Physica A 388 (2009) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Physica A. journal homepage:
|
|
|
- Kathryn Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Physica A Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physica A journal homepage: Low-temperature magnetization in nanofilms Vjekoslav Sajfert a,, Dušan Popov b, Bratislav Tošić c a Technical Faculty Mihajlo Pupin Zrenjanin, Serbia b Universitatea Politechnica, Timisoara, Romania c Vojvodina Academy of Science Arts, Novi Sad, Serbia a r t i c l e i n f o a b s t r a c t Article history: Received 9 April 008 Received in revised form 7 October 008 Available online November 008 PACS: i Ak a w The low-temperature magnetization of a film was analyzed by the use of exact Bose representation of spin operators that does not suffer from the presence of unphysical states. The magnetization of thin films has exponentially small temperature correctness, so that Dyson s proof about exponentially small correction coming from two bosons at ideal lattice point cannot be used in film analyses. The main conclusions of this work are that magnetic lattice of a thin film is more rigid than the macroscopic lattice that the autoreduction process the three layer film divides into two layer subfilms takes place in the film. 008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: Ultrathin magnetic films Low-temperature magnetization Exact Bose representation Two small parameters autoreduction Qualitative difference nano macrostructures 0. Introduction The problem of operators with mixed kinematics arose 80 years ago. Bosons fermions have clean kinematics while spin operators ], Pauli operators quasi-pauli operators 6] have mixed kinematics their kinematics is a combination of Bose Fermi kinematics. Mixed kinematics leads to statistical problems the calculation of mean values of operator products correspondingly to thermodynamical problems. Since thermodynamics deals with measurable quantities, correct evaluation of statistical means is necessary. At first the problem of mixed kinematics corresponding mixed statistics arose in quantum theory of magnetism. All attempts to solve this problem were based on the idea of finding an adequate boson representation of spin operators which would give correct statistical means. Following the appearance of lasers the interaction between optical excitations became topical. The original operators in the Hamiltonian of optical excitations Pauli quasi-pauli operators had mixed kinematics statistics too, boson representations of these operators were necessary for the explanation of nonlinear optical effects, such as energy shift in optical spectra two- three-photon absorption 7,8]. A short review of attempts concerning the problem of mixed kinematics is presented in the first section. The second section is dealing with the problem of the low-temperature magnetization in thin films the results of the second section are summarized in the conclusion. Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: addresses: sajfertv@ptt.rs V. Sajfert, dusan_popov@yahoo.co.uk D. Popov, btosic@yahoo.com B. Tošić /$ see front matter 008 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi:0.06/j.physa
2 36 V. Sajfert et al. / Physica A A short review of problems concerned with mixed kinematics The problem of the low-temperature magnetization of Heisenberg ferromagnet was started by Bloch 9] who approximated Heisenberg isotropic spin Hamiltonian with quadratic boson form. The Hamiltonian of Heisenberg ferromagnet is given by: H = SJ 0 S S z I, S S+ I, S S z S S z,, S + = S x + is y, S + = S x + is y are spin operators, are exchange integrals J 0 = l I l. The spin operators obey the following commutation relations:. S +, S ] = S z ; S +, S z] = S + ; S, S z] = S.. Bloch used boson representation of spin operators: S + = SB ; S = SB + ; S Sz = B+ B..3 obtained equivalent boson Hamiltonian: H = SJ 0 B + B S I, B + B.,.4 By diagonalisation of Hamiltonian.4, he found the dispersion law E = S J 0 J k J k = I 0 e i k using it he obtained the following expression for magnetization: σ = Sz S = S ζ 3/τ 3/ ; τ = Θ which is called Bloch s 3/ law. The Riemann s ζ function is given by: πi ; Θ = k BT.5 ζ p = n= n p..6 The next step in the theory of low-temperature magnetization was done by Holstein Primakoff 4], who used the following boson representation for spin operators: S + = S S z = S B + B. B+ B S B; S = SB + B+ B S Using this representation of spin operators, they obtained the expression for low-temperature magnetization:.7 σ = σ h + σ ah.8 σ h = ζ 3/ τ 3/ 3π ζ 5/τ 5/ 33π 6 ζ 7/τ 7/ + O τ 9/,.9 σ ah = 6πζ 3/ ζ 5/ τ 4..0 The terms in formula.9 are coming from exping the dispersion law in powers of magnitude k of k up to k 6 while anharmonic correction is the consequence of the interaction between spin waves. The result.8.0 was correct but the boson representation of spin operators, which is correct only if number of bosons at one lattice point is maximally equal to S arose discussions concerning the contributions of so-called unphysical states, i.e. the states with more than S boson per lattice point. The completed theory of the low-temperature magnetization was given by Dyson 0,]. He proved that the states with more than one boson at one lattice point involve exponentially small contributions in the low-temperature magnetization. Using this proof, he obtained that Holstein Primakoff s result was correct.
3 V. Sajfert et al. / Physica A Finally, the discussions about unphysical states were put ad acta by the appearance of Agranovich Toshich 3] boson representation of spin operators for spin operators S = /: ] S + ν ] = + ν! B+ν B ν B; S = B + ν + ν! B+ν B ν ; ν=0 ν=0 ν Sz = B + ν+ B ν+. + ν! ν=0 by exact boson representation of quasi-pauli operators 5]. It should be noticed that boson infinite series. satisfy commutation rules. for an arbitrary number of bosons. Using the representation., the exact results for the lowtemperature ordering parameter of antiferromagnet was determined ] the exact result for magnetization in case S > / was found in 6]. The correct result of Holstein Primakoff s formula.8 was obtained in 3]. Using the formula. Agranovich Toshich predicted the possibility of Bose condensation of Frenkel excitons. The similar idea was applied to ferromagnet in strong magnetic field µ B H >> I 4] the Bose condensation of spin waves was predicted. This prediction has been recently proved experimentally for YIG ferromagnet films in 5]. The exact Bose representation of spin operators. will be applied for the calculation of magnetization of ultrathin ferromagnet films with S = /. Ending this review of the low-temperature problems in determining magnetization, we quote the leading correction which is given by Bloch s approach in three layer film. This correction is proportional to τ Z it is clear that it is exponentially small., Zp q = n=. e nq n p. Low-temperature magnetization in three layer magnetic films with spin S = / The interest in magnetic problems has increased recently 6 4], but no has the problem of broken symmetry magnetic structures been in the foreground. We shall analyze the three layer magnetic film with spin S = / cut off in z direction from simple cubic ideal structure. The more compact clearer formulae will be obtained if we substitute spin operators with Pauli operators in accordance with the following formulae: S + = P, S = P + ; Sz = P + P; P, P + ] = P + P ; P + = P = 0. Using. the nearest neighbour approximation for a simple cubic structure, we obtain the Hamiltonian of three layer film in the following form: H = I,+ a + I, a + I,+ a + I, a + I,+ a + I, a P + P P + I,+ a P + a + I, a P a + I,+ a P + a + I, a P a + I,+ a P + a + I, a P a P + P I,+ a P + + a P + a + I, a P + a P a + I,+ a P + + a P + a + I, a P + a P a + I,+ a P + + a P + a + I, a P + + a P a a connects the nearest neighbours. In formula. the boundary conditions must be taken into account on the surfaces 0. It means that boundary conditions are:. I nx,n y,0;n x,n y, = I nx,n y,n z ;n x,n y,n z + = 0..3 The other exchange integrals will be denoted by I. The analysis will be carried out by means of the Pauli Green function Γ, t = θ t P t, P + 0] P t P + 0,.4 θ t is a Heaviside step-function. Differentiating Γ, t with respect to t taking into account that Ṗ = i h P, H], we obtain the equation for Pauli Green function Γ, t: i h d dt P t P + 0 = i hδ t δ, P + P + P, H] t P
4 38 V. Sajfert et al. / Physica A Further steps in the analysis are the following:. In accordance with.., Pauli operators will be substituted with: P = B B + B B ; P + = B+ B+ B+ B ;.6 P + P = B + B B + B in the Green function P, H] t P + 0 in correlation function, while in the higher order Green functions of the type P + t a P a t P b t P + 0 will be substituted with Bose operators, i.e. it will be taken that P = B. c. Applying Wick s theorem 5], we can write down: P t P + 0 B t B + t B t B t B + 0 B+ 0 B+ 0 B 0 B t B + 0 B+ t B t B t B + 0 B t B + 0 B+ 0 B 0 B t B + 0 B+ B 0 B t B + 0 B+ B 0 B t B It should be noticed that the higher order Green functions of the type B + BB B + B + B are rejected, since they are proportional to the square of boson concentration B + B. Inserting the formulae obtained by the application of Wick s theorem for bosons into.5, applying the boundary conditions.3, using the transformation for the boson Green function G, t = B t B + 0 in which translatory invariance in x, y plane is taken into account: G nx,n y,n z ;m x,m y,m z t = B nx,n y,n z t B + m x,m y,m z 0 = e iakxnx mx+iakyny my + k x,k y we obtain the following system of difference equations for the function α nz,m z kx, k y, ω : dωe iωt α nz,m z kx, k y, ω..8 n z = J α,mz + α 0,mz + ρα,mz = i h + B + B 0 δ,mz ; π.9 n z = 0 J J α,mz + ρ + ρ α 0,mz = i h + B + B 0 δ 0,mz ; π.0 n z = J J α,mz + ρ + ρ α,mz = i h π The notations in upper equations are the following: ρ = E I sin ak x + ak sin y I + I F + 3F IΦ ; + B + B 0 δ,mz.. ρ = I I F + F 3 IΦ ; Φ = Φ Φ ;. J = I F ; J = 4 I F; F = F F the functions F Φ are given by: F λ = k x,k y Φ λ = = ak q x,q y e E0 kx,ky,λ M k x, k y, q x, q y e E0 qx,qy,λ πτ 3/ Z 3/ λ ak 3 4 πτ Z λ = τ Z λ 7 + ak 3 8 πτ 3/ Z 3/ λ 9 + π λ τ Z + O τ 3 Z ; ] λ 6 π τ 5/ Z 5/ ] λ 6 π τ 3 Z 3 95 λ 768 π τ 5/ Z 5/ λ I Θ = λ.3 ] + O τ 7/ Z.4
5 V. Sajfert et al. / Physica A E 0 k x,k y,λ = I sin ak x + sin ak y + sin λπ 6 ; λ =,.5 M k x, k y, q x, q y = cos akx + cos ak y + cos aq x + cos aq y cos a k x q x cos a k y q y..6 It can be easily shown that all Eqs..9. after the substitution α nz,m z = a mz,λs nz,λ, λ=.7 S nz,λ = sin n z + ϕ λ + Y λ sin n z ϕ λ ; ] Y λ = + + cos ϕ 0.8 λ F + 3 Φ reduce to the unique one λ= J cos ϕ λ + ρ a mz,λ kx, k y, ω S nz,λ = i h π δ n z,m z ; n z, m z {0,, }.9 if the parameters ϕ λ satisfy the following equation: sin 3ϕ λ sin 3ϕ λ cos ϕ λ + sin ϕ λ cos ϕ λ sin ϕ λ F Φ = 0..0 The Kronecker symbol in.9 will be taken in the following form: δ nz,m z = λ= S nz,λt mz,λ. This system of algebraic equations enables us to calculate all introduced functions T mz,λ. Substituting. in.9 taking that. a mz,λ we reduce.9 into kx, k y, ω = b kx,k y,λ ω T mz,λ b kx,k y,λ ω = i + B + B 0 π ω ω, k x,k y,λ..3 ω kx,k y,λ = h E k x,k y,λ ; E k x,k y,λ = I sin ak x + ak sin y + ϕ λ sin IF IF 3 4 cos λπ 3 + IΦ. Combining.8,.7,., inversing Fourier s time-frequency transformation of the Green function.8, we obtain: G nx,n y,n z ;m x,m y,m z ω = i + B + B 0 e iak xn x m x+iak yn y m y S nz,λt mz,λ π k x,k y λ= ω ω 0 k x,k y,λ in this formula the unknown functions T mz,λ figure. They can be found from. putting δ nz,m z = for n z = m z δ nz,m z = 0 for n z m z. Having formula.5, we can find the spectral intensity, correlation function boson concentrations in the first approximation. We shall quote the first order boson concentration for subfilm 0,, only: B + B 0 = + B + B 0 k x,k y λ= S 0 n z,λ T 0 n z,λ E kx,ky,λ e Θ
6 330 V. Sajfert et al. / Physica A Fig.. Schematic presentation of autoreduction of three layer film into two equivalent two layer films. Now we shall determine the ordering parameter estimate the remaining order of magnitude. The expression for σ is given by: σ = P + P = B + B + 4 B + B 0]..7 Taking into account.6, we can write down: σ = k x,k y λ= S nz,λt nz,λ E kx,ky,λ e Θ. From formula.8 the term proportional B + B 0 B + B B + B 0 was rejected since it is extremely small. The fact that Eq..0 has only two real solutions in interval 0, π is of great importance. Since the number of film layers has three values, the transformation from configuration space to momentum space is not isomorphic. It is of the type 3 this means that the autoreduction takes place in the film 6 30]. The spin wave excitations exist in two layers only. It can be 0,, sets of layers. The set 0, is incompatible with the nearest neighbour approximation which was applied. Geometrically, it is clear that sets 0,, are completely equivalent see Fig.. It means that it is enough to examine magnetization in one of the mentioned subfilms. It was done for subfilm 0, it was found that magnetizations of layers are approximately given by: a is.8 σ n z = 0 = σ h n z = 0 + σ a n z = 0.9 σ h n z = 0 = τ Z σ a n z = 0 = aτ a = 8π Z Z 9 3 8π Z 0 Z..3 The magnetization for layer n z = is given by σ n z = = σ h n z = + σ a n z =.33 σ h n z = = τ Z 3 σ a n z = bτ b = 8π Z Z π Z 0 Z..36 In formulae.3.34 only the leading terms of magnetization are quoted.
7 V. Sajfert et al. / Physica A Conclusion Concluding this analysis, we would like to emphasize the following:. Magnetizations of layers 0 differ. It is the consequence of broken symmetry.. The temperature corrections are exponentially small due to the presence of zeta functions Z λ p. 3. The autoreduction of the n n type takes place in the film reducing the three layer ferromagnet into two layer one. 4. In connection with experimental fact that Bose condensation takes place of spin waves in ferromagnet film YIG, our intention is to examine theoretically the behaviour of thin magnetic films in extremely strong magnetic fields. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the Serbian Ministry of Science Technology: Grant No 4044, by Vojvodina Academy of Sciences Arts. References ] S.V. Tyablikov, Methods in the Quantum Theory in Magnetism, Plenum Press, New York, 967. ] N.N. Bogolubov, S.V. Tyablikov, Dokl. Akad. Nauk USSR ] V.M. Agranovich, B.S. Toshich, JETP ] T. Holstein, H. Primakoff, Phys.Rev ] D.I. Lalović, B.S. Tošić, R.B. Zakula, Phys. Rev ] D.I. Lalovi c, B.S. Tošić, R.B. Zakula, Phys. Rev ] N. Blombergen, Nonlinear Optics, Mir, Moscow, ] R. Loudon, l Phys. Rev ] F. Bloch, Z. Physik ] F.J. Dyson, Phys. Rev ] M.J. Skrinjar, B.S. Tošić, S.D. Stojanović, Rev. Res. Sci ] M.L. Kulić,Tošić, Phys. Stat. Sol. b K79. 3] Group of authors, Jubilee of Bratislav To sić. SFIN ] V.E. Demidov, O. Dzyapko, S.O. Demokritov, G.A. Melkov, A.N. Slavin, Phys. Rev. Lett ] V. Antonov, Electronic Structure Magneto-optical Properties of Solids, Kluwer Academic Publishers, ] K.H.J. Buschow, F.R. De Boer, Physics of Magnetism Magnetic Materials, Kluwer, New York, Boston, ] M. Getzlaff, Fundamentals of Magnetism, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, ] J. Stöhr, H.C. Siegmann, Magnetism from fundamentals to Nanoscale Dynamics, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, ] R.M. White, Quantum Theory of Magnetism, in: Magnetic Properties of Materials, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, ] S. Maekawa, T. Shinjo, Spin Dependent Transport in Magnetic Nanostructures, CRC Boca Raton, London, New York, Washington, D.C, 00. ] M. Pavkov, M. Skrinjar, D. Kapor, M. Pantić, S. Stojanović, Phys. Rev. B ] M. Manojlović, M. Pavkov, M. Škrinjar, M. Pantić, D. Kapor, S. Stojanović, Phys. Rev. B ] P. Fröbrich, P.J. Kuntz, Phys. Rep ] R. Radu, M. Etzkorn, R. Siebrecht, et al., Phys. Rev. B ] B.S. Tošić, Statistical Physics, Faculty of Science, Novi Sad, ] V. Sajfert, R. Ðajić, M. Ćetković, B. Tošić, Nanotechnology ] V. Sajfert, R. Ðajić, B.S. Tošić, J. Nanosci. Nanotech ] V. Sajfert, J. Setrajčić, B. Tošić, R. Ðajić, Czechoslovak J. Phys ] V. Sajfert, J.P. Setrajčić, S. Jaćimovski, B. Tošić, Physica E ] V. Sajfert, J. Setrajčić, D. Popov, B. Tošić, Physica A 353C
Behaviour of Thin Magnetic Films at Low Temperatures
 Copyright 009 American Scientific Publishers All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America Journal of Computational Theoretical anoscience Vol.6,, 009 Vjekoslav Sajfert, Dušan Popov, Ljiljana
Copyright 009 American Scientific Publishers All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America Journal of Computational Theoretical anoscience Vol.6,, 009 Vjekoslav Sajfert, Dušan Popov, Ljiljana
Phonon Contribution in Thermodynamics of Nano-Crystalline Films and Wires
 Vol. 5 9) ACTA PHYSICA POLOICA A o. 4 Proceedings of the Tenth Annual Conference of the Materials Research Society of Serbia September 8 Phonon Contribution in Thermodynamics of ano-crystalline Films and
Vol. 5 9) ACTA PHYSICA POLOICA A o. 4 Proceedings of the Tenth Annual Conference of the Materials Research Society of Serbia September 8 Phonon Contribution in Thermodynamics of ano-crystalline Films and
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 1 Nov 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 1 Nov 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 1 Nov 2011](/thumbs/93/111880633.jpg) V The next nearest neighbor effect on the D materials properties Maher Ahmed Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Western Ontario, London ON N6A K7, Canada and arxiv:.v [cond-mat.mes-hall]
V The next nearest neighbor effect on the D materials properties Maher Ahmed Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Western Ontario, London ON N6A K7, Canada and arxiv:.v [cond-mat.mes-hall]
The Quantum Heisenberg Ferromagnet
 The Quantum Heisenberg Ferromagnet Soon after Schrödinger discovered the wave equation of quantum mechanics, Heisenberg and Dirac developed the first successful quantum theory of ferromagnetism W. Heisenberg,
The Quantum Heisenberg Ferromagnet Soon after Schrödinger discovered the wave equation of quantum mechanics, Heisenberg and Dirac developed the first successful quantum theory of ferromagnetism W. Heisenberg,
acta physica slovaca vol. 56 No. 4, August 2006 P-FUNCTION OF THE PSEUDOHARMONIC OSCILLATOR IN TERMS OF KLAUDER-PERELOMOV COHERENT STATES
 acta physica slovaca vol. 56 No. 4, 445 453 August 26 P-FUNCTION OF THE PSEUDOHARMONIC OSCILLATOR IN TERMS OF KLAUDER-PERELOMOV COHERENT STATES D. Popov,a, D.M. Davidović b, D. Arsenović c, V. Sajfert
acta physica slovaca vol. 56 No. 4, 445 453 August 26 P-FUNCTION OF THE PSEUDOHARMONIC OSCILLATOR IN TERMS OF KLAUDER-PERELOMOV COHERENT STATES D. Popov,a, D.M. Davidović b, D. Arsenović c, V. Sajfert
Examination paper for TFY4210 Quantum theory of many-particle systems
 Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4210 Quantum theory of many-particle systems Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date:
Department of Physics Examination paper for TFY4210 Quantum theory of many-particle systems Academic contact during examination: Associate Professor John Ove Fjærestad Phone: 97 94 00 36 Examination date:
file:///c:/docume~1/dusan/locals~1/temp/_tc/isi%20-%2015%20... ISI Web of Knowledge Page 1 (Articles ) [ 1 ]
![file:///c:/docume~1/dusan/locals~1/temp/_tc/isi%20-%2015%20... ISI Web of Knowledge Page 1 (Articles ) [ 1 ] file:///c:/docume~1/dusan/locals~1/temp/_tc/isi%20-%2015%20... ISI Web of Knowledge Page 1 (Articles ) [ 1 ]](/thumbs/72/66847637.jpg) 1 of 12 19.10.2009 22:27 ISI Web of Knowledge Page 1 (Articles 1 -- 31) [ 1 ] Record 1 of 31 (Popov, D.); Pop, N (Pop, N.); Luminosu, I (Luminosu, I.); Chiritoiu, V (Chiritoiu, V.) Title: Density matrix
1 of 12 19.10.2009 22:27 ISI Web of Knowledge Page 1 (Articles 1 -- 31) [ 1 ] Record 1 of 31 (Popov, D.); Pop, N (Pop, N.); Luminosu, I (Luminosu, I.); Chiritoiu, V (Chiritoiu, V.) Title: Density matrix
Collective Effects. Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics
 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics: Lecture 3, 3 March 2006 Collective Effects in Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Physics Website: http://cncs.bnu.edu.cn/mccross/course/ Caltech
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors
 Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
A11046W1 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2015 Wednesday, 17 June, 2.30
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta. EECS Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku
 Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
Magnetic ordering of local moments
 Magnetic ordering Types of magnetic structure Ground state of the Heisenberg ferromagnet and antiferromagnet Spin wave High temperature susceptibility Mean field theory Magnetic ordering of local moments
Magnetic ordering Types of magnetic structure Ground state of the Heisenberg ferromagnet and antiferromagnet Spin wave High temperature susceptibility Mean field theory Magnetic ordering of local moments
Temperature Correlation Functions in the XXO Heisenberg Chain
 CONGRESSO NAZIONALE DI FISICA DELLA MATERIA Brescia, 13-16 June, 1994 Temperature Correlation Functions in the XXO Heisenberg Chain F. Colomo 1, A.G. Izergin 2,3, V.E. Korepin 4, V. Tognetti 1,5 1 I.N.F.N.,
CONGRESSO NAZIONALE DI FISICA DELLA MATERIA Brescia, 13-16 June, 1994 Temperature Correlation Functions in the XXO Heisenberg Chain F. Colomo 1, A.G. Izergin 2,3, V.E. Korepin 4, V. Tognetti 1,5 1 I.N.F.N.,
Green's Function in. Condensed Matter Physics. Wang Huaiyu. Alpha Science International Ltd. SCIENCE PRESS 2 Beijing \S7 Oxford, U.K.
 Green's Function in Condensed Matter Physics Wang Huaiyu SCIENCE PRESS 2 Beijing \S7 Oxford, U.K. Alpha Science International Ltd. CONTENTS Part I Green's Functions in Mathematical Physics Chapter 1 Time-Independent
Green's Function in Condensed Matter Physics Wang Huaiyu SCIENCE PRESS 2 Beijing \S7 Oxford, U.K. Alpha Science International Ltd. CONTENTS Part I Green's Functions in Mathematical Physics Chapter 1 Time-Independent
Quantum Quenches in Extended Systems
 Quantum Quenches in Extended Systems Spyros Sotiriadis 1 Pasquale Calabrese 2 John Cardy 1,3 1 Oxford University, Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, Oxford, UK 2 Dipartimento di Fisica Enrico
Quantum Quenches in Extended Systems Spyros Sotiriadis 1 Pasquale Calabrese 2 John Cardy 1,3 1 Oxford University, Rudolf Peierls Centre for Theoretical Physics, Oxford, UK 2 Dipartimento di Fisica Enrico
Phase Diagram for Magnon Condensate in Yttrium Iron Garnet film
 (Accepted by Nature Scientific Reports: Jan. 9, 013) Phase Diagram for Magnon Condensate in Yttrium Iron Garnet film Phase Diagram. We consider a YIG film of thickness d with in-plane magnetic field H
(Accepted by Nature Scientific Reports: Jan. 9, 013) Phase Diagram for Magnon Condensate in Yttrium Iron Garnet film Phase Diagram. We consider a YIG film of thickness d with in-plane magnetic field H
Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions
 134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
134 Phys620.nb 10 Magnets, 1D quantum system, and quantum Phase transitions In 1D, fermions can be mapped into bosons, and vice versa. 10.1. magnetization and frustrated magnets (in any dimensions) Consider
Problem Set No. 3: Canonical Quantization Due Date: Wednesday October 19, 2018, 5:00 pm. 1 Spin waves in a quantum Heisenberg antiferromagnet
 Physics 58, Fall Semester 018 Professor Eduardo Fradkin Problem Set No. 3: Canonical Quantization Due Date: Wednesday October 19, 018, 5:00 pm 1 Spin waves in a quantum Heisenberg antiferromagnet In this
Physics 58, Fall Semester 018 Professor Eduardo Fradkin Problem Set No. 3: Canonical Quantization Due Date: Wednesday October 19, 018, 5:00 pm 1 Spin waves in a quantum Heisenberg antiferromagnet In this
Green Functions in Many Body Quantum Mechanics
 Green Functions in Many Body Quantum Mechanics NOTE This section contains some advanced material, intended to give a brief introduction to methods used in many body quantum mechanics. The material at the
Green Functions in Many Body Quantum Mechanics NOTE This section contains some advanced material, intended to give a brief introduction to methods used in many body quantum mechanics. The material at the
Numerical Simulations of Faraday Waves in Binary Bose-Einstein Condensates
 Numerical Simulations of Faraday Waves in Binary Bose-Einstein Condensates Antun Balaž 1 and Alexandru Nicolin 2 1 Scientific Computing Laboratory, Institute of Physics Belgrade, University of Belgrade,
Numerical Simulations of Faraday Waves in Binary Bose-Einstein Condensates Antun Balaž 1 and Alexandru Nicolin 2 1 Scientific Computing Laboratory, Institute of Physics Belgrade, University of Belgrade,
The Mermin-Wagner Theorem
 June 24, 2010 Conclusion In one and two dimensions, continuous symmetries cannot be spontaneously broken at finite temperature in systems with sufficiently short-range interactions. Contents 1 How symmetry
June 24, 2010 Conclusion In one and two dimensions, continuous symmetries cannot be spontaneously broken at finite temperature in systems with sufficiently short-range interactions. Contents 1 How symmetry
Notes on Spin Operators and the Heisenberg Model. Physics : Winter, David G. Stroud
 Notes on Spin Operators and the Heisenberg Model Physics 880.06: Winter, 003-4 David G. Stroud In these notes I give a brief discussion of spin-1/ operators and their use in the Heisenberg model. 1. Spin
Notes on Spin Operators and the Heisenberg Model Physics 880.06: Winter, 003-4 David G. Stroud In these notes I give a brief discussion of spin-1/ operators and their use in the Heisenberg model. 1. Spin
Luigi Paolasini
 Luigi Paolasini paolasini@esrf.fr LECTURE 7: Magnetic excitations - Phase transitions and the Landau mean-field theory. - Heisenberg and Ising models. - Magnetic excitations. External parameter, as for
Luigi Paolasini paolasini@esrf.fr LECTURE 7: Magnetic excitations - Phase transitions and the Landau mean-field theory. - Heisenberg and Ising models. - Magnetic excitations. External parameter, as for
.O. Demokritov niversität Münster, Germany
 Quantum Thermodynamics of Magnons.O. Demokritov niversität Münster, Germany Magnon Frequency Population BEC-condensates http://www.uni-muenster.de/physik/ap/demokritov/ k z k y Group of NonLinea Magnetic
Quantum Thermodynamics of Magnons.O. Demokritov niversität Münster, Germany Magnon Frequency Population BEC-condensates http://www.uni-muenster.de/physik/ap/demokritov/ k z k y Group of NonLinea Magnetic
Week 5-6: Lectures The Charged Scalar Field
 Notes for Phys. 610, 2011. These summaries are meant to be informal, and are subject to revision, elaboration and correction. They will be based on material covered in class, but may differ from it by
Notes for Phys. 610, 2011. These summaries are meant to be informal, and are subject to revision, elaboration and correction. They will be based on material covered in class, but may differ from it by
The non-interacting Bose gas
 Chapter The non-interacting Bose gas Learning goals What is a Bose-Einstein condensate and why does it form? What determines the critical temperature and the condensate fraction? What changes for trapped
Chapter The non-interacting Bose gas Learning goals What is a Bose-Einstein condensate and why does it form? What determines the critical temperature and the condensate fraction? What changes for trapped
Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas
 / 6 Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas Giovanni Italo Martone with G. V. Shlyapnikov Worhshop on Exploring Nuclear Physics with Ultracold Atoms
/ 6 Drag force and superfluidity in the supersolid striped phase of a spin-orbit-coupled Bose gas Giovanni Italo Martone with G. V. Shlyapnikov Worhshop on Exploring Nuclear Physics with Ultracold Atoms
WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014)
 WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014) LIST OF PROBLEMS Chapter 1: Magnetism of Free Electrons and Atoms 1. Orbital and spin moments of an electron: Using the theory of angular momentum, calculate the orbital
WORLD SCIENTIFIC (2014) LIST OF PROBLEMS Chapter 1: Magnetism of Free Electrons and Atoms 1. Orbital and spin moments of an electron: Using the theory of angular momentum, calculate the orbital
Andreas Kreisel. Institut für Theoretische Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main. July,
 BEC of magnons and spin wave interactions in QAF Andreas Kreisel Institut für Theoretische Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main July, 18 2007 collaborators: N. Hasselmann, P. Kopietz
BEC of magnons and spin wave interactions in QAF Andreas Kreisel Institut für Theoretische Physik Johann Wolfgang Goethe Universität Frankfurt am Main July, 18 2007 collaborators: N. Hasselmann, P. Kopietz
Attempts at relativistic QM
 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics should incorporate both quantum mechanics and special relativity. However historically combining quantum mechanics and
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Section 10: Many Particle Quantum Mechanics Solutions
 Physics 143a: Quantum Mechanics I Section 10: Many Particle Quantum Mechanics Solutions Spring 015, Harvard Here is a summary of the most important points from this week (with a few of my own tidbits),
Physics 143a: Quantum Mechanics I Section 10: Many Particle Quantum Mechanics Solutions Spring 015, Harvard Here is a summary of the most important points from this week (with a few of my own tidbits),
Relativistic Dirac fermions on one-dimensional lattice
 Niodem Szpa DUE, 211-1-2 Relativistic Dirac fermions on one-dimensional lattice Niodem Szpa Universität Duisburg-Essen & Ralf Schützhold Plan: 2 Jan 211 Discretized relativistic Dirac fermions (in an external
Niodem Szpa DUE, 211-1-2 Relativistic Dirac fermions on one-dimensional lattice Niodem Szpa Universität Duisburg-Essen & Ralf Schützhold Plan: 2 Jan 211 Discretized relativistic Dirac fermions (in an external
CONTRASTING BEHAVIOR OF FREE-STANDING AND EMBEDDED MAGNETIC NANOPARTICLES
 (c) Romanian RRP 65(No. Reports in 3) Physics, 832 840 Vol. 2013 65, No. 3, P. 832 840, 2013 Dedicated to Professor Valentin I. Vlad s 70 th Anniversary CONTRASTING BEHAVIOR OF FREE-STANDING AND EMBEDDED
(c) Romanian RRP 65(No. Reports in 3) Physics, 832 840 Vol. 2013 65, No. 3, P. 832 840, 2013 Dedicated to Professor Valentin I. Vlad s 70 th Anniversary CONTRASTING BEHAVIOR OF FREE-STANDING AND EMBEDDED
Bose Einstein condensation of magnons and spin wave interactions in quantum antiferromagnets
 Bose Einstein condensation of magnons and spin wave interactions in quantum antiferromagnets Talk at Rutherford Appleton Lab, March 13, 2007 Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt collaborators: Nils Hasselmann,
Bose Einstein condensation of magnons and spin wave interactions in quantum antiferromagnets Talk at Rutherford Appleton Lab, March 13, 2007 Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt collaborators: Nils Hasselmann,
Giant Enhancement of Quantum Decoherence by Frustrated Environments
 ISSN 0021-3640, JETP Letters, 2006, Vol. 84, No. 2, pp. 99 103. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 2006.. Giant Enhancement of Quantum Decoherence by Frustrated Environments S. Yuan a, M. I. Katsnelson b, and
ISSN 0021-3640, JETP Letters, 2006, Vol. 84, No. 2, pp. 99 103. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 2006.. Giant Enhancement of Quantum Decoherence by Frustrated Environments S. Yuan a, M. I. Katsnelson b, and
Dynamical Correlation Functions for Linear Spin Systems
 University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Physics Faculty Publications Physics 1978 Dynamical Correlation Functions for Linear Spin Systems Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
University of Rhode Island DigitalCommons@URI Physics Faculty Publications Physics 1978 Dynamical Correlation Functions for Linear Spin Systems Gerhard Müller University of Rhode Island, gmuller@uri.edu
 Math Questions for the 2011 PhD Qualifier Exam 1. Evaluate the following definite integral 3" 4 where! ( x) is the Dirac! - function. # " 4 [ ( )] dx x 2! cos x 2. Consider the differential equation dx
Math Questions for the 2011 PhD Qualifier Exam 1. Evaluate the following definite integral 3" 4 where! ( x) is the Dirac! - function. # " 4 [ ( )] dx x 2! cos x 2. Consider the differential equation dx
Microwave transmission spectra in regular and irregular one-dimensional scattering arrangements
 Physica E 9 (2001) 384 388 www.elsevier.nl/locate/physe Microwave transmission spectra in regular and irregular one-dimensional scattering arrangements Ulrich Kuhl, Hans-Jurgen Stockmann Fachbereich Physik,
Physica E 9 (2001) 384 388 www.elsevier.nl/locate/physe Microwave transmission spectra in regular and irregular one-dimensional scattering arrangements Ulrich Kuhl, Hans-Jurgen Stockmann Fachbereich Physik,
The Mott Metal-Insulator Transition
 Florian Gebhard The Mott Metal-Insulator Transition Models and Methods With 38 Figures Springer 1. Metal Insulator Transitions 1 1.1 Classification of Metals and Insulators 2 1.1.1 Definition of Metal
Florian Gebhard The Mott Metal-Insulator Transition Models and Methods With 38 Figures Springer 1. Metal Insulator Transitions 1 1.1 Classification of Metals and Insulators 2 1.1.1 Definition of Metal
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Landau Theory of Second Order Phase Transitions. Order Parameter
 Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics Landau Theory of Second Order Phase Transitions Order Parameter Second order phase transitions occur when a new state of reduced symmetry develops continuously from
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics Landau Theory of Second Order Phase Transitions Order Parameter Second order phase transitions occur when a new state of reduced symmetry develops continuously from
Application of Mean-Field Jordan Wigner Transformation to Antiferromagnet System
 Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China 50 008 pp. 43 47 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, o. 1, July 15, 008 Application of Mean-Field Jordan Wigner Transformation to Antiferromagnet System LI Jia-Liang,
Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China 50 008 pp. 43 47 c Chinese Physical Society Vol. 50, o. 1, July 15, 008 Application of Mean-Field Jordan Wigner Transformation to Antiferromagnet System LI Jia-Liang,
Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors
 Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors Yuichiro K. Kato Institute of Engineering Innovation, The University of Tokyo Physics of non-interacting spins Optical spin injection and detection Spin manipulation
Electron spins in nonmagnetic semiconductors Yuichiro K. Kato Institute of Engineering Innovation, The University of Tokyo Physics of non-interacting spins Optical spin injection and detection Spin manipulation
Magnetization of Coupled Ultrathin Ferromagnetic Films
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 38 (2002) pp. 107 112 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 38, No. 1, July 15, 2002 Magnetization of Coupled Ultrathin Ferromagnetic Films WANG Huai-Yu, 1 ZHOU
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 38 (2002) pp. 107 112 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 38, No. 1, July 15, 2002 Magnetization of Coupled Ultrathin Ferromagnetic Films WANG Huai-Yu, 1 ZHOU
Frequency in Middle of Magnon Band Gap in a Layered Ferromagnetic Superlattice
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 54 (2010) pp. 1144 1150 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 54, No. 6, December 15, 2010 Frequency in Middle of Magnon Band Gap in a Layered Ferromagnetic
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 54 (2010) pp. 1144 1150 c Chinese Physical Society and IOP Publishing Ltd Vol. 54, No. 6, December 15, 2010 Frequency in Middle of Magnon Band Gap in a Layered Ferromagnetic
Quantum Many Body Theory
 Quantum Many Body Theory Victor Gurarie Week 4 4 Applications of the creation and annihilation operators 4.1 A tight binding model Consider bosonic particles which hops around on the lattice, for simplicity,
Quantum Many Body Theory Victor Gurarie Week 4 4 Applications of the creation and annihilation operators 4.1 A tight binding model Consider bosonic particles which hops around on the lattice, for simplicity,
2.1 Green Functions in Quantum Mechanics
 Chapter 2 Green Functions and Observables 2.1 Green Functions in Quantum Mechanics We will be interested in studying the properties of the ground state of a quantum mechanical many particle system. We
Chapter 2 Green Functions and Observables 2.1 Green Functions in Quantum Mechanics We will be interested in studying the properties of the ground state of a quantum mechanical many particle system. We
Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases
 Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Low-D Quantum Condensed Matter University of Amsterdam, 8.7.2013 Based
Topological phases of SU(N) spin chains and their realization in ultra-cold atom gases Thomas Quella University of Cologne Workshop on Low-D Quantum Condensed Matter University of Amsterdam, 8.7.2013 Based
Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality. Hans-Henning Klauss. Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden
 Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality Hans-Henning Klauss Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden 1 References [1] Stephen Blundell, Magnetism in Condensed
Phase Transitions in Condensed Matter Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and Universality Hans-Henning Klauss Institut für Festkörperphysik TU Dresden 1 References [1] Stephen Blundell, Magnetism in Condensed
The Condensate Equation for non-homogeneous Bosons. André F. Verbeure 1. Institute for Theoretical Fysics, K.U.Leuven (Belgium)
 The Condensate Equation for non-homogeneous Bosons André F. erbeure 1 Institute for Theoretical Fysics, K.U.Leuven (Belgium) Abstract: We consider Boson systems with non-ground state (q 0)-condensation.
The Condensate Equation for non-homogeneous Bosons André F. erbeure 1 Institute for Theoretical Fysics, K.U.Leuven (Belgium) Abstract: We consider Boson systems with non-ground state (q 0)-condensation.
Green s functions: calculation methods
 M. A. Gusmão IF-UFRGS 1 FIP161 Text 13 Green s functions: calculation methods Equations of motion One of the usual methods for evaluating Green s functions starts by writing an equation of motion for the
M. A. Gusmão IF-UFRGS 1 FIP161 Text 13 Green s functions: calculation methods Equations of motion One of the usual methods for evaluating Green s functions starts by writing an equation of motion for the
Discrete scale invariance and its logarithmic extension
 Nuclear Physics B 655 [FS] (2003 342 352 www.elsevier.com/locate/npe Discrete scale invariance and its logarithmic extension N. Abed-Pour a A. Aghamohammadi bd M.Khorrami cd M. Reza Rahimi Tabar def a
Nuclear Physics B 655 [FS] (2003 342 352 www.elsevier.com/locate/npe Discrete scale invariance and its logarithmic extension N. Abed-Pour a A. Aghamohammadi bd M.Khorrami cd M. Reza Rahimi Tabar def a
221B Lecture Notes Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking
 B Lecture Notes Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking is an ubiquitous concept in modern physics, especially in condensed matter and particle physics.
B Lecture Notes Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking is an ubiquitous concept in modern physics, especially in condensed matter and particle physics.
Decimation Technique on Sierpinski Gasket in External Magnetic Field
 Egypt.. Solids, Vol. (), No. (), (009 ) 5 Decimation Technique on Sierpinski Gasket in External Magnetic Field Khalid Bannora, G. Ismail and M. Abu Zeid ) Mathematics Department, Faculty of Science, Zagazig
Egypt.. Solids, Vol. (), No. (), (009 ) 5 Decimation Technique on Sierpinski Gasket in External Magnetic Field Khalid Bannora, G. Ismail and M. Abu Zeid ) Mathematics Department, Faculty of Science, Zagazig
Magnetism in Condensed Matter
 Magnetism in Condensed Matter STEPHEN BLUNDELL Department of Physics University of Oxford OXFORD 'UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Magnetic moments 1 1 1.1.1 Magnetic moments and angular momentum
Magnetism in Condensed Matter STEPHEN BLUNDELL Department of Physics University of Oxford OXFORD 'UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction 1.1 Magnetic moments 1 1 1.1.1 Magnetic moments and angular momentum
Validity of spin wave theory for the quantum Heisenberg model
 Validity of spin wave theory for the quantum Heisenberg model Michele Correggi, Alessandro Giuliani, and Robert Seiringer Dipartimento di Matematica e Fisica, Università di Roma Tre, L.go S. L. Murialdo,
Validity of spin wave theory for the quantum Heisenberg model Michele Correggi, Alessandro Giuliani, and Robert Seiringer Dipartimento di Matematica e Fisica, Università di Roma Tre, L.go S. L. Murialdo,
Identical Particles. Bosons and Fermions
 Identical Particles Bosons and Fermions In Quantum Mechanics there is no difference between particles and fields. The objects which we refer to as fields in classical physics (electromagnetic field, field
Identical Particles Bosons and Fermions In Quantum Mechanics there is no difference between particles and fields. The objects which we refer to as fields in classical physics (electromagnetic field, field
Nonlinear BEC Dynamics by Harmonic Modulation of s-wave Scattering Length
 Nonlinear BEC Dynamics by Harmonic Modulation of s-wave Scattering Length I. Vidanović, A. Balaž, H. Al-Jibbouri 2, A. Pelster 3 Scientific Computing Laboratory, Institute of Physics Belgrade, Serbia 2
Nonlinear BEC Dynamics by Harmonic Modulation of s-wave Scattering Length I. Vidanović, A. Balaž, H. Al-Jibbouri 2, A. Pelster 3 Scientific Computing Laboratory, Institute of Physics Belgrade, Serbia 2
Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators
 Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
Lecture 6 Berry s phase in Hall Effects and Topological Insulators Given the analogs between Berry s phase and vector potentials, it is not surprising that Berry s phase can be important in the Hall effect.
A Realization of Yangian and Its Applications to the Bi-spin System in an External Magnetic Field
 Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China) 39 003) pp. 1 5 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 39, No. 1, January 15, 003 A Realization of Yangian and Its Applications to the Bi-spin System in an External
Commun. Theor. Phys. Beijing, China) 39 003) pp. 1 5 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 39, No. 1, January 15, 003 A Realization of Yangian and Its Applications to the Bi-spin System in an External
Lecture 20: Effective field theory for the Bose- Hubbard model
 Lecture 20: Effective field theory for the Bose- Hubbard model In the previous lecture, we have sketched the expected phase diagram of the Bose-Hubbard model, and introduced a mean-field treatment that
Lecture 20: Effective field theory for the Bose- Hubbard model In the previous lecture, we have sketched the expected phase diagram of the Bose-Hubbard model, and introduced a mean-field treatment that
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 25 Aug 2000
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 25 Aug 2000 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 25 Aug 2000](/thumbs/84/91032342.jpg) LA-UR-00-XXXX February, 008 submitted to Physical Review Letters June st Generalized Jordan-Wigner Transformations C.D. Batista and G. Ortiz Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos,
LA-UR-00-XXXX February, 008 submitted to Physical Review Letters June st Generalized Jordan-Wigner Transformations C.D. Batista and G. Ortiz Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos,
1 The Heisenberg model
 1 The Heisenberg model 1.1 Definition of the model The model we will focus on is called the Heisenberg model. It has the following Hamiltonian: H = 1 J ij S i S j. (1) 2 i,j i j Here i and j refer to sites
1 The Heisenberg model 1.1 Definition of the model The model we will focus on is called the Heisenberg model. It has the following Hamiltonian: H = 1 J ij S i S j. (1) 2 i,j i j Here i and j refer to sites
THE ABSORPTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN A QUANTUM WIRE
 NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 04, 5 3, P. 378 383 THE ABSORPTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN A QUANTUM WIRE PACS 63.0.Kr,78.67.-n V. V. Karpunin,, V. A. Margulis Mordovian State Pedagogical
NANOSYSTEMS: PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY, MATHEMATICS, 04, 5 3, P. 378 383 THE ABSORPTION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN A QUANTUM WIRE PACS 63.0.Kr,78.67.-n V. V. Karpunin,, V. A. Margulis Mordovian State Pedagogical
Thickness Dependence of Magnetic Hysteresis of Ising Films in Nano-thickness Range
 CMU. J.Nat.Sci. Special Issue on Nanotechnology (2008) Vol. 7(1) 203 Thickness Dependence of Magnetic Hysteresis of Ising Films in Nano-thickness Range Atchara Punya 1*, Pitak Laoratanakul 2, Rattikorn
CMU. J.Nat.Sci. Special Issue on Nanotechnology (2008) Vol. 7(1) 203 Thickness Dependence of Magnetic Hysteresis of Ising Films in Nano-thickness Range Atchara Punya 1*, Pitak Laoratanakul 2, Rattikorn
Physics 607 Exam 2. ( ) = 1, Γ( z +1) = zγ( z) x n e x2 dx = 1. e x2
 Physics 607 Exam Please be well-organized, and show all significant steps clearly in all problems. You are graded on your work, so please do not just write down answers with no explanation! Do all your
Physics 607 Exam Please be well-organized, and show all significant steps clearly in all problems. You are graded on your work, so please do not just write down answers with no explanation! Do all your
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9
 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
Quantum Condensed Matter Physics Lecture 9 David Ritchie QCMP Lent/Easter 2018 http://www.sp.phy.cam.ac.uk/drp2/home 9.1 Quantum Condensed Matter Physics 1. Classical and Semi-classical models for electrons
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
Quantum Field Theory
 Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
Quantum Field Theory PHYS-P 621 Radovan Dermisek, Indiana University Notes based on: M. Srednicki, Quantum Field Theory 1 Attempts at relativistic QM based on S-1 A proper description of particle physics
On the Heisenberg and Schrödinger Pictures
 Journal of Modern Physics, 04, 5, 7-76 Published Online March 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/ournal/mp http://dx.doi.org/0.436/mp.04.5507 On the Heisenberg and Schrödinger Pictures Shigei Fuita, James
Journal of Modern Physics, 04, 5, 7-76 Published Online March 04 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/ournal/mp http://dx.doi.org/0.436/mp.04.5507 On the Heisenberg and Schrödinger Pictures Shigei Fuita, James
Quantum mechanics of many-fermion systems
 Quantum mechanics of many-fermion systems Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Identical particles: Fermions and Bosons 2. Simple examples: systems with two identical particles 3. Pauli principle
Quantum mechanics of many-fermion systems Kouichi Hagino Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan 1. Identical particles: Fermions and Bosons 2. Simple examples: systems with two identical particles 3. Pauli principle
Introduction to Recent Developments on p-band Physics in Optical Lattices
 Introduction to Recent Developments on p-band Physics in Optical Lattices Gaoyong Sun Institut für Theoretische Physik, Leibniz Universität Hannover Supervisors: Prof. Luis Santos Prof. Temo Vekua Lüneburg,
Introduction to Recent Developments on p-band Physics in Optical Lattices Gaoyong Sun Institut für Theoretische Physik, Leibniz Universität Hannover Supervisors: Prof. Luis Santos Prof. Temo Vekua Lüneburg,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 13 Apr 2006
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 13 Apr 2006 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 13 Apr 2006](/thumbs/73/69280856.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/060439v1 cond-mat.other] 13 Apr 006 Spin-wave instability for parallel pumping in ferromagnetic thin films under oblique field Kazue Kudo, Katsuhiro Nakamura Department of Applied Physics,
arxiv:cond-mat/060439v1 cond-mat.other] 13 Apr 006 Spin-wave instability for parallel pumping in ferromagnetic thin films under oblique field Kazue Kudo, Katsuhiro Nakamura Department of Applied Physics,
1 Fluctuations of the number of particles in a Bose-Einstein condensate
 Exam of Quantum Fluids M1 ICFP 217-218 Alice Sinatra and Alexander Evrard The exam consists of two independant exercises. The duration is 3 hours. 1 Fluctuations of the number of particles in a Bose-Einstein
Exam of Quantum Fluids M1 ICFP 217-218 Alice Sinatra and Alexander Evrard The exam consists of two independant exercises. The duration is 3 hours. 1 Fluctuations of the number of particles in a Bose-Einstein
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Sep 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Sep 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Sep 2005](/thumbs/93/111325734.jpg) 1 arxiv:cond-mat/0509103v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Sep 2005 Normal and Anomalous Averages for Systems with Bose-Einstein Condensate V.I. Yukalov 1,2 and E.P. Yukalova 1,3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik,
1 arxiv:cond-mat/0509103v1 [cond-mat.stat-mech] 5 Sep 2005 Normal and Anomalous Averages for Systems with Bose-Einstein Condensate V.I. Yukalov 1,2 and E.P. Yukalova 1,3 1 Institut für Theoretische Physik,
Infinitely long-range nonlocal potentials and the Bose-Einstein supersolid phase
 Armenian Journal of Physics, 8, vol., issue 3, pp.7-4 Infinitely long-range nonlocal potentials and the Bose-Einstein supersolid phase Moorad Alexanian Department of Physics and Physical Oceanography University
Armenian Journal of Physics, 8, vol., issue 3, pp.7-4 Infinitely long-range nonlocal potentials and the Bose-Einstein supersolid phase Moorad Alexanian Department of Physics and Physical Oceanography University
Talk online at
 Talk online at http://sachdev.physics.harvard.edu Outline 1. CFT3s in condensed matter physics Superfluid-insulator and Neel-valence bond solid transitions 2. Quantum-critical transport Collisionless-t0-hydrodynamic
Talk online at http://sachdev.physics.harvard.edu Outline 1. CFT3s in condensed matter physics Superfluid-insulator and Neel-valence bond solid transitions 2. Quantum-critical transport Collisionless-t0-hydrodynamic
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models
 Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
Two Dimensional Chern Insulators, the Qi-Wu-Zhang and Haldane Models Matthew Brooks, Introduction to Topological Insulators Seminar, Universität Konstanz Contents QWZ Model of Chern Insulators Haldane
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Physics Letters A.
 Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
Physics Letters A 374 (2010) 1063 1067 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Physics Letters A www.elsevier.com/locate/pla Macroscopic far-field observation of the sub-wavelength near-field dipole
Quantum Physics 2: Homework #6
 Quantum Physics : Homework #6 [Total 10 points] Due: 014.1.1(Mon) 1:30pm Exercises: 014.11.5(Tue)/11.6(Wed) 6:30 pm; 56-105 Questions for problems: 민홍기 hmin@snu.ac.kr Questions for grading: 모도영 modori518@snu.ac.kr
Quantum Physics : Homework #6 [Total 10 points] Due: 014.1.1(Mon) 1:30pm Exercises: 014.11.5(Tue)/11.6(Wed) 6:30 pm; 56-105 Questions for problems: 민홍기 hmin@snu.ac.kr Questions for grading: 모도영 modori518@snu.ac.kr
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 3: Quantum Mechanics
 Introduction to particle physics Lecture 3: Quantum Mechanics Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 Outline 1 Planck s hypothesis 2 Substantiating Planck s claim 3 More quantisation: Bohr
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 3: Quantum Mechanics Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 Outline 1 Planck s hypothesis 2 Substantiating Planck s claim 3 More quantisation: Bohr
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in 2D Fermi Gases
 Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Supporting Information: Topological Magnon Modes. in Patterned Ferrimagnetic Insulator Thin Films
 Supporting Information: Topological Magnon Modes in Patterned Ferrimagnetic Insulator Thin Films Yun-Mei Li,, Jiang Xiao,, and Kai Chang,,, SKLSM, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Supporting Information: Topological Magnon Modes in Patterned Ferrimagnetic Insulator Thin Films Yun-Mei Li,, Jiang Xiao,, and Kai Chang,,, SKLSM, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences,
Quantization of the Spins
 Chapter 5 Quantization of the Spins As pointed out already in chapter 3, the external degrees of freedom, position and momentum, of an ensemble of identical atoms is described by the Scödinger field operator.
Chapter 5 Quantization of the Spins As pointed out already in chapter 3, the external degrees of freedom, position and momentum, of an ensemble of identical atoms is described by the Scödinger field operator.
Statistical physics and light-front quantization. JR and S.J. Brodsky, Phys. Rev. D70, (2004) and hep-th/
 Statistical physics and light-front quantization Jörg Raufeisen (Heidelberg U.) JR and S.J. Brodsky, Phys. Rev. D70, 085017 (2004) and hep-th/0409157 Introduction: Dirac s Forms of Hamiltonian Dynamics
Statistical physics and light-front quantization Jörg Raufeisen (Heidelberg U.) JR and S.J. Brodsky, Phys. Rev. D70, 085017 (2004) and hep-th/0409157 Introduction: Dirac s Forms of Hamiltonian Dynamics
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997](/thumbs/89/98058524.jpg) Light scattering from a periodically modulated two dimensional arxiv:cond-mat/9703119v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997 electron gas with partially filled Landau levels Arne Brataas 1 and C. Zhang 2 and
Light scattering from a periodically modulated two dimensional arxiv:cond-mat/9703119v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 12 Mar 1997 electron gas with partially filled Landau levels Arne Brataas 1 and C. Zhang 2 and
Landau s Fermi Liquid Theory
 Thors Hans Hansson Stockholm University Outline 1 Fermi Liquids Why, What, and How? Why Fermi liquids? What is a Fermi liquids? Fermi Liquids How? 2 Landau s Phenomenological Approach The free Fermi gas
Thors Hans Hansson Stockholm University Outline 1 Fermi Liquids Why, What, and How? Why Fermi liquids? What is a Fermi liquids? Fermi Liquids How? 2 Landau s Phenomenological Approach The free Fermi gas
Bose-Einstein Condensation and Intermediate State of the. Photon Gas. Abstract
 Bose-Einstein Condensation and Intermediate State of the Photon Gas Levan N. Tsintsadze Venture Business Laboratory, Hiroshima University, Higashi-Hiroshima, Japan (July 19, 2002) Abstract Possibility
Bose-Einstein Condensation and Intermediate State of the Photon Gas Levan N. Tsintsadze Venture Business Laboratory, Hiroshima University, Higashi-Hiroshima, Japan (July 19, 2002) Abstract Possibility
Physical Chemistry II Exam 2 Solutions
 Chemistry 362 Spring 2017 Dr Jean M Standard March 10, 2017 Name KEY Physical Chemistry II Exam 2 Solutions 1) (14 points) Use the potential energy and momentum operators for the harmonic oscillator to
Chemistry 362 Spring 2017 Dr Jean M Standard March 10, 2017 Name KEY Physical Chemistry II Exam 2 Solutions 1) (14 points) Use the potential energy and momentum operators for the harmonic oscillator to
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS
 PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 76 4 MARCH 1996 NUMBER 10 Finite-Size Scaling and Universality above the Upper Critical Dimensionality Erik Luijten* and Henk W. J. Blöte Faculty of Applied Physics, Delft
PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS VOLUME 76 4 MARCH 1996 NUMBER 10 Finite-Size Scaling and Universality above the Upper Critical Dimensionality Erik Luijten* and Henk W. J. Blöte Faculty of Applied Physics, Delft
Theory Seminar Uni Marburg. Bose-Einstein Condensation and correlations in magnon systems
 Theory Seminar Uni Marburg 11 November, 2010 Bose-Einstein Condensation and correlations in magnon systems Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt 1.) Bose-Einstein condensation 2.) Interacting magnons in
Theory Seminar Uni Marburg 11 November, 2010 Bose-Einstein Condensation and correlations in magnon systems Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt 1.) Bose-Einstein condensation 2.) Interacting magnons in
Non-equilibrium time evolution of bosons from the functional renormalization group
 March 14, 2013, Condensed Matter Journal Club University of Florida at Gainesville Non-equilibrium time evolution of bosons from the functional renormalization group Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt
March 14, 2013, Condensed Matter Journal Club University of Florida at Gainesville Non-equilibrium time evolution of bosons from the functional renormalization group Peter Kopietz, Universität Frankfurt
Intermediate valence in Yb Intermetallic compounds
 Intermediate valence in Yb Intermetallic compounds Jon Lawrence University of California, Irvine This talk concerns rare earth intermediate valence (IV) metals, with a primary focus on certain Yb-based
Intermediate valence in Yb Intermetallic compounds Jon Lawrence University of California, Irvine This talk concerns rare earth intermediate valence (IV) metals, with a primary focus on certain Yb-based
Lecture 11: Long-wavelength expansion in the Neel state Energetic terms
 Lecture 11: Long-wavelength expansion in the Neel state Energetic terms In the last class we derived the low energy effective Hamiltonian for a Mott insulator. This derivation is an example of the kind
Lecture 11: Long-wavelength expansion in the Neel state Energetic terms In the last class we derived the low energy effective Hamiltonian for a Mott insulator. This derivation is an example of the kind
Controlling Spin Exchange Interactions of Ultracold Atoms in Optical Lattices
 Controlling Spin Exchange Interactions of Ultracold Atoms in Optical Lattices The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Controlling Spin Exchange Interactions of Ultracold Atoms in Optical Lattices The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Chapter 14. Ideal Bose gas Equation of state
 Chapter 14 Ideal Bose gas In this chapter, we shall study the thermodynamic properties of a gas of non-interacting bosons. We will show that the symmetrization of the wavefunction due to the indistinguishability
Chapter 14 Ideal Bose gas In this chapter, we shall study the thermodynamic properties of a gas of non-interacting bosons. We will show that the symmetrization of the wavefunction due to the indistinguishability
The Mandelstam Leibbrandt prescription and the Discretized Light Front Quantization.
 The Mandelstam Leibbrandt prescription and the Discretized Light Front Quantization. Roberto Soldati Dipartimento di Fisica A. Righi, Università di Bologna via Irnerio 46, 40126 Bologna, Italy Abstract
The Mandelstam Leibbrandt prescription and the Discretized Light Front Quantization. Roberto Soldati Dipartimento di Fisica A. Righi, Università di Bologna via Irnerio 46, 40126 Bologna, Italy Abstract
Dissipation of a two-mode squeezed vacuum state in the single-mode amplitude damping channel
 Dissipation of a two-mode squeezed vacuum state in the single-mode amplitude damping channel Zhou Nan-Run( ) a), Hu Li-Yun( ) b), and Fan Hong-Yi( ) c) a) Department of Electronic Information Engineering,
Dissipation of a two-mode squeezed vacuum state in the single-mode amplitude damping channel Zhou Nan-Run( ) a), Hu Li-Yun( ) b), and Fan Hong-Yi( ) c) a) Department of Electronic Information Engineering,
Supplementary Figure 3: Interaction effects in the proposed state preparation with Bloch oscillations. The numerical results are obtained by
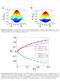 Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
