear Filtering Problem ~u m+1 = ~ f (~u m )+~ m+1 ~v m+1 = ~g(~u m+1 )+~ o m+1 I ~ f and ~g are nonlinear & deterministic I Noise/Errors
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 2016 Robert Nowak Probabilistic Graphical Models 1 Introduction We have focused mainly on linear models for signals, in particular the subspace model x = Uθ, where U is a n k matrix and θ R k is a vector
2016 Robert Nowak Probabilistic Graphical Models 1 Introduction We have focused mainly on linear models for signals, in particular the subspace model x = Uθ, where U is a n k matrix and θ R k is a vector
Ensemble Kalman Filter
 Ensemble Kalman Filter Geir Evensen and Laurent Bertino Hydro Research Centre, Bergen, Norway, Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Bergen, Norway The Ensemble Kalman Filter (EnKF) Represents
Ensemble Kalman Filter Geir Evensen and Laurent Bertino Hydro Research Centre, Bergen, Norway, Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Bergen, Norway The Ensemble Kalman Filter (EnKF) Represents
(Extended) Kalman Filter
 (Extended) Kalman Filter Brian Hunt 7 June 2013 Goals of Data Assimilation (DA) Estimate the state of a system based on both current and all past observations of the system, using a model for the system
(Extended) Kalman Filter Brian Hunt 7 June 2013 Goals of Data Assimilation (DA) Estimate the state of a system based on both current and all past observations of the system, using a model for the system
Gaussian Process Approximations of Stochastic Differential Equations
 Gaussian Process Approximations of Stochastic Differential Equations Cédric Archambeau Dan Cawford Manfred Opper John Shawe-Taylor May, 2006 1 Introduction Some of the most complex models routinely run
Gaussian Process Approximations of Stochastic Differential Equations Cédric Archambeau Dan Cawford Manfred Opper John Shawe-Taylor May, 2006 1 Introduction Some of the most complex models routinely run
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Bayes Filter Particle Filter and Monte Carlo Localization
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Bayes Filter Particle Filter and Monte Carlo Localization Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Kai Arras 1 Motivation Recall: Discrete filter Discretize the
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Bayes Filter Particle Filter and Monte Carlo Localization Wolfram Burgard, Cyrill Stachniss, Maren Bennewitz, Kai Arras 1 Motivation Recall: Discrete filter Discretize the
Convergence of Square Root Ensemble Kalman Filters in the Large Ensemble Limit
 Convergence of Square Root Ensemble Kalman Filters in the Large Ensemble Limit Evan Kwiatkowski, Jan Mandel University of Colorado Denver December 11, 2014 OUTLINE 2 Data Assimilation Bayesian Estimation
Convergence of Square Root Ensemble Kalman Filters in the Large Ensemble Limit Evan Kwiatkowski, Jan Mandel University of Colorado Denver December 11, 2014 OUTLINE 2 Data Assimilation Bayesian Estimation
Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression
 When we want more than point estimates Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression Nicole Beckage Ordinary Least Squares Regression and Lasso Regression return only point estimates But what if we
When we want more than point estimates Bayesian Regression Linear and Logistic Regression Nicole Beckage Ordinary Least Squares Regression and Lasso Regression return only point estimates But what if we
EnKF Review. P.L. Houtekamer 7th EnKF workshop Introduction to the EnKF. Challenges. The ultimate global EnKF algorithm
 Overview 1 2 3 Review of the Ensemble Kalman Filter for Atmospheric Data Assimilation 6th EnKF Purpose EnKF equations localization After the 6th EnKF (2014), I decided with Prof. Zhang to summarize progress
Overview 1 2 3 Review of the Ensemble Kalman Filter for Atmospheric Data Assimilation 6th EnKF Purpose EnKF equations localization After the 6th EnKF (2014), I decided with Prof. Zhang to summarize progress
Machine Learning Lecture 14
 Many slides adapted from B. Schiele, S. Roth, Z. Gharahmani Machine Learning Lecture 14 Undirected Graphical Models & Inference 23.06.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de
Many slides adapted from B. Schiele, S. Roth, Z. Gharahmani Machine Learning Lecture 14 Undirected Graphical Models & Inference 23.06.2015 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de/ leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de
Factor Graphs and Message Passing Algorithms Part 1: Introduction
 Factor Graphs and Message Passing Algorithms Part 1: Introduction Hans-Andrea Loeliger December 2007 1 The Two Basic Problems 1. Marginalization: Compute f k (x k ) f(x 1,..., x n ) x 1,..., x n except
Factor Graphs and Message Passing Algorithms Part 1: Introduction Hans-Andrea Loeliger December 2007 1 The Two Basic Problems 1. Marginalization: Compute f k (x k ) f(x 1,..., x n ) x 1,..., x n except
Lagrangian Data Assimilation and Manifold Detection for a Point-Vortex Model. David Darmon, AMSC Kayo Ide, AOSC, IPST, CSCAMM, ESSIC
 Lagrangian Data Assimilation and Manifold Detection for a Point-Vortex Model David Darmon, AMSC Kayo Ide, AOSC, IPST, CSCAMM, ESSIC Background Data Assimilation Iterative process Forecast Analysis Background
Lagrangian Data Assimilation and Manifold Detection for a Point-Vortex Model David Darmon, AMSC Kayo Ide, AOSC, IPST, CSCAMM, ESSIC Background Data Assimilation Iterative process Forecast Analysis Background
Chris Bishop s PRML Ch. 8: Graphical Models
 Chris Bishop s PRML Ch. 8: Graphical Models January 24, 2008 Introduction Visualize the structure of a probabilistic model Design and motivate new models Insights into the model s properties, in particular
Chris Bishop s PRML Ch. 8: Graphical Models January 24, 2008 Introduction Visualize the structure of a probabilistic model Design and motivate new models Insights into the model s properties, in particular
Learning With Bayesian Networks. Markus Kalisch ETH Zürich
 Learning With Bayesian Networks Markus Kalisch ETH Zürich Inference in BNs - Review P(Burglary JohnCalls=TRUE, MaryCalls=TRUE) Exact Inference: P(b j,m) = c Sum e Sum a P(b)P(e)P(a b,e)p(j a)p(m a) Deal
Learning With Bayesian Networks Markus Kalisch ETH Zürich Inference in BNs - Review P(Burglary JohnCalls=TRUE, MaryCalls=TRUE) Exact Inference: P(b j,m) = c Sum e Sum a P(b)P(e)P(a b,e)p(j a)p(m a) Deal
14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation
 10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Yu-Hsin Kuo, Amos Ng 1 Introduction Last lecture
10-708: Probabilistic Graphical Models 10-708, Spring 2014 14 : Theory of Variational Inference: Inner and Outer Approximation Lecturer: Eric P. Xing Scribes: Yu-Hsin Kuo, Amos Ng 1 Introduction Last lecture
Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference
 Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference Shaobo Han, Xuejun Liao and Lawrence Carin Duke University February 27, 2014 S. Han et al. Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference February 27, 2014
Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference Shaobo Han, Xuejun Liao and Lawrence Carin Duke University February 27, 2014 S. Han et al. Integrated Non-Factorized Variational Inference February 27, 2014
Polynomial Chaos and Karhunen-Loeve Expansion
 Polynomial Chaos and Karhunen-Loeve Expansion 1) Random Variables Consider a system that is modeled by R = M(x, t, X) where X is a random variable. We are interested in determining the probability of the
Polynomial Chaos and Karhunen-Loeve Expansion 1) Random Variables Consider a system that is modeled by R = M(x, t, X) where X is a random variable. We are interested in determining the probability of the
Nonlinear Filtering. With Polynomial Chaos. Raktim Bhattacharya. Aerospace Engineering, Texas A&M University uq.tamu.edu
 Nonlinear Filtering With Polynomial Chaos Raktim Bhattacharya Aerospace Engineering, Texas A&M University uq.tamu.edu Nonlinear Filtering with PC Problem Setup. Dynamics: ẋ = f(x, ) Sensor Model: ỹ = h(x)
Nonlinear Filtering With Polynomial Chaos Raktim Bhattacharya Aerospace Engineering, Texas A&M University uq.tamu.edu Nonlinear Filtering with PC Problem Setup. Dynamics: ẋ = f(x, ) Sensor Model: ỹ = h(x)
There are two things that are particularly nice about the first basis
 Orthogonality and the Gram-Schmidt Process In Chapter 4, we spent a great deal of time studying the problem of finding a basis for a vector space We know that a basis for a vector space can potentially
Orthogonality and the Gram-Schmidt Process In Chapter 4, we spent a great deal of time studying the problem of finding a basis for a vector space We know that a basis for a vector space can potentially
Lecture 8: Bayesian Networks
 Lecture 8: Bayesian Networks Bayesian Networks Inference in Bayesian Networks COMP-652 and ECSE 608, Lecture 8 - January 31, 2017 1 Bayes nets P(E) E=1 E=0 0.005 0.995 E B P(B) B=1 B=0 0.01 0.99 E=0 E=1
Lecture 8: Bayesian Networks Bayesian Networks Inference in Bayesian Networks COMP-652 and ECSE 608, Lecture 8 - January 31, 2017 1 Bayes nets P(E) E=1 E=0 0.005 0.995 E B P(B) B=1 B=0 0.01 0.99 E=0 E=1
Short tutorial on data assimilation
 Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Short tutorial on data assimilation 23 June 2015 Wolfgang Kurtz & Harrie-Jan Hendricks Franssen Institute of Bio- and Geosciences IBG-3 (Agrosphere), Forschungszentrum
Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Short tutorial on data assimilation 23 June 2015 Wolfgang Kurtz & Harrie-Jan Hendricks Franssen Institute of Bio- and Geosciences IBG-3 (Agrosphere), Forschungszentrum
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24
 Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Graphical Models: Approximate Inference Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ BELIEF PROPAGATION OR MESSAGE PASSING Each
Machine Learning for Data Science (CS4786) Lecture 24 Graphical Models: Approximate Inference Course Webpage : http://www.cs.cornell.edu/courses/cs4786/2016sp/ BELIEF PROPAGATION OR MESSAGE PASSING Each
A data-driven method for improving the correlation estimation in serial ensemble Kalman filter
 A data-driven method for improving the correlation estimation in serial ensemble Kalman filter Michèle De La Chevrotière, 1 John Harlim 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, 2 Department
A data-driven method for improving the correlation estimation in serial ensemble Kalman filter Michèle De La Chevrotière, 1 John Harlim 2 1 Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, 2 Department
Probabilistic Graphical Models
 Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 2950-P, Spring 2013 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 13: Learning in Gaussian Graphical Models, Non-Gaussian Inference, Monte Carlo Methods Some figures
Probabilistic Graphical Models Brown University CSCI 2950-P, Spring 2013 Prof. Erik Sudderth Lecture 13: Learning in Gaussian Graphical Models, Non-Gaussian Inference, Monte Carlo Methods Some figures
Why do we care? Measurements. Handling uncertainty over time: predicting, estimating, recognizing, learning. Dealing with time
 Handling uncertainty over time: predicting, estimating, recognizing, learning Chris Atkeson 2004 Why do we care? Speech recognition makes use of dependence of words and phonemes across time. Knowing where
Handling uncertainty over time: predicting, estimating, recognizing, learning Chris Atkeson 2004 Why do we care? Speech recognition makes use of dependence of words and phonemes across time. Knowing where
Markov Networks.
 Markov Networks www.biostat.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts Markov network syntax Markov network semantics Potential functions Partition function
Markov Networks www.biostat.wisc.edu/~dpage/cs760/ Goals for the lecture you should understand the following concepts Markov network syntax Markov network semantics Potential functions Partition function
variability and their application for environment protection
 Main factors of climate variability and their application for environment protection problems in Siberia Vladimir i Penenko & Elena Tsvetova Institute of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Geophysics
Main factors of climate variability and their application for environment protection problems in Siberia Vladimir i Penenko & Elena Tsvetova Institute of Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Geophysics
Optimal Prediction for Radiative Transfer: A New Perspective on Moment Closure
 Optimal Prediction for Radiative Transfer: A New Perspective on Moment Closure Benjamin Seibold MIT Applied Mathematics Mar 02 nd, 2009 Collaborator Martin Frank (TU Kaiserslautern) Partial Support NSF
Optimal Prediction for Radiative Transfer: A New Perspective on Moment Closure Benjamin Seibold MIT Applied Mathematics Mar 02 nd, 2009 Collaborator Martin Frank (TU Kaiserslautern) Partial Support NSF
Sampling Methods (11/30/04)
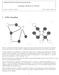 CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
CS281A/Stat241A: Statistical Learning Theory Sampling Methods (11/30/04) Lecturer: Michael I. Jordan Scribe: Jaspal S. Sandhu 1 Gibbs Sampling Figure 1: Undirected and directed graphs, respectively, with
Robotics. Mobile Robotics. Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart
 Robotics Mobile Robotics State estimation, Bayes filter, odometry, particle filter, Kalman filter, SLAM, joint Bayes filter, EKF SLAM, particle SLAM, graph-based SLAM Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart DARPA Grand
Robotics Mobile Robotics State estimation, Bayes filter, odometry, particle filter, Kalman filter, SLAM, joint Bayes filter, EKF SLAM, particle SLAM, graph-based SLAM Marc Toussaint U Stuttgart DARPA Grand
Local Positioning with Parallelepiped Moving Grid
 Local Positioning with Parallelepiped Moving Grid, WPNC06 16.3.2006, niilo.sirola@tut.fi p. 1/?? TA M P E R E U N I V E R S I T Y O F T E C H N O L O G Y M a t h e m a t i c s Local Positioning with Parallelepiped
Local Positioning with Parallelepiped Moving Grid, WPNC06 16.3.2006, niilo.sirola@tut.fi p. 1/?? TA M P E R E U N I V E R S I T Y O F T E C H N O L O G Y M a t h e m a t i c s Local Positioning with Parallelepiped
Introduction to Particle Filters for Data Assimilation
 Introduction to Particle Filters for Data Assimilation Mike Dowd Dept of Mathematics & Statistics (and Dept of Oceanography Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada STATMOS Summer School in Data Assimila5on,
Introduction to Particle Filters for Data Assimilation Mike Dowd Dept of Mathematics & Statistics (and Dept of Oceanography Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada STATMOS Summer School in Data Assimila5on,
Lagrangian Data Assimilation and Its Application to Geophysical Fluid Flows
 Lagrangian Data Assimilation and Its Application to Geophysical Fluid Flows Laura Slivinski June, 3 Laura Slivinski (Brown University) Lagrangian Data Assimilation June, 3 / 3 Data Assimilation Setup:
Lagrangian Data Assimilation and Its Application to Geophysical Fluid Flows Laura Slivinski June, 3 Laura Slivinski (Brown University) Lagrangian Data Assimilation June, 3 / 3 Data Assimilation Setup:
Fundamentals of Data Assimila1on
 014 GSI Community Tutorial NCAR Foothills Campus, Boulder, CO July 14-16, 014 Fundamentals of Data Assimila1on Milija Zupanski Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere Colorado State University
014 GSI Community Tutorial NCAR Foothills Campus, Boulder, CO July 14-16, 014 Fundamentals of Data Assimila1on Milija Zupanski Cooperative Institute for Research in the Atmosphere Colorado State University
The Ising model and Markov chain Monte Carlo
 The Ising model and Markov chain Monte Carlo Ramesh Sridharan These notes give a short description of the Ising model for images and an introduction to Metropolis-Hastings and Gibbs Markov Chain Monte
The Ising model and Markov chain Monte Carlo Ramesh Sridharan These notes give a short description of the Ising model for images and an introduction to Metropolis-Hastings and Gibbs Markov Chain Monte
Stochastic Models, Estimation and Control Peter S. Maybeck Volumes 1, 2 & 3 Tables of Contents
 Navtech Part #s Volume 1 #1277 Volume 2 #1278 Volume 3 #1279 3 Volume Set #1280 Stochastic Models, Estimation and Control Peter S. Maybeck Volumes 1, 2 & 3 Tables of Contents Volume 1 Preface Contents
Navtech Part #s Volume 1 #1277 Volume 2 #1278 Volume 3 #1279 3 Volume Set #1280 Stochastic Models, Estimation and Control Peter S. Maybeck Volumes 1, 2 & 3 Tables of Contents Volume 1 Preface Contents
Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning
 Christopher M. Bishop Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ÖSpri inger Contents Preface Mathematical notation Contents vii xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example: Polynomial Curve Fitting 4 1.2 Probability
Christopher M. Bishop Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning ÖSpri inger Contents Preface Mathematical notation Contents vii xi xiii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Example: Polynomial Curve Fitting 4 1.2 Probability
15-780: Grad AI Lecture 19: Graphical models, Monte Carlo methods. Geoff Gordon (this lecture) Tuomas Sandholm TAs Erik Zawadzki, Abe Othman
 15-780: Grad AI Lecture 19: Graphical models, Monte Carlo methods Geoff Gordon (this lecture) Tuomas Sandholm TAs Erik Zawadzki, Abe Othman Admin Reminder: midterm March 29 Reminder: project milestone
15-780: Grad AI Lecture 19: Graphical models, Monte Carlo methods Geoff Gordon (this lecture) Tuomas Sandholm TAs Erik Zawadzki, Abe Othman Admin Reminder: midterm March 29 Reminder: project milestone
Bayesian Machine Learning
 Bayesian Machine Learning Andrew Gordon Wilson ORIE 6741 Lecture 4 Occam s Razor, Model Construction, and Directed Graphical Models https://people.orie.cornell.edu/andrew/orie6741 Cornell University September
Bayesian Machine Learning Andrew Gordon Wilson ORIE 6741 Lecture 4 Occam s Razor, Model Construction, and Directed Graphical Models https://people.orie.cornell.edu/andrew/orie6741 Cornell University September
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods
 Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
Graphical Models and Kernel Methods Jerry Zhu Department of Computer Sciences University of Wisconsin Madison, USA MLSS June 17, 2014 1 / 123 Outline Graphical Models Probabilistic Inference Directed vs.
MCMC and Gibbs Sampling. Kayhan Batmanghelich
 MCMC and Gibbs Sampling Kayhan Batmanghelich 1 Approaches to inference l Exact inference algorithms l l l The elimination algorithm Message-passing algorithm (sum-product, belief propagation) The junction
MCMC and Gibbs Sampling Kayhan Batmanghelich 1 Approaches to inference l Exact inference algorithms l l l The elimination algorithm Message-passing algorithm (sum-product, belief propagation) The junction
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods for Stochastic Optimization
 Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods for Stochastic Optimization John R. Birge The University of Chicago Booth School of Business Joint work with Nicholas Polson, Chicago Booth. JRBirge U of Toronto, MIE,
Markov Chain Monte Carlo Methods for Stochastic Optimization John R. Birge The University of Chicago Booth School of Business Joint work with Nicholas Polson, Chicago Booth. JRBirge U of Toronto, MIE,
6.241 Dynamic Systems and Control
 6.241 Dynamic Systems and Control Lecture 24: H2 Synthesis Emilio Frazzoli Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology May 4, 2011 E. Frazzoli (MIT) Lecture 24: H 2 Synthesis May
6.241 Dynamic Systems and Control Lecture 24: H2 Synthesis Emilio Frazzoli Aeronautics and Astronautics Massachusetts Institute of Technology May 4, 2011 E. Frazzoli (MIT) Lecture 24: H 2 Synthesis May
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017
 ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
ECE521 week 3: 23/26 January 2017 Outline Probabilistic interpretation of linear regression - Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) - Maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation Bias-variance trade-off Linear
Particle Filtering Approaches for Dynamic Stochastic Optimization
 Particle Filtering Approaches for Dynamic Stochastic Optimization John R. Birge The University of Chicago Booth School of Business Joint work with Nicholas Polson, Chicago Booth. JRBirge I-Sim Workshop,
Particle Filtering Approaches for Dynamic Stochastic Optimization John R. Birge The University of Chicago Booth School of Business Joint work with Nicholas Polson, Chicago Booth. JRBirge I-Sim Workshop,
A Probabilistic Framework for solving Inverse Problems. Lambros S. Katafygiotis, Ph.D.
 A Probabilistic Framework for solving Inverse Problems Lambros S. Katafygiotis, Ph.D. OUTLINE Introduction to basic concepts of Bayesian Statistics Inverse Problems in Civil Engineering Probabilistic Model
A Probabilistic Framework for solving Inverse Problems Lambros S. Katafygiotis, Ph.D. OUTLINE Introduction to basic concepts of Bayesian Statistics Inverse Problems in Civil Engineering Probabilistic Model
Probabilistic Graphical Models (I)
 Probabilistic Graphical Models (I) Hongxin Zhang zhx@cad.zju.edu.cn State Key Lab of CAD&CG, ZJU 2015-03-31 Probabilistic Graphical Models Modeling many real-world problems => a large number of random
Probabilistic Graphical Models (I) Hongxin Zhang zhx@cad.zju.edu.cn State Key Lab of CAD&CG, ZJU 2015-03-31 Probabilistic Graphical Models Modeling many real-world problems => a large number of random
Bayesian Calibration of Simulators with Structured Discretization Uncertainty
 Bayesian Calibration of Simulators with Structured Discretization Uncertainty Oksana A. Chkrebtii Department of Statistics, The Ohio State University Joint work with Matthew T. Pratola (Statistics, The
Bayesian Calibration of Simulators with Structured Discretization Uncertainty Oksana A. Chkrebtii Department of Statistics, The Ohio State University Joint work with Matthew T. Pratola (Statistics, The
Approximate inference in Energy-Based Models
 CSC 2535: 2013 Lecture 3b Approximate inference in Energy-Based Models Geoffrey Hinton Two types of density model Stochastic generative model using directed acyclic graph (e.g. Bayes Net) Energy-based
CSC 2535: 2013 Lecture 3b Approximate inference in Energy-Based Models Geoffrey Hinton Two types of density model Stochastic generative model using directed acyclic graph (e.g. Bayes Net) Energy-based
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 Problem Set 3 Issued: Thursday, September 25, 2014 Due: Thursday,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.438 Algorithms For Inference Fall 2014 Problem Set 3 Issued: Thursday, September 25, 2014 Due: Thursday,
Bayesian Machine Learning - Lecture 7
 Bayesian Machine Learning - Lecture 7 Guido Sanguinetti Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation School of Informatics University of Edinburgh gsanguin@inf.ed.ac.uk March 4, 2015 Today s lecture 1
Bayesian Machine Learning - Lecture 7 Guido Sanguinetti Institute for Adaptive and Neural Computation School of Informatics University of Edinburgh gsanguin@inf.ed.ac.uk March 4, 2015 Today s lecture 1
p L yi z n m x N n xi
 y i z n x n N x i Overview Directed and undirected graphs Conditional independence Exact inference Latent variables and EM Variational inference Books statistical perspective Graphical Models, S. Lauritzen
y i z n x n N x i Overview Directed and undirected graphs Conditional independence Exact inference Latent variables and EM Variational inference Books statistical perspective Graphical Models, S. Lauritzen
Asynchronous data assimilation
 Ensemble Kalman Filter, lecture 2 Asynchronous data assimilation Pavel Sakov Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Norway This talk has been prepared in the course of evita-enkf project funded
Ensemble Kalman Filter, lecture 2 Asynchronous data assimilation Pavel Sakov Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Norway This talk has been prepared in the course of evita-enkf project funded
