Problem Set 4 is due Thursday. Problem Set 5 will be out today or tomorrow. Launch Latest from MASCOT
|
|
|
- Briana Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1
2 Problem Set 4 is due Thursday. Problem Set 5 will be out today or tomorrow. Launch Latest from MASCOT
3 3 Continuous Spectra: Thermal Radiation The equations below quantitatively summarize the light-emitting properties of solid objects. The hotter the object the bluer the glow. The Sun (6000K) peaks in the middle of the visible spectrum (0.5 micrometers / 500 nanometers) Room temperature objects (300K) peak deep in the infrared (10 um). Wien's Law The hotter the object the brighter the glow. The power emitted from each square centimeter of the surface of a hot object increases as the fourth power of the temperature. Double the temperature and the emission goes up 16 times! Stefan-Boltzmann Law
4 8 Thermal Radiation and Circumstellar Disks
5 9 Thermal Radiation and Circumstellar Disks
6 10 Submillimeter Galaxies The study of the first galaxies in the distant universe benefits from the fact that much of the stellar radiation gets reprocessed by dust via absorption and re-emission at a temperature of around 30K, thus a peak wavelength around 100um. Cosmological redshift moves this peak into the radio/submillimeter part of the spectrum. Galaxies actually become brighter as they become more distant in a given radio band.
7 11
8 14 Luminosity vs. Flux Flux is the amount of energy passing through a unit area per unit time. Luminosity is the total amount of energy leaving a source. The Sun's Luminosity is 4x106 Watts. The Inverse Square Law says that Solar flux drops off with distance as R. Luminosity Flux= 4π R
9 15 Spherical Blackbodies (and Cows) The emergent flux from each square meter (watts/m ) of a blackbody is st4 (Stefan-Boltzmann Law). The surface area of a sphere is 4pR so it is easy to take the unit area flux and turn it into a luminosity. 4 L=(4 π R )(σ T )
10 17 Spherical Blackbodies (and Cows) The emergent flux from each square meter (watts/m ) of a blackbody is st4 (Stefan-Boltzmann Law). The surface area of a sphere is 4pR 4 L=(4 π R )(σ T ) Stars are spherical. Stars approximate blackbodies A star s color gives away it s temperature via Wien s Law. Given you know T. Measure the distance and flux and thus luminosity determine R Have a means of measuring the stellar radius determines L and thus the distance (because you can measure the flux and apply the inverse square law)
11 18 Equilibrium Temperature of Planets The Sun's Luminosity is 4x106 Watts. The Inverse Square Law says that Solar flux drops off with distance as R. At Earth s distance (1.5 x 1011 meters) the solar flux is 1400 W/m Luminosity Flux= 4π R
12 19 Equilibrium Temperature of Planets A spherical planet or asteroid presents a circular cross section to the Sun's light. The intercepted energy per unit time is: input = (1 A)π r Flux= Luminosity 4 π R L sun 4πR r is the radius of the object R is the distance to the sun A is the albedo of the object (its reflectivity)
13 0 Equilibrium Temperature of Planets A spherical planet or asteroid presents a circular cross section to the Sun's light. The intercepted energy per unit time is: input = (1 A)π r Fraction absorbed Flux= Luminosity 4 π R cross section L sun 4πR solar flux at R r is the radius of the object R is the distance to the sun A is the albedo of the object (its reflectivity)
14 1 Equilibrium Temperature of Planets The planet/asteroid radiates with emission efficiency relative to a perfect blackbody (i.e. emissivity), e 4 output = 4 π r σ T ϵ where e is the emissivity (think of it as the radiative efficiency) and would in general be equal to (1-A), however both are wavelength dependent and if you are absorbing visible light but emitting infrared the two terms can be quite different. Flux= Luminosity 4πR input = (1 A) π r L sun 4π R r is the radius of the object R is the distance to the sun A is the albedo of the object (its reflectivity)
15 Equilibrium Temperature of Planets Setting the input equal to the output yields: T= ( L star (1 A) 16 π σ ϵ R ) 1/ 4 the temperature of an object falls off as the square root of its distance from its star and depends weakly on the luminosity of the star (one-quarter power) Flux= Luminosity 4πR input = (1 A) π r L sun 4π R r is the radius of the object R is the distance to the sun or star A is the albedo of the object (its reflectivity) e is the emissivity
16 3 Equilibrium Temperature of Planets For our Solar System, and assuming (1-A) = e (so equal absorption and emission efficiency) Calculate out everything for the Earth (R=1AU, Lstar = Lsun ) and the result is 77K. T= ( L star (1 A) 16 π σ ϵ R 1 T =77 K R AU Flux= Luminosity 4πR input = (1 A) π r L sun 4π R r is the radius of the object R is the distance to the sun A is the albedo of the object (its reflectivity) e is the emissivity ) 1/ 4
17 4 Equilibrium Temperature of Planets Generalizing to any stellar luminosity (where Lstar is in units of solar luminosities) T= ( L star (1 A) 16 π σ ϵ R 1/ 4 star L T =77 K R AU Flux= Luminosity 4πR input = (1 A) π r L sun 4π R r is the radius of the object R is the distance to the sun A is the albedo of the object (its reflectivity) e is the emissivity ) 1/ 4
18 5 Asteroid Radiometry Asteroids can have quite different visual reflectivity, but their emissivities are similar, typically close to e=1. Infrared flux measurements are used to pin down asteroid sizes. A e~1
19 6 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption Individual atoms produce/absorb light only at precise discrete wavelengths/colors (or specifically at certain exact energies).
20 7 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption Emission at specific wavelengths arises from the discrete nature of electronic orbits in atoms. Electrons can only be in configurations that have a specific energy. Jumping between these configurations (higher to lower energy) emits light. A photon of exactly the right energy can kick an electron from a lower to higher energy.
21 8 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption This property arises from the discrete nature of electronic orbits in atoms. Electrons can only be in configurations that have a specific energy. Jumping between these configurations (higher to lower energy) emits light. Conversely, a photon of exactly the right energy can kick an electron from a lower to higher energy.
22 9 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels Consider the electron in orbit around the atomic nucleus (in this case a proton) held in orbit by the electrostatic attraction between two opposite charges. 1 Ze F elec = 4 π ϵ0 r me v F centrip = r
23 30 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels Consider the electron in orbit around the atomic nucleus (in this case a proton) held in orbit by the electrostatic attraction between two opposite charges. 1 e F elec = 4 π ϵ0 r me v F centrip = r Add a quantum mechanical twist that the angular momentum is quantized in integer multiples (n) of h/p. nh me v r = π
24 31 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels Equating the force laws and substituting in the quantized angular momentum equation to get rid of v, solving for r we get: ϵ0 h x 10 meters r (n) = n = n Z π Z e me Never forgetting that n is an integer. F centrip me v = r me v r = F elec 1 e = 4 π ϵ0 r nh π v = nh π me r
25 3 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels What is the energy of an orbit as a function of r(n)? Equate the force equations and rearrange to get ½ mv for K.E. Ze K.E. = 8 π ϵ0 r Ze P.E. = 4 π ϵ0 r Ze Total = 8 π ϵ0 r (n) F centrip me v = r me v r = nh π F elec 1 e = 4 π ϵ0 r ϵ0 h 5.9 x meters r (n) = n = n Z π Z e me
26 33 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels The absolute energy of an energy level is not nearly as interesting as the energy difference between two levels (corresponding to the energy of an emitted or absorbed photon). Converting the physical constants to a quantitative energy (in electron volts): Δ E = 13.6 ev F centrip me v 1 e F elec = = 4 π ϵ0 r r me v r = nh π [ 1 n lower ϵ0 h 1 n upper ] 5.9 x meters r (n) = n = n Z π Z e me
27 34 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels Converting this energy to the equivalent wavelength via E=hc/l yields the wavelength of a photon emitted or absorbed in an electron transition between two energy levels λ = nm Z nlower nupper [ F centrip me v = r me v r = nh π 1 ] F elec 1 e = 4 π ϵ0 r ϵ0 h 5.9 x meters r (n) = n = n Z π Z e me
28 35 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels If nupper = then the wavelength/energy calculated is the energy required to ionize the last electron from an element (or the only electron from hydrogen λ = nm Z nlower n upper [ 1 ]
29 36 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels A series of hydrogen lines has a common lower state Dn = nlower nupper = 1 is alpha, Dn = is beta... 1 = Lyman (ultraviolet): Lyman a is 11.6 nm 1 (a) 3 1 (b) 4 1 (g).. = Balmer (visible): Balmer a, known as Ha, is nm Red Teal Blue 3 = Paschen (near infrared) 4 = Brackett (infrared), Brackett g is 165 nm 5 = Pfund (infrared) 6 = Humphries (infrared) λ = nm Z nlower n upper [ 1 ]
30 37 H-alpha Solar Images
31 38 The Highway to Apache Point / Sunspot, NM
32 39
33 40 A Classical Approach to Atomic Energy Levels A series of hydrogen lines has a common lower state Dn = nlower nupper = 1 is alpha, Dn = is beta... Energy spacing between transitions decrease with increasing n upper, becoming vanishingly small as nupper approaches infinity. These closely packed transitions create a band edge at a wavelength corresponding to ionization from the nlower energy level. The Balmer Jump in stellar spectra results from this clumping of highorder lines λ = nm Z nlower n upper [ 1 ]
34 um 1.68um
35 4
36 43 Radiative Lifetime Accelerated charges radiate. Consider an electron in the nd hydrogen energy level. How long does it take, classically, to radiate enough energy to reach the energy of the 1st level? Answer = 3x10-9 s (you get half that for a formal quantum mechanical solution). Bottom line an excited state decays quite rapidly emitting a photon equal in energy (wavelength) to the energy difference between levels. Selection rules driven by quantum mechanical principles (exclusion law, angular momentum restrictions) limit allowed transitions and can make lifetimes substantially longer that this simple classical result.
37 44 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption This property arises from the discrete nature of electronic orbits in atoms. Electrons can only be in configurations that have a specific energy. Jumping between these configurations (higher to lower energy) emits light. A photon of exactly the right energy can kick an electron from a lower to higher energy.
38 45 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption This property arises from the discrete nature of electronic orbits in atoms. Electrons can only be in configurations that have a specific energy. Jumping between these configurations (higher to lower energy) emits light. A photon of exactly the right energy can kick an electron from a lower to higher energy.
39 46 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption Spectral lines can reveal the elemental content of a planet or star's atmosphere. Line intensity reveals both the quantity of the element as well as the temperature.
40 47 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption Spectral line absorption arises when light from a continuous source passes through a cold gas. The gas atoms selectively remove (actually scatter) specific colors/energies.
41 48 The Doppler Shift The observed wavelength of a spectral line depends on the velocity of the source toward or away from the observer. The amount of the shift is proportional to the object's velocity relative to the speed of light (so typically the shift is tiny but measurable). λ shifted λ rest Δλ v = = λ rest λ rest c
42 49 The Doppler Shift Objects approaching an observer have wavelengths artificially shifted toward shorter wavelengths a blueshift. Objects moving away toward longer wavelengths a redshift Note that these are directions in the electromagnetic spectrum, not absolute colors. λ shifted λ rest Δλ v = = λ rest λ rest c
43 The Doppler Shift λ shifted λ rest Δλ v = = λ rest λ rest c Using the Doppler Shift we can measure the subtle motions (towards or away from us) of stars, galaxies and interstellar gas without ever seeing actual movement 50
44 51 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption Doppler velocities of individual atoms in a gas broaden spectral lines in a way that is characteristic of the temperature and density.
45 5 Spectral Line Emission/Absorption Collisions between atoms can shorten lifetimes and broaden lines. ℏ Δ E ΔT >
46 53 Giant vs. Dwarf Star Spectra The difference is surface gravity / photospheric pressure. The collision time between gas atoms for stars of the same surface temperature will be pressure dependent with a longer time between collisions in the low pressure (giant star) configuration.
47 54 Giant vs. Dwarf Star Spectra The difference is surface gravity / photospheric pressure. The collision time between gas atoms for stars of the same surface temperature will be pressure dependent with a longer time between collisions in the low pressure (giant star) configuration.
MASCOT Lander to deploy on Wednesday
 1 2 3 4 MASCOT Lander to deploy on Wednesday More visual imaging, hopping, and infrared spectroscopy = mineralogy http://spaceflight101.com/spacecraft/hayabusa-2/ 5 Synodic vs. Sidereal Month As with the
1 2 3 4 MASCOT Lander to deploy on Wednesday More visual imaging, hopping, and infrared spectroscopy = mineralogy http://spaceflight101.com/spacecraft/hayabusa-2/ 5 Synodic vs. Sidereal Month As with the
The Nature of Light. Chapter Five
 The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
The Nature of Light Chapter Five Guiding Questions 1. How fast does light travel? How can this speed be measured? 2. Why do we think light is a wave? What kind of wave is it? 3. How is the light from an
X Rays must be viewed from space used for detecting exotic objects such as neutron stars and black holes also observing the Sun.
 6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
6/25 How do we get information from the telescope? 1. Galileo drew pictures. 2. With the invention of photography, we began taking pictures of the view in the telescope. With telescopes that would rotate
Light and Atoms. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies. ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies !ATH REVIEW: #AST CLASS: "OMEWORK #1
 ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
ASTR 1120 General Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies!ATH REVIEW: Tonight, 5-6pm, in RAMY N1B23 "OMEWORK #1 -Due THU, Sept. 10, by 5pm, on Mastering Astronomy CLASS RECORDED STARTED - INFO WILL BE POSTED on CULEARN
Topics Covered in Chapter. Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation. A Subatomic Interlude II. A Subatomic Interlude. A Subatomic Interlude III
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation
 Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Light and Other Electromagnetic Radiation 1 Topics Covered in Chapter 1.Structure of Atoms 2.Origins of Electromagnetic Radiation 3.Objects with Different Temperature and their Electromagnetic Radiation
Assignments. For Wed. 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial)
 Assignments For Wed. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial) 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger Which forms of light are lower in energy and frequency than the
Assignments For Wed. Do Online Exercise 08 ( Doppler shift tutorial) 1 st Midterm is Friday, Oct. 12 Chapter 5 Light: The Cosmic Messenger Which forms of light are lower in energy and frequency than the
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Sir Joseph John Thomson J. J. Thomson 1856-1940 Discovered the electron Did extensive work with cathode ray deflections 1906 Nobel Prize for discovery of electron Early Models
Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5. What is light? What is a wave? Radiation carries information
 Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
Concepts: Properties of Electromagnetic Radiation Chapter 5 Electromagnetic waves Types of spectra Temperature Blackbody radiation Dual nature of radiation Atomic structure Interaction of light and matter
General Physics (PHY 2140)
 General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 33 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Atomic spectra Bohr s theory of hydrogen http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy140/ Chapter 8 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Atomic
General Physics (PHY 140) Lecture 33 Modern Physics Atomic Physics Atomic spectra Bohr s theory of hydrogen http://www.physics.wayne.edu/~apetrov/phy140/ Chapter 8 1 Lightning Review Last lecture: 1. Atomic
What is LIGHT? Reading Question
 Reading Question What is LIGHT? A. Light is a wave, like sound only much faster. B. Light is like little particles. Each one is a photon. C. Light is the absence of dark. D. A kind of energy we model with
Reading Question What is LIGHT? A. Light is a wave, like sound only much faster. B. Light is like little particles. Each one is a photon. C. Light is the absence of dark. D. A kind of energy we model with
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16]
![AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System. MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16]](/thumbs/78/77847540.jpg) AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] REVIEW Light as Information Bearer We can separate light into its different wavelengths (spectrum).
AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM II: Tuesday, April 5 [covering Lectures 10 through 16] REVIEW Light as Information Bearer We can separate light into its different wavelengths (spectrum).
Chapter 5 Light and Matter
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Chapter 5 Light and Matter Stars and galaxies are too far for us to send a spacecraft or to visit (in our lifetimes). All we can receive from them is light But there is much we can learn (composition,
Light. October 14, ) Exam Review 2) Introduction 3) Light Waves 4) Atoms 5) Light Sources
 Light October 14, 2002 1) Exam Review 2) Introduction 3) Light Waves 4) Atoms 5) Light Sources Waves You know of many types of waves water, sound, seismic, etc A wave is something oscillating back and
Light October 14, 2002 1) Exam Review 2) Introduction 3) Light Waves 4) Atoms 5) Light Sources Waves You know of many types of waves water, sound, seismic, etc A wave is something oscillating back and
Discussion Review Test #2. Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
 Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
Discussion Review Test #2 Units 12-19: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) Galileo used his observations of the changing phases of Venus to demonstrate that a. the sun moves around the Earth b. the universe
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
Astronomy The Nature of Light
 Astronomy The Nature of Light A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Measuring the speed of light Light is an electromagnetic wave The relationship between Light and temperature
Astronomy The Nature of Light A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Measuring the speed of light Light is an electromagnetic wave The relationship between Light and temperature
Quantum Mechanics and Stellar Spectroscopy.
 Quantum Mechanics and Stellar Spectroscopy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Recall the electric force. Like gravity it is a 1/r 2 force/ That is: F elec = Z 1 Z 2 e2 r 2 where Z 1 and Z 2 are the (integer) numbers
Quantum Mechanics and Stellar Spectroscopy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ Recall the electric force. Like gravity it is a 1/r 2 force/ That is: F elec = Z 1 Z 2 e2 r 2 where Z 1 and Z 2 are the (integer) numbers
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. How do we experience light? Colors of Light. How do light and matter interact?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos How do we experience light? The warmth of sunlight tells us that light is a form of energy We can measure the amount of energy emitted by a
Astro 210 Lecture 13 Feb 16, 2011
 Astro 210 Lecture 13 Feb 16, 2011 Announcements Hour Exam 1 in class Friday info online HW1 bonus problem due online Friday last Planetarium shows: tomorrow and Monday registration, report forms, info
Astro 210 Lecture 13 Feb 16, 2011 Announcements Hour Exam 1 in class Friday info online HW1 bonus problem due online Friday last Planetarium shows: tomorrow and Monday registration, report forms, info
Today. Spectra. Thermal Radiation. Wien s Law. Stefan-Boltzmann Law. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Spectra & Composition
 Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
Today Spectra Thermal Radiation Wien s Law Stefan-Boltzmann Law Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Spectra & Composition Spectrum Originally, the range of colors obtained by passing sunlight through
ASTRONOMY QUALIFYING EXAM August Possibly Useful Quantities
 L = 3.9 x 10 33 erg s 1 M = 2 x 10 33 g M bol = 4.74 R = 7 x 10 10 cm 1 A.U. = 1.5 x 10 13 cm 1 pc = 3.26 l.y. = 3.1 x 10 18 cm a = 7.56 x 10 15 erg cm 3 K 4 c= 3.0 x 10 10 cm s 1 σ = ac/4 = 5.7 x 10 5
L = 3.9 x 10 33 erg s 1 M = 2 x 10 33 g M bol = 4.74 R = 7 x 10 10 cm 1 A.U. = 1.5 x 10 13 cm 1 pc = 3.26 l.y. = 3.1 x 10 18 cm a = 7.56 x 10 15 erg cm 3 K 4 c= 3.0 x 10 10 cm s 1 σ = ac/4 = 5.7 x 10 5
Chapter 28. Atomic Physics
 Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
Chapter 28 Atomic Physics Quantum Numbers and Atomic Structure The characteristic wavelengths emitted by a hot gas can be understood using quantum numbers. No two electrons can have the same set of quantum
[10] Spectroscopy (9/28/17)
![[10] Spectroscopy (9/28/17) [10] Spectroscopy (9/28/17)](/thumbs/85/91855577.jpg) 1 [10] Spectroscopy (9/28/17) Upcoming Items 1. Homework #5 due on Tuesday 2. Midterm #1 October 10 3. Read Ch. 6.2 & 6.3 by next class (skim the rest of Ch. 6). Do the selfstudy quizzes APOD 9/28/16 2
1 [10] Spectroscopy (9/28/17) Upcoming Items 1. Homework #5 due on Tuesday 2. Midterm #1 October 10 3. Read Ch. 6.2 & 6.3 by next class (skim the rest of Ch. 6). Do the selfstudy quizzes APOD 9/28/16 2
Family of stars. Fred Sarazin Physics Department, Colorado School of Mines. PHGN324: Family of stars
 Family of stars Reminder: the stellar magnitude scale In the 1900 s, the magnitude scale was defined as follows: a difference of 5 in magnitude corresponds to a change of a factor 100 in brightness. Dm
Family of stars Reminder: the stellar magnitude scale In the 1900 s, the magnitude scale was defined as follows: a difference of 5 in magnitude corresponds to a change of a factor 100 in brightness. Dm
Chapter 6. Atoms and Starlight
 Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
Chapter 6 Atoms and Starlight What is light? Light is an electromagnetic wave. Wavelength and Frequency wavelength frequency = speed of light = constant Particles of Light Particles of light are called
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Observing Highlights. Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Lecture Outline
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Lab Observing Trip Next week: Tues (9/28) & Thurs (9/30) let me know ASAP if you have an official conflict (class, work) - website: http://astro.physics.uiowa.edu/~clang/sgu_fall10/observing_trip.html
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe Announcements Lab Observing Trip Next week: Tues (9/28) & Thurs (9/30) let me know ASAP if you have an official conflict (class, work) - website: http://astro.physics.uiowa.edu/~clang/sgu_fall10/observing_trip.html
10/31/2018. Chapter 7. Atoms Light and Spectra. Thursday Lab Announcement. Topics For Today s Class Black Body Radiation Laws
 Phys1411 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Thursday Lab Announcement Jonah will start the Lab at 6:00 PM. Two pieces of Glass and HST Lunar Phases Topics
Phys1411 Introductory Astronomy Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Thursday Lab Announcement Jonah will start the Lab at 6:00 PM. Two pieces of Glass and HST Lunar Phases Topics
aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously
 Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
Astronomy 1143 Quiz 2 Review
 Astronomy 1143 Quiz 2 Review Prof. Pradhan October 1, 2018 Light 1. What is light? Light is electromagnetic energy It is both a particle (photon) and a wave 2. How is light created and what can light interact
Astronomy 1143 Quiz 2 Review Prof. Pradhan October 1, 2018 Light 1. What is light? Light is electromagnetic energy It is both a particle (photon) and a wave 2. How is light created and what can light interact
ATOMIC MODELS. Models are formulated to fit the available data. Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral.
 ATOMIC MODELS Models are formulated to fit the available data. 1900 Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral. Atom was known to give off electrons. THOMPSON MODEL To satisfy the
ATOMIC MODELS Models are formulated to fit the available data. 1900 Atom was known to have certain size. Atom was known to be neutral. Atom was known to give off electrons. THOMPSON MODEL To satisfy the
Lecture 3: Emission and absorption
 Lecture 3: Emission and absorption Senior Astrophysics 2017-03-10 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 3: Emission and absorption 2017-03-10 1 / 35 Outline 1 Optical depth 2 Sources of radiation 3 Blackbody radiation
Lecture 3: Emission and absorption Senior Astrophysics 2017-03-10 Senior Astrophysics Lecture 3: Emission and absorption 2017-03-10 1 / 35 Outline 1 Optical depth 2 Sources of radiation 3 Blackbody radiation
Spectrum of Radiation. Importance of Radiation Transfer. Radiation Intensity and Wavelength. Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate
 Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Radiation Intensity and Wavelength frequency Planck s constant Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Radiation Intensity and Wavelength frequency Planck s constant Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption
Teacher of the Week DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS
 Teacher of the Week DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON E-2 STELLAR RADIATION IB Assessment Statements Topic E-2, Stellar Radiation and Stellar Types Energy Source E.2.1.
Teacher of the Week DEVIL PHYSICS THE BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS IB PHYSICS TSOKOS LESSON E-2 STELLAR RADIATION IB Assessment Statements Topic E-2, Stellar Radiation and Stellar Types Energy Source E.2.1.
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate
 Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption and emission Cloud and radiation Radiative-convective equilibrium
Lecture 3: Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate Solar and infrared radiation selective absorption and emission Selective absorption and emission Cloud and radiation Radiative-convective equilibrium
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS. Atoms. 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model. 6. Hydrogen spectrum
 CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
CONCEPT MAP ATOMS Atoms 1.Thomson model 2.Rutherford model 3.Bohr model 4.Emission line spectra 2a. Alpha scattering experiment 3a. Bohr s postulates 6. Hydrogen spectrum 8. De Broglie s explanation 5.Absorption
Lecture5PracticeQuiz.txt
 TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 6 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. The difference between radiation and sound is that a. radiation exhibits the Doppler effect, whereas sound does not. b. radiation travels much
TAKEN FROM HORIZONS 7TH EDITION CHAPTER 6 TUTORIAL QUIZ 1. The difference between radiation and sound is that a. radiation exhibits the Doppler effect, whereas sound does not. b. radiation travels much
Physics Homework Set I Su2015
 1) The particles which enter into chemical reactions are the atom's: 1) _ A) protons. B) positrons. C) mesons. D) electrons. E) neutrons. 2) Which of the following type of electromagnetic radiation has
1) The particles which enter into chemical reactions are the atom's: 1) _ A) protons. B) positrons. C) mesons. D) electrons. E) neutrons. 2) Which of the following type of electromagnetic radiation has
The Physics of Light, part 2. Astronomy 111
 Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Lecture 7: The Physics of Light, part 2 Astronomy 111 Spectra Twinkle, twinkle, little star, How I wonder what you are. Every type of atom, ion, and molecule has a unique spectrum Ion: an atom with electrons
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Electron Discharge tube (circa 1900 s) There is something ( cathode rays ) which is emitted by the cathode and causes glowing Unlike light, these rays are deflected
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Electron Discharge tube (circa 1900 s) There is something ( cathode rays ) which is emitted by the cathode and causes glowing Unlike light, these rays are deflected
Lecture #8. Light-matter interaction. Kirchoff s laws
 1 Lecture #8 Light-matter interaction Kirchoff s laws 2 Line emission/absorption Atoms: release and absorb photons with a predefined set of energies (discrete). The number of protons determine the chemical
1 Lecture #8 Light-matter interaction Kirchoff s laws 2 Line emission/absorption Atoms: release and absorb photons with a predefined set of energies (discrete). The number of protons determine the chemical
Types of Spectra. How do spectrum lines form? 3/30/09. Electron cloud. Atom. Nucleus
 The electron should be thought of as a distribution or cloud of probability around the nucleus that on average behave like a point particle on a fixed circular path Types of Spectra How do spectrum lines
The electron should be thought of as a distribution or cloud of probability around the nucleus that on average behave like a point particle on a fixed circular path Types of Spectra How do spectrum lines
Announcements. There is no homework next week. Tuesday s sections (right after the midterm) will be cancelled.
 1 Announcements The Midterm is one week away! Bring: Calculator, scantron (big red form), pencil No notes, cellphones, or books allowed. Homework #4 is due this thursday There is no homework next week.
1 Announcements The Midterm is one week away! Bring: Calculator, scantron (big red form), pencil No notes, cellphones, or books allowed. Homework #4 is due this thursday There is no homework next week.
Example: model a star using a two layer model: Radiation starts from the inner layer as blackbody radiation at temperature T in. T out.
 Next, consider an optically thick source: Already shown that in the interior, radiation will be described by the Planck function. Radiation escaping from the source will be modified because the temperature
Next, consider an optically thick source: Already shown that in the interior, radiation will be described by the Planck function. Radiation escaping from the source will be modified because the temperature
where n = (an integer) =
 5.111 Lecture Summary #5 Readings for today: Section 1.3 (1.6 in 3 rd ed) Atomic Spectra, Section 1.7 up to equation 9b (1.5 up to eq. 8b in 3 rd ed) Wavefunctions and Energy Levels, Section 1.8 (1.7 in
5.111 Lecture Summary #5 Readings for today: Section 1.3 (1.6 in 3 rd ed) Atomic Spectra, Section 1.7 up to equation 9b (1.5 up to eq. 8b in 3 rd ed) Wavefunctions and Energy Levels, Section 1.8 (1.7 in
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam
 Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
Review Questions for the new topics that will be on the Final Exam Be sure to review the lecture-tutorials and the material we covered on the first three exams. How does speed differ from velocity? Give
3/26/2018. Atoms Light and Spectra. Topics For Today s Class. Reminder. Topics For Today s Class. The Atom. Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Reminder Homework for Chapter 5, 6 and 7 is posted
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Phys1403 Stars and Galaxies Instructor: Dr. Goderya Chapter 7 Atoms Light and Spectra Reminder Homework for Chapter 5, 6 and 7 is posted
Astronomy 150 K. Nordsieck Spring Exam 1 Solutions. 1. ( T F ) In Madison the North Star, Polaris, is situated almost exactly at the zenith.
 Astronomy 150 K. Nordsieck Spring 2000 Exam 1 Solutions True or False (Circle T or F) 1. ( T F ) In Madison the North Star, Polaris, is situated almost exactly at the zenith. False. Polaris is near the
Astronomy 150 K. Nordsieck Spring 2000 Exam 1 Solutions True or False (Circle T or F) 1. ( T F ) In Madison the North Star, Polaris, is situated almost exactly at the zenith. False. Polaris is near the
Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars
 Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Doppler Shift At each point the emitter is at the center of a circular wavefront extending out from its present location. Spectroscopy, the Doppler Shift and Masses of Binary Stars http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/astropix.html
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom Discovery and Properties of the electron
 Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Chapter 27 Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom 27-1 Discovery and Properties of the electron Measure charge to mass ratio e/m (J. J. Thomson, 1897) When apply magnetic field only, the rays are
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4)
 Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Lecture Outline: Spectroscopy (Ch. 4) NOTE: These are just an outline of the lectures and a guide to the textbook. The material will be covered in more detail in class. We will cover nearly all of the
Guiding Questions. Stellar Evolution. Stars Evolve. Interstellar Medium and Nebulae
 Guiding Questions Stellar Evolution 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve? 2. What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? 3. What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun?
Guiding Questions Stellar Evolution 1. Why do astronomers think that stars evolve? 2. What kind of matter exists in the spaces between the stars? 3. What steps are involved in forming a star like the Sun?
Today. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Stellar Spectra & Composition. Doppler Effect & Motion. Extrasolar Planets
 Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Final Exam: Thursday 05/02 7:00 9:00 pm in STEW 183
 Final Exam: Thursday 05/02 7:00 9:00 pm in STEW 183 Covers all readings, lectures, homework from Chapters 17 through 30 Be sure to bring your student ID card, calculator, pencil, and up to three onepage
Final Exam: Thursday 05/02 7:00 9:00 pm in STEW 183 Covers all readings, lectures, homework from Chapters 17 through 30 Be sure to bring your student ID card, calculator, pencil, and up to three onepage
From Last Time Pearson Education, Inc.
 From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
From Last Time Light: Absorption, Emission, Transmission, Reflection, and Scattering c=λ x f E=h x f Light (electromagnetic radiation) extends from gamma rays (high E, high f, small λ) to radio waves (small
Astronomy 421. Lecture 14: Stellar Atmospheres III
 Astronomy 421 Lecture 14: Stellar Atmospheres III 1 Lecture 14 - Key concepts: Spectral line widths and shapes Curve of growth 2 There exists a stronger jump, the Lyman limit, occurring at the wavelength
Astronomy 421 Lecture 14: Stellar Atmospheres III 1 Lecture 14 - Key concepts: Spectral line widths and shapes Curve of growth 2 There exists a stronger jump, the Lyman limit, occurring at the wavelength
Light carries energy. Lecture 5 Understand Light. Is light. Light as a Particle. ANSWER: Both.
 Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
Light carries energy Lecture 5 Understand Light Reading: Chapter 6 You feel energy carried by light when light hits your skin. Energy Conservation: Radiation energy will be given to molecules making your
Astronomy II (ASTR-1020) Homework 2
 Astronomy II (ASTR-1020) Homework 2 Due: 10 February 2009 The answers of this multiple choice homework are to be indicated on a Scantron sheet (either Form # 822 N-E or Ref # ABF-882) which you are to
Astronomy II (ASTR-1020) Homework 2 Due: 10 February 2009 The answers of this multiple choice homework are to be indicated on a Scantron sheet (either Form # 822 N-E or Ref # ABF-882) which you are to
c = l Light: The Cosmic Messenger 1/23/18
 Reading for today s and Thur class: ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 3 Tues 23 Jan 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
Reading for today s and Thur class: ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 3 Tues 23 Jan 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
 Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Astronomy 10 HOMEWORK - Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Use a calculator whenever necessary. For full credit, always show your work and explain how you got your answer in full, complete sentences on a separate
Light and Atoms
 Light and Atoms ASTR 170 2010 S1 Daniel Zucker E7A 317 zucker@science.mq.edu.au ASTR170 Introductory Astronomy: II. Light and Atoms 1 Overview We ve looked at telescopes, spectrographs and spectra now
Light and Atoms ASTR 170 2010 S1 Daniel Zucker E7A 317 zucker@science.mq.edu.au ASTR170 Introductory Astronomy: II. Light and Atoms 1 Overview We ve looked at telescopes, spectrographs and spectra now
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016
 Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Announcement: Tonight s observing session with Stephanie Ho has been CANCELLED. She has rescheduled it for 8-9pm on Thursday Nov. 3 rd. Hopefully the clouds will part by then. Lecture
Astronomy 1 Fall 2016 Announcement: Tonight s observing session with Stephanie Ho has been CANCELLED. She has rescheduled it for 8-9pm on Thursday Nov. 3 rd. Hopefully the clouds will part by then. Lecture
Pictures of Atoms. 48 iron atoms on copper Made with a scanning tunnelling microscope
 A-toms = Not Cutable Democritus 420BC popularized the theory matter was made of Atoms: Too small to be seen Indivisible Surrounded by a void Solid No internal structure Pictures of Atoms 48 iron atoms
A-toms = Not Cutable Democritus 420BC popularized the theory matter was made of Atoms: Too small to be seen Indivisible Surrounded by a void Solid No internal structure Pictures of Atoms 48 iron atoms
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
 Astr 102: Introduction to Astronomy Fall Quarter 2009, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture 4: The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1 Understanding Stellar and Galaxy Properties, and Cosmology Four
Astr 102: Introduction to Astronomy Fall Quarter 2009, University of Washington, Željko Ivezić Lecture 4: The Electromagnetic Spectrum 1 Understanding Stellar and Galaxy Properties, and Cosmology Four
Properties of Stars (continued) Some Properties of Stars. What is brightness?
 Properties of Stars (continued) Some Properties of Stars Luminosity Temperature of the star s surface Mass Physical size 2 Chemical makeup 3 What is brightness? Apparent brightness is the energy flux (watts/m
Properties of Stars (continued) Some Properties of Stars Luminosity Temperature of the star s surface Mass Physical size 2 Chemical makeup 3 What is brightness? Apparent brightness is the energy flux (watts/m
Physics 1C Lecture 29A. Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29
 Physics 1C Lecture 29A Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29 Particle in a Box Let s consider a particle confined to a one-dimensional region in space. Following the quantum mechanics approach, we need to find
Physics 1C Lecture 29A Finish off Ch. 28 Start Ch. 29 Particle in a Box Let s consider a particle confined to a one-dimensional region in space. Following the quantum mechanics approach, we need to find
ASTRONOMY. Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
ASTRONOMY Chapter 5 RADIATION AND SPECTRA PowerPoint Image Slideshow FIGURE 5.1 Our Sun in Ultraviolet Light. This photograph of the Sun was taken at several different wavelengths of ultraviolet, which
Sources of radiation
 Sources of radiation Most important type of radiation is blackbody radiation. This is radiation that is in thermal equilibrium with matter at some temperature T. Lab source of blackbody radiation: hot
Sources of radiation Most important type of radiation is blackbody radiation. This is radiation that is in thermal equilibrium with matter at some temperature T. Lab source of blackbody radiation: hot
An electron can be liberated from a surface due to particle collisions an electron and a photon.
 Quantum Theory and the Atom the Bohr Atom The story so far... 1. Einstein argued that light is a photon (particle) and each photon has a discrete amount of energy associated with it governed by Planck's
Quantum Theory and the Atom the Bohr Atom The story so far... 1. Einstein argued that light is a photon (particle) and each photon has a discrete amount of energy associated with it governed by Planck's
Chapter 39. Particles Behaving as Waves
 Chapter 39 Particles Behaving as Waves 39.1 Electron Waves Light has a dual nature. Light exhibits both wave and particle characteristics. Louis de Broglie postulated in 1924 that if nature is symmetric,
Chapter 39 Particles Behaving as Waves 39.1 Electron Waves Light has a dual nature. Light exhibits both wave and particle characteristics. Louis de Broglie postulated in 1924 that if nature is symmetric,
Earth: the Goldilocks Planet
 Earth: the Goldilocks Planet Not too hot (460 C) Fig. 3-1 Not too cold (-55 C) Wave properties: Wavelength, velocity, and? Fig. 3-2 Reviewing units: Wavelength = distance (meters or nanometers, etc.) Velocity
Earth: the Goldilocks Planet Not too hot (460 C) Fig. 3-1 Not too cold (-55 C) Wave properties: Wavelength, velocity, and? Fig. 3-2 Reviewing units: Wavelength = distance (meters or nanometers, etc.) Velocity
Take away concepts. What is Energy? Solar Radiation Emission and Absorption. Energy: The ability to do work
 Solar Radiation Emission and Absorption Take away concepts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Conservation of energy. Black body radiation principle Emission wavelength and temperature (Wien s Law). Radiation vs. distance
Solar Radiation Emission and Absorption Take away concepts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Conservation of energy. Black body radiation principle Emission wavelength and temperature (Wien s Law). Radiation vs. distance
Review: Properties of a wave
 Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
A star is at a distance of 1.3 parsecs, what is its parallax?
 Stars Spectral lines from stars Binaries and the masses of stars Classifying stars: HR diagram Luminosity, radius, and temperature Vogt-Russell theorem Main sequence Evolution on the HR diagram A star
Stars Spectral lines from stars Binaries and the masses of stars Classifying stars: HR diagram Luminosity, radius, and temperature Vogt-Russell theorem Main sequence Evolution on the HR diagram A star
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
Ay Fall 2004 Lecture 6 (given by Tony Travouillon)
 Ay 122 - Fall 2004 Lecture 6 (given by Tony Travouillon) Stellar atmospheres, classification of stellar spectra (Many slides c/o Phil Armitage) Formation of spectral lines: 1.excitation Two key questions:
Ay 122 - Fall 2004 Lecture 6 (given by Tony Travouillon) Stellar atmospheres, classification of stellar spectra (Many slides c/o Phil Armitage) Formation of spectral lines: 1.excitation Two key questions:
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
ASTR : Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)... Study Guide for Midterm 1
 ASTR-1200-01: Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)........................ Study Guide for Midterm 1 The first midterm exam for ASTR-1200 takes place in class on Wednesday, February 13, 2019. The exam covers
ASTR-1200-01: Stars & Galaxies (Spring 2019)........................ Study Guide for Midterm 1 The first midterm exam for ASTR-1200 takes place in class on Wednesday, February 13, 2019. The exam covers
Today. Homework Due. Stars. Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions. proton-proton chain. CNO cycle. Stellar Lifetimes
 Today Stars Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions proton-proton chain CNO cycle Stellar Lifetimes Homework Due Stellar Properties Luminosity Surface Temperature Size Mass Composition Stellar Properties
Today Stars Properties (Recap) Nuclear Reactions proton-proton chain CNO cycle Stellar Lifetimes Homework Due Stellar Properties Luminosity Surface Temperature Size Mass Composition Stellar Properties
Instructor: Juhan Frank. Identify the correct answers by placing a check between the brackets ë ë. Check ALL
 Name:... ASTRONOMY 1102 í 1 Instructor: Juhan Frank Second Test ífall 1999í Friday October 15 Part I í Multiple Choice questions è3 ptsèquestion; total = 60 ptsè Identify the correct answers by placing
Name:... ASTRONOMY 1102 í 1 Instructor: Juhan Frank Second Test ífall 1999í Friday October 15 Part I í Multiple Choice questions è3 ptsèquestion; total = 60 ptsè Identify the correct answers by placing
Review from last class:
 Review from last class: Properties of photons Flux and luminosity, apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude, colors Spectroscopic observations. Doppler s effect and applications Distance measurements
Review from last class: Properties of photons Flux and luminosity, apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude, colors Spectroscopic observations. Doppler s effect and applications Distance measurements
15.1 Properties of Stars
 Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? How do we measure
Surveying the Stars 15.1 Properties of Stars Our goals for learning: How do we measure stellar luminosities? How do we measure stellar temperatures? How do we measure stellar masses? How do we measure
Light and Matter(LC)
 Light and Matter(LC) Every astronomy book that I ve seen has at least one chapter dedicated to the physics of light. Why are astronomers so interested in light? Everything* that we know about Astronomical
Light and Matter(LC) Every astronomy book that I ve seen has at least one chapter dedicated to the physics of light. Why are astronomers so interested in light? Everything* that we know about Astronomical
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation
 The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
The atom cont. +Investigating EM radiation Announcements: First midterm is 7:30pm on Sept 26, 2013 Will post a past midterm exam from 2011 today. We are covering Chapter 3 today. (Started on Wednesday)
Midterm Study Guide Astronomy 122
 Midterm Study Guide Astronomy 122 Introduction: 1. How is modern Astronomy different from Astrology? 2. What is the speed of light? Is it constant or changing? 3. What is an AU? Light-year? Parsec? Which
Midterm Study Guide Astronomy 122 Introduction: 1. How is modern Astronomy different from Astrology? 2. What is the speed of light? Is it constant or changing? 3. What is an AU? Light-year? Parsec? Which
Particle nature of light & Quantization
 Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Particle nature of light & Quantization A quantity is quantized if its possible values are limited to a discrete set. An example from classical physics is the allowed frequencies of standing waves on a
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics
 Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. White light is made up of many different colors. Interactions of Light with Matter
 Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Chapter 5 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos. 5.1 Light in Everyday Life. How do we experience light?
 Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages from the Cosmos 5.1 Light in Everyday Life Our goals for learning: How do we experience light? How do light and matter interact? How do we experience light?
Astronomy 1102 Exam #1 Chapters 1,2,5,6 & 16
 Astronomy 1102 Exam #1 Chapters 1,2,5,6 & 16 Chapter 1 Degrees- basic unit of angle measurement, designated by the symbol -a full circle is divided into 360 and a right angle measures 90. arc minutes-one-sixtieth
Astronomy 1102 Exam #1 Chapters 1,2,5,6 & 16 Chapter 1 Degrees- basic unit of angle measurement, designated by the symbol -a full circle is divided into 360 and a right angle measures 90. arc minutes-one-sixtieth
Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013
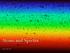 Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013 Announcements Second writing assignment due two weeks from today (again, on a news item of your choice). Be sure to make plans to visit one of the open observing nights
Atoms and Spectra October 8th, 2013 Announcements Second writing assignment due two weeks from today (again, on a news item of your choice). Be sure to make plans to visit one of the open observing nights
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation
 The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
The Nature of Light I: Electromagnetic Waves Spectra Kirchoff s Laws Temperature Blackbody radiation Electromagnetic Radiation (How we get most of our information about the cosmos) Examples of electromagnetic
The physics of stars. A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure.
 Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
Lecture 4 Stars The physics of stars A star begins simply as a roughly spherical ball of (mostly) hydrogen gas, responding only to gravity and it s own pressure. X-ray ultraviolet infrared radio To understand
Stellar Astrophysics: The Classification of Stellar Spectra
 Stellar Astrophysics: The Classification of Stellar Spectra Temperature and Color The intensity of light emitted by three hypothetical stars is plotted against wavelength The range of visible wavelengths
Stellar Astrophysics: The Classification of Stellar Spectra Temperature and Color The intensity of light emitted by three hypothetical stars is plotted against wavelength The range of visible wavelengths
Chapter 4. Spectroscopy. Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
CASE STUDY FOR USE WITH SECTION B
 GCE A level 325/0-A PHYSICS PH5 Assessment Unit CASE STUDY FOR USE WITH SECTION B Pre-Release Material To be opened on receipt A new copy of this Case Study will be given out in the examination 325 0A00
GCE A level 325/0-A PHYSICS PH5 Assessment Unit CASE STUDY FOR USE WITH SECTION B Pre-Release Material To be opened on receipt A new copy of this Case Study will be given out in the examination 325 0A00
= λ. Light: The Cosmic Messenger. Continuing Topics for Today 1/24/17. Your account on Mastering Astronomy. ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies
 REMINDER Your account on Mastering Astronomy ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 3 Tues 24 Jan 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
REMINDER Your account on Mastering Astronomy ASTR 1040 Stars & Galaxies SDO: Post-flare ejection from solar surface Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Piyush Agrawal, Connor Bice Lecture 3 Tues 24 Jan 2017 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre
Types of Stars 1/31/14 O B A F G K M. 8-6 Luminosity. 8-7 Stellar Temperatures
 Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Nature of Stars For nearby stars - measure distances with parallax 1 AU d p 8-2 Parallax A January ³ d = 1/p (arcsec) [pc] ³ 1pc when p=1arcsec; 1pc=206,265AU=3
Astronomy 113 Dr. Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. The Nature of Stars For nearby stars - measure distances with parallax 1 AU d p 8-2 Parallax A January ³ d = 1/p (arcsec) [pc] ³ 1pc when p=1arcsec; 1pc=206,265AU=3
Lecture: October 6, 2010
 Lecture: October 6, 2010 Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Tonight at 7:30 Problem Set 3 Due next Monday Second Exam October 25 Tides Since gravitational force decreases with (distance) 2, the
Lecture: October 6, 2010 Announcements: Next Observatory Opportunity: Tonight at 7:30 Problem Set 3 Due next Monday Second Exam October 25 Tides Since gravitational force decreases with (distance) 2, the
