Los Alamos National Laboratory Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 1 LA-UR
|
|
|
- Jeffery Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Rayleigh-Taylor instability is generated when a heavy fluid sits above a lighter fluid in a gravitational field. The flow behavior is described in terms of bubbles of light fluid rising into the heavier medium and spikes of heavy fluid dropping into the lighter. More generally a material interface is said to be Rayleigh-Taylor unstable whenever the fluid acceleration has an opposite direction to the density gradient. Rayleigh-Taylor instability occurs in a variety of applications ranging from thermal down drafts caused by the suspension of a cold body of air above a warm region, to instability in inertial confinement laser fusion. The classical study of Rayleigh-Taylor instability was for incompressible flows, but much recent work has been devoted to understanding the more complex compressible regime. A major component of this research is devoted to understanding the behavior and growth of the mixing region between the two fluids. Various models have been proposed to predict the rate of growth of the mixing region, and direct numerical simulation plays an important role both in validating the models as well as providing a computational laboratory to gain insight and understanding of the flow. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 1
2 A= h + l 2 g = 02. M = = c h l h = 1.4 t = M g A Kelvin-Hemholtz like shear flow is developed in the wakes of the bubble and spike generating a vortex around the side of both the bubbles and the spikes. The computation is performed in a regular grid and the grid-based tracking algorithm is used. From left to right t = 4, t = 8, t = 12 and t = 16. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 2
3 2 A= 02., M = 05., = 1.4 The computation is performed in a regular grid. The figures show views of the bubble and spike. The surface grid is show on the right. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 3
4 In this simulation there are four bubbles of different radii. The largest bubble moves ahead of the others and eventually pinches off from the main interface. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 4
5 Richtmyer-Meshkov instability is a material surface instability generated by the refraction of shock wave through a material interface. It occurs in such applications as inertial confinement fusion and such natural phenomena as a supernova explosion. The schematic diagram below illustrates the process. A shock refracts through a material surface imparting differential vorticity along the interface. This velocity shear in turn drives the penetration of the heavy fluid into the light fluid. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 5
6 Benjamin Experiment Meshkov Experiment Shocked Air = 1.27 g/l, P = 1.2 Bar Mach 1.2 Shock Air = 0.95 g/l, P = 0.8 Bar, = 1.09 Shocked Air = 2.3 g/l, P = 2.56 Bar Mach 1.52 Shock Air = 1.2 g/l, P = Bar, = cm SF 6 = 4.85 g/l P = 0.8 Bar = 1.09 He = g/l P = Bar = cm 3.75 cm 4.0 cm Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 6
7 Pressure plots at a series of times for the nonlinear air-sf 6 solution. A cascade of shock waves generated by the selfinteraction of the transmitted and reflected waves propagate back toward the interface and affect the perturbation growth rate at early and intermediate times. For reference we have labeled in the first frame the transmitted shock (T), the interface (I) and the reflected shock (R). Note that the color map has been adjusted so that the full range of color occurs within the region of interest (between the transmitted and reflected shocks). The blue regions at the left and right have pressures of 0.8 bars and 1.1 bars, respectively. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 7
8 A series of calculations were carried out for a set of three initial amplitudes of decreasing size. The figures show results for shocked air-sf 6 and air-he interfaces, respectively. Amplitude convergence is measured in terms of the relative difference between the nonlinear and linear solutions, (a(t) = a lin (t)) / (a lin (t) + a(0 )) where a(0 ) is the initial amplitude of the perturbation. The horizontal axis is in dimensionless time units kc 0 M 0 t, where k is the wave number of the perturbation, c 0 is the sound speed in the air ahead of the incident shock and M 0 is the incident shock Mach number. One dimensionless time unit is equivalent to approximately 14 s for air-sf 6 case and 12.2 s for air helium. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 8
9 This graph compares the results of experimental averages, front tracking simulation, linear theory and Richtmyer's impulsive model. Also shown are results of a least squares fit to the front tracking amplitude data over the period of experimental observation. Note that the front tracking average growth rate is indistinguishable from the experimental value in figure (b). The plus marks (+) show the results of one particular experiment. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 9
10 The full amplitude growth rate is defined as da/dt(t) = (v spike v bubble )/2. Note how certain events in the amplitude growth rate occur at either the spike or the bubble, but not both. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 10
11 The figures show comparisons of simulations of the Benjamin air-sf 6 experiment and the Meshkov air-he experiments with the solution to the linearized equations. The comparisons are at t = 195 µs on the left and 65 µs on the right. A key feature is that the linearized solutions fail to capture the sharp shock fronts seen in the full Euler solutions. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 11
12 Guy Dimonte, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Bruce Fryxell, Goddard Space Flight Center Michael L. Gittings, Science Applications International Corporation John W. Grove, Richard L. Holmes, Marilyn Schneider Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory David H. Sharp, Robert P. Weaver, Alexander L.Velikovich, Berkeley Research Associates Qiang Zhang, University at Stony Brook Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 12
13 Compare three independent codes RAGE: AMR, 2nd order Godunov hydro PROMETHEUS: Uniform grid, PPM hydro FronTier: Front tracking coupled with 2nd order Godunov hydro Validate codes against experimental data in a particularly interesting regime Improved confidence in predictive capabilities of simulations Study of validity and behavior of simulations and theories over a wide range of conditions Seven combinations of initial shock strength and initial perturbation amplitude Improve understanding of relationship between experiment, simulation and theory Variety of researchers involved helped Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 13
14 Beryllium mated to foam with a perturbed interface between them Plasmas at time of data acquisition Materials modeled as perfect gases Incident shock generated by ablation at rear surface of beryllium Perturbations: single-mode sinusoidal Shock Direction wavelength 100 µm, amplitude 10 µm Strong incident shock Mach 15.3 Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 14
15 Experimental Radiograph RAGE FronTier PROMETHEUS Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 15
16 Experimental Radiograph RAGE FronTier PROMETHEUS Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 16
17 RAGE FronTier PROMETHEUS Do any of the codes have the secondary structure right? How would we know? 1 2 Density (g/cc) Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 17
18 RAGE FronTier PROMETHEUS Pressure (Mbar) Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 18
19 Growth rate (µm/ns) Amplitude (µm) Time (ns) Amplitude (µm) Time (ns) Time (ns) FronTier RAGE PROMETHEUS Impulsive Model Linear Theory Zhang/Sohn Experimental Growth Rate Experiment/Face-on Ampl. Experiment/Side-on Ampl. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 19
20 Foam = 012. g/ cc, ρ = 006. g/ cc, correlation length = 20 m P= 01. Mbar v = 0 = 1.45 r = 25cos 8 Mach 30 Expanding Shock r = 0 10 Material Interface 800 µm, 400 y Unshocked Beryllium = 17. g/ cc, = 085. g/ cc, correlation length = 20 m ρ P = 01. Mbar v = 0 = µm, 400 x Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 20
21 Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 21
22 Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 22
23 Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 23
24 Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 24
25 The next computation is a simulation of the supersonic injection of a gas into a closed box. The initial flow parameters are: Region Outside of Jet Air, = 1.4 =1g/l = 1bar x = = y 0 Computational Region: width 25 cm, 400 x height 50 cm, 800 y Inlet, width = 2.5 cm Air, = 1.4 =10g/l = 10 bar y x x y = 0 cm / sec = 6.3 cm / µ sec = cm / µ sec = 6.3 cm / µ sec correlation length = 0.25 cm correlation time = 7.9 µ sec Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 25
26 t = 380 µsec t = 760 µsec Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 26
27 t = msec t = 1.52 msec Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 27
28 These calculations are intended to study the behavior of the refraction of a bow wave generated by a supersonic projectile through the surface of the ocean. The calculations show a projectile with the shape of an ellipse of diameters 3 by 0.5 meters, traveling at 500 meters per second at an altitude of 5 meters above a flat body of water. The projectile is traveling in air, which is modeled as a perfect gas with γ = 1.4 and density of 1 gram/liter and ambient pressure of 1 bar. The water is modeled as a stiffened polytropic gas, which has an equation of state of the form: and ρ = 1 gram/liter. P Γ + 1 e = + E, E = P, Γ = 6, and, P = 3040 bar Γ Γ Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 28
29 Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 29
30 . Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 30
31 . Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 31
32 . Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 32
33 Conservation and Front Tracking Algorithm makes conservation error on the order of the truncation error near the front. These are generally first order. Exact conservation requires the construction of adaptive space-time grids near the front. Conservation means that only waves that satisfy the Rankine-Hugoniot conditions can support discontinuities. Sharp fronts require that volume cells must not cross fronts. Thus the finite volume cells must be aligned in space and time with the discrete fronts if exact conservation of all quantities is to be imposed. Adaptive mesh algorithms and front tracking. Much of the infrastructure of FronTier assumes a regular rectangular grid. Current development efforts are being directed towards replacing the rectangular grid with a binary by dimension tree structured grid. Improved Three Dimensional Capabilities: continue to improve the robustness and performance of the three dimensional front tracking code to provide a computational tool for studying complex flows. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 33
34 More General Physics: Elasto-plasticity: FronTier now supports an elasto-plasticity library. Development is proceeding to implement improved solvers and interface propagation algorithms in this module. Multiphase flow models: many new theoretical models are being invented to describe meso-scale mixing in which the fluids are separate at a molecular level, but are entrained at length scales that are very small with respect to the computational grid spacing. Designing and implementing these methods is a major thrust in our development effort. Improved Performance on Parallel Computers: These are the machines we have, we want to use them as effectively as possible. FronTier already supports domain decomposition parallelism, continuing work will be devoted to scaling the code from the current processor mode to as many as 1000 processors. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 34
35 Improved usability of the code: Add a graphical user interface for problem setup. Enhance and add to the diagnostic capabilities of the code. Incorporation of new advances in finite different and finite element technology. Modular structure of the code can be improved to allow easier insertion of new finite difference methods. Implement unsplit solvers. Theoretical and Numerical Investigations Study the behavior of fluid mixing zones generated by Rayleigh- Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov instability. Study the role of vorticity in the growth of unstable features on an interface. Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 35
36 1. J. W. Grove, R. L. Holmes, D. H. Sharp, Y. Yang, and Q. Zhang, Quantitative theory of Richtmyer-Meshkov instability, Phys. Rev. Lett. 71 pp R. L. Holmes, J. W. Grove, and D. H. Sharp, Numerical investigation of Richtmyer- Meshkov instability using front tracking, J. Fluid Mech. 301 pp , Y. Chen, J. Glimm, D. H. Sharp, and Q. Zhang, A two-phase flow model of the Rayleigh- Taylor mixing zone, Phys. Fluids, 8, pp J. Glimm, X.-L. Li, R. Menikoff, D. H. Sharp, and Q. Zhang, A numerical study of bubble interactions in Rayleigh-Taylor instability for compressible fluids, Phys. Fluids A, 2 pp , J. Glimm, J. W. Grove, X.-L. Li, K.-M. Shyue, Q. Zhang, and Y. Zeng, Three dimensional front tracking, SIAM J. Sci. Comp. 19, pp D. L. Youngs, Numerical simulation of turbulent mixing by Rayleigh-Taylor instability, Physica D, 12, pp X.-L. Li, Study of three dimensional Rayleigh-Taylor instability in compressible fluids through level set method and parallel computation, Phys. Fluids A, 5, pp Hydrodynamic Methods Applications and Research 36
Spherical Richtmyer-Meshkov instability for axisymmetric flow
 Mathematics and Computers in Simulation 65 (2004) 417 430 Spherical Richtmyer-Meshkov instability for axisymmetric flow Srabasti Dutta a, James Glimm a,b, John W. Grove c, David H. Sharp d, Yongmin Zhang
Mathematics and Computers in Simulation 65 (2004) 417 430 Spherical Richtmyer-Meshkov instability for axisymmetric flow Srabasti Dutta a, James Glimm a,b, John W. Grove c, David H. Sharp d, Yongmin Zhang
A Vortex Model for Studying the Effect of Shock Proximity on Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability at High Mach Number
 A Vortex Model for Studying the Effect of Shock Proximity on Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability at High Mach Number H. F. Robey, S. G. Glendinning, J. A. Greenough, & S. V. Weber Lawrence Livermore National
A Vortex Model for Studying the Effect of Shock Proximity on Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability at High Mach Number H. F. Robey, S. G. Glendinning, J. A. Greenough, & S. V. Weber Lawrence Livermore National
2 In this paper, we give a brief summary of the front tracking algorithm for axisymmetric ow. We report simulations of spherical shock refraction by a
 A Fast Algorithm for Moving Interface Problems S. Dutta 1,J.Glimm 1 2,J.W.Grove 3,D.H.Sharp 4, and Y. Zhang 1 1 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, University at Stony Brook, Stony Brook,
A Fast Algorithm for Moving Interface Problems S. Dutta 1,J.Glimm 1 2,J.W.Grove 3,D.H.Sharp 4, and Y. Zhang 1 1 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, University at Stony Brook, Stony Brook,
Shock wave interactions in spherical and perturbed spherical geometries
 Nonlinear Analysis 63 (2005) 644 652 www.elsevier.com/locate/na Shock wave interactions in spherical and perturbed spherical geometries S. Dutta a, E. George a, J. Glimm a,b,, J.W. Grove c,h.jin a, T.
Nonlinear Analysis 63 (2005) 644 652 www.elsevier.com/locate/na Shock wave interactions in spherical and perturbed spherical geometries S. Dutta a, E. George a, J. Glimm a,b,, J.W. Grove c,h.jin a, T.
Oblique shock interaction with a cylindrical density interface
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 161 Oblique shock interaction with a cylindrical density interface P. Wayne 1, D. Olmstead 1, P. Vorobieff 1, C. R. Truman 1 & S. Kumar 2 1 Department of Mechanical
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 161 Oblique shock interaction with a cylindrical density interface P. Wayne 1, D. Olmstead 1, P. Vorobieff 1, C. R. Truman 1 & S. Kumar 2 1 Department of Mechanical
Inertial-Range Dynamics and Mixing: Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Cambridge, UK, 29 September to 3 October 2008
 Inertial-Range Dynamics and Mixing: Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Cambridge, UK, 29 September to 3 October 2008 MIXING DUE TO RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR INSTABILITY David Youngs AWE Aldermaston
Inertial-Range Dynamics and Mixing: Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Cambridge, UK, 29 September to 3 October 2008 MIXING DUE TO RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR INSTABILITY David Youngs AWE Aldermaston
470 SADOT ET AL. Vol. 127
 THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL SUPPLEMENT SERIES, 127:469È473, 2000 April ( 2000. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES ON THE NONLINEAR EVOLUTION OF THE RICHTMYER-MESHKOV
THE ASTROPHYSICAL JOURNAL SUPPLEMENT SERIES, 127:469È473, 2000 April ( 2000. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. STUDIES ON THE NONLINEAR EVOLUTION OF THE RICHTMYER-MESHKOV
Radiation-coupled front-tracking simulations for laser-driven shock experiments
 Nonlinear Analysis 6 (5) e65 e6 www.elsevier.com/locate/na Radiation-coupled front-tracking simulations for laser-driven shock experiments Yongmin Zhang a,, R. Paul Drake b, James Glimm a,c, John W. Grove
Nonlinear Analysis 6 (5) e65 e6 www.elsevier.com/locate/na Radiation-coupled front-tracking simulations for laser-driven shock experiments Yongmin Zhang a,, R. Paul Drake b, James Glimm a,c, John W. Grove
Viscous non-linear theory of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability. Abstract
 Viscous non-linear theory of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Pierre Carles and Stéphane Popinet Laboratoire de Modélisation en Mécanique, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Case 162, 4 place Jussieu, 75252
Viscous non-linear theory of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Pierre Carles and Stéphane Popinet Laboratoire de Modélisation en Mécanique, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Case 162, 4 place Jussieu, 75252
Numerical simulation of supernova-relevant laser-driven hydro experiments on OMEGA
 PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 7 JULY 2004 Numerical simulation of supernova-relevant laser-driven hydro experiments on OMEGA A. R. Miles a) Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, California
PHYSICS OF PLASMAS VOLUME 11, NUMBER 7 JULY 2004 Numerical simulation of supernova-relevant laser-driven hydro experiments on OMEGA A. R. Miles a) Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, California
On The Collapse of a Gas Cavity by an Imploding Molten Lead Shell and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability
 On The Collapse of a Gas Cavity by an Imploding Molten Lead Shell and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Victoria Suponitsky, Sandra Barsky, and Aaron Froese General Fusion Inc., 8-368 Bonneville Place, Burnaby,
On The Collapse of a Gas Cavity by an Imploding Molten Lead Shell and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Victoria Suponitsky, Sandra Barsky, and Aaron Froese General Fusion Inc., 8-368 Bonneville Place, Burnaby,
Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform Related content - Mix and hydrodynamic instabilities
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic instability measurements in DTlayered ICF capsules using the layered-hgr platform Related content - Mix and hydrodynamic instabilities
Effects of inclination angle on a shock-accelerated heavy gas column
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 171 Effects of inclination angle on a shock-accelerated heavy gas column D. Olmstead, C. R. Truman, P. Wayne & P. Vorobieff Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VIII 171 Effects of inclination angle on a shock-accelerated heavy gas column D. Olmstead, C. R. Truman, P. Wayne & P. Vorobieff Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Target Simulations. Roman Samulyak in collaboration with Y. Prykarpatskyy, T. Lu
 Muon Collider/Neutrino Factory Collaboration Meeting May 26 28, CERN, Geneva U.S. Department of Energy Target Simulations Roman Samulyak in collaboration with Y. Prykarpatskyy, T. Lu Center for Data Intensive
Muon Collider/Neutrino Factory Collaboration Meeting May 26 28, CERN, Geneva U.S. Department of Energy Target Simulations Roman Samulyak in collaboration with Y. Prykarpatskyy, T. Lu Center for Data Intensive
Turbulent mixing with physical mass diffusion
 Turbulent mixing with physical mass diffusion Xinfeng Liu, 1 Erwin George, 1 Wurigen Bo, 1 and J. Glimm 1,2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New
Turbulent mixing with physical mass diffusion Xinfeng Liu, 1 Erwin George, 1 Wurigen Bo, 1 and J. Glimm 1,2 1 Department of Applied Mathematics and Statistics, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New
GDR Turbulence Poitiers Octobre 2012 EXPERIMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION OF AN AIR/SF6 TURBULENT MIXING ZONE INDUCED BY THE RICHTMYER-MESHKOV INSTABILITY
 GDR Turbulence Poitiers Octobre 2012 EXPERIMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION OF AN AIR/SF6 TURBULENT MIXING ZONE INDUCED BY THE RICHTMYER-MESHKOV INSTABILITY G. Bouzgarrou, Y. Bury, S. Jamme and L. Joly ISAE-DAEP,
GDR Turbulence Poitiers Octobre 2012 EXPERIMENTAL CHARACTERIZATION OF AN AIR/SF6 TURBULENT MIXING ZONE INDUCED BY THE RICHTMYER-MESHKOV INSTABILITY G. Bouzgarrou, Y. Bury, S. Jamme and L. Joly ISAE-DAEP,
Validating the FLASH Code: Vortex Dominated Flows
 Validating the FLASH Code: Vortex Dominated Flows Greg Weirs, Vikram Dwarkadas, Tomek Plewa ASCI FLASH Center, University of Chicago vikram@flash.uchicago.edu, tomek@flash.uchicago.edu, weirs@flash.uchicago.edu
Validating the FLASH Code: Vortex Dominated Flows Greg Weirs, Vikram Dwarkadas, Tomek Plewa ASCI FLASH Center, University of Chicago vikram@flash.uchicago.edu, tomek@flash.uchicago.edu, weirs@flash.uchicago.edu
Analogues of Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov instabilities in flows with nonuniform particle and droplet seeding
 Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VI 17 Analogues of Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov instabilities in flows with nonuniform particle and droplet seeding P. Vorobieff 1, M. Anderson 1, J. Conroy
Computational Methods in Multiphase Flow VI 17 Analogues of Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov instabilities in flows with nonuniform particle and droplet seeding P. Vorobieff 1, M. Anderson 1, J. Conroy
Three Dimensional Models of RR Lyrae Pulsation
 Regional Variable Star Conference: Physics & Astronomy Department, Michigan State University: 40 Years of Variable Stars: A Celebration of Contributions by Horace A. Smith ed. K. Kinemuchi (Sunspot, NM:
Regional Variable Star Conference: Physics & Astronomy Department, Michigan State University: 40 Years of Variable Stars: A Celebration of Contributions by Horace A. Smith ed. K. Kinemuchi (Sunspot, NM:
Rayleigh Taylor Instability Experiments in a Cylindrically Convergent Geometry
 Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Investigation of an implicit solver for the simulation of bubble oscillations using Basilisk
 Investigation of an implicit solver for the simulation of bubble oscillations using Basilisk D. Fuster, and S. Popinet Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 6, CNRS, UMR 79 Institut Jean Le Rond d Alembert,
Investigation of an implicit solver for the simulation of bubble oscillations using Basilisk D. Fuster, and S. Popinet Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 6, CNRS, UMR 79 Institut Jean Le Rond d Alembert,
Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF To cite this article: V A Smalyuk et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Hydrodynamic growth experiments with the 3-D, native-roughness modulations on NIF To cite this article: V A Smalyuk et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser.
An Experimental Investigation of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability
 An Experimental Investigation of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Thesis by Sanjay Kumar In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology
An Experimental Investigation of Richtmyer-Meshkov Instability Thesis by Sanjay Kumar In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy California Institute of Technology
AA214B: NUMERICAL METHODS FOR COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS
 AA214B: NUMERICAL METHODS FOR COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS 1 / 29 AA214B: NUMERICAL METHODS FOR COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS Hierarchy of Mathematical Models 1 / 29 AA214B: NUMERICAL METHODS FOR COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS 2 / 29
AA214B: NUMERICAL METHODS FOR COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS 1 / 29 AA214B: NUMERICAL METHODS FOR COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS Hierarchy of Mathematical Models 1 / 29 AA214B: NUMERICAL METHODS FOR COMPRESSIBLE FLOWS 2 / 29
Gas Dynamics Equations: Computation
 Title: Name: Affil./Addr.: Gas Dynamics Equations: Computation Gui-Qiang G. Chen Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford 24 29 St Giles, Oxford, OX1 3LB, United Kingdom Homepage: http://people.maths.ox.ac.uk/chengq/
Title: Name: Affil./Addr.: Gas Dynamics Equations: Computation Gui-Qiang G. Chen Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford 24 29 St Giles, Oxford, OX1 3LB, United Kingdom Homepage: http://people.maths.ox.ac.uk/chengq/
Evolution of Hydrodynamic Instability on Planar Jelly Interface Driven by Explosion *
 World Journal of Mechanics, 2012, 2, 152-161 doi:10.4236/wjm.2012.23018 Published Online June 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjm) Evolution of Hydrodynamic Instability on Planar Jelly Interface Driven
World Journal of Mechanics, 2012, 2, 152-161 doi:10.4236/wjm.2012.23018 Published Online June 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjm) Evolution of Hydrodynamic Instability on Planar Jelly Interface Driven
Synergetic Growth of the Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in the Relativistic Jet. Jin Matsumoto RIKEN
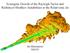 Synergetic Growth of the Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in the Relativistic Jet Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Morphological Dichotomy of the Jet 3C 31 Cygnus A FR I (Fanaroff-Riley Class I)
Synergetic Growth of the Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in the Relativistic Jet Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Morphological Dichotomy of the Jet 3C 31 Cygnus A FR I (Fanaroff-Riley Class I)
Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection:
 Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection: K-H instability, vorticity dynamics, R-T instability, capillary action, and cavitation William A. Sirignano University of California, Irvine -- Round liquid columns
Dynamics of Transient Liquid Injection: K-H instability, vorticity dynamics, R-T instability, capillary action, and cavitation William A. Sirignano University of California, Irvine -- Round liquid columns
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 4 Mar 2004
 Simulation of Vortex Dominated Flows Using the FLASH Code arxiv:astro-ph/0403109v1 4 Mar 2004 Vikram Dwarkadas, 1 Tomek Plewa, 1 Greg Weirs, 1 Chris Tomkins, 2 and Mark Marr-Lyon 2 1 ASCI FLASH Center,
Simulation of Vortex Dominated Flows Using the FLASH Code arxiv:astro-ph/0403109v1 4 Mar 2004 Vikram Dwarkadas, 1 Tomek Plewa, 1 Greg Weirs, 1 Chris Tomkins, 2 and Mark Marr-Lyon 2 1 ASCI FLASH Center,
Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA
 Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA Contributors: V. N. Goncharov P. A. Jaanimagi J. P. Knauer D. D. Meyerhofer O. V. Gotchev
Experiments on Dynamic Overpressure Stabilization of Ablative Richtmyer Meshkov Growth in ICF Targets on OMEGA Contributors: V. N. Goncharov P. A. Jaanimagi J. P. Knauer D. D. Meyerhofer O. V. Gotchev
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics
 OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
OMEGA Laser-Driven Hydrodynamic Jet Experiments with Relevance to Astrophysics Astronomical jets Experimental jets Instabilities 1.4 light years Ambient shocks Jet/ambient material interface 2.8 mm Collimated
Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion
 Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion R. Betti Fusion Science Center, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester IPAM/UCLA Long Program PL2012 - March 12
Theory and simulations of hydrodynamic instabilities in inertial fusion R. Betti Fusion Science Center, Laboratory for Laser Energetics, University of Rochester IPAM/UCLA Long Program PL2012 - March 12
Instabilities and Mixing in Supernova Envelopes During Explosion. Xuening Bai AST 541 Seminar Oct.21, 2009
 Instabilities and Mixing in Supernova Envelopes During Explosion Xuening Bai AST 541 Seminar Oct.21, 2009 Outline Overview Evidence of Mixing SN 1987A Evidence in supernova remnants Basic Physics Rayleigh-Taylor
Instabilities and Mixing in Supernova Envelopes During Explosion Xuening Bai AST 541 Seminar Oct.21, 2009 Outline Overview Evidence of Mixing SN 1987A Evidence in supernova remnants Basic Physics Rayleigh-Taylor
A Model of Laser Imprinting. V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V.
 A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V. Gotchev Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester The control of
A Model of Laser Imprinting V. N. Goncharov, S. Skupsky, R. P. J. Town, J. A. Delettrez, D. D. Meyerhofer, T. R. Boehly, and O.V. Gotchev Laboratory for Laser Energetics, U. of Rochester The control of
Planar and oblique shock wave interaction with a droplet seeded gas cylinder
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Mechanical Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 2-9-2010 Planar and oblique shock wave interaction with a droplet seeded gas cylinder Evan Johnson Follow this
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Mechanical Engineering ETDs Engineering ETDs 2-9-2010 Planar and oblique shock wave interaction with a droplet seeded gas cylinder Evan Johnson Follow this
Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components
 Chapter Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components The majority on high explosives (HEs) used are blend ones. Properties of components differ that produces interaction on the grain scale (mesoprocesses).
Chapter Simulation of mixing of heterogeneous HE components The majority on high explosives (HEs) used are blend ones. Properties of components differ that produces interaction on the grain scale (mesoprocesses).
9 Fluid Instabilities
 9. Stability of a shear flow In many situations, gaseous flows can be subject to fluid instabilities in which small perturbations can rapidly flow, thereby tapping a source of free energy. An important
9. Stability of a shear flow In many situations, gaseous flows can be subject to fluid instabilities in which small perturbations can rapidly flow, thereby tapping a source of free energy. An important
American Physical Society Division of Fluid Dynamics Meeting, San Antonio, TX, November 23 25, 2008.
 American Physical Society Division of Fluid Dynamics Meeting, San Antonio, TX, November 23 25, 2008. TURBULENT MIXING DUE TO RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR INSTABILITY David Youngs AWE Aldermaston UNITED KINGDOM British
American Physical Society Division of Fluid Dynamics Meeting, San Antonio, TX, November 23 25, 2008. TURBULENT MIXING DUE TO RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR INSTABILITY David Youngs AWE Aldermaston UNITED KINGDOM British
Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method. Jue Liao
 Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method Jue Liao Rayleigh-Taylor growth rates for arbitrary density profiles calculated with a variational method
Rayleigh-Taylor Growth Rates for Arbitrary Density Profiles Calculated with a Variational Method Jue Liao Rayleigh-Taylor growth rates for arbitrary density profiles calculated with a variational method
Jin Matsumoto. Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
 Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN) Schematic Picture of the GRB Jet Meszaros
Numerical Experiments of GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN) Schematic Picture of the GRB Jet Meszaros
SHOCK-HYDRODYNAMICS EXPERIMENTS ON THE NOVA LASER
 .- -.-..-........~... c UCRGJC-119184 PREPRINT SHOCK-HYDRODYNAMICS EXPERIMENTS ON THE NOVA LASER Paul Miller Tom Peyser Pete Stry Kim Budil Debbie Wojtowicz Eugene Burke Univemity of California Lawrence
.- -.-..-........~... c UCRGJC-119184 PREPRINT SHOCK-HYDRODYNAMICS EXPERIMENTS ON THE NOVA LASER Paul Miller Tom Peyser Pete Stry Kim Budil Debbie Wojtowicz Eugene Burke Univemity of California Lawrence
Shock Waves. 1 Steepening of sound waves. We have the result that the velocity of a sound wave in an arbitrary reference frame is given by: kˆ.
 Shock Waves Steepening of sound waves We have the result that the velocity of a sound wave in an arbitrary reference frame is given by: v u kˆ c s kˆ where u is the velocity of the fluid and k is the wave
Shock Waves Steepening of sound waves We have the result that the velocity of a sound wave in an arbitrary reference frame is given by: v u kˆ c s kˆ where u is the velocity of the fluid and k is the wave
Rayleigh Taylor Instability in Strong Media, Experimental Study
 Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Experimental and numerical study of the initial stages in the interaction process between a planar shock wave and a water column
 Experimental and numerical study of the initial stages in the interaction process between a planar shock wave and a water column Dan Igra and Kazuyoshi Takayama Shock Wave Research Center, Institute of
Experimental and numerical study of the initial stages in the interaction process between a planar shock wave and a water column Dan Igra and Kazuyoshi Takayama Shock Wave Research Center, Institute of
Fluid Dynamics. Massimo Ricotti. University of Maryland. Fluid Dynamics p.1/14
 Fluid Dynamics p.1/14 Fluid Dynamics Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Fluid Dynamics p.2/14 The equations of fluid dynamics are coupled PDEs that form an IVP (hyperbolic). Use
Fluid Dynamics p.1/14 Fluid Dynamics Massimo Ricotti ricotti@astro.umd.edu University of Maryland Fluid Dynamics p.2/14 The equations of fluid dynamics are coupled PDEs that form an IVP (hyperbolic). Use
An Introduction to Theories of Turbulence. James Glimm Stony Brook University
 An Introduction to Theories of Turbulence James Glimm Stony Brook University Topics not included (recent papers/theses, open for discussion during this visit) 1. Turbulent combustion 2. Turbulent mixing
An Introduction to Theories of Turbulence James Glimm Stony Brook University Topics not included (recent papers/theses, open for discussion during this visit) 1. Turbulent combustion 2. Turbulent mixing
THERMONUCLEAR weapons are extremely complex devices, both in design and operation. When a nuclear weapon detonates, it initiates a chain of physical
 THERMONUCLEAR weapons are extremely complex devices, both in design and operation. When a nuclear weapon detonates, it initiates a chain of physical processes ranging from chemical explosion to thermonuclear
THERMONUCLEAR weapons are extremely complex devices, both in design and operation. When a nuclear weapon detonates, it initiates a chain of physical processes ranging from chemical explosion to thermonuclear
ERROR ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE SHOCK INTERACTION PROBLEMS
 9 th ASCE Specialty Conference on Probabilistic Mechanics and Structural Reliability PMC2004-001 ERROR ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE SHOCK INTERACTION PROBLEMS Y. Yu, T. Lee, M. Zhao, J. Glimm, X. Li and K. Ke
9 th ASCE Specialty Conference on Probabilistic Mechanics and Structural Reliability PMC2004-001 ERROR ANALYSIS OF COMPOSITE SHOCK INTERACTION PROBLEMS Y. Yu, T. Lee, M. Zhao, J. Glimm, X. Li and K. Ke
Classical and ablative Richtmyer-Meshkov instability and other ICF-relevant plasma flows diagnosed with monochromatic x-ray imaging
 Classical and ablative Richtmyer-Meshkov instability and other ICF-relevant plasma flows diagnosed with monochromatic x-ray imaging Y Aglitskiy 1,2, M Karasik 2, A L Velikovich 2, N Metzler 1, S Zalesak
Classical and ablative Richtmyer-Meshkov instability and other ICF-relevant plasma flows diagnosed with monochromatic x-ray imaging Y Aglitskiy 1,2, M Karasik 2, A L Velikovich 2, N Metzler 1, S Zalesak
THE numerical simulation of the creation and evolution
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol III WCE, July 4-6,, London, U.K. Numerical Simulation of Compressible Two-phase Flows Using an Eulerian Type Reduced Model A. Ballil, Member, IAENG,
Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering Vol III WCE, July 4-6,, London, U.K. Numerical Simulation of Compressible Two-phase Flows Using an Eulerian Type Reduced Model A. Ballil, Member, IAENG,
Effect of Membrane on Measurements of Turbulent Mixing in Shock Tubes
 Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Originally published in Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Compressible Turbulent Mixing, ed. R. Young, J. Glimm & B. Boston. ISBN 9810229100, World Scientific (1996). Reproduced with the
Jin Matsumoto. Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
 Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN), Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Relativistic HD/MHD Flow for GRB Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborators: Nagataki, Ito, Mizuta, Barkov, Dainotti, Teraki (RIKEN), Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
STABILITY ANALYSIS FOR BUOYANCY-OPPOSED FLOWS IN POLOIDAL DUCTS OF THE DCLL BLANKET. N. Vetcha, S. Smolentsev and M. Abdou
 STABILITY ANALYSIS FOR BUOYANCY-OPPOSED FLOWS IN POLOIDAL DUCTS OF THE DCLL BLANKET N. Vetcha S. Smolentsev and M. Abdou Fusion Science and Technology Center at University of California Los Angeles CA
STABILITY ANALYSIS FOR BUOYANCY-OPPOSED FLOWS IN POLOIDAL DUCTS OF THE DCLL BLANKET N. Vetcha S. Smolentsev and M. Abdou Fusion Science and Technology Center at University of California Los Angeles CA
The Deflagration Phase of Type Ia SNe
 The Center for Astrophysical Thermonuclear Flashes The Deflagration Phase of Type Ia SNe Alan Calder ASC FLASH Center Type Ia Supernova Team Type Ia Supernovae and Cosmology August 5, 2004 An Advanced
The Center for Astrophysical Thermonuclear Flashes The Deflagration Phase of Type Ia SNe Alan Calder ASC FLASH Center Type Ia Supernova Team Type Ia Supernovae and Cosmology August 5, 2004 An Advanced
Computational Physics & Validation
 The Center for Astrophysical Thermonuclear Flashes Computational Physics & Validation Tomek Plewa Hua Pan, Timur Linde, Greg Weirs, Dahai Yu Todd Dupont Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) Academic
The Center for Astrophysical Thermonuclear Flashes Computational Physics & Validation Tomek Plewa Hua Pan, Timur Linde, Greg Weirs, Dahai Yu Todd Dupont Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) Academic
PHYS 643 Week 4: Compressible fluids Sound waves and shocks
 PHYS 643 Week 4: Compressible fluids Sound waves and shocks Sound waves Compressions in a gas propagate as sound waves. The simplest case to consider is a gas at uniform density and at rest. Small perturbations
PHYS 643 Week 4: Compressible fluids Sound waves and shocks Sound waves Compressions in a gas propagate as sound waves. The simplest case to consider is a gas at uniform density and at rest. Small perturbations
THE INTERACTION OF TURBULENCE WITH THE HELIOSPHERIC SHOCK
 THE INTERACTION OF TURBULENCE WITH THE HELIOSPHERIC SHOCK G.P. Zank, I. Kryukov, N. Pogorelov, S. Borovikov, Dastgeer Shaikh, and X. Ao CSPAR, University of Alabama in Huntsville Heliospheric observations
THE INTERACTION OF TURBULENCE WITH THE HELIOSPHERIC SHOCK G.P. Zank, I. Kryukov, N. Pogorelov, S. Borovikov, Dastgeer Shaikh, and X. Ao CSPAR, University of Alabama in Huntsville Heliospheric observations
The Fragmentation of expanding shells. Kazunari Iwasaki (Nagoya Univ.) Collaborate with S. Inutsuka (Nagoya Univ.) T. Tsuribe (Osaka Univ.
 .... The Fragmentation of expanding shells Kazunari Iwasaki (Nagoya Univ.) Collaborate with S. Inutsuka (Nagoya Univ.) T. Tsuribe (Osaka Univ.) 1 / 23 Outline Introduction Three Dimensional SPH Simulations
.... The Fragmentation of expanding shells Kazunari Iwasaki (Nagoya Univ.) Collaborate with S. Inutsuka (Nagoya Univ.) T. Tsuribe (Osaka Univ.) 1 / 23 Outline Introduction Three Dimensional SPH Simulations
7.2.1 Seismic waves. Waves in a mass- spring system
 7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
Comparison of Heterogeneous and Homogenized Numerical Models of Cavitation
 International Journal for Multiscale Computational Engineering, 4(3)377 390(2006) Comparison of Heterogeneous and Homogenized Numerical Models of Cavitation Roman Samulyak, 1, Yarema Prykarpatskyy, 3 Tianshi
International Journal for Multiscale Computational Engineering, 4(3)377 390(2006) Comparison of Heterogeneous and Homogenized Numerical Models of Cavitation Roman Samulyak, 1, Yarema Prykarpatskyy, 3 Tianshi
EhhhohmollsiE 'El', D-AiB4 751 A STUDY OF CHAOS AND MIXING IN RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR AND t/l RICHTMYER-NESHKOV UNST (U) NEWI YORK UNIV NY COURANT
 D-AiB4 751 A STUDY OF CHAOS AND MIXING IN RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR AND t/l RICHTMYER-NESHKOV UNST (U) NEWI YORK UNIV NY COURANT INST OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES C L GARDNER ET AL UNCLASSIFIED APR 87 AR-22770 6-MR
D-AiB4 751 A STUDY OF CHAOS AND MIXING IN RAYLEIGH-TAYLOR AND t/l RICHTMYER-NESHKOV UNST (U) NEWI YORK UNIV NY COURANT INST OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES C L GARDNER ET AL UNCLASSIFIED APR 87 AR-22770 6-MR
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 1 Nov 2005
 On the Hydrodynamic Interaction of Shock Waves with Interstellar Clouds. II. The Effect of Smooth Cloud Boundaries on Cloud Destruction and Cloud Turbulence Fumitaka Nakamura 1,2, Christopher F. McKee
On the Hydrodynamic Interaction of Shock Waves with Interstellar Clouds. II. The Effect of Smooth Cloud Boundaries on Cloud Destruction and Cloud Turbulence Fumitaka Nakamura 1,2, Christopher F. McKee
Rayleigh-Taylor Unstable Flames
 Rayleigh-Taylor Unstable Flames Elizabeth P. Hicks 1,2 and Robert Rosner 2 CIERA, Northwestern University 1 University of Chicago 2 CIERA Conference: September 2, 2011 1 Type Ia Supernovae Image: NASA
Rayleigh-Taylor Unstable Flames Elizabeth P. Hicks 1,2 and Robert Rosner 2 CIERA, Northwestern University 1 University of Chicago 2 CIERA Conference: September 2, 2011 1 Type Ia Supernovae Image: NASA
Using Numerical Simulations to explore a Mixing Mechanisms for Nova Enrichment Jonathan Dursi
 The Center for Astrophysical Thermonuclear Flashes Using Numerical Simulations to explore a Mixing Mechanisms for Nova Enrichment Jonathan Dursi May 21, 2001 Alan Calder, Alexandros Alexakis, James Truran,
The Center for Astrophysical Thermonuclear Flashes Using Numerical Simulations to explore a Mixing Mechanisms for Nova Enrichment Jonathan Dursi May 21, 2001 Alan Calder, Alexandros Alexakis, James Truran,
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19,
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 04104 007 High-resolution simulations and modeling of reshocked single-mode Richtmyer-Meshkov instability: Comparison to experimental data and to amplitude growth model predictions
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 04104 007 High-resolution simulations and modeling of reshocked single-mode Richtmyer-Meshkov instability: Comparison to experimental data and to amplitude growth model predictions
The Mathematics and Numerical Principles for Turbulent Mixing
 The Mathematics and Numerical Principles for Turbulent Mixing James Glimm1,3 With thanks to: Wurigen Bo1, Baolian Cheng2, Jian Du7, Bryan Fix1, Erwin George4, John Grove2, Xicheng Jia1, Hyeonseong Jin5,
The Mathematics and Numerical Principles for Turbulent Mixing James Glimm1,3 With thanks to: Wurigen Bo1, Baolian Cheng2, Jian Du7, Bryan Fix1, Erwin George4, John Grove2, Xicheng Jia1, Hyeonseong Jin5,
0.2. CONSERVATION LAW FOR FLUID 9
 0.2. CONSERVATION LAW FOR FLUID 9 Consider x-component of Eq. (26), we have D(ρu) + ρu( v) dv t = ρg x dv t S pi ds, (27) where ρg x is the x-component of the bodily force, and the surface integral is
0.2. CONSERVATION LAW FOR FLUID 9 Consider x-component of Eq. (26), we have D(ρu) + ρu( v) dv t = ρg x dv t S pi ds, (27) where ρg x is the x-component of the bodily force, and the surface integral is
Proton Radiographic and Numerical Modeling of Colliding, Diverging PBX-9502 Detonations
 Proton Radiographic and Numerical Modeling of Colliding, Diverging PBX-9502 Detonations Charles L. Mader, John D. Zumbro, and Eric N. Ferm Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 The Proton
Proton Radiographic and Numerical Modeling of Colliding, Diverging PBX-9502 Detonations Charles L. Mader, John D. Zumbro, and Eric N. Ferm Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos, NM 87545 The Proton
Jin Matsumoto. Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets. RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory
 Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Rayleigh-Taylor and Richtmyer-Meshkov Instabilities in Relativistic Hydrodynamic Jets Jin Matsumoto RIKEN Astrophysical Big Bang Laboratory Collaborator: Youhei Masada (Kobe University) What a relativistic
Francesco Califano. Physics Department, University of Pisa. The role of the magnetic field in the interaction of the solar wind with a magnetosphere
 Francesco Califano Physics Department, University of Pisa The role of the magnetic field in the interaction of the solar wind with a magnetosphere Collaboration with M. Faganello & F. Pegoraro Vien na,
Francesco Califano Physics Department, University of Pisa The role of the magnetic field in the interaction of the solar wind with a magnetosphere Collaboration with M. Faganello & F. Pegoraro Vien na,
Atwood number effects in buoyancy driven flows
 Advanced Computational Methods in Heat Transfer IX 259 Atwood number effects in buoyancy driven flows M. J. Andrews & F. F. Jebrail Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA Abstract Consideration is given to
Advanced Computational Methods in Heat Transfer IX 259 Atwood number effects in buoyancy driven flows M. J. Andrews & F. F. Jebrail Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA Abstract Consideration is given to
Numerical Studies of Supersonic Jet Impingement on a Flat Plate
 Numerical Studies of Supersonic Jet Impingement on a Flat Plate Overset Grid Symposium Dayton, OH Michael R. Brown Principal Engineer, Kratos/Digital Fusion Solutions Inc., Huntsville, AL. October 18,
Numerical Studies of Supersonic Jet Impingement on a Flat Plate Overset Grid Symposium Dayton, OH Michael R. Brown Principal Engineer, Kratos/Digital Fusion Solutions Inc., Huntsville, AL. October 18,
Application of a Laser Induced Fluorescence Model to the Numerical Simulation of Detonation Waves in Hydrogen-Oxygen-Diluent Mixtures
 Supplemental material for paper published in the International J of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 30, 6044-6060, 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.01.182 Application of a Laser Induced Fluorescence
Supplemental material for paper published in the International J of Hydrogen Energy, Vol. 30, 6044-6060, 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.01.182 Application of a Laser Induced Fluorescence
Wave Propagation in Bubbly Fluids and Cavitation Mitigation
 Wave Propagation in Bubbly Fluids and Cavitation Mitigation Tianshi Lu lu@math.wichita.edu ABSTRACT We studied the acoustic and shock wave propagation in bubbly fluids using direct numerical simulations
Wave Propagation in Bubbly Fluids and Cavitation Mitigation Tianshi Lu lu@math.wichita.edu ABSTRACT We studied the acoustic and shock wave propagation in bubbly fluids using direct numerical simulations
Limits of the potential flow approach to the single-mode Rayleigh-Taylor problem
 Limits of the potential flow approach to the single-mode Rayleigh-Taylor problem P. Ramaprabhu* and Guy Dimonte Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545, USA Yuan-Nan Young Department
Limits of the potential flow approach to the single-mode Rayleigh-Taylor problem P. Ramaprabhu* and Guy Dimonte Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87545, USA Yuan-Nan Young Department
Force analysis of underwater object with supercavitation evolution
 Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 42(8), December 2013, pp. 957-963 Force analysis of underwater object with supercavitation evolution B C Khoo 1,2,3* & J G Zheng 1,3 1 Department of Mechanical
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 42(8), December 2013, pp. 957-963 Force analysis of underwater object with supercavitation evolution B C Khoo 1,2,3* & J G Zheng 1,3 1 Department of Mechanical
Viscous simulations of shock-bubble interaction and Richtmyer-Meshkov instability
 Viscous simulations of shock-bubble interaction and Richtmyer-Meshkov instability M. CAPUANO a, C.BOGEY a, P.D.M SPELT a,b a. Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d Acoustique, UMR CNRS 5509, Ecole
Viscous simulations of shock-bubble interaction and Richtmyer-Meshkov instability M. CAPUANO a, C.BOGEY a, P.D.M SPELT a,b a. Laboratoire de Mécanique des Fluides et d Acoustique, UMR CNRS 5509, Ecole
CHAPTER 19. Fluid Instabilities. In this Chapter we discuss the following instabilities:
 CHAPTER 19 Fluid Instabilities In this Chapter we discuss the following instabilities: convective instability (Schwarzschild criterion) interface instabilities (Rayleight Taylor & Kelvin-Helmholtz) gravitational
CHAPTER 19 Fluid Instabilities In this Chapter we discuss the following instabilities: convective instability (Schwarzschild criterion) interface instabilities (Rayleight Taylor & Kelvin-Helmholtz) gravitational
Simulation of unsteady muzzle flow of a small-caliber gun
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 165 Simulation of unsteady muzzle flow of a small-caliber gun Y. Dayan & D. Touati Department of Computational Mechanics & Ballistics, IMI, Ammunition Group, Israel Abstract
Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 165 Simulation of unsteady muzzle flow of a small-caliber gun Y. Dayan & D. Touati Department of Computational Mechanics & Ballistics, IMI, Ammunition Group, Israel Abstract
Rayleigh Taylor Growth Measurements of 3-D Modulations
 Rayleigh Taylor Growth Measurements of -D Modulations in a Nonlinear Regime Introduction Rayleigh Taylor (RT), instability is of critical importance in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and astrophysics.
Rayleigh Taylor Growth Measurements of -D Modulations in a Nonlinear Regime Introduction Rayleigh Taylor (RT), instability is of critical importance in inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and astrophysics.
Simulation of Kelvin Helmholtz Instability with Flux-Corrected Transport Method
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 51 (2009) pp. 909 913 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 51, No. 5, May 15, 2009 Simulation of Kelvin Helmholtz Instability with Flux-Corrected
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 51 (2009) pp. 909 913 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 51, No. 5, May 15, 2009 Simulation of Kelvin Helmholtz Instability with Flux-Corrected
For example, for values of A x = 0 m /s, f 0 s, and L = 0 km, then E h = 0. and the motion may be influenced by horizontal friction if Corioli
 Lecture. Equations of Motion Scaling, Non-dimensional Numbers, Stability and Mixing We have learned how to express the forces per unit mass that cause acceleration in the ocean, except for the tidal forces
Lecture. Equations of Motion Scaling, Non-dimensional Numbers, Stability and Mixing We have learned how to express the forces per unit mass that cause acceleration in the ocean, except for the tidal forces
TAU Extensions for High Enthalpy Flows. Sebastian Karl AS-RF
 TAU Extensions for High Enthalpy Flows Sebastian Karl AS-RF Contents Motivation Extensions available in the current release: Numerical schemes for super- and hypersonic flow fields Models for gas mixtures,
TAU Extensions for High Enthalpy Flows Sebastian Karl AS-RF Contents Motivation Extensions available in the current release: Numerical schemes for super- and hypersonic flow fields Models for gas mixtures,
Leland Jameson Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation
 Leland Jameson Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Wind tunnel tests of airfoils Wind tunnels not infinite but some kind of closed loop Wind tunnel Yet another wind tunnel The
Leland Jameson Division of Mathematical Sciences National Science Foundation Wind tunnel tests of airfoils Wind tunnels not infinite but some kind of closed loop Wind tunnel Yet another wind tunnel The
Rayleigh-Taylor Driven Mixing in a Multiply Stratified Environment
 Rayleigh-Taylor Driven Mixing in a Multiply Stratified Environment Abstract Andrew George Weir Lawrie and Stuart Dalziel Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge
Rayleigh-Taylor Driven Mixing in a Multiply Stratified Environment Abstract Andrew George Weir Lawrie and Stuart Dalziel Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge
DEVELOPMENT OF CFD MODEL FOR A SWIRL STABILIZED SPRAY COMBUSTOR
 DRAFT Proceedings of ASME IMECE: International Mechanical Engineering Conference & Exposition Chicago, Illinois Nov. 5-10, 2006 IMECE2006-14867 DEVELOPMENT OF CFD MODEL FOR A SWIRL STABILIZED SPRAY COMBUSTOR
DRAFT Proceedings of ASME IMECE: International Mechanical Engineering Conference & Exposition Chicago, Illinois Nov. 5-10, 2006 IMECE2006-14867 DEVELOPMENT OF CFD MODEL FOR A SWIRL STABILIZED SPRAY COMBUSTOR
Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets
 1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
1 Laser Induced Shock Pressure Multiplication in Multi Layer Thin Foil Targets Mayank Shukla 1), Yogesh Kashyap 1), P. S. Sarkar 1), A. Sinha 1), H. C. Pant 2), R.S.Rao 1), N.K.Gupta 1), B.K.Godwal 1)
PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities
 PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities 1. Internal gravity waves Background state being perturbed: A stratified fluid in hydrostatic balance. It can be constant density like the ocean or compressible
PHYS 432 Physics of Fluids: Instabilities 1. Internal gravity waves Background state being perturbed: A stratified fluid in hydrostatic balance. It can be constant density like the ocean or compressible
Measurements of Magneto-Rayleigh-Taylor Instability Growth in Solid Liners on the 20 MA Z Facility
 Santa Fe Workshop on Science with High Power Lasers and Pulsed Power, August 4, 2010 Measurements of Magneto-Rayleigh-Taylor Instability Growth in Solid Liners on the 20 MA Z Facility +z Experiment Design,
Santa Fe Workshop on Science with High Power Lasers and Pulsed Power, August 4, 2010 Measurements of Magneto-Rayleigh-Taylor Instability Growth in Solid Liners on the 20 MA Z Facility +z Experiment Design,
Computational issues and algorithm assessment for shock/turbulence interaction problems
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln NASA Publications National Aeronautics and Space Administration 2007 Computational issues and algorithm assessment for shock/turbulence
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln NASA Publications National Aeronautics and Space Administration 2007 Computational issues and algorithm assessment for shock/turbulence
Nonlinear shape evolution of immiscible two-phase interface
 Nonlinear shape evolution of immiscible two-phase interface Francesco Capuano 1,2,*, Gennaro Coppola 1, Luigi de Luca 1 1 Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale (DII), Università di Napoli Federico II,
Nonlinear shape evolution of immiscible two-phase interface Francesco Capuano 1,2,*, Gennaro Coppola 1, Luigi de Luca 1 1 Dipartimento di Ingegneria Industriale (DII), Università di Napoli Federico II,
Progress in detailed modelling of low foot and high foot implosion experiments on the National Ignition Facility
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Progress in detailed modelling of low foot and high foot implosion experiments on the National Ignition Facility Related content - Capsule modeling
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Progress in detailed modelling of low foot and high foot implosion experiments on the National Ignition Facility Related content - Capsule modeling
Radiation hydrodynamics of tin targets for laser-plasma EUV sources
 Radiation hydrodynamics of tin targets for laser-plasma EUV sources M. M. Basko, V. G. Novikov, A. S. Grushin Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, Moscow, Russia RnD-ISAN, Troitsk, Moscow, Russia
Radiation hydrodynamics of tin targets for laser-plasma EUV sources M. M. Basko, V. G. Novikov, A. S. Grushin Keldysh Institute of Applied Mathematics, Moscow, Russia RnD-ISAN, Troitsk, Moscow, Russia
1. Introduction Some Basic Concepts
 1. Introduction Some Basic Concepts 1.What is a fluid? A substance that will go on deforming in the presence of a deforming force, however small 2. What Properties Do Fluids Have? Density ( ) Pressure
1. Introduction Some Basic Concepts 1.What is a fluid? A substance that will go on deforming in the presence of a deforming force, however small 2. What Properties Do Fluids Have? Density ( ) Pressure
Laser-plasma interactions
 Chapter 2 Laser-plasma interactions This chapter reviews a variety of processes which may take place during the interaction of a laser pulse with a plasma. The discussion focuses on the features that are
Chapter 2 Laser-plasma interactions This chapter reviews a variety of processes which may take place during the interaction of a laser pulse with a plasma. The discussion focuses on the features that are
An interface treating technique for compressible multi-medium flow with. Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method. Abstract
 An interface treating technique for compressible multi-medium flow with Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method Chunwu Wang 1 and Chi-Wang Shu 2 Abstract The high-order accurate Runge-Kutta discontinuous
An interface treating technique for compressible multi-medium flow with Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method Chunwu Wang 1 and Chi-Wang Shu 2 Abstract The high-order accurate Runge-Kutta discontinuous
Deforming Composite Grids for Fluid Structure Interactions
 Deforming Composite Grids for Fluid Structure Interactions Jeff Banks 1, Bill Henshaw 1, Don Schwendeman 2 1 Center for Applied Scientific Computing, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore,
Deforming Composite Grids for Fluid Structure Interactions Jeff Banks 1, Bill Henshaw 1, Don Schwendeman 2 1 Center for Applied Scientific Computing, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore,
Active Control of Separated Cascade Flow
 Chapter 5 Active Control of Separated Cascade Flow In this chapter, the possibility of active control using a synthetic jet applied to an unconventional axial stator-rotor arrangement is investigated.
Chapter 5 Active Control of Separated Cascade Flow In this chapter, the possibility of active control using a synthetic jet applied to an unconventional axial stator-rotor arrangement is investigated.
EFFECT OF LIQUID PHASE COMPRESSIBILITY ON MODELING OF GAS-LIQUID TWO-PHASE FLOWS USING TWO-FLUID MODEL
 EFFECT OF LIQUID PHASE COMPRESSIBILITY ON MODELING OF GAS-LIQUID TWO-PHASE FLOWS USING TWO-FLUID MODEL Vahid SHOKRI 1*,Kazem ESMAEILI 2 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sari Branch, Islamic Azad
EFFECT OF LIQUID PHASE COMPRESSIBILITY ON MODELING OF GAS-LIQUID TWO-PHASE FLOWS USING TWO-FLUID MODEL Vahid SHOKRI 1*,Kazem ESMAEILI 2 1,2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Sari Branch, Islamic Azad
Report Title Sharp Interface Algorithm for Large Density Ratio Incompressible Multiphase Magnetohydrodynamic Flows ABSTRACT A numerical algorithm and
 Report Title Sharp Interface Algorithm for Large Density Ratio Incompressible Multiphase Magnetohydrodynamic Flows ABSTRACT A numerical algorithm and the corresponding paralleled implementation for the
Report Title Sharp Interface Algorithm for Large Density Ratio Incompressible Multiphase Magnetohydrodynamic Flows ABSTRACT A numerical algorithm and the corresponding paralleled implementation for the
