Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
|
|
|
- Melina Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADPO TITLE: Unidirectional Anisotropy in Manganite Based Ferromagnetic-Antiferromagnetic Multilayers DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited This paper is part of the following report: TITLE: NATO Advanced Research Workshop on Nanostructured Films and Coatings. Series 3. High Technology - Volume 78 To order the complete compilation report, use: ADA The component part is provided here to allow users access to individually authored sections f proceedings, annals, symposia, etc. However, the component should be considered within [he context of the overall compilation report and not as a stand-alone technical report. The following component part numbers comprise the compilation report: ADPO11800 thru ADP UNCLASSIFIED
2 UNIDIRECTIONAL ANISOTROPY IN MANGANITE BASED FERROMAGNETIC-ANTIFERROMAGNETIC MULTILAYERS I. PANAGIOTOPOULOS 1, C. CHRISTIDES 2, M. PISSAS', AND D. NIARCHOS' 1. Institute ofmaterials Science, NCSR "Demokritos", Ag. Paraskevi Attiki, Greece 2. Department of Engineering Sciences, School of Engineering University of Patras, Patras, Greece 1. Introduction In mixed valence manganites a large negative magnetoresistance (MR), termed colossal magnetoresistance [1] (CMR), can be obtained due to a metal-insulator transition at the ferromagnetic Curie point [2]. However little progress has been made towards using these materials in applications, mainly due to the strong temperature dependence of the CMR effect and the large saturation fields (of the order of Tesla) required. Tunneling and grain boundary effects [3-8] as well as interface scattering [9] seem promising towards getting useful MR in these materials. In particular the high degree of spin polarization [10] makes these materials promising for spin-electronic device applications. In view of the above considerations, recently several publications have focused on the study of trilayers and multilayers based on mixed valence manganites [11-20]. The magnetic and magnetotransport properties of such structures are not a mere superposition of the response of the individual layers. This is a result of possible interface scattering [11-17], interlayer interactions [19,20] and stress effects due to lattice mismatch between the layers [11,12,14,16]. The sensitivity of double exchange and superexchange interactions to Mn-O bond lengths and Mn-O-Mn bond angles has been used as a structural tuning mechanism of magnetic and MR properties in bulk CMR manganites [21,22]. Such changes can be engineered through various substitutions that alter the configuration of Mn-O octahedra. In epitaxial thin films, strain due to lattice mismatch can give rise to structural deformations. Thus, depending on the substrate used, the film can be under ductile or tensile strain that results in changes of magnetic anisotropy and MR properties [23-27]. In what follows we report on the magnetic structural and MR properties of La 2 / 3 Ca 1 / 3 MnO3/Laj/ 3 Ca 2 / 3 MnO 3 multilayers showing exchange biasing effects. The La 2 / 3 Ca,, 3 MnO 3 layers are ferromagnetic (FM) and Lal/ 3 Cal/ 3 MnO 3 layers are antiferromagnetic (AF) [28]. The structural compatibility of the AF and FM layers permits coherent growth of the superlattices that satisfy the conditions for magnetic coupling at the interfaces. 177 G.M. Chow et al. (eds.), Nanostructured Films and Coatings, Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands.
3 178 The existence of unidirectional anisotropy due to exchange coupling between a FM and an AF phase was first reported in oxide-coated fine particles of Co [29]. The exchange anisotropy results in a displaced magnetic hysteresis loop when the sample is field cooled through the N6el temperature of the AF phase. In early studies, this loop displacement has been explained by assuming an ideal FM/AF interface with uncompensated moments in the atomic-plane of the AF layer at the FM/AF boundary [29]. Up to date exchange anisotropy effects have been studied mainly in AF/FM systems consisting of transition metal alloys and metallic oxides (e.g. FM= Co, NiFe, Fe 3 0 4, and AF=CoO, FeMn) [30], but not in manganites where the magnetic interactions cannot be described by direct-exchange. 2. Experimental details The films were deposited on (001) LaAIO 3 substrates by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) from bulk stoichiometric LanCai/ 3 MnO 3 target samples. The targets were prepared by standard solid state reaction from La 2 0 3, CaCO 3 and MnO 2 powders sintered at C for 5 days with two intermediate grindings. MR measurements were performed with a four-probe method and with the current parallel to the applied magnetic field. The 0-20 X-ray diffraction data were obtained with a Siemens D500 diffractometer using CUKR radiation and a secondary graphite monochromator. The magnetic measurements were performed in a SQUID magnetometer (Quandum Design). A series of Lav3Caj/3MnO 3 /Lal/ 3 CaWMnO 3 multilayers with equal AF (taf) and (tfm) FM layer thickness and bilayer thickness (A) ranging from 2 to 32 nm were grown along the (001) direction of the simple pseudocubic perovskite unit cell. The structural compatibility of the AF and FM layers permits coherent growth that favors magnetic coupling. In order to deposit in a multilayer form, the targets were mounted on a step-motor controlled rotatable carrier that allows the La2/3Ca 3 MnO 3 and Lal/3Ca2/3MnO 3 targets to be sequentially exposed in the beam path. The substrate was located at a distance of 6 cm from the target, by the edge of the visible extent of the plume. The substrate temperature (Ts) was C and the oxygen pressure in the chamber during the deposition was 0.03 Torr. The resulting rate at fluence of 1.5 J/cm 2 on the target was 0.4 A/pulse. 3. Structural Characterization The existence of the superstructure has been confirmed from the presence of lowangle superlattice Bragg-peaks and multiple satellite peaks around the (001), (002) and (003) Bragg-reflections of the constituents. In the low angle diffraction patterns the even order satellites are not observed due to the taf=tfm=a/ 2 condition.
4 , FM : I ilo ' I 8ML 0 M I o I ' 4 2l I ;I. v '¾.; I 0._I -2,, I (deg) Figure 1. The XRD pattern of a multilayer sample compared to those of single AF and FM layers. The main Bragg peak lies between the Bragg peaks observed in single AF and FM layer films and is surrounded by satellite peaks due to the layered structure (Fig. I). The existence of an average Bragg peak for A 510Onm indicates that for this range of bilayer thickness we have a coherent layer growth. The values of A were estimated by the formula A=nXcJ2(sin0n- sin0o) where 0, are diffraction angles of the n-th order satellite and 00 is the average Bragg peak, The (00t) LAO Bragg-peaks (f=1,2, and 3) interfere with the satellite peaks adjacent to the fundamental (zeroth order) peaks of the multilayer, introducing uncertainties in the quantitative analysis of the XRD spectra. Asymmetric intensity of the satellite peaks has been reported in multilayers in which a chemical and/or strained interfacial profile is assumed along the growth direction of the superlattice. Since for all the examined A values there are no traces of mixed (001) and (110) textures, cumulative roughness effects resulting to extra surface roughness and mosaic spread with increasing A can be excluded. 4. Magnetization and Magnetoresistance Measurements Magnetic hysteresis loops, measured at 10 K after cooling down from 300 K in zero field (ZFC) and in 10 koe (FC), for a LaAIO 3 /[FM(5 nm)/af(5 nm)]1 5 sample are shown in Fig.2. It is evident that the ZFC loop is symmetric around the zero field, while the FC loop is shifted towards negative fields. This effect can be attributed to exchange biasing at the AF/FM interface, since single-layered FM films do not exhibit any loop displacement after the FC process. If H, is the lower and H 2 is the higher field value where the average film magnetization becomes zero, then the exchange biasing field is
5 180 defined as the loop shift HEB= -(H 1 +H 2 )/2 and the coercivity as the halfwidth of the loop Hc=(H 1 -H 2 )/2. Thus, we calculate for the FC loop an HEB= Oe, and a Hc=800 Oe which is almost double compared to the Hc value obtained from the ZFC loop. Additional magnetic measurements were performed in order to investigate the origin of this effect. The temperature dependence of HEB and Hc values is shown in 1.0 -, zfc /.... '-- S... - H. -- FC H, Soo H (ke) Figure 2. Hysteresis loops, measured at 10 K Figure 3. Temperature dependence of exchnage after cooling down from 300 K in zero field biasing field (HEB) and coercive field (Hc) for (ZFC) and in 10 koe (FC), fo the A=10 rum A=10 rn multilayer. multilayer. Fig.3. These values were estimated from isothermal loops measured in constant temperature intervals, after FC the sample from 300 K down to 10 K in 10 koe and then warming up. It is evident that HEB decreases and disappears around the blocking temperature TB of 70 K. The Hc values exhibit a similar trend, indicating a connection between the mechanisms that give rise to coercivity and loop displacement. The excess coercivity observed below TB is induced by random exchange fields at the AF/FM interfaces. This low-temperature anisotropy can be treated as an additional energy barrier in the magnetic free energy, as in the case of superparamagnetic particles [23]. Since exchange biasing is an interface related phenomenon a strong dependence on the individual FM and AF layer thickness is expected. The maximum HEB is observed for the sample with A=10 nm. Hc follows the variation of HER with A, indicating that there is a significant contribution in Hc from the exchange anisotropy at the AF/FM interfaces. A decrease of HER at higher A is observed as expected due to the decreased contribution of the interfaces. However HEB also decreases at lower A due to the decreased contribution of the AF layers. Additional magnetic measurements were performed in order to investigate the origin of this effect. In Fig.4 the ZFC and FC measurements of the magnetization, normalized to the total FM volume of the sample, are shown for the above series of multilayers as a function of temperature. Both measurements were performed by warming up in 1 koe after having cooled in zero field and 10 koe respectively. The ZFC and FC curves coincide at temperatures higher than 100 K and become zero at about 250 K, where the Curie point Tc of the FM layers is expected. The ZFC curve exhibits a broad peak around the TB 70 K, whereas the FC curve exhibits a steep increase just below TB. It is reasonable to assume that in the FC measurement an increase of magnetization results from the alignment of interfacial magnetic moments, giving rise to unidirectional
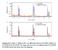
6 181,, FC A=2 nm_ A=5 nm 150 FC 1001 C 50 ZFC ZFC 0 ' 0C ', - 1 ' 200. I, I I 150 FC A=8nm 150 FC A=1"nm o s50 50 ZFC ,,.,, 200. a. 200 FC A=20 nm FC150 n FC A3n ZFC 50ZC 50 F T (K) Figure 4. Magnetization as a function of temperature for the series of [FM(A/2nm)/AF(A/2nm)] 15 multilayers. The measurements were performed by warming up in 1 koe after having cooled down to 10 K, in zero field (ZFC) and 10 koe (FC) respectively.
7 ' I ' 106 ' I ' A=2 nm-a=5 nm Ap/p %' 102 () 10' 6000 io (][" , 10, A=8 nm A=10 nm' O 10" 10 ' o 03 "14 102lO ~~ ':,-M o 0 10" 10' , A=20 nm A=32 nm !10, T (K) Figure 5. Resistivity, normalized to the 300 K value, as a function of temperature, measured in 50 koe (ph.) and in zero applied field (po) for the series of [FM(A/2)/AF(A/2)] 1 s multilayers. The CMR ratio Ap/pjro[po-prM/pH is plotted as a solid line.
8 anisotropy [161 below TB. Hence, the observed hump below TB in the ZFC curve can be attributed to thermally activated magnetic rotation over energy barriers caused by random exchange coupling at the AF/FM interfaces. Our magnetothermal measurements indicate that the TB does not change in the examined range of bilayer thickness and occurs at 70 K for all samples. To answer why TB remains more or less the same in the examined range of A values it is reasonable to consider that interfacial spin ordering is confined within a few atomic planes near the AF/FM interfaces, defining an active film volume Via. Thus, the appearance of exchange-biasing depends on the magnetic ordering of interfacial atomic planes which define a critical volume where thermal-activation energy becomes comparable to the magnetic energy at a certain blocking temperature, independent of A. Figure 5 shows the variation of the normalized resistivity as a function of temperature, measured in 50 koe (ph) and in zero applied field (po). The resistivity increases drastically as we cool down from 300 K, spanning almost four orders of magnitude. Also, the CMR ratio becomes maximum in the temperature range below TB. In Fig.5 the steep increase of resistivity at low temperatures is in contrast to the decrease of p observed in epitaxial FM films [24,25]. This provides further experimental evidence that the insulating behavior [26] of the AF layer is dominant at low-temperatures. This extra contribution in p is different for every specimen and modifies the shape of the resultant CMR curves (Fig.6). Clearly, the multilayers with A=5 and 8 nm exhibit a peak in the CMR response, indicating a special arrangement of spins at the AF/FM interfaces. As a consequence the characteristic CMR peak, that is usually reported nearby the ferromagnetic Tc of La2Caj/ 3 MnO 3 films [27] is not observed in the po versus temperature curve. This behavior is in agreement with the magnetothermal measurements (Fig.5), where it is evident that the most drastic change of the average film magnetization does not occur near the Tc of the individual FM layers but at TB Conclusion In summary, we have studied the variation of exchange biasing and coercive field as a function of A and temperature in La 2 / 3 Ca 1 / 3 MnO 3 ILalj 3 Cav 3 MnO 3 multilayers grown by PLD. The maximum HEB= 8 80 Oe was observed for the sample with A=10 mun. The exchange biasing mechanism sets-in below a blocking temperature of 70 K and induces: (i) an enhancement of Hc in the FC hysteresis loops, (ii) an increase of the MR ratio due to interface scattering around TB. It is interesting to note that in the series of multilayers studied here despite all variations in the AF and FM layer thicknesses TB does not vary considerably, signifying that the mechanism of spin ordering is confined within a few atomic planes near the AF/FM interfaces. This may be attributed to weak coupling of the interfacial spins to the core of the AF layer.
9 184 References 1. Jin, S., Tiefel, T.H., McCormack, M., Fatsnacht, R.A., Ramesh, R. Chen, L.H. (1994) Thousandfold change in resistivity in magnetioresistive La-Ca-Mn-O films, Science 264, Radaelli, P.G., Cox, D.E., Maresio, M., Cheong, S-W., Schiffer, P.E., and Ramirez, A.P. (1995) Simultaneous Structural, Magnetic, and Electronic Transitions in Lai.-CaMnO 3 with x=0.25 and x=0.50, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, Yu Lu, U, X.W., Gong, G.Q., Gang Xiao, Gupta, A., Lecoeur, P., Sun, J.Z., Wang, Y.Y. and Dravid, V.P. (1996) Large magnetotunneling effect at low magnetic fields in micrometer scale epitaxial Lao. 67 Sr MnO 3 tunnel junctions Phys. Rev. B54, R Mathur, N.D., Burnell, G., Isaac, S.P., Jackson, T.J., Teo, B.-S., MacManus-Driscoll, J.L., Cohen, L.F. Evetts, J.E. and Balmire, M.G. (1997) Large low field magnetoresistance in LaCaMnO induced by artificial grain boundaries, Nature 387, Steenbeck, K., Eick, T., Krisch, K., Schmidt, H-G., and Steinbeissh, E., (1998) Tunneling-like magnetoresistance in bicrystal LaSrMnO thin films, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, Srinitiwarawong, C.,and Ziese, M. (1998) Magnetoresistance of mechanically induced grain boundaries in LaCaMnO films, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, Ziese, M. (1999) Grain-boundary magnetoresistance: Spin-polarized inelastic tunneling through spinglass-like barrier, Phys. Rev. B60, R738-R Coey, J.M.D. (1999) Powder Magnetoresistance J. Appl. Phys. 85, Ziese, M., Sena, S., Shearwood, C., Blythe, H.J., Gibbs, M.R.J., Gehing, G.A. (1998) Voltage-controlled colossal magnetoresistance in manganite/normal-metal heterostructures Phys. Rev. B57, Wei, J.Y.T., Yeh, N.-C. Vasquez, R.P., Gupta, A., (1998) Tunneling evidence of half-metallicity in epitaxial films of ferromagnetic perovskite manganites and ferrimagnetic mangetite, J. Appl. Phys. 83, Gong, G.Q., Gupta, A., Gang Xiao, Lecoeur, P., and, McGuire, T.R., (1996) Perovskite oxide superlattices: magnetotransport and magnetic properties Phys. Rev. B54, R Kwon, C., Kim, K.-C., Robson, M.C., Gu, J.Y., Rajeswari, M., Venkatesan T, and. Ramesh, R.(1997) Desirable magnetotransport properties in doped Mn-oxide-based superlattices J.Appl. Phys. 81, Ghosh, K. Ogale, S.B,. P4, S.P, Robson, M., Eric Li, Jin, I., Zi-Wen Dong, Greene, R.L., Ramesh, R., Venkatesan, T., and Johnson, M., (1998) Positive giant magnetoresistance in a Fe 3 04/SrTiO 3 /Lao. 7 Sro. 3 MnO 3 heterostructure AppL Phys. Lett. 73, Rongsheng Cheng, Kebin Li, Shouguo Wang, Zhixiang Chen, Caoshui Xiong, Xiaojun Xu and Yuheng Zhang, (1998). The special magnetoresistive effect in trilayered films of manganite perovskites, Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, Sun, J.Z., Abraham, D.W., Roche, K., and Parkin, S.S.P. (1998) Temperature and bias dependence of magnetoresistance in doped manganite thin film trilayer junctions, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, Wiedenhorst, B., Hoefener, C., Yafeng Lu, Klein, J., Alff, L Gross, R. Freitag, B.H. Mader, W. (1999) Strain effects and microstructure of epitaxial manganite thin films and heterostructures, Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, Sahana, M, Hedge, M.S., Prasad, V., and Subamanyam, S.V. (1999) Electrical resistivity and enhanced magnetoresistance in LaPbMnO/LaMnO superlattices J. Appl. Phys. 85, Panagiotopoulos, I., Christides, C., Pissas, M., and Niarchos, D.(1999) Exchange biasing mechanism in Lal3Ca 1 3MnO 3 / La 1 3Ca2rMnO 3 multilayers Phys. Rev. B 60, Izumi, M., Murakami, Y., Konishi, Y., Manako, T., Kawasaki, M., Tokura, Y., (1999) Structure characterization and magnetic properties of oxide superlattices LaSrMnO/LaSrFeO Phys. Rev. B60, Nikolaev, K.R., Bhattachrya A., Kraus, P.A., Vas'ko, V.A., Cooley, W.K., and Goldman, A.M., (1999) Indications of antiferromagnteic interlayer coupling in Lav 3 Ba1/ 3 MnO 3 ILaNiO 3 multilayers Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, Fontcuberta J., Martinez, B., Seffar, A., Pinol S., Garcia-Munoz, J.L. and Obradors, X. (1997) Colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic manganites: Structural tuning and mechanisms Phys. Rev. Lett. 76, Kuwahara, H., Moritomo, Y., Tomioka, Y., Asamitsu, A., Kasai, M. and Tokura, Y. (1997) Low-field colossal magnetoresistance in bandwidth-controlled manganites J. Appl. Phys. 81, Koo T.Y., Park, S.H. Lee K-B., Jeong, Y.H. (1997) Anisotropic strains and magnetoresistance of Lao. 7 Cao. 3 MnO 3 AppL Phys. Left. 71,
10 24. Wang H. S. and Qi Li, (1998).Strain-induced large low-field magnetoresistance in Pro. 67 Sro. 33 MnO 3 ultrathin films Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, O'Donnel, J. Rzchowski, M.S. Eckstein, J.N. and Bozovic, I. (1998).Magnetoelastic coupling and magnetic anisotropy in LaCaMnO films Appl. Phys. Lett. 72, Wang, H. S. Qi Li, Kai Liu and Chien, C.L. (1999).Low-field magnetoresistance and anisotropy in ultrathin PrSrMnO films grown on different substrates Appl. Phys. Lett. 74, Nath, T. K. Rao, R. A. Lavric, D. Eom, C. B. Wu, L. and Tsui, F. (1998).Effect of three-dimensional strain states on magnetic anisotropy of LaCaMnO epitaxial thin films AppL Phys. Lett. 73, Millis, J. (1998) Lattice effects in magnetoresistive manganese perovskites Nature 392, Meiklejohn, W. H. and Bean, C. P. (1957) New Magnetic Anisotropy Phys. Rev. 105, For a recent review on Exchange Biasing phenomena see Nogues, J. and Schuller, Ivan K. (1999) Exchange Bias J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 192,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in. manganite multilayers
 Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Enhancement of magnetoresistance in manganite multilayers A.Venimadhav #, M.S Hegde #, V. Prasad* and S.V. Subramanyam* #Solid state and structural chemistry unit, Indian institute of science, Bangalore-12,
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of
 Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Anisotropic magnetoresistance and spin polarization of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 / SrTiO 3 superlattices L. M. Wang Department of Electrical Engineering, Da-Yeh University, Chang-Hwa 515, Taiwan, R. O. C. The
Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface
 Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
Submitted to Applied Physics Letters 09/22/03 Antiferromagnetism at the YBa 2 Cu 3 O 7 / La 2/3 Ca 1/3 MnO 3 interface N. Haberkorn Universidad Nacional del Sur, Avda. Alem 1253, Bahía Blanca, 8000 Bs.
with micrometer wide atomic terraces
 Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Epitaxial growth and properties of La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films with micrometer wide atomic terraces Wei Yuan 1, Yuelei Zhao 1, Chi Tang 2, Tang Su 1, Qi Song 1, Jing Shi 2,a), and Wei Han 1,3,b) 1 International
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films
 Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
Magnetic Circular Dichroism spectroscopy in epitaxial La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 thin films T. K. Nath 1 and J. R. Neal 2, G. A. Gehring 2 1 Dept. of Physics and Meteorology, Indian Institute Technology of Kharagpur,
The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites La 2.3 x Y x Ca 0.7 Mn 2 O 7
 J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 10 (1998) L191 L198. Printed in the UK PII: S0953-8984(98)89199-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR The metal insulator transition and ferromagnetism in the electron-doped layered manganites
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES. J. M. De Teresa
 MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
MAGNETORESISTANCE PHENOMENA IN MAGNETIC MATERIALS AND DEVICES J. M. De Teresa Instituto de Ciencia de Materiales de Aragón, Universidad de Zaragoza-CSIC, Facultad de Ciencias, 50009 Zaragoza, Spain. E-mail:
Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites
 Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
Materials Chemistry and Physics 72 (2001) 281 285 Chemical control of colossal magnetoresistance in manganites Chih-Hung Shen a, Ru-Shi Liu a,, Ravi Gundakaram a, Shu-Fen Hu b, Jauyn Grace Lin c, Chao-Yuan
The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials
 Chapter 1 The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials When the ferromagnetic (FM) materials are contacted with antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials, the magnetic properties of FM materials are drastically
Chapter 1 The exchange interaction between FM and AFM materials When the ferromagnetic (FM) materials are contacted with antiferromagnetic (AFM) materials, the magnetic properties of FM materials are drastically
Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 (x = 0 and 0.
 Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Solid State Communications 141 (2007) 348 353 www.elsevier.com/locate/ssc Comparison of the magnetic and electrical transport properties of La 2/3 Ca 1/3 Mn 1 x Cr x O 3 and La 2/3+x Ca 1/3 x Mn 1 x Cr
Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple perovskite manganite NdMnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
University of Wollongong Research Online Australian Institute for Innovative Materials - Papers Australian Institute for Innovative Materials 2012 Positive and negative exchange bias effects in the simple
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic
 Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Anisotropic magnetocaloric effect in all-ferromagnetic (La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 ) superlattices S. Thota, Q. Zhang, F. Guillou, U. Lüders, N. Barrier, W. Prellier * and A. Wahl Laboratoire CRISMAT,
Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers
 Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers S. M. Zhou, 1,2 L. Sun, 3 P. C. Searson, 3 and C. L. Chien 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
Perpendicular exchange bias and magnetic anisotropy in CoOÕpermalloy multilayers S. M. Zhou, 1,2 L. Sun, 3 P. C. Searson, 3 and C. L. Chien 1 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
I. Vrejoiu, E. Pippel, E. Nikulina, and D. Hesse Max Planck Institute of Microstructure Physics, D Halle, Germany. (Dated: October 18, 2018)
 Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Magnetic Properties of Pr 0.7 Ca 0.3 MnO 3 /SrRuO 3 Superlattices M. Ziese Division of Superconductivity and Magnetism, University of Leipzig, D-04103 Leipzig, Germany arxiv:1103.2299v1 [cond-mat.str-el]
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study
 Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Strain-induced single-domain growth of epitaxial SrRuO 3 layers on SrTiO 3 : a high-temperature x-ray diffraction study Arturas Vailionis 1, Wolter Siemons 1,2, Gertjan Koster 1 1 Geballe Laboratory for
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations
 Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
Exchange bias in core/shell magnetic nanoparticles: experimental results and numerical simulations Xavier Batlle, A. Labarta, Ò. Iglesias, M. García del Muro and M. Kovylina Goup of Magnetic Nanomaterials
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties
 Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Chapter 2 Magnetic Properties Abstract The magnetic properties of a material are the basis of their applications. Specifically, the contrast agents that will be developed in Chaps. 4 and 5 use their magnetic
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic
 Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
Giant exchange bias in a single-phase magnet with two magnetic sublattices Y. Sun, 1,a) J.-Z. Cong, 1 Y.-S. Chai, 1 L.-Q. Yan, 1 Y.-L. Zhao, 1 S.-G. Wang, 1 W. Ning, 2 and Y.-H Zhang 2 1 Beijing National
Transport and Magnetic Properties of La 0.85 Ca Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 21, No. 1 (29), S86-9 Transport and Magnetic Properties of La.85 Ca. 15 Mn 1-x Al x O 3 Manganites G ANJUM and S MOLLAH Department of Physics, Aligarh Muslim University,
Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and magnetocaloric effect in La0.7Ca0.3MnO3
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2011 Multifunctionality from coexistence of large magnetoresistance and
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Aug 2002
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Aug 2002 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 28 Aug 2002](/thumbs/75/71660699.jpg) Low frequency 1/ f noise in doped manganite grain-boundary junctions J. B. Philipp, L. Alff, A. Marx, and R. Gross Walther-Meissner-Institut, Bayerische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Walter-Meissner-Straße
Low frequency 1/ f noise in doped manganite grain-boundary junctions J. B. Philipp, L. Alff, A. Marx, and R. Gross Walther-Meissner-Institut, Bayerische Akademie der Wissenschaften, Walter-Meissner-Straße
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Reversible Electric Control of Exchange Bias in a Multiferroic Field Effect Device S. M. Wu 1, 2, Shane A. Cybart 1, 2, P. Yu 1, 2, M. D. Abrodos 1, J. Zhang 1, R. Ramesh 1, 2
Exchange biasing in as-prepared Co/FeMn bilayers and magnetic properties of ultrathin single layer films
 Thin Solid Films 485 (25) 212 217 www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Exchange biasing in as-prepared Co/FeMn bilayers and magnetic properties of ultrathin single layer films S.P. Hao a, Y.X. Sui b, R. Shan a,
Thin Solid Films 485 (25) 212 217 www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Exchange biasing in as-prepared Co/FeMn bilayers and magnetic properties of ultrathin single layer films S.P. Hao a, Y.X. Sui b, R. Shan a,
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film
 Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Reversible Structural Transition in Epitaxial Manganite Film Q. Zhan 1,R.Yu 1*,L.L.He 1,D.X.Li 1,J.Li 2,S.Y.Xu 2, and C. K. Ong 2 1 Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute of Metal
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Cu-doped manganites La 0.85 Te 0.15 Mn 1-x Cu x O 3 ( 0 x 0. 20 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G.
Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional Oxide p-n Heterojunctions
 Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Advances in Science and Technology Vol. 45 (2006) pp. 2582-2587 online at http://www.scientific.net (2006) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Fabrication and Characteristic Investigation of Multifunctional
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport. Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR)
 Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Ferromagnetism and Electronic Transport There are a number of effects that couple magnetization to electrical resistance. These include: Ordinary magnetoresistance (OMR) Anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR)
Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2. Elke Arenholz
 Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2 Elke Arenholz Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720 Kai Liu Department of Physics,
Angular dependence of the magnetization reversal in exchange biased Fe/MnF 2 Elke Arenholz Advanced Light Source, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720 Kai Liu Department of Physics,
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012267 TITLE: Exchange Coupling and Spin-Flip Transition of CoFe204/alpha-Fe2O3 Bilayered Films DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012267 TITLE: Exchange Coupling and Spin-Flip Transition of CoFe204/alpha-Fe2O3 Bilayered Films DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public
Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x. O 3 perovskite material
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Structural and magnetic characterization of the new GdMn 1-x Fe x O 3 perovskite material To cite this article: J A Cardona Vasquez et al 2016 J.
Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 37, No. 4, June 2014, pp. 809 813. Indian Academy of Sciences. Magnetization reversal and ferrimagnetism in Pr 1 x Nd x MnO 3 SANJAY BISWAS, MOMIN HOSSAIN KHAN and SUDIPTA PAL*
Emission studies of the gas-phase oxidation of Mn during pulsed laser deposition of manganates in O 2 and N 2 O atmospheres
 Emission studies of the gas-phase oxidation of Mn during pulsed laser deposition of manganates in O 2 and N 2 O atmospheres P. Lecoeur, A. Gupta, a) and P. R. Duncombe IBM Research Division, T. J. Watson
Emission studies of the gas-phase oxidation of Mn during pulsed laser deposition of manganates in O 2 and N 2 O atmospheres P. Lecoeur, A. Gupta, a) and P. R. Duncombe IBM Research Division, T. J. Watson
Colossal magnetoresistance:
 Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Colossal magnetoresistance: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The simplest example of magnetoresistance is transverse magnetoresistance associated with the Hall effect: H + + + + + + + + + + E y - -
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar
 Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Recent Developments in Magnetoelectrics Vaijayanti Palkar Department of Condensed Matter Physics & Materials Science Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Mumbai 400 005, India. Tata Institute of Fundamental
Si, X. X. Xi, and Q. X. JIA
 LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
LA-UR-01-1929 Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Title: DIELECTRIC PROPERTIES OF Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 THIN FILMS WITH VARIOUS STRAIN STATES Author(s): B. H. PARK, E. J. PETERSON, J. LEE,
Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La 0.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ) 0.3 CoO 3 System
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 674 21 Materials Research Society Magnetic Properties and Scaling Behavior in Perovskite like La.7 (Ba 1-x Pb x ).3 CoO 3 System Chiung-Hsiung Chen, Ting-Sheng Huang and
Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets. A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems
 Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems Dr. J. Sort Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA)
Imprinting domain/spin configurations in antiferromagnets A way to tailor hysteresis loops in ferromagnetic-antiferromagnetic systems Dr. J. Sort Institució Catalana de Recerca i Estudis Avançats (ICREA)
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 -
 Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
Interface ferromagnetism and orbital reconstruction in BiFeO 3 - La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 heterostructures P. Yu 1, J. -S. Lee 2, S. Okamoto 3, M. D. Rossell 4, M. Huijben 1,5, C. -H. Yang 1, Q. He 1, J. -X.
No. 3 An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in MFM results, it is suggested that the PS in LSMO is not a charge seg
 Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Vol 11 No 3, March 2002 cfl 2002 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1009-1963/2002/11(03)/0288-05 Chinese Physics and IOP Publishing Ltd An investigation of phase separation by magnetic force microscopy in La 0:45Sr 0:55MnO
Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering
 Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering G.J. Mankey, V.V. Krishnamurthy, F.D. Mackey and I. Zoto University of Alabama in collaboration with J.L. Robertson and M.L. Crow Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Probing Magnetic Order with Neutron Scattering G.J. Mankey, V.V. Krishnamurthy, F.D. Mackey and I. Zoto University of Alabama in collaboration with J.L. Robertson and M.L. Crow Oak Ridge National Laboratory
UNCLASSIFIED UNCLASSIFIED
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012814 TITLE: Optical Effect of Electric Field on Indirect Exciton Luminescence *n Double Quantum Wells of GaAs DISTRIBUTION:
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012814 TITLE: Optical Effect of Electric Field on Indirect Exciton Luminescence *n Double Quantum Wells of GaAs DISTRIBUTION:
Temperature Dependence of Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Ferromagnetic Layer Coupled with Polycrystalline Antiferromagnetic Layer
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 623 628 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 4, April 15, 2004 Temperature Dependence of Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Ferromagnetic Layer
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 41 (2004) pp. 623 628 c International Academic Publishers Vol. 41, No. 4, April 15, 2004 Temperature Dependence of Exchange Bias and Coercivity in Ferromagnetic Layer
Assessment of Variation in Zero Field Hall Constant of Colossal Magnetoresistive Manganites (Re1-x AxMnO3)
 ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
ESSENCE - International Journal for Environmental Rehabilitation and Conservation Panwar & Kumar/VIII [2] 2017/103 107 Volume VIII [2] 2017 [103 107] [ISSN 0975-6272] [www.essence-journal.com] Assessment
Lateral length scales in exchange bias
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2005 Europhys. Lett., 71 (2), pp. 297 303 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10078-2 Lateral length scales in exchange bias I. V. Roshchin 1,O.Petracic 1,2,R.Morales 1,3,Z.-P.Li
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2005 Europhys. Lett., 71 (2), pp. 297 303 (2005) DOI: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10078-2 Lateral length scales in exchange bias I. V. Roshchin 1,O.Petracic 1,2,R.Morales 1,3,Z.-P.Li
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in
 Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Buffer-Enhanced Electrical-Pulse-Induced-Resistive Memory Effect in Thin Film Perovskites Xin CHEN,* Naijuan WU, Alex IGNATIEV Texas Center for Advanced Materials, University of Houston, Houston, TX 77204,
Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Te x MnO 3
 phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
phys stat sol (a) 202, No 14, 2776 2780 (2005) / DOI 101002/pssa200520093 Simulation of the temperature-dependent resistivity of La 1 x Dong-yi Guan, Qing-li Zhou, Kui-juan Jin *, Guo-tai Tan, Zheng-hao
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Supplementary Figure 1: Fitting of the x-ray diffraction data by FULLPROF method. (a) O-LPCMO and (b) R-LPCMO. The orange (red) line is the x-ray diffraction data of O-LPCMO (R-LPCMO) and the blue (black)
Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition. of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress
 Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress Surendra Singh, 1 M. R. Fitzsimmons, 2 T. Lookman, 2 H. Jeen 3,4 and
Manipulation of the magnetic order parameter and the metal-insulatortransition of a manganite thin film with applied elastic stress Surendra Singh, 1 M. R. Fitzsimmons, 2 T. Lookman, 2 H. Jeen 3,4 and
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface
 What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
What so special about LaAlO3/SrTiO3 interface? Magnetism, Superconductivity and their coexistence at the interface Pramod Verma Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012 July 24, 2014 Pramod Verma
Influence of Size on the Properties of Materials
 Influence of Size on the Properties of Materials M. J. O Shea Kansas State University mjoshea@phys.ksu.edu If you cannot get the papers connected to this work, please e-mail me for a copy 1. General Introduction
Influence of Size on the Properties of Materials M. J. O Shea Kansas State University mjoshea@phys.ksu.edu If you cannot get the papers connected to this work, please e-mail me for a copy 1. General Introduction
Unclassified Unclassified Unclassified UL Standard Form 2981Rev. 2-89) (EG)
 REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE 1 Form Approved R R OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing
REPORT DOCUMENTATION PAGE 1 Form Approved R R OMB No. 0704-0188 Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 1 hour per response, including the time for reviewing
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012188 TITLE: Nanostructured NiFe204 Soft Magnetic Ferrite DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012188 TITLE: Nanostructured NiFe204 Soft Magnetic Ferrite DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013208 TITLE: Computational and Experimental Studies on Strain Induced Effects in InGaAs/GaAs HFET Structure Using C-V Profiling
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP013208 TITLE: Computational and Experimental Studies on Strain Induced Effects in InGaAs/GaAs HFET Structure Using C-V Profiling
Giant Magnetoresistance
 Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
Giant Magnetoresistance N. Shirato urse: Solid State Physics 2, Spring 2010, Instructor: Dr. Elbio Dagotto Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012830 TITLE: XPS Study of Cu-Clusters and Atoms in Cu/SiO2 Composite Films DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012830 TITLE: XPS Study of Cu-Clusters and Atoms in Cu/SiO2 Composite Films DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3. Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and
 Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
Magnetoresistance of 2D and 3D Electron Gas in LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 Heterostructures: Influence of Magnetic Ordering, Interface Scattering and Dimensionality X. Wang 1,2, W.M Lü 1,2, A. Annadi 1,2, Z.Q. Liu
Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2 artificial lattices by polarized neutron reflection
 Proc. Int. Conf. and Summer School on Advanced Silicide Technology 2014 JJAP Conf. Proc. 3 (2015) 011503 2015 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2
Proc. Int. Conf. and Summer School on Advanced Silicide Technology 2014 JJAP Conf. Proc. 3 (2015) 011503 2015 The Japan Society of Applied Physics Observation of magnetization alignment switching in Fe3Si/FeSi2
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012791 TITLE: Delta-Doping of GaAs by Sn DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited Availability: Hard
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012791 TITLE: Delta-Doping of GaAs by Sn DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited Availability: Hard
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films
 Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Planar Hall Effect in Magnetite (100) Films Xuesong Jin, Rafael Ramos*, Y. Zhou, C. McEvoy and I.V. Shvets SFI Nanoscience Laboratories, School of Physics, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland 1 Abstract.
Electric field control of magnetization using AFM/FM interfaces. Xiaoshan Xu
 Electric field control of magnetization using AFM/FM interfaces Xiaoshan Xu Magnetoelectric effects α = μ 0 M E H M H = 0, E = 0 = 0 (General magnetoelectrics) M H = 0, E = 0 0, P H = 0, E = 0 0, (Multiferroics)
Electric field control of magnetization using AFM/FM interfaces Xiaoshan Xu Magnetoelectric effects α = μ 0 M E H M H = 0, E = 0 = 0 (General magnetoelectrics) M H = 0, E = 0 0, P H = 0, E = 0 0, (Multiferroics)
Hidden Interfaces and High-Temperature Magnetism in Intrinsic Topological Insulator - Ferromagnetic Insulator Heterostructures
 Hidden Interfaces and High-Temperature Magnetism in Intrinsic Topological Insulator - Ferromagnetic Insulator Heterostructures Valeria Lauter Quantum Condensed Matter Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Hidden Interfaces and High-Temperature Magnetism in Intrinsic Topological Insulator - Ferromagnetic Insulator Heterostructures Valeria Lauter Quantum Condensed Matter Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory,
Advanced Lab Course. Tunneling Magneto Resistance
 Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Advanced Lab Course Tunneling Magneto Resistance M06 As of: 015-04-01 Aim: Measurement of tunneling magnetoresistance for different sample sizes and recording the TMR in dependency on the voltage. Content
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.
![Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998. Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires. with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998.](/thumbs/90/104152266.jpg) Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Magnetoresistance due to Domain Walls in Micron Scale Fe Wires with Stripe Domains arxiv:cond-mat/9803101v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 9 Mar 1998 A. D. Kent a, U. Ruediger a, J. Yu a, S. Zhang a, P. M. Levy a
Electric field effects on magnetotransport properties of multiferroic Py/YMnO 3 /Pt heterostructures
 Electric field effects on magnetotransport properties of multiferroic Py/YMnO 3 /Pt heterostructures V. Laukhin 1,2, X. Martí 1, V. Skumryev 2,3, D. Hrabovsky 1, F. Sánchez 1, M.V. García-Cuenca 4, C.
Electric field effects on magnetotransport properties of multiferroic Py/YMnO 3 /Pt heterostructures V. Laukhin 1,2, X. Martí 1, V. Skumryev 2,3, D. Hrabovsky 1, F. Sánchez 1, M.V. García-Cuenca 4, C.
Mössbauer study of the relationship between magnetic properties and Jahn Teller distortion in La 1 x Ba x (Mn,Fe)O 3 perovskites
 phys. stat. sol. (b) 242, No. 14, 293 2937 (25) / DOI 1.12/pssb.25412 Mössbauer study of the relationship between magnetic properties and Jahn Teller distortion in La 1 x Ba x (Mn,Fe)O 3 perovskites Zhi-qi
phys. stat. sol. (b) 242, No. 14, 293 2937 (25) / DOI 1.12/pssb.25412 Mössbauer study of the relationship between magnetic properties and Jahn Teller distortion in La 1 x Ba x (Mn,Fe)O 3 perovskites Zhi-qi
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase. Alok Banerjee
 Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
Kinetically arrested long-range magnetic ordered phase Alok Banerjee (alok@csr.ernet.in) UGC-DAE Consortium for Scientific Research (CSR) (Formerly: Inter University Consortium for DAE Facilities) http://www.csr.ernet.in/
P. Khatua IIT Kanpur. D. Temple MCNC, Electronic Technologies. A. K. Majumdar, S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata
 The scaling law and its universality in the anomalous Hall effect of giant magnetoresistive Fe/Cr multilayers A. K. Majumdar S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata & Department of Physics
The scaling law and its universality in the anomalous Hall effect of giant magnetoresistive Fe/Cr multilayers A. K. Majumdar S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata & Department of Physics
Synthesizing and Characterizing Sr 2 FeMoO 6 Bulk and Thin Films
 Undergraduate Review Volume 4 Article 14 2008 Synthesizing and Characterizing Sr 2 Bulk and Thin Films Louis Bianchini Follow this and additional works at: http://vc.bridgew.edu/undergrad_rev Part of the
Undergraduate Review Volume 4 Article 14 2008 Synthesizing and Characterizing Sr 2 Bulk and Thin Films Louis Bianchini Follow this and additional works at: http://vc.bridgew.edu/undergrad_rev Part of the
Artificially layered structures
 http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
http://accessscience.com/popup.ap x?id=053450&name=print Close Window ENCYCLOPEDIA ARTICLE Artificially layered structures Manufactured, reproducibly layered structures having layer thicknesses approaching
Material Science II. d Electron systems
 Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Material Science II. d Electron systems 1. Electronic structure of transition-metal ions (May 23) 2. Crystal structure and band structure (June 13) 3. Mott s (June 20) 4. Metal- transition (June 27) 5.
Magnetoresistance Oscillations in Thin Inclined Magnetic Films
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 39, No. 6, December 2001, pp. 1055 1059 Magnetoresistance Oscillations in Thin Inclined Magnetic Films Ilsu Rhee and Kiwon Yang Department of Physics, Kyungpook
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 39, No. 6, December 2001, pp. 1055 1059 Magnetoresistance Oscillations in Thin Inclined Magnetic Films Ilsu Rhee and Kiwon Yang Department of Physics, Kyungpook
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials
 Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Making the Invisible Visible: Probing Antiferromagnetic Order in Novel Materials Elke Arenholz Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Antiferromagnetic contrast in X-ray absorption Ni in NiO Neel Temperature
Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7
 The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
The Open Condensed Matter Physics Journal, 2009, 2, 19-24 19 Open Access Anomalous Structural Change of Layered Perovskite Manganites La 2-2x Sr 1+2x Mn 2 O 7 Aihua Wang 1,2, Tao Liu 3, Yang Liu 4, Guohui
Phenomenology and Models of Exchange Bias in Core /Shell Nanoparticles
 Phenomenology and Models of Exchange Bias in Core /Shell Nanoparticles Xavier Batlle and Amílcar Labarta Departament de Física Fonamental and Institut de Nanociència i Nanotecnologia Universitat de Barcelona,
Phenomenology and Models of Exchange Bias in Core /Shell Nanoparticles Xavier Batlle and Amílcar Labarta Departament de Física Fonamental and Institut de Nanociència i Nanotecnologia Universitat de Barcelona,
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped
 Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
Structural, magnetic and transport properties in the Pr-doped manganites La 0.9-x Pr x e 0.1 MnO 3 ( 0 x 0. 9 ) J.Yang 1, W. H. Song 1, Y. Q. Ma 1, R. L. Zhang 1, B. C. Zhao 1, Z.G. Sheng 1, G. H. Zheng
J 12 J 23 J 34. Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world. Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER
 Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: LOCAL (ATOMIC) MAGNETIC MOMENTS m d or f electrons Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER H exc J S S i j
Driving forces in the nano-magnetism world Intra-atomic exchange, electron correlation effects: LOCAL (ATOMIC) MAGNETIC MOMENTS m d or f electrons Inter-atomic exchange: MAGNETIC ORDER H exc J S S i j
1 Corresponding author:
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Study of Cr-doped GaN Surface Grown by RF Plasma Molecular Beam Epitaxy Muhammad B. Haider, Rong Yang, Hamad Al-Brithen, Costel Constantin, Arthur R. Smith 1, Gabriel Caruntu
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy Study of Cr-doped GaN Surface Grown by RF Plasma Molecular Beam Epitaxy Muhammad B. Haider, Rong Yang, Hamad Al-Brithen, Costel Constantin, Arthur R. Smith 1, Gabriel Caruntu
Holcomb Group Capabilities
 Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Holcomb Group Capabilities Synchrotron Radiation & Ultrafast Optics West Virginia University mikel.holcomb@mail.wvu.edu The Physicists New Playground The interface is the device. - Herbert Kroemer, beginning
Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films
 Intensity(a.u.) LSMO(002) ZnO(110) LAO(002) Supporting Information for Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films Aiping Chen 1, *, Marcus Weigand 1, Zhenxing
Intensity(a.u.) LSMO(002) ZnO(110) LAO(002) Supporting Information for Evolution of microstructure, strain and physical properties in oxide nanocomposite films Aiping Chen 1, *, Marcus Weigand 1, Zhenxing
Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles
 Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles Authors: Chen-Min Liu, Lin Guo*, Rong-Ming Wang*, Yuan Deng, Hui-Bin Xu, Shihe Yang* Supporting Information S1. Sample characterization
Title: Magnetic chains of metal formed by assembly of small nanoparticles Authors: Chen-Min Liu, Lin Guo*, Rong-Ming Wang*, Yuan Deng, Hui-Bin Xu, Shihe Yang* Supporting Information S1. Sample characterization
Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor. (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction
 Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction D. Chiba 1, 2*, Y. Sato 1, T. Kita 2, 1, F. Matsukura 1, 2, and H. Ohno 1, 2 1 Laboratory
Current-driven Magnetization Reversal in a Ferromagnetic Semiconductor (Ga,Mn)As/GaAs/(Ga,Mn)As Tunnel Junction D. Chiba 1, 2*, Y. Sato 1, T. Kita 2, 1, F. Matsukura 1, 2, and H. Ohno 1, 2 1 Laboratory
Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 211 (2000) 105}110 Relation between structure, charge ordering and magnetotransport properties in Nd manganites W. Schuddinck *, G. Van Tendeloo, A. BarnabeH,
Field dependent magnetization of BiFeO 3 in ultrathin La 0.7 Sr 0.3 MnO 3 /BiFeO 3 superlattice
 Field dependent magnetization of BiFeO 3 in ultrathin La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 /BiFeO 3 superlattice Surendra Singh, 1 J. Xiong, 2 A. P. Chen, 2 M R Fitzsimmons, 3 Q. X. Jia 2 1 Solid State Physics Division, Bhabha
Field dependent magnetization of BiFeO 3 in ultrathin La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 /BiFeO 3 superlattice Surendra Singh, 1 J. Xiong, 2 A. P. Chen, 2 M R Fitzsimmons, 3 Q. X. Jia 2 1 Solid State Physics Division, Bhabha
Nanoxide electronics
 Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Nanoxide electronics Alexey Kalabukhov Quantum Device Physics Laboratory MC2, room D515 Alexei.kalaboukhov@chalmers.se Playing Lego with oxide materials: G. Rijnders, D.H.A. Blank, Nature 433, 369 (2005)
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides. Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625
 Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Photoemission and the electronic structure of magnetic oxides Dan Dessau University of Colorado, Boulder Duane F625 Dessau@Colorado.edu Einstein s Photoelectric effect XPS, UPS, ARPES BE e- hn D.O.S. occupied
Giant magnetoresistance in electrodeposited Co-Cu/Cu multilayers: origin of absence of oscillatory behaviour
 Published in: Phys. Rev. B 79, 174421/1-13 (2009) Giant magnetoresistance in electrodeposited Co-Cu/Cu multilayers: origin of absence of oscillatory behaviour I. Bakonyi*, E. Simon, B.G. Tóth, L. Péter
Published in: Phys. Rev. B 79, 174421/1-13 (2009) Giant magnetoresistance in electrodeposited Co-Cu/Cu multilayers: origin of absence of oscillatory behaviour I. Bakonyi*, E. Simon, B.G. Tóth, L. Péter
Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers
 Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 300 (2006) 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/jmmm Coupled perpendicular magnetization in Fe/Cu/Fe trilayers D. Repetto, A. Enders, K. Kern Max Planck Institut
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Titanium d xy ferromagnetism at the LaAlO 3 /SrTiO 3 interface J.-S. Lee 1,*, Y. W. Xie 2, H. K. Sato 3, C. Bell 3, Y. Hikita 3, H. Y. Hwang 2,3, C.-C. Kao 1 1 Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource,
Sci. Rep., 2015, 1, 8460
 Fermi Level shifting, Charge Transfer and Induced Magnetic Coupling at La0.7Ca0.3MnO3/LaNiO3 Interface Xingkun Ning, Zhanjie Wang & Zhidong Zhang Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute
Fermi Level shifting, Charge Transfer and Induced Magnetic Coupling at La0.7Ca0.3MnO3/LaNiO3 Interface Xingkun Ning, Zhanjie Wang & Zhidong Zhang Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, Institute
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR:
 High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
High T C copper oxide superconductors and CMR: Ram Seshadri (seshadri@mrl.ucsb.edu) The Ruddlesden-Popper phases: Ruddlesden-Popper phases are intergrowths of perovskite slabs with rock salt slabs. First
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998](/thumbs/78/78285667.jpg) Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Interplay of the -type charge ordering and the -type spin ordering in a half-doped bilayer manganite Sr Mn arxiv:cond-mat/981119v [cond-mat.str-el] 19 Nov 1998 M. Kubota, 1 H. Yoshizawa, 1 Y. Moritomo,
Magnetic and transport properties of the ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructures In,Mn As/ Ga,Al Sb
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 8 15 FEBRUARY 1999-II Magnetic and transport properties of the ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructures In,Mn As/ Ga,Al Sb A. Oiwa, A. Endo, S. Katsumoto,* and Y.
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 59, NUMBER 8 15 FEBRUARY 1999-II Magnetic and transport properties of the ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructures In,Mn As/ Ga,Al Sb A. Oiwa, A. Endo, S. Katsumoto,* and Y.
Australian Journal of Physics
 CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
CSIRO PUBLISHING Australian Journal of Physics Volume 52, 1999 CSIRO Australia 1999 A journal for the publication of original research in all branches of physics www.publish.csiro.au/journals/ajp All enquiries
Stripes developed at the strong limit of nematicity in FeSe film
 Stripes developed at the strong limit of nematicity in FeSe film Wei Li ( ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University IASTU Seminar, Sep. 19, 2017 Acknowledgements Tsinghua University Prof. Qi-Kun Xue,
Stripes developed at the strong limit of nematicity in FeSe film Wei Li ( ) Department of Physics, Tsinghua University IASTU Seminar, Sep. 19, 2017 Acknowledgements Tsinghua University Prof. Qi-Kun Xue,
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) La (Sr Ca )MnO x x 3. *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu. a, a b
 International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
International Journal of Inorganic Materials 3 (2001) 1063 1072 Chemical pressure controlled colossal magnetoresistance effects in q La (Sr Ca )MnO R.S. Liu *, C.H. Shen, S.F. Hu a, a b a Department of
Thin Film Bi-based Perovskites for High Energy Density Capacitor Applications
 ..SKELETON.. Thin Film Bi-based Perovskites for High Energy Density Capacitor Applications Colin Shear Advisor: Dr. Brady Gibbons 2010 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Motivation and Objective...
..SKELETON.. Thin Film Bi-based Perovskites for High Energy Density Capacitor Applications Colin Shear Advisor: Dr. Brady Gibbons 2010 Table of Contents Chapter 1 Introduction... 1 1.1 Motivation and Objective...
Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions
 Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions Ryan Stearrett Ryan Stearrett, W. G. Wang, Xiaoming Kou, J. F. Feng, J. M. D. Coey, J. Q. Xiao, and E. R. Nowak, Physical
Influence of exchange bias on magnetic losses in CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB tunnel junctions Ryan Stearrett Ryan Stearrett, W. G. Wang, Xiaoming Kou, J. F. Feng, J. M. D. Coey, J. Q. Xiao, and E. R. Nowak, Physical
SEEING Phase Transitions with. Magnetic Force Microscopy. Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin. Alex de Lozanne
 SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
SEEING Phase Transitions with Magnetic Force Microscopy Alex de Lozanne Dept. of Physics, University of Texas at Austin LOZANNE@PHYSICS.UTEXAS.EDU Defense: Mon Dec. 5, 10am, 14.218 CURRENT GROUP: Dr.Weida
Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice
 UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012151 TITLE: Chemical Bonding of Polymer on Carbon Nanotube DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
UNCLASSIFIED Defense Technical Information Center Compilation Part Notice ADP012151 TITLE: Chemical Bonding of Polymer on Carbon Nanotube DISTRIBUTION: Approved for public release, distribution unlimited
MnO. Sr x. La 1-x. Temperature (K) Paramagnetic. Metal T C. Paramagnetic Insulator. Ferromagnetic. Metal T N. Ferromagnetic. Spin-canted Insulator
 Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
Temperature (K) 6 5 4 3 2 Paramagnetic Insulator Resistivity (1-3 Ω cm) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 La.7 Sr.3 MnO 3 (x =.3) 1 2 3 4 5 Temperature (K) T C Ferromagnetic Metal Paramagnetic Metal T N 1 Ferromagnetic
