Pekar s Ansatz and the Ground-State Symmetry of a Bound Polaron
|
|
|
- Rudolf Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pekar s Ansatz and the Ground-State Symmetry of a Bound Polaron Rohan Ghanta Georgia Institute of Technology March 9, 018
2 The Polaron Model In 1937 H. Fröhlich proposed a model known today as the Fröhlich polaron of an electron interacting with the quantized optical modes (phonons) of an ionic crystal (Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 160 (1937)). We consider a Fröhlich polaron bound in an external electric potential (impurity in a crystal). The Hilbert space associated with the system is H = L (R 3 ) F, where F := n 0 n s L (R 3 ) is a symmetric (phonon) Fock space over L (R 3 ).
3 Fröhlich Hamiltonian It is described by the Hamiltonian H V a = p a V (ax)+ a R 3 k a kdk p a (p) 3/ R3 h a k e ik x + a k e ik xi dk k p = i x is the electron momentum V L 3/ (R 3 )+L (R 3 ) is nonnegative and vanishes at infinity a k and a k are creation and annihlation operators on F satisfying [a k,a k 0 ]=d(k k 0 ) a > 0 is the electron-phonon coupling parameter
4 The Ground State The Fröhlich Hamiltonian is H V a = p a V (ax)+ a R 3 k a kdk p a (p) 3/ R3 h a k e ik x + a k e ik xi dk k The ground-state energy is E F a (V )= inf k k H =1, H V a A normalized function in H that achieves the ground-state energy is called a ground-state wave function.
5 Existence and Uniqueness of a Ground State The Fröhlich Hamiltonian is H V a = p a V (ax)+ a R 3 k a kdk p a (p) 3/ R3 h a k e ik x + a k e ik xi dk k Fix a > 0. Suppose the external potential satisfies the following two conditions: 1 p a V (ax) has a negative energy bound state in L (R 3 ),and a V (ax) is relatively form-bounded with respect to p with form bound strictly less than one. Then there exists a unique ground-state wave function V a H.
6 Pekar s Produkt-Ansatz The Fröhlich Hamiltonian is H V a = p a V (ax)+ a R 3 k a kdk E F a (V )= inf k k H =1 p a (p) 3/, H V a R3 h a k e ik x + a k e ik xi dk k The electron-phonon interaction term in the Hamiltonian makes it di to calculate the ground-state energy of the polaron. S.I. Pekar s Ansatz (Issledovaniya po Elektronnoi Teorii Kirstallov. Gostekhizdat, Moskow, 1951) When a is large, the ground-state wave function is a product of a normalized electronic wave function in L (R 3 ) and a normalized coherent state in Fock space: (x, ):=f(x) ( ). cult
7 Pekar s Produkt-Ansatz S.I. Pekar s Ansatz (Issledovaniya po Elektronnoi Teorii Kirstallov. Gostekhizdat, Moskow, 1951) When a is large, the ground-state wave function is a product of a normalized electronic wave function in L (R 3 ) and a normalized coherent state in Fock space: (x, ):=f(x) ( ). = exp k! z(k) + z(k)a k 0i 0i is the vacuum in F, z(k) L (R 3 ). a k =z(k) and h, i F = 1.
8 Pekar s Produkt-Ansatz Note: = exp k Writing rˆ f (k)= 1 z(k) (p) 3/ R + z(k)a k 0i and a k =z(k). R eik x 3 f dx, wecalculatewithpekar sansatz: D E f, Ha V f = R R 3 f dx a R R 3 f V (ax)dx " + dk z(k) p ap rˆ f (k) z(k) R 3 k p ap rˆ # f (k) z(k) k = R R 3 f dx a R R 3 f V (ax)dx 0 z(k) p ap rˆ f (k) k R 3 4pa 1 rˆ f (k) Adk k
9 Pekar s Produkt-Ansatz Note: = exp k Writing rˆ f (k)= 1 z(k) (p) 3/ R + z(k)a k 0i and a k =z(k). R eik x 3 f dx, wecalculatewithpekar sansatz: D E f, Ha V f = R R 3 f dx a R R 3 f V (ax)dx " + dk z(k) p ap rˆ f (k) z(k) R 3 k p ap rˆ # f (k) z(k) k = R R 3 f dx a R R 3 f V (ax)dx 0 z(k) p ap rˆ f (k) k R 3 4pa 1 rˆ f (k) Adk k
10 Pekar s Produkt-Ansatz It follows that E F a (V ) apple inf kfk =k k F =1 D f = a e P (V ),, H V a f E where e P (V ) given by the Pekar minimization problem: inf kfk =1 8 < : e P (V ):= R 3 f f V (x) dx R 3 R 3 9 f(x) f(y) = dx dy x y ;. P.L. Lions showed that the Pekar minimization problem admits a minimizer (Ann. Inst. H. Poin. Non-Linear. 1, 1984).
11 Pekar s Ground State Pekar s Product State Let j V (x) be a minimizer for the Pekar energy e P (V ). Fora large, the ground-state wave function is a 3 jv (ax) V a, where and V a = exp k za V (k)= p ap k (p) 3/ za V (k)! + za V (k)a k 0i R 3 e ik x a 3 jv (ax) dx.
12 Exact Ground-State Energy in the Strong-Coupling Limit Recall that Ea F (V ) apple a e P (V ),where 8 < e P (V )= inf kfk =1: R 3 f f V (x) dx 9 f(x) f(y) = dx dy x y ;. R 3 R 3 However, it was shown by M.D. Donsker and S.R.S. Varadhan that Pekar s upper bound is in fact exact in the strong-coupling limit (Comm. Pure. Appl. Math. 36, 1983): Ground-State Energy Ea F (V ) lim a! a = e P (V ). A simple proof was later given by E.H. Lieb and L.E. Thomas (Comm. Math. Phys. 183, 1995).
13 What about the Ground-State Wave Function? Pekar s Product State Let j V (x) be a minimizer for the Pekar energy e P (V ). Fora large, the ground-state wave function is a 3 jv (ax) V a, where and V a = exp k za V (k)= p ap k (p) 3/ za V (k)! + za V (k)a k 0i R 3 e ik x a 3 jv (ax) dx.
14 If Pekar Minimizer is Unique... Adapting an argument of E.H. Lieb and B. Simon in Thomas-Fermi theory (Adv. Math. 3(1), 1977), we know: Convergence of Electron Density Suppose the Pekar minimization problem for the energy e P (V ) admits a unique minimizer j V.ThenforallW L 3/ (R 3 )+L (R 3 ), But... lim 1 a! a 3 R 3 k V x a k F W (x)dx = j V (x) W (x)dx. a R 3 What if the minimizers for the Pekar energy e P (V ) are not unique?
15 A Discrepancy in Spherical Symmetry Mexican Hat-type Potential Let R >. Consider the potential V R C c (R 3 ),where0applev R apple 1and 8 < 0 when x apple 1 V R (x)= 1 when apple x apple R. : 0 when x R + 1 For all a > 0andR >, the ground-state is unique and its electron density k (x) is therefore a radial function! V R a k F Nonradiality of Pekar Minimizers For R large, the Pekar problem for the energy e P (V R ) admits only nonradial minimizers. V R a
16 A Discrepancy in Spherical Symmetry Nonradiality of Pekar Minimizers (RG) For R large, the Pekar problem for the energy e P (V R ) admits only nonradial minimizers. If j VR (x) is a minimizer, then j VR (Rx) is also a minimizer for all R SO(3). The radial ground-state electron density k converge weakly to a nonradial minmimizer j VR (x). V R a k F (x) cannot
17 Assuming the Minimizers are Unique up to Rotation... Convergence to Rotational Average Let R be large enough so that the minimization problem for e P (V R ) admits only nonradial minimizers, and assume that the nonradial minimizer j VR (x) is unique up to rotation. Let g be the Haar measure on SO(3). Then,forallW L 3/ (R 3 )+L (R 3 ) 1 V lim a! a 3 k R x apple R 3 a k F W (x)dx = a R 3 SO(3) j VR (Rx) dg(r) W (x)dx
N polaron systems and mathematics
 N polaron systems and mathematics (with R. Frank, E. Lieb, and R. Seiringer) Outline A very brief history of the polaron Lower bounds on the ground state energy for polarons Recent results on the binding
N polaron systems and mathematics (with R. Frank, E. Lieb, and R. Seiringer) Outline A very brief history of the polaron Lower bounds on the ground state energy for polarons Recent results on the binding
arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 28 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 28 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [math.ap] 28 Mar 2014](/thumbs/85/91332009.jpg) GROUNDSTATES OF NONLINEAR CHOQUARD EQUATIONS: HARDY-LITTLEWOOD-SOBOLEV CRITICAL EXPONENT VITALY MOROZ AND JEAN VAN SCHAFTINGEN arxiv:1403.7414v1 [math.ap] 28 Mar 2014 Abstract. We consider nonlinear Choquard
GROUNDSTATES OF NONLINEAR CHOQUARD EQUATIONS: HARDY-LITTLEWOOD-SOBOLEV CRITICAL EXPONENT VITALY MOROZ AND JEAN VAN SCHAFTINGEN arxiv:1403.7414v1 [math.ap] 28 Mar 2014 Abstract. We consider nonlinear Choquard
Non-radial solutions to a bi-harmonic equation with negative exponent
 Non-radial solutions to a bi-harmonic equation with negative exponent Ali Hyder Department of Mathematics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver BC V6TZ2, Canada ali.hyder@math.ubc.ca Juncheng Wei
Non-radial solutions to a bi-harmonic equation with negative exponent Ali Hyder Department of Mathematics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver BC V6TZ2, Canada ali.hyder@math.ubc.ca Juncheng Wei
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Inverse Problems in Engineering: Theory and Practice, Cambridge, UK, 11-15th July 2005
 Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Inverse Problems in Engineering: Theory and Practice, Cambridge, UK, 11-15th July 2005 SOME INVERSE SCATTERING PROBLEMS FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL SCHRÖDINGER
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Inverse Problems in Engineering: Theory and Practice, Cambridge, UK, 11-15th July 2005 SOME INVERSE SCATTERING PROBLEMS FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL SCHRÖDINGER
NONEXISTENCE OF MINIMIZER FOR THOMAS-FERMI-DIRAC-VON WEIZSÄCKER MODEL. x y
 NONEXISTENCE OF MINIMIZER FOR THOMAS-FERMI-DIRAC-VON WEIZSÄCKER MODEL JIANFENG LU AND FELIX OTTO In this paper, we study the following energy functional () E(ϕ) := ϕ 2 + F(ϕ 2 ) dx + D(ϕ 2,ϕ 2 ), R 3 where
NONEXISTENCE OF MINIMIZER FOR THOMAS-FERMI-DIRAC-VON WEIZSÄCKER MODEL JIANFENG LU AND FELIX OTTO In this paper, we study the following energy functional () E(ϕ) := ϕ 2 + F(ϕ 2 ) dx + D(ϕ 2,ϕ 2 ), R 3 where
On semilinear elliptic equations with nonlocal nonlinearity
 On semilinear elliptic equations with nonlocal nonlinearity Shinji Kawano Department of Mathematics Hokkaido University Sapporo 060-0810, Japan Abstract We consider the problem 8 < A A + A p ka A 2 dx
On semilinear elliptic equations with nonlocal nonlinearity Shinji Kawano Department of Mathematics Hokkaido University Sapporo 060-0810, Japan Abstract We consider the problem 8 < A A + A p ka A 2 dx
A Brief Introduction to Thomas-Fermi Model in Partial Differential Equations
 A Brief Introduction to Thomas-Fermi Model in Partial Differential Equations Aditya Kumar Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University, Montreal, QC December 16, 2012 1 Introduction Created
A Brief Introduction to Thomas-Fermi Model in Partial Differential Equations Aditya Kumar Department of Mathematics and Statistics McGill University, Montreal, QC December 16, 2012 1 Introduction Created
EIGENFUNCTIONS OF DIRAC OPERATORS AT THE THRESHOLD ENERGIES
 EIGENFUNCTIONS OF DIRAC OPERATORS AT THE THRESHOLD ENERGIES TOMIO UMEDA Abstract. We show that the eigenspaces of the Dirac operator H = α (D A(x)) + mβ at the threshold energies ±m are coincide with the
EIGENFUNCTIONS OF DIRAC OPERATORS AT THE THRESHOLD ENERGIES TOMIO UMEDA Abstract. We show that the eigenspaces of the Dirac operator H = α (D A(x)) + mβ at the threshold energies ±m are coincide with the
On the infimum of the excitation spectrum of a homogeneous Bose gas. H.D. Cornean, J. Dereziński,
 On the infimum of the excitation spectrum of a homogeneous Bose gas H.D. Cornean, J. Dereziński, P. Ziń. 1 Homogeneous Bose gas n bosons on R d interacting with a 2-body potential v are ( described by
On the infimum of the excitation spectrum of a homogeneous Bose gas H.D. Cornean, J. Dereziński, P. Ziń. 1 Homogeneous Bose gas n bosons on R d interacting with a 2-body potential v are ( described by
Kramers degeneracy theorem in nonrelativistic QED
 Kramers degeneracy theorem in nonrelativistic QED arxiv:0809.447v [math-ph] 25 Sep 2008 Michael Loss, Tadahiro Miyao and Herbert Spohn Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Mathematics, Atlanta, Georgia
Kramers degeneracy theorem in nonrelativistic QED arxiv:0809.447v [math-ph] 25 Sep 2008 Michael Loss, Tadahiro Miyao and Herbert Spohn Georgia Institute of Technology, School of Mathematics, Atlanta, Georgia
Bielefeld Course on Nonlinear Waves - June 29, Department of Mathematics University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Solitons on Manifolds
 Joint work (on various projects) with Pierre Albin (UIUC), Hans Christianson (UNC), Jason Metcalfe (UNC), Michael Taylor (UNC), Laurent Thomann (Nantes) Department of Mathematics University of North Carolina,
Joint work (on various projects) with Pierre Albin (UIUC), Hans Christianson (UNC), Jason Metcalfe (UNC), Michael Taylor (UNC), Laurent Thomann (Nantes) Department of Mathematics University of North Carolina,
GROUND-STATES FOR THE LIQUID DROP AND TFDW MODELS WITH LONG-RANGE ATTRACTION
 GROUND-STATES FOR THE LIQUID DROP AND TFDW MODELS WITH LONG-RANGE ATTRACTION STAN ALAMA, LIA BRONSARD, RUSTUM CHOKSI, AND IHSAN TOPALOGLU Abstract. We prove that both the liquid drop model in with an attractive
GROUND-STATES FOR THE LIQUID DROP AND TFDW MODELS WITH LONG-RANGE ATTRACTION STAN ALAMA, LIA BRONSARD, RUSTUM CHOKSI, AND IHSAN TOPALOGLU Abstract. We prove that both the liquid drop model in with an attractive
Note that it is traditional to draw the diagram for semiconductors rotated 90 degrees, i.e. the version on the right above.
 5 Semiconductors The nearly free electron model applies equally in the case where the Fermi level lies within a small band gap (semiconductors), as it does when the Fermi level lies within a band (metal)
5 Semiconductors The nearly free electron model applies equally in the case where the Fermi level lies within a small band gap (semiconductors), as it does when the Fermi level lies within a band (metal)
On the relation between scaling properties of functionals and existence of constrained minimizers
 On the relation between scaling properties of functionals and existence of constrained minimizers Jacopo Bellazzini Dipartimento di Matematica Applicata U. Dini Università di Pisa January 11, 2011 J. Bellazzini
On the relation between scaling properties of functionals and existence of constrained minimizers Jacopo Bellazzini Dipartimento di Matematica Applicata U. Dini Università di Pisa January 11, 2011 J. Bellazzini
Math 205b Homework 2 Solutions
 Math 5b Homework Solutions January 5, 5 Problem (R-S, II.) () For the R case, we just expand the right hand side and use the symmetry of the inner product: ( x y x y ) = = ((x, x) (y, y) (x, y) (y, x)
Math 5b Homework Solutions January 5, 5 Problem (R-S, II.) () For the R case, we just expand the right hand side and use the symmetry of the inner product: ( x y x y ) = = ((x, x) (y, y) (x, y) (y, x)
Derivation of Pekar s polaron from a microscopic model of quantum crystal
 Derivation of Pekar s polaron from a microscopic model of quantum crystal Mathieu LEWIN Mathieu.Lewin@math.cnrs.fr (CNRS & University of Cergy-Pontoise) joint work with Nicolas Rougerie (Grenoble, France)
Derivation of Pekar s polaron from a microscopic model of quantum crystal Mathieu LEWIN Mathieu.Lewin@math.cnrs.fr (CNRS & University of Cergy-Pontoise) joint work with Nicolas Rougerie (Grenoble, France)
MATH 104: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 2008/09 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS. Let f : R R be continuous periodic with period, i.e. f(x + ) = f(x) for all x R. Prove the following: (a) f is bounded above below
MATH 04: INTRODUCTORY ANALYSIS SPRING 008/09 PROBLEM SET 8 SOLUTIONS. Let f : R R be continuous periodic with period, i.e. f(x + ) = f(x) for all x R. Prove the following: (a) f is bounded above below
Contribution of the spin-zeeman term to the binding energy for hydrogen in non-relativistic QED.
 Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (2013), 307 320 Contribution of the spin-zeeman term to the binding energy for hydrogen in non-relativistic QED. Jean-Marie Barbaroux
Annals of the University of Bucharest (mathematical series) 4 (LXII) (2013), 307 320 Contribution of the spin-zeeman term to the binding energy for hydrogen in non-relativistic QED. Jean-Marie Barbaroux
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 13 Oct 2010
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 13 Oct 2010 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 13 Oct 2010](/thumbs/96/127015217.jpg) BINDING, STABILITY, AND NON-BINDING OF MLTI-POLARON SYSTEMS RPERT L. FRANK, ELLIOTT H. LIEB, ROBERT SEIRINGER, AND LAWRENCE E. THOMAS arxiv:1010.0737v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 13 Oct 2010 Abstract. The binding
BINDING, STABILITY, AND NON-BINDING OF MLTI-POLARON SYSTEMS RPERT L. FRANK, ELLIOTT H. LIEB, ROBERT SEIRINGER, AND LAWRENCE E. THOMAS arxiv:1010.0737v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 13 Oct 2010 Abstract. The binding
Complex Solutions to the Klein-Gordon Equation
 University of Rochester Quantum Field Theory II Professor Sarada Rajeev Complex Solutions to the Klein-Gordon Equation David Mayrhofer PHY 39 Independent Study Paper April 0th, 08 Introduction At this
University of Rochester Quantum Field Theory II Professor Sarada Rajeev Complex Solutions to the Klein-Gordon Equation David Mayrhofer PHY 39 Independent Study Paper April 0th, 08 Introduction At this
Analysis II: Basic knowledge of real analysis: Part V, Power Series, Differentiation, and Taylor Series
 .... Analysis II: Basic knowledge of real analysis: Part V, Power Series, Differentiation, and Taylor Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American March 4, 20
.... Analysis II: Basic knowledge of real analysis: Part V, Power Series, Differentiation, and Taylor Series Kenichi Maruno Department of Mathematics, The University of Texas - Pan American March 4, 20
Section 4: The Quantum Scalar Field
 Physics 8.323 Section 4: The Quantum Scalar Field February 2012 c 2012 W. Taylor 8.323 Section 4: Quantum scalar field 1 / 19 4.1 Canonical Quantization Free scalar field equation (Klein-Gordon) ( µ µ
Physics 8.323 Section 4: The Quantum Scalar Field February 2012 c 2012 W. Taylor 8.323 Section 4: Quantum scalar field 1 / 19 4.1 Canonical Quantization Free scalar field equation (Klein-Gordon) ( µ µ
POSITIVE GROUND STATE SOLUTIONS FOR SOME NON-AUTONOMOUS KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS
 ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 47, Number 1, 2017 POSITIVE GROUND STATE SOLUTIONS FOR SOME NON-AUTONOMOUS KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS QILIN XIE AND SHIWANG MA ABSTRACT. In this paper, we study
ROCKY MOUNTAIN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 47, Number 1, 2017 POSITIVE GROUND STATE SOLUTIONS FOR SOME NON-AUTONOMOUS KIRCHHOFF TYPE PROBLEMS QILIN XIE AND SHIWANG MA ABSTRACT. In this paper, we study
MULTIPLE SOLUTIONS FOR CRITICAL ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS WITH FRACTIONAL LAPLACIAN
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 016 (016), No. 97, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MULTIPLE SOLUTIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 016 (016), No. 97, pp. 1 11. ISSN: 107-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu ftp ejde.math.txstate.edu MULTIPLE SOLUTIONS
GROUND STATE SOLUTIONS FOR CHOQUARD TYPE EQUATIONS WITH A SINGULAR POTENTIAL. 1. Introduction In this article, we study the Choquard type equation
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), o. 52, pp. 1 14. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu GROUD STATE SOLUTIOS FOR CHOQUARD TYPE EQUATIOS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 2017 (2017), o. 52, pp. 1 14. ISS: 1072-6691. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu GROUD STATE SOLUTIOS FOR CHOQUARD TYPE EQUATIOS
arxiv: v3 [math-ph] 19 Oct 2017
![arxiv: v3 [math-ph] 19 Oct 2017 arxiv: v3 [math-ph] 19 Oct 2017](/thumbs/94/118694632.jpg) ABSECE OF A GROUD STATE FOR BOSOIC COULOMB SYSTEMS WITH CRITICAL CHARGE YUKIMI GOTO arxiv:1605.02949v3 [math-ph] 19 Oct 2017 Abstract. We consider bosonic Coulomb systems with -particles and K static nuclei.
ABSECE OF A GROUD STATE FOR BOSOIC COULOMB SYSTEMS WITH CRITICAL CHARGE YUKIMI GOTO arxiv:1605.02949v3 [math-ph] 19 Oct 2017 Abstract. We consider bosonic Coulomb systems with -particles and K static nuclei.
Quantum Mechanics II
 Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler March 8, 011 1 Lecture 19 1.1 Second Quantization Recall our results from simple harmonic oscillator. We know the Hamiltonian very well so no need to repeat here.
Quantum Mechanics II Prof. Boris Altshuler March 8, 011 1 Lecture 19 1.1 Second Quantization Recall our results from simple harmonic oscillator. We know the Hamiltonian very well so no need to repeat here.
Fisher information and Stam inequality on a finite group
 Fisher information and Stam inequality on a finite group Paolo Gibilisco and Tommaso Isola February, 2008 Abstract We prove a discrete version of Stam inequality for random variables taking values on a
Fisher information and Stam inequality on a finite group Paolo Gibilisco and Tommaso Isola February, 2008 Abstract We prove a discrete version of Stam inequality for random variables taking values on a
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta. EECS Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku
 Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
Lecture 6 Photons, electrons and other quanta EECS 598-002 Winter 2006 Nanophotonics and Nano-scale Fabrication P.C.Ku From classical to quantum theory In the beginning of the 20 th century, experiments
A NOTE ON POSITIVE DEFINITE NORM DEPENDENT FUNCTIONS
 A NOTE ON POSITIVE DEFINITE NORM DEPENDENT FUNCTIONS ALEXANDER KOLDOBSKY Abstract. Let K be an origin symmetric star body in R n. We prove, under very mild conditions on the function f : [, ) R, that if
A NOTE ON POSITIVE DEFINITE NORM DEPENDENT FUNCTIONS ALEXANDER KOLDOBSKY Abstract. Let K be an origin symmetric star body in R n. We prove, under very mild conditions on the function f : [, ) R, that if
Local time path integrals and their application to Lévy random walks
 Local time path integrals and their application to Lévy random walks Václav Zatloukal (www.zatlovac.eu) Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague talk given
Local time path integrals and their application to Lévy random walks Václav Zatloukal (www.zatlovac.eu) Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering Czech Technical University in Prague talk given
Interaction with External Sources
 Chapter 4 Interaction with External Sources 4. Classical Fields and Green s Functions We start our discussion of sources with classical (non-quantized) fields. Consider L = 2 (@ µ (x)) 2 2 m2 (x) 2 + J(x)
Chapter 4 Interaction with External Sources 4. Classical Fields and Green s Functions We start our discussion of sources with classical (non-quantized) fields. Consider L = 2 (@ µ (x)) 2 2 m2 (x) 2 + J(x)
EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE EQUATIONS WITH UNBOUNDED POTENTIAL. 1. Introduction In this article, we consider the Kirchhoff type problem
 Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 207 (207), No. 84, pp. 2. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE EQUATIONS
Electronic Journal of Differential Equations, Vol. 207 (207), No. 84, pp. 2. ISSN: 072-669. URL: http://ejde.math.txstate.edu or http://ejde.math.unt.edu EXISTENCE OF SOLUTIONS FOR KIRCHHOFF TYPE EQUATIONS
The correlation energy of charged quantum systems. Jan Philip Solovej University of Copenhagen
 The correlation energy of charged quantum systems Jan Philip Solovej University of Copenhagen Workshop on Quantum Spectra and Dynamics Israel, June 28 - July 5, 2000 1 Quantum Mechanics of charged Particles
The correlation energy of charged quantum systems Jan Philip Solovej University of Copenhagen Workshop on Quantum Spectra and Dynamics Israel, June 28 - July 5, 2000 1 Quantum Mechanics of charged Particles
Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables
 Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables January 25, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 4 January 25, 2013 1 / 13 Agenda
Math 408 - Mathematical Statistics Lecture 4. Continuous Random Variables and Transformations of Random Variables January 25, 2013 Konstantin Zuev (USC) Math 408, Lecture 4 January 25, 2013 1 / 13 Agenda
SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS. Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S. L. Yadava. 1. Introduction
 Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
Topological Methods in Nonlinear Analysis Journal of the Juliusz Schauder Center Volume 21, 2003, 211 226 SYMMETRY RESULTS FOR PERTURBED PROBLEMS AND RELATED QUESTIONS Massimo Grosi Filomena Pacella S.
The 4th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures Great Park, Windsor, UK, August 6-18, 2007
 The 4th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures Great Park, Windsor, UK, August 6-18, 2007 Kondo Effect in Metals and Quantum Dots Jan von Delft
The 4th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures Great Park, Windsor, UK, August 6-18, 2007 Kondo Effect in Metals and Quantum Dots Jan von Delft
Non-relativistic Quantum Electrodynamics
 Rigorous Aspects of Relaxation to the Ground State Institut für Analysis, Dynamik und Modellierung October 25, 2010 Overview 1 Definition of the model Second quantization Non-relativistic QED 2 Existence
Rigorous Aspects of Relaxation to the Ground State Institut für Analysis, Dynamik und Modellierung October 25, 2010 Overview 1 Definition of the model Second quantization Non-relativistic QED 2 Existence
arxiv: v2 [math-ph] 10 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v2 [math-ph] 10 Nov 2016 arxiv: v2 [math-ph] 10 Nov 2016](/thumbs/93/113448402.jpg) NONEXISTENCE IN THOMAS-FERMI-DIRAC-VON WEIZSÄCKER THEORY WITH SMALL NUCLEAR CHARGES PHAN THÀNH NAM AND HANNE VAN DEN BOSCH arxiv:1603.07368v2 [math-ph] 10 Nov 2016 Abstract. We study the ionization problem
NONEXISTENCE IN THOMAS-FERMI-DIRAC-VON WEIZSÄCKER THEORY WITH SMALL NUCLEAR CHARGES PHAN THÀNH NAM AND HANNE VAN DEN BOSCH arxiv:1603.07368v2 [math-ph] 10 Nov 2016 Abstract. We study the ionization problem
Classification of algebraic surfaces up to fourth degree. Vinogradova Anna
 Classification of algebraic surfaces up to fourth degree Vinogradova Anna Bases of algebraic surfaces Degree of the algebraic equation Quantity of factors The algebraic surfaces are described by algebraic
Classification of algebraic surfaces up to fourth degree Vinogradova Anna Bases of algebraic surfaces Degree of the algebraic equation Quantity of factors The algebraic surfaces are described by algebraic
Fermi polaron-polaritons in MoSe 2
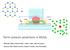 Fermi polaron-polaritons in MoSe 2 Meinrad Sidler, Patrick Back, Ovidiu Cotlet, Ajit Srivastava, Thomas Fink, Martin Kroner, Eugene Demler, Atac Imamoglu Quantum impurity problem Nonperturbative interaction
Fermi polaron-polaritons in MoSe 2 Meinrad Sidler, Patrick Back, Ovidiu Cotlet, Ajit Srivastava, Thomas Fink, Martin Kroner, Eugene Demler, Atac Imamoglu Quantum impurity problem Nonperturbative interaction
u( x) = g( y) ds y ( 1 ) U solves u = 0 in U; u = 0 on U. ( 3)
 M ath 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecture 4 ( S ep. 6, 2 0 0 9 ) Properties and Estimates of Laplace s and Poisson s Equations In our last lecture we derived the formulas for the solutions of Poisson s equation
M ath 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecture 4 ( S ep. 6, 2 0 0 9 ) Properties and Estimates of Laplace s and Poisson s Equations In our last lecture we derived the formulas for the solutions of Poisson s equation
BLOWUP THEORY FOR THE CRITICAL NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS REVISITED
 BLOWUP THEORY FOR THE CRITICAL NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS REVISITED TAOUFIK HMIDI AND SAHBI KERAANI Abstract. In this note we prove a refined version of compactness lemma adapted to the blowup analysis
BLOWUP THEORY FOR THE CRITICAL NONLINEAR SCHRÖDINGER EQUATIONS REVISITED TAOUFIK HMIDI AND SAHBI KERAANI Abstract. In this note we prove a refined version of compactness lemma adapted to the blowup analysis
Schrödinger-Klein-Gordon system as a classical limit of a scalar Quantum Field Theory.
 Schrödinger-Klein-Gordon system as a classical limit of a scalar Quantum Field Theory. (in collaboration with Marco Falconi) Zied Ammari Rennes University, IRMAR BECAM, 28 October 2014 The Yukawa Theory
Schrödinger-Klein-Gordon system as a classical limit of a scalar Quantum Field Theory. (in collaboration with Marco Falconi) Zied Ammari Rennes University, IRMAR BECAM, 28 October 2014 The Yukawa Theory
CLASSIFICATION OF NON-ABELIAN CHERN-SIMONS VORTICES
 CLASSIFICATION OF NON-ABELIAN CHERN-SIMONS VORTICES arxiv:hep-th/9310182v1 27 Oct 1993 Gerald V. Dunne Department of Physics University of Connecticut 2152 Hillside Road Storrs, CT 06269 USA dunne@hep.phys.uconn.edu
CLASSIFICATION OF NON-ABELIAN CHERN-SIMONS VORTICES arxiv:hep-th/9310182v1 27 Oct 1993 Gerald V. Dunne Department of Physics University of Connecticut 2152 Hillside Road Storrs, CT 06269 USA dunne@hep.phys.uconn.edu
1 Continuity Classes C m (Ω)
 0.1 Norms 0.1 Norms A norm on a linear space X is a function : X R with the properties: Positive Definite: x 0 x X (nonnegative) x = 0 x = 0 (strictly positive) λx = λ x x X, λ C(homogeneous) x + y x +
0.1 Norms 0.1 Norms A norm on a linear space X is a function : X R with the properties: Positive Definite: x 0 x X (nonnegative) x = 0 x = 0 (strictly positive) λx = λ x x X, λ C(homogeneous) x + y x +
221B Lecture Notes Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking
 B Lecture Notes Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking is an ubiquitous concept in modern physics, especially in condensed matter and particle physics.
B Lecture Notes Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking is an ubiquitous concept in modern physics, especially in condensed matter and particle physics.
2D Electrostatics and the Density of Quantum Fluids
 2D Electrostatics and the Density of Quantum Fluids Jakob Yngvason, University of Vienna with Elliott H. Lieb, Princeton University and Nicolas Rougerie, University of Grenoble Yerevan, September 5, 2016
2D Electrostatics and the Density of Quantum Fluids Jakob Yngvason, University of Vienna with Elliott H. Lieb, Princeton University and Nicolas Rougerie, University of Grenoble Yerevan, September 5, 2016
New Identities for Weak KAM Theory
 New Identities for Weak KAM Theory Lawrence C. Evans Department of Mathematics University of California, Berkeley Abstract This paper records for the Hamiltonian H = p + W (x) some old and new identities
New Identities for Weak KAM Theory Lawrence C. Evans Department of Mathematics University of California, Berkeley Abstract This paper records for the Hamiltonian H = p + W (x) some old and new identities
31st Jerusalem Winter School in Theoretical Physics: Problem Set 2
 31st Jerusalem Winter School in Theoretical Physics: Problem Set Contents Frank Verstraete: Quantum Information and Quantum Matter : 3 : Solution to Problem 9 7 Daniel Harlow: Black Holes and Quantum Information
31st Jerusalem Winter School in Theoretical Physics: Problem Set Contents Frank Verstraete: Quantum Information and Quantum Matter : 3 : Solution to Problem 9 7 Daniel Harlow: Black Holes and Quantum Information
Problem Set No. 1: Quantization of Non-Relativistic Fermi Systems Due Date: September 14, Second Quantization of an Elastic Solid
 Physics 56, Fall Semester 5 Professor Eduardo Fradkin Problem Set No. : Quantization of Non-Relativistic Fermi Systems Due Date: September 4, 5 Second Quantization of an Elastic Solid Consider a three-dimensional
Physics 56, Fall Semester 5 Professor Eduardo Fradkin Problem Set No. : Quantization of Non-Relativistic Fermi Systems Due Date: September 4, 5 Second Quantization of an Elastic Solid Consider a three-dimensional
Supercell method for the computation of energies of crystals
 Supercell method for the computation of energies of crystals David Gontier CEREMADE, Université Paris-Dauphine Warwick EPSRC Symposium: Density Functional Theory and Beyond: Analysis and Computation Warwick,
Supercell method for the computation of energies of crystals David Gontier CEREMADE, Université Paris-Dauphine Warwick EPSRC Symposium: Density Functional Theory and Beyond: Analysis and Computation Warwick,
Stochastic UV renormalization
 Stochastic UV renormalization Fumio Hiroshima Faculty of Mathematics, Kyushu University joint work with MGubinelli and J Lőrinczi 2014/10/15 Tohoku University F Hiroshima UV renormalization 1 Nelson model
Stochastic UV renormalization Fumio Hiroshima Faculty of Mathematics, Kyushu University joint work with MGubinelli and J Lőrinczi 2014/10/15 Tohoku University F Hiroshima UV renormalization 1 Nelson model
Ground-State Energies of Coulomb Systems and Reduced One-Particle Density Matrices
 Ground-State Energies of Coulomb Systems and Reduced One-Particle Density Matrices Heinz Siedentop Chennai, August 16, 2010 I. Introduction Atomic Schrödinger operator H N,Z := N n=1 self-adjointly realized
Ground-State Energies of Coulomb Systems and Reduced One-Particle Density Matrices Heinz Siedentop Chennai, August 16, 2010 I. Introduction Atomic Schrödinger operator H N,Z := N n=1 self-adjointly realized
in BECs Fabian Grusdt Physics Department and Research Center OPTIMAS, University of Kaiserslautern, Germany
 1 Polaron Seminar, AG Widera AG Fleischhauer, 05/06/14 Introduction to polaron physics in BECs Fabian Grusdt Physics Department and Research Center OPTIMAS, University of Kaiserslautern, Germany Graduate
1 Polaron Seminar, AG Widera AG Fleischhauer, 05/06/14 Introduction to polaron physics in BECs Fabian Grusdt Physics Department and Research Center OPTIMAS, University of Kaiserslautern, Germany Graduate
Piecewise Smooth Solutions to the Burgers-Hilbert Equation
 Piecewise Smooth Solutions to the Burgers-Hilbert Equation Alberto Bressan and Tianyou Zhang Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, University Park, Pa 68, USA e-mails: bressan@mathpsuedu, zhang
Piecewise Smooth Solutions to the Burgers-Hilbert Equation Alberto Bressan and Tianyou Zhang Department of Mathematics, Penn State University, University Park, Pa 68, USA e-mails: bressan@mathpsuedu, zhang
ABSOLUTELY CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM OF A TYPICAL SCHRÖDINGER OPERATOR WITH A SLOWLY DECAYING POTENTIAL
 ABSOLUTELY CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM OF A TYPICAL SCHRÖDINGER OPERATOR WITH A SLOWLY DECAYING POTENTIAL OLEG SAFRONOV 1. Main results We study the absolutely continuous spectrum of a Schrödinger operator 1 H
ABSOLUTELY CONTINUOUS SPECTRUM OF A TYPICAL SCHRÖDINGER OPERATOR WITH A SLOWLY DECAYING POTENTIAL OLEG SAFRONOV 1. Main results We study the absolutely continuous spectrum of a Schrödinger operator 1 H
arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 4 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 4 Sep 2009 arxiv: v1 [math.dg] 4 Sep 2009](/thumbs/88/116447457.jpg) SOME ESTIMATES OF WANG-YAU QUASILOCAL ENERGY arxiv:0909.0880v1 [math.dg] 4 Sep 2009 PENGZI MIAO 1, LUEN-FAI TAM 2 AND NAQING XIE 3 Abstract. Given a spacelike 2-surface in a spacetime N and a constant
SOME ESTIMATES OF WANG-YAU QUASILOCAL ENERGY arxiv:0909.0880v1 [math.dg] 4 Sep 2009 PENGZI MIAO 1, LUEN-FAI TAM 2 AND NAQING XIE 3 Abstract. Given a spacelike 2-surface in a spacetime N and a constant
ON THE HÖLDER CONTINUITY OF MATRIX FUNCTIONS FOR NORMAL MATRICES
 Volume 10 (2009), Issue 4, Article 91, 5 pp. ON THE HÖLDER CONTINUITY O MATRIX UNCTIONS OR NORMAL MATRICES THOMAS P. WIHLER MATHEMATICS INSTITUTE UNIVERSITY O BERN SIDLERSTRASSE 5, CH-3012 BERN SWITZERLAND.
Volume 10 (2009), Issue 4, Article 91, 5 pp. ON THE HÖLDER CONTINUITY O MATRIX UNCTIONS OR NORMAL MATRICES THOMAS P. WIHLER MATHEMATICS INSTITUTE UNIVERSITY O BERN SIDLERSTRASSE 5, CH-3012 BERN SWITZERLAND.
WANNIER TRANSFORM APERIODIC SOLIDS. for. Jean BELLISSARD. Collaboration:
 WANNIER TRANSFORM for APERIODIC SOLIDS Jean BELLISSARD Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta School of Mathematics & School of Physics e-mail: jeanbel@math.gatech.edu Collaboration: G. DE NITTIS (SISSA,
WANNIER TRANSFORM for APERIODIC SOLIDS Jean BELLISSARD Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta School of Mathematics & School of Physics e-mail: jeanbel@math.gatech.edu Collaboration: G. DE NITTIS (SISSA,
PHY 396 K. Problem set #7. Due October 25, 2012 (Thursday).
 PHY 396 K. Problem set #7. Due October 25, 2012 (Thursday. 1. Quantum mechanics of a fixed number of relativistic particles does not work (except as an approximation because of problems with relativistic
PHY 396 K. Problem set #7. Due October 25, 2012 (Thursday. 1. Quantum mechanics of a fixed number of relativistic particles does not work (except as an approximation because of problems with relativistic
ON PARABOLIC HARNACK INEQUALITY
 ON PARABOLIC HARNACK INEQUALITY JIAXIN HU Abstract. We show that the parabolic Harnack inequality is equivalent to the near-diagonal lower bound of the Dirichlet heat kernel on any ball in a metric measure-energy
ON PARABOLIC HARNACK INEQUALITY JIAXIN HU Abstract. We show that the parabolic Harnack inequality is equivalent to the near-diagonal lower bound of the Dirichlet heat kernel on any ball in a metric measure-energy
Large time behavior of reaction-diffusion equations with Bessel generators
 Large time behavior of reaction-diffusion equations with Bessel generators José Alfredo López-Mimbela Nicolas Privault Abstract We investigate explosion in finite time of one-dimensional semilinear equations
Large time behavior of reaction-diffusion equations with Bessel generators José Alfredo López-Mimbela Nicolas Privault Abstract We investigate explosion in finite time of one-dimensional semilinear equations
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014
 Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
Solutions Final Exam May. 14, 2014 1. Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer (i.e., prove the claim, derive a contradiction or give a counter-example). (a) (10
Ann. Funct. Anal. 1 (2010), no. 1, A nnals of F unctional A nalysis ISSN: (electronic) URL:
 Ann. Funct. Anal. (00), no., 44 50 A nnals of F unctional A nalysis ISSN: 008-875 (electronic) URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ A FIXED POINT APPROACH TO THE STABILITY OF ϕ-morphisms ON HILBERT C -MODULES
Ann. Funct. Anal. (00), no., 44 50 A nnals of F unctional A nalysis ISSN: 008-875 (electronic) URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ A FIXED POINT APPROACH TO THE STABILITY OF ϕ-morphisms ON HILBERT C -MODULES
Non-homogeneous semilinear elliptic equations involving critical Sobolev exponent
 Non-homogeneous semilinear elliptic equations involving critical Sobolev exponent Yūki Naito a and Tokushi Sato b a Department of Mathematics, Ehime University, Matsuyama 790-8577, Japan b Mathematical
Non-homogeneous semilinear elliptic equations involving critical Sobolev exponent Yūki Naito a and Tokushi Sato b a Department of Mathematics, Ehime University, Matsuyama 790-8577, Japan b Mathematical
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics
 Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
STRONG CONVERGENCE OF AN IMPLICIT ITERATION PROCESS FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY NONEXPANSIVE IN THE INTERMEDIATE SENSE MAPPINGS IN BANACH SPACES
 Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 36 Number 2 (2012), Pages 237 249. STRONG CONVERGENCE OF AN IMPLICIT ITERATION PROCESS FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY NONEXPANSIVE IN THE INTERMEDIATE SENSE MAPPINGS IN BANACH
Kragujevac Journal of Mathematics Volume 36 Number 2 (2012), Pages 237 249. STRONG CONVERGENCE OF AN IMPLICIT ITERATION PROCESS FOR ASYMPTOTICALLY NONEXPANSIVE IN THE INTERMEDIATE SENSE MAPPINGS IN BANACH
A Direct Proof of Caristi s Fixed Point Theorem
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 46, 2289-2294 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.66190 A Direct Proof of Caristi s Fixed Point Theorem Wei-Shih Du Department
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol. 10, 2016, no. 46, 2289-2294 HIKARI Ltd, www.m-hikari.com http://dx.doi.org/10.12988/ams.2016.66190 A Direct Proof of Caristi s Fixed Point Theorem Wei-Shih Du Department
On the Investigation of Quantum Interactions of Rubidium 87 with Optical Cavity Modes using Monte Carlo Wavefunction Method
 ustralian Journal of Basic and pplied Sciences, 6(13): 8-3, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 On the Investigation of Quantum Interactions of Rubidium with Optical avity Modes using Monte arlo Wavefunction Method Md. Mijanur
ustralian Journal of Basic and pplied Sciences, 6(13): 8-3, 1 ISSN 1991-8178 On the Investigation of Quantum Interactions of Rubidium with Optical avity Modes using Monte arlo Wavefunction Method Md. Mijanur
Homework I, Solutions
 Homework I, Solutions I: (15 points) Exercise on lower semi-continuity: Let X be a normed space and f : X R be a function. We say that f is lower semi - continuous at x 0 if for every ε > 0 there exists
Homework I, Solutions I: (15 points) Exercise on lower semi-continuity: Let X be a normed space and f : X R be a function. We say that f is lower semi - continuous at x 0 if for every ε > 0 there exists
Limit-point / limit-circle classification of second-order differential operators and PT -QM
 Limit-point / limit-circle classification of second-order differential operators and PT -QM TU Ilmenau 19th December 2016 TU Ilmenau Seite 1 / 24 TU Ilmenau Seite 2 / 24 PT -symmetry Definition (Bender
Limit-point / limit-circle classification of second-order differential operators and PT -QM TU Ilmenau 19th December 2016 TU Ilmenau Seite 1 / 24 TU Ilmenau Seite 2 / 24 PT -symmetry Definition (Bender
Some unified algorithms for finding minimum norm fixed point of nonexpansive semigroups in Hilbert spaces
 An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 19(1), 211, 331 346 Some unified algorithms for finding minimum norm fixed point of nonexpansive semigroups in Hilbert spaces Yonghong Yao, Yeong-Cheng Liou Abstract
An. Şt. Univ. Ovidius Constanţa Vol. 19(1), 211, 331 346 Some unified algorithms for finding minimum norm fixed point of nonexpansive semigroups in Hilbert spaces Yonghong Yao, Yeong-Cheng Liou Abstract
A CALDERÓN PROBLEM WITH FREQUENCY-DIFFERENTIAL DATA IN DISPERSIVE MEDIA. has a unique solution. The Dirichlet-to-Neumann map
 A CALDERÓN PROBLEM WITH FREQUENCY-DIFFERENTIAL DATA IN DISPERSIVE MEDIA SUNGWHAN KIM AND ALEXANDRU TAMASAN ABSTRACT. We consider the problem of identifying a complex valued coefficient γ(x, ω) in the conductivity
A CALDERÓN PROBLEM WITH FREQUENCY-DIFFERENTIAL DATA IN DISPERSIVE MEDIA SUNGWHAN KIM AND ALEXANDRU TAMASAN ABSTRACT. We consider the problem of identifying a complex valued coefficient γ(x, ω) in the conductivity
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 10550
 SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 0550. Find the critical numbers of f(x) = 6 x2 x /3. We have f (x) = 3 x 3 x 2/3 = [ x 5/3 ] 3 x 2/3. So x = 0 is a critical point. For x 0, the equation f (x) = 0 can be written
SOLUTIONS TO EXAM 2, MATH 0550. Find the critical numbers of f(x) = 6 x2 x /3. We have f (x) = 3 x 3 x 2/3 = [ x 5/3 ] 3 x 2/3. So x = 0 is a critical point. For x 0, the equation f (x) = 0 can be written
Volume: The Disk Method. Using the integral to find volume.
 Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
Volume: The Disk Method Using the integral to find volume. If a region in a plane is revolved about a line, the resulting solid is a solid of revolution and the line is called the axis of revolution. y
IBVPs for linear and integrable nonlinear evolution PDEs
 IBVPs for linear and integrable nonlinear evolution PDEs Dionyssis Mantzavinos Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge. Edinburgh, May 31, 212. Dionyssis Mantzavinos
IBVPs for linear and integrable nonlinear evolution PDEs Dionyssis Mantzavinos Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics, University of Cambridge. Edinburgh, May 31, 212. Dionyssis Mantzavinos
University of Toronto Department of Statistics
 Norm Comparisons for Data Augmentation by James P. Hobert Department of Statistics University of Florida and Jeffrey S. Rosenthal Department of Statistics University of Toronto Technical Report No. 0704
Norm Comparisons for Data Augmentation by James P. Hobert Department of Statistics University of Florida and Jeffrey S. Rosenthal Department of Statistics University of Toronto Technical Report No. 0704
Ferromagnetic Ordering of Energy Levels for XXZ Spin Chains
 Ferromagnetic Ordering of Energy Levels for XXZ Spin Chains Bruno Nachtergaele and Wolfgang L. Spitzer Department of Mathematics University of California, Davis Davis, CA 95616-8633, USA bxn@math.ucdavis.edu
Ferromagnetic Ordering of Energy Levels for XXZ Spin Chains Bruno Nachtergaele and Wolfgang L. Spitzer Department of Mathematics University of California, Davis Davis, CA 95616-8633, USA bxn@math.ucdavis.edu
arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 30 Dec 2017
![arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 30 Dec 2017 arxiv: v1 [quant-ph] 30 Dec 2017](/thumbs/84/91166188.jpg) Emergent Coulomb forces in reducible Quantum Electrodynamics arxiv:1801.00115v1 [quant-ph] 30 Dec 2017 Jan Naudts Universiteit Antwerpen Jan.Naudts@uantwerpen.be https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4646-1190 Abstract
Emergent Coulomb forces in reducible Quantum Electrodynamics arxiv:1801.00115v1 [quant-ph] 30 Dec 2017 Jan Naudts Universiteit Antwerpen Jan.Naudts@uantwerpen.be https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4646-1190 Abstract
Chapter 4: Summary. Solve lattice vibration equation of one atom/unitcellcase Consider a set of ions M separated by a distance a,
 Chapter 4: Summary Solve lattice vibration equation of one atom/unitcellcase case. Consider a set of ions M separated by a distance a, R na for integral n. Let u( na) be the displacement. Assuming only
Chapter 4: Summary Solve lattice vibration equation of one atom/unitcellcase case. Consider a set of ions M separated by a distance a, R na for integral n. Let u( na) be the displacement. Assuming only
General Lower Bounds for Resonances in One Dimension*
 Commun. Math. Phys. 86, 221-225 (1982) Communications in Mathematical Physics Springer-Verlag 1982 General Lower Bounds for Resonances in One Dimension* Evans M. Harrell II Department of Mathematics, The
Commun. Math. Phys. 86, 221-225 (1982) Communications in Mathematical Physics Springer-Verlag 1982 General Lower Bounds for Resonances in One Dimension* Evans M. Harrell II Department of Mathematics, The
Many-Body Quantum Mechanics
 Quasi-Classical Limit for Quantum Particle-Field Systems Michele Correggi Many-Body Quantum Mechanics CRM, Montréal joint work with M. Falconi (Tübingen) and M. Olivieri (Roma 1) M. Correggi (Roma 1) Quasi-Classical
Quasi-Classical Limit for Quantum Particle-Field Systems Michele Correggi Many-Body Quantum Mechanics CRM, Montréal joint work with M. Falconi (Tübingen) and M. Olivieri (Roma 1) M. Correggi (Roma 1) Quasi-Classical
Radial Symmetry of Minimizers for Some Translation and Rotation Invariant Functionals
 journal of differential equations 124, 378388 (1996) article no. 0015 Radial Symmetry of Minimizers for Some Translation and Rotation Invariant Functionals Orlando Lopes IMECCUNICAMPCaixa Postal 1170 13081-970,
journal of differential equations 124, 378388 (1996) article no. 0015 Radial Symmetry of Minimizers for Some Translation and Rotation Invariant Functionals Orlando Lopes IMECCUNICAMPCaixa Postal 1170 13081-970,
COMPACTLY SUPPORTED ORTHONORMAL COMPLEX WAVELETS WITH DILATION 4 AND SYMMETRY
 COMPACTLY SUPPORTED ORTHONORMAL COMPLEX WAVELETS WITH DILATION 4 AND SYMMETRY BIN HAN AND HUI JI Abstract. In this paper, we provide a family of compactly supported orthonormal complex wavelets with dilation
COMPACTLY SUPPORTED ORTHONORMAL COMPLEX WAVELETS WITH DILATION 4 AND SYMMETRY BIN HAN AND HUI JI Abstract. In this paper, we provide a family of compactly supported orthonormal complex wavelets with dilation
Bosonization of a Finite Number of Non-Relativistic Fermions and Applications
 Bosonization of a Finite Number of Non-Relativistic Fermions and Applications p. 1/4 Bosonization of a Finite Number of Non-Relativistic Fermions and Applications Avinash Dhar Tata Institute of Fundamental
Bosonization of a Finite Number of Non-Relativistic Fermions and Applications p. 1/4 Bosonization of a Finite Number of Non-Relativistic Fermions and Applications Avinash Dhar Tata Institute of Fundamental
Strongly nonlinear multiplicative inequalities involving nonlocal operators
 Strongly nonlinear multiplicative inequalities involving nonlocal operators Agnieszka Ka lamajska University of Warsaw Bȩdlewo, 3rd Conference on Nonlocal Operators and Partial Differential Equations,
Strongly nonlinear multiplicative inequalities involving nonlocal operators Agnieszka Ka lamajska University of Warsaw Bȩdlewo, 3rd Conference on Nonlocal Operators and Partial Differential Equations,
Second quantization: where quantization and particles come from?
 110 Phys460.nb 7 Second quantization: where quantization and particles come from? 7.1. Lagrangian mechanics and canonical quantization Q: How do we quantize a general system? 7.1.1.Lagrangian Lagrangian
110 Phys460.nb 7 Second quantization: where quantization and particles come from? 7.1. Lagrangian mechanics and canonical quantization Q: How do we quantize a general system? 7.1.1.Lagrangian Lagrangian
Monotone variational inequalities, generalized equilibrium problems and fixed point methods
 Wang Fixed Point Theory and Applications 2014, 2014:236 R E S E A R C H Open Access Monotone variational inequalities, generalized equilibrium problems and fixed point methods Shenghua Wang * * Correspondence:
Wang Fixed Point Theory and Applications 2014, 2014:236 R E S E A R C H Open Access Monotone variational inequalities, generalized equilibrium problems and fixed point methods Shenghua Wang * * Correspondence:
VANISHING-CONCENTRATION-COMPACTNESS ALTERNATIVE FOR THE TRUDINGER-MOSER INEQUALITY IN R N
 VAISHIG-COCETRATIO-COMPACTESS ALTERATIVE FOR THE TRUDIGER-MOSER IEQUALITY I R Abstract. Let 2, a > 0 0 < b. Our aim is to clarify the influence of the constraint S a,b = { u W 1, (R ) u a + u b = 1 } on
VAISHIG-COCETRATIO-COMPACTESS ALTERATIVE FOR THE TRUDIGER-MOSER IEQUALITY I R Abstract. Let 2, a > 0 0 < b. Our aim is to clarify the influence of the constraint S a,b = { u W 1, (R ) u a + u b = 1 } on
Symmetry and monotonicity of least energy solutions
 Symmetry and monotonicity of least energy solutions Jaeyoung BYEO, Louis JEAJEA and Mihai MARIŞ Abstract We give a simple proof of the fact that for a large class of quasilinear elliptic equations and
Symmetry and monotonicity of least energy solutions Jaeyoung BYEO, Louis JEAJEA and Mihai MARIŞ Abstract We give a simple proof of the fact that for a large class of quasilinear elliptic equations and
Math 240 (Driver) Qual Exam (9/12/2017)
 1 Name: I.D. #: Math 240 (Driver) Qual Exam (9/12/2017) Instructions: Clearly explain and justify your answers. You may cite theorems from the text, notes, or class as long as they are not what the problem
1 Name: I.D. #: Math 240 (Driver) Qual Exam (9/12/2017) Instructions: Clearly explain and justify your answers. You may cite theorems from the text, notes, or class as long as they are not what the problem
Holonomy groups. Thomas Leistner. Mathematics Colloquium School of Mathematics and Physics The University of Queensland. October 31, 2011 May 28, 2012
 Holonomy groups Thomas Leistner Mathematics Colloquium School of Mathematics and Physics The University of Queensland October 31, 2011 May 28, 2012 1/17 The notion of holonomy groups is based on Parallel
Holonomy groups Thomas Leistner Mathematics Colloquium School of Mathematics and Physics The University of Queensland October 31, 2011 May 28, 2012 1/17 The notion of holonomy groups is based on Parallel
An Introduction to Lattice Vibrations
 An Introduction to Lattice Vibrations Andreas Wacker 1 Mathematical Physics, Lund University November 3, 2015 1 Introduction Ideally, the atoms in a crystal are positioned in a regular manner following
An Introduction to Lattice Vibrations Andreas Wacker 1 Mathematical Physics, Lund University November 3, 2015 1 Introduction Ideally, the atoms in a crystal are positioned in a regular manner following
On the N-tuple Wave Solutions of the Korteweg-de Vnes Equation
 Publ. RIMS, Kyoto Univ. 8 (1972/73), 419-427 On the N-tuple Wave Solutions of the Korteweg-de Vnes Equation By Shunichi TANAKA* 1. Introduction In this paper, we discuss properties of the N-tuple wave
Publ. RIMS, Kyoto Univ. 8 (1972/73), 419-427 On the N-tuple Wave Solutions of the Korteweg-de Vnes Equation By Shunichi TANAKA* 1. Introduction In this paper, we discuss properties of the N-tuple wave
Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory
 Phys 769 Selected Topics in Condensed Matter Physics Summer 010 Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory Lecturer: Anthony J. Leggett TA: Bill Coish 1 Introduction Most matter, in particular most insulating
Phys 769 Selected Topics in Condensed Matter Physics Summer 010 Lecture 4: Basic elements of band theory Lecturer: Anthony J. Leggett TA: Bill Coish 1 Introduction Most matter, in particular most insulating
Welcome back to PHY 3305
 Welcome back to PHY 335 Today s Lecture: Hydrogen Atom Pt 1 Sad, quantum surfer, Alone, forlorn on the beach, His wave form collapsed. ThinkGeek.com via Ben Wise AnNouncements Reading Assignment for Nov
Welcome back to PHY 335 Today s Lecture: Hydrogen Atom Pt 1 Sad, quantum surfer, Alone, forlorn on the beach, His wave form collapsed. ThinkGeek.com via Ben Wise AnNouncements Reading Assignment for Nov
The Gross-Pitaevskii Equation and the Hydrodynamic Expansion of BECs
 The Gross-Pitaevskii Equation and the Hydrodynamic Expansion of BECs RHI seminar Pascal Büscher i ( t Φ (r, t) = 2 2 ) 2m + V ext(r) + g Φ (r, t) 2 Φ (r, t) 27 Nov 2008 RHI seminar Pascal Büscher 1 (Stamper-Kurn
The Gross-Pitaevskii Equation and the Hydrodynamic Expansion of BECs RHI seminar Pascal Büscher i ( t Φ (r, t) = 2 2 ) 2m + V ext(r) + g Φ (r, t) 2 Φ (r, t) 27 Nov 2008 RHI seminar Pascal Büscher 1 (Stamper-Kurn
Bose Description of Pauli Spin Operators and Related Coherent States
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 43 (5) pp. 7 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 43, No., January 5, 5 Bose Description of Pauli Spin Operators and Related Coherent States JIANG Nian-Quan,,
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 43 (5) pp. 7 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 43, No., January 5, 5 Bose Description of Pauli Spin Operators and Related Coherent States JIANG Nian-Quan,,
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 13 Apr 2012
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 13 Apr 2012 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 13 Apr 2012](/thumbs/80/82527965.jpg) IINEAR DECOMPOSITIONS FOR THE PRODUCT SPACE H MO UONG DANG KY arxiv:204.304v [math.ca] 3 Apr 202 Abstract. In this paper, we improve a recent result by i and Peng on products of functions in H (Rd and
IINEAR DECOMPOSITIONS FOR THE PRODUCT SPACE H MO UONG DANG KY arxiv:204.304v [math.ca] 3 Apr 202 Abstract. In this paper, we improve a recent result by i and Peng on products of functions in H (Rd and
