General Physics Contest 2012
|
|
|
- Delphia Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 General Physics Contest May 6, (9:am-:5am), Total of 5 pages. Some useful constants: Gas constant R = 8.34 J/mol K Electron mass m e = kg Electron charge e =.6-9 C Electric constant (permittivity) ε = C /N m Magnetic constant (permeability) μ = 4π -7 T m/a Gravitational constant G = N m /kg Mass of Sun =.99 3 kg Mass of Earth = kg Radius of Earth = m Radius of Sun = m Part I Single Choice ( Questions, 3% for each, Use B pencil, No Deduction, Find the Best Choice):. A sports car traveling on a straight road has an initial velocity of m/s; it gains velocity steadily, and 5 s later its velocity is 5 m/s. The acceleration is (A) 5 m/s (B) 4 m/s (C) 3 m/s (D) m/s (E) m/s.. A baseball is thrown at a velocity of 8 m/s at an angle of 3 above the horizontal. What is the maximum height of the ball? (A) m (B) 7 m (C) 8 m (D) m (E) 4 m. 3. An object of mass m is observed to move in a straight line with velocity given by v=bt -ct, where b and c are positive constants. The expression for the force on the object as a function of time is (A) mbt -mct (B) mbt -mct (C) mbt-mc (D) mbt-mc (E) mbt -.5mct. 4. A stone of mass. kg is tied to a string of length.8 m. If you hold the end of this string in your hand and whirl the stone around a circle at the rate of revolutions per second, what is the tension in the string? Ignore gravity in this problem. (A) N (B) 5 N (C) 3 N (D) 4 N (E) 45 N. 5. A fisherman starts his outboard motor by applying a steady tangential force of N by means of a starter rope. The flywheel has a moment of inertia of.5 kg.m and a diameter of. m. Ignoring the effects of friction and the opposing torque due to the compression of the motor, what is the angular speed of the flywheel after it has turned through half a revolution starting from rest? (A) 35.4 rad/s (B) 5. rad/s (C) 56. rad/s (D) 5.6 rad/s (E) 4.5 rad/s. 6. A meteoroid (a chunk of rock) is initially at rest in interplanetary space at a large distance from the Sun. Under the influence of gravity, the meteoroid begins to fall toward the Sun along a straight radial line. With what speed does it strike the Sun? (A) 88 km/s (B) 3 km/s (C) 483 km/s (D) 68 km/s (E) 7 km/s. 7. Electrons in a TV tube are accelerated essentially from rest to a speed of m/s in the electron gun at the back of the tube. If the electron gun is 8. cm long and if the acceleration in the gun is constant, what force is exerted on each electron? (A) N (B) N (C) N (D) N (E) N. 8. A rotating wheel 8 cm in diameter is decelerating at. rad/s. What should be the initial angular speed if the wheel is to stop after exactly one revolution? (A).8 rad/s (B).9 rad/s (C). rad/s (D).4 rad/s (E).6 rad/s. 9. The moment of inertia of the Earth about an axis through the poles is kg m. What is the spin angular momentum? (A).6 33 kg m /s (B).3 33 kg m /s (C) kg m /s (D) kg m /s (E) kg m /s.
2 . A rocket of mass 4 kg, starting from rest, is acted on by a net force of 5 N for s. What is the final velocity of the rocket? (A) 4 m/s (B) m/s (C) m/s (D) 5 m/s (E) 5 m/s.. The figure shows a rectangular brass plate at in which there is cut a rectangular hole of dimension indicated. If the temperature of the plate is raised to 5 : (A) x will increase and y will decrease (B) x will decrease and y will increase (C) both x and y will increase (D) both x and y will decrease (E) depends on the dimension z.. A quantity of an ideal gas is compressed to half its initial volume. The process may be adiabatic, isothermal or isobaric. The greatest amount of work is required if the process is: (A) adiabatic (B) isothermal (C) isobaric (D) adiabatic or isothermal (both require the same work; isobaric requires less) (E) isothermal or isobaric (both require the same work; adiabatic requires less). 3. The Principle of Equipartition of Energy states that the energy of a gas is shared equally: (A) among the molecules (B) between kinetic and potential energy (C) between translational and vibrational kinetic energy (D)among the relevant degrees of freedom (E) between heat and work. 4. A heat engine operates between K and K. In each cycle it takes J from the hot reservoir, loses 5 J to the cold reservoir and does 75 J of work. This heat engine violates: (A) both the first and second laws of thermodynamics (B) the first law but not the second law of thermodynamics (C) the second law but not the first law of thermodynamics (D) neither the first law nor the second law of thermodynamics (E) cannot answer without knowing the mechanical equivalent of heat. 5. Choose the INCORRECT statement: (A) Gauss s law holds in a vacuum (B) Gauss s law states that the net number of lines crossing any closed surface in an outward direction is proportional to the net charge enclosed within the surface (C) Coulomb s law can be derived from Gauss s law and symmetry (D) Gauss s law applies to a closed surface of any shape (E) according to Gauss s law, if a closed surface encloses no charge, then the electric field must vanish everywhere on the Gaussian surface. 6. A parallel plate capacitor is charged and then disconnected from the source. Using insulating handles, the plates are brought closer together. Therefore: (A) the charge on each plate increased (B) the charge on each plate decreased (C) the potential difference between the plates increased (D) the potential difference between the plates decreased (E) the capacitance decreased. 7. A magnetic field CANNOT: (A) exert a force on a charge (B) accelerate a charge (C) change the momentum of a charge (D) change the kinetic energy of a charge (E) change the velocity of a charge.
3 8. Which graph below correctly gives the magnitude of the B field due to an infinitely long straight current carrying wire as a function or the distance r from the wire? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) 9. A square loop of wire moves with a constant speed v from a field free region, through a region of uniform B field as shown. Which of the five graphs correctly shows the induced current I in the loop as a function of time t? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E). In the diagram, assume that all the lines of B generated by coil # pass through coil #. Coil # has turns and coil # has 4 turns. Then: (A) the current in coil # will be /4 that in coil # (B) the voltage in coil # will be /4 that in coil # (C) the current will be the same in the two coils (D) the voltage will be the same in the two coils (E) the power supplied to coil # is equal to the power delivered by coil #. 3
4 Part II: Multiple Choice (8 Questions, 5% for each, Use B pencil, With Deduction):. A man and a boy, initially at rest on frictionless ice, push each other apart. After a short time, (A) the man is further from the starting point. (B) the boy is further from the starting point. (C) neither is further from the starting point. (D) the man is moving with a higher speed. (E) the boy is moving with a higher speed.. A spring having force constant 5 N/m is loaded with a mass of kg. Which answers are correct in the followings? (A) The period of vibration is.8 s. (B) The period of vibration is.56 s. (C) If the mass is displaced 3 cm and then released. The velocity with which it passes through the equilibrium position is.5 m/s. (D) If the mass is displaced 3 cm and then released. The velocity with which it passes through the equilibrium position is 5 m/s. (E) If the mass is displaced 3 cm and then released. The velocity with which it passes through the equilibrium position is 5 m/s. 3. A space shuttle is in circular orbit 5 km above earth s surface. Which answers are correct? (A) Its orbital speed is 7.8 km/s. (B) Its orbital speed is 3.9 km/s. (C) Its orbital period is around 536 s. (D) Its orbital period is around 3893 s. (E) Its orbital period is around 946 s. 4. A particle moves as follows as a function of time: X = 3. m cos (. radian/s T + π/3), where distance (X) is measured in meters (m) and time (T) in seconds (s). Which answers are correct in the followings? (A) The amplitude of the simple harmonic motion is 3. m. (B) The amplitude of the simple harmonic motion is 6. m. (C) The angular frequency is. radian/s. (D) The angular frequency is.38 cycle/s. (E) The angular frequency is 6.8 radian/s. 5. One mole of ideal monatomic gas is taken around the reversible cycle of Fig. 5. The isothermals are at 5K and 3K. (R is the gas constant) (A) Q = 5Rln, (B) Q =-3R, (C) Q 3 =-3Rln, (D) the work done in one cycle is Rln, (E) the efficiency of the engine is.4. Fig. 5 4
5 6. In A. J. Dempster s mass spectrometer (Fig. 6), two isotopes with masses m and m are accelerated from rest by a potential difference V. They then enter a uniform field B normal to the magnetic field lines. (Assume both isotopes have the same charge q) (A) Both kinetic energies of the accelerated particles are qv (B) The speed of isotope with m is v = qv / m (C) The radius of the path in the magnetic field for the isotope with Fig. 6 m is r m V qb = / (D) r r = m m, (E) r r = m m 7. A cylindrical capacitor consists of a central conductor of radius a surrounded by a cylindrical shell of radius b, as shown in Fig. 7. We assume that the cable is long enough for us to neglect end effects and the linear charge on the central conductor is λ C/m. k = 4πε ) ( (A) The electric field in the region a<r<b is E r =kλ/r (B) The electric field in the region a<r<b is E r =kλ/r (C) The potential difference between the conductors is kλln(b/a) (D) The potential difference between the conductors is kλ(b/a) (E) The capacitance of a length L assuming that air is between the plates: C = πε L ln( b / a) Fig.7 8. A toroidal coil is tightly wound with N turns and carries a current I. We assume that it has a rectangular cross section, as shown in Fig.8. NI a (A) The magnetic field strength within the toroid is B = πr b NI (B) The magnetic field strength within the toroid is B = πr N I (C) The total energy within the toroid is U = 4π h b ln a N h a (D) The self-inductance of the toroid is L = π b N h b (E) The self-inductance of the toroid is L = ln π a Fig. 8 5
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives
 AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
AP Physics C Mechanics Objectives I. KINEMATICS A. Motion in One Dimension 1. The relationships among position, velocity and acceleration a. Given a graph of position vs. time, identify or sketch a graph
The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest.
 T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
T2-2 [195 marks] 1. The graph shows how an external force applied to an object of mass 2.0 kg varies with time. The object is initially at rest. What is the speed of the object after 0.60 s? A. 7.0 ms
Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy?
 Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
Tuesday, June 15, 2010 Page: 1 Q1. Which of the following is the correct combination of dimensions for energy? A) ML 2 /T 2 B) LT 2 /M C) MLT D) M 2 L 3 T E) ML/T 2 Q2. Two cars are initially 150 kilometers
AP Physics B Summer Assignment
 BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
BERGEN COUNTY TECHNICAL SCHOOL AP Physics B Summer Assignment 2011 Solve all problems on separate paper. This will be due the first week of school. If you need any help you can e-mail Mr. Zavorotniy at
All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (1:30 PM 4:30 PM) Page 1 of 6 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
(1:30 PM 4:30 PM) Page 1 of 6 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will look
General Physics Contest 2010
 General Physics Contest 2010 May 22, 2010 (9:10-10:50), Total 6 pages Part I : Choice Questions (20 single-choice questions of 3% each. Use 2B pencil to mark the answer.) 1. A particle moving along the
General Physics Contest 2010 May 22, 2010 (9:10-10:50), Total 6 pages Part I : Choice Questions (20 single-choice questions of 3% each. Use 2B pencil to mark the answer.) 1. A particle moving along the
Rotation. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
- 5 - TEST 2. This test is on the final sections of this session's syllabus and. should be attempted by all students.
 - 5 - TEST 2 This test is on the final sections of this session's syllabus and should be attempted by all students. QUESTION 1 [Marks 23] A thin non-conducting rod is bent to form the arc of a circle of
- 5 - TEST 2 This test is on the final sections of this session's syllabus and should be attempted by all students. QUESTION 1 [Marks 23] A thin non-conducting rod is bent to form the arc of a circle of
Axis Balanced Forces Centripetal force. Change in velocity Circular Motion Circular orbit Collision. Conservation of Energy
 When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
When something changes its velocity The rate of change of velocity of a moving object. Can result from a change in speed and/or a change in direction On surface of earth, value is 9.8 ms-²; increases nearer
g E. An object whose weight on 6 Earth is 5.0 N is dropped from rest above the Moon s surface. What is its momentum after falling for 3.0s?
 PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Take the acceleration due to gravity, g E, as 10 m s on the surface of the Earth. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon is g E. n object whose weight on
PhysicsndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Take the acceleration due to gravity, g E, as 10 m s on the surface of the Earth. The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon is g E. n object whose weight on
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems
 Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Energy Conservation AP
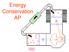 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade
 EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade Winter 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 2 marks. 1. The mass of the two wheels shown in the diagram is the same. A force of 1 N is exerted on the
EXAM 3 MECHANICS 40% of the final grade Winter 2018 Name: Each multiple-choice question is worth 2 marks. 1. The mass of the two wheels shown in the diagram is the same. A force of 1 N is exerted on the
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (3:30 pm 6:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
(3:30 pm 6:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero?
 1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
1. For which of the following motions of an object must the acceleration always be zero? I. Any motion in a straight line II. Simple harmonic motion III. Any motion in a circle I only II only III that
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) m 3 B) m 3 C) m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3
 1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 16, 2000 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 16, 2000 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
is acting on a body of mass m = 3.0 kg and changes its velocity from an initial
 PHYS 101 second major Exam Term 102 (Zero Version) Q1. A 15.0-kg block is pulled over a rough, horizontal surface by a constant force of 70.0 N acting at an angle of 20.0 above the horizontal. The block
PHYS 101 second major Exam Term 102 (Zero Version) Q1. A 15.0-kg block is pulled over a rough, horizontal surface by a constant force of 70.0 N acting at an angle of 20.0 above the horizontal. The block
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers.
 (1:30 pm 4:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
(1:30 pm 4:30 pm) PAGE NO.: 1 of 7 All questions are of equal value. No marks are subtracted for wrong answers. Record all answers on the computer score sheet provided. USE PENCIL ONLY! Black pen will
PY205N Spring The vectors a, b, and c. are related by c = a b. The diagram below that best illustrates this relationship is (a) I
 PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
PY205N Spring 2013 Final exam, practice version MODIFIED This practice exam is to help students prepare for the final exam to be given at the end of the semester. Please note that while problems on this
Advanced Higher Physics. Rotational motion
 Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
Wallace Hall Academy Physics Department Advanced Higher Physics Rotational motion Problems AH Physics: Rotational Motion 1 2013 Data Common Physical Quantities QUANTITY SYMBOL VALUE Gravitational acceleration
r r Sample Final questions for PS 150
 Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
Sample Final questions for PS 150 1) Which of the following is an accurate statement? A) Rotating a vector about an axis passing through the tip of the vector does not change the vector. B) The magnitude
(A) 10 m (B) 20 m (C) 25 m (D) 30 m (E) 40 m
 PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
PSI AP Physics C Work and Energy (Algebra Based) Multiple Choice Questions (use g = 10 m/s 2 ) 1. A student throws a ball upwards from the ground level where gravitational potential energy is zero. At
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam December 13, 2011 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): N. Sullivan PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2004 Final Exam December 13, 2011 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Multiple Choice Questions Choose the best answer and write the corresponding letter in the space provided on the solution workbook.
 Los Altos Physics Spring 2006 MC Sample Multiple Choice Questions Choose the best answer and write the corresponding letter in the space provided on the solution workbook. Version # 1_ 1. A football player
Los Altos Physics Spring 2006 MC Sample Multiple Choice Questions Choose the best answer and write the corresponding letter in the space provided on the solution workbook. Version # 1_ 1. A football player
Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, Mechanics Test
 Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, 2005 Mechanics Test Please answer the following questions on the supplied answer sheet. You may write on this test booklet,
Twentieth SLAPT Physics Contest Southern Illinois University Edwardsville April 30, 2005 Mechanics Test Please answer the following questions on the supplied answer sheet. You may write on this test booklet,
Test 7 wersja angielska
 Test 7 wersja angielska 7.1A One revolution is the same as: A) 1 rad B) 57 rad C) π/2 rad D) π rad E) 2π rad 7.2A. If a wheel turns with constant angular speed then: A) each point on its rim moves with
Test 7 wersja angielska 7.1A One revolution is the same as: A) 1 rad B) 57 rad C) π/2 rad D) π rad E) 2π rad 7.2A. If a wheel turns with constant angular speed then: A) each point on its rim moves with
Review PHYS114 Chapters 4-7
 Review PHYS114 Chapters 4-7 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 27 kg object is accelerated at a rate of 1.7 m/s 2. What force does
Review PHYS114 Chapters 4-7 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A 27 kg object is accelerated at a rate of 1.7 m/s 2. What force does
time/s force/n Polesworth High School 1
 1. A toy locomotive of mass 0.50kg is initially at rest on a horizontal track. The locomotive is powered by a twisted rubber band which, as it unwinds, exerts a force which varies with time as shown in
1. A toy locomotive of mass 0.50kg is initially at rest on a horizontal track. The locomotive is powered by a twisted rubber band which, as it unwinds, exerts a force which varies with time as shown in
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems. Kinetic Energy and
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Kinetic energy Work Work-energy theorem Gravitational work Work of spring forces Power 1. A single force acts on a 5.0-kg object in such
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Kinetic energy Work Work-energy theorem Gravitational work Work of spring forces Power 1. A single force acts on a 5.0-kg object in such
Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1
 Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1 1. Which is true of two vectors whose sum is zero? (C) 2. Which graph represents an object moving to the left at a constant speed? (C) 3. Which graph represents
Physics 12 Final Exam Review Booklet # 1 1. Which is true of two vectors whose sum is zero? (C) 2. Which graph represents an object moving to the left at a constant speed? (C) 3. Which graph represents
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
AIPMT 2015 (Code: E) DETAILED SOLUTION
 AIPMT 2015 (Code: E) DETAILED SOLUTION Physics 1. If energy (E), velocity (V) and time (T) are chosen as the fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be: (1) [EV 2 T 1 ]
AIPMT 2015 (Code: E) DETAILED SOLUTION Physics 1. If energy (E), velocity (V) and time (T) are chosen as the fundamental quantities, the dimensional formula of surface tension will be: (1) [EV 2 T 1 ]
Conservation of Energy Challenge Problems Problem 1
 Conservation of Energy Challenge Problems Problem 1 An object of mass m is released from rest at a height h above the surface of a table. The object slides along the inside of the loop-the-loop track consisting
Conservation of Energy Challenge Problems Problem 1 An object of mass m is released from rest at a height h above the surface of a table. The object slides along the inside of the loop-the-loop track consisting
Practice Final C. 1. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart.
 1. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart. 6. The graph below represents the relationship between gravitational force and mass for objects near the surface of Earth. The worker s
1. The diagram below shows a worker using a rope to pull a cart. 6. The graph below represents the relationship between gravitational force and mass for objects near the surface of Earth. The worker s
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #2 November 15, 2001 Time: 90 minutes NAME: STUDENT NO.: (Last) Please Print (Given) LECTURE SECTION
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM MONDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2010
 PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM MONDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2010 Name (printed): Nine-digit ID Number: Section Number: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS: i. Put away all materials except for pens, pencils,
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2010 FINAL EXAM MONDAY, DECEMBER 13, 2010 Name (printed): Nine-digit ID Number: Section Number: Recitation Instructor: INSTRUCTIONS: i. Put away all materials except for pens, pencils,
The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is directly proportional to the frequency.
 Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
Q1.For a body performing simple harmonic motion, which one of the following statements is correct? The maximum kinetic energy is directly proportional to the frequency. The time for one oscillation is
Rotational Motion Examples:
 Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Rotational Motion Examples: 1. A 60. cm diameter wheel rotates through 50. rad. a. What distance will it move? b. How many times will the wheel rotate in this time? 2. A saw blade is spinning at 2000.
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 14, 013 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 14, 013 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
The diagram below shows a block on a horizontal frictionless surface. A 100.-newton force acts on the block at an angle of 30. above the horizontal.
 Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Name: 1) 2) 3) Two students are pushing a car. What should be the angle of each student's arms with respect to the flat ground to maximize the horizontal component of the force? A) 90 B) 0 C) 30 D) 45
Physics 12 Final exam review key
 Physics 12 Final exam review key 1) A scalar field differs from a vector field in that A. a scalar field acts in only one direction B. a vector field acts in only one direction C. direction is irrelevant
Physics 12 Final exam review key 1) A scalar field differs from a vector field in that A. a scalar field acts in only one direction B. a vector field acts in only one direction C. direction is irrelevant
NAME. (2) Choose the graph below that represents the velocity vs. time for constant, nonzero acceleration in one dimension.
 (1) The figure shows a lever (which is a uniform bar, length d and mass M), hinged at the bottom and supported steadily by a rope. The rope is attached a distance d/4 from the hinge. The two angles are
(1) The figure shows a lever (which is a uniform bar, length d and mass M), hinged at the bottom and supported steadily by a rope. The rope is attached a distance d/4 from the hinge. The two angles are
SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book)
 PHYS 111-01 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book) 1. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO. NAME: (Given) (Family) 2. For the problems, write clearly and neatly and be sure to show your work. Answers without
PHYS 111-01 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM (Closed Book) 1. DO NOT OPEN THE EXAM UNTIL TOLD TO DO SO. NAME: (Given) (Family) 2. For the problems, write clearly and neatly and be sure to show your work. Answers without
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006
 Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
Physics 201, Practice Midterm Exam 3, Fall 2006 1. A figure skater is spinning with arms stretched out. A moment later she rapidly brings her arms close to her body, but maintains her dynamic equilibrium.
PHYSICS - CLUTCH CH 22: ELECTRIC FORCE & FIELD; GAUSS' LAW
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRIC CHARGE e Atoms are built up of protons, neutrons and electrons p, n e ELECTRIC CHARGE is a property of matter, similar to MASS: MASS (m) ELECTRIC CHARGE (Q) - Mass
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRIC CHARGE e Atoms are built up of protons, neutrons and electrons p, n e ELECTRIC CHARGE is a property of matter, similar to MASS: MASS (m) ELECTRIC CHARGE (Q) - Mass
AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice
 AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice 1. A spool of thread has an average radius of 1.00 cm. If the spool contains 62.8 m of thread, how many turns of thread are on the spool? "Average radius" allows us to
AP practice ch 7-8 Multiple Choice 1. A spool of thread has an average radius of 1.00 cm. If the spool contains 62.8 m of thread, how many turns of thread are on the spool? "Average radius" allows us to
Physics Test Review: Mechanics Session: Name:
 Directions: For each statement or question, write in the answer box, the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below
Directions: For each statement or question, write in the answer box, the number of the word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The diagram below
Chapter 8, Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics. 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience:
 CHAPTER 8 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience: a. a constant angular speed b. an angular acceleration c. a constant moment of inertia d. an increasing moment of inertia
CHAPTER 8 3. If a net torque is applied to an object, that object will experience: a. a constant angular speed b. an angular acceleration c. a constant moment of inertia d. an increasing moment of inertia
Old Exam. Question Chapter 7 072
 Old Exam. Question Chapter 7 072 Q1.Fig 1 shows a simple pendulum, consisting of a ball of mass M = 0.50 kg, attached to one end of a massless string of length L = 1.5 m. The other end is fixed. If the
Old Exam. Question Chapter 7 072 Q1.Fig 1 shows a simple pendulum, consisting of a ball of mass M = 0.50 kg, attached to one end of a massless string of length L = 1.5 m. The other end is fixed. If the
Physics 2220 Fall 2010 George Williams THIRD MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS
 Physics 2220 Fall 2010 George Williams THIRD MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS Solution sets are available on the course web site. A data sheet is provided. Problems marked by "*" do not have solutions. 1. An
Physics 2220 Fall 2010 George Williams THIRD MIDTERM - REVIEW PROBLEMS Solution sets are available on the course web site. A data sheet is provided. Problems marked by "*" do not have solutions. 1. An
2007 Academic Challenge
 2007 Academic Challenge PHYSICS TEST - REGIONAL This Test Consists of 35 Questions Physics Test Production Team Len Storm, Eastern Illinois University Author/Team Coordinator Doug Brandt, Eastern Illinois
2007 Academic Challenge PHYSICS TEST - REGIONAL This Test Consists of 35 Questions Physics Test Production Team Len Storm, Eastern Illinois University Author/Team Coordinator Doug Brandt, Eastern Illinois
1 MR SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 2013
 SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
SAMPLE EXAM 3 FALL 013 1. A merry-go-round rotates from rest with an angular acceleration of 1.56 rad/s. How long does it take to rotate through the first rev? A) s B) 4 s C) 6 s D) 8 s E) 10 s. A wheel,
Use the following to answer question 1:
 Use the following to answer question 1: On an amusement park ride, passengers are seated in a horizontal circle of radius 7.5 m. The seats begin from rest and are uniformly accelerated for 21 seconds to
Use the following to answer question 1: On an amusement park ride, passengers are seated in a horizontal circle of radius 7.5 m. The seats begin from rest and are uniformly accelerated for 21 seconds to
On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
 Instructor(s): Field/inzler PHYSICS DEPATMENT PHY 2053 Final Exam April 27, 2013 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Instructor(s): Field/inzler PHYSICS DEPATMENT PHY 2053 Final Exam April 27, 2013 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this examination.
Suggested Problems. Chapter 1
 Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Suggested Problems Ch1: 49, 51, 86, 89, 93, 95, 96, 102. Ch2: 9, 18, 20, 44, 51, 74, 75, 93. Ch3: 4, 14, 46, 54, 56, 75, 91, 80, 82, 83. Ch4: 15, 59, 60, 62. Ch5: 14, 52, 54, 65, 67, 83, 87, 88, 91, 93,
Phys102 Final-163 Zero Version Coordinator: Saleem Rao Tuesday, August 22, 2017 Page: 1. = m/s
 Coordinator: Saleem Rao Tuesday, August 22, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. A 125 cm long string has a mass of 2.00 g and a tension of 7.00 N. Find the lowest resonant frequency of the string. A) 2.5 Hz B) 53.0 Hz C)
Coordinator: Saleem Rao Tuesday, August 22, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. A 125 cm long string has a mass of 2.00 g and a tension of 7.00 N. Find the lowest resonant frequency of the string. A) 2.5 Hz B) 53.0 Hz C)
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω. What's a radian?
 We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
We define angular displacement, θ, and angular velocity, ω Units: θ = rad ω = rad/s What's a radian? Radian is the ratio between the length of an arc and its radius note: counterclockwise is + clockwise
TutorBreeze.com 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION. 3. If the angular velocity of a spinning body points out of the page, then describe how is the body spinning?
 1. rpm is about rad/s. 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION 2. A wheel rotates with constant angular acceleration of π rad/s 2. During the time interval from t 1 to t 2, its angular displacement is π rad. At time t 2
1. rpm is about rad/s. 7. ROTATIONAL MOTION 2. A wheel rotates with constant angular acceleration of π rad/s 2. During the time interval from t 1 to t 2, its angular displacement is π rad. At time t 2
Base your answers to questions 5 and 6 on the information below.
 1. A car travels 90. meters due north in 15 seconds. Then the car turns around and travels 40. meters due south in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the car during this 20.-second
1. A car travels 90. meters due north in 15 seconds. Then the car turns around and travels 40. meters due south in 5.0 seconds. What is the magnitude of the average velocity of the car during this 20.-second
Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet
 PHYSICS 01 Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet LINEAR ANGULAR Time t t Displacement x; (x = rθ) θ Velocity v = Δx/Δt; (v = rω) ω = Δθ/Δt Acceleration a = Δv/Δt; (a = rα) α = Δω/Δt (
PHYSICS 01 Translational Motion Rotational Motion Equations Sheet LINEAR ANGULAR Time t t Displacement x; (x = rθ) θ Velocity v = Δx/Δt; (v = rω) ω = Δθ/Δt Acceleration a = Δv/Δt; (a = rα) α = Δω/Δt (
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 5.3 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 80 minutes STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please check): 0
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 5.3 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 80 minutes STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please check): 0
Regents Physics. Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems
 Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Name Physics Midterm Review - Multiple Choice Problems Regents Physics 1. A car traveling on a straight road at 15.0 meters per second accelerates uniformly to a speed of 21.0 meters per second in 12.0
Physics 111 Final Exam May 5, 2015
 Physics 111 Final Exam May 5, 2015 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Physics 111 Final Exam May 5, 2015 Name Section University ID Please fill in your computer answer sheet as follows: 1) In the NAME grid, fill in your last name, leave one blank space, then your first name.
Sample Final Exam 02 Physics 106 (Answers on last page)
 Sample Final Exam 02 Physics 106 (Answers on last page) Name (Print): 4 Digit ID: Section: Instructions: 1. There are 30 multiple choice questions on the test. There is no penalty for guessing, so you
Sample Final Exam 02 Physics 106 (Answers on last page) Name (Print): 4 Digit ID: Section: Instructions: 1. There are 30 multiple choice questions on the test. There is no penalty for guessing, so you
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Final Campagnari Section Test Form D
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Final Campagnari Section Test Form D Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron.
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Final Campagnari Section Test Form D Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron.
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Final Campagnari Section Test Form A
 Physics 6b Winter 2015 Final Campagnari Section Test Form A Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron.
Physics 6b Winter 2015 Final Campagnari Section Test Form A Fill out name and perm number on the scantron. Do not forget to bubble in the Test Form (A, B, C, or, D). At the end, only turn in the scantron.
6. Find the net torque on the wheel in Figure about the axle through O if a = 10.0 cm and b = 25.0 cm.
 1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
1. During a certain period of time, the angular position of a swinging door is described by θ = 5.00 + 10.0t + 2.00t 2, where θ is in radians and t is in seconds. Determine the angular position, angular
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 19, 2015 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 19, 2015 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 9, 011 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 115.3 Physics and the Universe FINAL EXAMINATION December 9, 011 NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) Time: 3 hours STUDENT
Class 11 GURU GOBIND SINGH PUBLIC SCHOOL PHYSICS CHAPTER 1: UNITS & MEASUREMENT
 CHAPTER 1: UNITS & MEASUREMENT 1. Assuming that the mass (m) of the largest stone that can be moved by a flowing river depends only upon the velocity, the density ρ of water and the acceleration due to
CHAPTER 1: UNITS & MEASUREMENT 1. Assuming that the mass (m) of the largest stone that can be moved by a flowing river depends only upon the velocity, the density ρ of water and the acceleration due to
ENGINEERING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS IN MATHEMATICS NOTE: ANSWER ANY 11 QUESTIONS OUT OF 16 QUESTIONS
 ENGINEERING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS IN MATHEMATICS NOTE: ANSWER ANY QUESTIONS OUT OF 6 QUESTIONS. Evaluate 3 lim 4 + 3. Find the equation of the straight line passing through (3,) which is perpendicular
ENGINEERING ENTRANCE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS IN MATHEMATICS NOTE: ANSWER ANY QUESTIONS OUT OF 6 QUESTIONS. Evaluate 3 lim 4 + 3. Find the equation of the straight line passing through (3,) which is perpendicular
Physics-MC Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1.
 Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
Physics-MC 2006-7 Page 1 of 29 Inertia, Force and Motion 1. 3. 2. Three blocks of equal mass are placed on a smooth horizontal surface as shown in the figure above. A constant force F is applied to block
KCET PHYSICS 2014 Version Code: C-2
 KCET PHYSICS 04 Version Code: C-. A solenoid has length 0.4 cm, radius cm and 400 turns of wire. If a current of 5 A is passed through this solenoid, what is the magnetic field inside the solenoid? ().8
KCET PHYSICS 04 Version Code: C-. A solenoid has length 0.4 cm, radius cm and 400 turns of wire. If a current of 5 A is passed through this solenoid, what is the magnetic field inside the solenoid? ().8
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014
 PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014 EXAM 2: April 3, 2014 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
PHYSICS 221 SPRING 2014 EXAM 2: April 3, 2014 8:15-10:15pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 25 multiple-choice questions plus 2 extra credit questions,
Study Guide Final Exam Solutions. Part A: Kinetic Theory, First Law of Thermodynamics, Heat Engines
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics 8.0T Fall 004 Study Guide Final Exam Solutions Part A: Kinetic Theory, First Law of Thermodynamics, Heat Engines Problem Energy Transformation,
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Physics 8.0T Fall 004 Study Guide Final Exam Solutions Part A: Kinetic Theory, First Law of Thermodynamics, Heat Engines Problem Energy Transformation,
Name: Date: Period: AP Physics C Rotational Motion HO19
 1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
1.) A wheel turns with constant acceleration 0.450 rad/s 2. (9-9) Rotational Motion H19 How much time does it take to reach an angular velocity of 8.00 rad/s, starting from rest? Through how many revolutions
(1) +0.2 m/s (2) +0.4 m/s (3) +0.6 m/s (4) +1 m/s (5) +0.8 m/s
 77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
77777 77777 Instructor: Biswas/Ihas/Whiting PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHY 2053 Exam 2, 120 minutes November 13, 2009 Name (print, last first): Signature: On my honor, I have neither given nor received unauthorized
Practice Test for Midterm Exam
 A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8
 PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
PHY241 - General Physics I Dr. Carlson, Fall 2013 Prep Exam 3 PREP Chapters 6, 7, 8 Name TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. 1) Astronauts in orbiting satellites
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM
 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Annual Exam 2016 Subject: Physics A Level Time: 3 hours Section A: Answer all questions in this section 1. a) For an object to be in equilibrium, two conditions must
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Annual Exam 2016 Subject: Physics A Level Time: 3 hours Section A: Answer all questions in this section 1. a) For an object to be in equilibrium, two conditions must
Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017
 A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
A Correlation of Physics for Scientists and Engineers 4th Edition, 2017 To the AP Physics C: Mechanics Course Descriptions AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not
PHYSICS 1. Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes. g = 10 m s in all problems.
 Note: To simplify calculations, you may use PHYSICS 1 Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes 2 g = 10 m s in all problems. Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by
Note: To simplify calculations, you may use PHYSICS 1 Section I 40 Questions Time 90 minutes 2 g = 10 m s in all problems. Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion
 PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
PSI AP Physics I Rotational Motion Multiple-Choice questions 1. Which of the following is the unit for angular displacement? A. meters B. seconds C. radians D. radians per second 2. An object moves from
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper
 Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
Topic 2 Revision questions Paper 1 3.1.2018 1. [1 mark] The graph shows the variation of the acceleration a of an object with time t. What is the change in speed of the object shown by the graph? A. 0.5
GCE AS and A Level. Physics A. AS exams 2009 onwards A2 exams 2010 onwards. Unit 4A: Approved specimen question paper. Version 1.3
 GE S and Level Physics S exams 009 onwards exams 010 onwards Unit 4: pproved specimen question paper Version 1.3 General ertificate of Education 010 dvanced Examination abc version 1.3 PHYSIS Unit 4: Fields
GE S and Level Physics S exams 009 onwards exams 010 onwards Unit 4: pproved specimen question paper Version 1.3 General ertificate of Education 010 dvanced Examination abc version 1.3 PHYSIS Unit 4: Fields
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Department of Physics Phys102 Homework Term 001
 King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Department of Physics Phys102 Homework Term 001 Chapter 16 1. The equation of a certain traveling wave on a string is given by y( x, t ) = (0.2cm) sin( 0.1x
King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals Department of Physics Phys102 Homework Term 001 Chapter 16 1. The equation of a certain traveling wave on a string is given by y( x, t ) = (0.2cm) sin( 0.1x
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
Physics 2B Winter 2012 Final Exam Practice
 Physics 2B Winter 2012 Final Exam Practice 1) When the distance between two charges is increased, the force between the charges A) increases directly with the square of the distance. B) increases directly
Physics 2B Winter 2012 Final Exam Practice 1) When the distance between two charges is increased, the force between the charges A) increases directly with the square of the distance. B) increases directly
Dynamics Test K/U 28 T/I 16 C 26 A 30
 Name: Dynamics Test K/U 28 T/I 16 C 26 A 30 A. True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The normal force that acts on an object is always equal in magnitude and opposite
Name: Dynamics Test K/U 28 T/I 16 C 26 A 30 A. True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. The normal force that acts on an object is always equal in magnitude and opposite
Phys101 Second Major-162 Zero Version Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Saturday, March 25, 2017 Page: 1
 Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Saturday, March 25, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. Only two horizontal forces act on a 3.0 kg body that can move over a frictionless floor. One force is 20 N, acting due east, and the other
Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Saturday, March 25, 2017 Page: 1 Q1. Only two horizontal forces act on a 3.0 kg body that can move over a frictionless floor. One force is 20 N, acting due east, and the other
Preliminary Examination - Day 2 August 15, 2014
 UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day 2 August 15, 2014 This test covers the topics of Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic 1) and Mechanics (Topic 2). Each
UNL - Department of Physics and Astronomy Preliminary Examination - Day 2 August 15, 2014 This test covers the topics of Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics (Topic 1) and Mechanics (Topic 2). Each
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Physics. Student Materials Advanced Higher. Tutorial Problems Mechanics HIGHER STILL. Spring 2000
 Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
Spring 2000 HIGHER STILL Physics Student Materials Advanced Higher Tutorial Problems Mechanics TUTORIAL 1 You will find tutorials on each topic. The fully worked out answers are available. The idea is
Chapter 19 Practice Test 2
 Chapter 19 Practice Test PHYSICS C Physics C has two exams: Physics C (Mechanics) and Physics C (Electricity & Magnetism): Physics C (Mechanics) Physics C (Electricity & Magnetism) First 45 min. Sec. I,
Chapter 19 Practice Test PHYSICS C Physics C has two exams: Physics C (Mechanics) and Physics C (Electricity & Magnetism): Physics C (Mechanics) Physics C (Electricity & Magnetism) First 45 min. Sec. I,
Name: School Name: PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION
 PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION - 2013 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Please note that i^, j^, and k^ are unit vectors along the x-axis,
PHYSICS CONTEST EXAMINATION - 2013 Unless otherwise specified, please use g as the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the earth. Please note that i^, j^, and k^ are unit vectors along the x-axis,
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions (In summer 2014 we have not covered questions 30-35,40,41) 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor
