Chapter 2 Physics in Action Sample Problem 1 A weightlifter uses a force of 325 N to lift a set of weights 2.00 m off the ground. How much work did th
|
|
|
- Samantha Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 Chapter Physics in Action Sample Problem 1 A weightlifter uses a force of 35 N to lift a set of weights.00 m off the ground. How much work did the weightlifter do? Strategy: You can use the following equation for calculating work: Given: Solution: W = F d F = 35 N d =.00 m W = F. d = 35 N.00 m = 650 N. m or 650 J Work done by the weightlifter is 650 J. Sample Problem How much energy is stored in a pole with a spring constant of 15 N/m if it is deflected 1.6 m? Strategy: You can use the following equation for calculating elastic potential energy: EPE = 1 kx Given: Solution: k = 15 N/m x = 1.6 m EPE = 1 kx 1 i 15 N m i 1. 6 m = 19. N i m or19j = ( ) Elastic potential energy in the pole is 19 J. Active Physics 6
8 Section 8 Potential and Kinetic Energy: Energy in the Pole Vault Sample Problem 3 One of the highest pop flies ever recorded in baseball was about 17 m. What is the gravitational potential energy of a baseball with a mass of 145 g that is hit that high into the air? Use the value of 9.8 m/s for the acceleration due to gravity. Strategy: You can use the following equation for calculating gravitational potential energy: GPE = mgh Given: m = h = 145 g or kg 17 m g = 9.8 m/s Solution: GPE = mgh = kg 9.8 m/s 17 m = 44 kg. m /s or 44 J The gravitational potential energy of the baseball is 44 J. Sample Problem 4 A football player has a mass of kg and runs at a speed of 6.0 m/s. What is his kinetic energy? Strategy: You can use the equation for calculating kinetic energy. Given: Solution: KE = 1 mv m = kg v = 60. ms 1 KE = mv 1 = m kg s 1 = m kg s 6 m s = 1800 kg. m / s or 1800 J The kinetic energy of the football player is 1800 J. Checking Up 1. What is required for the energy of an object to change?. From where does the penny that is launched into the air get its energy? 3. From where does the pole vaulter get the energy needed to bend the pole and then rise over the bar? 4. What are the units for work, kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, and spring potential energy? 7 Active Physics
9
10 Section 8 Potential and Kinetic Energy: Energy in the Pole Vault Although the energy equations were stated first, notice that they result from the idea that whenever work is done, energies change. The energy equations simply reflect the amount of work done. This is where the statement energy is stored work originates. Sample Problem 1 Your teacher gives you a pop-up toy. When you push down on it, it sticks to the desk for a moment and then pops into the air. a) If the toy has a mass of g and leaps 1.0 m off the table, how much potential energy does it have at its point of maximum height? (Use g = 9.80 m/s.) Strategy: The toy at its peak has a type of energy that depends on its position in Earth s gravitational field. So you need to use the formula for gravitational potential energy. Given: m = gor kg h = 1.0 m Solution: GPE = mgh = ( kg)(9.8 m )(. 1 0m) s = 118. kg i m / s or 1.18 J b) When the toy jumps off the desk, with what speed does it leave? Strategy: At the point where it jumps off the desk, the toy has its maximum amount of kinetic energy. This is what becomes the potential energy at the peak of its trajectory. Because energy is conserved, these two values will be equal kinetic energy at the bottom equals the potential energy at the peak. Given: GPE = 118. J Solution: GPE = KE KE = 1 mv Since you know that the KE must be equal to 1.18 J and you know the mass is kg, you can use your calculator to 1 find a value for v such that mv = 118. J. Alternatively, you can practice your algebra skills and find the value directly. You can use algebra to rearrange the equation to solve for v. KE v = 1 m 118. J = kg = 490. ms ( ) c) If you push the toy down.0 cm to make it stick to the desk, what is the spring constant of the spring in the toy? Strategy: The kinetic energy to make the toy leap off the desk came from doing work on the spring and storing it as elastic potential energy. Using the conservation of energy, this energy was then transformed into kinetic energy. 9 Active Physics
11
12
13
14 Section 8 Potential and Kinetic Energy: Energy in the Pole Vault 9. a) Using energy considerations only, calculate the speed the rock is going when it gets to the bottom of the cliff. b) Can you do this calculation if you do not know the mass of the rock? What does this imply for the speeds of falling objects when friction is not considered? Active Physics Plus A bow is strung with a bowstring that has a spring constant, k, of 1500 N/m. a) If you pull the bowstring back 5 cm, how much work have you done on it? b) If the string is pushing against an arrow that has a mass of 0.10 kg, how fast is the arrow going when it leaves the bow? 10. An exercise spring has a spring constant of 315 N/m. Active Physics Plus a) How much work is required to stretch the spring 30 cm? b) What force is needed to stretch the spring 30 cm? 11. A toy car (m = 0.04 kg) is released from rest and slides down a frictionless track 1 m high. At the bottom of the track it slides along a horizontal portion until it hits a spring (k = 18 N/m). The spring is attached to an immovable object. What is the maximum compression of the spring? 1. The unit for energy is the joule. It is also the unit of work. One joule is the work done by a force of one newton over a distance of one meter (1 J = 1 N i 1 m). a) Using F = ma, show that 1N= 1kgi1 m s. b) Using GPE = mgh, show that GPE is measured in joules. c) Using KE = 1 mv, show that KE is measured in joules. d) Using EPE = 1 kx, show that EPE is measured in joules. (Hint: The spring constant k has units of N/m, as you can see from the equation F = kx.) 13. A high diver jumps off the diving board, travels up and then down twirling her body. Explain high diving in terms of energy transformations among EPE, GPE, and KE. 14. A volleyball player is setting the ball by hitting it directly up with her hands. Describe the energy transformations in the volleyball play. 15. A long fly ball in baseball can be described in terms of energy transformations. Can you make your descriptions entertaining so that it can be used in a sports announcer s voice-over? 16. Preparing for the Chapter Challenge Describe how the law of conservation of energy applies to the sport you are going to describe in your voice-over. Include a specific example you might be able to use in your voice-over. 33 Active Physics
s_3x03 Page 1 Physics Samples
 Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
Physics Samples KE, PE, Springs 1. A 1.0-kilogram rubber ball traveling east at 4.0 meters per second hits a wall and bounces back toward the west at 2.0 meters per second. Compared to the kinetic energy
2. What would happen to his acceleration if his speed were half? Energy The ability to do work
 1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
1. A 40 kilogram boy is traveling around a carousel with radius 0.5 meters at a constant speed of 1.7 meters per second. Calculate his centripetal acceleration. 2. What would happen to his acceleration
- Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key -
 NAME: DATE: PERIOD: PHYSICS - Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key - - Is Energy Conserved? - Determine the max height that a 5kg cannonball will reach if fired vertically with an initial velocity
NAME: DATE: PERIOD: PHYSICS - Conservation of Energy Notes Teacher Key - - Is Energy Conserved? - Determine the max height that a 5kg cannonball will reach if fired vertically with an initial velocity
Physics 2414 Group Exercise 8. Conservation of Energy
 Physics 244 Group Exercise 8 Name : OUID : Name 2: OUID 2: Name 3: OUID 3: Name 4: OUID 4: Section Number: Solutions Solutions Conservation of Energy A mass m moves from point i to point f under the action
Physics 244 Group Exercise 8 Name : OUID : Name 2: OUID 2: Name 3: OUID 3: Name 4: OUID 4: Section Number: Solutions Solutions Conservation of Energy A mass m moves from point i to point f under the action
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
2 possibilities. 2.) Work is done and... 1.) Work is done and... *** The function of work is to change energy ***
 Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Work-Energy Theorem and Energy Conservation *** The function of work is to change energy *** 2 possibilities 1.) Work is done and... or 2.) Work is done and... 1 EX: A 100 N box is 10 m above the ground
Mechanical Energy I. Name: Date: Section C D F. Mr. Alex Rawson Physics
 Name: Date: Section C D F Mechanical Energy I Mr. Alex Rawson Physics 1. One of the two Olympic weightlifting events is called the Clean and Jerk, shown below. As of Athens 2004, the record for Clean and
Name: Date: Section C D F Mechanical Energy I Mr. Alex Rawson Physics 1. One of the two Olympic weightlifting events is called the Clean and Jerk, shown below. As of Athens 2004, the record for Clean and
Healy/DiMurro. Vibrations 2016
 Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
Name Vibrations 2016 Healy/DiMurro 1. In the diagram below, an ideal pendulum released from point A swings freely through point B. 4. As the pendulum swings freely from A to B as shown in the diagram to
Work and Energy. Work
 Work and Energy Objectives: Students will define work. Students will define and give examples of different forms of energy. Students will describe and give examples of kinetic energy and potential energy.
Work and Energy Objectives: Students will define work. Students will define and give examples of different forms of energy. Students will describe and give examples of kinetic energy and potential energy.
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
WEP-Energy. 2. If the speed of a car is doubled, the kinetic energy of the car is 1. quadrupled 2. quartered 3. doubled 4. halved
 1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
1. A 1-kilogram rock is dropped from a cliff 90 meters high. After falling 20 meters, the kinetic energy of the rock is approximately 1. 20 J 2. 200 J 3. 700 J 4. 900 J 2. If the speed of a car is doubled,
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist
 Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
Momentum & Energy Review Checklist Impulse and Momentum 3.1.1 Use equations to calculate impulse; momentum; initial speed; final speed; force; or time. An object with a mass of 5 kilograms is moving at
WORK & ENERGY Work Work Energy Thm. Kinetic Energy Power Potential Energy Conservation of Energy
 WORK & ENERGY Work Work Energy Thm. Kinetic Energy Power Potential Energy Conservation of Energy WORK & ENERGY Work: Transfer of energy through motion Energy: Ability to cause Change Kinetic Energy: Energy
WORK & ENERGY Work Work Energy Thm. Kinetic Energy Power Potential Energy Conservation of Energy WORK & ENERGY Work: Transfer of energy through motion Energy: Ability to cause Change Kinetic Energy: Energy
5. A car moves with a constant speed in a clockwise direction around a circular path of radius r, as represented in the diagram above.
 1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
1. The magnitude of the gravitational force between two objects is 20. Newtons. If the mass of each object were doubled, the magnitude of the gravitational force between the objects would be A) 5.0 N B)
(f ) From the graph, obtain the height of the tube given the mass of the dart is 20 grams and the constant force applied in the tube is 2 newtons.
 1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
1. Bowling Ball A is dropped from a point halfway up a cliff. A second identical bowling ball, B, is dropped simultaneously from the top of the cliff. Comparing the bowling balls at the instant they reach
General Physics I Work & Energy
 General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
General Physics I Work & Energy Forms of Energy Kinetic: Energy of motion. A car on the highway has kinetic energy. We have to remove this energy to stop it. The brakes of a car get HOT! This is an example
Review. Kinetic Energy Work Hooke s s Law Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Power 1/91
 Review Kinetic Energy Work Hooke s s Law Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Power 1/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton B. Watt C. Joule D. Meter E. Second 2/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton
Review Kinetic Energy Work Hooke s s Law Potential Energy Conservation of Energy Power 1/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton B. Watt C. Joule D. Meter E. Second 2/91 The unit of work is the A. Newton
Potential and Kinetic Energy
 Potential and Kinetic Energy 1 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is a system? 3 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 A system is an object or a group of objects.
Potential and Kinetic Energy 1 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 Potential and Kinetic Energy 2 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 What is a system? 3 of 31 Boardworks Ltd 2016 A system is an object or a group of objects.
= 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ. T.E. initial. = T.E. Final. = P.E. final. + K.E. initial. + P.E. initial. K.E. initial =
 Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
Practice Template K.E. = 1 2 mv2 P.E. height = mgh P.E. spring = 1 2 kx2 dw =! F! d! r = Fdr cosθ Energy Conservation T.E. initial = T.E. Final (1) Isolated system P.E. initial (2) Energy added E added
2 nd Term Final. Revision Sheet. Students Name: Grade: 9 A/B. Subject: Physics. Teacher Signature
 2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 9 A/B Subject: Physics Teacher Signature 1 PHYSICS WORKSHEET GRADE: 9 MULTIPLE CHOICES In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase
2 nd Term Final Revision Sheet Students Name: Grade: 9 A/B Subject: Physics Teacher Signature 1 PHYSICS WORKSHEET GRADE: 9 MULTIPLE CHOICES In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Energy Storage and Transfer Model: Review Sheet
 Name Energy Storage and Transfer Model: Review Sheet Date Pd 1. A softball (m = 180 g) traveling at 22.3 m/s moves a fielder's glove backward 25 cm when the ball is caught. a. Construct an energy bar graph
Name Energy Storage and Transfer Model: Review Sheet Date Pd 1. A softball (m = 180 g) traveling at 22.3 m/s moves a fielder's glove backward 25 cm when the ball is caught. a. Construct an energy bar graph
Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes
 Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
Physics 1 Name Lesson 7. Homework Work and Energy Problem Solving Outcomes Date 1. Define work. 2. Define energy. 3. Determine the work done by a constant force. Period 4. Determine the work done by a
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations
 Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Chapter 6 Energy and Oscillations Conservation of Energy In this chapter we will discuss one of the most important and fundamental principles in the universe. Energy is conserved. This means that in any
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 Assessment Chapter Test A ork and Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. In which of the
Assessment Chapter Test A ork and Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question. 1. In which of the
Chapter 12 Vibrations and Waves Simple Harmonic Motion page
 Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
Chapter 2 Vibrations and Waves 2- Simple Harmonic Motion page 438-45 Hooke s Law Periodic motion the object has a repeated motion that follows the same path, the object swings to and fro. Examples: a pendulum
As the mass travels along the track, the maximum height it will reach above point E will be closest to A) 10. m B) 20. m C) 30. m D) 40.
 1. As a pendulum swings from position A to position B as shown in the diagram, its total mechanical energy (neglecting friction) A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same 2. Base your answer to the
1. As a pendulum swings from position A to position B as shown in the diagram, its total mechanical energy (neglecting friction) A) decreases B) increases C) remains the same 2. Base your answer to the
MECHANICAL (TOTAL) ENERGY
 DO NOW: 1/19 If you haven t already, please take the short google form survey posted on Edmodo Please turn in your Work done by friction Lab in the top tray POTENTIAL ENERGY Stored energy An object that
DO NOW: 1/19 If you haven t already, please take the short google form survey posted on Edmodo Please turn in your Work done by friction Lab in the top tray POTENTIAL ENERGY Stored energy An object that
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
1 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?
 Page of 3 Work Power And Energy TEACHER ANSWER KEY March 09, 200. A spring has a spring constant of 20 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?. 2.
Page of 3 Work Power And Energy TEACHER ANSWER KEY March 09, 200. A spring has a spring constant of 20 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter?. 2.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws
 Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
Momentum, Impulse, Work, Energy, Power, and Conservation Laws 1. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second.
CHAPTER 6: IN AN ISOLATED SYSTEM, ENERGY IS TRANSFERRED FROM ONE OBJECT TO ANOTHER WHENEVER WORK IS DONE
 CHAPTER 6: IN AN ISOLATED SYSTEM, ENERGY IS TRANSFERRED FROM ONE OBJECT TO ANOTHER WHENEVER WORK IS DONE 6.1 Work and Energy In science, work is done when a force acts over a displacement; energy is transferred.
CHAPTER 6: IN AN ISOLATED SYSTEM, ENERGY IS TRANSFERRED FROM ONE OBJECT TO ANOTHER WHENEVER WORK IS DONE 6.1 Work and Energy In science, work is done when a force acts over a displacement; energy is transferred.
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
Page 1. Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is A) 34 m B) 30.
 Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Name: 1) If a man walks 17 meters east then 17 meters south, the magnitude of the man's displacement is 34 m 30. m 17 m 24 m 2) The graph below represents the motion of a body that is moving with 6) Which
Science 20 Physics Review
 Science 20 Physics Review Name 1. Which velocity-time graph below best represents the motion of an object sliding down a frictionless slope? a. b. c. d. Numerical response 1 The roadrunner is moving at
Science 20 Physics Review Name 1. Which velocity-time graph below best represents the motion of an object sliding down a frictionless slope? a. b. c. d. Numerical response 1 The roadrunner is moving at
Chapter 5: Energy. Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy
 Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Chapter 5: Energy Energy is one of the most important concepts in the world of science. Common forms of Energy Mechanical Chemical Thermal Electromagnetic Nuclear One form of energy can be converted to
Ch 5 Work and Energy
 Ch 5 Work and Energy Energy Provide a different (scalar) approach to solving some physics problems. Work Links the energy approach to the force (Newton s Laws) approach. Mechanical energy Kinetic energy
Ch 5 Work and Energy Energy Provide a different (scalar) approach to solving some physics problems. Work Links the energy approach to the force (Newton s Laws) approach. Mechanical energy Kinetic energy
Energy: Forms and Changes
 Energy: Forms and Changes Nature of Energy Energy is all around you! You can hear energy as sound. You can see energy as light. And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy You use energy when you: hit
Energy: Forms and Changes Nature of Energy Energy is all around you! You can hear energy as sound. You can see energy as light. And you can feel it as wind. Nature of Energy You use energy when you: hit
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
Name 09-MAR-04. Work Power and Energy
 Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
Page 1 of 16 Work Power and Energy Name 09-MAR-04 1. A spring has a spring constant of 120 newtons/meter. How much potential energy is stored in the spring as it is stretched 0.20 meter? 1. 2.4 J 3. 12
4.) A baseball that weighs 1.6 N leaves a bat with a speed of 40.0 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the ball. 130 J
 AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
AP Physics-B Energy And Its Conservation Introduction: Energy is a term that most of us take for granted and use quite freely. We assume we know what we are talking about when speaking of energy. In truth,
Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4
 Name Date Period Objectives: Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4 1) Find the energy stored within the rubber band cannon for various displacements. 2) Find the
Name Date Period Objectives: Lab: Energy-Rubber Band Cannon C O N C E P T U A L P H Y S I C S : U N I T 4 1) Find the energy stored within the rubber band cannon for various displacements. 2) Find the
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Name: 3834-1 - Page 1 1) If a woman runs 100 meters north and then 70 meters south, her total displacement is A) 170 m south B) 170 m north C) 30 m south D) 30 m north 2) The graph below represents the
Physics Midterm Review KEY
 Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Name: Date: 1. Which quantities are scalar? A. speed and work B. velocity and force C. distance and acceleration D. momentum and power 2. A 160.-kilogram space vehicle is traveling along a straight line
Conservation of Energy Review
 onservation of Energy Review Name: ate: 1. An electrostatic force exists between two +3.20 10 19 -coulomb point charges separated by a distance of 0.030 meter. As the distance between the two point charges
onservation of Energy Review Name: ate: 1. An electrostatic force exists between two +3.20 10 19 -coulomb point charges separated by a distance of 0.030 meter. As the distance between the two point charges
Slide 1 / 76. Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems
 Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
Slide 1 / 76 Work & Energy Multiple Choice Problems Slide 2 / 76 1 A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to
AP Physics C - Mechanics
 Slide 1 / 84 Slide 2 / 84 P Physics C - Mechanics Energy Problem Solving Techniques 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 84 Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE,
Slide 1 / 84 Slide 2 / 84 P Physics C - Mechanics Energy Problem Solving Techniques 2015-12-03 www.njctl.org Table of Contents Slide 3 / 84 Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE,
Work and energy. 15 m. c. Find the work done by the normal force exerted by the incline on the crate.
 Work and energy 1. A 10.0-kg crate is pulled 15.0 m up along a frictionless incline as shown in the figure below. The crate starts at rest and has a final speed of 6.00 m/s. motor 15 m 5 a. Draw the free-body
Work and energy 1. A 10.0-kg crate is pulled 15.0 m up along a frictionless incline as shown in the figure below. The crate starts at rest and has a final speed of 6.00 m/s. motor 15 m 5 a. Draw the free-body
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY
 CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
CHAPTER 6 WORK AND ENERGY ANSWERS TO FOCUS ON CONCEPTS QUESTIONS (e) When the force is perpendicular to the displacement, as in C, there is no work When the force points in the same direction as the displacement,
Energy Problem Solving Techniques.
 1 Energy Problem Solving Techniques www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE, KE and EPE Problem Solving Conservation of Energy Problem Solving
1 Energy Problem Solving Techniques www.njctl.org 2 Table of Contents Introduction Gravitational Potential Energy Problem Solving GPE, KE and EPE Problem Solving Conservation of Energy Problem Solving
AP Mechanics Summer Assignment
 2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
2012-2013 AP Mechanics Summer Assignment To be completed in summer Submit for grade in September Name: Date: Equations: Kinematics (For #1 and #2 questions: use following equations only. Need to show derivation
15.1 Energy and Its Forms. Energy and Work. How are energy and work related? Energy is the ability to do work. Work is a transfer of energy.
 Energy and Work How are energy and work related? Energy is the ability to do work. Work is a transfer of energy. Energy and Work Energy has different forms. A. The sun gives off energy in the form of heat
Energy and Work How are energy and work related? Energy is the ability to do work. Work is a transfer of energy. Energy and Work Energy has different forms. A. The sun gives off energy in the form of heat
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
9.2 Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY
 9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
9. Work & Energy Homework - KINETIC, GRAVITATIONAL & SPRING ENERGY KINETIC ENERGY QUESTIONS 9.H Energy.doc 1. A 500 kilogram car is driving at 15 meters/second. Calculate its kinetic energy? How much does
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy
 PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Multiple-Choice questions 1. A driver in a 2000 kg Porsche wishes to pass a slow moving school bus on a 4 lane road. What is the average power in watts required to accelerate
Page 1. Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work!
 Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
Name: Section This assignment is due at the first class in 2019 Part I Show all work! 7164-1 - Page 1 1) A car travels at constant speed around a section of horizontal, circular track. On the diagram provided
The Story of Energy. Forms and Functions
 The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
The Story of Energy Forms and Functions What are 5 things E helps us do? Batteries store energy! This car uses a lot of energy Even this sleeping puppy is using stored energy. We get our energy from FOOD!
Gravitational Energy using Gizmos
 Name: Date: Gravitational Energy using Gizmos Using your Gizmo app, open the Potential energy on shelves Gizmo Vocabulary: gravitational energy, Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
Name: Date: Gravitational Energy using Gizmos Using your Gizmo app, open the Potential energy on shelves Gizmo Vocabulary: gravitational energy, Prior Knowledge Questions (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo.)
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
WORK, POWER, & ENERGY In physics, work is done when a force acting on an object causes it to move a distance. There are several good examples of work which can be observed everyday - a person pushing a
GPE = m g h. GPE = w h. k = f d. PE elastic = ½ k d 2. Work = Force x distance. KE = ½ m v 2
 1 NAME PERIOD PHYSICS GUIDESHEET ENERGY CONVERSIONS POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT CLASS OVERHEAD NOTES (5 pts/page) (Plus 5 pts/page for sample questions)
1 NAME PERIOD PHYSICS GUIDESHEET ENERGY CONVERSIONS POTENTIAL AND KINETIC ENERGY ACTIVITY LESSON DESCRIPTION SCORE/POINTS 1. NT CLASS OVERHEAD NOTES (5 pts/page) (Plus 5 pts/page for sample questions)
WORK, POWER & ENERGY
 WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
WORK, POWER & ENERGY Work An applied force acting over a displacement. The force being applied must be parallel to the displacement for work to be occurring. Work Force displacement Units: Newton meter
Practice Exam 2. Name: Date: ID: A. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Date: _ Practice Exam 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A roller-coaster car has a mass of 500 kg when fully loaded with passengers.
Name: Date: _ Practice Exam 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A roller-coaster car has a mass of 500 kg when fully loaded with passengers.
1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B km C. 25 km D. 45 km E. 50 km
 Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Name: Physics I Mid Term Exam Review Multiple Choice Questions Date: Mr. Tiesler 1. A train moves at a constant velocity of 90 km/h. How far will it move in 0.25 h? A. 10 km B. 22.5 km C. 25 km D. 45 km
Energy Conservation AP
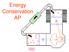 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Name: Physics 644 Date: / / Review: Work, Energy, Power Work. 1. What are the two important variables for work? (hint: look at the equation!
 Name: Physics 644 Date: / / Review: Work, Energy, Power Work 1. What are the two important variables for work? (hint: look at the equation!) 2. Is work done in the following situations? A. Is work done
Name: Physics 644 Date: / / Review: Work, Energy, Power Work 1. What are the two important variables for work? (hint: look at the equation!) 2. Is work done in the following situations? A. Is work done
Work and Energy Chapter Questions. 2. Contrast the effects of external forces and internal forces on the total energy of a system.
 PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Chapter Questions 1. Define a system, the environment and the system boundary. 2. Contrast the effects of external forces and internal forces on the total energy of a system.
PSI AP Physics I Work and Energy Chapter Questions 1. Define a system, the environment and the system boundary. 2. Contrast the effects of external forces and internal forces on the total energy of a system.
Slide 1 / 113. Slide 2 / th Grade. Energy of Objects in Motion Classwork-Homework Slide 3 / 113. Classwork #1: Energy
 Slide 1 / 113 Slide 2 / 113 8th Grade Energy of Objects in Motion Classwork-Homework 2015-08-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 113 Classwork #1: Energy 1 Define Energy. Slide 4 / 113 2 What two things are necessary
Slide 1 / 113 Slide 2 / 113 8th Grade Energy of Objects in Motion Classwork-Homework 2015-08-25 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 113 Classwork #1: Energy 1 Define Energy. Slide 4 / 113 2 What two things are necessary
PH7_UnitPacketCompleteKey
 Page 1 of 45 Page 2 of 45 Unit Packet Contents 1. Unit Objectives 2. Notes: Potential / Kinetic Energy 3. Guided Practice: Potential and Kinetic Energy 4. Independent Practice Potential and Kinetic Energy
Page 1 of 45 Page 2 of 45 Unit Packet Contents 1. Unit Objectives 2. Notes: Potential / Kinetic Energy 3. Guided Practice: Potential and Kinetic Energy 4. Independent Practice Potential and Kinetic Energy
If there is now a constant air resistance force of 35 N, what is the new maximum height the ball attains?
 A 1kg ball is launched straight up into the air with an initial speed of 64 m/s. Using only energy considerations, determine the maximum height the ball attains assuming there is no air resistance. If
A 1kg ball is launched straight up into the air with an initial speed of 64 m/s. Using only energy considerations, determine the maximum height the ball attains assuming there is no air resistance. If
Elastic Potential Energy
 Elastic Potential Energy If you pull on a spring and stretch it, then you do work. That is because you are applying a force over a displacement. Your pull is the force and the amount that you stretch the
Elastic Potential Energy If you pull on a spring and stretch it, then you do work. That is because you are applying a force over a displacement. Your pull is the force and the amount that you stretch the
8. The graph below shows a beetle s movement along a plant stem.
 Name: Block: Date: Introductory Physics: Midyear Review 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast
Name: Block: Date: Introductory Physics: Midyear Review 1. Motion and Forces Central Concept: Newton s laws of motion and gravitation describe and predict the motion of most objects. 1.1 Compare and contrast
Name Period Date. Record all givens, draw a picture, arrow all vectors, write the formula, substitute and solve. units
 Example Problems 8.4 Conservation of Energy E1. A monkey does 0.45 joule of work compressing the spring in a pop-up toy. If the mass of the toy is 0.00 kilogram, calculate the maximum vertical height that
Example Problems 8.4 Conservation of Energy E1. A monkey does 0.45 joule of work compressing the spring in a pop-up toy. If the mass of the toy is 0.00 kilogram, calculate the maximum vertical height that
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM
 1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
1 of 6 10/21/2009 6:33 PM Chapter 10 Homework Due: 9:00am on Thursday, October 22, 2009 Note: To understand how points are awarded, read your instructor's Grading Policy. [Return to Standard Assignment
(D) Based on Ft = m v, doubling the mass would require twice the time for same momentum change
 1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
1. A car of mass m, traveling at speed v, stops in time t when maximum braking force is applied. Assuming the braking force is independent of mass, what time would be required to stop a car of mass m traveling
Conservative vs. Non-conservative forces Gravitational Potential Energy. Conservation of Mechanical energy
 Next topic Conservative vs. Non-conservative forces Gravitational Potential Energy Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical energy Work done by non-conservative forces and changes in mechanical energy
Next topic Conservative vs. Non-conservative forces Gravitational Potential Energy Mechanical Energy Conservation of Mechanical energy Work done by non-conservative forces and changes in mechanical energy
8th Grade. Energy of Objects in Motion. Energy and its Forms. Slide 1 / 122 Slide 2 / 122. Slide 3 / 122. Slide 4 / 122.
 Slide / 22 Slide 2 / 22 8th Grade Energy of Objects of Motion 205-0-28 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 22 Energy of Objects in Motion Slide 4 / 22 Review from Last Unit Energy and its Forms Mechanical Energy Energy
Slide / 22 Slide 2 / 22 8th Grade Energy of Objects of Motion 205-0-28 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 22 Energy of Objects in Motion Slide 4 / 22 Review from Last Unit Energy and its Forms Mechanical Energy Energy
Chapter 6 Work and Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
Chapter 6 Work and Energy Midterm exams will be available next Thursday. Assignment 6 Textbook (Giancoli, 6 th edition), Chapter 6: Due on Thursday, November 5 1. On page 162 of Giancoli, problem 4. 2.
KEY NNHS Introductory Physics: MCAS Review Packet #2
 2. Conservation of Energy and Momentum Broad Concept: The laws of conservation of energy and momentum provide alternate approaches to predict and describe the movement of objects. 1.) Which of the following
2. Conservation of Energy and Momentum Broad Concept: The laws of conservation of energy and momentum provide alternate approaches to predict and describe the movement of objects. 1.) Which of the following
Physics 23 Notes Chapter 6 Part Two
 Physics 23 Notes Chapter 6 Part Two Dr. Alward Conservation of Energy Object moves freely upward under the influence of Earth only. Its acceleration is a = -g. v 2 = vo 2 + 2ax = vo 2-2g (h-ho) = vo 2-2gh
Physics 23 Notes Chapter 6 Part Two Dr. Alward Conservation of Energy Object moves freely upward under the influence of Earth only. Its acceleration is a = -g. v 2 = vo 2 + 2ax = vo 2-2g (h-ho) = vo 2-2gh
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name
 AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
AP Physics 1 Work Energy and Power Practice Test Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Two objects, one of mass m and the other
S15--AP Q1 Work and Energy PRACTICE
 Name: Class: Date: S15--AP Q1 Work and Energy PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Rupel pushes a box 5.00 m by applying a 25.0-N horizontal
Name: Class: Date: S15--AP Q1 Work and Energy PRACTICE Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Rupel pushes a box 5.00 m by applying a 25.0-N horizontal
5.3. Conservation of Energy
 5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
5.3. Conservation of Energy Conservation of Energy Energy is never created or destroyed. Any time work is done, it is only transformed from one form to another: Kinetic Energy Potential Energy Gravitational,
Practice Final C. 1. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart.
 1. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart. 6. The graph below represents the relationship between gravitational force and mass for objects near the surface of Earth. The worker s
1. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart. 6. The graph below represents the relationship between gravitational force and mass for objects near the surface of Earth. The worker s
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY. Chapter 6 (cont.)
 KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY Chapter 6 (cont.) The Two Types of Mechanical Energy Energy- the ability to do work- measured in joules Potential Energy- energy that arises because of an object s position
Rollercoaster Physics: Energy
 Physics Regular 1314 Williams Rollercoaster Physics: Energy Packet -1 / Chapter 6 1 2 Name Unit VII: Worksheet 3a For each situation shown below: 1. Show your choice of system in the energy flow diagram,
Physics Regular 1314 Williams Rollercoaster Physics: Energy Packet -1 / Chapter 6 1 2 Name Unit VII: Worksheet 3a For each situation shown below: 1. Show your choice of system in the energy flow diagram,
Physics. Chapter 7 Energy
 Physics Chapter 7 Energy Work How long does a force act? Last week, we meant time as in impulse (Ft) This week, we will take how long to mean distance Force x distance (Fd) is what we call WORK W = Fd
Physics Chapter 7 Energy Work How long does a force act? Last week, we meant time as in impulse (Ft) This week, we will take how long to mean distance Force x distance (Fd) is what we call WORK W = Fd
Physics 1A, Summer 2011, Summer Session 1 Quiz 3, Version A 1
 Physics 1A, Summer 2011, Summer Session 1 Quiz 3, Version A 1 Closed book and closed notes. No work needs to be shown. 1. Three rocks are thrown with identical speeds from the top of the same building.
Physics 1A, Summer 2011, Summer Session 1 Quiz 3, Version A 1 Closed book and closed notes. No work needs to be shown. 1. Three rocks are thrown with identical speeds from the top of the same building.
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
Chapter 6 Work, Energy, and Power What Is Physics All About? Matter Energy Force Work Done by a Constant Force The definition of work, when the force is parallel to the displacement: W = Fs SI unit: newton-meter
AP PHYSICS 1. Energy 2016 EDITION
 AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
AP PHYSICS 1 Energy 2016 EDITION Copyright 2016 National Math + Initiative, Dallas, Texas. All rights reserved. Visit us online at www.nms.org. 1 Pre-Assessment Questions Consider a system which could
Section 3. Spring Potential Energy: More Energy. What Do You See? What Do You Think? Investigate
 Thrills and Chills Section 3 Spring Potential Energy: More Energy Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section 3 SC.91.N..4 Explain that scientific knowledge is
Thrills and Chills Section 3 Spring Potential Energy: More Energy Florida Next Generation Sunshine State Standards: Additional Benchmarks met in Section 3 SC.91.N..4 Explain that scientific knowledge is
7.6(B) distinguish between physical and chemical changes in matter in the digestive system; and
 7.6(B) distinguish between physical and chemical changes in matter in the digestive system; and 7.7(B) illustrate the transformation of energy within an organism such as the transfer from chemical energy
7.6(B) distinguish between physical and chemical changes in matter in the digestive system; and 7.7(B) illustrate the transformation of energy within an organism such as the transfer from chemical energy
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
Work/nergy 1. student throws a ball upward where the initial potential energy is 0. t a height of 15 meters the ball has a potential energy of 60 joules and is moving upward with a kinetic energy of 40
The important variables for work are distance and force. Yes, work is done because the force and the movement are in the
 Name: Physics 670 Date: / / Review (Key): Work, Energy, Power Work 1. What are the two important variables for work? (hint: look at the equation!) The important variables for work are distance and force.
Name: Physics 670 Date: / / Review (Key): Work, Energy, Power Work 1. What are the two important variables for work? (hint: look at the equation!) The important variables for work are distance and force.
LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE. Rotational Kinetic Energy. K = ½ I ω 2
 LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE Work, Energy and Power CJ - Assignment 3 6.5 The Conservation of Mechanical Energy Problems 3, 34, 38, 40 page 190 Work Kinetic Energy Rotational Kinetic Energy W = F d cosθ KE
LAST NAME FIRST NAME DATE Work, Energy and Power CJ - Assignment 3 6.5 The Conservation of Mechanical Energy Problems 3, 34, 38, 40 page 190 Work Kinetic Energy Rotational Kinetic Energy W = F d cosθ KE
What is Energy? Which has more energy? Who has more energy? 1/24/2017
 What is Energy? Energy is a measure of an object s ability to cause a change in itself and/or its surroundings Read pages 61-7 Which has more energy? Who has more energy? Mississippi River Cargo Barge
What is Energy? Energy is a measure of an object s ability to cause a change in itself and/or its surroundings Read pages 61-7 Which has more energy? Who has more energy? Mississippi River Cargo Barge
D) No, because of the way work is defined D) remains constant at zero. D) 0 J D) zero
 CHAPTER 6 REVIEW NAME 1) Can work be done on a system if there is no motion? A) Yes, if an outside force is provided. B) Yes, since motion is only relative. C) No, since a system which is not moving has
CHAPTER 6 REVIEW NAME 1) Can work be done on a system if there is no motion? A) Yes, if an outside force is provided. B) Yes, since motion is only relative. C) No, since a system which is not moving has
Energy Whiteboard Problems
 Energy Whiteboard Problems 1. (a) Consider an object that is thrown vertically up into the air. Draw a graph of gravitational force vs. height for that object. (b) Based on your experience with the formula
Energy Whiteboard Problems 1. (a) Consider an object that is thrown vertically up into the air. Draw a graph of gravitational force vs. height for that object. (b) Based on your experience with the formula
Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy
 Welcome back to Physics 15 Today s agenda: Work Power Physics 15 Spring 017 Lecture 10-1 1 Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy For an object of mass m near the surface of the earth: U g = mgh h is height
Welcome back to Physics 15 Today s agenda: Work Power Physics 15 Spring 017 Lecture 10-1 1 Recall: Gravitational Potential Energy For an object of mass m near the surface of the earth: U g = mgh h is height
Power: Sources of Energy
 Chapter 5 Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
Chapter 5 Energy Power: Sources of Energy Tidal Power SF Bay Tidal Power Project Main Ideas (Encyclopedia of Physics) Energy is an abstract quantity that an object is said to possess. It is not something
In the last lecture the concept of kinetic energy was introduced. Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy that an object has by virtue of its motion
 1 PHYS:100 LETUE 9 MEHANIS (8) I. onservation of Energy In the last lecture the concept of kinetic energy was introduced. Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy that an object has by virtue of its motion KINETI
1 PHYS:100 LETUE 9 MEHANIS (8) I. onservation of Energy In the last lecture the concept of kinetic energy was introduced. Kinetic energy (KE) is the energy that an object has by virtue of its motion KINETI
