Mt. Douglas Secondary
|
|
|
- Barry Long
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 57.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation A linear equation means the equation of a straight line, and can be written in one of two forms. Standard Form: a + b = c Slope Intercept Form: = m + b with m = slope = rise run = 1 1, for points (, ) and (, ) b = -intercept We can graph these linear equations b plotting a few points and then drawing a line through the points. Alwas plot at least 3 points when graphing a linear equation to assure the graph is a straight line. Eas Method 1 (b standard form) Step 1: To find -intercept, set =. To find -intercept, set =. Step : Then pick an value for, and solve for to get a third point. Step 3: Plot 3 points from steps 1 and, and draw a straight line through them. Note: The -intercept is where the graph crosses the -ais. It could be anwhere on the -ais. Anwhere on the -ais is where =. Eample 1 Graph 3 + = Three points picked Solve for three missing values 3 + = 3() + = = = 3 + () = = 3 + = 3( ) + = = 1 = Therefore, ordered pairs are: 3 Plot these 3 points (, 3), (, ), and (, ) and draw a straight line through the points. Note: The arrows on the line indicate it continues indefinitel in both directions. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
2 58 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11 Eas Method (b slope intercept form) Step 1: Transform equation into form = m + b. Step : Plot the -intercept or an known point. Step 3: Travel up if slope is positive or down if slope is negative, b the distance given b the rise. Then travel right a distance given b the run. Plot a point at the new point. Draw a line connecting the three points. Repeat (up/down, then right) for the new point. or Step : Let = three values that are divisible b the run or denominator of slope. Step 3: Solve for. Step : Plot three points from step and draw a line through them. Eample Graph + 3 = 1 Transform into = 3 + Plot the -intercept of (A), go down, and right 3 units. Label new point B (3, ). From B, go down and right 3 units; new point C is (, ). Then draw a straight line through the 3 points, ABC. A -intercept rise B run 3 C Pick three points divisible b 3 or Solve for missing values 3 3 = 3 + = 3 () + = = 3 + = 3 (3) + = = 3 + = 3 ( 3) + = Therefore, ordered pairs are: 3 3 Plot these 3 points (, ), (3, ), and ( 3, ) and draw a straight line through the points. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
3 Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 59 Summar To Graph a Linear Equation Step 1: Find at least three ordered pairs that are solutions to the linear equations. The third point provides a check point; if a ruler does not pass through all three points, a mistake has been made. Step : Plot the points that correspond to these ordered pairs on a coordinate sstem. Step 3: Draw a straight line through these points. Solve Linear Sstem Algebraicall Two or more equations considered together are called a sstem of equations. The ordered pair or pairs that is/are common to all linear equations in a sstem is called a solution of the sstem. Eample 1 Is (, ) a solution to = and + 3 = 8? Check = () ( ) = = true + 3 = 8 + 3( ) = 8 8 = 8 true Because (, ) is a solution to both equations, it is a solution to the sstem. Eample Is ( 1, 3) a solution to + = 1 and 3 = 9? Check + = 1 ( 1) + 3 = 1 1 = 1true 3 = 9 1 3(3) = 9 1 = 9 false Because ( 1, 3) is a solution to onl one equation and not both, it is not a solution to the sstem. Eas Addition Method (Elimination Method) Step 1: Write equation of the sstem in general form a + b = c. Step : Multipl the terms of one or both of the equations b a constant such that the coefficients of or are different onl in their sign. Step 3: Add the equations and solve the resulting equation. Step : Substitute the value obtained in step 3 into either of the original equations, and solve for the remaining variable. Step 5: Steps 3 and gives the solution to the sstem. Step : Take values from steps 3 and, and substitute into the equation not used in step to check if the solution works in both equations. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
4 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11 Eample 1 Solve: 3 = + = 8 To eliminate, multipl the second equation b. Add the results to obtain an equation that has onl one variable. 3 = ( + = 8) 3 = = 1 7 = 1 = Substitute the value into either original equation and solve for. Eample Solve: + 3 = 5 3 = 8 + = 8 + () = 8 = Check solution (, ) in the other equation. 3 = () 3() = = Therefore, solution (, ) = (, ). To eliminate, multipl equation one b, and equation two b 3, then add the results. ( + 3 = 5) 3(3 = 8) 8 + = 1 9 = 17 = 3 = Substitute the value of into either original equation. + 3 = 5 Eample 3 Solve: 3 = 1 + = 3 () + 3 = 5 3 = 3 = 1 Check solution (, 1) in the other equation. 3 = 8 3() ( 1) = 8 8 = 8 Therefore, solution (, ) = (, 1) To eliminate, multipl equation one b, then add the results. (3 = 1) = + = 3 + = 3 = 5 Not true for an value of (, ) Therefore, there is no solution, the lines must be parallel. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
5 Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 1 Eample Solve: + 5 = 1 = To eliminate, multipl equation one b, then add the results. ( + 5 = ) +1 = 1 = 1 = = True for all values of (, ) Therefore, there are infinite solutions so the lines must coincide. Eas Substitution Method Step 1: Solve one equation for one of its variables in terms of the other variable. Step : Substitute the equation from step 1 into the other equation and solve that equation. Step 3: Take the value solved for in step and substitute the value into an equation containing both variables (usuall, the equation obtained in step 1). Step : Check the solution b taking the values in step and 3 into the equation not used in step 3. Eample 1 Solve: + 3 = 1 3 = 7 Look at both equations. Pick the one which will be easiest to change into = or = Begin b solving for in equation two. Substitute this epression for into equation one and solve for. + 3 = 1 = (3 7)= = 1 11 = = To find the value of, substitute = into the revised equation two. = 3 7 = 3() 7 = 1 Check solution (, 1) in the other equation. + 3 = 1 () + 3( 1) = 1 1 = 1 Therefore, solution (, ) = (, 1). Eample Solve: = 3 = 5 Solve for in equation two, and substitute value into equation one. = = 3 5 (3 5) = 1 = 11 = = Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
6 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11 Use = to find the value of. = 3 5 = 3() 5 = 5 = 1 Check solution (1, ) in the other equation. = (1) = = Therefore, solution (, ) = (1, ) Note: the same solution is arrived at if ou start b solving for in equation one, =, then substitute this value of into equation two. Problem Solving Man students think this is a difficult topic, but with some helpful tips students are capable of being ver successful solving these tpes of problems. Steps to follow in Problem Solving Step 1: Read the problem ver carefull to determine what ou are asked to solve. Step : Let and be the unknown variables. (Note: other letters can be used for the variables, eg., l = length, w = width.) Step 3: If possible, draw a diagram, or make a table, to help organize the data. Step : Epress all equations in terms of and (or other appropriate letters). Step 5: Use an appropriate method such as the addition or substitution method to solve for the unknown. Step : Check answer to make sure all conditions are satisfied in our problem. Eample 1 Adult tickets for the school pla are $1. and children s tickets are $8.. If a theatre holds 3 seats and the sold out performance brings in $38., how man children and adults attended the pla? Let = adult tickets and = child tickets. Then one equation must deal with the number of tickets and the other equation must deal with revenue of the tickets. So + = 3 (number of tickets) = 38 (revenue of tickets) Use Substitution Method + = = 38 Adult Tickets Children Tickets Total No. of Tickets 3 Revenue $ So = 3 Substitute for : 1 + 8(3 ) = = 38 = 88 = + = 3 + = 3 = 8 check: (, 8) = 38 1() + 8(8) = 38 True Therefore, adult tickets and 8 children s tickets were sold. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
7 Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 3 Eample A small airplane makes a km trip in 7 1 hours, and makes the return trip in hours. If the plane travels at a constant speed, and the wind blows at a constant rate, find the airplane s airspeed and the speed of the wind. Let = speed of airplane with no wind Let = speed of the wind Speed (km/h) Time (hr) Distance (km) With Wind + Against Wind 7 1 Then + is speed of plane going with the wind is speed of plane going against the wind d = s t + = = ( + ) = 3 = ( ) 7 1 = 7 = 3 + = 3 + = = Therefore, speed of airplane is 3 km/h, and wind speed is km/h. Eample 3 A chemist has two acid solutions in stock: one that is a 5% solution and the other an 8% solution. How much of each solution should be mied to obtain 1 millilitres of a 8% solution? Let = number of millilitres of 5% solution used Let = number of millilitres of 8% solution used + = =.8(1) 5% Solution 8% Solution Total Acid (ml) 1 Strength B substitution: = 1 + = (1 ) = 8 + = = 8 = = Therefore, we need millilitres of the 5% solution, and millilitres of the 8% solution. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
8 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11.1 Eercise Set 1. Determine whether the given ordered pair is a solution to the following equation: a) (, 3); 3 5 = 9 b) (, ); = c) (1, 1); 3 = 5 d) (, 8); 1 1 = 3 e) (, ); = f) ( 1, 3); = 1. Graph the following equations. a) + 3 = b) + = c) 1 = d) 3 + = 5 e) 3. = f) = 1 Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
9 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 5 Foundations of Math 11. g) = h) = 3 i) = ( 1) + 1 j) k) = 3 1 l) m) =3 n) = 3 = 1 ( ) + = Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
10 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11 Solve Linear Sstems Algebraicall 3. The Addition Method a) = 17 = 8 b) + 3 = = c) 7 3 = = 1 d) 5 + = = e) 5 3 = = f) 3 = + = g) 3 = + = 1 h) 3 + = 1 8 = 7 Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
11 Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 7 3. i) 3 + = = 7 j) 19 = 3 5 = k) = = 1.55 l). + =.. =.9. The substitution method. a) = = b) = + = 1 c) = 8 3 = 5 d) s + t = 3 3s + t = Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
12 8 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11. e) = = 1 f) = 3 + = g) 3a + b = 5a 3b = 1 h) 3 = = 7 8 i) 1 3 = = 5 j) 3 = + 3 = k) 3 + = = 7 l) + 9 = 1 7 = 3 Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
13 Foundations of Math 11 Section.1 Review: Graphing a Linear Equation 9 5. Problem Solving with Two and Three Variables. a) Attila has $5 to invest. He invests some in the stock market which earns 8%, and some in bonds that earns % on his investment. If the total interest earned was $35, how much did Attila invest in stock and how much in bonds? b) Jerr has 8 coins, consisting of dimes and quarters. If the total value of his coins is $15., how man dimes does he have? c) Tricia has one brand of coffee that sells for $7.5 per kg, and another brand that sells for $9. per kg. How man kilograms of each brand must she use to make a blend of 5 kilograms at $7.98 per kg? d) A barrel of wine has 8% alcohol, another barrel has 15% alcohol. How much of each must be mied to have 1 litres of 1.% alcohol wine? e) Renting a mobile home for das and driving 8 km costs $8.. If the trip was 7 das and ou drove 1 km, the cost would be $139.. What is the cost per da, and the cost per kilometre for renting the mobile home? f) Mar works part time selling both hats and scarves. One week she earns $11. b selling 8 hats and 1 scarves. The following week she sold 1 hats and scarves, and earned $18.. How much does she earn for each hat and each scarf she sells? Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
14 7 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math g) A plane travels 835 km in 7 hours with a tailwind, but onl 187 km with a headwind in the same time. Find the speed of the plane, and the speed of the wind. h) A boat took hours to make a downstream trip with a km/h current. The return trip against the current took 5 hours. What distance did the boat travel in one direction? i) Tickets for a school lotter are $. each or 3 for $5.. The school sold 3 tickets and the total amount of mone taken in was $58.. How man people bought onl a single ticket? j) A car travels 8 kilometres in the same time that a truck travels kilometres. The speed of the car is 1 kilometres per hour faster than the truck. Determine the car and truck speeds. k) How man litres each of 5% antifreeze and % antifreeze must be combined to get 1 litres of solution that is 1.5% antifreeze? l) Merilee bought kg of coffee and 3 kg of tea, paing $39. She later needed 1 kg of coffee and kg of tea, costing $. How much did she pa for each kg of coffee and tea? Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
15 Foundations of Math 11 Section. Linear Inequalities 71. Linear Inequalities The solution for a linear inequalit is a section of the coordinate plane called a half-plane. The boundar is found b replacing the inequalit sign with an equal sign and graphing the linear equation. If the inequalit equation has the smbol or, the boundar line is included in the solution, and is represented b a solid line. If the inequalit equation has the smbol > or <, the boundar line is not included in the solution, and is represented b a dashed line. Graphing a Linear Inequalit Eas Method of Graphing a Linear Inequalit Step 1: Graph the linear equalit equation. Use a solid line if the original inequalit equation includes = ( or ), or a dashed line if the original equation does not include = (< or >). Step : This step ma be completed in was as follows: Method 1 (inequalit in the form a + b c or a + b > c) Choose a test point not on the line and substitute the point into the inequalit equation. If the inequalit is true, shade the half-plane containing the test point. If not true, shade the other half-plane (not containing the test point). Method (inequalit equation in slope intercept form, < m + b or m + b) Look at the inequalit equation; if is greater than, or greater than or equal, graph upper half-plane, if is less than, or less than or equal, graph lower half-plane. Eample 1 3 or 3 Step 1: Graph the linear equation 3 =. Since the inequalit includes =, use a solid line. Step : Method 1 test point (, ) 3 () 3() true statement Therefore, shade region that has (, ). Method Equation is 3 Therefore, graph upper half-plane. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
16 7 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11 Solve Sstems of Linear Inequalities Steps to follow are the same as graphing a single linear inequalit, ecept that the solution must be the intersection of all inequalit equations. This is the region where all points satisf all the inequalities at the same time. Eample 1 Solve: > = > has a dashed line + = has a solid line Test Point (, ) from region A > 3 no + 3 no Test Point (5, 1) from region C > 3 es + 3 es Test Point (, ) from region B > 3 no + 3 es Test Point (, 3) from region D > 3 es + 3 no A B C D The onl region with a test point that satisfies both inequalities is region C. Eample Solve: 3 + > 3 + = 3 3 > has a solid line = has a dashed line Test Point (, ) from region A 3 + es > no Test Point (5, 1) from region C 3 + no > es Test Point (, ) from region B 3 + no > no Test Point (, 3) from region D 3 + es > es A D B C Solution is the shading of region D. Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
17 Foundations of Math 11 Section. Linear Inequalities 73 Eample 3 Graph the sstem of linear inequalities: 3 > > + 15 For 3 graph solid line = 3, then shade to right. > graph dashed line = then shade up. > graph dashed line =, then shade up + 15 graph solid line 1 + 5, then shade down. Eample Write a sstem of linear inequalities that has the given graph: A B C Points of intersect are A (, ), B (, ) and C (, ) Equation of vertical line is ( ) Equation of dashed line BC has slope m = ( ) = = 1 3 = m + b using C (, ), = 1 3 ()+ b b = 1 3 Equation of solid line AC has slope m = ( ) > = 1 -intercept is + Thus, the sstem is, > ,and + Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
18 7 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math 11. Eercise Set 1. Graph the following inequalities on the grid provided. a) 3 + b) < c) 1 3 f) +3 > 3 h) < < + g) 3 1 e) + 3 d). 3 > Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
19 Section. Linear Inequalities 75 Foundations of Math 11. Graph the sstems of linear inequalities; shade in the solution. a) < + c) d) h) + 3 f) < g) 3 + > + + e) b) Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
20 7 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math Write a sstem of linear inequalities that forms the given graph. a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
21 Foundations of Math 11 Section. Linear Inequalities 77. The Winnipeg Moose need at least 9 points to make the plaoffs. A win is worth points and a tie 1 point. Graph the sstem, and label the corner points. 5. The size of a hocke rink must be between 19 and ft in length, and between 8 and 85 ft in width. Graph the sstem, and label the corner points. t w w l. A person has up to $5 to invest. His financial advisor recommends that at least $35 be invested in stocks and at most $1 in bonds. Graph the sstem, and label the corner points. 7. A skate manufacturer can produce as man as pairs of hocke skates, and 5 pairs of figure skates, per da. It takes 3 hours of labour to produce a pair of hocke skates, and hours of labour to produce a pair of figure skates. The compan has up to hours available for production each da. Graph the sstem, and label the corner points. Bonds f Stocks h Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
22 78 Chapter Linear Sstems Foundations of Math A test is made up of multiple-choice and openended questions. It takes up to 3 minutes to do a multiple-choice question, and up to minutes for an open-ended question. Total time is minutes, and ou ma answer no more than 18 questions. Graph the sstem, and label the corner points. 9. A store sells two brands of TVs. Brand A sells at least twice as much as brand B. The store must carr at least 1 of brand B, and has room for no more than 9 TVs. Graph the sstem, and label the corner points. B O A M Copright b Crescent Beach Publishing All rights reserved. Cancop has ruled that this book is not covered b their licensing agreement. No part of this publication ma be reproduced without eplicit permission of the publisher.
Solve each system by graphing. Check your solution. y =-3x x + y = 5 y =-7
 Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Practice Solving Sstems b Graphing Solve each sstem b graphing. Check our solution. 1. =- + 3 = - (1, ). = 1 - (, 1) =-3 + 5 3. = 3 + + = 1 (, 3). =-5 = - 7. = 3-5 3 - = 0 (1, 5) 5. -3 + = 5 =-7 (, 7).
Name Date PD. Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Name Date PD Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Sstems of Equations Vocabular: A sstem of linear equations is A solution of a sstem of linear equations is Points of Intersection (POI) are the same thing
Name Date PD Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Sstems of Equations Vocabular: A sstem of linear equations is A solution of a sstem of linear equations is Points of Intersection (POI) are the same thing
Lecture Guide. Math 42 - Elementary Algebra. Stephen Toner. Introductory Algebra, 3rd edition. Miller, O'Neill, Hyde. Victor Valley College
 Lecture Guide Math 42 - Elementar Algebra to accompan Introductor Algebra, 3rd edition Miller, O'Neill, Hde Prepared b Stephen Toner Victor Valle College Accompaning videos can be found at www.mathvideos.net.
Lecture Guide Math 42 - Elementar Algebra to accompan Introductor Algebra, 3rd edition Miller, O'Neill, Hde Prepared b Stephen Toner Victor Valle College Accompaning videos can be found at www.mathvideos.net.
8.4. If we let x denote the number of gallons pumped, then the price y in dollars can $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.70 $ $1.
 8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
8.4 An Introduction to Functions: Linear Functions, Applications, and Models We often describe one quantit in terms of another; for eample, the growth of a plant is related to the amount of light it receives,
CHAPTER 6: LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Name: Date: Period: CHAPTER : LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS Notes #: Section.: Solving Linear Sstems b Substitution The solution to a sstem of equations represents the where the. It would be great if
Name: Date: Period: CHAPTER : LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS Notes #: Section.: Solving Linear Sstems b Substitution The solution to a sstem of equations represents the where the. It would be great if
MEP Pupil Text 16. The following statements illustrate the meaning of each of them.
 MEP Pupil Tet Inequalities. Inequalities on a Number Line An inequalit involves one of the four smbols >,, < or. The following statements illustrate the meaning of each of them. > : is greater than. :
MEP Pupil Tet Inequalities. Inequalities on a Number Line An inequalit involves one of the four smbols >,, < or. The following statements illustrate the meaning of each of them. > : is greater than. :
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
Name Date Chapter 5 Maintaining Mathematical Proficienc Graph the equation. 1. + =. = 3 3. 5 + = 10. 3 = 5. 3 = 6. 3 + = 1 Solve the inequalit. Graph the solution. 7. a 3 > 8. c 9. d 5 < 3 10. 8 3r 5 r
Unit 26 Solving Inequalities Inequalities on a Number Line Solution of Linear Inequalities (Inequations)
 UNIT Solving Inequalities: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Algebra Unit Solving Inequalities Student Tet Contents Section. Inequalities on a Number Line. of Linear Inequalities (Inequations). Inequalities
UNIT Solving Inequalities: Student Tet Contents STRAND G: Algebra Unit Solving Inequalities Student Tet Contents Section. Inequalities on a Number Line. of Linear Inequalities (Inequations). Inequalities
7.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
7.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Objectives: Learn how to solve a sstem of linear equations b graphing Learn how to model a real-life situation using a sstem of linear equations With an equation, an
Math098 Practice Final Test
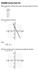 Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
Math098 Practice Final Test Find an equation of the line that contains the points listed in the table. 1) 0-6 1-2 -4 3-3 4-2 Find an equation of the line. 2) 10-10 - 10 - -10 Solve. 3) 2 = 3 + 4 Find the
CHAPTER 6: LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 Name: Date: Period: CHAPTER : LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS Notes #: Section.: Solving Linear Sstems b Substitution The solution to a sstem of equations represents the where the. It would be great if
Name: Date: Period: CHAPTER : LINEAR SYSTEMS AND THEIR GRAPHS Notes #: Section.: Solving Linear Sstems b Substitution The solution to a sstem of equations represents the where the. It would be great if
Math 154A Elementary Algebra Fall 2014 Final Exam Study Guide
 Math A Elementar Algebra Fall 0 Final Eam Stud Guide The eam is on Tuesda, December 6 th from 6:00pm 8:0pm. You are allowed a scientific calculator and a " b 6" inde card for notes. On our inde card be
Math A Elementar Algebra Fall 0 Final Eam Stud Guide The eam is on Tuesda, December 6 th from 6:00pm 8:0pm. You are allowed a scientific calculator and a " b 6" inde card for notes. On our inde card be
x. 4. 2x 10 4x. 10 x
 CCGPS UNIT Semester 1 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of Reasoning with Equations and Quantities Name: Date: Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and eplain the reasoning MCC9-1.A.REI.1 Eplain
CCGPS UNIT Semester 1 COORDINATE ALGEBRA Page 1 of Reasoning with Equations and Quantities Name: Date: Understand solving equations as a process of reasoning and eplain the reasoning MCC9-1.A.REI.1 Eplain
(c) ( 5) 2. (d) 3. (c) 3(5 7) 2 6(3) (d) (9 13) ( 3) Question 4. Multiply using the distributive property and collect like terms if possible.
 Name: Chapter 1 Question 1. Evaluate the following epressions. (a) 5 (c) ( 5) (b) 5 (d) ( 1 ) 3 3 Question. Evaluate the following epressions. (a) 0 5() 3 4 (c) 3(5 7) 6(3) (b) 9 + (8 5) (d) (9 13) + 15
Name: Chapter 1 Question 1. Evaluate the following epressions. (a) 5 (c) ( 5) (b) 5 (d) ( 1 ) 3 3 Question. Evaluate the following epressions. (a) 0 5() 3 4 (c) 3(5 7) 6(3) (b) 9 + (8 5) (d) (9 13) + 15
Ch 3 Alg 2 Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Systems of Equations
 Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Ch 3 Alg Note Sheet.doc 3.1 Graphing Sstems of Equations Sstems of Linear Equations A sstem of equations is a set of two or more equations that use the same variables. If the graph of each equation =.4
Identify the domain and the range of the relation from the graph. 8)
 INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST Use the given conditions to write an equation for the line. 1) a) Passing through (, -) and parallel to = - +. b) Passing through (, 7) and parallel to - 3 = 10 c)
INTERMEDIATE ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR TEST Use the given conditions to write an equation for the line. 1) a) Passing through (, -) and parallel to = - +. b) Passing through (, 7) and parallel to - 3 = 10 c)
Review of Elementary Algebra Content
 Review of Elementar Algebra Content 0 1 Table of Contents Fractions...1 Integers...5 Order of Operations...9 Eponents...11 Polnomials...18 Factoring... Solving Linear Equations...1 Solving Linear Inequalities...
Review of Elementar Algebra Content 0 1 Table of Contents Fractions...1 Integers...5 Order of Operations...9 Eponents...11 Polnomials...18 Factoring... Solving Linear Equations...1 Solving Linear Inequalities...
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Systems by Graphing
 Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
Section 3.1 Solving Linear Sstems b Graphing Name: Period: Objective(s): Solve a sstem of linear equations in two variables using graphing. Essential Question: Eplain how to tell from a graph of a sstem
Chapter 5: Systems of Equations
 Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
Chapter : Sstems of Equations Section.: Sstems in Two Variables... 0 Section. Eercises... 9 Section.: Sstems in Three Variables... Section. Eercises... Section.: Linear Inequalities... Section.: Eercises.
LESSON #11 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
Lesson 5.1 Solving Systems of Equations
 Lesson 5.1 Solving Sstems of Equations 1. Verif whether or not the given ordered pair is a solution to the sstem. If it is not a solution, eplain wh not. a. (, 3) b. (, 0) c. (5, 3) 0.5 1 0.5 2 0.75 0.75
Lesson 5.1 Solving Sstems of Equations 1. Verif whether or not the given ordered pair is a solution to the sstem. If it is not a solution, eplain wh not. a. (, 3) b. (, 0) c. (5, 3) 0.5 1 0.5 2 0.75 0.75
Algebra 1 CP Semester Exam Review
 Name: Hr: Algebra CP Semester Eam Review GET ORGANIZED. Successful studing begins with being organized. Bring this packet with ou to class ever da. DO NOT FALL BEHIND. Do the problems that are assigned
Name: Hr: Algebra CP Semester Eam Review GET ORGANIZED. Successful studing begins with being organized. Bring this packet with ou to class ever da. DO NOT FALL BEHIND. Do the problems that are assigned
13.1 2X2 Systems of Equations
 . X Sstems of Equations In this section we want to spend some time reviewing sstems of equations. Recall there are two basic techniques we use for solving a sstem of equations: Elimination and Substitution.
. X Sstems of Equations In this section we want to spend some time reviewing sstems of equations. Recall there are two basic techniques we use for solving a sstem of equations: Elimination and Substitution.
7.1 Guided Practice (p. 401) 1. to find an ordered pair that satisfies each of the equations in the system. solution of the system.
 CHAPTER 7 Think and Discuss (p. 9). 6,00,000 units. 0,00,000 6,00,000 4,400,000 renters Skill Review (p. 96) 9r 4r 6r. 8.. 0.d.d d 4. w 4 w 4 w 4 w 4 w. 6. 7 g g 9 g 7 g 6 g 0 7 8 40 40 40 7. 6 8. 8 9....
CHAPTER 7 Think and Discuss (p. 9). 6,00,000 units. 0,00,000 6,00,000 4,400,000 renters Skill Review (p. 96) 9r 4r 6r. 8.. 0.d.d d 4. w 4 w 4 w 4 w 4 w. 6. 7 g g 9 g 7 g 6 g 0 7 8 40 40 40 7. 6 8. 8 9....
Systems of Linear Inequalities
 . Sstems of Linear Inequalities sstem of linear inequalities? How can ou sketch the graph of a ACTIVITY: Graphing Linear Inequalities Work with a partner. Match the linear inequalit with its graph. + Inequalit
. Sstems of Linear Inequalities sstem of linear inequalities? How can ou sketch the graph of a ACTIVITY: Graphing Linear Inequalities Work with a partner. Match the linear inequalit with its graph. + Inequalit
LESSON #12 - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
LESSON # - FORMS OF A LINE COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II Linear functions come in a variet of forms. The two shown below have been introduced in Common Core Algebra I and Common Core Geometr. TWO COMMON FORMS
c. x x < 60 d. x x =9. What are the first four terms of the sequence? a. 12, 21, 30, 39 b.
 Algebra I Unit Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities Post Test... A famil s cell phone plan costs $ per month for, minutes and cents per minute over the limit. This month, the famil paid $..
Algebra I Unit Reasoning with Linear Equations and Inequalities Post Test... A famil s cell phone plan costs $ per month for, minutes and cents per minute over the limit. This month, the famil paid $..
MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED
 FOM 11 T GRAPHING LINEAR INEQUALITIES & SET NOTATION - 1 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) INEQUALITY = a mathematical statement that contains one of these four inequalit signs: ,.
FOM 11 T GRAPHING LINEAR INEQUALITIES & SET NOTATION - 1 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) INEQUALITY = a mathematical statement that contains one of these four inequalit signs: ,.
y x can be solved using the quadratic equation Y1 ( x 5), then the other is
 Math 0 Precalculus Sstem of Equation Review Questions Multiple Choice. The sstem of equations A. 7 0 7 0 0 0 and can be solved using the quadratic equation. In solving the quadratic equation 0 ( ) intersection
Math 0 Precalculus Sstem of Equation Review Questions Multiple Choice. The sstem of equations A. 7 0 7 0 0 0 and can be solved using the quadratic equation. In solving the quadratic equation 0 ( ) intersection
1. Simplify each expression and write all answers without negative exponents. for variable L.
 MATH 0: PRACTICE FINAL Spring, 007 Chapter # :. Simplif each epression and write all answers without negative eponents. ( ab ) Ans. b 9 7a 6 Ans.. Solve each equation. 5( ) = 5 5 Ans. man solutions + 7
MATH 0: PRACTICE FINAL Spring, 007 Chapter # :. Simplif each epression and write all answers without negative eponents. ( ab ) Ans. b 9 7a 6 Ans.. Solve each equation. 5( ) = 5 5 Ans. man solutions + 7
I. ORDER OF OPERATIONS
 ALGEBRA II HONORS REVIEW PACKET NAME This packet contains all of the material that you should have mastered in Algebra I. You are responsible for reviewing this material over the summer and expect an assessment
ALGEBRA II HONORS REVIEW PACKET NAME This packet contains all of the material that you should have mastered in Algebra I. You are responsible for reviewing this material over the summer and expect an assessment
Ready To Go On? Skills Intervention 2-1 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities
 A Read To Go n? Skills Intervention -1 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities Find these vocabular words in Lesson -1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular equation solution of an equation linear
A Read To Go n? Skills Intervention -1 Solving Linear Equations and Inequalities Find these vocabular words in Lesson -1 and the Multilingual Glossar. Vocabular equation solution of an equation linear
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Spring 2017 Master ( Master Templates)
 Test 1 Review #1 Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Spring 017 Master ( Master Templates) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for. = 8 18. Solve for. = + a b 3. Solve for. a b = L 30. Two trains leave stations miles
Test 1 Review #1 Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Spring 017 Master ( Master Templates) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for. = 8 18. Solve for. = + a b 3. Solve for. a b = L 30. Two trains leave stations miles
Chapter 6: Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities
 Lesson 6-1: Graphing Sstems of Equations Date: Eample 1: Use the graph to determine whether each sstem is consistent or inconsistent and if it is independent or dependent. a. = 1 and = + 1 b. = 1 and =
Lesson 6-1: Graphing Sstems of Equations Date: Eample 1: Use the graph to determine whether each sstem is consistent or inconsistent and if it is independent or dependent. a. = 1 and = + 1 b. = 1 and =
Algebra 2 Unit 1 Practice
 Algebra Unit Practice LESSON - Use this information for Items. Aaron has $ to rent a bike in the cit. It costs $ per hour to rent a bike. The additional fee for a helmet is $ for the entire ride.. Write
Algebra Unit Practice LESSON - Use this information for Items. Aaron has $ to rent a bike in the cit. It costs $ per hour to rent a bike. The additional fee for a helmet is $ for the entire ride.. Write
An assessment of these skills will occur the first week of school.
 Fort Zumwalt West High School Pre-AP Algebra SUMMER REVIEW PACKET Name: * This packet is to be handed in to our Pre AP Algebra teacher on the first da of the school ear. *All work must be shown in the
Fort Zumwalt West High School Pre-AP Algebra SUMMER REVIEW PACKET Name: * This packet is to be handed in to our Pre AP Algebra teacher on the first da of the school ear. *All work must be shown in the
Part I: No Calculators Allowed
 Name of Math lover: m favorite student Math 60: ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Xtra Practice for the Last Eam Question : What s going to be on the final eam? Answer : Material from Chapter 1 to Chapter 9. Date: To
Name of Math lover: m favorite student Math 60: ELEMENTARY ALGEBRA Xtra Practice for the Last Eam Question : What s going to be on the final eam? Answer : Material from Chapter 1 to Chapter 9. Date: To
Fair Game Review. Chapter = How many calculators are sold when the profit is $425? Solve the equation. Check your solution.
 Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
Name Date Chapter 4 Fair Game Review Solve the equation. Check our solution.. 8 3 = 3 2. 4a + a = 2 3. 9 = 4( 3k 4) 7k 4. ( m) 2 5 6 2 = 8 5. 5 t + 8t = 3 6. 3 5h 2 h + 4 = 0 2 7. The profit P (in dollars)
Intermediate Algebra Math 097. Evaluates/Practice Tests. For solutions, refer to the back of the PAN.
 Intermediate Algebra Math 097 Evaluates/Practice Tests For solutions, refer to the back of the PAN. Page of 8 Take this practice test to be sure that ou are prepared for the final quiz in Evaluate.. Solve
Intermediate Algebra Math 097 Evaluates/Practice Tests For solutions, refer to the back of the PAN. Page of 8 Take this practice test to be sure that ou are prepared for the final quiz in Evaluate.. Solve
Module 3, Section 4 Analytic Geometry II
 Principles of Mathematics 11 Section, Introduction 01 Introduction, Section Analtic Geometr II As the lesson titles show, this section etends what ou have learned about Analtic Geometr to several related
Principles of Mathematics 11 Section, Introduction 01 Introduction, Section Analtic Geometr II As the lesson titles show, this section etends what ou have learned about Analtic Geometr to several related
MATH 1710 College Algebra Final Exam Review
 MATH 7 College Algebra Final Eam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) There were 80 people at a pla. The admission price was $
MATH 7 College Algebra Final Eam Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. ) There were 80 people at a pla. The admission price was $
Fair Game Review. Chapter 2. and y = 5. Evaluate the expression when x = xy 2. 4x. Evaluate the expression when a = 9 and b = 4.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Algebra I. Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176. Slide 3 / 176. Slide 4 / 176. Slide 6 / 176. Slide 5 / 176. System of Linear Equations.
 Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176 Algebra I Sstem of Linear Equations 21-11-2 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 176 Slide 4 / 176 Table of Contents Solving Sstems b Graphing Solving Sstems b Substitution Solving Sstems
Slide 1 / 176 Slide 2 / 176 Algebra I Sstem of Linear Equations 21-11-2 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 176 Slide 4 / 176 Table of Contents Solving Sstems b Graphing Solving Sstems b Substitution Solving Sstems
Linear Programming. Maximize the function. P = Ax + By + C. subject to the constraints. a 1 x + b 1 y < c 1 a 2 x + b 2 y < c 2
 Linear Programming Man real world problems require the optimization of some function subject to a collection of constraints. Note: Think of optimizing as maimizing or minimizing for MATH1010. For eample,
Linear Programming Man real world problems require the optimization of some function subject to a collection of constraints. Note: Think of optimizing as maimizing or minimizing for MATH1010. For eample,
Topic 1: Writing and Solving Equations and Inequalities
 Topic 1: Writing and Solving Equations and Inequalities In #1 3, solve each equation. Use inverse operations. 1. 8 21 5 = 15 2. 3 10 = 2(4 5) 3. 2( + 2) = 2 + 1 4. The rectangle and square have equivalent
Topic 1: Writing and Solving Equations and Inequalities In #1 3, solve each equation. Use inverse operations. 1. 8 21 5 = 15 2. 3 10 = 2(4 5) 3. 2( + 2) = 2 + 1 4. The rectangle and square have equivalent
MATH 103 Sample Final Exam Review
 MATH 0 Sample Final Eam Review This review is a collection of sample questions used b instructors of this course at Missouri State Universit. It contains a sampling of problems representing the material
MATH 0 Sample Final Eam Review This review is a collection of sample questions used b instructors of this course at Missouri State Universit. It contains a sampling of problems representing the material
Mathematics. Sample Test Questions Booklet
 Collegiate Assessment of Academic Proficienc Mathematics Sample Test Questions Booklet 009 b ACT, Inc. All rights reserved. NTE: This booklet is covered b Federal copright laws that prohibit the reproduction
Collegiate Assessment of Academic Proficienc Mathematics Sample Test Questions Booklet 009 b ACT, Inc. All rights reserved. NTE: This booklet is covered b Federal copright laws that prohibit the reproduction
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Graphing
 8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
8.1 Sstems of Linear Equations: Solving b Graphing 8.1 OBJECTIVE 1. Find the solution(s) for a set of linear equations b graphing NOTE There is no other ordered pair that satisfies both equations. From
Note: Two perpendicular lines form a system of the first type. (Nothing special about being )
 Math 100 Elementary Algebra Sec 7.1: Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Two or more equations [inequalities] in several variables that are considered simultaneously are called a system of equations [inequalities].
Math 100 Elementary Algebra Sec 7.1: Solving Linear Systems by Graphing Two or more equations [inequalities] in several variables that are considered simultaneously are called a system of equations [inequalities].
Mt. Douglas Secondary
 Foundations of Math 11 Section 7.1 Quadratic Functions 31 7.1 Quadratic Functions Mt. Douglas Secondar Quadratic functions are found in everda situations, not just in our math classroom. Tossing a ball
Foundations of Math 11 Section 7.1 Quadratic Functions 31 7.1 Quadratic Functions Mt. Douglas Secondar Quadratic functions are found in everda situations, not just in our math classroom. Tossing a ball
Systems of Linear Equations
 Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Sstems of Linear Equations Monetar Sstems Overload Lesson 3-1 Learning Targets: Use graphing, substitution, and elimination to solve sstems of linear equations in two variables. Formulate sstems of linear
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday November Inequalities and Linear Optimization
 WWW.CEMC.UWATERLOO.CA The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING Intermediate Math Circles Wednesda November 21 2012 Inequalities and Linear Optimization Review: Our goal is to solve sstems
WWW.CEMC.UWATERLOO.CA The CENTRE for EDUCATION in MATHEMATICS and COMPUTING Intermediate Math Circles Wednesda November 21 2012 Inequalities and Linear Optimization Review: Our goal is to solve sstems
Algebra I. Administered May 2014 RELEASED
 STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
STAAR State of Teas Assessments of Academic Readiness Algebra I Administered Ma 0 RELEASED Copright 0, Teas Education Agenc. All rights reserved. Reproduction of all or portions of this work is prohibited
Systems of Linear Equations
 HW Mark: 10 9 8 7 6 RE-Submit Systems of Linear Equations This booklet belongs to: Period LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES Questions that I find difficult Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW
HW Mark: 10 9 8 7 6 RE-Submit Systems of Linear Equations This booklet belongs to: Period LESSON # DATE QUESTIONS FROM NOTES Questions that I find difficult Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. Pg. REVIEW
June If you want, you may scan your assignment and convert it to a.pdf file and it to me.
 Summer Assignment Pre-Calculus Honors June 2016 Dear Student: This assignment is a mandatory part of the Pre-Calculus Honors course. Students who do not complete the assignment will be placed in the regular
Summer Assignment Pre-Calculus Honors June 2016 Dear Student: This assignment is a mandatory part of the Pre-Calculus Honors course. Students who do not complete the assignment will be placed in the regular
Unit 2: Rational Expressions
 Rational Epressions Pure Math 0 Notes Unit : Rational Epressions -: Simplifing Rational Epressions Rational Epressions: - fractions with polnomials as numerator and / or denominator. To Simplif (Reduce)
Rational Epressions Pure Math 0 Notes Unit : Rational Epressions -: Simplifing Rational Epressions Rational Epressions: - fractions with polnomials as numerator and / or denominator. To Simplif (Reduce)
Can a system of linear equations have no solution? Can a system of linear equations have many solutions?
 5. Solving Special Sstems of Linear Equations Can a sstem of linear equations have no solution? Can a sstem of linear equations have man solutions? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with
5. Solving Special Sstems of Linear Equations Can a sstem of linear equations have no solution? Can a sstem of linear equations have man solutions? ACTIVITY: Writing a Sstem of Linear Equations Work with
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the Square
 Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Mini-Lecture 8.1 Solving Quadratic Equations b Completing the Square Learning Objectives: 1. Use the square root propert to solve quadratic equations.. Solve quadratic equations b completing the square.
Diaz Math 080 Midterm Review: Modules A-F Page 1 of 7
 Diaz Math 080 Midterm Review: Modules A-F Page 1 of 7 1. Use the rule for order of operations to simplif the epression: 11 9 7. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: 7( + ) 6(5 9) 3. If a = 3,
Diaz Math 080 Midterm Review: Modules A-F Page 1 of 7 1. Use the rule for order of operations to simplif the epression: 11 9 7. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: 7( + ) 6(5 9) 3. If a = 3,
5.7 Start Thinking. 5.7 Warm Up. 5.7 Cumulative Review Warm Up
 .7 Start Thinking Graph the linear inequalities < + and > 9 on the same coordinate plane. What does the area shaded for both inequalities represent? What does the area shaded for just one of the inequalities
.7 Start Thinking Graph the linear inequalities < + and > 9 on the same coordinate plane. What does the area shaded for both inequalities represent? What does the area shaded for just one of the inequalities
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Math 1 Final Eam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve. 1) - - 6 = - + 7 1) ) 6 + 7(- - ) = -8 - ) ) - t + t = 6 t + 1 ) Solve
Math 1 Final Eam Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve. 1) - - 6 = - + 7 1) ) 6 + 7(- - ) = -8 - ) ) - t + t = 6 t + 1 ) Solve
Solving Systems Using Tables and Graphs
 3-1 Solving Sstems Using Tables and Graphs Vocabular Review 1. Cross out the equation that is NOT in slope-intercept form. 1 5 7 r 5 s a 5!3b 1 5 3 1 7 5 13 Vocabular Builder linear sstem (noun) LIN ee
3-1 Solving Sstems Using Tables and Graphs Vocabular Review 1. Cross out the equation that is NOT in slope-intercept form. 1 5 7 r 5 s a 5!3b 1 5 3 1 7 5 13 Vocabular Builder linear sstem (noun) LIN ee
Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences
 CONDENSED LESSON.1 Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences In this lesson, ou Write eplicit formulas for arithmetic sequences Write linear equations in intercept form You learned about recursive formulas
CONDENSED LESSON.1 Linear Equations and Arithmetic Sequences In this lesson, ou Write eplicit formulas for arithmetic sequences Write linear equations in intercept form You learned about recursive formulas
MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED
 FOM 11 T1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR INEQUALITIES 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) A SYSTEM OF LINEAR INEQUALITIES = a problem where or more inequalities are graphed on the same grid, the solution
FOM 11 T1 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR INEQUALITIES 1 MATH SPEAK - TO BE UNDERSTOOD AND MEMORIZED 1) A SYSTEM OF LINEAR INEQUALITIES = a problem where or more inequalities are graphed on the same grid, the solution
Name Date. and y = 5.
 Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Name Date Chapter Fair Game Review Evaluate the epression when = and =.... 0 +. 8( ) Evaluate the epression when a = 9 and b =.. ab. a ( b + ) 7. b b 7 8. 7b + ( ab ) 9. You go to the movies with five
Math 10C: Systems of Equations PRACTICE EXAM
 Math 10C: Systems of Equations PRACTICE EXAM 1. An online music store offers two payment methods: 1) The customer pays a monthly subscription fee of 8.00 and songs can be downloaded for 0.70 each. 2) The
Math 10C: Systems of Equations PRACTICE EXAM 1. An online music store offers two payment methods: 1) The customer pays a monthly subscription fee of 8.00 and songs can be downloaded for 0.70 each. 2) The
Chapter Start Thinking! For use before Activity 6.1. For use before Activity Start Thinking! For use before Lesson
 . Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
. Enrichment and Etension. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b is an number ecept.. a =, b =. a =, b =. a =, b =. Check students work.. Puzzle PAY HIM Etension. Start Thinking! For use before
Math Review Part C Advanced Level (Up to end of MAT 053)
 Math Review Part C Advanced Level (Up to end of MAT 05) A scientific calculator is allowed. Answers provided in the final section. Math Review Part C Advanced Level Advanced Level Algebra ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
Math Review Part C Advanced Level (Up to end of MAT 05) A scientific calculator is allowed. Answers provided in the final section. Math Review Part C Advanced Level Advanced Level Algebra ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS
Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Adding
 8.2 Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Adding 8.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve systems using the addition method 2. Solve applications of systems of equations The graphical method of solving equations, shown
8.2 Systems of Linear Equations: Solving by Adding 8.2 OBJECTIVES 1. Solve systems using the addition method 2. Solve applications of systems of equations The graphical method of solving equations, shown
( 7, 3) means x = 7 and y = 3. ( 7, 3) works in both equations so. Section 5 1: Solving a System of Linear Equations by Graphing
 Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
Section 5 : Solving a Sstem of Linear Equations b Graphing What is a sstem of Linear Equations? A sstem of linear equations is a list of two or more linear equations that each represents the graph of a
PreAP Algebra 2 Unit 1 and Unit 2 Review Name A#
 PreAP Algebra Unit and Unit Review Name A# Domain and Range:. The graph of the square root function f is shown below. - - - - - - - - - - Interval Notation Domain: Range: Inequalit Notation Domain: Range:.
PreAP Algebra Unit and Unit Review Name A# Domain and Range:. The graph of the square root function f is shown below. - - - - - - - - - - Interval Notation Domain: Range: Inequalit Notation Domain: Range:.
Dœs Chase count when determining the weight and the cost?
 PROBLEM 1 Whitewater Rafting Chase is an eperienced whitewater rafter who guides groups of adults and children out on the water for amazing adventures. The super-raft he uses can hold 00 pounds of weight.
PROBLEM 1 Whitewater Rafting Chase is an eperienced whitewater rafter who guides groups of adults and children out on the water for amazing adventures. The super-raft he uses can hold 00 pounds of weight.
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0).
 This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
This is Solving Linear Systems, chapter 3 from the book Advanced Algebra (index.html) (v. 1.0). This book is licensed under a Creative Commons by-nc-sa 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 5.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Widgets, Dumbbells, and Dumpsters Multiple Representations of Linear Functions Vocabular Write the term that best completes each statement.. A(n) is
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson. Name Date Widgets, Dumbbells, and Dumpsters Multiple Representations of Linear Functions Vocabular Write the term that best completes each statement.. A(n) is
California State University, Northridge
 California State Universit, Northridge MATH 09 HYBRID WORKBOOKS Spring 00 Chapter Equations, Inequalities and Applications. The Addition Propert of Equalit Learning Objectives:. Use the Addition Propert
California State Universit, Northridge MATH 09 HYBRID WORKBOOKS Spring 00 Chapter Equations, Inequalities and Applications. The Addition Propert of Equalit Learning Objectives:. Use the Addition Propert
74 Maths Quest 10 for Victoria
 Linear graphs Maria is working in the kitchen making some high energ biscuits using peanuts and chocolate chips. She wants to make less than g of biscuits but wants the biscuits to contain at least 8 g
Linear graphs Maria is working in the kitchen making some high energ biscuits using peanuts and chocolate chips. She wants to make less than g of biscuits but wants the biscuits to contain at least 8 g
LESSON #42 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART 2 COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II
 LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
LESSON #4 - INVERSES OF FUNCTIONS AND FUNCTION NOTATION PART COMMON CORE ALGEBRA II You will recall from unit 1 that in order to find the inverse of a function, ou must switch and and solve for. Also,
Unit 3: Relations and Functions
 Unit 3: Relations and Functions 5-1: Binar Relations Binar Relation: - a set ordered pairs (coordinates) that include two variables (elements). (, ) = horizontal = vertical Domain: - all the -values (first
Unit 3: Relations and Functions 5-1: Binar Relations Binar Relation: - a set ordered pairs (coordinates) that include two variables (elements). (, ) = horizontal = vertical Domain: - all the -values (first
SCC Ch 3. Math 124 Intermediate Algebra: Part II Sec 3.1: Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables
 Math 124 Intermediate Algebra: Part II Sec 3.1: Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Overview of Math 124 Chapter 3: Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities (omit 3.4, 3.5) Chapter 7: Quadratic
Math 124 Intermediate Algebra: Part II Sec 3.1: Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables Overview of Math 124 Chapter 3: Systems of Linear Equations and Inequalities (omit 3.4, 3.5) Chapter 7: Quadratic
Chapter 4. Chapter 4 Opener. Section 4.1. Big Ideas Math Blue Worked-Out Solutions. x 2. Try It Yourself (p. 147) x 0 1. y ( ) x 2
 Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. 7). As the input decreases b, the output increases b.. Input As the input increases b, the output increases b.. As the input decreases b, the output decreases
Chapter Chapter Opener Tr It Yourself (p. 7). As the input decreases b, the output increases b.. Input As the input increases b, the output increases b.. As the input decreases b, the output decreases
Semester 1 Final REVIEW
 Algebra Name s dc0p[8\ MKkuvtXaI esmoifntrw\araef GLSLFCA.l F pa\lglb ArNiigphHtsT qrievsneprqvlevdn. Semester Final REVIEW Evaluate each using the values given. ) z + ; use = -, and z = - ) ( - z) ; use
Algebra Name s dc0p[8\ MKkuvtXaI esmoifntrw\araef GLSLFCA.l F pa\lglb ArNiigphHtsT qrievsneprqvlevdn. Semester Final REVIEW Evaluate each using the values given. ) z + ; use = -, and z = - ) ( - z) ; use
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 4.. 4..4 Students have been solving equations even before Algebra. Now the focus on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions,
Systems of Equations and Inequalities
 Chapter 6 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Sstems of Equations and Inequalities. The least common multiple of 0 and is 0.. Two lines in the same plane are parallel
Chapter 6 Sstems of Equations and Inequalities Prerequisite Skills for the chapter Sstems of Equations and Inequalities. The least common multiple of 0 and is 0.. Two lines in the same plane are parallel
b(n) = 4n, where n represents the number of students in the class. What is the independent
 Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing movie tickets that sell for $ each C The cost,, after a $ discount,
Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing movie tickets that sell for $ each C The cost,, after a $ discount,
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER
 THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER ALGEBRA EOC PRACTICE Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing
THIS IS A CLASS SET - DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAPER ALGEBRA EOC PRACTICE Which situation can be represented b =? A The number of eggs,, in dozen eggs for sale after dozen eggs are sold B The cost,, of buing
7.1 Solving Systems of Equations
 Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
Date: Precalculus Notes: Unit 7 Systems of Equations and Matrices 7.1 Solving Systems of Equations Syllabus Objectives: 8.1 The student will solve a given system of equations or system of inequalities.
NAME DATE PERIOD. Graphing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form
 NAME DATE PERID 4-1 Skills Practice Graphing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form Write an equation of a line in slope-intercept form with the given slope and -intercept. 1. slope: 5, -intercept: -3. slope:
NAME DATE PERID 4-1 Skills Practice Graphing Equations in Slope-Intercept Form Write an equation of a line in slope-intercept form with the given slope and -intercept. 1. slope: 5, -intercept: -3. slope:
N5 R1.1 Linear Equations - Revision
 N5 R Linear Equations - Revision This revision pack covers the skills at Unit Assessment and eam level for Linear Equations so ou can evaluate our learning of this outcome. It is important that ou prepare
N5 R Linear Equations - Revision This revision pack covers the skills at Unit Assessment and eam level for Linear Equations so ou can evaluate our learning of this outcome. It is important that ou prepare
Analytic Geometry 300 UNIT 9 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY. An air traffi c controller uses algebra and geometry to help airplanes get from one point to another.
 UNIT 9 Analtic Geometr An air traffi c controller uses algebra and geometr to help airplanes get from one point to another. 00 UNIT 9 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Copright 00, K Inc. All rights reserved. This material
UNIT 9 Analtic Geometr An air traffi c controller uses algebra and geometr to help airplanes get from one point to another. 00 UNIT 9 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Copright 00, K Inc. All rights reserved. This material
Test 1 Review #5. Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Fall 2016 Master (Prof. Fleischner)
 Test 1 Review #5 Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Fall 016 Master (Prof. Fleischner) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for n. d = m + 9n. Solve for b. r = 5 b + a 3. Solve for C. A = 7 8 B + C ALEKS Test 1 Review
Test 1 Review #5 Intermediate Algebra / MAT 135 Fall 016 Master (Prof. Fleischner) Student Name/ID: 1. Solve for n. d = m + 9n. Solve for b. r = 5 b + a 3. Solve for C. A = 7 8 B + C ALEKS Test 1 Review
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS
 SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 3.. 3..4 In this course, one focus is on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions, students are able to solve equations
SOLVING SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS 3.. 3..4 In this course, one focus is on what a solution means, both algebraicall and graphicall. B understanding the nature of solutions, students are able to solve equations
MATH 021 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS
 MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
MATH 01 UNIT 1 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENTS General Instructions You will notice that most of the homework assignments for a section have more than one part. Usuall, the part (A) questions ask for eplanations,
M practice SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 M101 7.1-7.3 practice SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the sstem b substitution. 1) - 2 = -16 2-2 = -22 1) 2) 4-5 = 8 9 + 3 = 75
M101 7.1-7.3 practice SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Solve the sstem b substitution. 1) - 2 = -16 2-2 = -22 1) 2) 4-5 = 8 9 + 3 = 75
12.1 Systems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination
 . Sstems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination Sstems of two linear equations in two variables A sstem of equations is a collection of two or more equations. A solution of a sstem in two variables
. Sstems of Linear equations: Substitution and Elimination Sstems of two linear equations in two variables A sstem of equations is a collection of two or more equations. A solution of a sstem in two variables
REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM
 Math H REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM DO NOT WRITE ON PACKET! Do on binder paper, show support work. On this packet leave all fractional answers in improper fractional form (ecept where appropriate
Math H REVIEW PACKET FOR END OF COURSE EXAM DO NOT WRITE ON PACKET! Do on binder paper, show support work. On this packet leave all fractional answers in improper fractional form (ecept where appropriate
What if both of the variables cancel out?
 Name:. Solving Sstems of Equations Algebraicall Lesson Essential Question: How do ou solve a sstem of equations algebraicall? SUBSTITUTION ELIMINATION Definition- Definition- - = -6 + = - - = -6 + = -
Name:. Solving Sstems of Equations Algebraicall Lesson Essential Question: How do ou solve a sstem of equations algebraicall? SUBSTITUTION ELIMINATION Definition- Definition- - = -6 + = - - = -6 + = -
Diaz Math 080 Midterm Review: Modules A-F Page 1 of 7
 Diaz Math 080 Midterm Review: Modules A-F Page 1 of 7 1. Use the rule for order of operations to simplif the epression: 11 9 7. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: 7(4 + 4) 6(5 9) 3. If a = 3,
Diaz Math 080 Midterm Review: Modules A-F Page 1 of 7 1. Use the rule for order of operations to simplif the epression: 11 9 7. Perform the indicated operations and simplif: 7(4 + 4) 6(5 9) 3. If a = 3,
Unit 6 Systems of Equations
 1 Unit 6 Systems of Equations General Outcome: Develop algebraic and graphical reasoning through the study of relations Specific Outcomes: 6.1 Solve problems that involve systems of linear equations in
1 Unit 6 Systems of Equations General Outcome: Develop algebraic and graphical reasoning through the study of relations Specific Outcomes: 6.1 Solve problems that involve systems of linear equations in
