Lecture 3 : Bifurcation Analysis
|
|
|
- Aubrey Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 3 : Bifurcation Analysis D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis October - December 2008 D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
2 General settings 4 basic bifurcations (as long as there is only one unstable mode!) steady state solutions (Imω c = 0) z pitchfork z transcritical z limit point periodic solutions(imω c 0) z Hopf More complex bifurcations often leading to chaos, when several unstable modes are interacting. D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
3 3d order autocatalysis in an open well-stirred reactor 3d order autocatalysis in an open well-stirred reactor Bifurcation analysis dx dt dx dt = kax 2 k X τ (X 0 X) (A + 2X k k 3X) = x 3 + λx 2 µx + µ (after scaling) Elimination of x 2 term through transformation z = x λ 3 or, dz dt = z + λ «3 + λ z + λ «2 µ z + λ «+ µ dz λ 2 «2λ 3 dt = z3 + 3 µ z + 27 µλ «3 + µ (I) D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
4 3d order autocatalysis in an open well-stirred reactor First consider case where constant term vanishes. Condition on µ and λ for this : µ = 2λ3 9 (λ 3) Eq. for z becomes Steady states : dz dt = z3 + λ3 9λ 2 9 (λ 3) z (II) (λ > 3, since µ > 0 for physical reasons) z = 0 (λ > 9) q z ± = λ λ 9 3 λ 3 (λ > 9) z = 0 (λ < 9) Notice that trivial state z = 0 becomes unstable beyond the bifurcation point λ c. The stability of bifurcating branches can be checked straightforwardly (supercritical bifurcation). This example is in fact paradigmatic : any system in the vicinity of a pitchfork bifurcation can be reduced to eq. (II) (normal form) where z is a combination of the variables (order parameter). All other variables follow z passively D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
5 3d order autocatalysis in an open well-stirred reactor In the more general case where the constant term in (I) does not vanish, write equation as dz dt = z3 + uz + v According to the theory of cubic equations, we have the following situation for the steady states : v (1) (2) 1solution 3 solutions u D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
6 3d order autocatalysis in an open well-stirred reactor Limit point bifurcations! z z v u u fixed, (1) v fixed, (2) D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
7 For b > a : amplified oscillations of the linearized system Nonlinearities saturate growth and lead to an attracting periodic solution represented by a closed curve in phase space (limit cycle). stable limit cycle Y unstable steady state xs = a, ys = b/a X D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
8 Minimal nonlinear system illustrating onset of limit cycle : Poincare model dx dt dy dt = λx ω 0 y x `x 2 + y 2 = ω 0 x + λy y `x 2 + y 2 Keeping only linear terms yields eigenvalues of matrix J = λ «equal to ω0 ω = λ±iω 0 : ω 0 λ λ < 0 : damped oscillations ; λ > 0 : amplified oscillations ; λ = 0 : Hopf bifurcation point D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
9 Nonlinear analysis : switch to polar coordinates x = rcosφ, y = rsinφ. Multiplying first eq. by x and second eq. by y and adding yields : dr = λr r3 (I) dt (formally similar to normal form of pitchfork bifurcation except that r is here positive) Multiplying first equation by y and second equation by x and subtracting yields : dφ dt = ω 0 (II) D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
10 (I) and (II) are actually the normal form equations of a system undergoing a Hopf bifurcation. Solutions of (I) as t r = 0 for λ < 0 r = 0 for λ > 0 r = λ 1/2 for λ > 0 D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
11 Solutions of (II) φ = φ 0 + ω 0 t In the phase plane, for λ > 0 for λ < 0 y y unstable steady state x=y=0 r stable fixed point (focus) x=y=0 x x stable limit cycle system runs on cycle at constant angular velocity D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
12 Some global results related to limit cycles in two variable systems : 1. Bendixson s criterion dx dy = f (x, y) dt For a closed trajectory to exist, f x + g y must change sign in the (x, y) plane or vanish identically. 2. Bendixson s theorem The region bounded by a closed trajectory in (x, y) plane contains at least one fixed point (steady state solution) = g (x, y) dt 3. Poincare-Bendixson s theorem Any trajectory staying in a finite region of (x, y) phase space either approaches a fixed point or a periodic orbit. As a corollary, chaotic behavior in continuous time systems can only arise in the presence of at least three coupled variables. D. Sumpter & S.C. Nicolis
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS. Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations
 TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
TWO DIMENSIONAL FLOWS Lecture 5: Limit Cycles and Bifurcations 5. Limit cycles A limit cycle is an isolated closed trajectory [ isolated means that neighbouring trajectories are not closed] Fig. 5.1.1
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: August 22, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Jan Meibohm,
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: August 22, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Jan Meibohm,
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations
 7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
7 Two-dimensional bifurcations As in one-dimensional systems: fixed points may be created, destroyed, or change stability as parameters are varied (change of topological equivalence ). In addition closed
Lecture 5. Outline: Limit Cycles. Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles. Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps
 Lecture 5 Outline: Limit Cycles Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles Gradient systems Liapunov functions Dulacs criterion Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps Limit
Lecture 5 Outline: Limit Cycles Definition and examples How to rule out limit cycles Gradient systems Liapunov functions Dulacs criterion Poincare-Bendixson theorem Hopf bifurcations Poincare maps Limit
Edward Lorenz. Professor of Meteorology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 The Lorenz system Edward Lorenz Professor of Meteorology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology In 1963 derived a three dimensional system in efforts to model long range predictions for the weather
The Lorenz system Edward Lorenz Professor of Meteorology at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology In 1963 derived a three dimensional system in efforts to model long range predictions for the weather
= F ( x; µ) (1) where x is a 2-dimensional vector, µ is a parameter, and F :
 1 Bifurcations Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 A bifurcation is a qualitative change
1 Bifurcations Richard Bertram Department of Mathematics and Programs in Neuroscience and Molecular Biophysics Florida State University Tallahassee, Florida 32306 A bifurcation is a qualitative change
Numerical techniques: Deterministic Dynamical Systems
 Numerical techniques: Deterministic Dynamical Systems Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht, The Netherlands Transition behavior
Numerical techniques: Deterministic Dynamical Systems Henk Dijkstra Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Utrecht, The Netherlands Transition behavior
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II.
 Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Winter 2009/2010 Filip
Mathematical Foundations of Neuroscience - Lecture 7. Bifurcations II. Filip Piękniewski Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland Winter 2009/2010 Filip
Part II. Dynamical Systems. Year
 Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 34 Paper 1, Section II 30A Consider the dynamical system where β > 1 is a constant. ẋ = x + x 3 + βxy 2, ẏ = y + βx 2
Part II Year 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2017 34 Paper 1, Section II 30A Consider the dynamical system where β > 1 is a constant. ẋ = x + x 3 + βxy 2, ẏ = y + βx 2
Bifurcation of Fixed Points
 Bifurcation of Fixed Points CDS140B Lecturer: Wang Sang Koon Winter, 2005 1 Introduction ẏ = g(y, λ). where y R n, λ R p. Suppose it has a fixed point at (y 0, λ 0 ), i.e., g(y 0, λ 0 ) = 0. Two Questions:
Bifurcation of Fixed Points CDS140B Lecturer: Wang Sang Koon Winter, 2005 1 Introduction ẏ = g(y, λ). where y R n, λ R p. Suppose it has a fixed point at (y 0, λ 0 ), i.e., g(y 0, λ 0 ) = 0. Two Questions:
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 4. Bifurcations Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Local bifurcations for vector fields 1.1 The problem 1.2 The extended centre
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 4. Bifurcations Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Local bifurcations for vector fields 1.1 The problem 1.2 The extended centre
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems
 B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
B5.6 Nonlinear Systems 5. Global Bifurcations, Homoclinic chaos, Melnikov s method Alain Goriely 2018 Mathematical Institute, University of Oxford Table of contents 1. Motivation 1.1 The problem 1.2 A
Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics. Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS
 Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Dynamical Systems: A Basic Primer 1 1 Basic bifurcations 1.1 Fixed points and linear
Boulder School for Condensed Matter and Materials Physics Laurette Tuckerman PMMH-ESPCI-CNRS laurette@pmmh.espci.fr Dynamical Systems: A Basic Primer 1 1 Basic bifurcations 1.1 Fixed points and linear
MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation
 MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation 1 Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions When we were considering one-dimensional systems, we saw that subtle changes in parameter
MATH 415, WEEK 11: Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions, Hopf Bifurcation 1 Bifurcations in Multiple Dimensions When we were considering one-dimensional systems, we saw that subtle changes in parameter
1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point is a saddle point
 Solving a Linear System τ = trace(a) = a + d = λ 1 + λ 2 λ 1,2 = τ± = det(a) = ad bc = λ 1 λ 2 Classification of Fixed Points τ 2 4 1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point
Solving a Linear System τ = trace(a) = a + d = λ 1 + λ 2 λ 1,2 = τ± = det(a) = ad bc = λ 1 λ 2 Classification of Fixed Points τ 2 4 1. < 0: the eigenvalues are real and have opposite signs; the fixed point
2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2)
 2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2) As argued in Lecture 1 the population of non-overlapping generations can be modelled as a discrete dynamical system. This is an example of an
2 Discrete growth models, logistic map (Murray, Chapter 2) As argued in Lecture 1 the population of non-overlapping generations can be modelled as a discrete dynamical system. This is an example of an
LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7
 15-382 COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCE S18 LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7 INSTRUCTOR: GIANNI A. DI CARO GEOMETRIES IN THE PHASE SPACE Damped pendulum One cp in the region between two separatrix Separatrix Basin
15-382 COLLECTIVE INTELLIGENCE S18 LECTURE 8: DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS 7 INSTRUCTOR: GIANNI A. DI CARO GEOMETRIES IN THE PHASE SPACE Damped pendulum One cp in the region between two separatrix Separatrix Basin
Stabilization of Hyperbolic Chaos by the Pyragas Method
 Journal of Mathematics and System Science 4 (014) 755-76 D DAVID PUBLISHING Stabilization of Hyperbolic Chaos by the Pyragas Method Sergey Belyakin, Arsen Dzanoev, Sergey Kuznetsov Physics Faculty, Moscow
Journal of Mathematics and System Science 4 (014) 755-76 D DAVID PUBLISHING Stabilization of Hyperbolic Chaos by the Pyragas Method Sergey Belyakin, Arsen Dzanoev, Sergey Kuznetsov Physics Faculty, Moscow
Phase Synchronization
 Phase Synchronization Lecture by: Zhibin Guo Notes by: Xiang Fan May 10, 2016 1 Introduction For any mode or fluctuation, we always have where S(x, t) is phase. If a mode amplitude satisfies ϕ k = ϕ k
Phase Synchronization Lecture by: Zhibin Guo Notes by: Xiang Fan May 10, 2016 1 Introduction For any mode or fluctuation, we always have where S(x, t) is phase. If a mode amplitude satisfies ϕ k = ϕ k
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7)
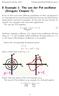 8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
8 Example 1: The van der Pol oscillator (Strogatz Chapter 7) So far we have seen some different possibilities of what can happen in two-dimensional systems (local and global attractors and bifurcations)
Practice Problems for Final Exam
 Math 1280 Spring 2016 Practice Problems for Final Exam Part 2 (Sections 6.6, 6.7, 6.8, and chapter 7) S o l u t i o n s 1. Show that the given system has a nonlinear center at the origin. ẋ = 9y 5y 5,
Math 1280 Spring 2016 Practice Problems for Final Exam Part 2 (Sections 6.6, 6.7, 6.8, and chapter 7) S o l u t i o n s 1. Show that the given system has a nonlinear center at the origin. ẋ = 9y 5y 5,
One Dimensional Dynamical Systems
 16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
16 CHAPTER 2 One Dimensional Dynamical Systems We begin by analyzing some dynamical systems with one-dimensional phase spaces, and in particular their bifurcations. All equations in this Chapter are scalar
6. Well-Stirred Reactors III
 6. Well-Stirred Reactors III Reactors reaction rate or reaction velocity defined for a closed system of uniform pressure, temperature, and composition situation in a real reactor is usually quite different
6. Well-Stirred Reactors III Reactors reaction rate or reaction velocity defined for a closed system of uniform pressure, temperature, and composition situation in a real reactor is usually quite different
Modelling biological oscillations
 Modelling biological oscillations Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-23836: Computational Modelling with MATLAB Outline Outline of Topics Van der Pol equation Van
Modelling biological oscillations Shan He School for Computational Science University of Birmingham Module 06-23836: Computational Modelling with MATLAB Outline Outline of Topics Van der Pol equation Van
More Details Fixed point of mapping is point that maps into itself, i.e., x n+1 = x n.
 More Details Fixed point of mapping is point that maps into itself, i.e., x n+1 = x n. If there are points which, after many iterations of map then fixed point called an attractor. fixed point, If λ
More Details Fixed point of mapping is point that maps into itself, i.e., x n+1 = x n. If there are points which, after many iterations of map then fixed point called an attractor. fixed point, If λ
Some Dynamical Behaviors In Lorenz Model
 International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. Issue. 7 Some Dynamical Behaviors In Lorenz Model Dr. Nabajyoti Das Assistant Professor, Department of Mathematics, Jawaharlal
International Journal Of Computational Engineering Research (ijceronline.com) Vol. Issue. 7 Some Dynamical Behaviors In Lorenz Model Dr. Nabajyoti Das Assistant Professor, Department of Mathematics, Jawaharlal
Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos
 Stephen Wiggins Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos Second Edition With 250 Figures 4jj Springer I Series Preface v L I Preface to the Second Edition vii Introduction 1 1 Equilibrium
Stephen Wiggins Introduction to Applied Nonlinear Dynamical Systems and Chaos Second Edition With 250 Figures 4jj Springer I Series Preface v L I Preface to the Second Edition vii Introduction 1 1 Equilibrium
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 14, 2019, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 14, 2019, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
Chaos. Lendert Gelens. KU Leuven - Vrije Universiteit Brussel Nonlinear dynamics course - VUB
 Chaos Lendert Gelens KU Leuven - Vrije Universiteit Brussel www.gelenslab.org Nonlinear dynamics course - VUB Examples of chaotic systems: the double pendulum? θ 1 θ θ 2 Examples of chaotic systems: the
Chaos Lendert Gelens KU Leuven - Vrije Universiteit Brussel www.gelenslab.org Nonlinear dynamics course - VUB Examples of chaotic systems: the double pendulum? θ 1 θ θ 2 Examples of chaotic systems: the
Clearly the passage of an eigenvalue through to the positive real half plane leads to a qualitative change in the phase portrait, i.e.
 Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
Bifurcations We have already seen how the loss of stiffness in a linear oscillator leads to instability. In a practical situation the stiffness may not degrade in a linear fashion, and instability may
ME 680- Spring Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems
 ME 680- Spring 2014 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems 1 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems Logistic equation: n = rn(1 n) velocity function Equilibria or fied points : initial conditions
ME 680- Spring 2014 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems 1 Geometrical Analysis of 1-D Dynamical Systems Logistic equation: n = rn(1 n) velocity function Equilibria or fied points : initial conditions
6.2 Brief review of fundamental concepts about chaotic systems
 6.2 Brief review of fundamental concepts about chaotic systems Lorenz (1963) introduced a 3-variable model that is a prototypical example of chaos theory. These equations were derived as a simplification
6.2 Brief review of fundamental concepts about chaotic systems Lorenz (1963) introduced a 3-variable model that is a prototypical example of chaos theory. These equations were derived as a simplification
Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 2014
 Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
Math 54. Treibergs Half of Final Exam Name: Practice Problems October 28, 24 Half of the final will be over material since the last midterm exam, such as the practice problems given here. The other half
STABILITY. Phase portraits and local stability
 MAS271 Methods for differential equations Dr. R. Jain STABILITY Phase portraits and local stability We are interested in system of ordinary differential equations of the form ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y),
MAS271 Methods for differential equations Dr. R. Jain STABILITY Phase portraits and local stability We are interested in system of ordinary differential equations of the form ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y),
7. Well-Stirred Reactors IV
 7. Well-Stirred Reactors IV The Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction: Models and Experiments Oregonator [based on the FKN mechanism; Field, R. J. & Noyes, R. M.: Oscillations in chemical systems. IV. Limit cycle
7. Well-Stirred Reactors IV The Belousov-Zhabotinsky Reaction: Models and Experiments Oregonator [based on the FKN mechanism; Field, R. J. & Noyes, R. M.: Oscillations in chemical systems. IV. Limit cycle
6-3 Solving Systems by Elimination
 Another method for solving systems of equations is elimination. Like substitution, the goal of elimination is to get one equation that has only one variable. To do this by elimination, you add the two
Another method for solving systems of equations is elimination. Like substitution, the goal of elimination is to get one equation that has only one variable. To do this by elimination, you add the two
MATH 614 Dynamical Systems and Chaos Lecture 24: Bifurcation theory in higher dimensions. The Hopf bifurcation.
 MATH 614 Dynamical Systems and Chaos Lecture 24: Bifurcation theory in higher dimensions. The Hopf bifurcation. Bifurcation theory The object of bifurcation theory is to study changes that maps undergo
MATH 614 Dynamical Systems and Chaos Lecture 24: Bifurcation theory in higher dimensions. The Hopf bifurcation. Bifurcation theory The object of bifurcation theory is to study changes that maps undergo
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 08, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: January 08, 2018, at 08 30 12 30 Johanneberg Kristian
Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10)
 Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10) Mason A. Porter 15/05/2010 1 Question 1 i. (6 points) Define a saddle-node bifurcation and show that the first order system dx dt = r x e x
Solutions for B8b (Nonlinear Systems) Fake Past Exam (TT 10) Mason A. Porter 15/05/2010 1 Question 1 i. (6 points) Define a saddle-node bifurcation and show that the first order system dx dt = r x e x
Lotka Volterra Predator-Prey Model with a Predating Scavenger
 Lotka Volterra Predator-Prey Model with a Predating Scavenger Monica Pescitelli Georgia College December 13, 2013 Abstract The classic Lotka Volterra equations are used to model the population dynamics
Lotka Volterra Predator-Prey Model with a Predating Scavenger Monica Pescitelli Georgia College December 13, 2013 Abstract The classic Lotka Volterra equations are used to model the population dynamics
CONTROLLING IN BETWEEN THE LORENZ AND THE CHEN SYSTEMS
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 12, No. 6 (22) 1417 1422 c World Scientific Publishing Company CONTROLLING IN BETWEEN THE LORENZ AND THE CHEN SYSTEMS JINHU LÜ Institute of Systems
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 12, No. 6 (22) 1417 1422 c World Scientific Publishing Company CONTROLLING IN BETWEEN THE LORENZ AND THE CHEN SYSTEMS JINHU LÜ Institute of Systems
Quadratic autocatalysis in an extended continuousflow stirred tank reactor (ECSTR)
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2016 Quadratic autocatalysis in an extended continuousflow
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences - Papers: Part A Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2016 Quadratic autocatalysis in an extended continuousflow
Summary of topics relevant for the final. p. 1
 Summary of topics relevant for the final p. 1 Outline Scalar difference equations General theory of ODEs Linear ODEs Linear maps Analysis near fixed points (linearization) Bifurcations How to analyze a
Summary of topics relevant for the final p. 1 Outline Scalar difference equations General theory of ODEs Linear ODEs Linear maps Analysis near fixed points (linearization) Bifurcations How to analyze a
DYNAMICS OF THREE COUPLED VAN DER POL OSCILLATORS WITH APPLICATION TO CIRCADIAN RHYTHMS
 Proceedings of IDETC/CIE 2005 ASME 2005 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference September 24-28, 2005, Long Beach, California USA DETC2005-84017
Proceedings of IDETC/CIE 2005 ASME 2005 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers and Information in Engineering Conference September 24-28, 2005, Long Beach, California USA DETC2005-84017
Dynamical systems tutorial. Gregor Schöner, INI, RUB
 Dynamical systems tutorial Gregor Schöner, INI, RUB Dynamical systems: Tutorial the word dynamics time-varying measures range of a quantity forces causing/accounting for movement => dynamical systems dynamical
Dynamical systems tutorial Gregor Schöner, INI, RUB Dynamical systems: Tutorial the word dynamics time-varying measures range of a quantity forces causing/accounting for movement => dynamical systems dynamical
ẋ = f(x, y), ẏ = g(x, y), (x, y) D, can only have periodic solutions if (f,g) changes sign in D or if (f,g)=0in D.
 4 Periodic Solutions We have shown that in the case of an autonomous equation the periodic solutions correspond with closed orbits in phase-space. Autonomous two-dimensional systems with phase-space R
4 Periodic Solutions We have shown that in the case of an autonomous equation the periodic solutions correspond with closed orbits in phase-space. Autonomous two-dimensional systems with phase-space R
Mathematical Modeling I
 Mathematical Modeling I Dr. Zachariah Sinkala Department of Mathematical Sciences Middle Tennessee State University Murfreesboro Tennessee 37132, USA November 5, 2011 1d systems To understand more complex
Mathematical Modeling I Dr. Zachariah Sinkala Department of Mathematical Sciences Middle Tennessee State University Murfreesboro Tennessee 37132, USA November 5, 2011 1d systems To understand more complex
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS, AND AN INTRODUCTION TO CHAOS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS, AND AN INTRODUCTION TO CHAOS Morris W. Hirsch University of California, Berkeley Stephen Smale University of California, Berkeley Robert L. Devaney Boston University
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS, AND AN INTRODUCTION TO CHAOS Morris W. Hirsch University of California, Berkeley Stephen Smale University of California, Berkeley Robert L. Devaney Boston University
5.2.2 Planar Andronov-Hopf bifurcation
 138 CHAPTER 5. LOCAL BIFURCATION THEORY 5.. Planar Andronov-Hopf bifurcation What happens if a planar system has an equilibrium x = x 0 at some parameter value α = α 0 with eigenvalues λ 1, = ±iω 0, ω
138 CHAPTER 5. LOCAL BIFURCATION THEORY 5.. Planar Andronov-Hopf bifurcation What happens if a planar system has an equilibrium x = x 0 at some parameter value α = α 0 with eigenvalues λ 1, = ±iω 0, ω
21-256: Partial differentiation
 21-256: Partial differentiation Clive Newstead, Thursday 5th June 2014 This is a summary of the important results about partial derivatives and the chain rule that you should know. Partial derivatives
21-256: Partial differentiation Clive Newstead, Thursday 5th June 2014 This is a summary of the important results about partial derivatives and the chain rule that you should know. Partial derivatives
Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part I: Theoretical Techniques. Lecture 4: Discrete systems + Chaos. Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325
 Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part I: Theoretical Techniques Lecture 4: Discrete systems + Chaos Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325 Discrete maps x n+1 = f(x n ) Discrete time steps. x 0
Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part I: Theoretical Techniques Lecture 4: Discrete systems + Chaos Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325 Discrete maps x n+1 = f(x n ) Discrete time steps. x 0
Dynamical Systems Analysis Using Differential Geometry
 Dynamical Systems Analysis Using Differential Geometry Jean-Marc GINOUX and Bruno ROSSETTO Laboratoire P.R.O.T.E.E., équipe EBMA / ISO Université du Sud Toulon-Var, B.P. 3, 83957, La Garde, ginoux@univ-tln.fr,
Dynamical Systems Analysis Using Differential Geometry Jean-Marc GINOUX and Bruno ROSSETTO Laboratoire P.R.O.T.E.E., équipe EBMA / ISO Université du Sud Toulon-Var, B.P. 3, 83957, La Garde, ginoux@univ-tln.fr,
Chapter 1 Bifurcations and Chaos in Dynamical Systems
 Chapter 1 Bifurcations and Chaos in Dynamical Systems Complex system theory deals with dynamical systems containing often a large number of variables. It extends dynamical system theory, which deals with
Chapter 1 Bifurcations and Chaos in Dynamical Systems Complex system theory deals with dynamical systems containing often a large number of variables. It extends dynamical system theory, which deals with
THREE DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS. Lecture 6: The Lorenz Equations
 THREE DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS Lecture 6: The Lorenz Equations 6. The Lorenz (1963) Equations The Lorenz equations were originally derived by Saltzman (1962) as a minimalist model of thermal convection in a
THREE DIMENSIONAL SYSTEMS Lecture 6: The Lorenz Equations 6. The Lorenz (1963) Equations The Lorenz equations were originally derived by Saltzman (1962) as a minimalist model of thermal convection in a
Chaos Control of the Chaotic Symmetric Gyroscope System
 48 Chaos Control of the Chaotic Symmetric Gyroscope System * Barış CEVHER, Yılmaz UYAROĞLU and 3 Selçuk EMIROĞLU,,3 Faculty of Engineering, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Sakarya
48 Chaos Control of the Chaotic Symmetric Gyroscope System * Barış CEVHER, Yılmaz UYAROĞLU and 3 Selçuk EMIROĞLU,,3 Faculty of Engineering, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Sakarya
Modelling Research Group
 Modelling Research Group The Importance of Noise in Dynamical Systems E. Staunton, P.T. Piiroinen November 20, 2015 Eoghan Staunton Modelling Research Group 2015 1 / 12 Introduction Historically mathematicians
Modelling Research Group The Importance of Noise in Dynamical Systems E. Staunton, P.T. Piiroinen November 20, 2015 Eoghan Staunton Modelling Research Group 2015 1 / 12 Introduction Historically mathematicians
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET. EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS. COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD
 CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: April 06, 2018, at 14 00 18 00 Johanneberg Kristian
CHALMERS, GÖTEBORGS UNIVERSITET EXAM for DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS COURSE CODES: TIF 155, FIM770GU, PhD Time: Place: Teachers: Allowed material: Not allowed: April 06, 2018, at 14 00 18 00 Johanneberg Kristian
Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part II: Biology Applications. Lecture 10: Coupled Systems. Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325
 Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part II: Biology Applications Lecture 10: Coupled Systems. Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325 Foreword In order to model populations of physical/biological
Dynamical Systems and Chaos Part II: Biology Applications Lecture 10: Coupled Systems. Ilya Potapov Mathematics Department, TUT Room TD325 Foreword In order to model populations of physical/biological
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis
 Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2010 r. Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/53
Nonlinear Control Lecture 2:Phase Plane Analysis Farzaneh Abdollahi Department of Electrical Engineering Amirkabir University of Technology Fall 2010 r. Farzaneh Abdollahi Nonlinear Control Lecture 2 1/53
Applied Dynamical Systems
 Applied Dynamical Systems Recommended Reading: (1) Morris W. Hirsch, Stephen Smale, and Robert L. Devaney. Differential equations, dynamical systems, and an introduction to chaos. Elsevier/Academic Press,
Applied Dynamical Systems Recommended Reading: (1) Morris W. Hirsch, Stephen Smale, and Robert L. Devaney. Differential equations, dynamical systems, and an introduction to chaos. Elsevier/Academic Press,
Lecture 1: A Preliminary to Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos
 Lecture 1: A Preliminary to Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos Autonomous Systems A set of coupled autonomous 1st-order ODEs. Here "autonomous" means that the right hand side of the equations does not explicitly
Lecture 1: A Preliminary to Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos Autonomous Systems A set of coupled autonomous 1st-order ODEs. Here "autonomous" means that the right hand side of the equations does not explicitly
arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017
![arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017 arxiv: v1 [nlin.ao] 19 May 2017](/thumbs/74/70757831.jpg) Feature-rich bifurcations in a simple electronic circuit Debdipta Goswami 1, and Subhankar Ray 2, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA
Feature-rich bifurcations in a simple electronic circuit Debdipta Goswami 1, and Subhankar Ray 2, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA
The Higgins-Selkov oscillator
 The Higgins-Selkov oscillator May 14, 2014 Here I analyse the long-time behaviour of the Higgins-Selkov oscillator. The system is ẋ = k 0 k 1 xy 2, (1 ẏ = k 1 xy 2 k 2 y. (2 The unknowns x and y, being
The Higgins-Selkov oscillator May 14, 2014 Here I analyse the long-time behaviour of the Higgins-Selkov oscillator. The system is ẋ = k 0 k 1 xy 2, (1 ẏ = k 1 xy 2 k 2 y. (2 The unknowns x and y, being
CENTER MANIFOLD AND NORMAL FORM THEORIES
 3 rd Sperlonga Summer School on Mechanics and Engineering Sciences 3-7 September 013 SPERLONGA CENTER MANIFOLD AND NORMAL FORM THEORIES ANGELO LUONGO 1 THE CENTER MANIFOLD METHOD Existence of an invariant
3 rd Sperlonga Summer School on Mechanics and Engineering Sciences 3-7 September 013 SPERLONGA CENTER MANIFOLD AND NORMAL FORM THEORIES ANGELO LUONGO 1 THE CENTER MANIFOLD METHOD Existence of an invariant
Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area
 ISSN 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 ( No. 4, pp. 85-9 Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area Debasis Mukherjee Department
ISSN 746-733, England, UK World Journal of Modelling and Simulation Vol. 8 ( No. 4, pp. 85-9 Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Prey-predator System with a Reserved Area Debasis Mukherjee Department
Solution to Homework #5 Roy Malka 1. Questions 2,3,4 of Homework #5 of M. Cross class. dv (x) dx
 Solution to Homework #5 Roy Malka. Questions 2,,4 of Homework #5 of M. Cross class. Bifurcations: (M. Cross) Consider the bifurcations of the stationary solutions of a particle undergoing damped one dimensional
Solution to Homework #5 Roy Malka. Questions 2,,4 of Homework #5 of M. Cross class. Bifurcations: (M. Cross) Consider the bifurcations of the stationary solutions of a particle undergoing damped one dimensional
Nonlinear Dynamic Systems Homework 1
 Nonlinear Dynamic Systems Homework 1 1. A particle of mass m is constrained to travel along the path shown in Figure 1, which is described by the following function yx = 5x + 1x 4, 1 where x is defined
Nonlinear Dynamic Systems Homework 1 1. A particle of mass m is constrained to travel along the path shown in Figure 1, which is described by the following function yx = 5x + 1x 4, 1 where x is defined
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time. delay
 Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
Difference Resonances in a controlled van der Pol-Duffing oscillator involving time delay This paper was published in the journal Chaos, Solitions & Fractals, vol.4, no., pp.975-98, Oct 9 J.C. Ji, N. Zhang,
Analysis of a lumped model of neocortex to study epileptiform ac
 of a lumped model of neocortex to study epileptiform activity Sid Visser Hil Meijer Stephan van Gils March 21, 2012 What is epilepsy? Pathology Neurological disorder, affecting 1% of world population Characterized
of a lumped model of neocortex to study epileptiform activity Sid Visser Hil Meijer Stephan van Gils March 21, 2012 What is epilepsy? Pathology Neurological disorder, affecting 1% of world population Characterized
Problem Set Number 2, j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014)
 Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
Problem Set Number 2, 18.385j/2.036j MIT (Fall 2014) Rodolfo R. Rosales (MIT, Math. Dept.,Cambridge, MA 02139) Due Mon., September 29, 2014. 1 Inverse function problem #01. Statement: Inverse function
8.385 MIT (Rosales) Hopf Bifurcations. 2 Contents Hopf bifurcation for second order scalar equations. 3. Reduction of general phase plane case to seco
 8.385 MIT Hopf Bifurcations. Rodolfo R. Rosales Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 239 September 25, 999 Abstract In two dimensions a Hopf bifurcation
8.385 MIT Hopf Bifurcations. Rodolfo R. Rosales Department of Mathematics Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, Massachusetts MA 239 September 25, 999 Abstract In two dimensions a Hopf bifurcation
The Big, Big Picture (Bifurcations II)
 The Big, Big Picture (Bifurcations II) Reading for this lecture: NDAC, Chapter 8 and Sec. 10.0-10.4. 1 Beyond fixed points: Bifurcation: Qualitative change in behavior as a control parameter is (slowly)
The Big, Big Picture (Bifurcations II) Reading for this lecture: NDAC, Chapter 8 and Sec. 10.0-10.4. 1 Beyond fixed points: Bifurcation: Qualitative change in behavior as a control parameter is (slowly)
APPPHYS217 Tuesday 25 May 2010
 APPPHYS7 Tuesday 5 May Our aim today is to take a brief tour of some topics in nonlinear dynamics. Some good references include: [Perko] Lawrence Perko Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems (Springer-Verlag
APPPHYS7 Tuesday 5 May Our aim today is to take a brief tour of some topics in nonlinear dynamics. Some good references include: [Perko] Lawrence Perko Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems (Springer-Verlag
A Producer-Consumer Model With Stoichiometry
 A Producer-Consumer Model With Stoichiometry Plan B project toward the completion of the Master of Science degree in Mathematics at University of Minnesota Duluth Respectfully submitted by Laura Joan Zimmermann
A Producer-Consumer Model With Stoichiometry Plan B project toward the completion of the Master of Science degree in Mathematics at University of Minnesota Duluth Respectfully submitted by Laura Joan Zimmermann
Chapter 23. Predicting Chaos The Shift Map and Symbolic Dynamics
 Chapter 23 Predicting Chaos We have discussed methods for diagnosing chaos, but what about predicting the existence of chaos in a dynamical system. This is a much harder problem, and it seems that the
Chapter 23 Predicting Chaos We have discussed methods for diagnosing chaos, but what about predicting the existence of chaos in a dynamical system. This is a much harder problem, and it seems that the
A Study of the Van der Pol Equation
 A Study of the Van der Pol Equation Kai Zhe Tan, s1465711 September 16, 2016 Abstract The Van der Pol equation is famous for modelling biological systems as well as being a good model to study its multiple
A Study of the Van der Pol Equation Kai Zhe Tan, s1465711 September 16, 2016 Abstract The Van der Pol equation is famous for modelling biological systems as well as being a good model to study its multiple
2.034: Nonlinear Dynamics and Waves. Term Project: Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear oscillators Mostafa Momen
 2.034: Nonlinear Dynamics and Waves Term Project: Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear oscillators Mostafa Momen May 2015 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1 Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear
2.034: Nonlinear Dynamics and Waves Term Project: Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear oscillators Mostafa Momen May 2015 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 1 Nonlinear dynamics of piece-wise linear
DYNAMICS OF ASYMMETRIC NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER
 8 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 8-19 (2003) DYNAMICS OF ASYMMETRIC NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER Chiou-Fong Chung and Chiang-Nan Chang* Key words: bifurcation, absorber,
8 Journal of Marine Science and Technology, Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 8-19 (2003) DYNAMICS OF ASYMMETRIC NONLINEAR VIBRATION ABSORBER Chiou-Fong Chung and Chiang-Nan Chang* Key words: bifurcation, absorber,
8.1 Bifurcations of Equilibria
 1 81 Bifurcations of Equilibria Bifurcation theory studies qualitative changes in solutions as a parameter varies In general one could study the bifurcation theory of ODEs PDEs integro-differential equations
1 81 Bifurcations of Equilibria Bifurcation theory studies qualitative changes in solutions as a parameter varies In general one could study the bifurcation theory of ODEs PDEs integro-differential equations
MATH 415, WEEK 12 & 13: Higher-Dimensional Systems, Lorenz Equations, Chaotic Behavior
 MATH 415, WEEK 1 & 13: Higher-Dimensional Systems, Lorenz Equations, Chaotic Behavior 1 Higher-Dimensional Systems Consider the following system of differential equations: dx = x y dt dy dt = xy y dz dt
MATH 415, WEEK 1 & 13: Higher-Dimensional Systems, Lorenz Equations, Chaotic Behavior 1 Higher-Dimensional Systems Consider the following system of differential equations: dx = x y dt dy dt = xy y dz dt
Application demonstration. BifTools. Maple Package for Bifurcation Analysis in Dynamical Systems
 Application demonstration BifTools Maple Package for Bifurcation Analysis in Dynamical Systems Introduction Milen Borisov, Neli Dimitrova Department of Biomathematics Institute of Mathematics and Informatics
Application demonstration BifTools Maple Package for Bifurcation Analysis in Dynamical Systems Introduction Milen Borisov, Neli Dimitrova Department of Biomathematics Institute of Mathematics and Informatics
Modelling and Mathematical Methods in Process and Chemical Engineering
 Modelling and Mathematical Methods in Process and Chemical Engineering Solution Series 3 1. Population dynamics: Gendercide The system admits two steady states The Jacobi matrix is ẋ = (1 p)xy k 1 x ẏ
Modelling and Mathematical Methods in Process and Chemical Engineering Solution Series 3 1. Population dynamics: Gendercide The system admits two steady states The Jacobi matrix is ẋ = (1 p)xy k 1 x ẏ
Complicated behavior of dynamical systems. Mathematical methods and computer experiments.
 Complicated behavior of dynamical systems. Mathematical methods and computer experiments. Kuznetsov N.V. 1, Leonov G.A. 1, and Seledzhi S.M. 1 St.Petersburg State University Universitetsky pr. 28 198504
Complicated behavior of dynamical systems. Mathematical methods and computer experiments. Kuznetsov N.V. 1, Leonov G.A. 1, and Seledzhi S.M. 1 St.Petersburg State University Universitetsky pr. 28 198504
The Sine Map. Jory Griffin. May 1, 2013
 The Sine Map Jory Griffin May, 23 Introduction Unimodal maps on the unit interval are among the most studied dynamical systems. Perhaps the two most frequently mentioned are the logistic map and the tent
The Sine Map Jory Griffin May, 23 Introduction Unimodal maps on the unit interval are among the most studied dynamical systems. Perhaps the two most frequently mentioned are the logistic map and the tent
CHAPTER 6 HOPF-BIFURCATION IN A TWO DIMENSIONAL NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 CHAPTER 6 HOPF-BIFURCATION IN A TWO DIMENSIONAL NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION [Discussion on this chapter is based on our paper entitled Hopf-Bifurcation Ina Two Dimensional Nonlinear Differential Equation,
CHAPTER 6 HOPF-BIFURCATION IN A TWO DIMENSIONAL NONLINEAR DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION [Discussion on this chapter is based on our paper entitled Hopf-Bifurcation Ina Two Dimensional Nonlinear Differential Equation,
Math Assignment 6
 Math 2280 - Assignment 6 Dylan Zwick Fall 2013 Section 3.7-1, 5, 10, 17, 19 Section 3.8-1, 3, 5, 8, 13 Section 4.1-1, 2, 13, 15, 22 Section 4.2-1, 10, 19, 28 1 Section 3.7 - Electrical Circuits 3.7.1 This
Math 2280 - Assignment 6 Dylan Zwick Fall 2013 Section 3.7-1, 5, 10, 17, 19 Section 3.8-1, 3, 5, 8, 13 Section 4.1-1, 2, 13, 15, 22 Section 4.2-1, 10, 19, 28 1 Section 3.7 - Electrical Circuits 3.7.1 This
Hopf Bifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators
 The Open Acoustics Journal 8 9-3 9 Open Access Hopf ifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators Jianping Cai *a and Jianhe Shen b a Department of
The Open Acoustics Journal 8 9-3 9 Open Access Hopf ifurcation Analysis and Approximation of Limit Cycle in Coupled Van Der Pol and Duffing Oscillators Jianping Cai *a and Jianhe Shen b a Department of
Models Involving Interactions between Predator and Prey Populations
 Models Involving Interactions between Predator and Prey Populations Matthew Mitchell Georgia College and State University December 30, 2015 Abstract Predator-prey models are used to show the intricate
Models Involving Interactions between Predator and Prey Populations Matthew Mitchell Georgia College and State University December 30, 2015 Abstract Predator-prey models are used to show the intricate
Controlling Chaos in a State-Dependent Nonlinear System
 Electronic version of an article published as International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos Vol. 12, No. 5, 2002, 1111-1119, DOI: 10.1142/S0218127402004942 World Scientific Publishing Company, https://www.worldscientific.com/worldscinet/ijbc
Electronic version of an article published as International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos Vol. 12, No. 5, 2002, 1111-1119, DOI: 10.1142/S0218127402004942 World Scientific Publishing Company, https://www.worldscientific.com/worldscinet/ijbc
CALCULATION OF NONLINEAR VIBRATIONS OF PIECEWISE-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING THE SHOOTING METHOD
 Vietnam Journal of Mechanics, VAST, Vol. 34, No. 3 (2012), pp. 157 167 CALCULATION OF NONLINEAR VIBRATIONS OF PIECEWISE-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING THE SHOOTING METHOD Nguyen Van Khang, Hoang Manh Cuong, Nguyen
Vietnam Journal of Mechanics, VAST, Vol. 34, No. 3 (2012), pp. 157 167 CALCULATION OF NONLINEAR VIBRATIONS OF PIECEWISE-LINEAR SYSTEMS USING THE SHOOTING METHOD Nguyen Van Khang, Hoang Manh Cuong, Nguyen
Final Exam December 20, 2011
 Final Exam December 20, 2011 Math 420 - Ordinary Differential Equations No credit will be given for answers without mathematical or logical justification. Simplify answers as much as possible. Leave solutions
Final Exam December 20, 2011 Math 420 - Ordinary Differential Equations No credit will be given for answers without mathematical or logical justification. Simplify answers as much as possible. Leave solutions
CDS 101/110a: Lecture 2.1 Dynamic Behavior
 CDS 11/11a: Lecture 2.1 Dynamic Behavior Richard M. Murray 6 October 28 Goals: Learn to use phase portraits to visualize behavior of dynamical systems Understand different types of stability for an equilibrium
CDS 11/11a: Lecture 2.1 Dynamic Behavior Richard M. Murray 6 October 28 Goals: Learn to use phase portraits to visualize behavior of dynamical systems Understand different types of stability for an equilibrium
/. 3D. a very abstract sort of problem, this research is a step on the way to applicable knowledge.
 /. 3D Corwin Atwood-Stone Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 691, USA (Dated: May 7, 009) A simulation of the mutual orbital motion of a point and a stick of equal masses in three
/. 3D Corwin Atwood-Stone Physics Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, Ohio 691, USA (Dated: May 7, 009) A simulation of the mutual orbital motion of a point and a stick of equal masses in three
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS, AND AN INTRODUCTION TO CHAOS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS, AND AN INTRODUCTION TO CHAOS Morris W. Hirsch University of California, Berkeley Stephen Smale University of California, Berkeley Robert L. Devaney Boston University
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS, DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS, AND AN INTRODUCTION TO CHAOS Morris W. Hirsch University of California, Berkeley Stephen Smale University of California, Berkeley Robert L. Devaney Boston University
Lectures on Periodic Orbits
 Lectures on Periodic Orbits 11 February 2009 Most of the contents of these notes can found in any typical text on dynamical systems, most notably Strogatz [1994], Perko [2001] and Verhulst [1996]. Complete
Lectures on Periodic Orbits 11 February 2009 Most of the contents of these notes can found in any typical text on dynamical systems, most notably Strogatz [1994], Perko [2001] and Verhulst [1996]. Complete
2 Lecture 2: Amplitude equations and Hopf bifurcations
 Lecture : Amplitude equations and Hopf bifurcations This lecture completes the brief discussion of steady-state bifurcations by discussing vector fields that describe the dynamics near a bifurcation. From
Lecture : Amplitude equations and Hopf bifurcations This lecture completes the brief discussion of steady-state bifurcations by discussing vector fields that describe the dynamics near a bifurcation. From
PHY411 Lecture notes Part 4
 PHY411 Lecture notes Part 4 Alice Quillen February 1, 2016 Contents 0.1 Introduction.................................... 2 1 Bifurcations of one-dimensional dynamical systems 2 1.1 Saddle-node bifurcation.............................
PHY411 Lecture notes Part 4 Alice Quillen February 1, 2016 Contents 0.1 Introduction.................................... 2 1 Bifurcations of one-dimensional dynamical systems 2 1.1 Saddle-node bifurcation.............................
Hopf bifurcations, and Some variations of diffusive logistic equation JUNPING SHIddd
 Hopf bifurcations, and Some variations of diffusive logistic equation JUNPING SHIddd College of William and Mary Williamsburg, Virginia 23187 Mathematical Applications in Ecology and Evolution Workshop
Hopf bifurcations, and Some variations of diffusive logistic equation JUNPING SHIddd College of William and Mary Williamsburg, Virginia 23187 Mathematical Applications in Ecology and Evolution Workshop
EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1
 EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1 Murat Arcak January 21 2016 1 Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Essentially Nonlinear Phenomena Continued
EE222 - Spring 16 - Lecture 2 Notes 1 Murat Arcak January 21 2016 1 Licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Essentially Nonlinear Phenomena Continued
Example of a Blue Sky Catastrophe
 PUB:[SXG.TEMP]TRANS2913EL.PS 16-OCT-2001 11:08:53.21 SXG Page: 99 (1) Amer. Math. Soc. Transl. (2) Vol. 200, 2000 Example of a Blue Sky Catastrophe Nikolaĭ Gavrilov and Andrey Shilnikov To the memory of
PUB:[SXG.TEMP]TRANS2913EL.PS 16-OCT-2001 11:08:53.21 SXG Page: 99 (1) Amer. Math. Soc. Transl. (2) Vol. 200, 2000 Example of a Blue Sky Catastrophe Nikolaĭ Gavrilov and Andrey Shilnikov To the memory of
