Nucleation in a Fermi liquid at negative pressure
|
|
|
- Jodie Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nucleation in a Fermi liquid at negative pressure Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure associé aux Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7 et au CNRS 24 rue Lhomond Paris Cedex 05, France Department of Physics, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island Experimental investigation of cavitation in liquid helium 3 has revealed a singular behaviour in the degenerate region at low temperature. As the temperature decreases below 80 mk, the cavitation pressure becomes significantly more negative. To investigate this, we have extrapolated the Fermi parameters in the negative pressure region. This allowed us to calculate the zero sound velocity, which we found to remain finite at the spinodal limit where the first sound velocity vanishes. We discuss the impact on the nucleation of the gas phase in terms of a quantum stiffness of the Fermi liquid. As a result we predict a cavitation pressure which is nearer to the spinodal line than previously thought. PACS numbers: Ay, Jd, Qb Cavitation has been studied in both isotopes of helium. Using a focused acoustic wave, a small volume of liquid was quenched into the negative pressure region for a short time, and the pressure threshold at which bubble nucleation becomes likely (the cavitation pressure P cav ) was measured. Our group has performed these experiments in the low temperature region, and reported the existence of two cavitation regimes in helium 4 1,2 : at high temperature, P cav becomes less negative when the temperature increases, and below 600 mk, it is temperature independent. This was attributed to a crossover from a thermally activated regime to a quantum regime. At negative pressures, the liquid is metastable and an energy barrier E b must be overcome for liquid-gas separation to occur; E b decreases as the pressure is more negative and vanishes at the absolute limit of metastability, the socalled spinodal pressure. At high enough temperature, bubble nucleation is triggered by thermal fluctuations: the lower the temperature, the lower
2 Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris the energy barrier that can be overcome, and the more negative the cavitation pressure. Close to the absolute zero, thermal fluctuations have such a small energy that the most favourable process for nucleation is the quantum tunneling through the barrier; the nucleation rate then becomes temperature independent, as does the cavitation pressure. In helium 4, the observed crossover temperature is consistent with the theoretical predictions 3,4, once adiabatic cooling in the sound wave is taken into account 1. In liquid helium 3, the situation is somewhat different. At high temperature, the cavitation pressure increases with temperature as expected in the thermally activated regime. However, at low temperature P cav does not level to the quantum plateau which was predicted below 120 mk; on the contrary, below 80 mk it starts to be significantly more negative with decreasing temperature 5,2. Possible experimental artifacts (thermal gradients 2, thermal effect of the sound wave 6 ) were ruled out and the search for a theoretical interpretation began. The viscosity of liquid helium 3 diverges as 1/T 2 in the Fermi liquid region, that is below 100 mk 7. Dissipation effects were considered by Jezek et al. 8 : they concluded that the crossover temperature could be lowered to 50 mk with a dissipation parameter corresponding to the measured viscosity at 100 mk under saturated vapor pressure; however, they note that by using the macroscopic viscosity coefficient, overestimating the dissipation effects is likely. Furthermore, lowering the crossover temperature is not sufficient to explain the sharp variation of the cavitation pressure, and we have tried to find another interpretation. In Fermi liquids, there is a particular mode of sound propagation called zero sound; it was first predicted by Landau 9 and later demonstrated experimentally 10. In the ballistic regime, when the lifetime τ of the quasiparticles becomes longer than the period T sound = 1/f of the sound wave, the sound can still propagate because of the interaction between quasiparticles. It was first suggested by Balibar et al. 6 that at the spinodal, whereas the first sound velocity c 1 vanishes, the zero sound velocity c 0 could remain finite, and that the liquid would then present a finite stiffness for the high-frequency motions; they explained that this would lower the crossover temperature. In this communication, we present an estimate of the zero sound velocity at the spinodal and we consider its effect on both the quantum and the thermally activated nucleation regime. The zero sound velocity and the corresponding distortion of the Fermi surface ν(θ, φ) are calculated by solving the following equation 10,11 : (s cos θ) ν(θ, φ) = cos θ F (χ) ν(θ, φ ) dω 4π, (1) where s = c 0 /v F (v F being the Fermi velocity), χ is the angle between the momentum of two quasiparticles and dω is the volume element. F is a
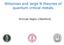
3 Nucleation in a Fermi liquid at negative pressure 500 Velocity (m s -1 ) Spinodal density Density (kg m -3 ) Fig. 1. Characteristic velocities in degenerate helium 3: Fermi (solid line), first sound (dashed line) and zero sound (dotted line) velocities. Full circles are experimental data for the first sound velocity taken from Ref. 15. function describing the quasiparticles interaction; it is usually replaced by the first terms of its expansion along the base of the Legendre polynomials. The coefficients F l of this expansion are the Fermi parameters. The first F l are related to measurable quantities and are thus known experimentally. To estimate the velocity of zero sound at negative pressures we proceed as follows: (1) we first estimate c 1 using an extrapolation of measured data at positive pressures using the method proposed by Maris (see Appendix of Ref. 2); (2) Greywall has measured the effective mass m for positive pressures 12,13. His data can be fit well by the equation [ m m = a2 1 ρ ] 2, (2) ρ c with a = and ρ c = kg m 3 ; the form of this fit was proposed by Stringari 14 on the basis of a microscopic model. We then use this equation to estimate m at negative pressure. This then gives F 1 through the relation F 1 = 3[(m /m) 1]; (3) F 0 is then extrapolated using ( ) m c 2 1 F 0 = 3 m 1. (3) v F (4) Finally, F 2 is obtained by means of a simple polynomial extrapolation of the data compiled in Ref. 15. It is interesting to note that, at the spinodal, c 1 = 0 implies F 0 = 1: the classical mechanical instability at the spinodal coincides with a fermionic instability occurring when F l = (2l + 1) 16. By numerically solving Eq. 1 with the two first Fermi parameters 17, we find the zero sound velocity: the result is displayed on Fig. 1; taking F 2 into account affects our results only slightly (by less than 2.5 %) 17. This
4 Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris calculation shows that whereas the first and zero sound velocities are close at positive pressure, they depart from each other at negative pressure; we find that at the spinodal, whereas the first sound velocity vanishes, the zero sound velocity becomes equal to the Fermi velocity v F 80 m s 1. Indeed, for Eq. 1 to have a real solution, that is to observe zero sound modes which are not strongly damped, one must have c 0 > v 11 F : the departure between c 0 and c 1 is thus a strong physical effect, independent of the chosen extrapolations. We now turn to the crossover frequency from first to zero sound at a given temperature f 0 1 (T ) (or equivalently the crossover temperature at a given frequency): this is obtained by solving 2πf 0 1 (T )τ(t ) = 1. The lifetime τ of the quasiparticles is related to the viscosity η, the density and the effective mass 10 : τ = 5η ρv F m m. (4) In the degenerate Fermi liquid region, ηt 2 is constant at a given density and this constant decreases with density 7,10. At 100 mk, this gives a crossover frequency f 0 1 less than 1.5 GHz at saturated vapor pressure and a polynomial extrapolation of ηt 2 even gives f 0 1 < 1 GHz near the spinodal; this is to be compared with the thermal frequency k B T/h 2 GHz at 100 mk, and to the tunneling frequency in the quantum cavitation regime, f Q 10 GHz 3. Let us now consider the effect of zero sound on nucleation: density fluctuations propagate in the zero sound mode with a higher phase velocity than in the first sound mode, so that nucleation rates driven by the faster fluctuations should decrease. In the quantum cavitation regime, the nucleation rate is related to the action calculated for the time that the system takes to pass under the barrier. The quantum regime previously predicted 3,4 is a high frequency process which must in fact be described by zero sound, which increases the action and decreases the corresponding nucleation rate. As for the thermally activated cavitation, we also think that the cavitation rate is reduced. The critical nuclei for nucleation were calculated to be spheres of radius R c 1 nm; at low temperature, this becomes small compared to the mean free path l of the quasiparticles: close to the spinodal, l = vf τ 11 nm at 100 mk and 45 nm at 50 mk. The thermal fluctuations leading to these critical nuclei involve a superposition of collective modes with different wavelengths, centered on the wavelength R c ; consequently, most of these fluctuations must be described by zero sound. We believe that the present approach based on Landau s theory is valid at this scale because the Fermi length l F = h/(m v F ) 0.14 nm at the spinodal remains small compared to R c, so that a local Fermi surface can be defined; this surface undergoes a non-spherically symmetric deformation because of the radial mass transfer which occurs during the evolution from the homogeneous liquid to
5 Nucleation in a Fermi liquid at negative pressure 10 R c (nm) P-P (bar) s Fig. 2. Critical radius as a function of the pressure distance to the spinodal P P s. The full circles corresponds to our numerical calculations and the solid line is a fit by a 1/4 power law. the critical profile, with a density hollow at the center. The energy of one phonon of wavelength R c is hc 0 /R c, instead of hc 1 /R c : the ratio, c 1 /c 0, is less than 0.35 for P cav P s < 10 mbar, which is the pressure range calculated by previous theories at low temperature in the conditions of the experiment. There will therefore be fewer fluctuations leading to a critical nucleus than expected before. We thus believe that in both regimes, the nucleation rate is decreased, and that cavitation only occurs if all the critical fluctuations are described by first sound. We can evaluate where this different regime should take place: it requires R c > l. This condition is fulfilled at pressure close enough to the spinodal pressure where R c diverges. This divergence was predicted by Lifshitz and Kagan 18, who made an analytical calculation in a generic case. Following Xiong and Maris 19, we have calculated numerically the critical density profiles with Maris equation of state for liquid helium; this equation of state has a singular behavior which Maris justifies with a renormalization calculation 20. Our calculations give the critical radius R c in the region very close to the spinodal. Fig. 2 shows that R c diverges following a 1/4 power law when the pressure approaches the spinodal. This shows that R c = 10 nm when the pressure is at only mbar from the spinodal pressure. In the degenerate region, cavitation therefore occurs at pressures closer to the spinodal by three orders of magnitude than what was estimated before. For these large critical radii, we think that the quantum fluctuations leading to tunneling will have low enough frequency to be described with first sound. But as the crossover temperature from quantum to thermal cavitation decreases when the pressure approaches the spinodal pressure 19, it is not clear if the quantum regime still exists and at which temperature it
6 Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris is reached. This point requires further investigation. In conclusion, we have extrapolated the first Fermi parameters of liquid helium 3 into the negative pressure region. This allowed us to calculate the zero sound velocity. We find that this velocity is non vanishing at the spinodal, contrary to the first sound velocity. This results in a quantum stiffness of the liquid in the degenerate Fermi liquid region. On these grounds, we find that the pressure required for cavitation to occur must be much closer to the spinodal than previously predicted, so that the critical fluctuations remain in the first sound regime. Another consequence is that the crossover from thermally activated cavitation to quantum cavitation is shifted to lower temperatures than predicted by previous theories, if not suppressed. This picture is consistent with the experimental measurements. REFERENCES 1. H. Lambaré, P. Roche, S. Balibar, H. J. Maris, O. A. Andreeva, C. Guthmann, K. O. Keshishev, and E. Rolley, Eur. Phys. J. B2, 381 (1998). 2. F. Caupin and S. Balibar, Phys. Rev. B 64, (2001). 3. H. J. Maris, J. Low Temp. Phys. 98, 403 (1995). 4. M. Guilleumas, M. Barranco, D. M. Jezek, R. J. Lombard, and M. Pi, Phys. Rev. B54, (1996). 5. F. Caupin and S. Balibar, Physica B , 212 (2000). 6. S. Balibar, F. Caupin, P. Roche, and H. J. Maris, J. Low Temp. Phys. 113, 459 (1998). 7. J. C. Wheatley, Rev. Mod. Phys., 47, 415 (1975). 8. D. M. Jezek, M. Pi, and M. Barranco, Phys. Rev. B60, 3048 (1999). 9. L. D. Landau, Zh. Eksper. Teor. Fiz (1957) [Soviet Physics JETP 5, 101 (1957)]. 10. J. Wilks, The properties of liquid and solid helium (Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1967), Chap G. Baym and C. Pethick, Landau Fermi-liquid theory (J. Wiley and Sons, New York, 1991), Chap D. S. Greywall, Phys. Rev. B27, 2747 (1983). 13. D. S. Greywall, Phys. Rev. B33, 7520 (1986). 14. S. Stringari, Phys. Lett. A106, 267 (1984). 15. W. P. Halperin and E. Varoquaux, in : Helium 3, edited by W. P. Halperin and L. P. Pitaevskii (North Holland, Amsterdam, 1990). 16. I. Y. Pomeranchuk, Zh. Eksper. Teor. Fiz. 35, 524 (1958) [Soviet Physics JETP 7, 361 (1959)]. 17. F. Caupin, Ph. D. thesis, Université Paris 6, I. M. Lifshitz and Y. Kagan, Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 62, 385 (1972) [Sov. Phys. JETP 35, 206 (1972)]. 19. Q. Xiong and H. J. Maris, J. Low Temp. Phys. 77, 347 (1989). 20. H. J. Maris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 45 (1991).
The expansion coefficient of liquid helium 3 and the shape of its stability limit
 The expansion coefficient of liquid helium 3 and the shape of its stability limit Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure
The expansion coefficient of liquid helium 3 and the shape of its stability limit Frédéric Caupin, Sébastien Balibar and Humphrey J. Maris Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure
Quantum Cavitation: a comparison between superfluid helium-4 and normal liquid helium-3
 Quantum Cavitation: a comparison between superfluid helium-4 and normal liquid helium-3 S. Balibar, F. Caupin, P. Roche and H.J.Maris Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure associé
Quantum Cavitation: a comparison between superfluid helium-4 and normal liquid helium-3 S. Balibar, F. Caupin, P. Roche and H.J.Maris Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure associé
Acoustic nucleation of solid helium 4 on a clean glass plate
 Acoustic nucleation of solid helium 4 on a clean glass plate X. Chavanne, S. Balibar, and F. Caupin Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure, associé aux Universités Paris 6 et
Acoustic nucleation of solid helium 4 on a clean glass plate X. Chavanne, S. Balibar, and F. Caupin Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure, associé aux Universités Paris 6 et
Density Functional Theory of the Interface between Solid and Superfluid Helium 4
 Density Functional Theory of the Interface between Solid and Superfluid Helium 4 Frédéric Caupin and Tomoki Minoguchi Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure associé aux Universités
Density Functional Theory of the Interface between Solid and Superfluid Helium 4 Frédéric Caupin and Tomoki Minoguchi Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l Ecole Normale Supérieure associé aux Universités
Path-integral Monte Carlo simulation of helium at negative pressures
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Path-integral Monte Carlo simulation of helium at negative pressures Gregory H. Bauer, David M. Ceperley, and Nigel Goldenfeld Department of Physics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Path-integral Monte Carlo simulation of helium at negative pressures Gregory H. Bauer, David M. Ceperley, and Nigel Goldenfeld Department of Physics,
Properties of Metastable Solid Helium Below the Normal Melting Pressure
 J Low Temp Phys (2009) 155: 290 302 DOI 10.1007/s10909-009-9881-3 Properties of Metastable Solid Helium Below the Normal Melting Pressure Humphrey J. Maris Received: 26 February 2009 / Accepted: 3 April
J Low Temp Phys (2009) 155: 290 302 DOI 10.1007/s10909-009-9881-3 Properties of Metastable Solid Helium Below the Normal Melting Pressure Humphrey J. Maris Received: 26 February 2009 / Accepted: 3 April
SÉBASTIEN BALIBAR AND FRÉDÉRIC CAUPIN. associé au CNRS et aux Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7, 24 rue Lhomond, Paris Cedex 05, France
 THE LIMITS OF METASTABILITY OF LIQUID HELIUM SÉBASTIEN BALIBAR AND FRÉDÉRIC CAUPIN Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l'ecole Normale Supérieure, associé au CNRS et aux Universités Paris 6 et Paris
THE LIMITS OF METASTABILITY OF LIQUID HELIUM SÉBASTIEN BALIBAR AND FRÉDÉRIC CAUPIN Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l'ecole Normale Supérieure, associé au CNRS et aux Universités Paris 6 et Paris
Liquid Helium up to 160 bar
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 136, Nos. 1/2, July 2004 ( 2004) Liquid Helium up to 160 bar F. Werner, G. Beaume, A. Hobeika, S. Nascimbène, C. Herrmann, F. Caupin, and S. Balibar* Laboratoire
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 136, Nos. 1/2, July 2004 ( 2004) Liquid Helium up to 160 bar F. Werner, G. Beaume, A. Hobeika, S. Nascimbène, C. Herrmann, F. Caupin, and S. Balibar* Laboratoire
Elastic Properties of Polycrystalline Solid Helium
 JLowTempPhys(2010)160:5 11 DOI 10.1007/s10909-010-0173-8 Elastic Properties of Polycrystalline Solid Helium Humphrey J. Maris Sebastien Balibar Received: 29 March 2010 / Accepted: 16 April 2010 / Published
JLowTempPhys(2010)160:5 11 DOI 10.1007/s10909-010-0173-8 Elastic Properties of Polycrystalline Solid Helium Humphrey J. Maris Sebastien Balibar Received: 29 March 2010 / Accepted: 16 April 2010 / Published
Thermodynamic Properties of Superfluid 4 He at Negative Pressure
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 129, Nos. 1/2, October 2002 ( 2002) Thermodynamic Properties of Superfluid 4 He at Negative Pressure H. J. Maris 1 and D. O. Edwards 2 1 Department of Physics,
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 129, Nos. 1/2, October 2002 ( 2002) Thermodynamic Properties of Superfluid 4 He at Negative Pressure H. J. Maris 1 and D. O. Edwards 2 1 Department of Physics,
Holographic zero sound at finite temperature
 Holographic zero sound at finite temperature Richard Davison and Andrei Starinets Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics Oxford University arxiv: 1109.XXXX [hep-th] Holographic Duality and Condensed
Holographic zero sound at finite temperature Richard Davison and Andrei Starinets Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics Oxford University arxiv: 1109.XXXX [hep-th] Holographic Duality and Condensed
Density of States in Superconductor -Normal. Metal-Superconductor Junctions arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Nov 1998.
![Density of States in Superconductor -Normal. Metal-Superconductor Junctions arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Nov 1998. Density of States in Superconductor -Normal. Metal-Superconductor Junctions arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Nov 1998.](/thumbs/87/96954508.jpg) Density of States in Superconductor -Normal Metal-Superconductor Junctions arxiv:cond-mat/97756v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Nov 1998 F. Zhou 1,, P. Charlat, B. Spivak 1, B.Pannetier 1 Physics Department, University
Density of States in Superconductor -Normal Metal-Superconductor Junctions arxiv:cond-mat/97756v [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Nov 1998 F. Zhou 1,, P. Charlat, B. Spivak 1, B.Pannetier 1 Physics Department, University
Comments on Heterogeneous Nucleation in Helium
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 120, Nos. 56, 2000 Comments on Heterogeneous Nucleation in Helium S. Balibar, 1, * T. Mizusaki, 2 and Y. Sasaki 2 1 Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l'ecole
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 120, Nos. 56, 2000 Comments on Heterogeneous Nucleation in Helium S. Balibar, 1, * T. Mizusaki, 2 and Y. Sasaki 2 1 Laboratoire de Physique Statistique de l'ecole
Supplemental Material for Curvature-dependence of the liquid-vapor surface tension beyond the Tolman approximation
 Supplemental Material for Curvature-dependence of the liquid-vapor surface tension beyond the Tolman approximation Nicolas Bruot and Frédéric Caupin Institut Lumière Matière, UMR536 Université Claude Bernard
Supplemental Material for Curvature-dependence of the liquid-vapor surface tension beyond the Tolman approximation Nicolas Bruot and Frédéric Caupin Institut Lumière Matière, UMR536 Université Claude Bernard
Possible long-range step interaction in 4He due to step oscillation
 Possible longrange step interaction in 4He due to step oscillation M. Uwaha To cite this version: M. Uwaha. Possible longrange step interaction in 4He due to step oscillation. Journal de Physique, 1990,
Possible longrange step interaction in 4He due to step oscillation M. Uwaha To cite this version: M. Uwaha. Possible longrange step interaction in 4He due to step oscillation. Journal de Physique, 1990,
New Measurements of Wetting by Helium Mixtures
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 140, Nos. 1/2, July 2005 ( 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10909-005-6010-9 New Measurements of Wetting by Helium Mixtures Ryosuke Ishiguro and Sébastien Balibar Laboratoire
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 140, Nos. 1/2, July 2005 ( 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10909-005-6010-9 New Measurements of Wetting by Helium Mixtures Ryosuke Ishiguro and Sébastien Balibar Laboratoire
Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Equilibrium Properties
 Quantum Liquids LECTURE I-II Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Phenomenology and Microscopic Foundations LECTURE III Superfluidity. Bogoliubov theory. Bose-Einstein condensation. LECTURE IV Luttinger Liquids.
Quantum Liquids LECTURE I-II Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Phenomenology and Microscopic Foundations LECTURE III Superfluidity. Bogoliubov theory. Bose-Einstein condensation. LECTURE IV Luttinger Liquids.
Critical Casimir effect and wetting by helium mixtures
 Critical Casimir effect and wetting by helium mixtures Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki, Frederic Caupin, Etienne Rolley To cite this version: Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki,
Critical Casimir effect and wetting by helium mixtures Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki, Frederic Caupin, Etienne Rolley To cite this version: Sebastien Balibar, Tomohiro Ueno, Takao Mizusaki,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 29 Dec 1996
 Chaotic enhancement of hydrogen atoms excitation in magnetic and microwave fields Giuliano Benenti, Giulio Casati Università di Milano, sede di Como, Via Lucini 3, 22100 Como, Italy arxiv:cond-mat/9612238v1
Chaotic enhancement of hydrogen atoms excitation in magnetic and microwave fields Giuliano Benenti, Giulio Casati Università di Milano, sede di Como, Via Lucini 3, 22100 Como, Italy arxiv:cond-mat/9612238v1
Superfluidity. v s. E. V. Thuneberg Department of Physical Sciences, P.O.Box 3000, FIN University of Oulu, Finland (Dated: June 8, 2012)
 Superfluidity E. V. Thuneberg Department of Physical Sciences, P.O.Box 3000, FIN-90014 University of Oulu, Finland (Dated: June 8, 01) PACS numbers: 67.40.-w, 67.57.-z, 74., 03.75.-b I. INTRODUCTION Fluids
Superfluidity E. V. Thuneberg Department of Physical Sciences, P.O.Box 3000, FIN-90014 University of Oulu, Finland (Dated: June 8, 01) PACS numbers: 67.40.-w, 67.57.-z, 74., 03.75.-b I. INTRODUCTION Fluids
Turbulence over arrays of obstacles in low temperature helium gas
 Eur. Phys. J. B 8, 363 369 (2) THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL B c EDP Sciences Società Italiana di Fisica Springer-Verlag 2 Turbulence over arrays of obstacles in low temperature helium gas H. Willaime
Eur. Phys. J. B 8, 363 369 (2) THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL B c EDP Sciences Società Italiana di Fisica Springer-Verlag 2 Turbulence over arrays of obstacles in low temperature helium gas H. Willaime
Landau damping of transverse quadrupole oscillations of an elongated Bose-Einstein condensate
 PHYSICAL REVIEW A 67, 053607 2003 Landau damping of transverse quadrupole oscillations of an elongated Bose-Einstein condensate M. Guilleumas 1 and L. P. Pitaevskii 2,3 1 Departament d Estructura i Constituents
PHYSICAL REVIEW A 67, 053607 2003 Landau damping of transverse quadrupole oscillations of an elongated Bose-Einstein condensate M. Guilleumas 1 and L. P. Pitaevskii 2,3 1 Departament d Estructura i Constituents
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 6 Mar 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 6 Mar 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 6 Mar 2005](/thumbs/82/86201785.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0503133v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 6 Mar 2005 Variant Monte Carlo algorithm for driven elastic strings in random media Abstract Alberto Rosso a and Werner Krauth b a Université de Genève 4, DPMC,
arxiv:cond-mat/0503133v1 [cond-mat.dis-nn] 6 Mar 2005 Variant Monte Carlo algorithm for driven elastic strings in random media Abstract Alberto Rosso a and Werner Krauth b a Université de Genève 4, DPMC,
A coherent picture for water at extreme negative pressure
 A coherent picture for water at extreme negative pressure Mouna El Mekki Azouzi 1, Claire Ramboz 2, Jean-François Lenain 3 and Frédéric Caupin 1 1 Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée et Nanostructures,
A coherent picture for water at extreme negative pressure Mouna El Mekki Azouzi 1, Claire Ramboz 2, Jean-François Lenain 3 and Frédéric Caupin 1 1 Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée et Nanostructures,
Looking back at superfluid helium
 Looking back at superfluid helium Sebastien Balibar To cite this version: Sebastien Balibar. Looking back at superfluid helium. Conference Bose Einstein Condensation, Institut henri Poincaré, Paris, 29
Looking back at superfluid helium Sebastien Balibar To cite this version: Sebastien Balibar. Looking back at superfluid helium. Conference Bose Einstein Condensation, Institut henri Poincaré, Paris, 29
CCMS Summer 2007 Lecture Series Fermi- and non-fermi Liquids Lecture 3: Fermi-liquid Theory
 CCMS Summer 2007 Lecture Series Fermi- and non-fermi Liquids Lecture 3: Fermi-liquid Theory Dmitrii L. Maslov maslov@phys.ufl.edu (Dated: July 22, 2007) 1 Notation 1 Here and thereafter, L1 stands for
CCMS Summer 2007 Lecture Series Fermi- and non-fermi Liquids Lecture 3: Fermi-liquid Theory Dmitrii L. Maslov maslov@phys.ufl.edu (Dated: July 22, 2007) 1 Notation 1 Here and thereafter, L1 stands for
Fermi Liquid and BCS Phase Transition
 Fermi Liquid and BCS Phase Transition Yu, Zhenhua November 2, 25 Abstract Landau fermi liquid theory is introduced as a successful theory describing the low energy properties of most fermi systems. Besides
Fermi Liquid and BCS Phase Transition Yu, Zhenhua November 2, 25 Abstract Landau fermi liquid theory is introduced as a successful theory describing the low energy properties of most fermi systems. Besides
Zero-Temprature Relaxation in Pure Fermi Liquids and Ferromagnetic Metals
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 110, Nos. 1/2, 1998 Zero-Temprature Relaxation in Pure Fermi Liquids and Ferromagnetic Metals A. E. Meyerovich and A. Stepaniants Department of Physics, University
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 110, Nos. 1/2, 1998 Zero-Temprature Relaxation in Pure Fermi Liquids and Ferromagnetic Metals A. E. Meyerovich and A. Stepaniants Department of Physics, University
Semiclassical theory of the quasi two-dimensional trapped Bose gas
 May 8 EPL, 8 (8) 3 doi:.9/95-575/8/3 www.epljournal.org Semiclassical theory of the quasi two-dimensional trapped Bose gas Markus Holzmann,, Maguelonne Chevallier 3 and Werner Krauth 3(a) LPTMC, Université
May 8 EPL, 8 (8) 3 doi:.9/95-575/8/3 www.epljournal.org Semiclassical theory of the quasi two-dimensional trapped Bose gas Markus Holzmann,, Maguelonne Chevallier 3 and Werner Krauth 3(a) LPTMC, Université
Quantum Fluids and Solids. Christian Enss (4He) & Henri Godfrin (3He)
 Quantum Fluids and Solids Christian Enss (4He) & Henri Godfrin (3He) What Do We Consider as Quantum Matter? φ Lennard Jones Potential σ ε r De Boer quantum parameter: De Broglie wavelength: Introduction
Quantum Fluids and Solids Christian Enss (4He) & Henri Godfrin (3He) What Do We Consider as Quantum Matter? φ Lennard Jones Potential σ ε r De Boer quantum parameter: De Broglie wavelength: Introduction
Neutrons on a surface of liquid helium.
 Neutrons on a surface of liquid helium. P. Grigoriev*, O. Zimmer**, A. Grigoriev +, and T. Ziman** * L. D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Chernogolovka, Russia; **Institute Laue-Laungevin, Grenoble,
Neutrons on a surface of liquid helium. P. Grigoriev*, O. Zimmer**, A. Grigoriev +, and T. Ziman** * L. D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics, Chernogolovka, Russia; **Institute Laue-Laungevin, Grenoble,
Degenerate atom-molecule mixture in a cold Fermi gas
 Degenerate atom-molecule mixture in a cold Fermi gas Koelmans, S.J.J.M.F.; Shlyapniov, G.V.; Salomon, C. Published in: Physical Review A : Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.69.031602
Degenerate atom-molecule mixture in a cold Fermi gas Koelmans, S.J.J.M.F.; Shlyapniov, G.V.; Salomon, C. Published in: Physical Review A : Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevA.69.031602
Publication P American Physical Society (APS) Reprinted by permission of American Physical Society.
 Publication P3 V. B. Eltsov, A. I. Golov, R. de Graaf, R. Hänninen, M. Krusius, V. S. L'vov, and R. E. Solntsev. 2007. Quantum turbulence in a propagating superfluid vortex front. Physical Review Letters,
Publication P3 V. B. Eltsov, A. I. Golov, R. de Graaf, R. Hänninen, M. Krusius, V. S. L'vov, and R. E. Solntsev. 2007. Quantum turbulence in a propagating superfluid vortex front. Physical Review Letters,
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 4 Mar 2014](/thumbs/85/93003961.jpg) ARTICLE Competing solutions of Landau s kinetic equation for zero sound and first sound in thin arbitrarily polarized Fermi-liquid films arxiv:403.0643v [cond-mat.other] 4 Mar 04 David Z. Li, R. H. Anderson,
ARTICLE Competing solutions of Landau s kinetic equation for zero sound and first sound in thin arbitrarily polarized Fermi-liquid films arxiv:403.0643v [cond-mat.other] 4 Mar 04 David Z. Li, R. H. Anderson,
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors
 Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas
 Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova Banff, May 205 Collaboration with: Francesco Ancilotto and Flavio Toigo Summary.
Shock waves in the unitary Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova Banff, May 205 Collaboration with: Francesco Ancilotto and Flavio Toigo Summary.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Collapse of superconductivity in a hybrid tin graphene Josephson junction array by Zheng Han et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Determination of the electronic mobility of graphene. 1.a extraction from
Collapse of superconductivity in a hybrid tin graphene Josephson junction array by Zheng Han et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION 1. Determination of the electronic mobility of graphene. 1.a extraction from
RECENT TOPICS IN THE THEORY OF SUPERFLUID 3 He
 RECENT TOPICS IN THE THEORY OF SUPERFLUID 3 He Lecture at ISSP Tokyo 13.5.2003 ErkkiThuneberg Department of physical sciences, University of Oulu Janne Viljas and Risto Hänninen Low temperature laboratory,
RECENT TOPICS IN THE THEORY OF SUPERFLUID 3 He Lecture at ISSP Tokyo 13.5.2003 ErkkiThuneberg Department of physical sciences, University of Oulu Janne Viljas and Risto Hänninen Low temperature laboratory,
QUANTUM BOUND STATES WITH ZERO BINDING ENERGY
 ψ hepth@xxx/940554 LA-UR-94-374 QUANTUM BOUND STATES WITH ZERO BINDING ENERGY Jamil Daboul Physics Department, Ben Gurion University of the Negev Beer Sheva, Israel and Michael Martin Nieto 2 Theoretical
ψ hepth@xxx/940554 LA-UR-94-374 QUANTUM BOUND STATES WITH ZERO BINDING ENERGY Jamil Daboul Physics Department, Ben Gurion University of the Negev Beer Sheva, Israel and Michael Martin Nieto 2 Theoretical
Physics 127a: Class Notes
 Physics 127a: Class Notes Lecture 15: Statistical Mechanics of Superfluidity Elementary excitations/quasiparticles In general, it is hard to list the energy eigenstates, needed to calculate the statistical
Physics 127a: Class Notes Lecture 15: Statistical Mechanics of Superfluidity Elementary excitations/quasiparticles In general, it is hard to list the energy eigenstates, needed to calculate the statistical
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 24 Jul 2001](/thumbs/91/105500630.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/010751v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Jul 001 Beyond the Thomas-Fermi Approximation for Nonlinear Dynamics of Trapped Bose-Condensed Gases Alexander L. Zubarev and Yeong E. Kim Department of Physics,
arxiv:cond-mat/010751v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 4 Jul 001 Beyond the Thomas-Fermi Approximation for Nonlinear Dynamics of Trapped Bose-Condensed Gases Alexander L. Zubarev and Yeong E. Kim Department of Physics,
arxiv: v3 [gr-qc] 30 Mar 2009
![arxiv: v3 [gr-qc] 30 Mar 2009 arxiv: v3 [gr-qc] 30 Mar 2009](/thumbs/87/96370633.jpg) THE JEANS MECHANISM AND BULK-VISCOSITY EFFECTS Nakia Carlevaro a, b and Giovanni Montani b, c, d, e a Department of Physics, Polo Scientifico Università degli Studi di Firenze, INFN Section of Florence,
THE JEANS MECHANISM AND BULK-VISCOSITY EFFECTS Nakia Carlevaro a, b and Giovanni Montani b, c, d, e a Department of Physics, Polo Scientifico Università degli Studi di Firenze, INFN Section of Florence,
Mechanisms of Interaction between Ultrasound and Sound in Liquids with Bubbles: Singular Focusing
 Acoustical Physics, Vol. 47, No., 1, pp. 14 144. Translated from Akusticheskiœ Zhurnal, Vol. 47, No., 1, pp. 178 18. Original Russian Text Copyright 1 by Akhatov, Khismatullin. REVIEWS Mechanisms of Interaction
Acoustical Physics, Vol. 47, No., 1, pp. 14 144. Translated from Akusticheskiœ Zhurnal, Vol. 47, No., 1, pp. 178 18. Original Russian Text Copyright 1 by Akhatov, Khismatullin. REVIEWS Mechanisms of Interaction
Monte Carlo Simulation of Bose Einstein Condensation in Traps
 Monte Carlo Simulation of Bose Einstein Condensation in Traps J. L. DuBois, H. R. Glyde Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware Newark, Delaware 19716, USA 1. INTRODUCTION In this paper
Monte Carlo Simulation of Bose Einstein Condensation in Traps J. L. DuBois, H. R. Glyde Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware Newark, Delaware 19716, USA 1. INTRODUCTION In this paper
LOCAL MOMENTS NEAR THE METAL-INSULATOR TRANSITION
 LOCAL MOMENTS NEAR THE METAL-INSULATOR TRANSITION Subir Sachdev Center for Theoretical Physics, P.O. Box 6666 Yale University, New Haven, CT 06511 This paper reviews recent progress in understanding the
LOCAL MOMENTS NEAR THE METAL-INSULATOR TRANSITION Subir Sachdev Center for Theoretical Physics, P.O. Box 6666 Yale University, New Haven, CT 06511 This paper reviews recent progress in understanding the
CMB Fluctuation Amplitude from Dark Energy Partitions
 SLAC-PUB-10916 Dec 2004 CMB Fluctuation Amplitude from Dark Energy Partitions James V. Lindesay, jlslac@slac.stanford.edu H. Pierre Noyes, noyes@slac.stanford.edu Stanford Linear Accelerator Center MS
SLAC-PUB-10916 Dec 2004 CMB Fluctuation Amplitude from Dark Energy Partitions James V. Lindesay, jlslac@slac.stanford.edu H. Pierre Noyes, noyes@slac.stanford.edu Stanford Linear Accelerator Center MS
Remarks on the tunneling limit of strong-field photoionization
 Remarks on the tunneling limit of strong-field photoionization Jarosław H. Bauer * Katedra Fizyki Teoretycznej Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego, Ul. Pomorska 149/153, 90-36 Łódź, Poland Some results from a recent
Remarks on the tunneling limit of strong-field photoionization Jarosław H. Bauer * Katedra Fizyki Teoretycznej Uniwersytetu Łódzkiego, Ul. Pomorska 149/153, 90-36 Łódź, Poland Some results from a recent
arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009
![arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009 arxiv: v1 [nucl-th] 7 Apr 2009](/thumbs/90/103476070.jpg) Thermodynamic properties of nuclear matter with three-body forces V. Somà, and P. Bożek,, Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, PL-- Kraków, Poland Institute of Physics, Rzeszów University, PL--99 Rzeszów,
Thermodynamic properties of nuclear matter with three-body forces V. Somà, and P. Bożek,, Institute of Nuclear Physics PAN, PL-- Kraków, Poland Institute of Physics, Rzeszów University, PL--99 Rzeszów,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 13 Mar 1998
 Stability of Solution of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation for the Bose-Einstein Condensation arxiv:cond-mat/9803174v1 13 Mar 1998 Yeong E. Kim and Alexander L. Zubarev Department of Physics, Purdue University
Stability of Solution of the Nonlinear Schrödinger Equation for the Bose-Einstein Condensation arxiv:cond-mat/9803174v1 13 Mar 1998 Yeong E. Kim and Alexander L. Zubarev Department of Physics, Purdue University
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 4 Aug 2003
 Conductivity of thermally fluctuating superconductors in two dimensions Subir Sachdev arxiv:cond-mat/0308063 v1 4 Aug 2003 Abstract Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven CT
Conductivity of thermally fluctuating superconductors in two dimensions Subir Sachdev arxiv:cond-mat/0308063 v1 4 Aug 2003 Abstract Department of Physics, Yale University, P.O. Box 208120, New Haven CT
1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate
 Physics 223b Lecture 4 Caltech, 04/11/18 1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate 1.6 Superfluid phase: topological defect Besides such smooth gapless excitations, superfluid can also support a very
Physics 223b Lecture 4 Caltech, 04/11/18 1 Superfluidity and Bose Einstein Condensate 1.6 Superfluid phase: topological defect Besides such smooth gapless excitations, superfluid can also support a very
!!"#!$%&' coefficient, D, naturally vary with different gases, but their
 Qualifying Examination Statistical Mechanics Fall, 2017 1. (Irreversible processes and fluctuations, 20 points + 5 bonus points) Please explain the physics behind the following phenomena in Statistical
Qualifying Examination Statistical Mechanics Fall, 2017 1. (Irreversible processes and fluctuations, 20 points + 5 bonus points) Please explain the physics behind the following phenomena in Statistical
Supplementary Figure 1: Depiction of Silicon Fabrication Process Process flow for patterning of Silicon wafer. 1. Growth of thick oxide using a wet
 Supplementary Figure 1: Depiction of Silicon Fabrication Process Process flow for patterning of Silicon wafer. 1. Growth of thick oxide using a wet oxidation process in an atmospheric pressure tube furnace.
Supplementary Figure 1: Depiction of Silicon Fabrication Process Process flow for patterning of Silicon wafer. 1. Growth of thick oxide using a wet oxidation process in an atmospheric pressure tube furnace.
Gaussian fluctuations in an ideal bose-gas a simple model
 Gaussian fluctuations in an ideal bose-gas a simple model A Petrova,, O Nedopekin, D Tayurskii and Q A Wang LUNAM Universite, ISMANS, Laboratoire de Physique Statistique et Systeme Complexes, 44, Avenue
Gaussian fluctuations in an ideal bose-gas a simple model A Petrova,, O Nedopekin, D Tayurskii and Q A Wang LUNAM Universite, ISMANS, Laboratoire de Physique Statistique et Systeme Complexes, 44, Avenue
Landau-Fermi liquid theory
 Landau- 1 Chennai Mathematical Institute April 25, 2011 1 Final year project under Prof. K. Narayan, CMI Interacting fermion system I Basic properties of metals (heat capacity, susceptibility,...) were
Landau- 1 Chennai Mathematical Institute April 25, 2011 1 Final year project under Prof. K. Narayan, CMI Interacting fermion system I Basic properties of metals (heat capacity, susceptibility,...) were
A novel type of incommensurate phase in quartz: The elongated-triangle phase
 A novel type of incommensurate phase in quartz: The elongated-triangle phase P. Saint-Grégoire, E. Snoeck and C. Roucau CEMES-LOE, BP 4347, 31055, Toulouse, Cédex, France I. Luk yanchuk L. D. Landau Institute
A novel type of incommensurate phase in quartz: The elongated-triangle phase P. Saint-Grégoire, E. Snoeck and C. Roucau CEMES-LOE, BP 4347, 31055, Toulouse, Cédex, France I. Luk yanchuk L. D. Landau Institute
CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI. INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY
 CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY E-mail: pietroni@pd.infn.it The formation of topological defects in a second order
CRITICAL SLOWING DOWN AND DEFECT FORMATION M. PIETRONI INFN - Sezione di Padova, via F. Marzolo 8, Padova, I-35131, ITALY E-mail: pietroni@pd.infn.it The formation of topological defects in a second order
Publications. Articles:
 Publications Articles: 1. R. Combescot Coupling between Planes and Chains in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 : A Possible Solution for the Order Parameter Controversy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 3732-3735 2. X. Leyronas
Publications Articles: 1. R. Combescot Coupling between Planes and Chains in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 : A Possible Solution for the Order Parameter Controversy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 3732-3735 2. X. Leyronas
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
A BCS Bose-Einstein crossover theory and its application to the cuprates
 A BCS Bose-Einstein crossover theory and its application to the cuprates Qijin Chen, Ioan Kosztin, Boldizsár Jankó, and K. Levin Citation: AIP Conf. Proc. 483, 22 (1999); doi: 10.1063/1.59579 View online:
A BCS Bose-Einstein crossover theory and its application to the cuprates Qijin Chen, Ioan Kosztin, Boldizsár Jankó, and K. Levin Citation: AIP Conf. Proc. 483, 22 (1999); doi: 10.1063/1.59579 View online:
Observations of the Motion of Single Electrons in Liquid Helium
 J Low Temp Phys (2007) 148: 199 206 DOI 10.1007/s10909-007-9373-2 Observations of the Motion of Single Electrons in Liquid Helium Wei Guo Humphrey J. Maris Published online: 31 May 2007 Springer Science+Business
J Low Temp Phys (2007) 148: 199 206 DOI 10.1007/s10909-007-9373-2 Observations of the Motion of Single Electrons in Liquid Helium Wei Guo Humphrey J. Maris Published online: 31 May 2007 Springer Science+Business
SUPERFLUIDTY IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES
 College de France, May 14, 2013 SUPERFLUIDTY IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES Sandro Stringari Università di Trento CNR-INFM PLAN OF THE LECTURES Lecture 1. Superfluidity in ultra cold atomic gases: examples
College de France, May 14, 2013 SUPERFLUIDTY IN ULTRACOLD ATOMIC GASES Sandro Stringari Università di Trento CNR-INFM PLAN OF THE LECTURES Lecture 1. Superfluidity in ultra cold atomic gases: examples
Wilsonian and large N theories of quantum critical metals. Srinivas Raghu (Stanford)
 Wilsonian and large N theories of quantum critical metals Srinivas Raghu (Stanford) Collaborators and References R. Mahajan, D. Ramirez, S. Kachru, and SR, PRB 88, 115116 (2013). A. Liam Fitzpatrick, S.
Wilsonian and large N theories of quantum critical metals Srinivas Raghu (Stanford) Collaborators and References R. Mahajan, D. Ramirez, S. Kachru, and SR, PRB 88, 115116 (2013). A. Liam Fitzpatrick, S.
The phonon dispersion relation of a Bose-Einstein condensate
 The phonon dispersion relation of a Bose-Einstein condensate I. Shammass, 1 S. Rinott, 2 A. Berkovitz, 2 R. Schley, 2 and J. Steinhauer 2 1 Department of Condensed Matter Physics, Weizmann Institute of
The phonon dispersion relation of a Bose-Einstein condensate I. Shammass, 1 S. Rinott, 2 A. Berkovitz, 2 R. Schley, 2 and J. Steinhauer 2 1 Department of Condensed Matter Physics, Weizmann Institute of
p 0 Transition in Superconductor-Ferromagnet-Superconductor Junctions 1
 JETP Letters, Vol. 74, No. 6, 2001, pp. 323 327. From Pis ma v Zhurnal Éksperimental noœ i Teoreticheskoœ Fiziki, Vol. 74, No. 6, 2001, pp. 357 361. Original English Text Copyright 2001 by Chtchelkatchev,
JETP Letters, Vol. 74, No. 6, 2001, pp. 323 327. From Pis ma v Zhurnal Éksperimental noœ i Teoreticheskoœ Fiziki, Vol. 74, No. 6, 2001, pp. 357 361. Original English Text Copyright 2001 by Chtchelkatchev,
Neutrino Interactions in Dense Matter
 Neutrino Interactions in Dense Matter 7th RESCEU International Symposium, Tokyo 11-14 November, 2008 C. J. Pethick Nordita and Niels Bohr International Academy Messages: Rates of neutrino processes important
Neutrino Interactions in Dense Matter 7th RESCEU International Symposium, Tokyo 11-14 November, 2008 C. J. Pethick Nordita and Niels Bohr International Academy Messages: Rates of neutrino processes important
Linear Theory of Evolution to an Unstable State
 Chapter 2 Linear Theory of Evolution to an Unstable State c 2012 by William Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 1 October 2012 2.1 Introduction The simple theory of nucleation that we introduced in
Chapter 2 Linear Theory of Evolution to an Unstable State c 2012 by William Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 1 October 2012 2.1 Introduction The simple theory of nucleation that we introduced in
VIII. Phase Transformations. Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition
 VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
Phenomenological Theories of Nucleation
 Chapter 1 Phenomenological Theories of Nucleation c 2012 by William Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 16 September 2012 1.1 Introduction These chapters discuss the problems of nucleation, spinodal
Chapter 1 Phenomenological Theories of Nucleation c 2012 by William Klein, Harvey Gould, and Jan Tobochnik 16 September 2012 1.1 Introduction These chapters discuss the problems of nucleation, spinodal
Full list of Frédéric Caupin s scientific communications
 Full list of Frédéric Caupin s scientific communications Thesis PhD thesis, Université Paris 6, spécialité Physique Quantique, supervised by Sébastien Balibar: Cavitation in helium 3: a Fermi liquid at
Full list of Frédéric Caupin s scientific communications Thesis PhD thesis, Université Paris 6, spécialité Physique Quantique, supervised by Sébastien Balibar: Cavitation in helium 3: a Fermi liquid at
Cold Metastable Neon Atoms Towards Degenerated Ne*- Ensembles
 Cold Metastable Neon Atoms Towards Degenerated Ne*- Ensembles Supported by the DFG Schwerpunktprogramm SPP 1116 and the European Research Training Network Cold Quantum Gases Peter Spoden, Martin Zinner,
Cold Metastable Neon Atoms Towards Degenerated Ne*- Ensembles Supported by the DFG Schwerpunktprogramm SPP 1116 and the European Research Training Network Cold Quantum Gases Peter Spoden, Martin Zinner,
Magnetic domain theory in dynamics
 Chapter 3 Magnetic domain theory in dynamics Microscale magnetization reversal dynamics is one of the hot issues, because of a great demand for fast response and high density data storage devices, for
Chapter 3 Magnetic domain theory in dynamics Microscale magnetization reversal dynamics is one of the hot issues, because of a great demand for fast response and high density data storage devices, for
A broad band detector of Gravitational Waves: The dual torus
 A broad band detector of Gravitational Waves: The dual torus M.BONALDI 1, M.CERDONIO 2, L.CONTI 2, M.PINARD 3, G.A.PRODI 4, L.TAFFARELLO 5, J.P.ZENDRI 5 1 Istituto di Fotonica e Nanotecnologie, ITC-CNR,
A broad band detector of Gravitational Waves: The dual torus M.BONALDI 1, M.CERDONIO 2, L.CONTI 2, M.PINARD 3, G.A.PRODI 4, L.TAFFARELLO 5, J.P.ZENDRI 5 1 Istituto di Fotonica e Nanotecnologie, ITC-CNR,
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
 PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 84 20 MARCH 2000 NUMBER 12 Bose-Einstein Condensation in Quasi-2D Trapped Gases D. S. Petrov, 1,2 M. Holzmann, 3,4 and G. V. Shlyapnikov 1,2,4 1 FOM Institute for Atomic
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 84 20 MARCH 2000 NUMBER 12 Bose-Einstein Condensation in Quasi-2D Trapped Gases D. S. Petrov, 1,2 M. Holzmann, 3,4 and G. V. Shlyapnikov 1,2,4 1 FOM Institute for Atomic
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 25 Jan 2012
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 25 Jan 2012 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.other] 25 Jan 2012](/thumbs/74/70882788.jpg) Knudsen-Hydrodynamic Crossover in Liquid He in High Porosity Aerogel H. Takeuchi, S. Higashitani, and K. Nagai Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, Kagamiyama -7-, Higashi-Hiroshima
Knudsen-Hydrodynamic Crossover in Liquid He in High Porosity Aerogel H. Takeuchi, S. Higashitani, and K. Nagai Graduate School of Integrated Arts and Sciences, Hiroshima University, Kagamiyama -7-, Higashi-Hiroshima
Infrared absorption and emission spectrum of electron bubbles attached to linear vortices in liquid 4 He
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics - QFS2009 manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Infrared absorption and emission spectrum of electron bubbles attached to linear vortices in liquid 4 He D.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics - QFS2009 manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Infrared absorption and emission spectrum of electron bubbles attached to linear vortices in liquid 4 He D.
Study of Supersolidity and Shear Modulus Anomaly of 4 He in a Triple Compound Oscillator
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series Study of Supersolidity and Shear Modulus Anomaly of 4 He in a Triple Compound Oscillator To cite this article: Xiao Mi et al 01 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400 01047 Related
Journal of Physics: Conference Series Study of Supersolidity and Shear Modulus Anomaly of 4 He in a Triple Compound Oscillator To cite this article: Xiao Mi et al 01 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 400 01047 Related
Atomic Motion in a Laser Standing Wave
 Atomic Motion in a Laser Standing Wave J. DaJjbard, C. Salomon, A. Aspect, H. MetcaJf( *), A. Heidmann, and C. Cohen- Tannoudji Laboratoire de Spectroscopie Hertzienne de l'ens et Collège de France, 24
Atomic Motion in a Laser Standing Wave J. DaJjbard, C. Salomon, A. Aspect, H. MetcaJf( *), A. Heidmann, and C. Cohen- Tannoudji Laboratoire de Spectroscopie Hertzienne de l'ens et Collège de France, 24
Pairing in Nuclear and Neutron Matter Screening effects
 Pairing Degrees of Freedom in Nuclei and Nuclear Medium Seattle, Nov. 14-17, 2005 Outline: Pairing in Nuclear and Neutron Matter Screening effects U. Lombardo pairing due to the nuclear (realistic) interaction
Pairing Degrees of Freedom in Nuclei and Nuclear Medium Seattle, Nov. 14-17, 2005 Outline: Pairing in Nuclear and Neutron Matter Screening effects U. Lombardo pairing due to the nuclear (realistic) interaction
Superfluidity and Condensation
 Christian Veit 4th of June, 2013 2 / 29 The discovery of superfluidity Early 1930 s: Peculiar things happen in 4 He below the λ-temperature T λ = 2.17 K 1938: Kapitza, Allen & Misener measure resistance
Christian Veit 4th of June, 2013 2 / 29 The discovery of superfluidity Early 1930 s: Peculiar things happen in 4 He below the λ-temperature T λ = 2.17 K 1938: Kapitza, Allen & Misener measure resistance
Effective interaction dependence of the liquid-gas phase transition in symmetric nuclear matter
 Effective interaction dependence of the liquid-gas phase transition in symmetric nuclear matter Arnau Rios Department of Physics, Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford,
Effective interaction dependence of the liquid-gas phase transition in symmetric nuclear matter Arnau Rios Department of Physics, Faculty of Engineering and Physical Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford,
Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line.
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers
 Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers M. E. Gracheva, V. A. Kashurnikov, a) and I. A. Rudnev Moscow State Engineering Physics
Features of the melting dynamics of a vortex lattice in a high-t c superconductor in the presence of pinning centers M. E. Gracheva, V. A. Kashurnikov, a) and I. A. Rudnev Moscow State Engineering Physics
Division of drops of a liquid crystal in the case of a cholesteric-smectic-a phase transition
 'C. K. Chen, A. R. B. de Castro, and '0. A. Aktsipetrov, E. D. Mishina, and A. Lett. 37, 707 (198311. 30. A. Aktsipetrov and E. D. Mishina, Pis'ma Z Fiz. 38, 442 (1983) [JETP Lett. 38, 535 (19a3)l. 4C.
'C. K. Chen, A. R. B. de Castro, and '0. A. Aktsipetrov, E. D. Mishina, and A. Lett. 37, 707 (198311. 30. A. Aktsipetrov and E. D. Mishina, Pis'ma Z Fiz. 38, 442 (1983) [JETP Lett. 38, 535 (19a3)l. 4C.
Electrons and cavitation in liquid helium
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 5 1 FEBRUARY 1998-I Electrons and cavitation in liquid helium J. Classen,* C.-K. Su, M. Mohazzab, and H. J. Maris Department of Physics, Brown University, Providence,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 5 1 FEBRUARY 1998-I Electrons and cavitation in liquid helium J. Classen,* C.-K. Su, M. Mohazzab, and H. J. Maris Department of Physics, Brown University, Providence,
ERRATA. Observation of the Local Structure of Landau Bands in a Disordered Conductor [Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1540 (1997)]
![ERRATA. Observation of the Local Structure of Landau Bands in a Disordered Conductor [Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1540 (1997)] ERRATA. Observation of the Local Structure of Landau Bands in a Disordered Conductor [Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1540 (1997)]](/thumbs/88/115990000.jpg) ERRATA Observation of the Local Structure of Landau Bands in a Disordered Conductor [Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1540 (1997)] T. Schmidt, R. J. Haug, Vladimir I. Fal ko, K. v. Klitzing, A. Förster, and H. Lüth
ERRATA Observation of the Local Structure of Landau Bands in a Disordered Conductor [Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 1540 (1997)] T. Schmidt, R. J. Haug, Vladimir I. Fal ko, K. v. Klitzing, A. Förster, and H. Lüth
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact
 Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Thermodynamics of nuclei in thermal contact Karl-Heinz Schmidt, Beatriz Jurado CENBG, CNRS/IN2P3, Chemin du Solarium B.P. 120, 33175 Gradignan, France Abstract: The behaviour of a di-nuclear system in
Features of interaction of microwaves with He II
 Features of interaction of microwaves with He II V.D. Khodusov and A.S. Naumovets V.N.Karazin Kharkov National University, 4 Svobody sq., 6077 Kharkov, Ukraine Based on interrelation between the thermodynamic
Features of interaction of microwaves with He II V.D. Khodusov and A.S. Naumovets V.N.Karazin Kharkov National University, 4 Svobody sq., 6077 Kharkov, Ukraine Based on interrelation between the thermodynamic
Viscous non-linear theory of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability. Abstract
 Viscous non-linear theory of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Pierre Carles and Stéphane Popinet Laboratoire de Modélisation en Mécanique, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Case 162, 4 place Jussieu, 75252
Viscous non-linear theory of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Pierre Carles and Stéphane Popinet Laboratoire de Modélisation en Mécanique, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Case 162, 4 place Jussieu, 75252
On the Critical Exponents for the l Transition in Liquid Helium
 ISSN 0021-3640, JETP Letters, 2007, Vol. 86, No. 1, pp. 39 45. Original Russian Text A.A. Pogorelov, I.M. Suslov, 2007, published in Pis ma v Zhurnal Éksperimental noœ i Teoreticheskoœ Fiziki, 2007, Vol.
ISSN 0021-3640, JETP Letters, 2007, Vol. 86, No. 1, pp. 39 45. Original Russian Text A.A. Pogorelov, I.M. Suslov, 2007, published in Pis ma v Zhurnal Éksperimental noœ i Teoreticheskoœ Fiziki, 2007, Vol.
The Superuid Transition in Liquid Helium 4
 Master M2 Sciences de la Matière ENS de Lyon 2015-2016 Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena The Superuid Transition in Liquid Helium 4 Jason Reneuve January 15, 2016 Abstract At T λ = 2.17K, helium
Master M2 Sciences de la Matière ENS de Lyon 2015-2016 Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena The Superuid Transition in Liquid Helium 4 Jason Reneuve January 15, 2016 Abstract At T λ = 2.17K, helium
Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model
 Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model Yakov M. Strelniker, Shlomo Havlin, Richard Berkovits, and Aviad Frydman Minerva Center, Jack and Pearl Resnick Institute of Advanced Technology,
Resistance distribution in the hopping percolation model Yakov M. Strelniker, Shlomo Havlin, Richard Berkovits, and Aviad Frydman Minerva Center, Jack and Pearl Resnick Institute of Advanced Technology,
Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars
 1 Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars U. Lombardo a, Caiwan Shen a,n.vangiai b,w.zuo c a INFN-LNS,via S.Sofia 44 95129 Catania, Italy b Institut de Physique Nucléaire,F-91406, Orsay France c Institute
1 Neutrino Mean Free Path in Neutron Stars U. Lombardo a, Caiwan Shen a,n.vangiai b,w.zuo c a INFN-LNS,via S.Sofia 44 95129 Catania, Italy b Institut de Physique Nucléaire,F-91406, Orsay France c Institute
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Dec 2009 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 14 Dec 2009](/thumbs/75/72684721.jpg) Decoherence and relaxation of single electron excitations in quantum Hall edge channels. arxiv:97.2996v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 4 Dec 29 P. Degiovanni, Ch. Grenier, and G. Fève 2,3 () Université de Lyon,
Decoherence and relaxation of single electron excitations in quantum Hall edge channels. arxiv:97.2996v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 4 Dec 29 P. Degiovanni, Ch. Grenier, and G. Fève 2,3 () Université de Lyon,
New phases of liquid 3 He at low temperature
 New phases of liquid 3 He at low temperature Jitong Yu December 11, 2007 1. Abstract This paper introduces the properties of superfluid 3 He by a brief review of the history of experimental discovery and
New phases of liquid 3 He at low temperature Jitong Yu December 11, 2007 1. Abstract This paper introduces the properties of superfluid 3 He by a brief review of the history of experimental discovery and
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Aug 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Aug 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Aug 2007](/thumbs/94/119649341.jpg) Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:0708.414v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Aug 007 Luca Salasnich 1 and Flavio Toigo Shell Effects in the First Sound Velocity
Journal of Low Temperature Physics manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) arxiv:0708.414v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 30 Aug 007 Luca Salasnich 1 and Flavio Toigo Shell Effects in the First Sound Velocity
Landau s Fermi Liquid Theory
 Thors Hans Hansson Stockholm University Outline 1 Fermi Liquids Why, What, and How? Why Fermi liquids? What is a Fermi liquids? Fermi Liquids How? 2 Landau s Phenomenological Approach The free Fermi gas
Thors Hans Hansson Stockholm University Outline 1 Fermi Liquids Why, What, and How? Why Fermi liquids? What is a Fermi liquids? Fermi Liquids How? 2 Landau s Phenomenological Approach The free Fermi gas
V. FERMI LIQUID THEORY
 V. FERMI LIQUID THEORY Markus Holzmann LPMMC, Maison de Magistère, Grenoble, and LPTMC, Jussieu, Paris markus@lptl.jussieu.fr http://www.lptl.jussieu.fr/users/markus/cours.html (Dated: March 30, 2010)
V. FERMI LIQUID THEORY Markus Holzmann LPMMC, Maison de Magistère, Grenoble, and LPTMC, Jussieu, Paris markus@lptl.jussieu.fr http://www.lptl.jussieu.fr/users/markus/cours.html (Dated: March 30, 2010)
arxiv:chao-dyn/ v1 27 Nov 1998
 Kolmogorov equation in fully developed turbulence F. Moisy, P. Tabeling, H. Willaime Laboratoire de Physique Statistique, École Normale Supérieure 24 rue Lhomond, 75231 Paris (France) arxiv:chao-dyn/9812002v1
Kolmogorov equation in fully developed turbulence F. Moisy, P. Tabeling, H. Willaime Laboratoire de Physique Statistique, École Normale Supérieure 24 rue Lhomond, 75231 Paris (France) arxiv:chao-dyn/9812002v1
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3
 The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
The Superfluid Phase s of Helium 3 DIETER VOLLHARD T Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen, Federal Republic of German y PETER WÖLFL E Universität Karlsruhe Federal Republic of Germany PREFACE
