Solutions to MAT 117 Test #3
|
|
|
- Rafe Williamson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solutions to MAT 7 Test #3 Because there are two versions of the test, solutions will only be given for Form C. Differences from the Form D version will be given. (The values for Form C appear above those of Form D in the brackets.). [5 pts] Simplify algebraically: 5 3i 4 i 5 9i 8 i Solution: Multiply the numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator to rationalize the denominator : 5 3i 4 i 5 3i 4 i 4 + i 4 + i (5 3i)(4 + i) (4 i)(4 + i) 0 + 5i i 3i 6 + 4i 4i i 0 7i i. 7 For Version D: 5 9i 8 i 5 9i 8 i 8 + i 8 + i (5 9i)(8 + i) (8 i)(8 + i) i 7i 9i i 8i i 40 67i i. 65 Grading: +3 points for multiplying numerator and denominator by 4+i (or 8+i), + points for simplifying. Grading for common errors: 3 points for subtraction instead of division; points if the numerator and denominator were mutliplied by 4 i or i 4 (or 8 i or i 8); point if the denominator was missing.. [5 pts] Find all roots of { x 5 7x 4 + 8x 3 6x } + 3x 4 x 5 x 4 7x 3 + x 0 8x + Solution: The Rational Root Test implies (for version C) that every rational solution is one of ±, ±, ±3, ±4, ±6, ±8, ±, ±4. These values can be tested using synthetic division, long division, substitution, or graphing. (A graphing calculator can be used with XMIN 4, XMAX 4, YMIN 0, and YMAX 0; you are then looking to see where the graph crosses the x-axis.) The numbers and 3 turn out to be roots. Dividing x 5 7x 4 + 8x 3 6x + 3x 4 by x yields: or x 4 5x 3 + 8x 0x +. Dividing this quotient by x 3 yields:
2 or x 3 x + x 4. This polynomial has one more nice root:. Dividing it by x produces or x +. This polynomial has no real roots; the quadratic formula provides the remaining roots: ± i. The polynomial then has the following roots: (with multiplicity ), 3, and ± i. In version D, the Rational Root Test implies that ±, ±, ±3, ±4, ±6, and ± are the only rational numbers which can be roots; the ones which turn out to be genuine roots are and 3. Dividing x 5 x 4 7x 3 + x 8x + by x and x + 3 produces x 3 x + x. This cubic polynomial has as a root, and x 3 x + x divided by x is x +, which has the roots ±i. The roots of x 5 x 4 7x 3 + x 8x + are then (multiplicity ), 3, and ±i. (And if you think this problem was bad, you should check out the polynomial on the standard 7 test... ) Grading: + point per root, + point for doing the Rational Root Test. Grading for common mistakes: point for ± (version C), ±i (version C),,, 3 collectively (version C),,, 3 collectively (version D), ± (version D). 3. [5 pts] Find a third degree polynomial with integer coefficients that has the given zeros: x x 5i 6i Solution: If a polynomial with integer coefficients has 5i as a root, it must also have its conjugate ( 5i) as a root. Thus, this polynomial must have x, x 5i, and x + 5i as factors. One such polynomial is (x )(x 5i)(x + 5i) (x )(x + 5) x 3 x + 5x 5. For version D, a polynomial that works is (x )(x 6i)(x + 6i) (x )(x + 36) x 3 x + 36x 36. (Any integer, nonzero multiple of this polynomial will also work, incidentally.) Grading: +3 points for the factored form, + points for multiplying out. Grading for common mistakes: point for (x )(x + 5) (C) or (x )(x + 6) (D), points if the coefficients were not integers; 3 points for (x )(x 6i) (D).
3 4. For the function f(x) x 6x 9 x 9x 4 a. [ pts] Find the x-intercept(s). Solution: The x-intercept(s) is/are the values of x such that f(x) 0. Since f(x) is a rational function, f(x) 0 when the numerator is zero. Hence the x-intercept of f(x) is 0 (for C and D). b. [ pts] Find the y-intercept(s). Solution: The y-intercept is where x 0, or f(0). Since f(0) 0, the y-intercept (for C and D) is 0. c. [ pts] Find the equation(s) of the horizontal asymptote(s). Solution: Whether f(x) has a horizontal asymptote depends on what the leading terms of the numerator and denominator are; i.e., the long-term behavior. When x is big, f(x) is approximately x 6x x 0 (for C), or 6x 9x 0 (for D). In either case, f(x) has a horizontal 9x asymptote of y 0 (since the long-term behavior of f(x) is 0). d. [ pts] Find the equation(s) of the vertical asymptote(s). Solution: The vertical asymptotes of a rational function are the values of x where you are dividing by zero; they are where the denominator is zero. For (C), they are the solutions to 6x 9 0 or x ±3/4; for (D) they are the solutions to 9x 4 0: x ±/3. e. [ pts] Sketch a complete graph, incorporating the information found in parts a d. Solution: See the webpage at checkman/7/soln3.html. Grading: parts (a) (d) were on a 0-- point basis; for (e), + points were awarded only if the correct graph was sketched, or if all the work for (a) (d) was present, and the graph was based on this work. 4,500 6 / 5. [5 pts] We invest $ into an account that compounds quarterly at an annual rate of 7,500 8 %. / 7 / How much is in the account after 9 years? / Solution: Use the compound interest formula (provided on the test). For (C), P 4500, r 6.5% 0.65, n 4 (compounded quarterly), and t 7.5, so ( A P + r ) nt ( ) $5,30.84; n 4 for (D), P 7500, r 0.85, n 4, and t 9.5, so ( A P + r ) nt ( ) $4, n 4 Grading: +3 points for substituting values, + points for calculation. Grading for mistakes: point for r or 8.5; points if the initial amount was added; points for the wrong formula. 3
4 05, In 999, the population of the town of Gilbert, AZ, was. This year, 00, Gilbert s 0,000 population is 7,000. Assume that the population of Gilbert grows according to the exponential model P (t) Ae kt, where t is the number of years since 999. a. [5 pts] Find the exact exponential model that models the population of Gilbert as a function of time t. (That is, find A and k.) Solution: Values need to be found for A and k. These values need to satisfy P (0) (for C) and P () The first equation implies that Ae k0 Ae 0 A, and the second implies that e k. Solving for k: ek, or k ln ( ) 7, 05 so k ( ) 7 ln Thus P (t) 05000e t. 05 For (D), the process is the same, except that P (0) 0000 and thus k ( 7 ln , so P (t) 0000e t. Grading: + points for A, +3 points for k. Grading for common mistakes: +3 points (total) if only the equations for P (0) and P () are given; 3 points for P A k (function notation mistaken for multiplication). b. [5 pts] Gilbert s webpage predicts that in the year 005, the population will be 30,000. From the model you just found, predict the population of Gilbert in the year 005. Solution: The year 005 corresponds to t The answer is then P (6), which is 05000e ,7 (for C) or approximately 57,005 (for D). Grading: + points for t 6; +3 points for evaluating P (6). Grading for common mistakes: 3 points if P (t) was assumed to be linear. c. [5 pts] According to this model, when will the population reach half a million (500,000)? Solution: The answer is the value of t such that P (t) For C, this involves solving the equation 500,000 05,000e t 500, then 05 e t ( ) 500 ln t, 05 ( ) 500 so t ln This corresponds to the date , 05 which occurs during the year 07. ( ) 500 For (D), the process is the same, except that then t ln.75. This 0 occurs during the year 00. Grading: + points for the equation P (t) , + points for solving for t, + point for finding the year. Grading for common mistakes: 3 points if the model was assumed to be linear. ) 4
5 7. [5 pts] Evaluate the expression log 4 64 log 4 6 Solution: The quick way to do this (for C) is to notice that , so log 4 64 log 4 log log log The change of base formula can also be used: For (D), form. 64 log 4 64 log 0 log log 4 6 log 4 log log 4 4 log 4 4. Grading for common mistakes: + points total if the formula was converted to exponential 8. [5 pts] Rewrite the expression { 5 3 } in logarithmic form. 8 Solution: For (C): log 5 5 3; for (D): log Grading for common mistakes: points if two numbers were in the wrong position; 3 points if no number was in the correct position; point for log 3 8 (no ). } 9. Consider the function given by y { e 4x e x a. [5 pts] Graph this function and its inverse function on the same set of axes.. Solution: The inverse function is the reflection of the function y e 4x about the line y x. See the webpage. Grading: points for ln x, log x, ln 4x, log 4 x; 3 points for e 4x, e 4x, e 4x, e 4x, e x, e x, e x, e x. b. [5 pts] State the inverse function. Solution: To find the inverse of the function y e 4x (version C), solve for x in terms of y: ln y log e y 4x, so x 4 ln y. Thus the inverse function is g(x) 4 ln x. For (D), the inverse function is ln x. Grading: point for ln x, log x, ln 4x, log 4 x; 3 points for e 4x, e 4x, e 4x, e 4x, e x, e x, e x, e x. c. [5 pts] Label the functions, asymptotes and intercepts. Solution: There is only one asymptote for the original function, y 0, and the original function intersects the y-axis at (0, ) (and nowhere else). The inverse function has a vertical asymptote x 0, and it intersects the x-axis at (, 0). Grading: + point for labelling the functions, + point for each asymptote, and + point for each intercept. 5
6 0. Using the properties of logarithms, a. [5 pts] Write the following as a sum, difference, or multiple of logarithms: ( ) 5x ln y 3 ( ) 6x ln y 4 Solution: For (C): For (D): ln ln ( ) 5x y 3 ln(5x) ln(y 3 ) ln(5) + ln x 3 ln y. ( ) 6x y 4 ln(6x) ln(y 4 ) ln(6) + ln x 4 ln y. Grading: +3 points for the first equality, + points for the second (one point for splitting up 5x or 6x, and one point for rewriting ln y 3 or ln y 4 ). b. [5 pts] Write as a single logarithm: ln x + ln(x + 4) 6 ln y 4 ln z 5 6 ln x + 9 ln(x + ) 3 ln y ln z 7 Solution: The best way to write this as a single logarithm is to group together the terms which are being added, and group together the ones which are being subtracted. Then, for (C), for (D): 5 ln x + ln(x + 4) 6 ln y 4 ln z ln x/5 + ln(x + 4) ln y 6 ln z 4 [ ln x /5 + ln(x + 4) ] [ ln y 6 + ln z 4] ( x ln x /5 (x + 4) ln y 6 z 4 /5 (x + 4) ) ln y 6 z 4 ; 6 7 ln x + 9 ln(x + ) 3 ln y ln z ln x6/7 + ln(x + ) 9 ln y 3 ln z [ ln x 6/7 + ln(x + ) 9] [ ln y 3 + ln z ] ( x ln x 6/7 (x + ) 9 ln y 3 z 6/7 (x + ) 9 ) ln y 3 z. Grading for common mistakes: +3 points total for ln x/5 ln(x + 4) ln y 6 ln z 4 (C) or ln x6/7 ln(x + ) 9 ln y 3 ln z (D); point if the ln was omitted;. 6
7 . In the Fall Semester, students in a psychology class with a size of 00 were told they would be given a memory test the following semester. The test was graded out of 00 points. The test went like this: In the following Spring Semester, the students were shown pictures of their classmates from the previous Fall. They were to identify the picture with the name of the student. The students were given the same test for the next 5 months. The average score of the memory test was given by the model: 80 5 log0 (t + 3) f(t), 0 t 5, log 0 (t + 7) where t is the time in months. a. [5 pts] What was the average score of the original exam? Solution: The average score of the original exam is f(0). For (C), this is 80 5 log 0 (0+3) 77.6; for (D), it is log 0 (0 + 7) 73.. Grading: + points for t 0; +3 points for evaluating f(0). Grading for common mistakes: point for arithmetic; points for a problem with evaluating the log 0 factor; points for 80 (C) or 78. (D). b. [5 pts] What would you predict, from this model, the average score of the exam to be after two years? Solution: Since t is the time in months since the initial exam, t 4. Then the (expected) average score after two years is f(4), which is 80 5 log 0 (7) 7.8 (for C) or log 0(3) 69.5 (for D). Grading: + points for t 4, +3 points for evaluating f(t). Grading for common mistakes: point for t. c. [5 pts] When would you expect the average score to be 65 %? 60 Solution: This problem had some unexpected leeway. The intended objective was to determine the value of t for which f(t) 65 (for C) or 60 (for D). For version C, this means solving the equation 80 5 log 0 (t + 3) 65, which is done as follows: Version C 80 5 log 0 (t + 3) log 0 (t + 3) 3 log 0 (t + 3) t t Version D log 0 (t + 7) log 0 (t + 7) 73/90 log 0 (t + 7) t /90 t 0 73/ (Note that 997 months is approximately 83 years, and 073 months is approximately 89 / years. This shows that the model has probably been stretched too far; how many 0-year-olds can remember 65% of their classmates at age 8?) Some people evidently evaluated f(t) for increasing values of t (or graphed the function and traced or zoomed in on the graph) until a value of 65.9 was obtained, and the value of t was then noted. For version C of the test, this occurs at t 663, and for version D at t 79. Full credit 7
8 was given for any value of t in the appropriate range, provided there was enough supporting work. Grading; + points for the equation f(t) 65 (or 60), +3 points for finding t. Grading for common errors: points if f(t) was assumed to be linear; +3 points total for a correct answer but no work. Full credit was given for any value of t between 663 and 997 for version C, and for any value of t between 79 and 073 for version D.. [5 pts] Complete the table below for a savings account in which interest is compounded continuously. Initial Investment Annual % Rate Time to Double Amount after 4,000 3 $ years 6, years 8 Solution: Since the interest is compounded continually, we need to use the formula A P e rt. To find the amount after 0 years (8 years for version D), we will need the annual interest rate, so we have to find the Annual % Rate first. The doubling time of our investment is 3 years (5 years for D), so we need to solve the equation for C, and for D. This we do as follows: Version C e 3r e 3r 3r ln e r e r 5 Version D e 5r e 5r 5r ln r ln r ln Thus 3.% goes under Annual % Rate for version C, and 3.9% goes under Annual % Rate for version D. To find the amount after a certain number of years, we just need to find A: for (C), and A 4000 e $40,97.70 A 6000 e $8,88.60 for (D). This number goes under Amount after X years. Grading: +3 points for the annual interest rate, + points for the amount after 8 or 0 years. Grading for common mistakes: points if the amount after 8 (or 0) years was not in dollars (but some other units). Round-off errors resulted in slightly different answers; these were checked as they occured. MAT 7 Website: checkman/7/ 8
Intermediate Algebra Chapter 12 Review
 Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 Review Set up a Table of Coordinates and graph the given functions. Find the y-intercept. Label at least three points on the graph. Your graph must have the correct shape.
Intermediate Algebra Chapter 1 Review Set up a Table of Coordinates and graph the given functions. Find the y-intercept. Label at least three points on the graph. Your graph must have the correct shape.
The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts.
 Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Math 141 Review for Final The final is cumulative, but with more emphasis on chapters 3 and 4. There will be two parts. Part 1 (no calculator) graphing (polynomial, rational, linear, exponential, and logarithmic
Math 137 Exam #3 Review Guide
 Math 7 Exam # Review Guide The third exam will cover Sections.-.6, 4.-4.7. The problems on this review guide are representative of the type of problems worked on homework and during class time. Do not
Math 7 Exam # Review Guide The third exam will cover Sections.-.6, 4.-4.7. The problems on this review guide are representative of the type of problems worked on homework and during class time. Do not
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. (b) Find the center and the radius of the circle given above.
 INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
INTERNET MAT 117 Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (b) Find the center and
Mock Final Exam Name. Solve and check the linear equation. 1) (-8x + 8) + 1 = -7(x + 3) A) {- 30} B) {- 6} C) {30} D) {- 28}
 Mock Final Exam Name Solve and check the linear equation. 1) (-8x + 8) + 1 = -7(x + 3) 1) A) {- 30} B) {- 6} C) {30} D) {- 28} First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the
Mock Final Exam Name Solve and check the linear equation. 1) (-8x + 8) + 1 = -7(x + 3) 1) A) {- 30} B) {- 6} C) {30} D) {- 28} First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the
INTERNET MAT 117. Solution for the Review Problems. (1) Let us consider the circle with equation. x 2 + 2x + y 2 + 3y = 3 4. (x + 1) 2 + (y + 3 2
 INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
INTERNET MAT 117 Solution for the Review Problems (1) Let us consider the circle with equation x 2 + y 2 + 2x + 3y + 3 4 = 0. (a) Find the standard form of the equation of the circle given above. (i) Group
Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function.
 Test Instructions Objectives Section 5.1 Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function. Form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Graph
Test Instructions Objectives Section 5.1 Section 5.1 Determine if a function is a polynomial function. State the degree of a polynomial function. Form a polynomial whose zeros and degree are given. Graph
Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet. Calculator Questions
 Name: Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet Calculator Questions 1. Solve the equation. Check for extraneous solutions. (Sec. 1.6) 2 8 37 2. Graph the inequality 31. (Sec. 2.8) 3. If y varies directly
Name: Algebra II CP Final Exam Review Packet Calculator Questions 1. Solve the equation. Check for extraneous solutions. (Sec. 1.6) 2 8 37 2. Graph the inequality 31. (Sec. 2.8) 3. If y varies directly
GOOD LUCK! 2. a b c d e 12. a b c d e. 3. a b c d e 13. a b c d e. 4. a b c d e 14. a b c d e. 5. a b c d e 15. a b c d e. 6. a b c d e 16.
 MA109 College Algebra Fall 2018 Practice Final Exam 2018-12-12 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be
MA109 College Algebra Fall 2018 Practice Final Exam 2018-12-12 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. You have two hours to do this exam. No books or notes may be
Review questions for Math 111 final. Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points
 Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points 1. True or False questions (17 pts) a. Common Logarithmic functions cross the y axis at (0,1) b. A square matrix has as many
Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points 1. True or False questions (17 pts) a. Common Logarithmic functions cross the y axis at (0,1) b. A square matrix has as many
1.) Suppose the graph of f(x) looks like this (each tick mark denotes 1 unit). x y
 College Algebra Summer 2014 Exam File Exam #1 1.) Suppose the graph of f(x) looks like this (each tick mark denotes 1 unit). Graph g(x) = -0.5 f(x + 1) - 3 2.) Consider the following table of values. x
College Algebra Summer 2014 Exam File Exam #1 1.) Suppose the graph of f(x) looks like this (each tick mark denotes 1 unit). Graph g(x) = -0.5 f(x + 1) - 3 2.) Consider the following table of values. x
CHAPTER FIVE. Solutions for Section 5.1. Skill Refresher. Exercises
 CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 265 Solutions for Section 5.1 Skill Refresher S1. Since 1,000,000 = 10 6, we have x = 6. S2. Since 0.01 = 10 2, we have t = 2. S3. Since e 3 = ( e 3) 1/2 = e 3/2, we have z =
CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 265 Solutions for Section 5.1 Skill Refresher S1. Since 1,000,000 = 10 6, we have x = 6. S2. Since 0.01 = 10 2, we have t = 2. S3. Since e 3 = ( e 3) 1/2 = e 3/2, we have z =
Name Advanced Math Functions & Statistics. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C.
 1. Compare and contrast the following graphs. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C. 2. For R, S, and T as defined below, which of the following products is undefined? A. RT B. TR C. TS D. ST E. RS
1. Compare and contrast the following graphs. Non- Graphing Calculator Section A. B. C. 2. For R, S, and T as defined below, which of the following products is undefined? A. RT B. TR C. TS D. ST E. RS
f(x) = 2x + 5 3x 1. f 1 (x) = x + 5 3x 2. f(x) = 102x x
 1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = 3
 Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
Example. Determine the inverse of the given function (if it exists). f(x) = g(x) = p x + x We know want to look at two di erent types of functions, called logarithmic functions and exponential functions.
The Exponential function f with base b is f (x) = b x where b > 0, b 1, x a real number
 Chapter 4: 4.1: Exponential Functions Definition: Graphs of y = b x Exponential and Logarithmic Functions The Exponential function f with base b is f (x) = b x where b > 0, b 1, x a real number Graph:
Chapter 4: 4.1: Exponential Functions Definition: Graphs of y = b x Exponential and Logarithmic Functions The Exponential function f with base b is f (x) = b x where b > 0, b 1, x a real number Graph:
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
3 Polynomial and Rational Functions 3.1 Polynomial Functions and their Graphs So far, we have learned how to graph polynomials of degree 0, 1, and. Degree 0 polynomial functions are things like f(x) =,
Lesson 5 Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Lesson 5 Section 5.1: Linear Functions vs. Exponential Functions 1. Complete the table below. Function Linear or Exponential? Linear: Increasing or Decreasing? Exponential: Growth or Decay?
Name: Date: Lesson 5 Section 5.1: Linear Functions vs. Exponential Functions 1. Complete the table below. Function Linear or Exponential? Linear: Increasing or Decreasing? Exponential: Growth or Decay?
ALGEBRA 2 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
 Class: Date: ALGEBRA 2 FINAL EXAM REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Classify 6x 5 + x + x 2 + by degree. quintic c. quartic cubic d.
Class: Date: ALGEBRA 2 FINAL EXAM REVIEW Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. Classify 6x 5 + x + x 2 + by degree. quintic c. quartic cubic d.
Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications
 34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
34 Section 4.2 Logarithmic Functions & Applications Recall that exponential functions are one-to-one since every horizontal line passes through at most one point on the graph of y = b x. So, an exponential
+ i sin. + i sin. = 2 cos
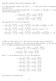 Math 11 Lesieutre); Exam review I; December 4, 017 1. a) Find all complex numbers z for which z = 8. Write your answers in rectangular non-polar) form. We are going to use de Moivre s theorem. For 1, r
Math 11 Lesieutre); Exam review I; December 4, 017 1. a) Find all complex numbers z for which z = 8. Write your answers in rectangular non-polar) form. We are going to use de Moivre s theorem. For 1, r
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Learning Targets 1. I can evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. 2. I can solve problems involving exponential growth & decay. 3. I can evaluate expressions
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Learning Targets 1. I can evaluate, analyze, and graph exponential functions. 2. I can solve problems involving exponential growth & decay. 3. I can evaluate expressions
More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4
 MATH 11009: More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4 Dividend: The number or expression you are dividing into. Divisor: The number or expression you are dividing by. Synthetic division: Synthetic division
MATH 11009: More Polynomial Equations Section 6.4 Dividend: The number or expression you are dividing into. Divisor: The number or expression you are dividing by. Synthetic division: Synthetic division
MAC Module 8. Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I. Learning Objectives. - Exponential Functions - Logarithmic Functions
 MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I. Rev.S08
 MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
MAC 1105 Module 8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions I Learning Objectives Upon completing this module, you should be able to: 1. Distinguish between linear and exponential growth. 2. Model data with
Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts. d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2., y 1 + y 2. ( x 1 + x 2 2
 Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts 1. The distance between the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2. 2. The midpoint of the line segment from A(x
Internet Mat117 Formulas and Concepts 1. The distance between the points A(x 1, y 1 ) and B(x 2, y 2 ) in the plane is d(a, B) = (x 2 x 1 ) 2 + (y 2 y 1 ) 2. 2. The midpoint of the line segment from A(x
d. What are the steps for finding the y intercepts algebraically?(hint: what is equal to 0?)
 st Semester Pre Calculus Exam Review You will not receive hints on your exam. Make certain you know how to answer each of the following questions. This is a test grade. Your WORK and EXPLANATIONS are graded
st Semester Pre Calculus Exam Review You will not receive hints on your exam. Make certain you know how to answer each of the following questions. This is a test grade. Your WORK and EXPLANATIONS are graded
Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review
 Name: Class: Date: Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review Directions: You may write on this review packet. Remember that this packet is similar to the questions that you will have on your final exam. Attempt
Name: Class: Date: Algebra 2 Honors: Final Exam Review Directions: You may write on this review packet. Remember that this packet is similar to the questions that you will have on your final exam. Attempt
Please print the following information in case your scan sheet is misplaced:
 MATH 1100 Common Final Exam FALL 010 December 10, 010 Please print the following information in case your scan sheet is misplaced: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The exam consists of 40 multiple
MATH 1100 Common Final Exam FALL 010 December 10, 010 Please print the following information in case your scan sheet is misplaced: Name: Instructor: Student ID: Section/Time: The exam consists of 40 multiple
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment. Due Date: First day of school.
 AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: Due Date: First day of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus AB. All of the
AP Calculus AB Summer Assignment Name: Due Date: First day of school. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Calculus AB. All of the
College Algebra and College Algebra with Review Final Review
 The final exam comprises 30 questions. Each of the 20 multiple choice questions is worth 3 points and each of the 10 open-ended questions is worth 4 points. Instructions for the Actual Final Exam: Work
The final exam comprises 30 questions. Each of the 20 multiple choice questions is worth 3 points and each of the 10 open-ended questions is worth 4 points. Instructions for the Actual Final Exam: Work
My Math Plan Assessment #3 Study Guide
 My Math Plan Assessment # Study Guide 1. Identify the vertex of the parabola with the given equation. f(x) = (x 5) 2 7 2. Find the value of the function. Find f( 6) for f(x) = 2x + 11. Graph the linear
My Math Plan Assessment # Study Guide 1. Identify the vertex of the parabola with the given equation. f(x) = (x 5) 2 7 2. Find the value of the function. Find f( 6) for f(x) = 2x + 11. Graph the linear
EXAM 3 Tuesday, March 18, 2003
 MATH 12001 Precalculus: Algebra & Trigonometry Spring 2003 Sections 2 & 3 Darci L. Kracht Name: Score: /100. 115 pts available EXAM 3 Tuesday, March 18, 2003 Part I: NO CALCULATORS. (You must turn this
MATH 12001 Precalculus: Algebra & Trigonometry Spring 2003 Sections 2 & 3 Darci L. Kracht Name: Score: /100. 115 pts available EXAM 3 Tuesday, March 18, 2003 Part I: NO CALCULATORS. (You must turn this
MATH 32 FALL 2013 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS. 1 cos( 2. is in the first quadrant, so its sine is positive. Finally, csc( π 8 ) = 2 2.
 MATH FALL 01 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS (1) (1 points) Evalute the following (a) tan(0) Solution: tan(0) = 0. (b) csc( π 8 ) Solution: csc( π 8 ) = 1 sin( π 8 ) To find sin( π 8 ), we ll use the half angle formula:
MATH FALL 01 FINAL EXAM SOLUTIONS (1) (1 points) Evalute the following (a) tan(0) Solution: tan(0) = 0. (b) csc( π 8 ) Solution: csc( π 8 ) = 1 sin( π 8 ) To find sin( π 8 ), we ll use the half angle formula:
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3 x 9 D) 27. y 4 D) -8x 3 y 6.
 Precalculus Review - Spring 018 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the exponential expression. Assume that variables represent
Precalculus Review - Spring 018 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the exponential expression. Assume that variables represent
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
3 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 3.2 Logarithmic Functions and Their Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. What You Should Learn
Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review
 Class: Date: Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review Short Answer. Evaluate the series 5n. 8 n =. Evaluate the series (n + ). n = What is the sum of the finite arithmetic series?. 9+ + 5+ 8+ + + 59. 6 + 9
Class: Date: Algebra II Honors Final Exam Review Short Answer. Evaluate the series 5n. 8 n =. Evaluate the series (n + ). n = What is the sum of the finite arithmetic series?. 9+ + 5+ 8+ + + 59. 6 + 9
Lecture 7: Sections 2.3 and 2.4 Rational and Exponential Functions. Recall that a power function has the form f(x) = x r where r is a real number.
 L7-1 Lecture 7: Sections 2.3 and 2.4 Rational and Exponential Functions Recall that a power function has the form f(x) = x r where r is a real number. f(x) = x 1/2 f(x) = x 1/3 ex. Sketch the graph of
L7-1 Lecture 7: Sections 2.3 and 2.4 Rational and Exponential Functions Recall that a power function has the form f(x) = x r where r is a real number. f(x) = x 1/2 f(x) = x 1/3 ex. Sketch the graph of
Lesson 6 Practice Problems
 Name: Date: Lesson 6 Section 6.1: Writing Exponential Models 1. Complete the following table. Growth Rate as a % Growth Rate as a decimal Growth Factor 13% 0.13 1.13 21% 7% 0.20 0.05 1.25 1.075 2.03 2.
Name: Date: Lesson 6 Section 6.1: Writing Exponential Models 1. Complete the following table. Growth Rate as a % Growth Rate as a decimal Growth Factor 13% 0.13 1.13 21% 7% 0.20 0.05 1.25 1.075 2.03 2.
4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
 590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
590 Chapter 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.4 Graphs of Logarithmic Functions In this section, you will: Learning Objectives 4.4.1 Identify the domain of a logarithmic function. 4.4.2 Graph logarithmic
5.1. EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS
 5.1. EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS 1 What You Should Learn Recognize and evaluate exponential functions with base a. Graph exponential functions and use the One-to-One Property. Recognize, evaluate,
5.1. EXPONENTIAL FUNCTIONS AND THEIR GRAPHS 1 What You Should Learn Recognize and evaluate exponential functions with base a. Graph exponential functions and use the One-to-One Property. Recognize, evaluate,
MAT 210 Test #1 Solutions, Form A
 1. Where are the following functions continuous? a. ln(x 2 1) MAT 210 Test #1 Solutions, Form A Solution: The ln function is continuous when what you are taking the log of is positive. Hence, we need x
1. Where are the following functions continuous? a. ln(x 2 1) MAT 210 Test #1 Solutions, Form A Solution: The ln function is continuous when what you are taking the log of is positive. Hence, we need x
Practice Test - Chapter 2
 Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.1 Exponential Functions Definition 4.1 If a > 0 and a 1, then the exponential function with base a is given by fx) = a x. Examples: fx) = x, gx) = 10 x, hx) =
4 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 4.1 Exponential Functions Definition 4.1 If a > 0 and a 1, then the exponential function with base a is given by fx) = a x. Examples: fx) = x, gx) = 10 x, hx) =
A repeated root is a root that occurs more than once in a polynomial function.
 Unit 2A, Lesson 3.3 Finding Zeros Synthetic division, along with your knowledge of end behavior and turning points, can be used to identify the x-intercepts of a polynomial function. This information allows
Unit 2A, Lesson 3.3 Finding Zeros Synthetic division, along with your knowledge of end behavior and turning points, can be used to identify the x-intercepts of a polynomial function. This information allows
Final Exam Review: Study Guide Math 3
 Final Exam Review: Study Guide Math 3 Name: Day 1 Functions, Graphing, Regression Relation: Function: Domain: Range: Asymptote: Hole: Graphs of Functions f(x) = x f(x) = f(x) = x f(x) = x 3 Key Ideas Key
Final Exam Review: Study Guide Math 3 Name: Day 1 Functions, Graphing, Regression Relation: Function: Domain: Range: Asymptote: Hole: Graphs of Functions f(x) = x f(x) = f(x) = x f(x) = x 3 Key Ideas Key
Practice Test - Chapter 2
 Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Graph and analyze each function. Describe the domain, range, intercepts, end behavior, continuity, and where the function is increasing or decreasing. 1. f (x) = 0.25x 3 Evaluate the function for several
Algebra II: Chapter 4 Semester Review Multiple Choice: Select the letter that best answers the question. D. Vertex: ( 1, 3.5) Max. Value: 1.
 Algebra II: Chapter Semester Review Name Multiple Choice: Select the letter that best answers the question. 1. Determine the vertex and axis of symmetry of the. Determine the vertex and the maximum or
Algebra II: Chapter Semester Review Name Multiple Choice: Select the letter that best answers the question. 1. Determine the vertex and axis of symmetry of the. Determine the vertex and the maximum or
3.3 Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions
 71_00.qxp 12/27/06 1:25 PM Page 276 276 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions. Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions Long Division of Polynomials Consider the graph of f x 6x 19x 2 16x 4. Notice in Figure.2
71_00.qxp 12/27/06 1:25 PM Page 276 276 Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions. Real Zeros of Polynomial Functions Long Division of Polynomials Consider the graph of f x 6x 19x 2 16x 4. Notice in Figure.2
Final Exam C Name i D) 2. Solve the equation by factoring. 4) x2 = x + 72 A) {1, 72} B) {-8, 9} C) {-8, -9} D) {8, 9} 9 ± i
 Final Exam C Name First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the equation. 7 ) x + + 3 x - = 6 (x + )(x - ) ) A) No restrictions; {} B) x -, ; C) x -; {} D) x -, ; {2} Add
Final Exam C Name First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the equation. 7 ) x + + 3 x - = 6 (x + )(x - ) ) A) No restrictions; {} B) x -, ; C) x -; {} D) x -, ; {2} Add
MAT 107 College Algebra Fall 2013 Name. Final Exam, Version X
 MAT 107 College Algebra Fall 013 Name Final Exam, Version X EKU ID Instructor Part 1: No calculators are allowed on this section. Show all work on your paper. Circle your answer. Each question is worth
MAT 107 College Algebra Fall 013 Name Final Exam, Version X EKU ID Instructor Part 1: No calculators are allowed on this section. Show all work on your paper. Circle your answer. Each question is worth
Polynomials. Exponents. End Behavior. Writing. Solving Factoring. Graphing. End Behavior. Polynomial Notes. Synthetic Division.
 Polynomials Polynomials 1. P 1: Exponents 2. P 2: Factoring Polynomials 3. P 3: End Behavior 4. P 4: Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Writing real root x= 10 or (x+10) local maximum Exponents real root x=10
Polynomials Polynomials 1. P 1: Exponents 2. P 2: Factoring Polynomials 3. P 3: End Behavior 4. P 4: Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Writing real root x= 10 or (x+10) local maximum Exponents real root x=10
Math M111: Lecture Notes For Chapter 10
 Math M: Lecture Notes For Chapter 0 Sections 0.: Inverse Function Inverse function (interchange and y): Find the equation of the inverses for: y = + 5 ; y = + 4 3 Function (from section 3.5): (Vertical
Math M: Lecture Notes For Chapter 0 Sections 0.: Inverse Function Inverse function (interchange and y): Find the equation of the inverses for: y = + 5 ; y = + 4 3 Function (from section 3.5): (Vertical
Part I: Multiple Choice Questions
 Name: Part I: Multiple Choice Questions. What is the slope of the line y=3 A) 0 B) -3 ) C) 3 D) Undefined. What is the slope of the line perpendicular to the line x + 4y = 3 A) -/ B) / ) C) - D) 3. Find
Name: Part I: Multiple Choice Questions. What is the slope of the line y=3 A) 0 B) -3 ) C) 3 D) Undefined. What is the slope of the line perpendicular to the line x + 4y = 3 A) -/ B) / ) C) - D) 3. Find
Final Exam A Name. 20 i C) Solve the equation by factoring. 4) x2 = x + 30 A) {-5, 6} B) {5, 6} C) {1, 30} D) {-5, -6} -9 ± i 3 14
 Final Exam A Name First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the equation. 1 1) x + 3 + 5 x - 3 = 30 (x + 3)(x - 3) 1) A) x -3, 3; B) x -3, 3; {4} C) No restrictions; {3} D)
Final Exam A Name First, write the value(s) that make the denominator(s) zero. Then solve the equation. 1 1) x + 3 + 5 x - 3 = 30 (x + 3)(x - 3) 1) A) x -3, 3; B) x -3, 3; {4} C) No restrictions; {3} D)
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 4
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 2 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 2 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 2 1.3 Algebraic
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 2 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 2 1.2 Factoring Polynomials........................................ 2 1.3 Algebraic
INSTRUCTIONS USEFUL FORMULAS
 MATH 1100 College Algebra Spring 18 Exam 1 February 15, 2018 Name Student ID Instructor Class time INSTRUCTIONS 1. Do not open until you are told to do so. 2. Do not ask questions during the exam. 3. CAREFULLY
MATH 1100 College Algebra Spring 18 Exam 1 February 15, 2018 Name Student ID Instructor Class time INSTRUCTIONS 1. Do not open until you are told to do so. 2. Do not ask questions during the exam. 3. CAREFULLY
H-Pre-Calculus Targets Chapter I can write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of the function.
 H-Pre-Calculus Targets Chapter Section. Sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.. I can write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of the function. Identify
H-Pre-Calculus Targets Chapter Section. Sketch and analyze graphs of quadratic functions.. I can write quadratic functions in standard form and use the results to sketch graphs of the function. Identify
CURRICULUM CATALOG. Algebra II (3135) VA
 2018-19 CURRICULUM CATALOG Algebra II (3135) VA Table of Contents COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 2: LINEAR FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT 3: INEQUALITIES AND ABSOLUTE VALUE... 2 UNIT
2018-19 CURRICULUM CATALOG Algebra II (3135) VA Table of Contents COURSE OVERVIEW... 1 UNIT 1: STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS... 1 UNIT 2: LINEAR FUNCTIONS... 2 UNIT 3: INEQUALITIES AND ABSOLUTE VALUE... 2 UNIT
MAT 111 Final Exam Fall 2013 Name: If solving graphically, sketch a graph and label the solution.
 MAT 111 Final Exam Fall 2013 Name: Show all work on test to receive credit. Draw a box around your answer. If solving algebraically, show all steps. If solving graphically, sketch a graph and label the
MAT 111 Final Exam Fall 2013 Name: Show all work on test to receive credit. Draw a box around your answer. If solving algebraically, show all steps. If solving graphically, sketch a graph and label the
A Partial List of Topics: Math Spring 2009
 A Partial List of Topics: Math 112 - Spring 2009 This is a partial compilation of a majority of the topics covered this semester and may not include everything which might appear on the exam. The purpose
A Partial List of Topics: Math 112 - Spring 2009 This is a partial compilation of a majority of the topics covered this semester and may not include everything which might appear on the exam. The purpose
Course Outline. Linear Equations Linear Inequalities (1.6)
 Course Outline Functions/Graphing Solving Equations Applications Definitions of function, graph, domain, range, x- and y- intercepts, vertical line test(.-.) Linear functions (.-.5) -Parallel and perpendicular
Course Outline Functions/Graphing Solving Equations Applications Definitions of function, graph, domain, range, x- and y- intercepts, vertical line test(.-.) Linear functions (.-.5) -Parallel and perpendicular
Transformations of Functions and Exponential Functions January 24, / 35
 Exponential Functions January 24, 2017 Exponential Functions January 24, 2017 1 / 35 Review of Section 1.2 Reminder: Week-in-Review, Help Sessions, Oce Hours Mathematical Models Linear Regression Function
Exponential Functions January 24, 2017 Exponential Functions January 24, 2017 1 / 35 Review of Section 1.2 Reminder: Week-in-Review, Help Sessions, Oce Hours Mathematical Models Linear Regression Function
8 + 6) x 2 ) y = h(x)
 . a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
. a. Horizontal shift 6 left and vertical shift up. Notice B' is ( 6, ) and B is (0, 0). b. h(x) = 0.5(x + 6) + (Enter in a grapher to check.) c. Use the graph. Notice A' to see h(x) crosses the x-axis
ID: ID: ID: of 39 1/18/ :43 AM. Student: Date: Instructor: Alfredo Alvarez Course: 2017 Spring Math 1314
 1 of 39 1/18/017 10:43 AM Student: Date: Instructor: Alfredo Alvarez Course: 017 Spring Math 1314 Assignment: Practice Final 1. Graph the equation. y= x 3 ID: 1.1-11. Perform the multiplication and write
1 of 39 1/18/017 10:43 AM Student: Date: Instructor: Alfredo Alvarez Course: 017 Spring Math 1314 Assignment: Practice Final 1. Graph the equation. y= x 3 ID: 1.1-11. Perform the multiplication and write
Final Exam Study Guide Mathematical Thinking, Fall 2003
 Final Exam Study Guide Mathematical Thinking, Fall 2003 Chapter R Chapter R contains a lot of basic definitions and notations that are used throughout the rest of the book. Most of you are probably comfortable
Final Exam Study Guide Mathematical Thinking, Fall 2003 Chapter R Chapter R contains a lot of basic definitions and notations that are used throughout the rest of the book. Most of you are probably comfortable
Teacher: Mr. Chafayay. Name: Class & Block : Date: ID: A. 3 Which function is represented by the graph?
 Teacher: Mr hafayay Name: lass & lock : ate: I: Midterm Exam Math III H Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question Which function is represented by the
Teacher: Mr hafayay Name: lass & lock : ate: I: Midterm Exam Math III H Multiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question Which function is represented by the
The above statement is the false product rule! The correct product rule gives g (x) = 3x 4 cos x+ 12x 3 sin x. for all angles θ.
 Math 7A Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 6-8 (Ebersole,.7-.4 (Stewart DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam. You
Math 7A Practice Midterm III Solutions Ch. 6-8 (Ebersole,.7-.4 (Stewart DISCLAIMER. This collection of practice problems is not guaranteed to be identical, in length or content, to the actual exam. You
Exponential Functions and Their Graphs (Section 3-1)
 Exponential Functions and Their Graphs (Section 3-1) Essential Question: How do you graph an exponential function? Students will write a summary describing the steps for graphing an exponential function.
Exponential Functions and Their Graphs (Section 3-1) Essential Question: How do you graph an exponential function? Students will write a summary describing the steps for graphing an exponential function.
Math 108 Final Exam Page 1 NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED.
 Math 108 Final Exam Page 1 Spring 2016 Answer Key NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED. Write a coherent, well organized, properly notated process or you will not receive credit for your answer. ALL work
Math 108 Final Exam Page 1 Spring 2016 Answer Key NO CALCULATORS OR CELL PHONES ALLOWED. Write a coherent, well organized, properly notated process or you will not receive credit for your answer. ALL work
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. C) x 8. C) y = x + 3 2
 Precalculus Fall Final Exam Review Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression. Assume that the variables
Precalculus Fall Final Exam Review Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression. Assume that the variables
7.1 Exponential Functions
 7.1 Exponential Functions 1. What is 16 3/2? Definition of Exponential Functions Question. What is 2 2? Theorem. To evaluate a b, when b is irrational (so b is not a fraction of integers), we approximate
7.1 Exponential Functions 1. What is 16 3/2? Definition of Exponential Functions Question. What is 2 2? Theorem. To evaluate a b, when b is irrational (so b is not a fraction of integers), we approximate
CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 4: Polynomial and Rational Functions 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models 4.2 Graphing Polynomial Functions 4.3 Polynomial
Final Exam Study Aid
 Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
Foundations of Math II Unit 5: Solving Equations
 Foundations of Math II Unit 5: Solving Equations Academics High School Mathematics 5.1 Warm Up Solving Linear Equations Using Graphing, Tables, and Algebraic Properties On the graph below, graph the following
Foundations of Math II Unit 5: Solving Equations Academics High School Mathematics 5.1 Warm Up Solving Linear Equations Using Graphing, Tables, and Algebraic Properties On the graph below, graph the following
Miller Objectives Alignment Math
 Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
Miller Objectives Alignment Math 1050 1 College Algebra Course Objectives Spring Semester 2016 1. Use algebraic methods to solve a variety of problems involving exponential, logarithmic, polynomial, and
Algebra 2B Semester Credit by Exam Information
 Algebra B Semester Credit by Exam Information Plano ISD Now uses the Texas Tech University ISD Credit by Exam Test for Algebra Format: second semester consists of 5 multiple choice questions and 5 open
Algebra B Semester Credit by Exam Information Plano ISD Now uses the Texas Tech University ISD Credit by Exam Test for Algebra Format: second semester consists of 5 multiple choice questions and 5 open
Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work.
 Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (4pts) Write two examples of each kind of number: natural integer rational irrational 2. (12pts) Simplify: ( a) 3 4 2 + 4 2 ) = 3 b) 3 20 7 15
Spring 06/MAT 140/Worksheet 1 Name: Show all your work. 1. (4pts) Write two examples of each kind of number: natural integer rational irrational 2. (12pts) Simplify: ( a) 3 4 2 + 4 2 ) = 3 b) 3 20 7 15
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
Calculus I - Homework Chapter 2 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Determine whether the graph is the graph of a function. 1) 1)
Final Review. Non-calculator problems are indicated. 1. (No calculator) Graph the function: y = x 3 + 2
 Algebra II Final Review Name Non-calculator problems are indicated. 1. (No calculator) Graph the function: y = x 3 + 2 2. (No calculator) Given the function y = -2 x + 3-1 and the value x = -5, find the
Algebra II Final Review Name Non-calculator problems are indicated. 1. (No calculator) Graph the function: y = x 3 + 2 2. (No calculator) Given the function y = -2 x + 3-1 and the value x = -5, find the
An equation of the form y = ab x where a 0 and the base b is a positive. x-axis (equation: y = 0) set of all real numbers
 Algebra 2 Notes Section 7.1: Graph Exponential Growth Functions Objective(s): To graph and use exponential growth functions. Vocabulary: I. Exponential Function: An equation of the form y = ab x where
Algebra 2 Notes Section 7.1: Graph Exponential Growth Functions Objective(s): To graph and use exponential growth functions. Vocabulary: I. Exponential Function: An equation of the form y = ab x where
Chapter Five Notes N P U2C5
 Chapter Five Notes N P UC5 Name Period Section 5.: Linear and Quadratic Functions with Modeling In every math class you have had since algebra you have worked with equations. Most of those equations have
Chapter Five Notes N P UC5 Name Period Section 5.: Linear and Quadratic Functions with Modeling In every math class you have had since algebra you have worked with equations. Most of those equations have
Chapter 1A -- Real Numbers. iff. Math Symbols: Sets of Numbers
 Fry Texas A&M University! Fall 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 1A! Page 1 Chapter 1A -- Real Numbers Math Symbols: iff or Example: Let A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16,...} and let B = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18,
Fry Texas A&M University! Fall 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 1A! Page 1 Chapter 1A -- Real Numbers Math Symbols: iff or Example: Let A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16,...} and let B = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18,
1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
 Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Princeton High School
 Princeton High School Mathematics Department PreCalculus Summer Assignment Summer assignment vision and purpose: The Mathematics Department of Princeton Public Schools looks to build both confidence and
Princeton High School Mathematics Department PreCalculus Summer Assignment Summer assignment vision and purpose: The Mathematics Department of Princeton Public Schools looks to build both confidence and
Algebra II End of Course Exam Answer Key Segment I. Scientific Calculator Only
 Algebra II End of Course Exam Answer Key Segment I Scientific Calculator Only Question 1 Reporting Category: Modeling & Problem Solving Common Core Standard: A-REI.4a: Solve quadratic equations in one
Algebra II End of Course Exam Answer Key Segment I Scientific Calculator Only Question 1 Reporting Category: Modeling & Problem Solving Common Core Standard: A-REI.4a: Solve quadratic equations in one
Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree
 Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Polynomial Function P(x) P(x) = a degree 0 P(x) = ax +b (degree 1) Graph Horizontal line through (0,a) line with y intercept (0,b) and slope a P(x) = ax
Section 4.2 Polynomial Functions of Higher Degree Polynomial Function P(x) P(x) = a degree 0 P(x) = ax +b (degree 1) Graph Horizontal line through (0,a) line with y intercept (0,b) and slope a P(x) = ax
3. Solve the following inequalities and express your answer in interval notation.
 Youngstown State University College Algebra Final Exam Review (Math 50). Find all Real solutions for the following: a) x 2 + 5x = 6 b) 9 x2 x 8 = 0 c) (x 2) 2 = 6 d) 4x = 8 x 2 e) x 2 + 4x = 5 f) 36x 3
Youngstown State University College Algebra Final Exam Review (Math 50). Find all Real solutions for the following: a) x 2 + 5x = 6 b) 9 x2 x 8 = 0 c) (x 2) 2 = 6 d) 4x = 8 x 2 e) x 2 + 4x = 5 f) 36x 3
COURSE SYLLABUS Part I Course Title: MATH College Algebra Credit Hours: 4, (4 Lecture 0 Lab G) OTM-TMM001
 COURSE SYLLABUS Part I Course Title: MATH 1340 - College Algebra Credit Hours: 4, (4 Lecture 0 Lab G) OTM-TMM001 Course Description: College Algebra in conjunction with MATH 1350, Pre-Calculus, provides
COURSE SYLLABUS Part I Course Title: MATH 1340 - College Algebra Credit Hours: 4, (4 Lecture 0 Lab G) OTM-TMM001 Course Description: College Algebra in conjunction with MATH 1350, Pre-Calculus, provides
for every x in the gomain of g
 Section.7 Definition of Inverse Function Let f and g be two functions such that f(g(x)) = x for every x in the gomain of g and g(f(x)) = x for every x in the gomain of f Under these conditions, the function
Section.7 Definition of Inverse Function Let f and g be two functions such that f(g(x)) = x for every x in the gomain of g and g(f(x)) = x for every x in the gomain of f Under these conditions, the function
3 Inequalities Absolute Values Inequalities and Intervals... 18
 Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 1. Factoring Polynomials........................................ 1. Algebraic and Fractional
Contents 1 Real Numbers, Exponents, and Radicals 1.1 Rationalizing the Denominator................................... 1. Factoring Polynomials........................................ 1. Algebraic and Fractional
CME Project, Algebra Correlated to: Michigan High School Content Expectations, Algebra 1
 STRAND 1: QUANTITATIVE LITERACY AND LOGIC STANDARD L1: REASONING ABOUT NUMBERS, SYSTEMS, AND QUANTITATIVE SITUATIONS Based on their knowledge of the properties of arithmetic, students understand and reason
STRAND 1: QUANTITATIVE LITERACY AND LOGIC STANDARD L1: REASONING ABOUT NUMBERS, SYSTEMS, AND QUANTITATIVE SITUATIONS Based on their knowledge of the properties of arithmetic, students understand and reason
. As x gets really large, the last terms drops off and f(x) ½x
 Pre-AP Algebra 2 Unit 8 -Lesson 3 End behavior of rational functions Objectives: Students will be able to: Determine end behavior by dividing and seeing what terms drop out as x Know that there will be
Pre-AP Algebra 2 Unit 8 -Lesson 3 End behavior of rational functions Objectives: Students will be able to: Determine end behavior by dividing and seeing what terms drop out as x Know that there will be
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
 Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Chapter Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency Simplify the expression. 1. 8x 9x 2. 25r 5 7r r + 3. 3 ( 3x 5) + + x. 3y ( 2y 5) + 11 5. 3( h 7) 7( 10 h) 2 2 +. 5 8x + 5x + 8x Find the volume or surface area
Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models
 Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models Learning Objectives: 1. Identify Polynomial Functions and Their Degree 2. Graph Polynomial Functions Using Transformations 3. Identify the Real Zeros of a Polynomial
Section 4.1: Polynomial Functions and Models Learning Objectives: 1. Identify Polynomial Functions and Their Degree 2. Graph Polynomial Functions Using Transformations 3. Identify the Real Zeros of a Polynomial
COLLEGE ALGEBRA FINAL REVIEW 9) 4 = 7. 13) 3log(4x 4) + 8 = ) Write as the sum of difference of logarithms; express powers as factors.
 Solve. 1) x 1 8 ) ( x ) x x 9 ) x 1 x 4) x + x 0 ) x + 9y 6) t t 4 7) y 8 4 x COLLEGE ALGEBRA FINAL REVIEW x 8) 81 x + 9) 4 7.07 x 10) 10 + 1e 10 11) solve for L P R K M + K L T 1) a) log x log( x+ 6)
Solve. 1) x 1 8 ) ( x ) x x 9 ) x 1 x 4) x + x 0 ) x + 9y 6) t t 4 7) y 8 4 x COLLEGE ALGEBRA FINAL REVIEW x 8) 81 x + 9) 4 7.07 x 10) 10 + 1e 10 11) solve for L P R K M + K L T 1) a) log x log( x+ 6)
PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS
 Name: Date : IM 3 UNIT TEST Linear Functions Teacher: Mr. Santowski and Mr. Smith Score: PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS SHOW ALL WORK AND WRITE ALL ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED. Maximum marks will
Name: Date : IM 3 UNIT TEST Linear Functions Teacher: Mr. Santowski and Mr. Smith Score: PART 1 - CALCULATOR ACTIVE QUESTIONS SHOW ALL WORK AND WRITE ALL ANSWERS IN THE SPACES PROVIDED. Maximum marks will
2015 2nd Semester Exam Review
 Algebra 2 2015 2nd Semester Exam Review 1. Write a function whose graph is a translation of the graph of the function in two directions. Describe the translation. 2. What are the solutions to the equation?
Algebra 2 2015 2nd Semester Exam Review 1. Write a function whose graph is a translation of the graph of the function in two directions. Describe the translation. 2. What are the solutions to the equation?
8.1 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Products. Learning Outcome To use properties of exponents involving products
 8.1 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Products Learning Outcome To use properties of exponents involving products Product of Powers Property Let a be a real number, and let m and n be positive integers.
8.1 Apply Exponent Properties Involving Products Learning Outcome To use properties of exponents involving products Product of Powers Property Let a be a real number, and let m and n be positive integers.
Chapter 14: Basics of Functions
 Math 91 Final Exam Study Guide Name Chapter 14: Basics of Functions Find the domain and range. 1) {(5,1), (5,-4), (6,7), (3,4), (-9,-6)} Find the indicated function value. 2) Find f(3) when f(x) = x2 +
Math 91 Final Exam Study Guide Name Chapter 14: Basics of Functions Find the domain and range. 1) {(5,1), (5,-4), (6,7), (3,4), (-9,-6)} Find the indicated function value. 2) Find f(3) when f(x) = x2 +
